A Novel Sidelobe Reduction Algorithm Based on Two-Dimensional Sidelobe Correction Using D-SVA for Squint SAR Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sidelobe Control Algorithms for SAR Images
2.1. Traditional Linear Windowing
2.2. Nonlinear Apodization (Windowing)
2.3. Dual-Delta Factorization
2.4. Iterative Adaptive Approach (IAA)
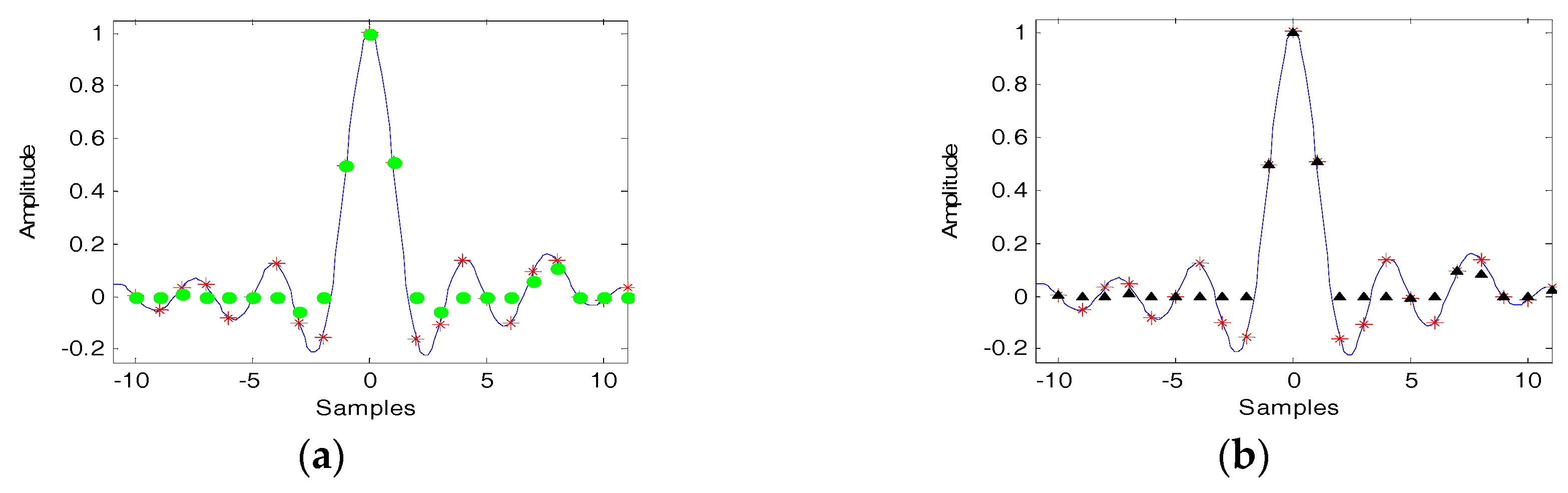
3. Non-Integer Nyquist SVA Algorithm
- Calculate the value of g′(m) for ω1 = 0 and ω1 = ω1_max (the upper limit of Equation (9)).
- If the two values of g′(m) are opposite in sign, the output equals to zero at pixel m.
- Otherwise, the output equals to the lowest magnitude.
4. Two-Dimensional Sidelobe Correction Using D-SVA for Squint SAR Images
4.1. D-SVA for Non-Integer Nyquist Sampled Imagery
4.1.1. Additional SVA Algorithm
- Calculate the value of g″(m) for ω′1 = 0 and ω′1 = ω′1_max (the upper limit of Equation (13)).
- If the two values of g″(m) are opposite in sign, the output equals to zero at pixel m.
- Otherwise, the output equals to the lowest magnitude.
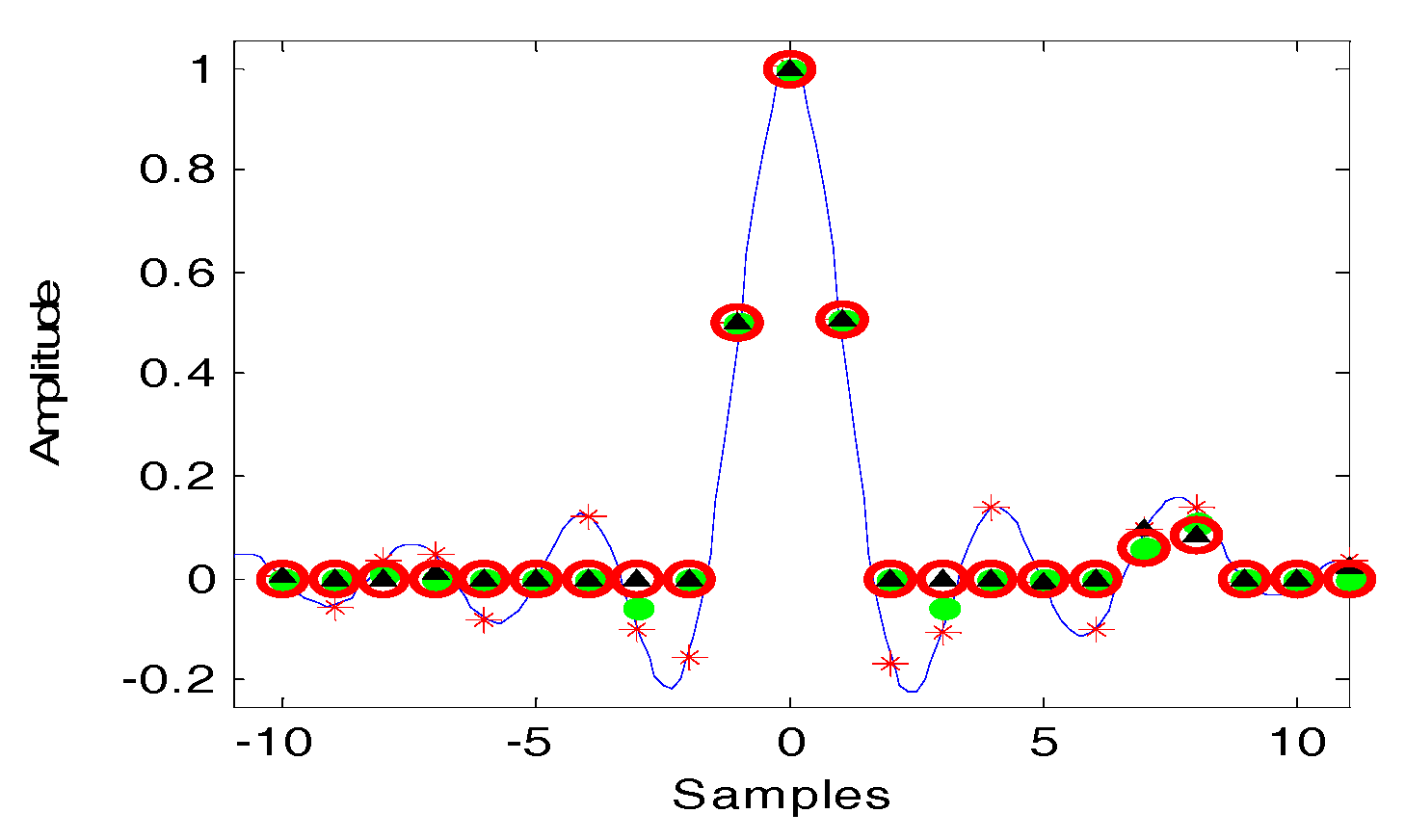
4.1.2. D-SVA Algorithm
4.2. Specturm Correction for Squint SAR Images
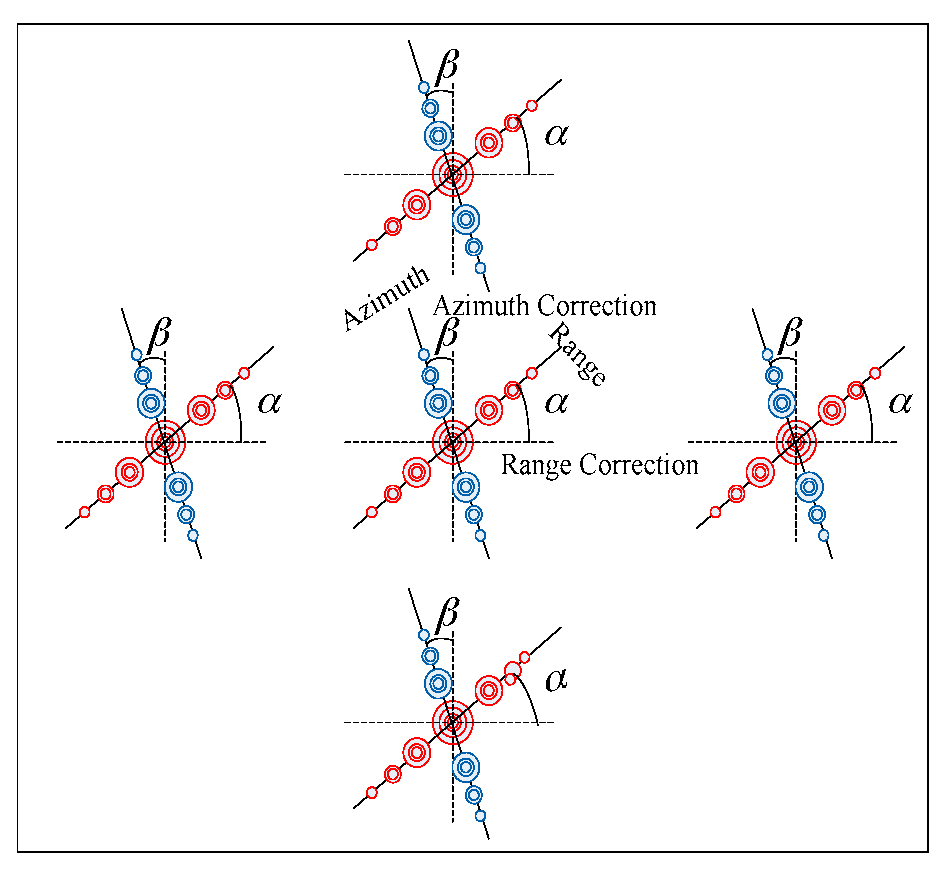
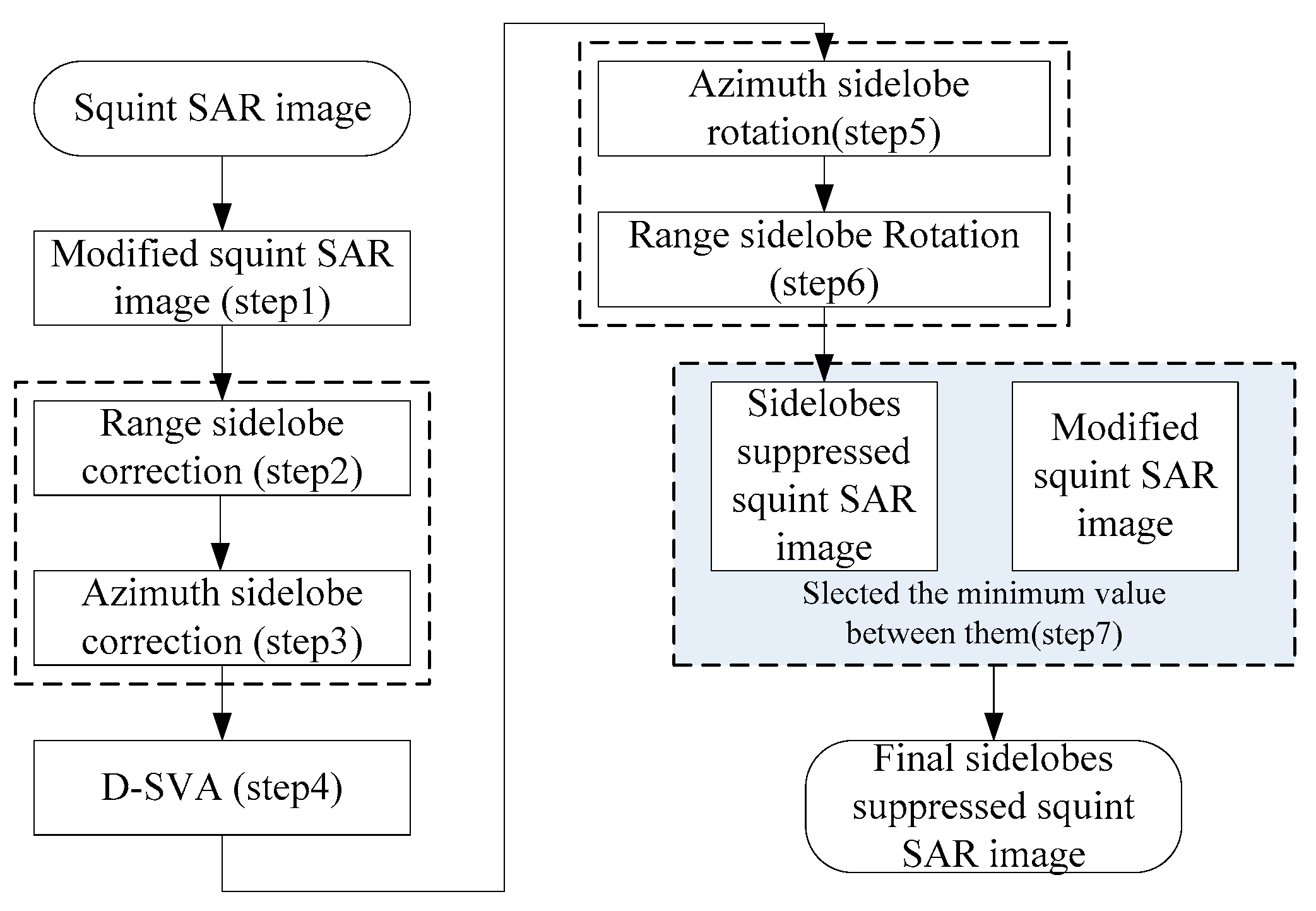
4.3. Sidelobe Reduction for Squint SAR Images
- First, transform the squint SAR images E0 into frequency domain and shift the center of the frequency spectrum to the data’s center. Then by applying an inverse IFT to the data in time domain, the new data E1 is recorded.
- Range sidelobe correction
- 3.
- Azimuth sidelobe correction
- 4.
- Use D-SVA to process the range and azimuth, obtaining E4.
- 5.
- Use azimuth phase shift term to rotate the azimuth sidelobes for E4:
- 6.
- Use range phase shift term to rotate the range sidelobes for E5:
- 7.
- At each spatial location, select the minimum value between E6 and E1 as output.
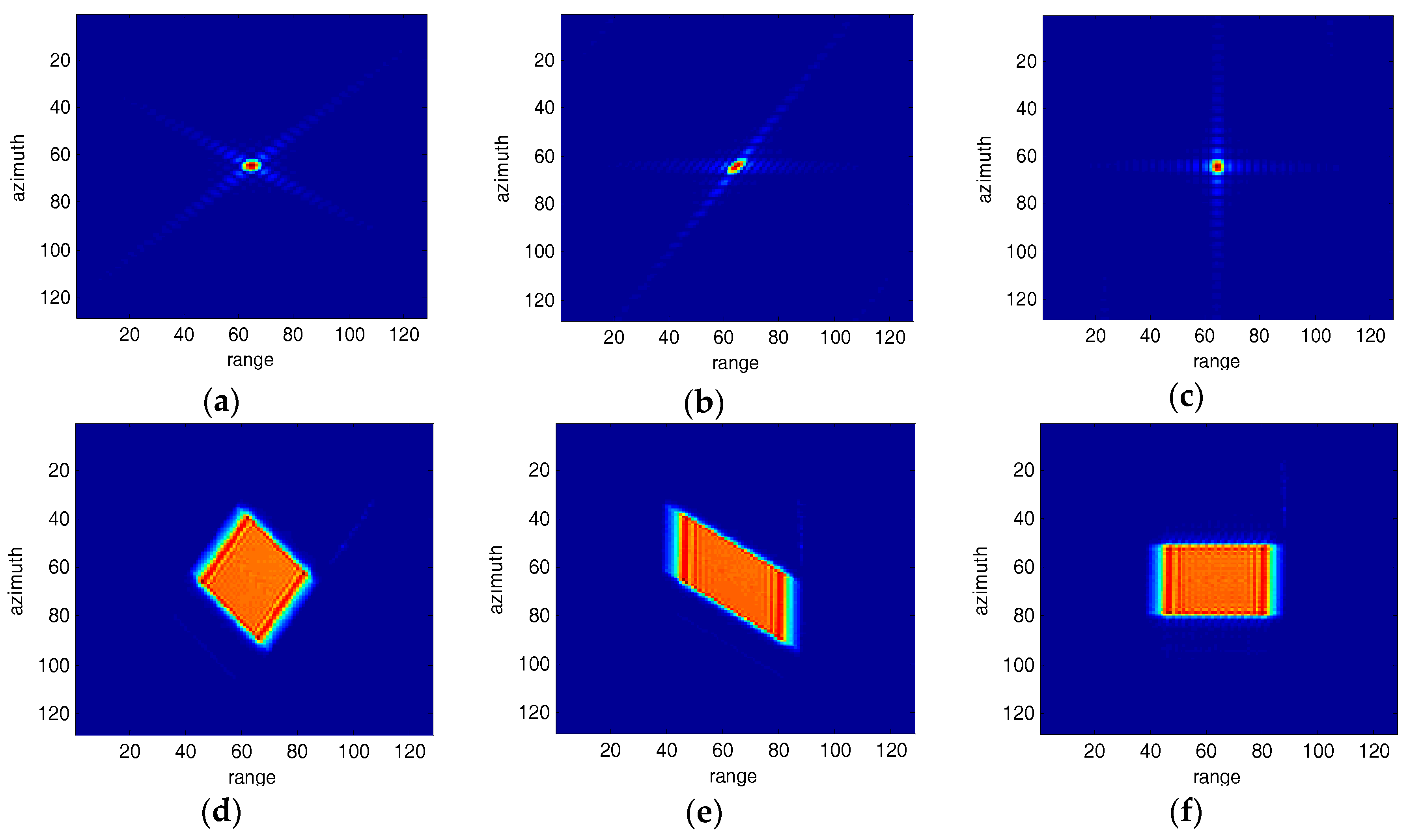
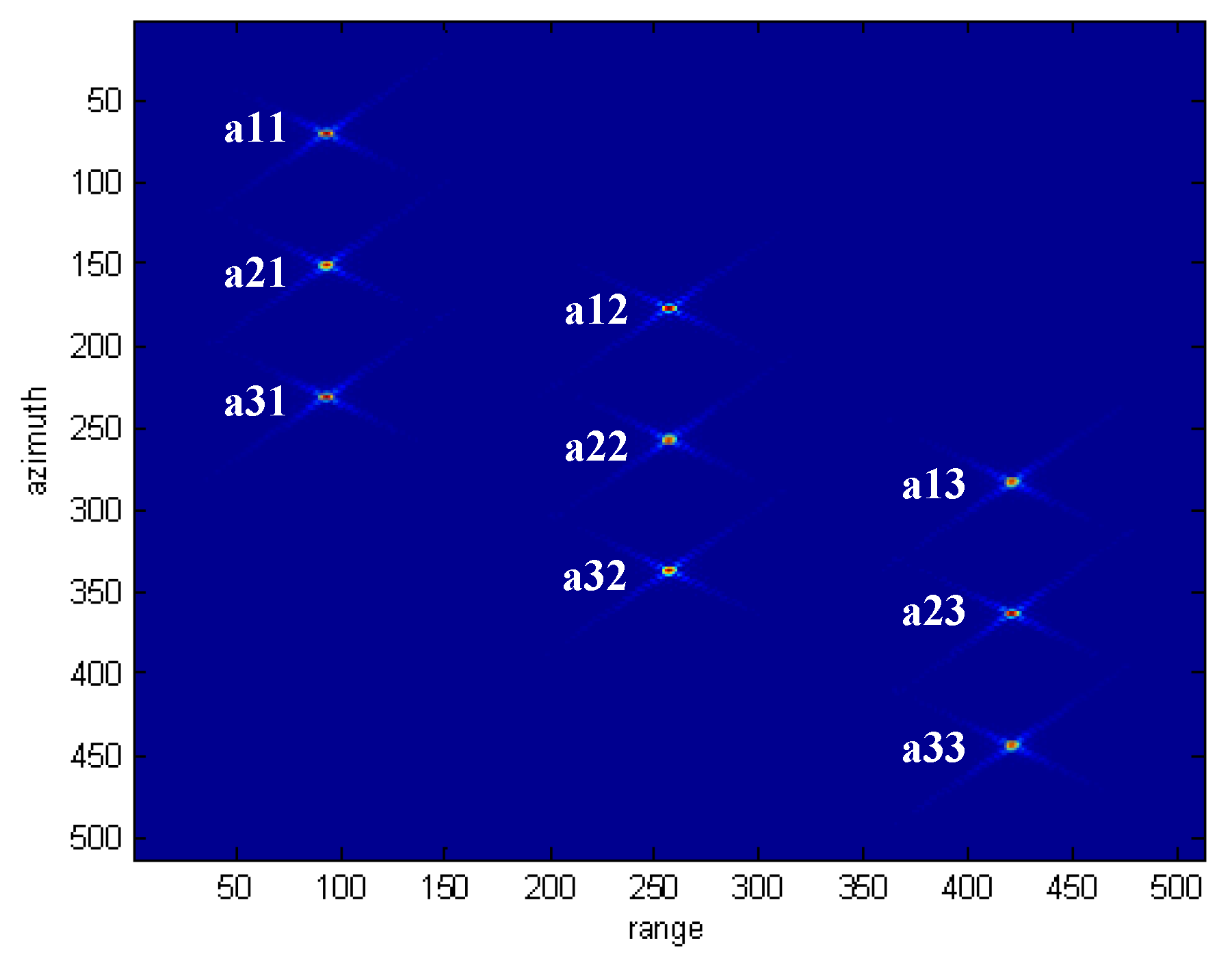
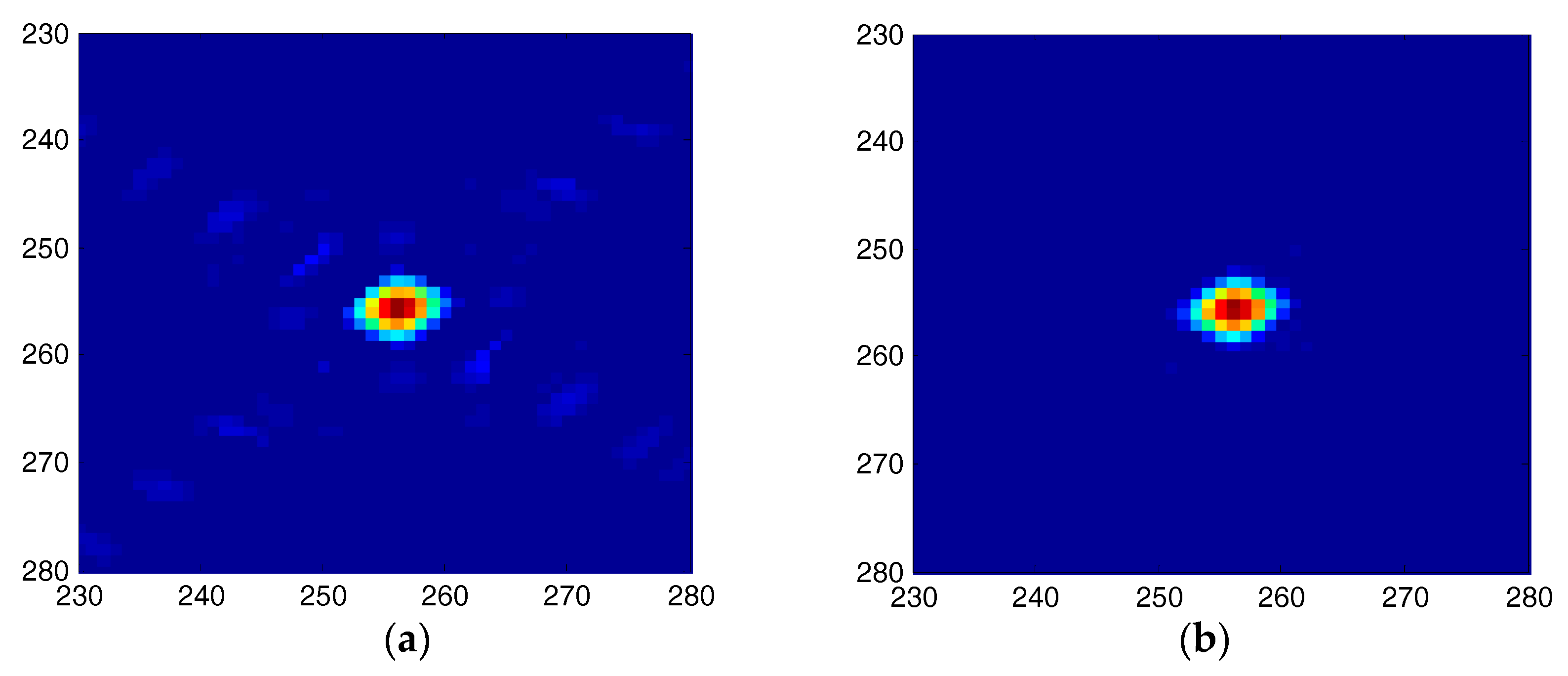
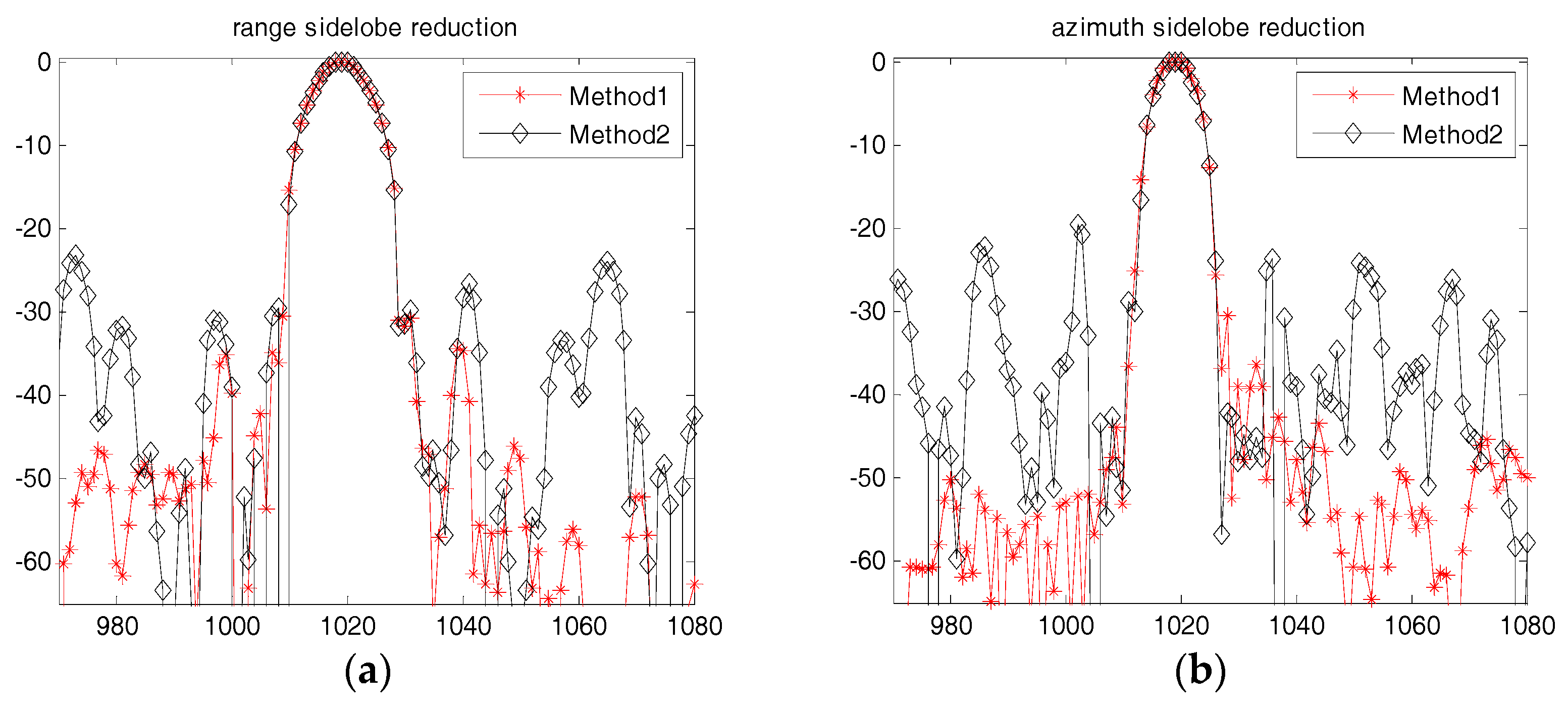
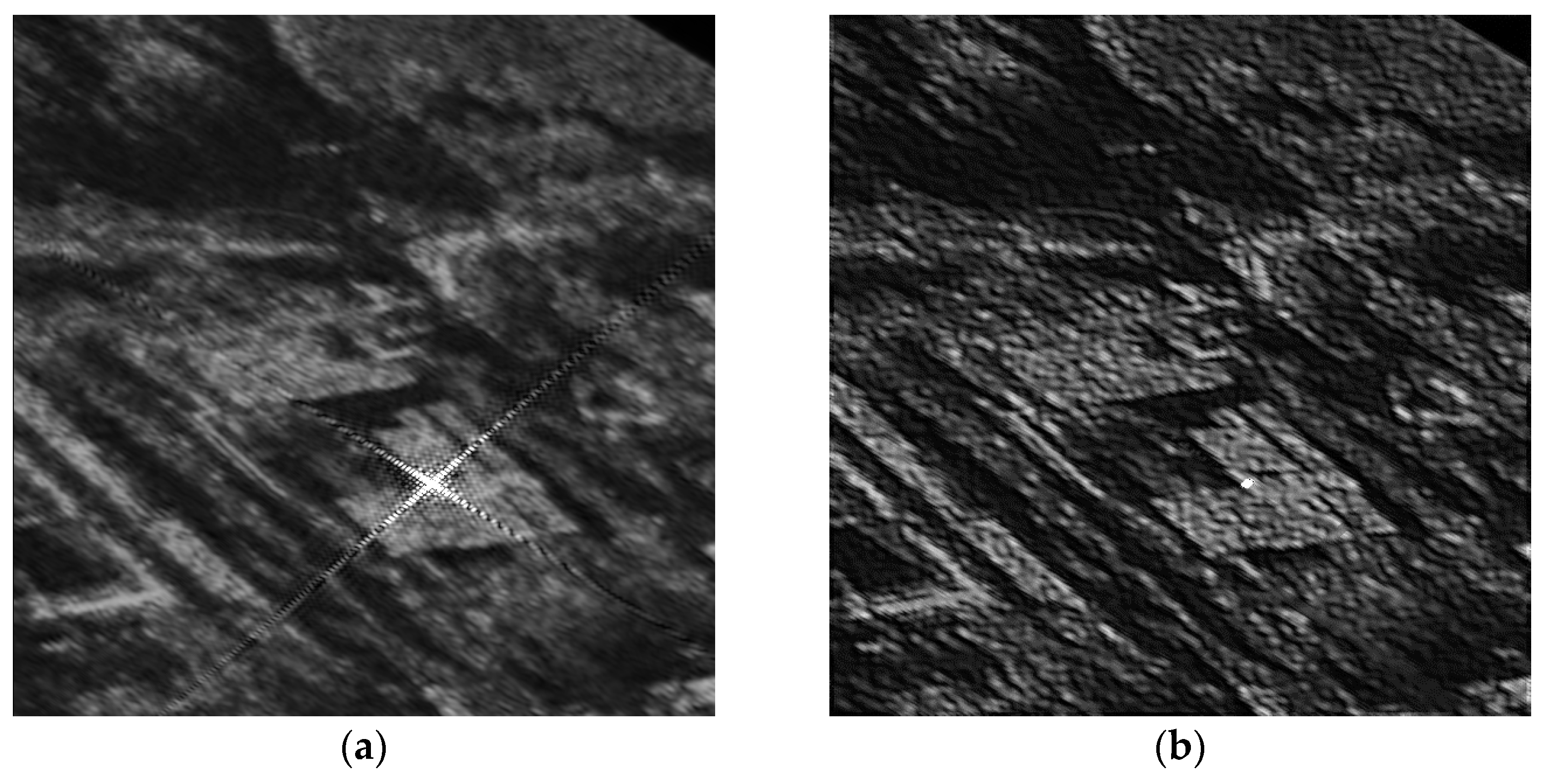
5. Simulation Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Z.C.; Wu, J.J.; Li, Z.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Yang, J.Y. Highly Squint SAR Data Focusing Based on Keystone Transform and Azimuth Extended Nonlinear Chirp Scaling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- An, D.X.; Huang, X.T.; Jin, T.; Zhou, Z.M. Extended Nonlinear Chirp Scaling Algorithm for High-Resolution Squint SAR Data Focusing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3595–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankwitz, H.C.; Dallaire, R.J.; Fienup, J.R. Nonlinear apodization for sidelobe control in SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1995, 31, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.H. Generalization of Spatially Variant Apodization to Noninteger Nyquist Sampling Rates. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Rubio, C.; Llorente-Romano, S.; Burgos-García, M. Robust SVA method for every sampling rate condition. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Wang, Y.F.; Xu, X.H.; Zhou, C.Y.; Cui, P.F. A SAR sidelobe suppression algorithm based on modified spatially variant apodization. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Wang, S.; Hou, B.; Wang, Y. A resample-based SVA algorithm for sidelobe reduction of SAR/ISAR imagery with noninteger Nyquist sampling rate. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Ling, F. A Novel SAR Sidelobe Suppression Method via Dual-Delta Factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1576–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Rubio, C.; Llorente-Romano, S.; Burgos-García, M. Spatially variant apodization for squint synthetic aperture radar images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGraaf, S.R. Sidelobe Reduction via Adaptive FIR Filtering in SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1994, 3, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sok-Son, J.; Thomas, G.; Flores, B.C. Range-Doppler Radar Imaging and Motion Compensation; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 218–230. [Google Scholar]
- Stankwitz, H.C.; Kosek, M.R. Sparse Aperture Fill for SAR Using Super-SVA. In Proceedings of the 1966 IEEE National Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 13–16 May 1996; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, C.; Wang, Y.F.; Xu, X.H.; Zhou, C.Y.; Cui, P.F. A Super-Resolution Algorithm for Synthetic Aperture Radar Based on Modified Spatially Variant apodization. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.G.; Woo, J.C.; Kim, Y.S. Noniterative Super-Resolution Technique Combining SVA with Modified Geometric Mean Filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Wang, P.B. Sidelobe Suppression Algorithm for SAR Imaging Based on Iterative Adaptive Approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Marina Bay Sands, Singapore, 1–4 September 2015; pp. 443–446. [Google Scholar]
- Long, T.; Li, Y.; Ding, Z.; Liu, L. Interpolation method for geometric correction in highly squint synthetic aperture radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2012, 6, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
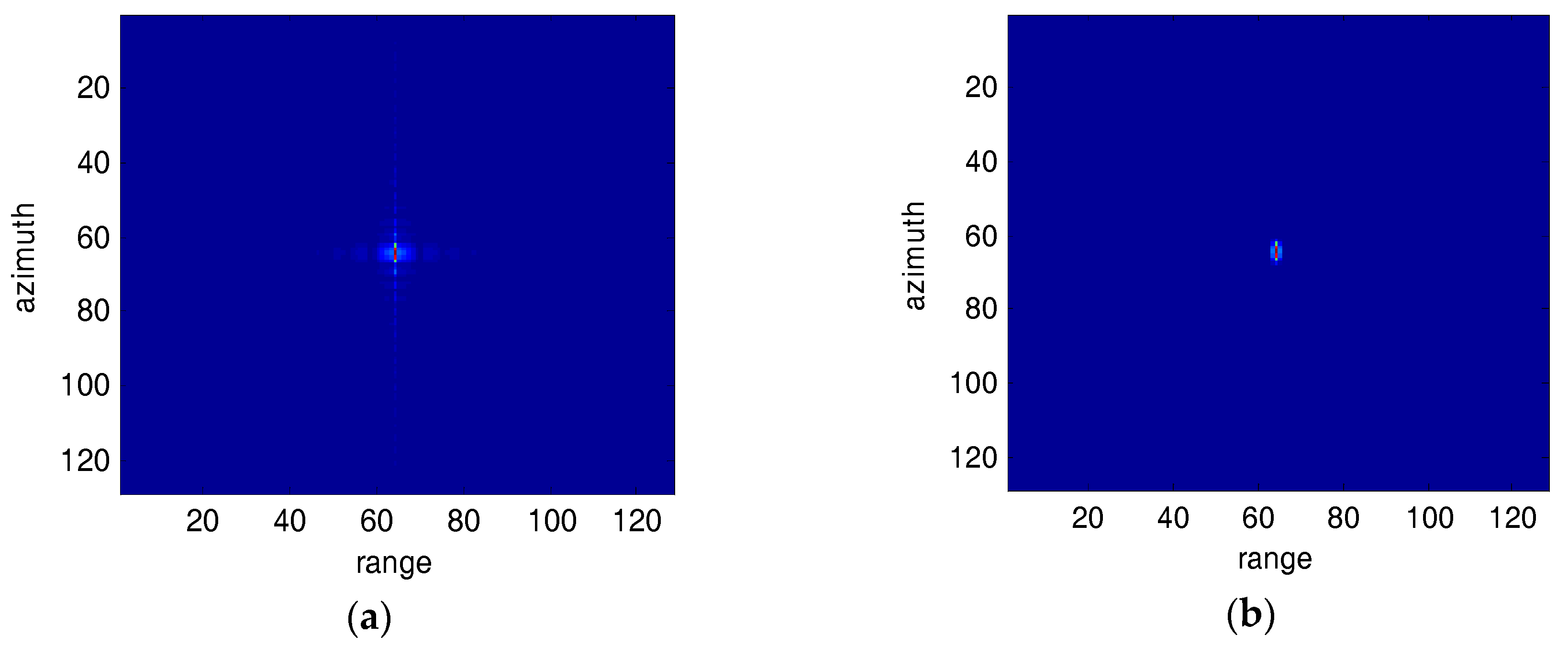
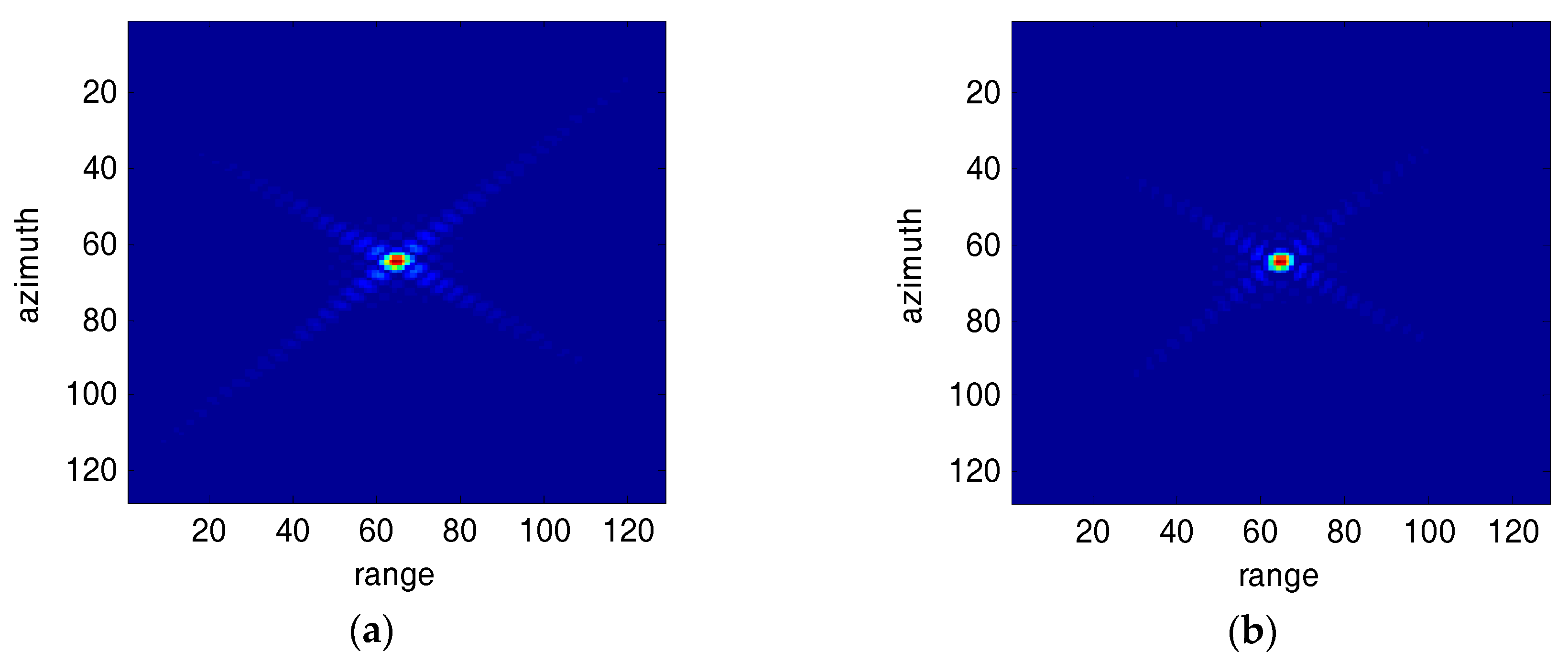
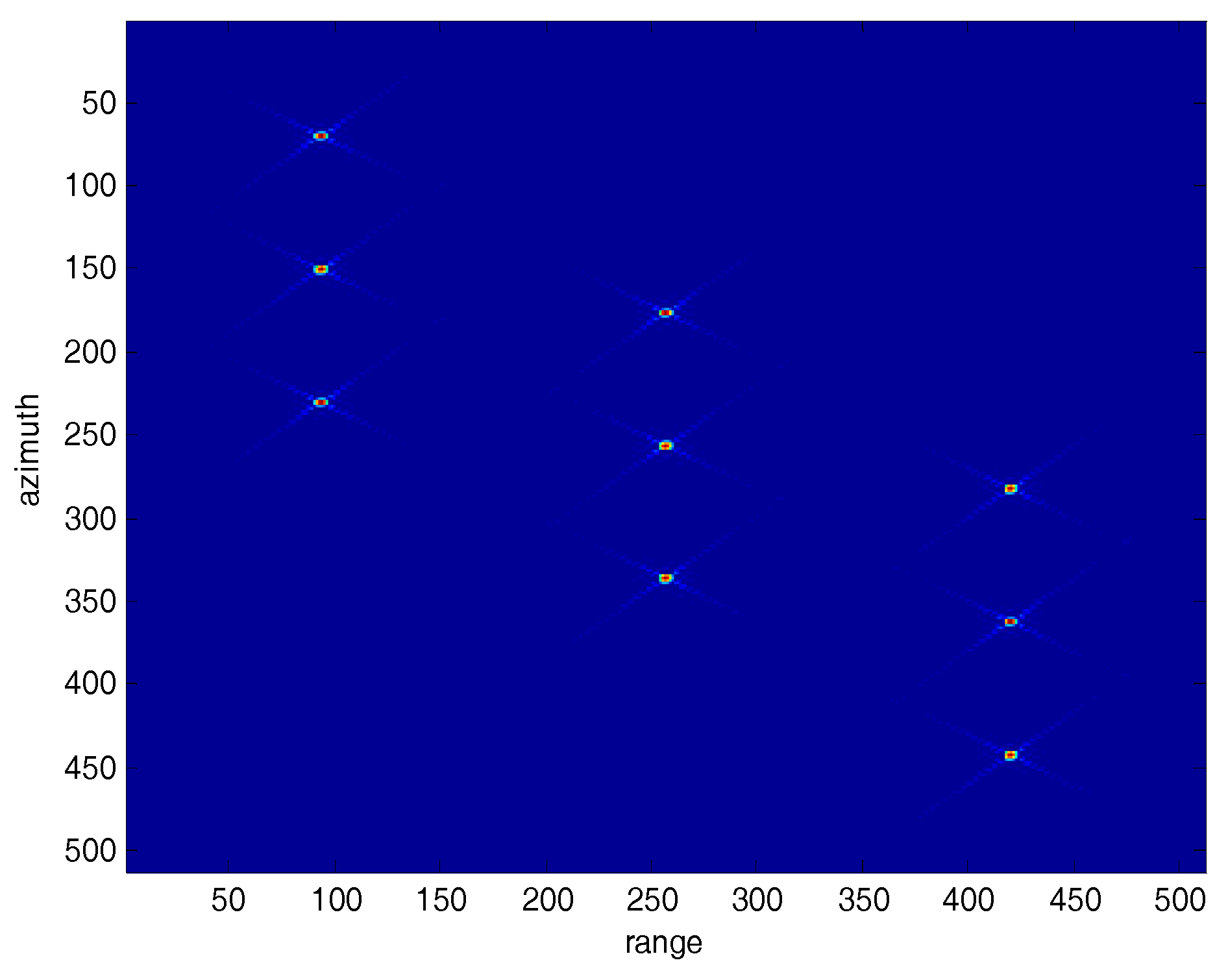

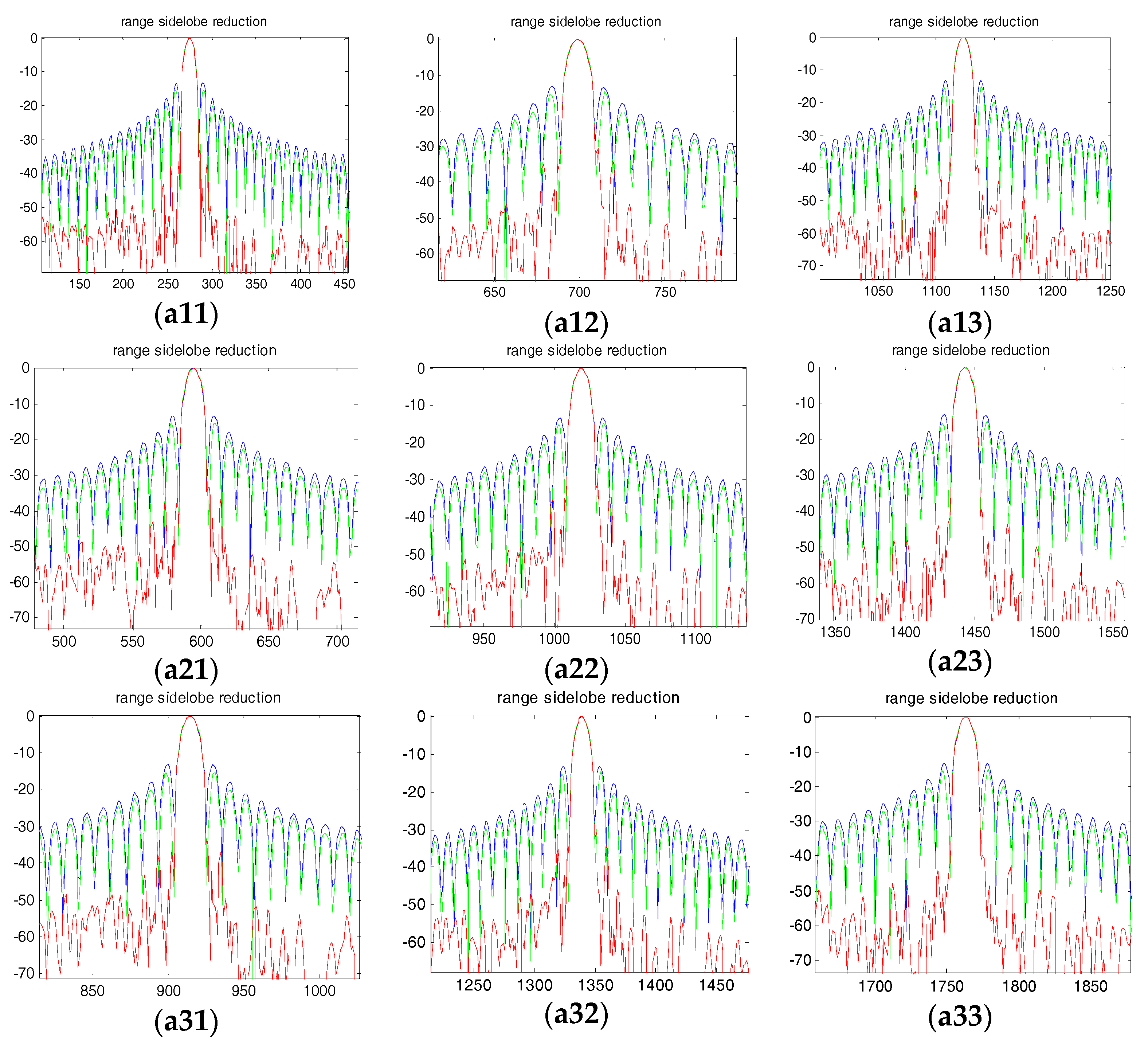
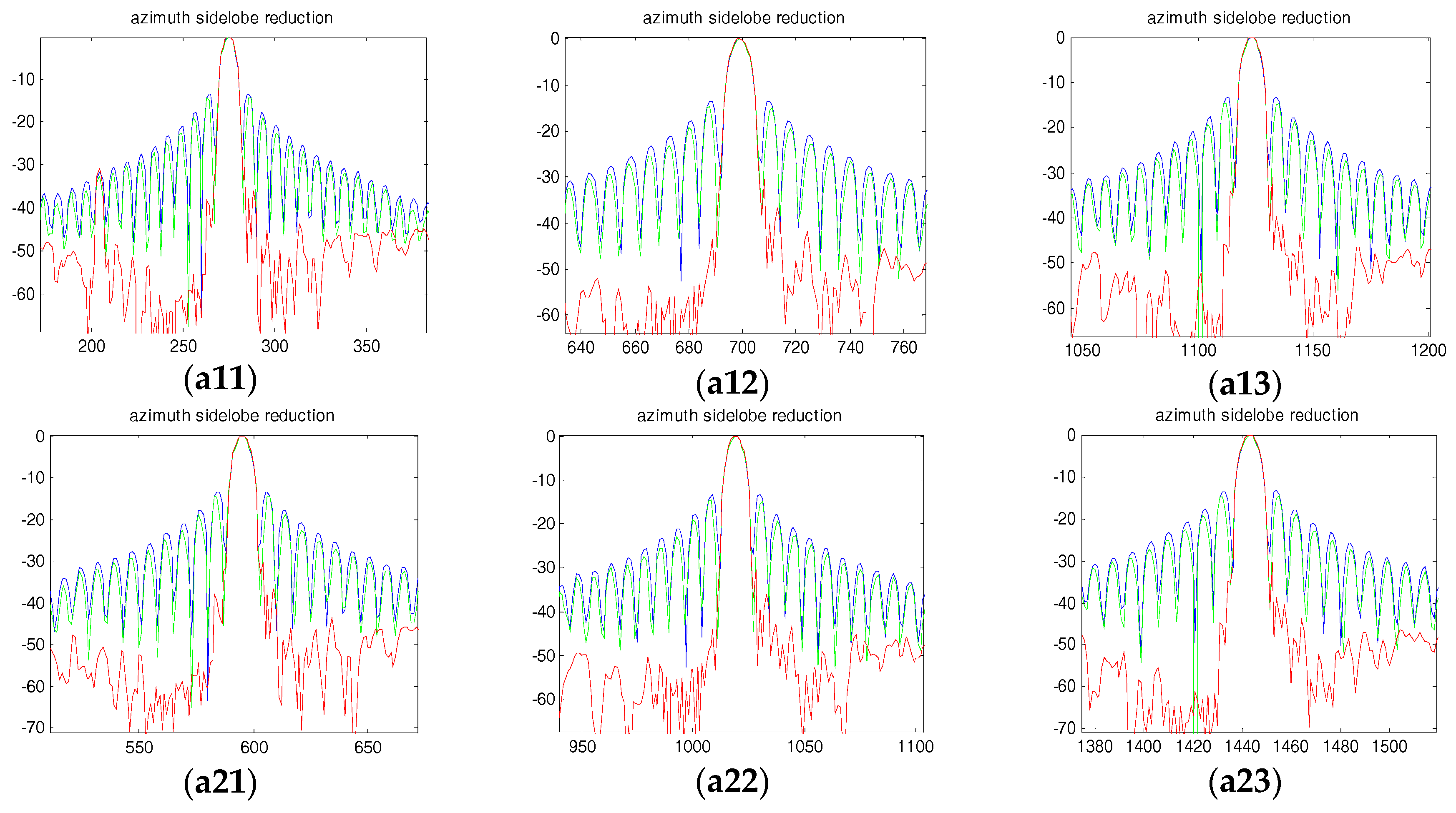
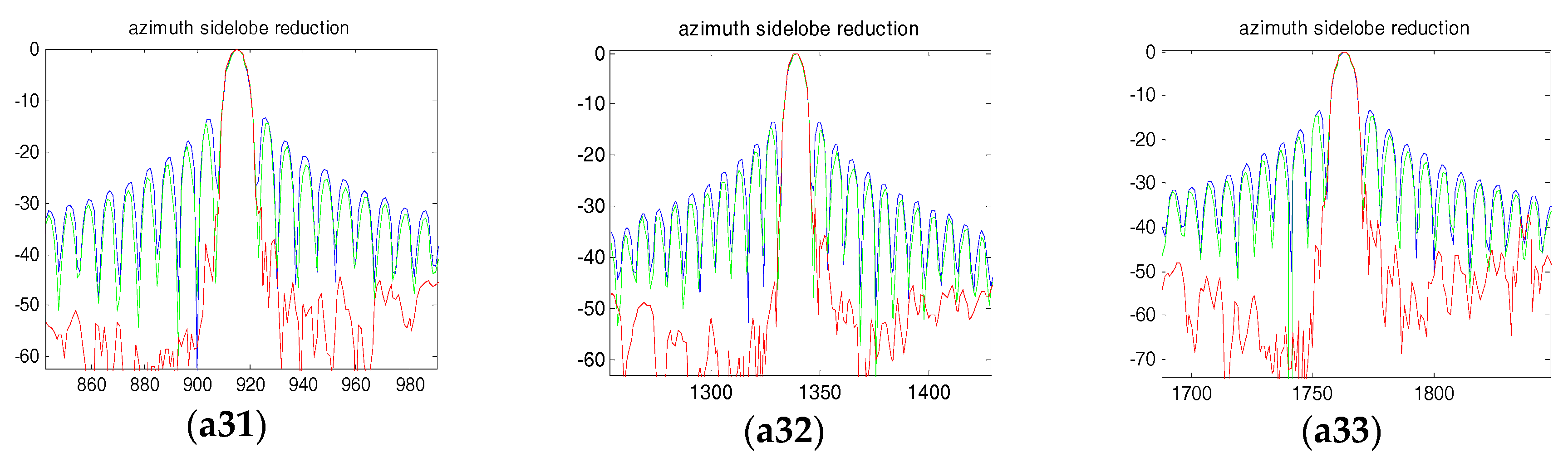
| Parameters | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 0.05657 | m |
| Pulse bandwidth | 100 | MHz |
| Sampling rate | 120 | MHz |
| Velocity | 250 | m/s |
| Pulse duration | 1 | |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 500 | Hz |
| Squint angle | 40 | deg |
| Synthetic aperture time | 2.5136 | sec |
| Central slant range | 22.057 | Km |
| Performance Index | Traditional SVA | Proposed Framework | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a11 | Range PSLR | −15.38 dB | −33.13 dB |
| Azimuth PSLR | −14.42 dB | −30.63 dB | |
| a12 | Range PSLR | −14.73 dB | −30.64 dB |
| Azimuth PSLR | −14.67 dB | −30.51 dB | |
| a13 | Range PSLR | −14.95 dB | −39.42 dB |
| Azimuth PSLR | −14.54 dB | −30.88 dB | |
| a21 | Range PSLR | −15.36 dB | −33.36 dB |
| Azimuth PSLR | −14.42 dB | −30.64 dB | |
| a22 | Range PSLR | −14.72 dB | −30.80 dB |
| Azimuth PSLR | −14.63 dB | −30.44 dB | |
| a23 | Range PSLR | −15.04 dB | −39.62 dB |
| Azimuth PSLR | −14.59 dB | 30.43 dB | |
| a31 | Range PSLR | −15.33 dB | −33.58 dB |
| Azimuth PSLR | −14.43 dB | −30.84 dB | |
| a32 | Range PSLR | −14.75 dB | −30.85 dB |
| Azimuth PSLR | −14.61 dB | −30.26 dB | |
| a33 | Range PSLR | −15.07 dB | −41.15 dB |
| Azimuth PSLR | −14.59 dB | −30.34 dB | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, L. A Novel Sidelobe Reduction Algorithm Based on Two-Dimensional Sidelobe Correction Using D-SVA for Squint SAR Images. Sensors 2018, 18, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030783
Liu M, Li Z, Liu L. A Novel Sidelobe Reduction Algorithm Based on Two-Dimensional Sidelobe Correction Using D-SVA for Squint SAR Images. Sensors. 2018; 18(3):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030783
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Min, Zhou Li, and Lu Liu. 2018. "A Novel Sidelobe Reduction Algorithm Based on Two-Dimensional Sidelobe Correction Using D-SVA for Squint SAR Images" Sensors 18, no. 3: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030783
APA StyleLiu, M., Li, Z., & Liu, L. (2018). A Novel Sidelobe Reduction Algorithm Based on Two-Dimensional Sidelobe Correction Using D-SVA for Squint SAR Images. Sensors, 18(3), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030783





