Embedding Dimension Selection for Adaptive Singular Spectrum Analysis of EEG Signal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
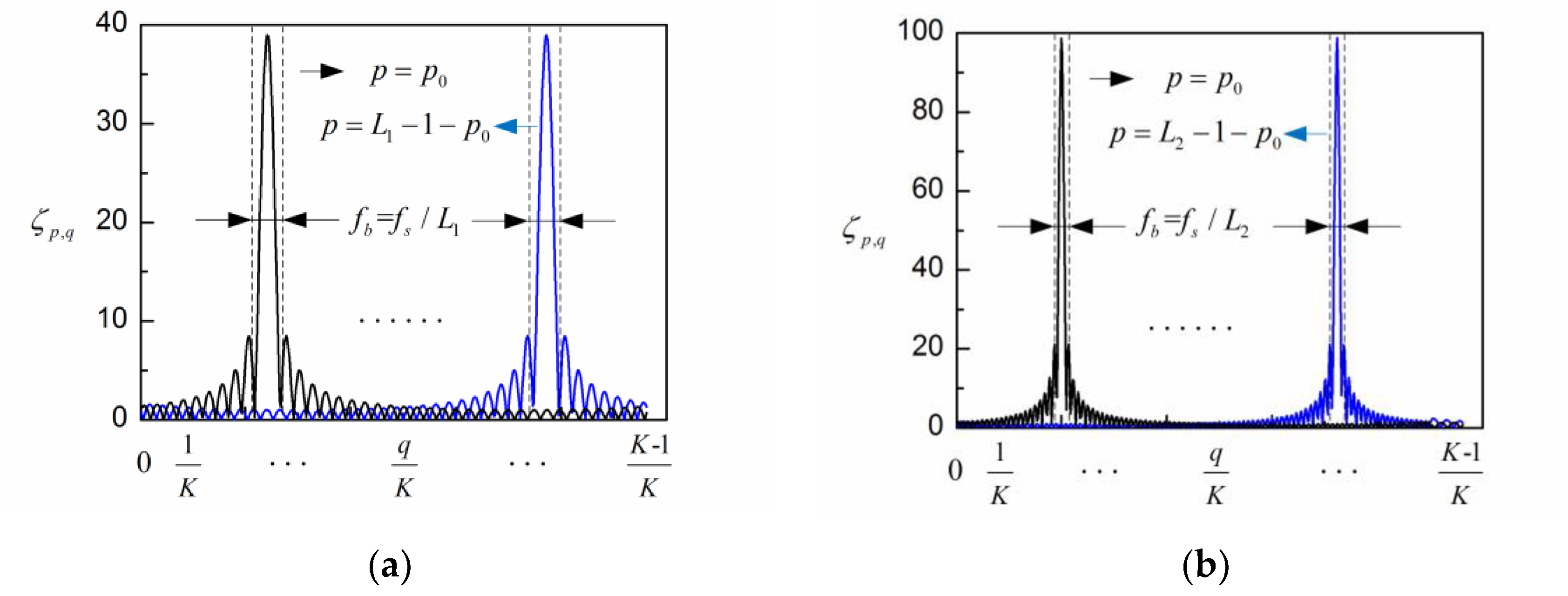
2. Adaptive Singular Spectrum Analysis Method for EEG Processing
3. Simulation Results and Discussion
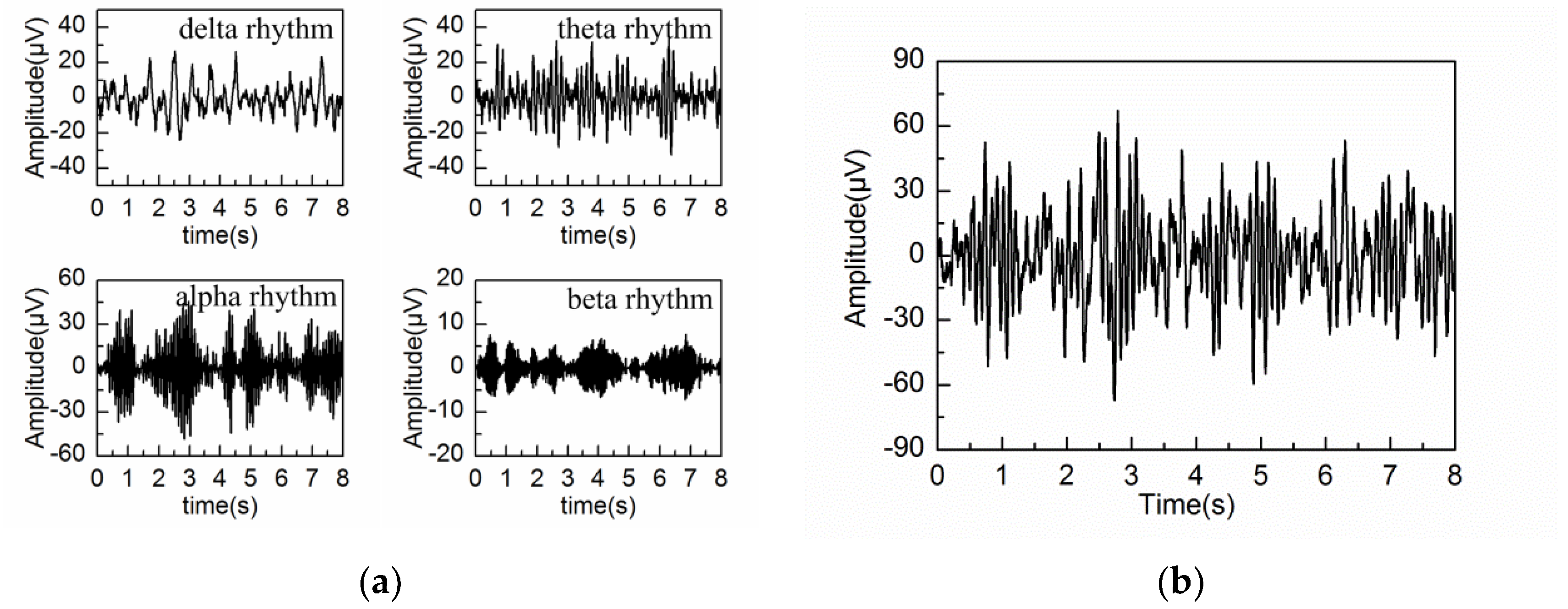
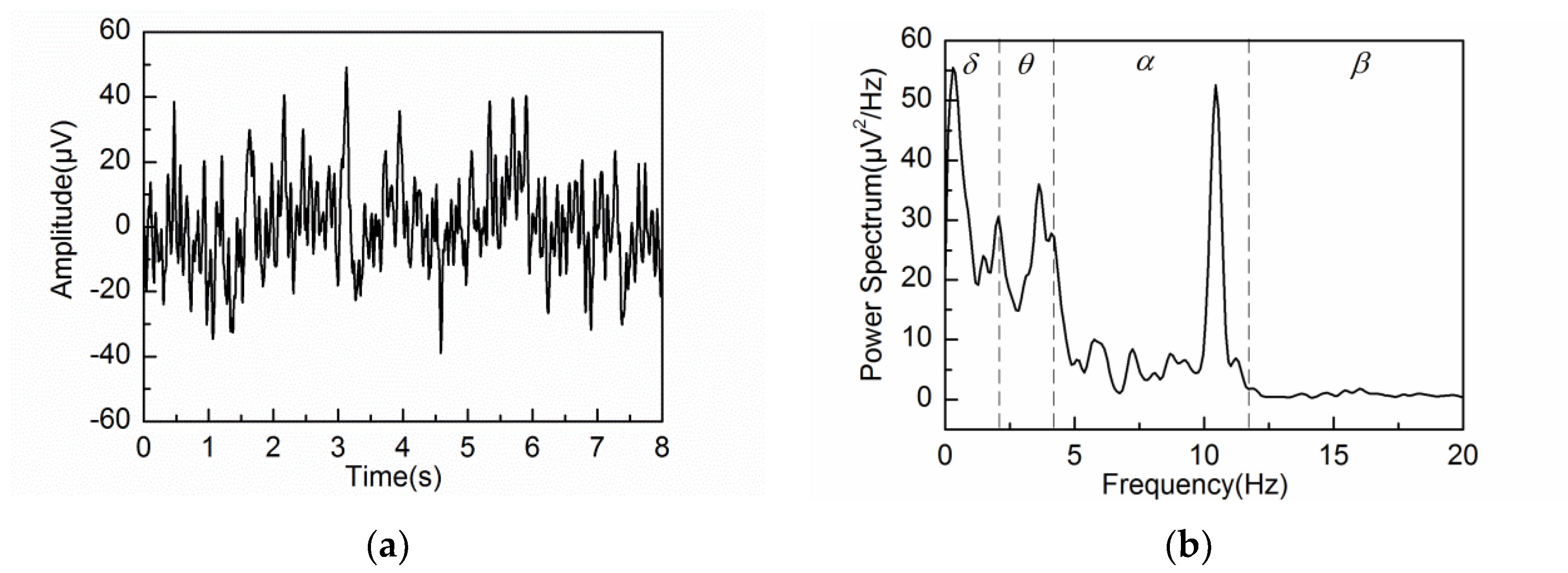
3.1. Markov Process Amplitude EEG Model
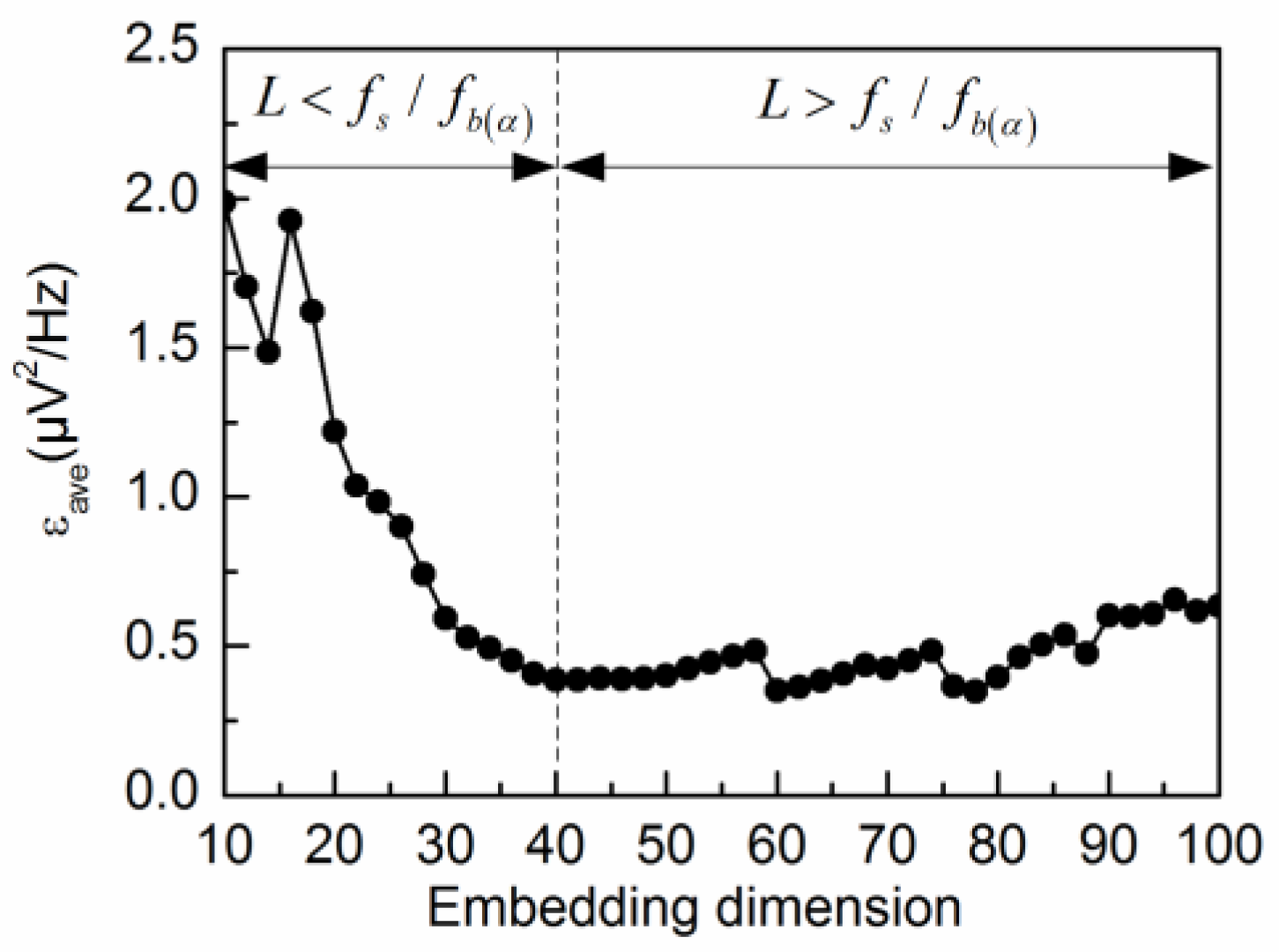
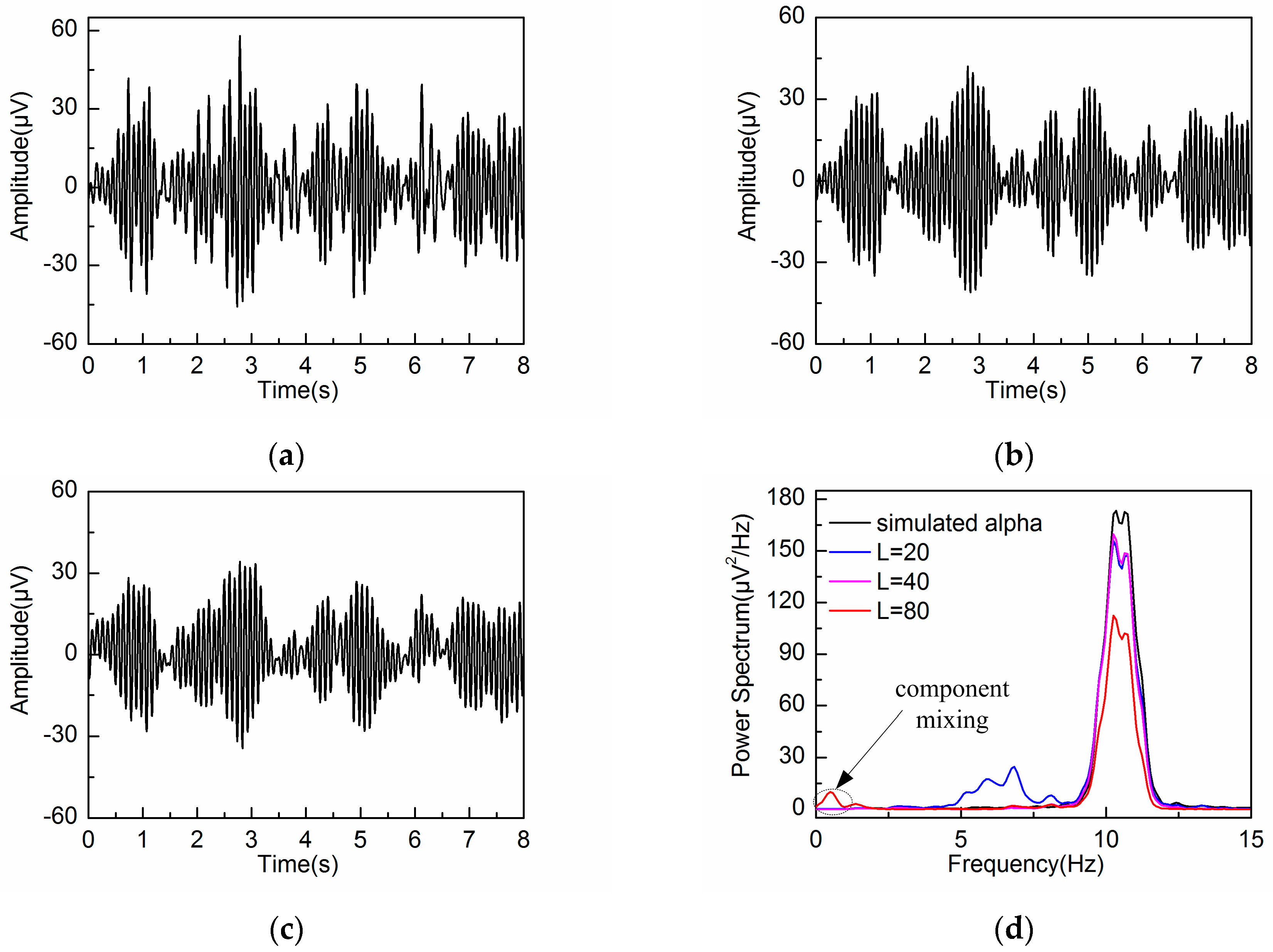
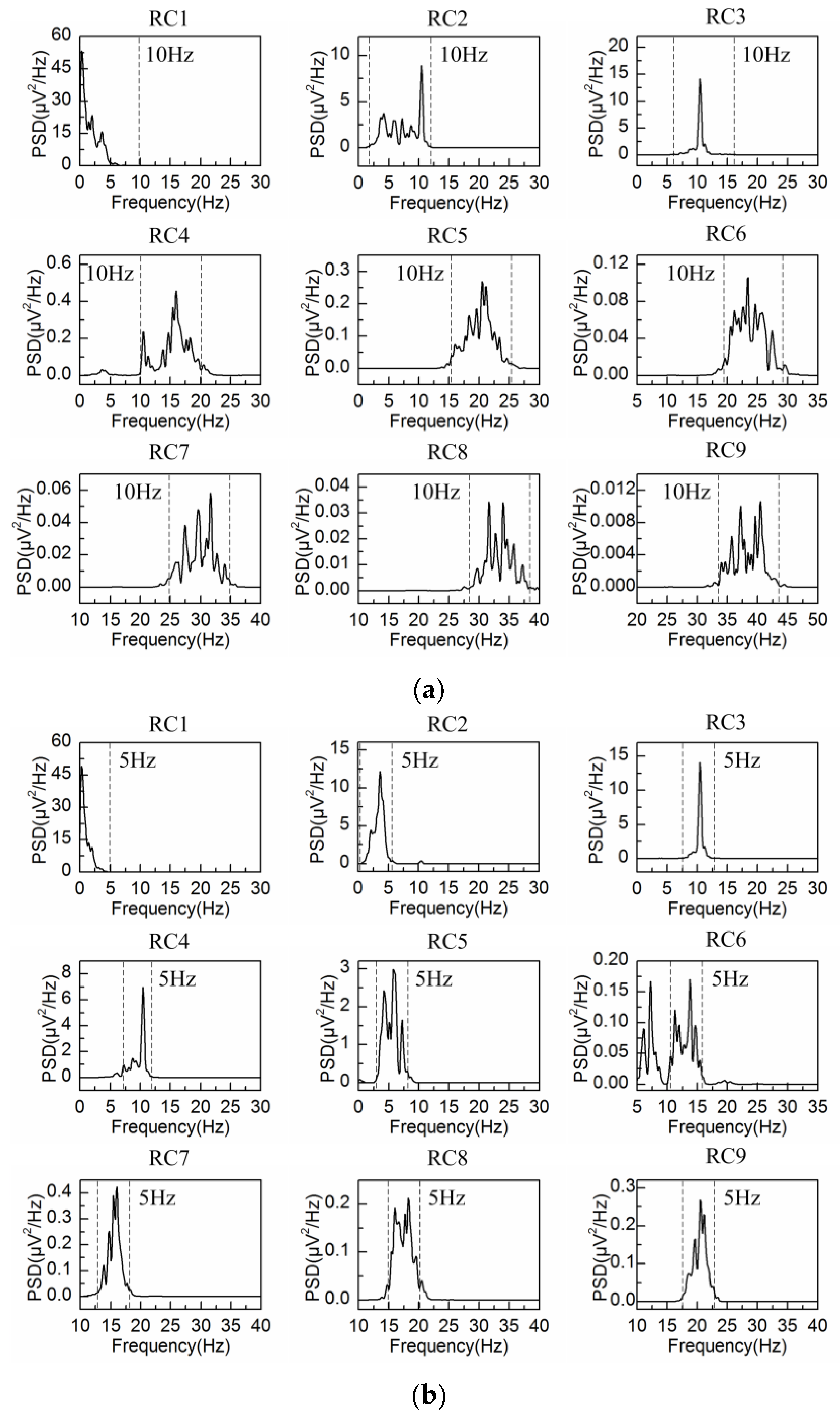
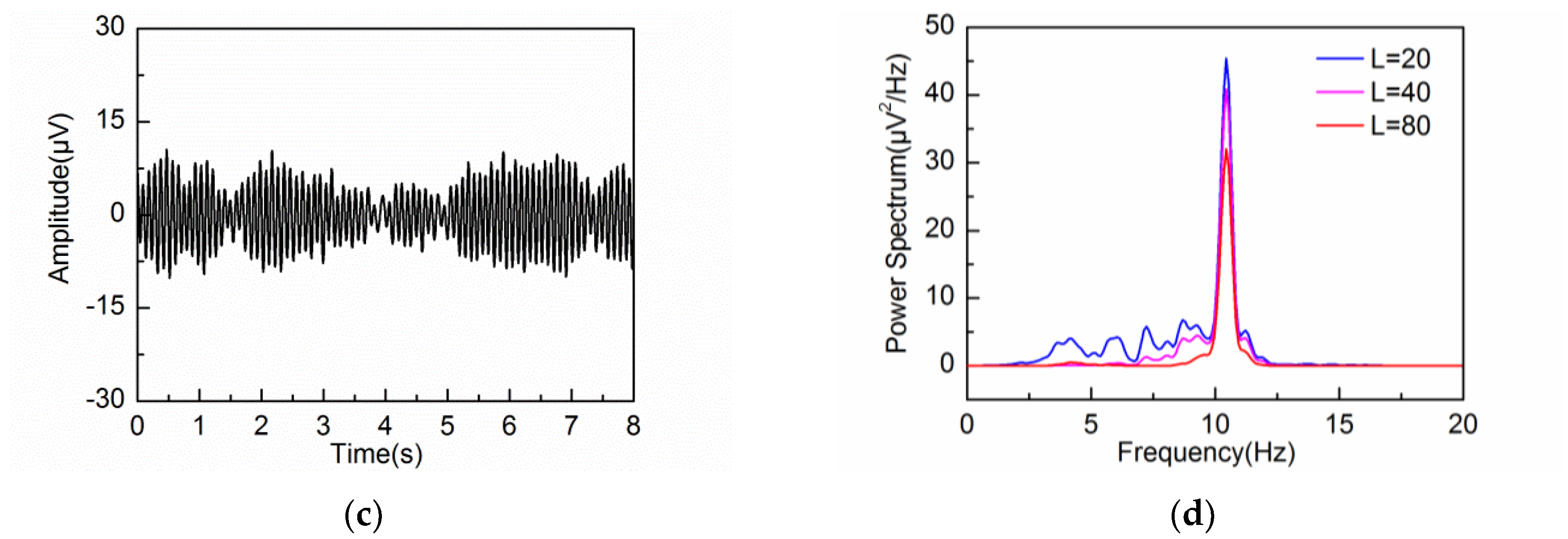
3.2. Adaptive Singular Spectrum Analysis for Simulated EEG signal
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Measurement Setup and Experimental Procedure
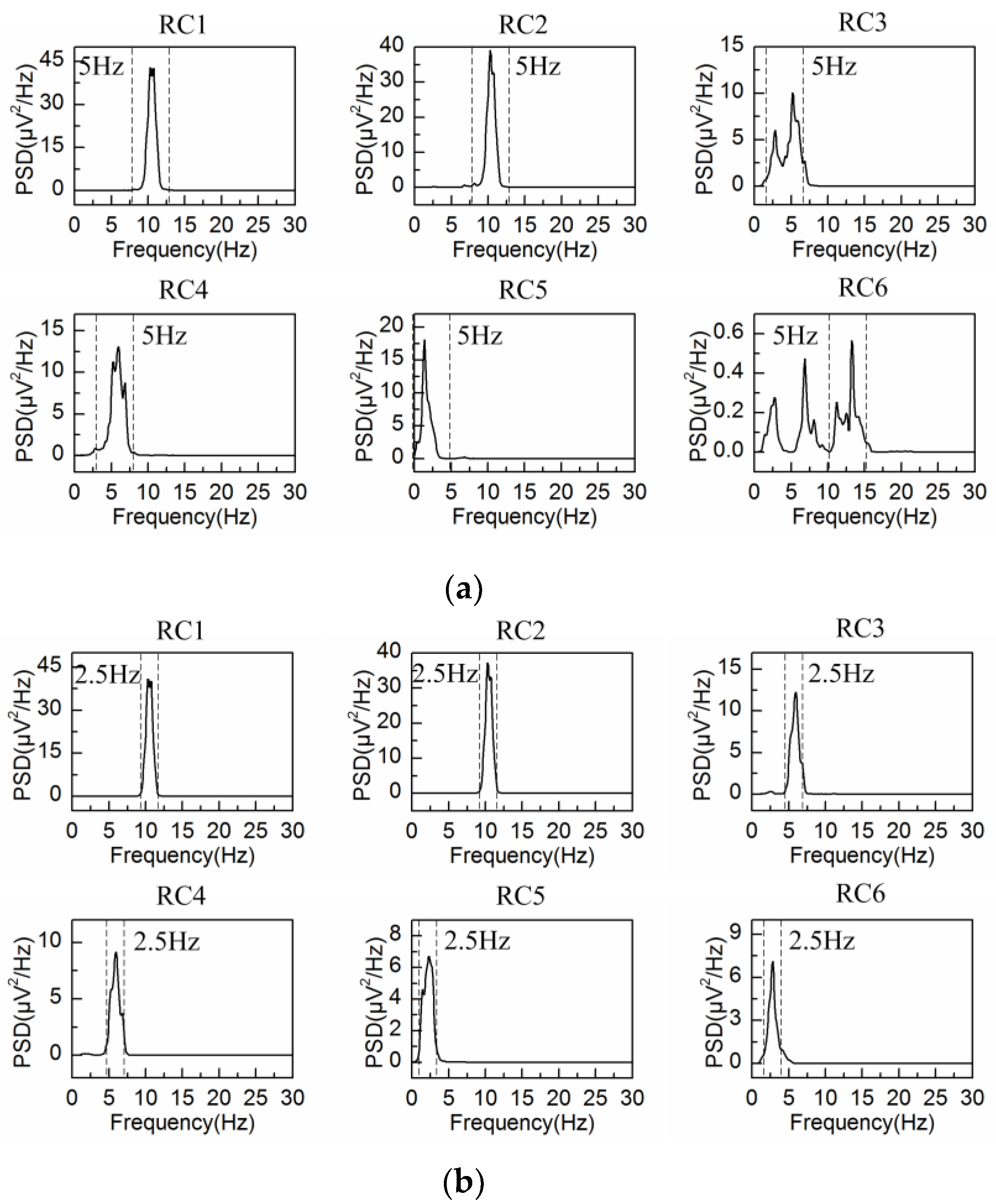
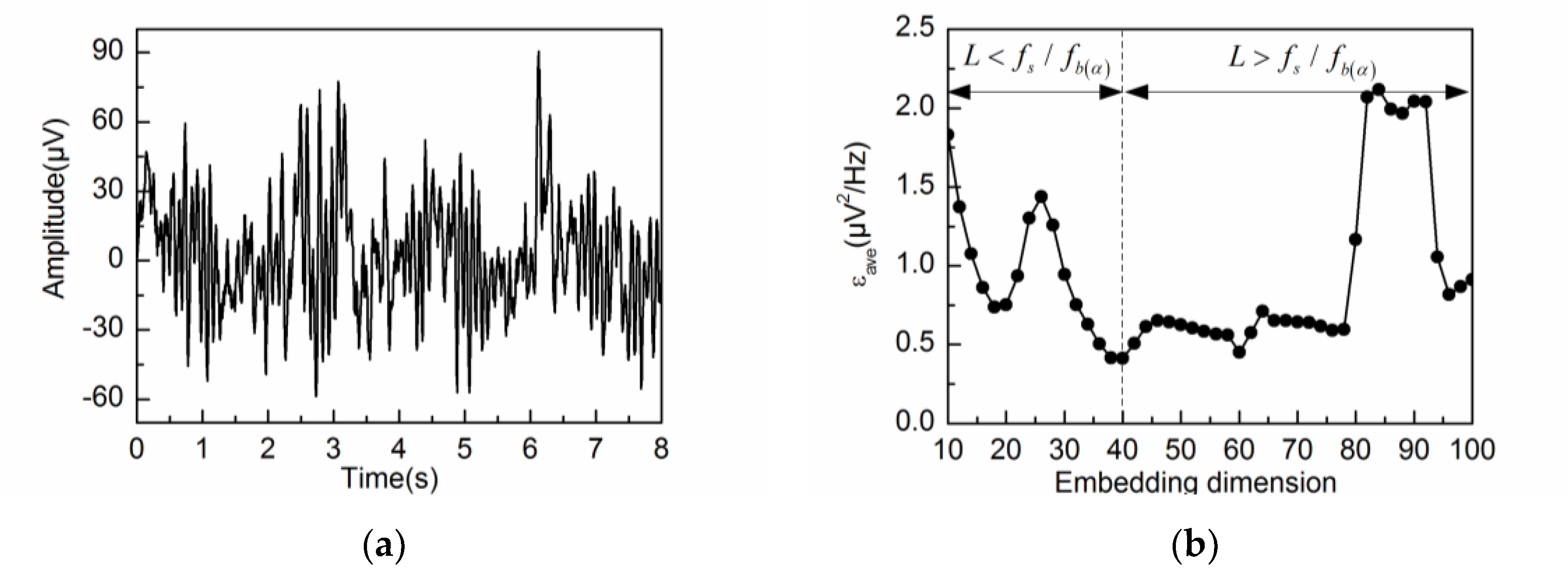
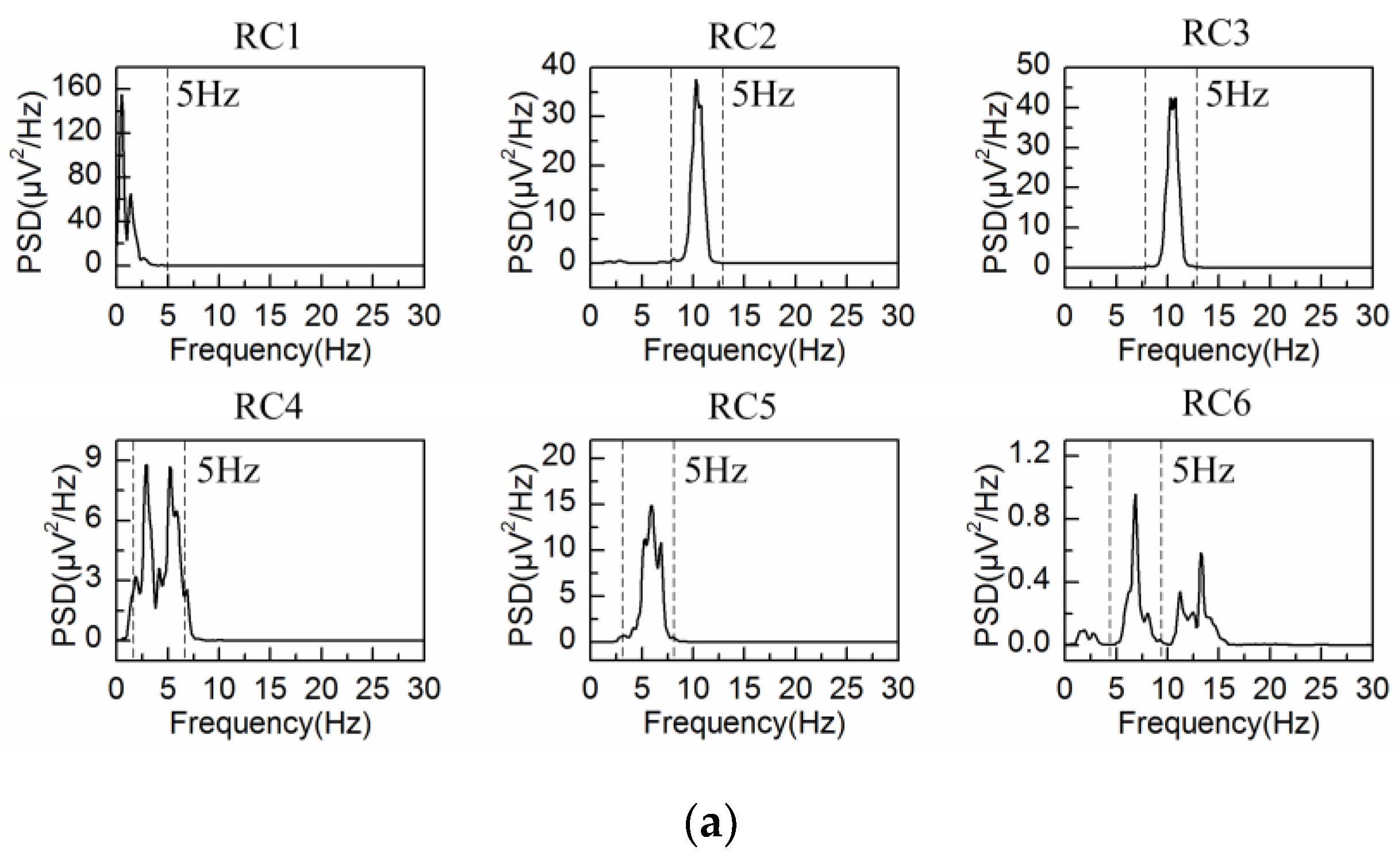
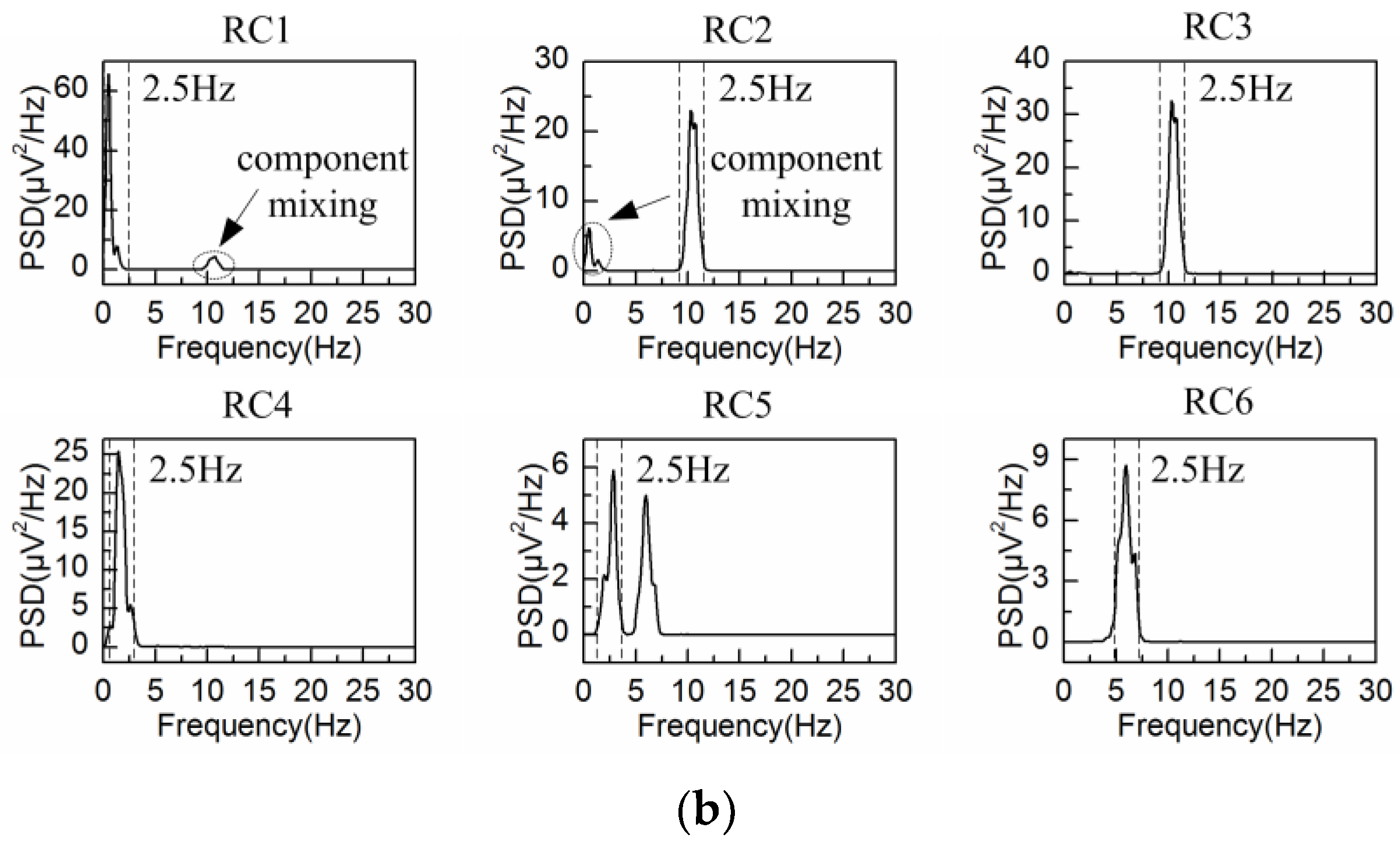
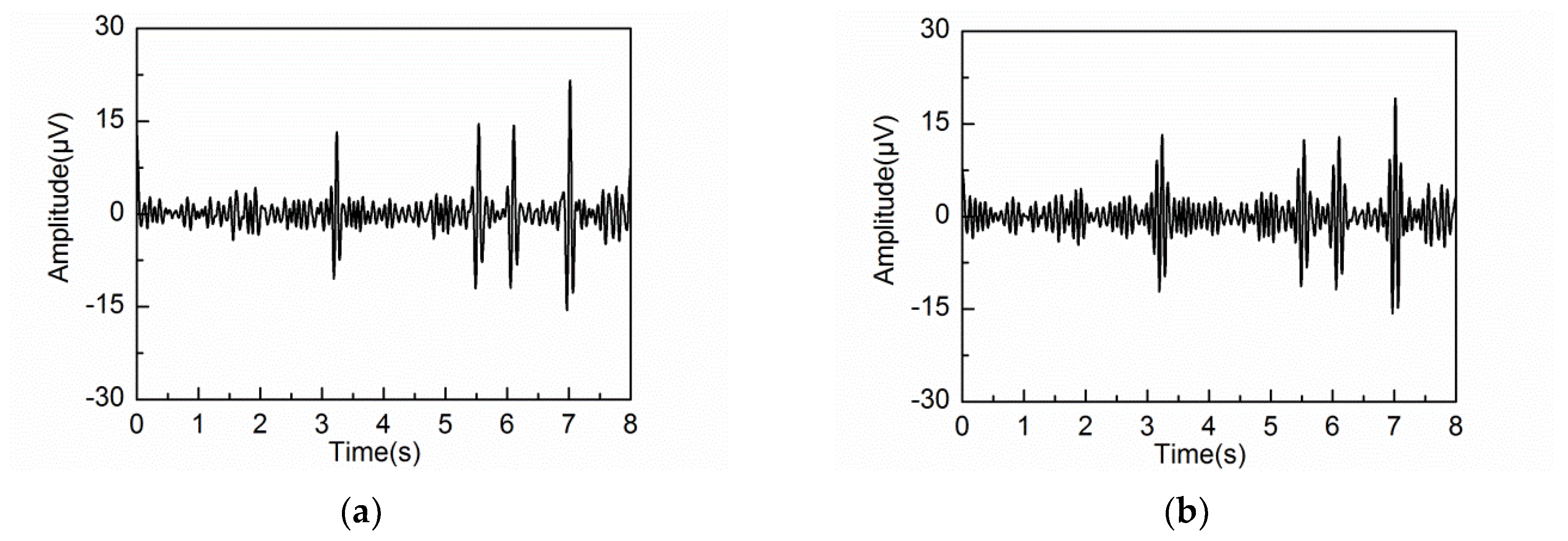
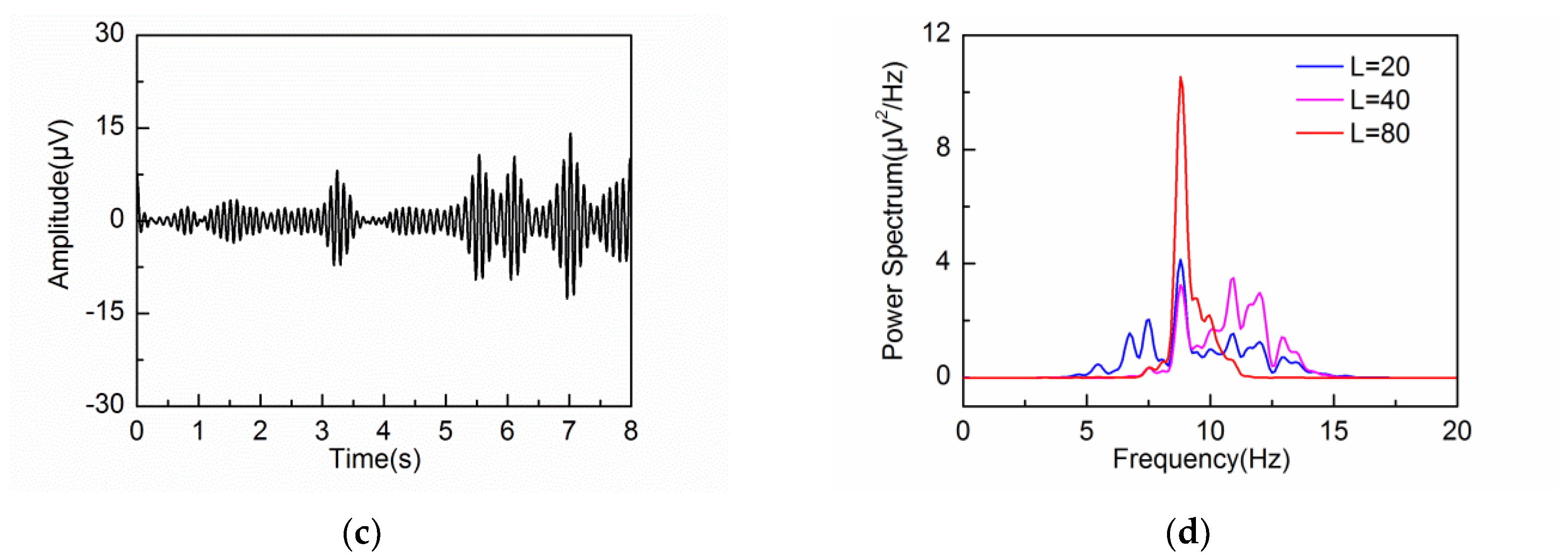
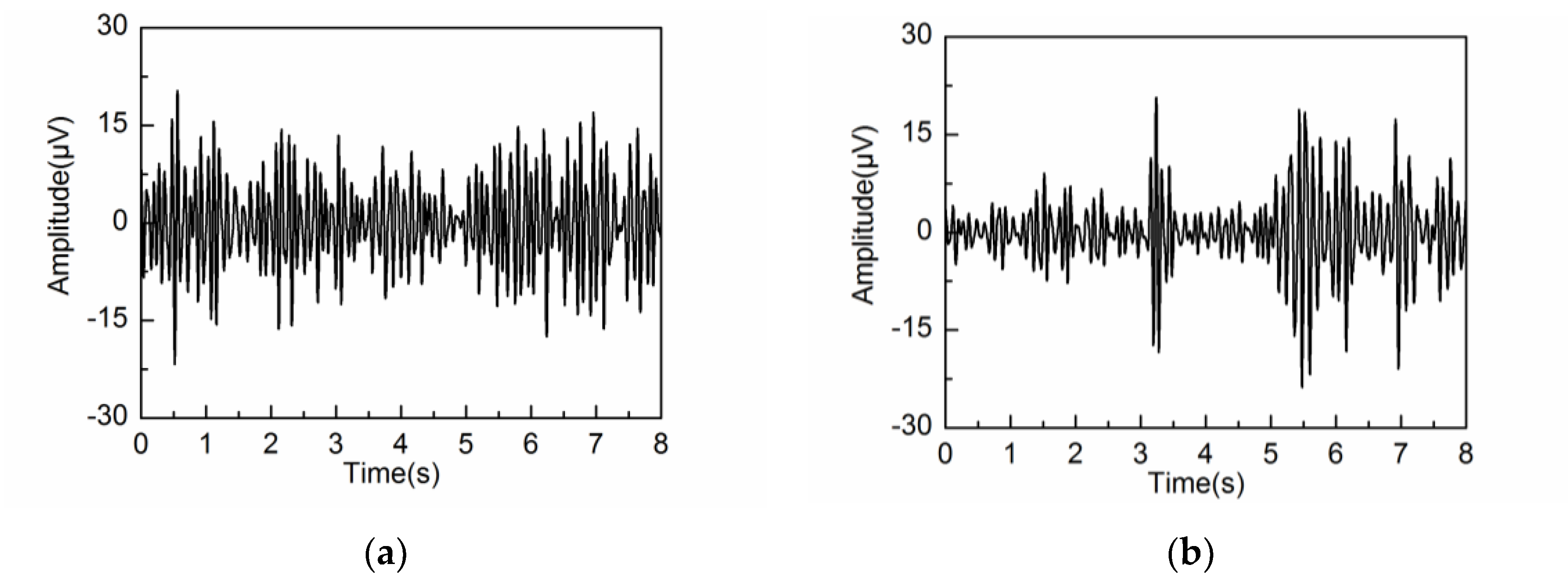
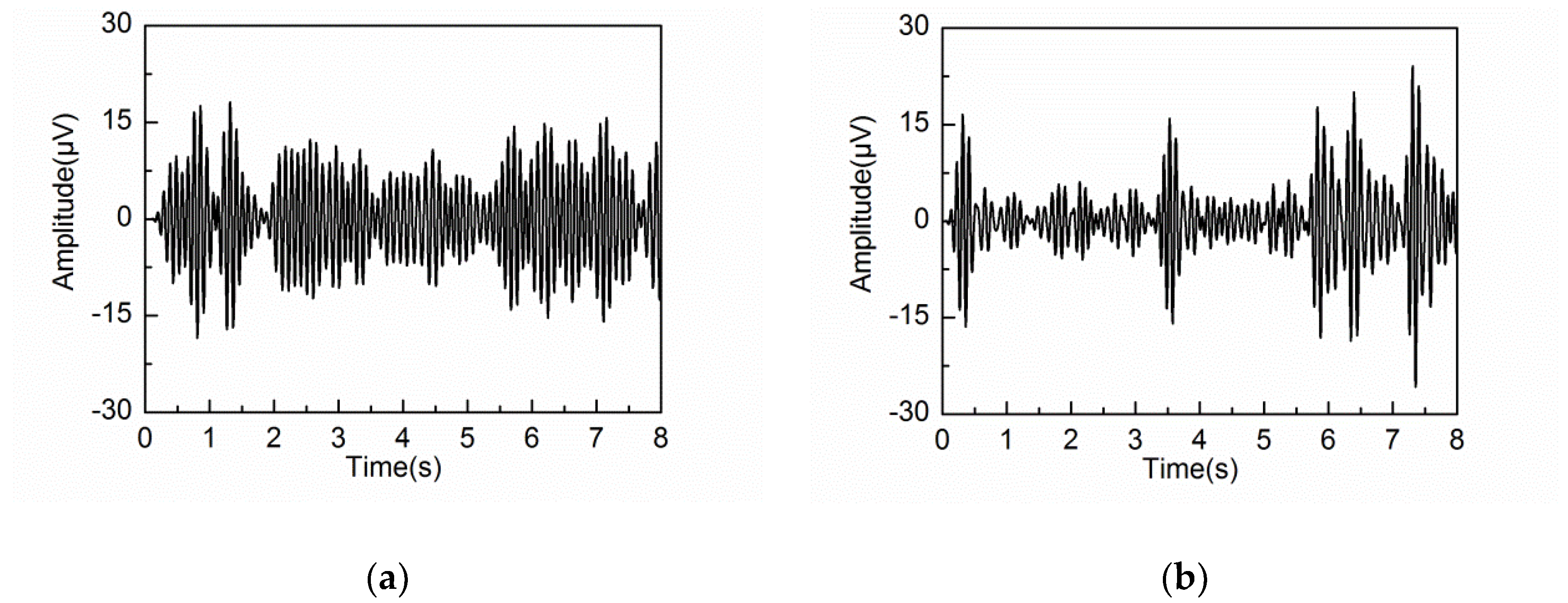
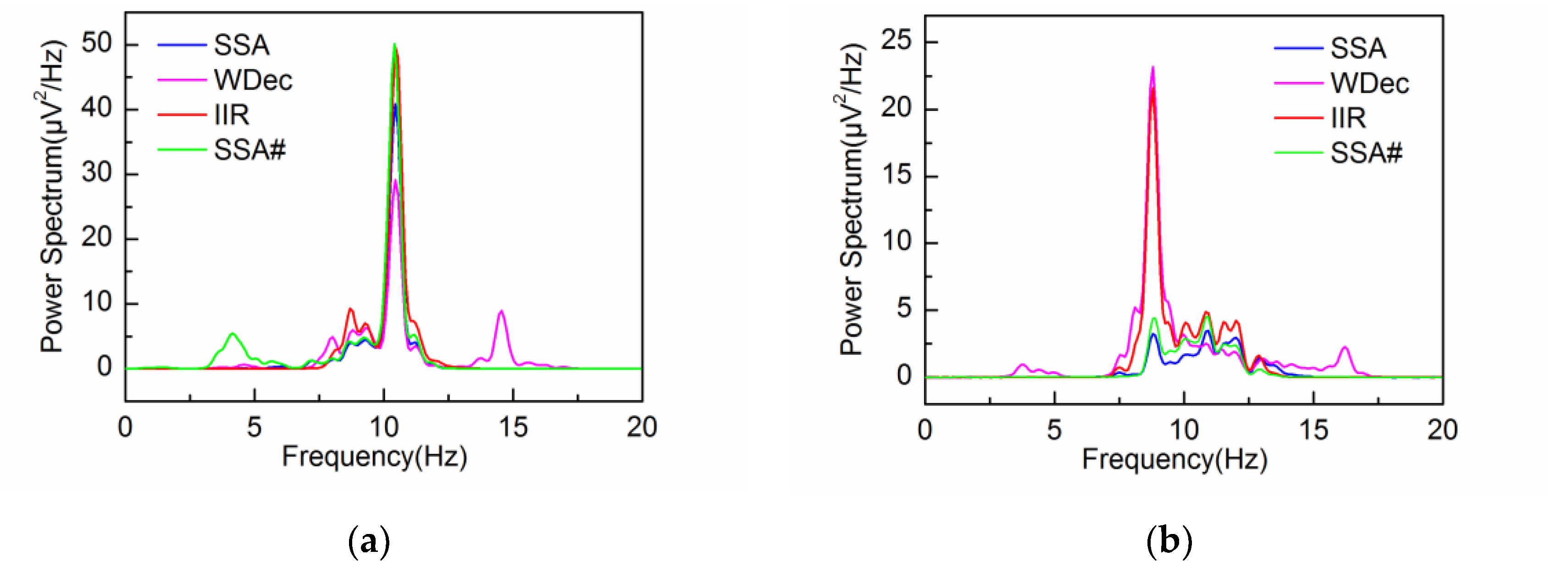
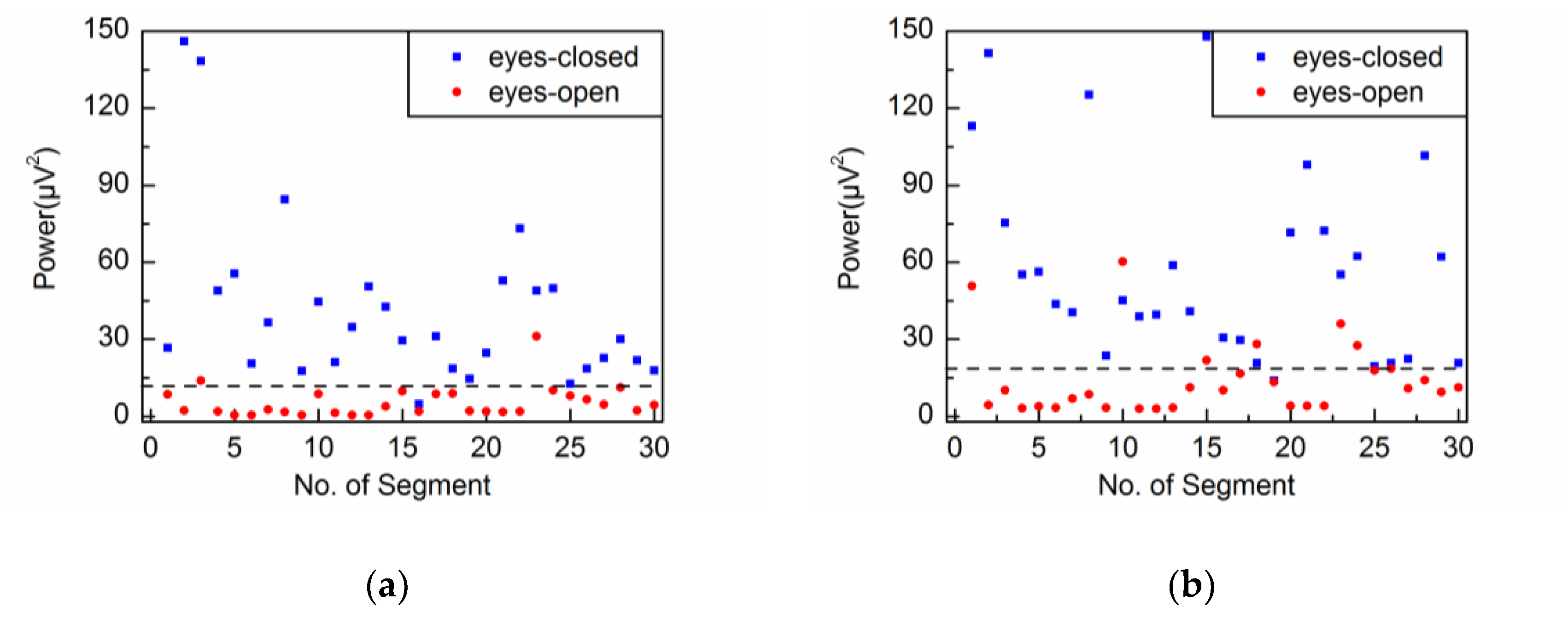
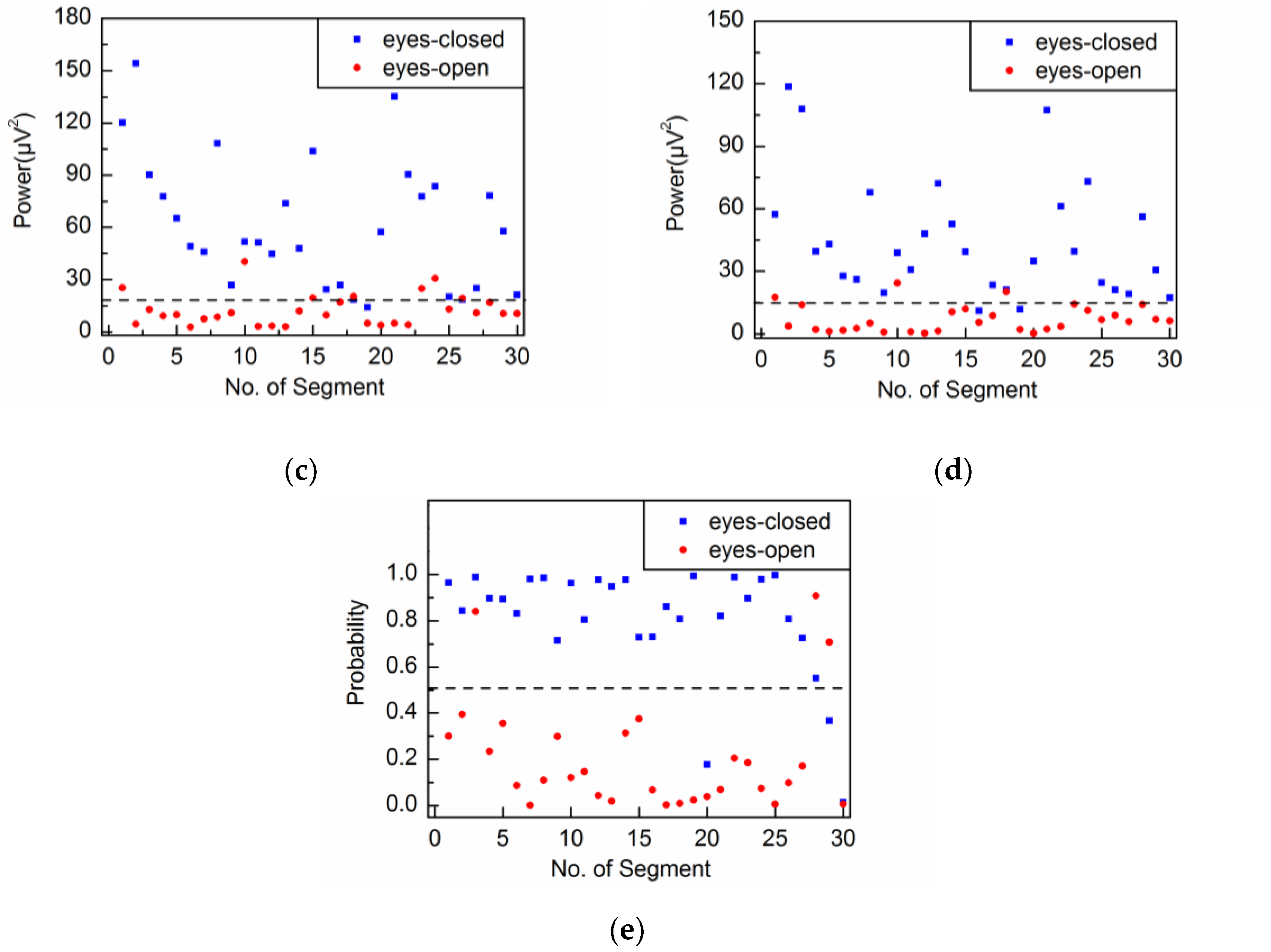
4.2. Adaptive Singular Spectrum Analysis for Real EEG Signal
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teplan, M. Fundamentals of EEG measurement. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2002, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, N.; Meile, M.J.; Nicolaidis, S. EEG alpha activity reflects attentional demands and beta activity reflects emotional and cognitive processes. Science 1985, 228, 750–752. [Google Scholar]
- Schacter, D.L. EEG theta waves and psychological phenomena: A review and analysis. Biol. Psychol. 1977, 5, 47–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmony, T.; Fernández, T.; Silva, J.; Bernal, J.; Díaz-Comas, L.; Reyes, A.; Marosi, E.; Rodríguez, M.; Rodríguez, M. EEG delta activity: An indicator of attention to internal processing during performance of mental tasks. Int. J. Psuchophysiol. 1996, 24, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delisle-Rodriguez, D.; Villa-Parra, A.; Bastos-Filho, T.; López-Delis, A.; Frizera-Neto, A.; Krishnan, S.; Rocon, E. Adaptive Spatial Filter Based on Similarity Indices to Preserve the Neural Information on EEG Signals during On-Line Processing. Sensors 2017, 17, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Jia, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. A tensor-based scheme for stroke patients’ motor imagery EEG analysis in BCI-FES rehabilitation training. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 222, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantini, D.; Perrucci, M.G.; Del Gratta, C.; Romani, G.L.; Corbetta, M. Electrophysiological signatures of resting state networks in the human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13170–13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urigüen, J.A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. EEG artifact removal—State-of-the-art and guidelines. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 31001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feis, R.A.; Smith, S.M.; Filippini, N.; Douaud, G.; Dopper, E.G.P.; Heise, V.; Trachtenberg, A.J.; Swieten, J.C.V.; Buchem, M.A.V.; Rombouts, S.A.R.B. ICA-based artifact removal diminishes scan site differences in multi-center resting-state fMRI. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, I.; Nicolaou, N.; Nasuto, S.J.; Warwick, K. Automated artifact removal from the electroencephalogram: A comparative study. Clin. Eng. Neurosci. 2013, 44, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, R.R.; Vélez-Pérez, H.; Ranta, R.; Dorr, V.L.; Maquin, D.; Maillard, L. Blind source separation, wavelet denoising and discriminant analysis for EEG artefacts and noise cancelling. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2012, 7, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wilson, G.; Russell, C. Removal of ocular artifacts from electro-encephalogram by adaptive filtering. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2004, 42, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, P.N.; Shanamugan, D.; Chourasia, A.; Ghole, A.R.; Acharyya, A.; Naik, G. Automated Detection and Correction of Eye Blink and Muscular Artefacts in EEG Signal for Analysis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 1881–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Jadhav, P.; Adapa, B.; Acharyya, A.; Naik, G.R. Online and automated reliable system design to remove blink and muscle artefact in EEG. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 6784–6787. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, R.; Ling, S.H.; San, P.P.; Naik, G.R.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tran, Y.; Craig, A.; Nguyen, H.T. Improving EEG-Based Driver Fatigue Classification Using Sparse-Deep Belief Networks. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golyandina, N.; Zhigljavsky, A. Singular Spectrum Analysis for Time Series; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sanei, S.; Hassani, H. Singular Spectrum Analysis of Biomedical Signals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, C.C.; Chandran, V.; Acharya, U.R.; Lim, C.M. Application of higher order statistics/spectra in biomedical signals—A review. Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 679. [Google Scholar]
- Maddirala, A.K.; Shaik, R.A. Motion artifact removal from single channel electroencephalogram signals using singular spectrum analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 30, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddirala, A.K.; Shaik, R.A. Removal of EOG Artifacts from single channel EEG signals using combined singular spectrum analysis and adaptive noise canceler. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 8279–8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.M.; Enshaeifar, S.; Ghavami, M.; Sanei, S. Classification of awake, REM and NREM from EEG via singular spectrum analysis. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 4769–4772. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, S.M.; Kouchaki, S.; Ghavami, M.; Sanei, S. Improving time–frequency domain sleep EEG classification via singular spectrum analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 273, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akar, S.A.; Kara, S.; Latifoğlu, F.; Bilgic, V. Investigation of the noise effect on fractal dimension of EEG in schizophrenia patients using wavelet and SSA-based approaches. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2015, 18, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.R.; Tomé, A.M.; Lang, E.W.; Gruber, P.; Silva, A.M.D. On the use of clustering and local singular spectrum analysis to remove ocular artifacts from electroencephalograms. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Montreal, QC, Canada, 31 July–4 August 2005; pp. 2514–2519. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, H.; Guo, S.; Ran, L.; Peng, W. An adaptive singular spectrum analysis method for extracting brain rhythms of electroencephalography. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3474. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, A.R.; Tomé, A.M.; Lang, E.W.; Gruber, P.; Da Silva, A.M. Automatic removal of high-amplitude artefacts from single-channel electroencephalograms. Comput. Methods Prog. Biol. 2006, 83, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.J.; Lowe, D. Extracting multisource brain activity from a single electromagnetic channel. Artif. Intell. Med. 2003, 28, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, S.; Ghodsi, M.; Hassani, H. An adaptive singular spectrum analysis approach to murmur detection from heart sounds. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golyandina, N.; Nekrutkin, V.; Zhigljavsky, A.A. Analysis of Time Series Structure: SSA and Related Techniques; Chapman & Hall CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 81–82. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, R.M. Toeplitz and circulant matrices: A review. Found. Trends® Commun. Inf. Theory 2006, 2, 155–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dong, Y.; Yu, C.; Hou, Z. Singular Spectrum Analysis Window Length Selection in Processing Capacitive Captured Biopotential Signals. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 7183–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, D.S.G. Circulant matrices and time series analysis. Int. J. Math. Educ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 33, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzo, E.; Carniel, R.; Fasino, D. Relationship between Singular Spectrum Analysis and Fourier analysis: Theory and application to the monitoring of volcanic activity. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 60, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudvand, R.; Zokaei, M. On the singular values of the Hankel matrix with application in singular spectrum analysis. Chil. J. Stat. 2012, 3, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, O.; Nakamura, M.; Nishida, S.; Ikeda, A.A.; Shibasaki, H. Markov process amplitude EEG model for spontaneous background activity. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 18, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnashash, H.; Alassaf, Y.; Paul, J.; Thakor, N. EEG signal modeling using adaptive Markov process amplitude. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; Long, X.; Zuo, X.; Yan, C.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; He, Y.; Zang, Y. Functional connectivity between the thalamus and visual cortex under eyes closed and eyes open conditions: A resting-state fMRI study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Zahhad, M.; Ahmed, S.M.; Abbas, S.N. A new multi-level approach to EEG based human authentication using eye blinking. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2016, 82, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Symbol | Value | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spontaneous EEG | /Hz | 2.50 | Delta rhythm |
| 0.99 | |||
| 2.26 | |||
| /Hz | 6.00 | Theta rhythm | |
| 0.97 | |||
| 2.78 | |||
| /Hz | 10.50 | Alpha rhythm | |
| 0.99 | |||
| 2.35 | |||
| /Hz | 21.50 | Beta rhythm | |
| 0.99 | |||
| 0.36 | |||
| Artifacts | / | 50 | Amplitude of EOG |
| /s | 3 | Period of EOG | |
| /s | 0.3 | Pulse width of EOG | |
| / | 10 | Amplitude of baseline drift | |
| /Hz | 0.5 | Frequency of baseline drift | |
| Noise | /dBW | 1 | Power of white noise |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Hu, H.; Ji, L.; Wang, P. Embedding Dimension Selection for Adaptive Singular Spectrum Analysis of EEG Signal. Sensors 2018, 18, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030697
Xu S, Hu H, Ji L, Wang P. Embedding Dimension Selection for Adaptive Singular Spectrum Analysis of EEG Signal. Sensors. 2018; 18(3):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030697
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shanzhi, Hai Hu, Linhong Ji, and Peng Wang. 2018. "Embedding Dimension Selection for Adaptive Singular Spectrum Analysis of EEG Signal" Sensors 18, no. 3: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030697
APA StyleXu, S., Hu, H., Ji, L., & Wang, P. (2018). Embedding Dimension Selection for Adaptive Singular Spectrum Analysis of EEG Signal. Sensors, 18(3), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030697




