Application of Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks to Signals Collected from a Sensor Network for Autonomous Gas Source Localization in Outdoor Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
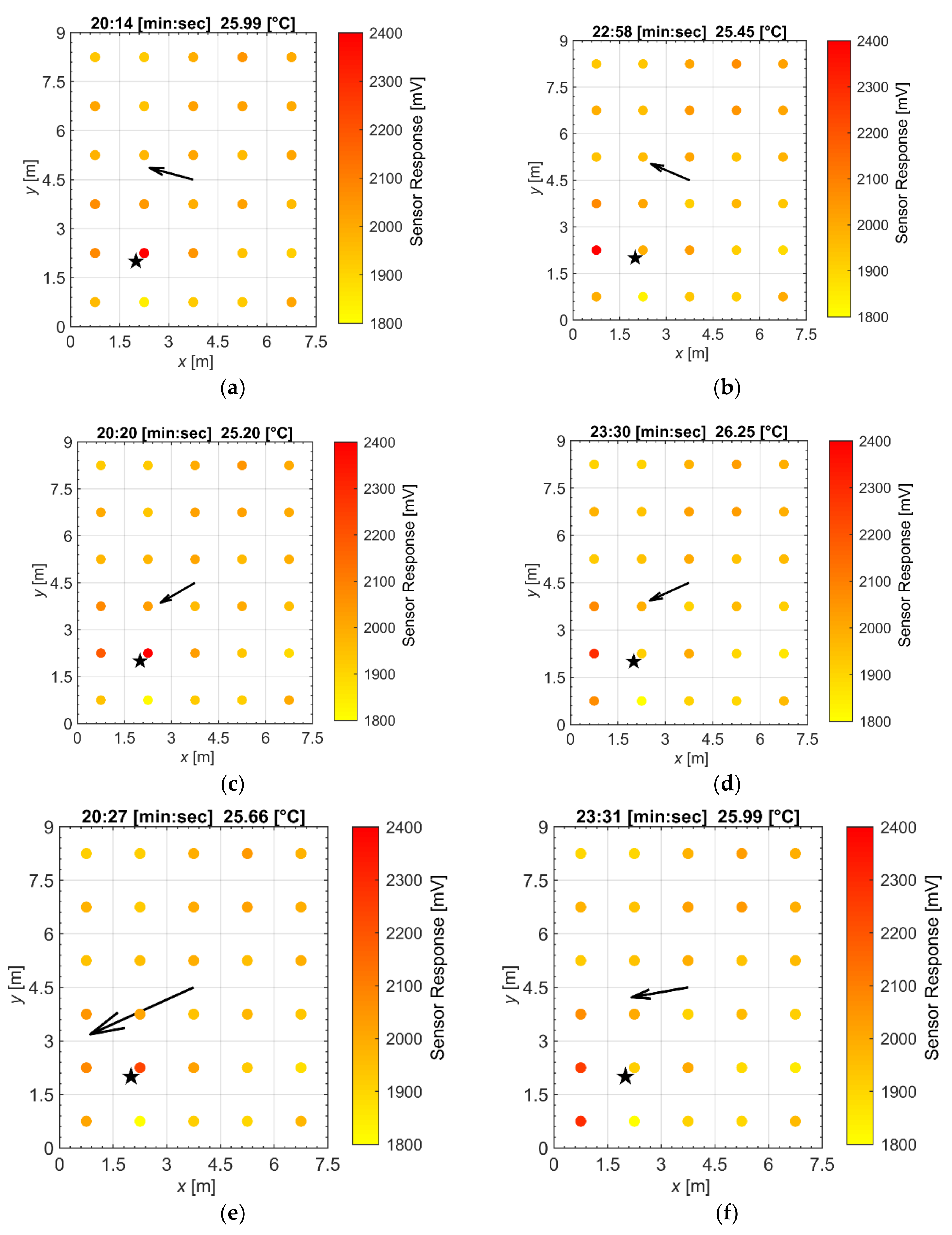
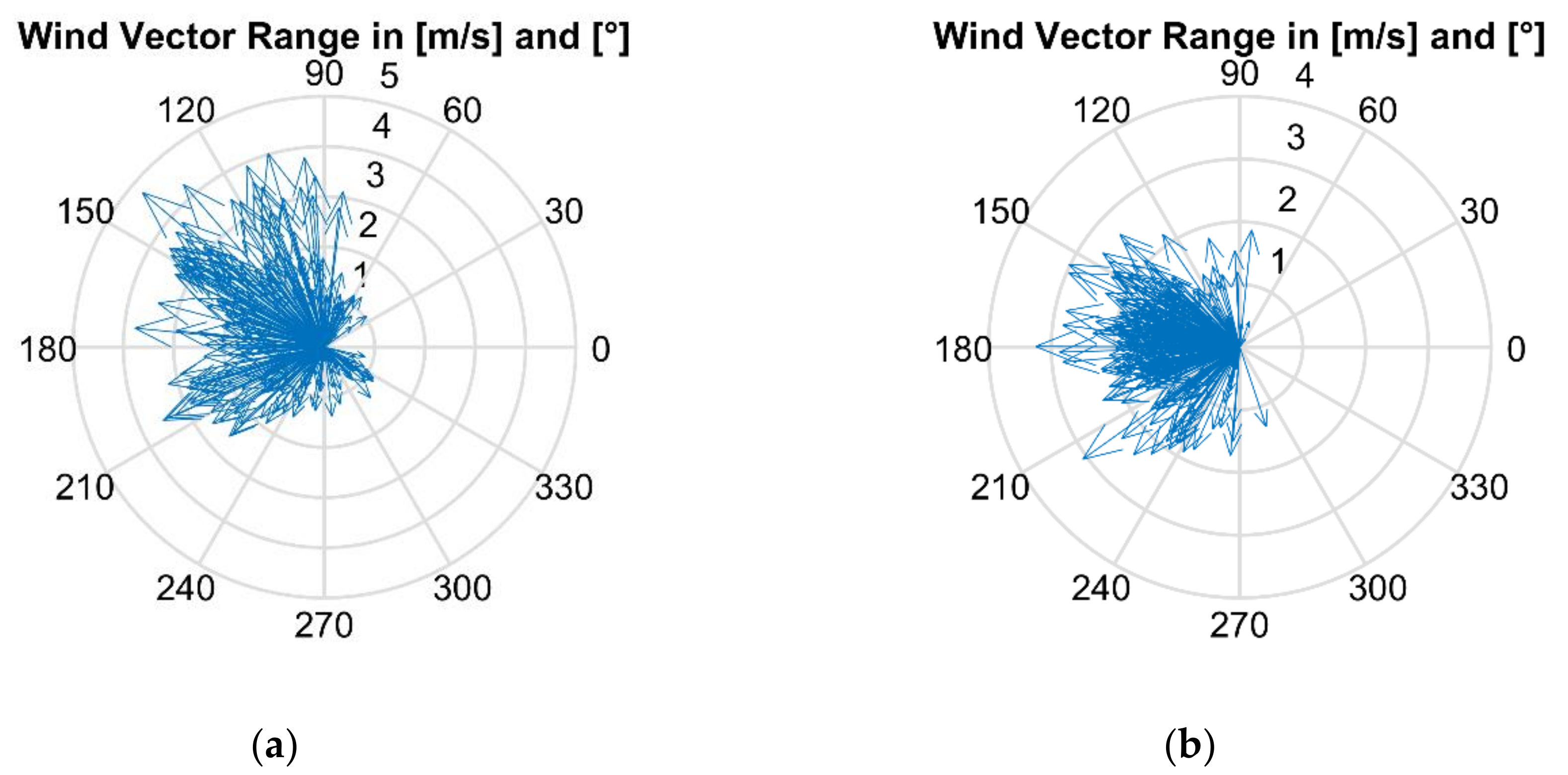
2.1. Experimental Data
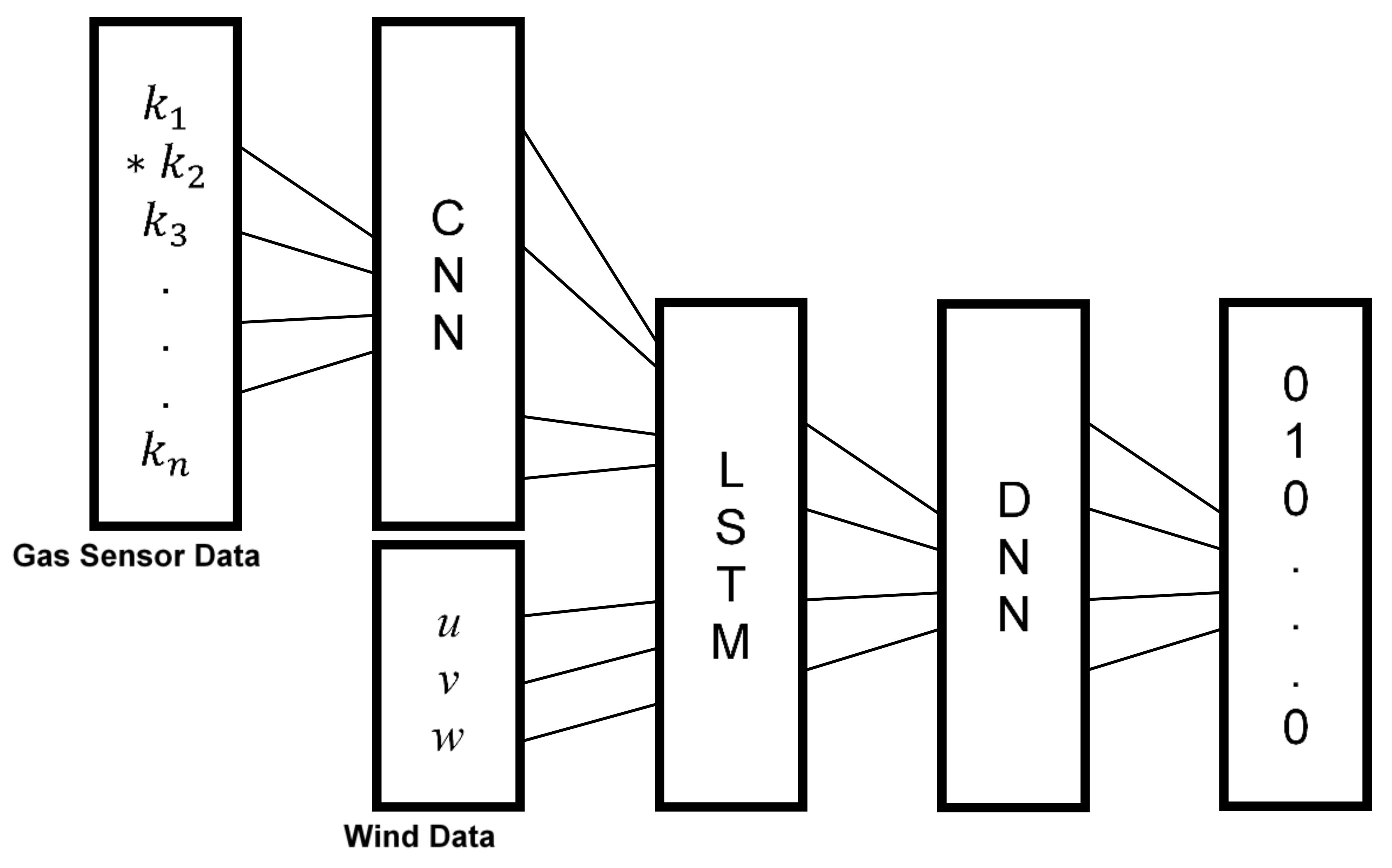
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Optimizations
2.4. Training and Validation
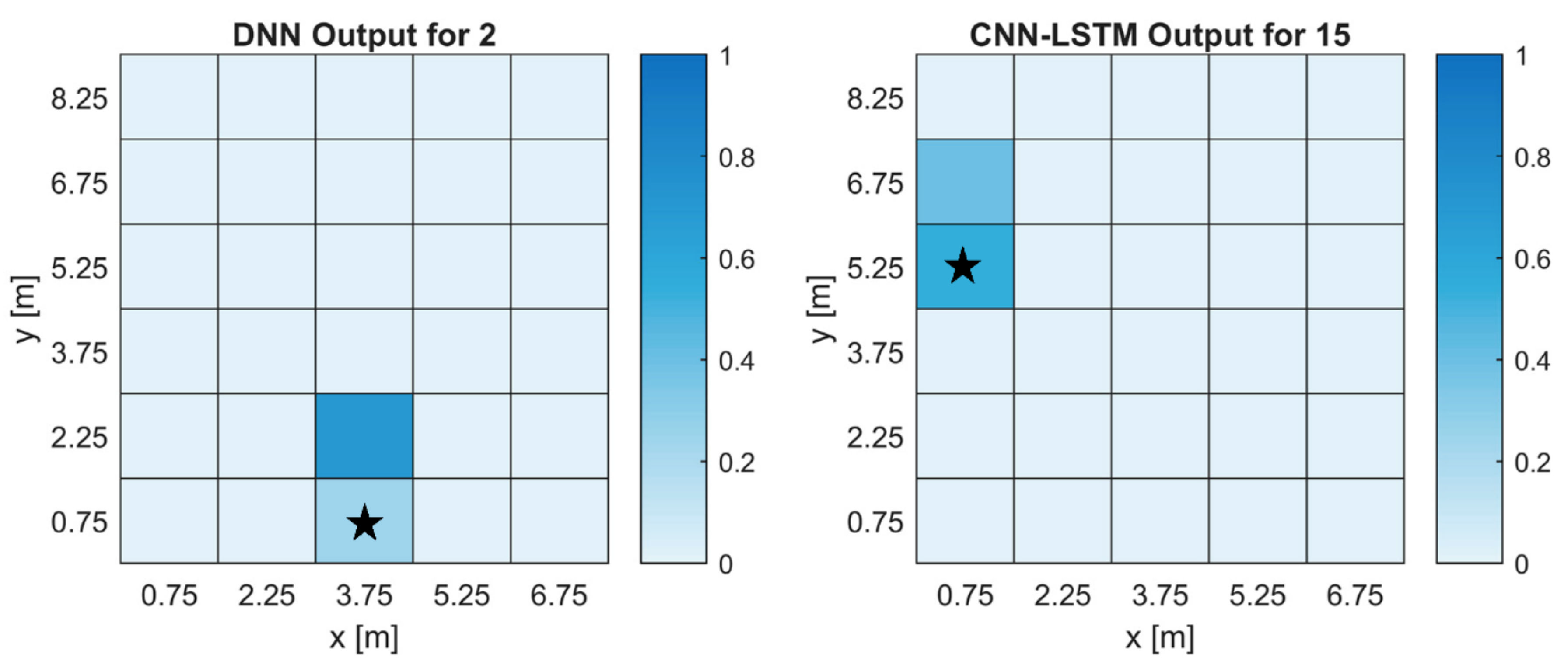
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernandez Bennetts, V.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Neumann, P.P.; Trincavelli, M. Mobile robots for localizing gas emission sources on landfill sites: Is bio-inspiration the way to go? Front. Neuroeng. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoghue, A.M. Occupational health hazards in mining: An overview. Occup. Med. 2004, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, H.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Matsukura, H.; Hernandez Bennetts, V.; Schaffernicht, E. Using chemical sensors as “noses” for mobile robots. In Essentials of Machine Olfaction and Taste, 1st ed.; Nakamoto, T., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Singapore, 2016; pp. 219–245. ISBN 9781118768488. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, H.; Wada, Y.; Matsukura, H. Chemical sensing in robotic applications: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 3163–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, M.A.; Avondet, J.L.; Zheng, E. The role of vision in odor-plume tracking by walking and flying insects. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 4121–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, H.; Nakayama, G.; Nakamoto, T.; Moriizumi, T. Controlling a gas/odor plume-tracking robot based on transient responses of gas sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2005, 5, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochmatter, T.; Raemy, X.; Matthey, L.; Indra, S.; Martinoli, A. A comparison of casting and spiraling algorithms for odor source localization in laminar flow. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 1138–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.G.; Meng, Q.H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, M. Odor source localization using a mobile robot in outdoor airflow environments with a particle filter algorithm. Auton. Robots 2011, 30, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.P.; Hernandez Bennetts, V.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Bartholmai, M.; Schiller, J.H. Gas source localization with a micro-drone using bio-inspired and particle filter-based algorithms. Adv. Robot. 2013, 27, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthes, J.; Gröll, L.; Keller, H.B. Source localization by spatially distributed electronic noses for advection and diffusion. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.L.; Meng, Q.H.; Zeng, M.; Sun, B.; Li, W.; Ding, C.J. Distributed least-squares estimation of a remote chemical source via convex combination in wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2014, 14, 11444–11466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfouz, S.; Mourad-Chehade, F.; Honeine, P.; Farah, J.; Snoussi, H. Gas source parameter estimation using machine learning in WSNs. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 5795–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsironi, E.; Barros, P.; Wermter, S. Gesture recognition with a Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 27–29 April 2016; pp. 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Tsironi, E.; Barros, P.; Weber, C.; Wermter, S. An analysis of Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Networks for gesture recognition. Neurocomputing 2017, 268, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, J.; Hendricks, L.A.; Rohrbach, M.; Venugopalan, S.; Guadarrama, S.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Networks for visual recognition and description. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Yan, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, J.M. Locating hazardous gas leaks in the atmosphere via modified genetic, MCMC and particle swarm optimization algorithms. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 157, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonollosa, J.; Rodríguez-Luján, I.; Trincavelli, M.; Vergara, A.; Huerta, R. Chemical discrimination in turbulent gas mixtures with MOX sensors validated by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sensors 2014, 14, 19336–19353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Part I, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhurber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Cummins, F. Learning to forget: Continual prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2451–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]



| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Validation Error | Epoch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-LSTM | 95.0% | 96.5% | 95.0% | 94.7% | 0.0115 | 160 |
| LSTM | 85.0% | 87.3% | 85.0% | 84.9% | 0.0307 | 310 |
| CNN-DNN | 90.0% | 92.7% | 90.0% | 89.1% | 0.0273 | 260 |
| DNN | 91.1% | 93.0% | 91.1% | 90.6% | 0.0200 | 350 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Validation Error | Epoch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-LSTM | 93.9% | 95.6% | 93.9% | 93.6% | 0.0116 | 300 |
| LSTM | 88.9% | 89.9% | 88.9% | 88.4% | 0.0214 | 290 |
| CNN-DNN | 93.3% | 94.8% | 93.3% | 93.0% | 0.0135 | 300 |
| DNN | 88.3% | 91.6% | 88.3% | 87.6% | 0.0206 | 270 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilgera, C.; Yamamoto, A.; Sawano, M.; Matsukura, H.; Ishida, H. Application of Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks to Signals Collected from a Sensor Network for Autonomous Gas Source Localization in Outdoor Environments. Sensors 2018, 18, 4484. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124484
Bilgera C, Yamamoto A, Sawano M, Matsukura H, Ishida H. Application of Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks to Signals Collected from a Sensor Network for Autonomous Gas Source Localization in Outdoor Environments. Sensors. 2018; 18(12):4484. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124484
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilgera, Christian, Akifumi Yamamoto, Maki Sawano, Haruka Matsukura, and Hiroshi Ishida. 2018. "Application of Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks to Signals Collected from a Sensor Network for Autonomous Gas Source Localization in Outdoor Environments" Sensors 18, no. 12: 4484. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124484
APA StyleBilgera, C., Yamamoto, A., Sawano, M., Matsukura, H., & Ishida, H. (2018). Application of Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks to Signals Collected from a Sensor Network for Autonomous Gas Source Localization in Outdoor Environments. Sensors, 18(12), 4484. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124484





