OSCANN: Technical Characterization of a Novel Gaze Tracking Analyzer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
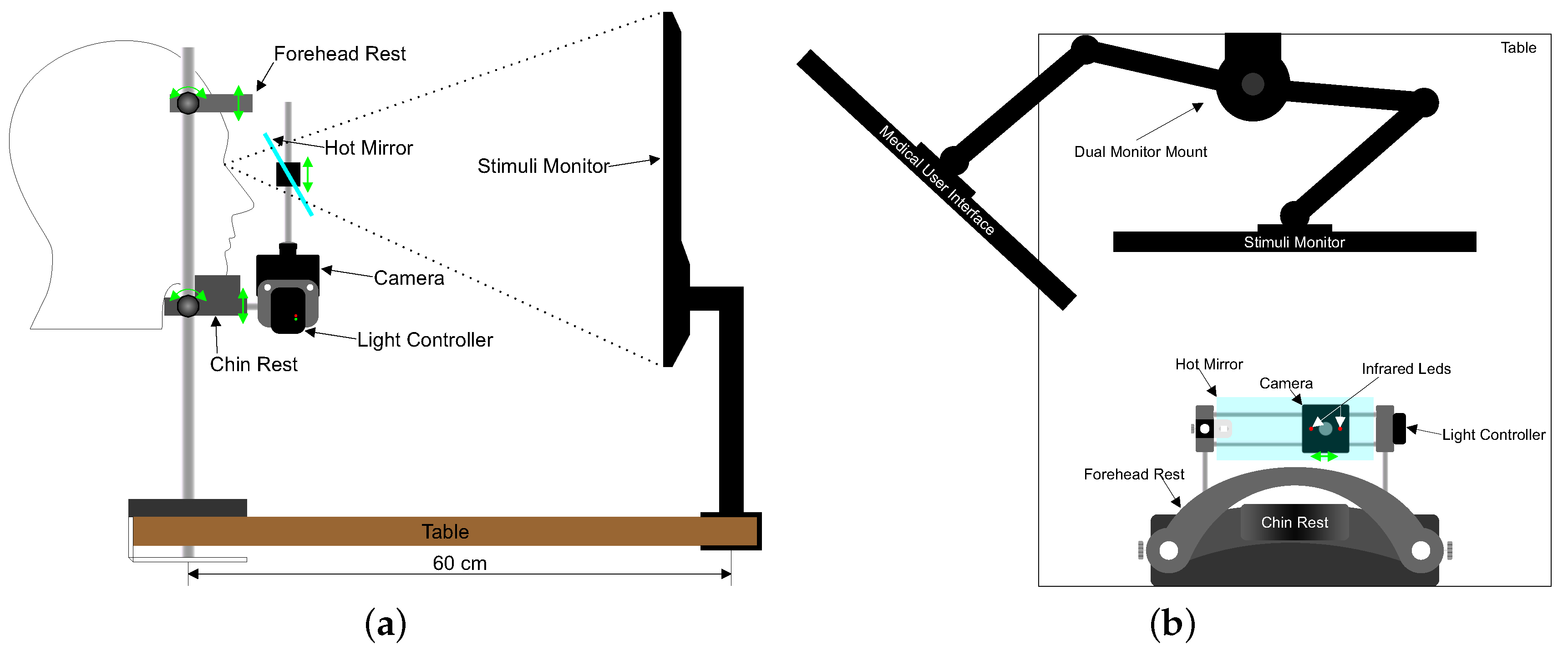
2.1. Apparatus
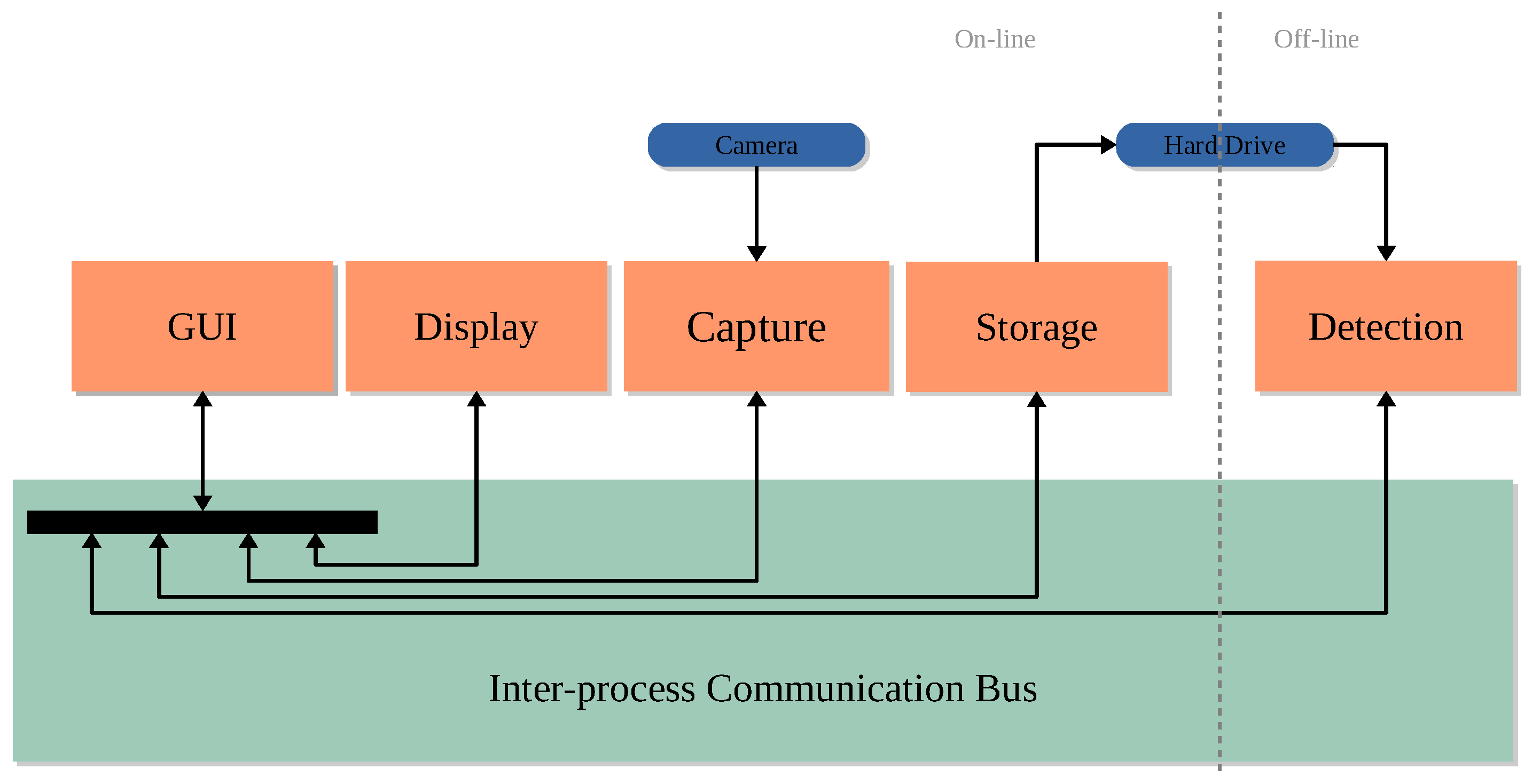
2.2. Software
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Operators
3.2. Participants
3.3. Stimuli
3.4. Artificial Eye
3.5. Environment
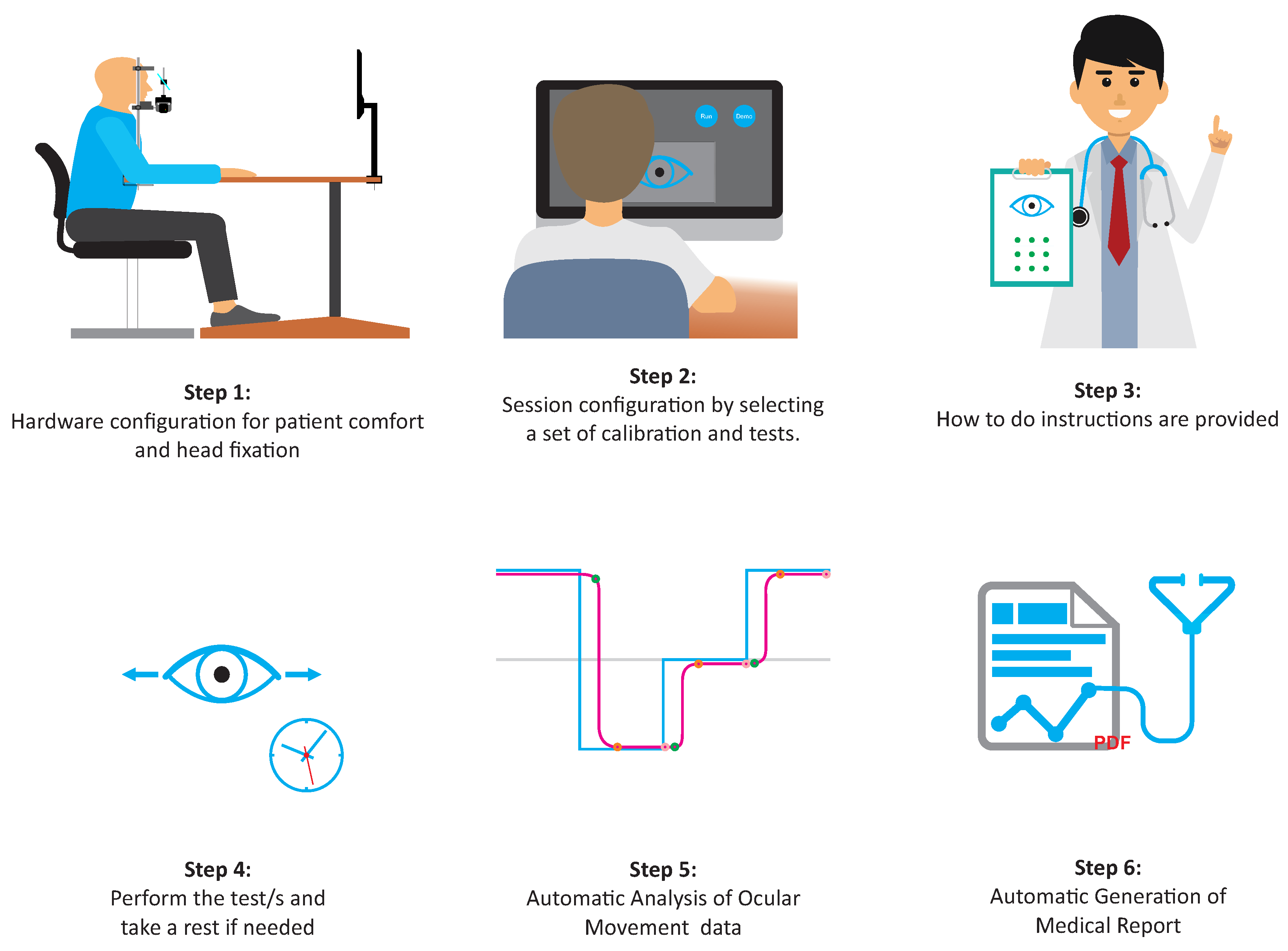
3.6. Procedure
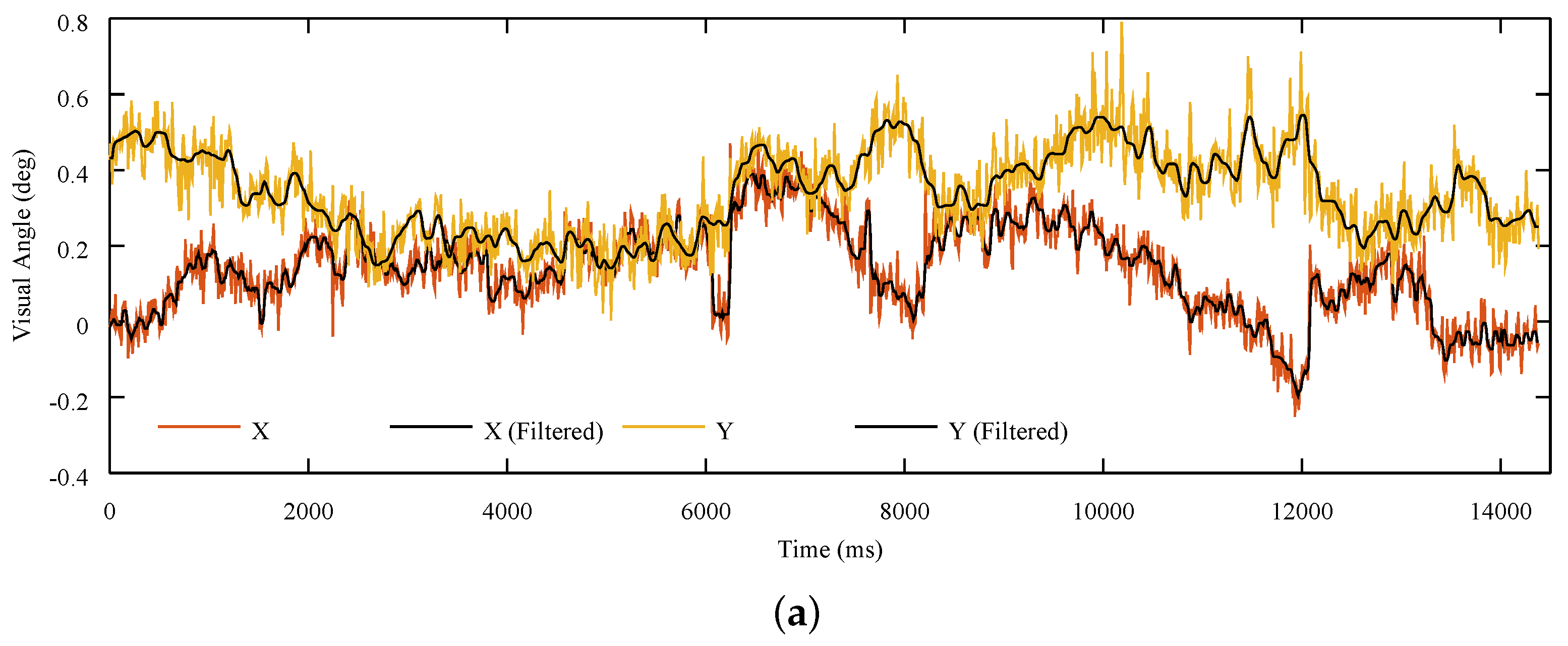
3.7. Data Analysis
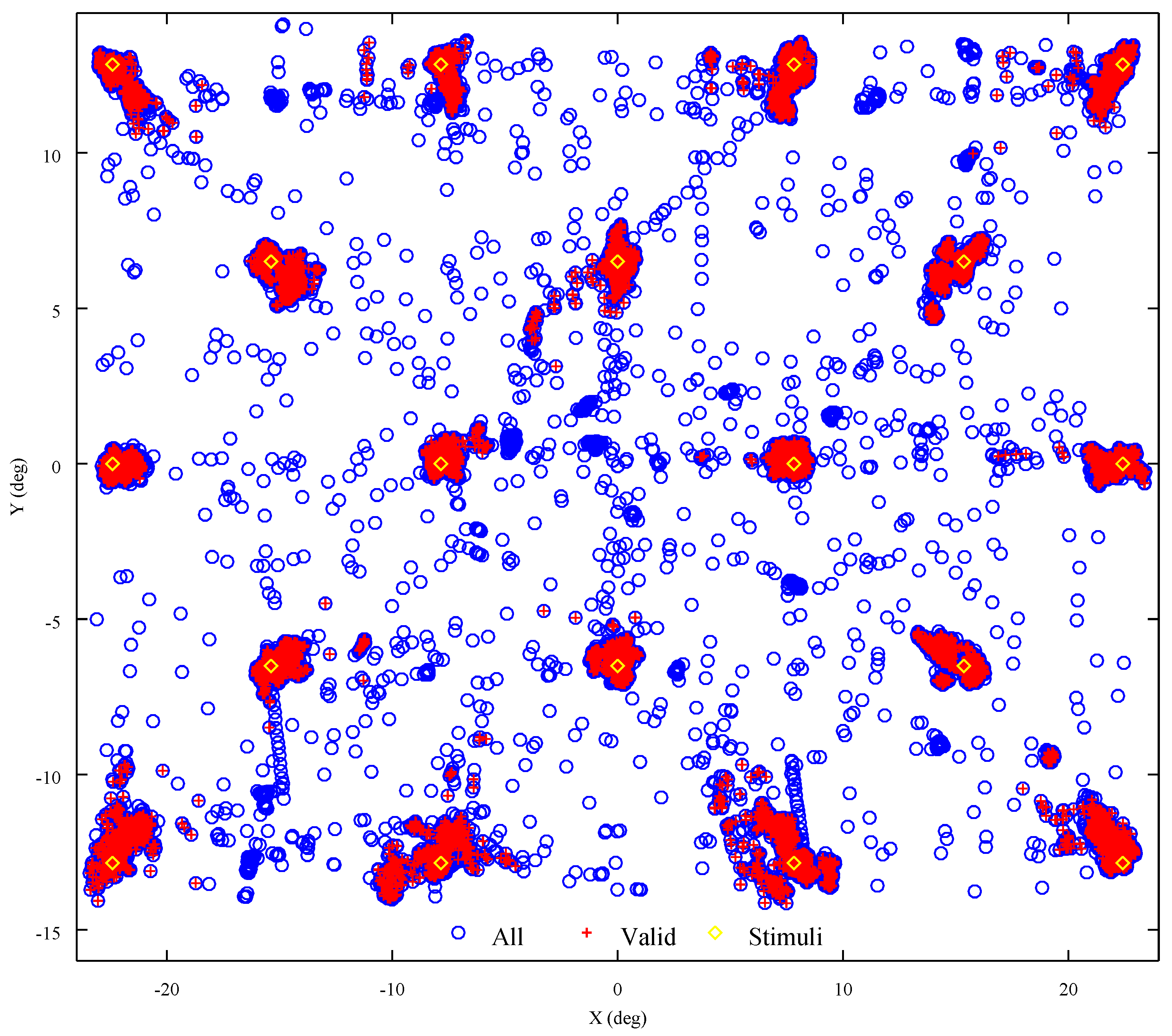
3.8. Accuracy
3.9. Precision
4. Results
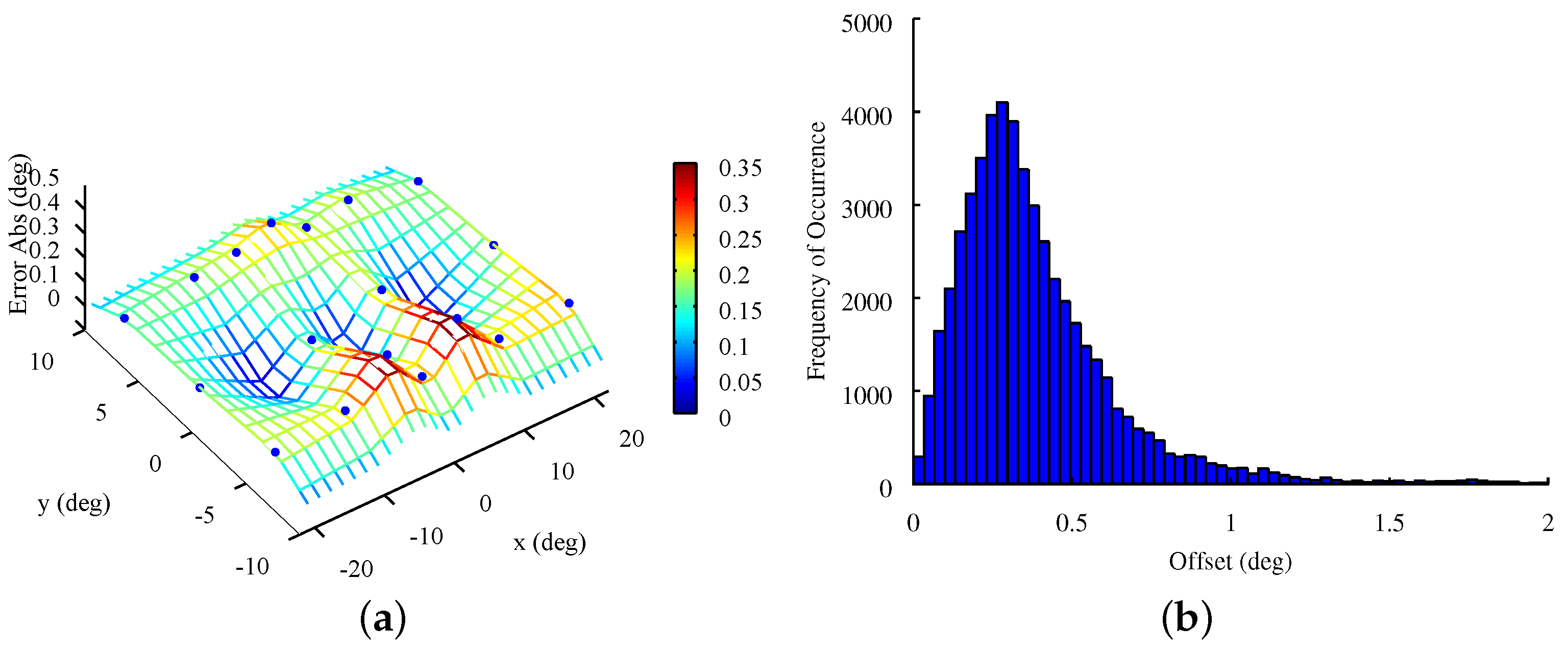
4.1. Accuracy
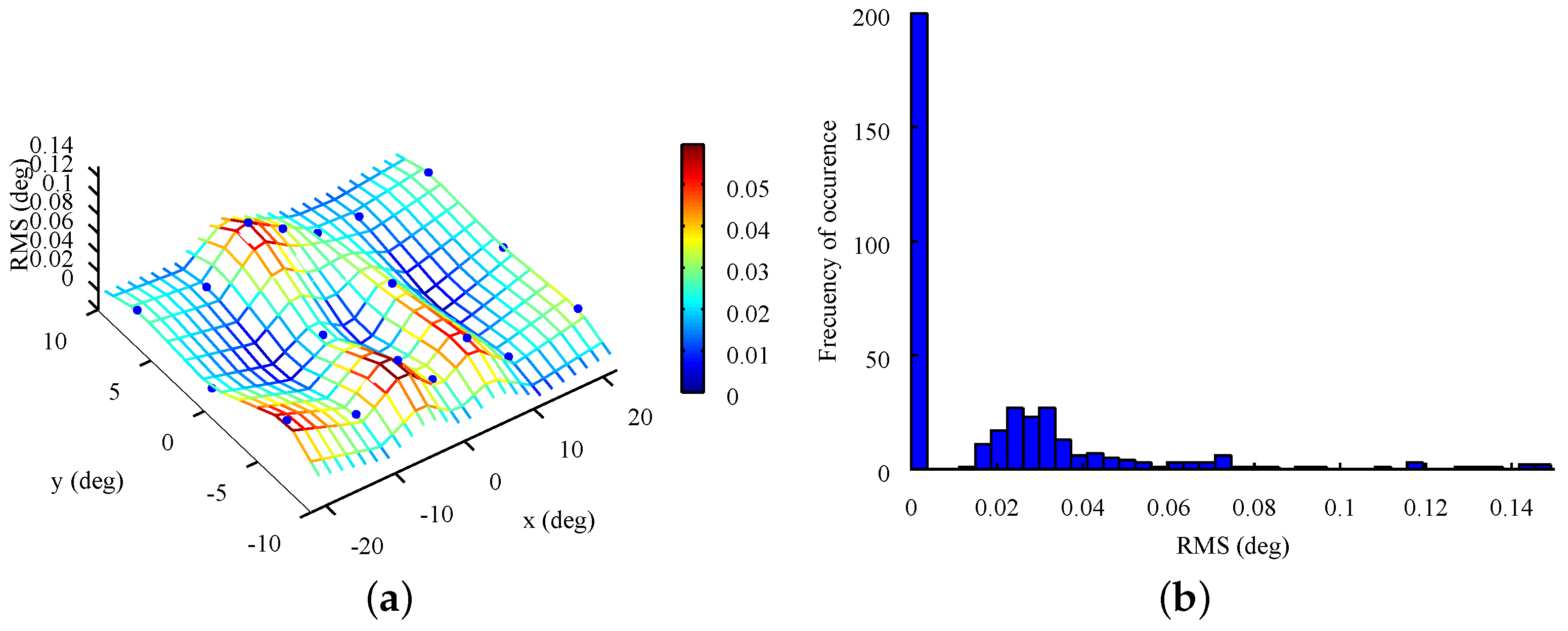
4.2. Precision
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacAskill, M.R.; Anderson, T.J. Eye movements in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.A. The Mechanics of Human Saccadic Eye Movement. J. Physiol. 1964, 174, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.; Yoon, H.; Park, K.S. A novel wearable forehead EOG measurement system for human computer interfaces. Sensors 2017, 17, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukander, K. A system for tracking gaze on handheld devices. Behav. Res. Methods 2006, 38, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, J.; Vazquez, Y.; Glimcher, P.W.; Pesaran, B.; Louie, K. Oculomatic: High speed, reliable, and accurate open-source eye tracking for humans and non-human primates. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 270, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farivar, R.; Michaud-Landry, D. Construction and Operation of a High-Speed, High-Precision Eye Tracker for Tight Stimulus Synchronization and Real-Time Gaze Monitoring in Human and Animal Subjects. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, D.W.; Ji, Q. In the Eye of the Beholder: A Survey of Models for Eyes and Gaze. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 478–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakar, M.E.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ashraf, K.; Kakar, M.A.; Hamdullah; Jan, S.; Razzaq, A. Prevalence of tick infestation in different breeds of cattle in balochistan. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2017, 27, 797–802. [Google Scholar]
- Bedell, H.E.; Stevenson, S.B. Eye movement testing in clinical examination. Vis. Res. 2013, 90, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frutos-Pascual, M.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. Assessing visual attention using eye tracking sensors in intelligent cognitive therapies based on serious games. Sensors 2015, 15, 11092–11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsley, M.; Eliot, M.; Knight, B.A.; Reilly, R. Current Trends in Eye Tracking Research; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–345. [Google Scholar]
- Duchowski, A. Eye Tracking Methodology: Theory and Practice; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 1–328. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrolaza, J.J.; Villanueva, A.; Villanueva, M.; Cabeza, R. Error characterization and compensation in eye tracking systems. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications—ETRA ’12, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 28–30 March 2012; p. 205. [Google Scholar]
- Hammoud, R.I. Passive Eye Monitoring: Algorithms, Applications and Experiments; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; p. 481. [Google Scholar]
- Nyström, M.; Andersson, R.; Holmqvist, K.; van de Weijer, J. The influence of calibration method and eye physiology on eyetracking data quality. Behav. Res. Methods 2013, 45, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, J.T. Estimating peak velocity of rapid eye movements. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1998, 30, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelus, M.; Pelz, J.B. Top-down control of eye movements: Yarbus revisited. Vis. Cogn. 2009, 17, 790–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Snodderly, D.M.; Poletti, M. Eye movements between saccades: Measuring ocular drift and tremor. Vis. Res. 2016, 122, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Mulvey, F.B.; Pelz, J.B.; Holmqvist, K. A study of artificial eyes for the measurement of precision in eye-trackers. Behav. Res. Methods 2017, 49, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmqvist, K.; Nyström, M.; Mulvey, F. Eye tracker data quality. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications—ETRA ’12, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 28–30 March 2012; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1, p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Tobii Technology. Accuracy and Precision Test Report Tobii T60 XL Eye Tracker; Tobii Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, F.; He, G. Real-Time Eye Detection and Tracking under Various Light Conditions. Data Sci. J. 2007, 6, S636–S640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, K.; Nyström, M.; Andersson, R.; Dewhurst, R.; Jarodzka, H.; Van De Weijer, J. Eye Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide to Methods and Measures, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 1–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Pupil Labs. Pupil Labs Eye-Tracker Technical Specifications & Performance; Pupil Labs: Bangkok, Thailand, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- SR Research. EyeLink 1000 Specifications; SR Research: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Clemotte, A.; Velasco, M.; Torricelli, D.; Raya, R.; Ceres, R. Accuracy and Precision of the Tobii X2-30 Eye-tracking under Non Ideal Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics, Rome, Italy, 25–26 October 2014; pp. 111–116. [Google Scholar]

| Data Set | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volunteers | A | Volunteers | B | ||||||||
| Valid | All | Valid | All | ||||||||
| Normal (8) | 0.314 | 0.188 | 0.325 | 0.190 | Normal (9) | 0.427 | 0.384 | 0.457 | 0.493 | ||
| Lens (3) | 0.565 | 0.611 | 0.621 | 0.753 | Lens (2) | 0.543 | 0.538 | 0.622 | 0.900 | ||
| All (11) | 0.383 | 0.376 | 0.406 | 0.447 | All (11) | 0.445 | 0.404 | 0.483 | 0.581 | ||
| Data Set | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volunteers | A | Volunteers | B | ||||||||
| Valid | All | Valid | All | ||||||||
| Normal (8) | 0.034 | 0.011 | 0.130 | 0.019 | Normal (9) | 0.039 | 0.023 | 0.236 | 0.247 | ||
| Lens (3) | 0.027 | 0.024 | 0.101 | 0.013 | Lens (2) | 0.040 | 0.006 | 0.114 | 0.012 | ||
| All (11) | 0.032 | 0.014 | 0.122 | 0.021 | All (11) | 0.036 | 0.016 | 0.151 | 0.081 | ||
| Data Set | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volunteers | A | Volunteers | B | ||||||||
| Valid | All | Valid | All | ||||||||
| Normal (8) | 0.038 | 0.049 | 0.171 | 0.408 | Normal (9) | 0.053 | 0.039 | 0.467 | 0.795 | ||
| Lens (3) | 0.075 | 0.104 | 0.443 | 0.717 | Lens (2) | 0.153 | 0.189 | 0.962 | 1.204 | ||
| All (11) | 0.048 | 0.069 | 0.244 | 0.521 | All (11) | 0.071 | 0.079 | 0.557 | 0.668 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández, E.; Hernández, S.; Molina, D.; Acebrón, R.; García Cena, C.E. OSCANN: Technical Characterization of a Novel Gaze Tracking Analyzer. Sensors 2018, 18, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020522
Hernández E, Hernández S, Molina D, Acebrón R, García Cena CE. OSCANN: Technical Characterization of a Novel Gaze Tracking Analyzer. Sensors. 2018; 18(2):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020522
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández, Erik, Santiago Hernández, David Molina, Rafael Acebrón, and Cecilia E. García Cena. 2018. "OSCANN: Technical Characterization of a Novel Gaze Tracking Analyzer" Sensors 18, no. 2: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020522
APA StyleHernández, E., Hernández, S., Molina, D., Acebrón, R., & García Cena, C. E. (2018). OSCANN: Technical Characterization of a Novel Gaze Tracking Analyzer. Sensors, 18(2), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020522






