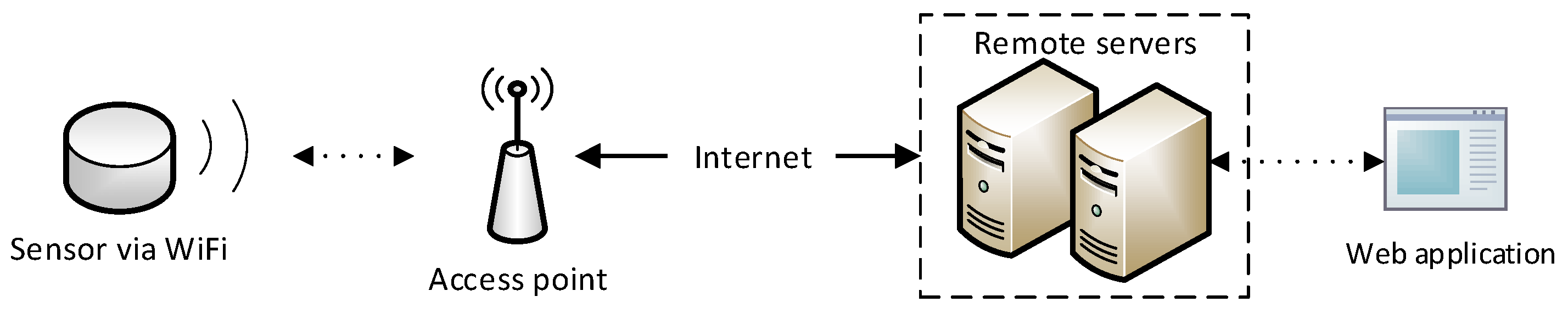
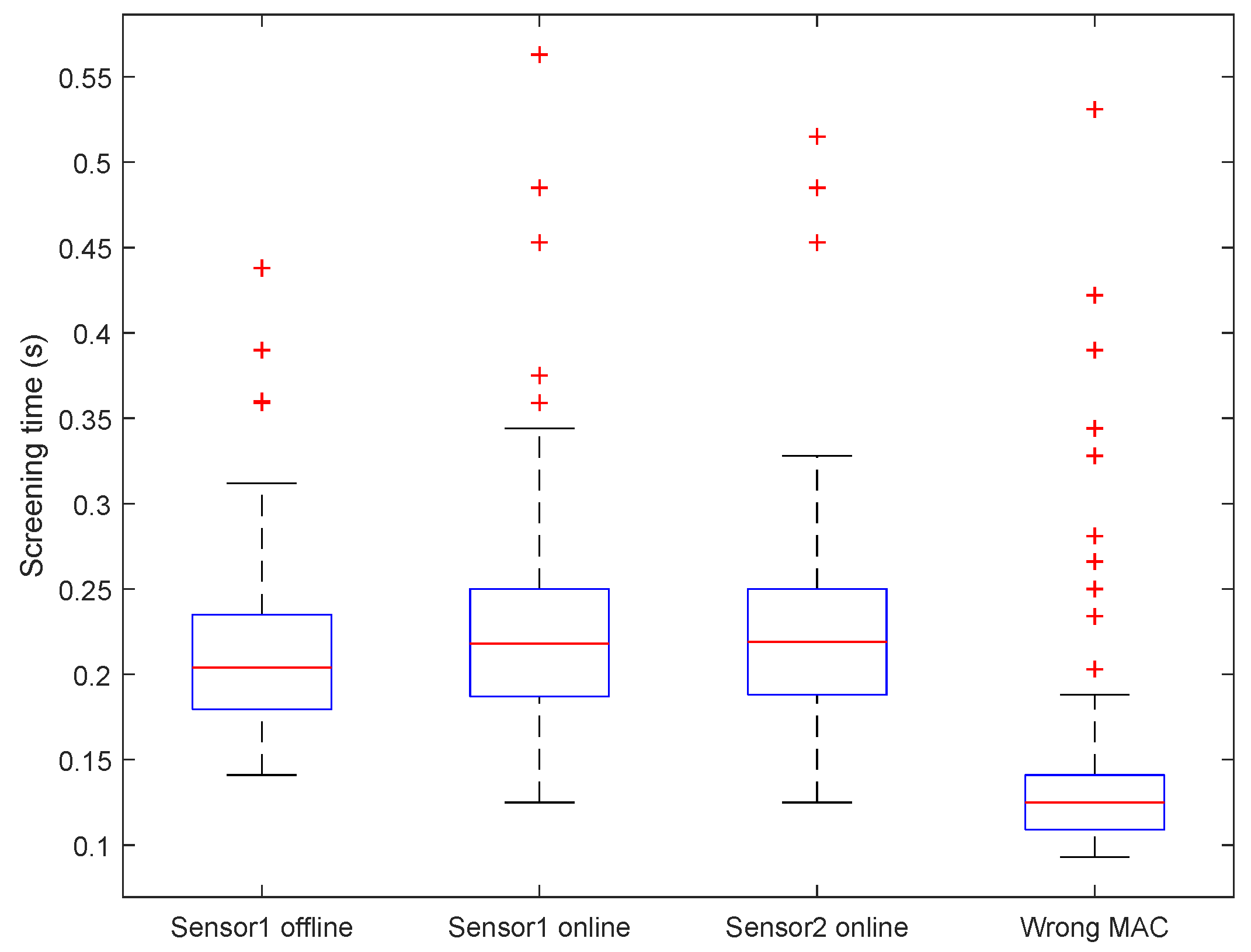
In this section, we introduce data pollution methodology against the a.com system in different scenarios. We first introduce how to pollute data of a victim sensor if we physically possess the sensor, or if the victim sensor’s MAC address is known. We then discuss how to enumerate the MAC addresses of every a.com sensor so that we can pollute any sensor of the a.com system.
2.4.2. Knowing a MAC
In this scenario (denoted as Scenario B), physical access to an a.com sensor is no longer permitted. A plausible approach is to fabricate all messages from scratch to imitate the victim sensor if we know the MAC address of the victim sensor.
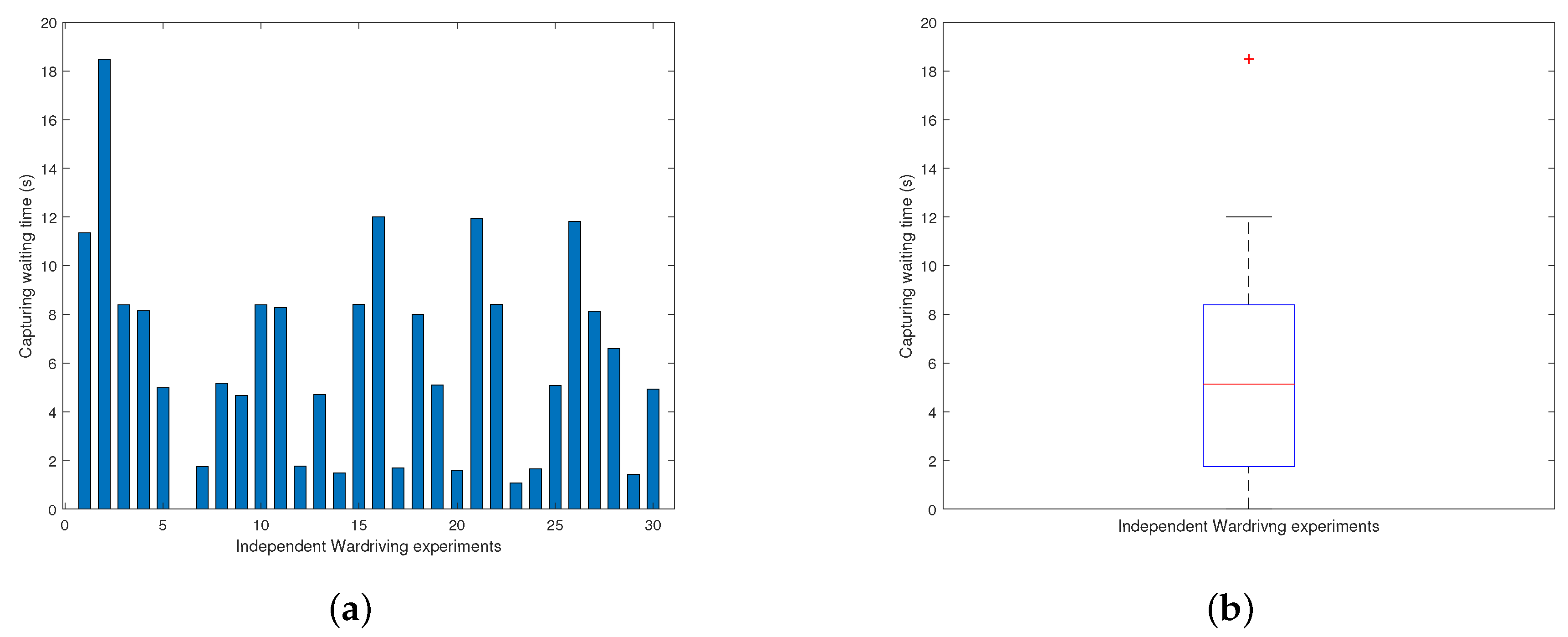
There are indeed multiple ways to obtain a sensor’s MAC address without physical possession. We now present one representative approach with only publicly available information within the scope of the a.com system. In this approach, we utilize the observable geographical locations of registered sensors on the a.com Map. Thus the issue becomes, given the geographical location of a sensor, without direct physical access to the sensor and the possibility of direct network manipulation, can its MAC address still be attained? To carry out this task, we leverage wardriving, which refers to scanning and sniffing for WiFi network information in a moving vehicle by using a laptop or other computer devices.
In demonstration, we ask a volunteer to set up an a.com sensor within his/her household. We know no information for the sensor of interest, including its MAC address, but only the geographical location of the volunteer’s household. By wardriving around the volunteer’s household using the popular sniffing tool kismet [
39], we successfully intercept WiFi network communication information in the surrounding area. Although traffic from multiple active WiFi networks are merged together through this process, the desired sensor MAC address can still be spotted with ease. This is because, by convention, the first 6 hex digits (prefixes) of the 12 digits MAC address represents a specific manufacture. The a.com sensors contain a specific WiFi microchip ESP8266 in which the prefix of the MAC address belongs to one of several pre-assigned prefixes owned by the manufacturer Espressif Systems. MAC address prefixes allocated to a vendor such as Espressif can be looked up at various websites [
40], by which 24 MAC address prefixes are found given to Espressif Systems (
Table 5). By using prefix patterns, we match and find the actual sensor MAC via wardriving without encountering any ambiguous situations in sensor MAC recognition during wardriving. Nonetheless, even if ambiguity appears, we can leverage message responses from the a.com server to easily distinguish the actual sensor MAC from other candidates.
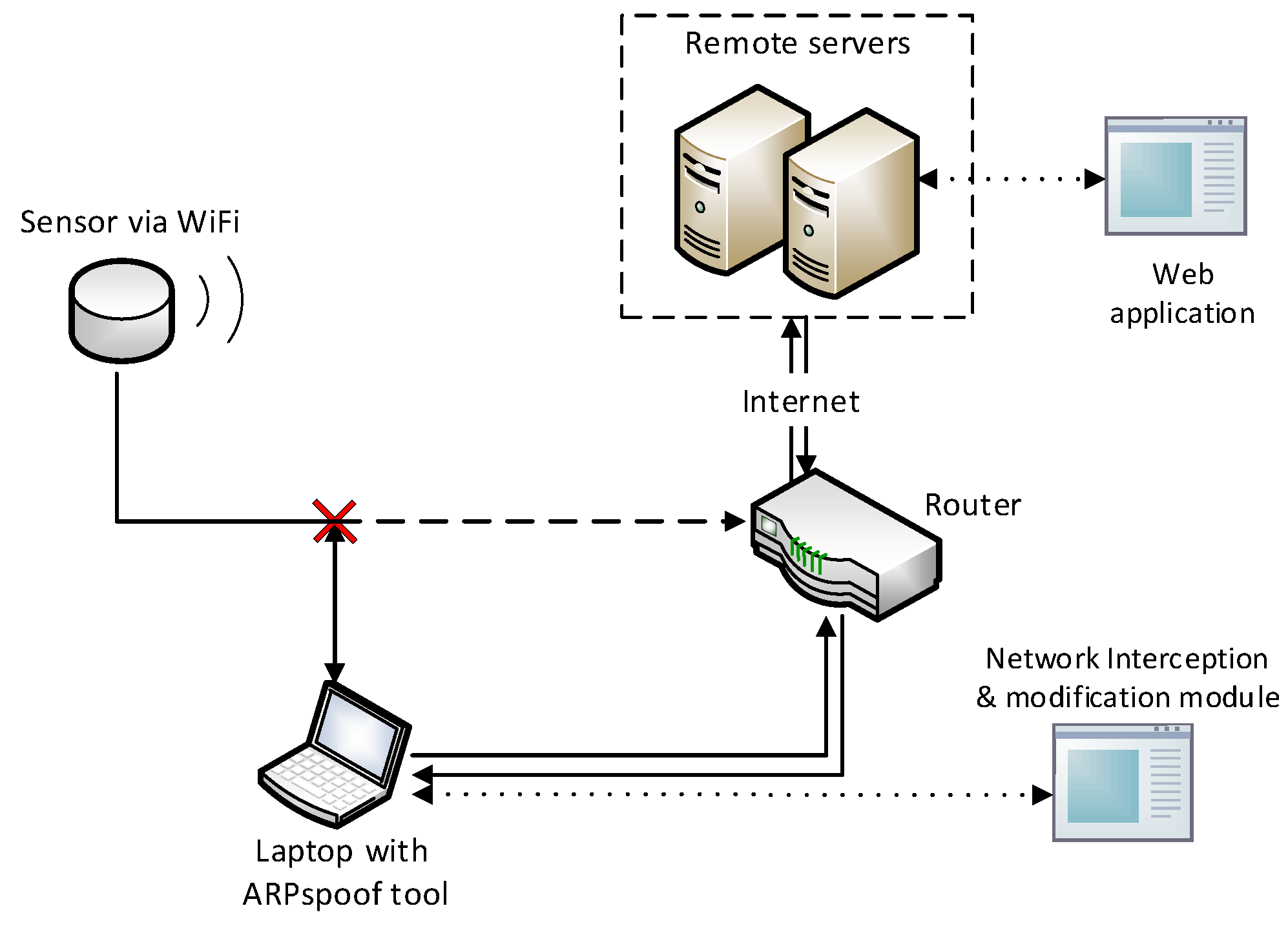
Once knowing a specific registered sensor’s MAC address, we pollute its data sent to the a.com system by creating a fake sensor (a computer program), fabricate messages according to the discovered data formats, and send the fabricated data to corresponding servers. The fabricated messages will contain the victim sensor’s MAC address, and will be accepted by the servers as authentic data from the specific victim sensor. We call this attack as a spoofing attack since the fake sensor pretends to be the victim sensor and sends fake data to a.com web servers.
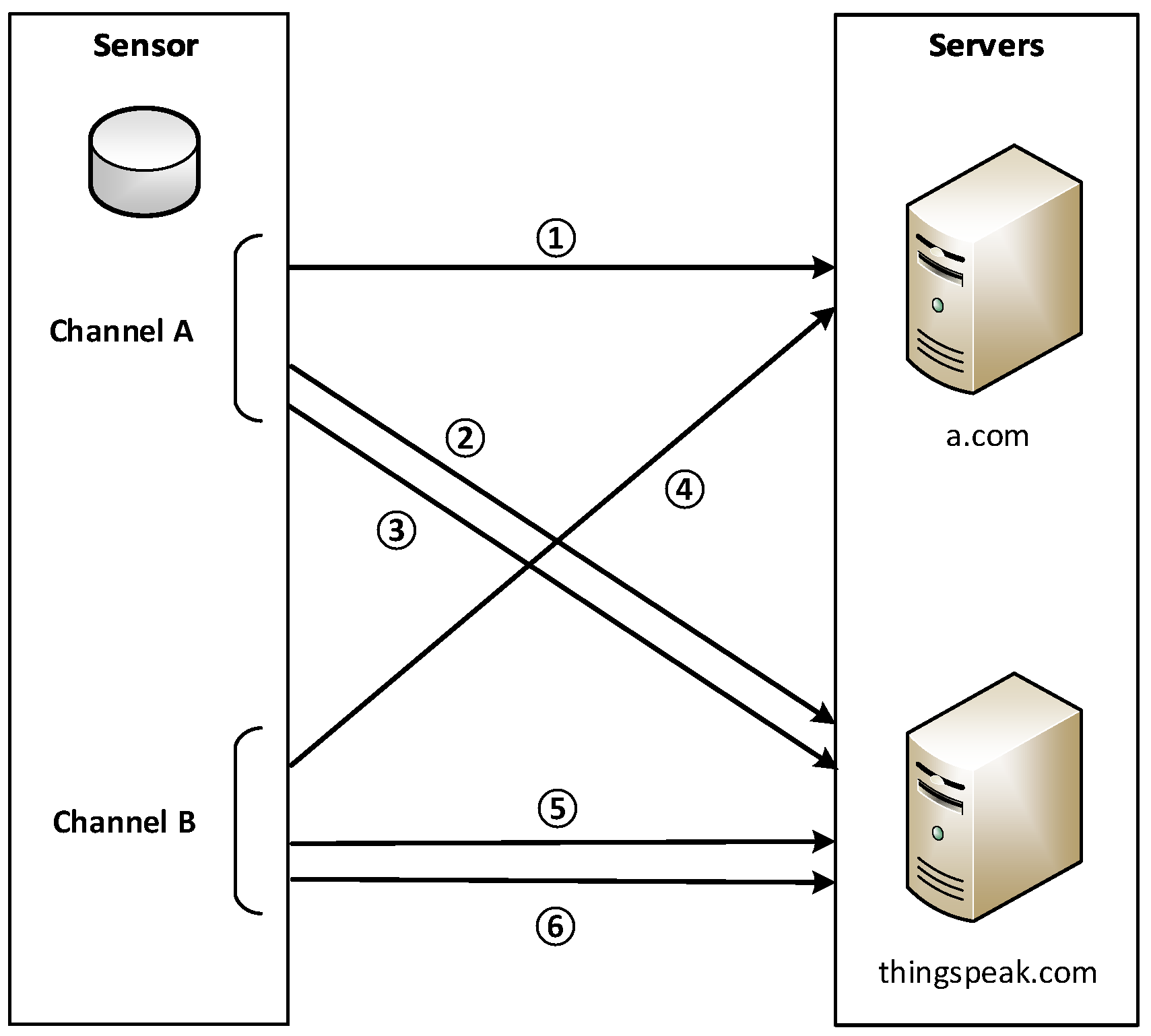
In the spoofing attack, a.com servers receive two sets of data for one sensor: authentic data from the victim sensor, and fabricated data from the fake sensor. The servers merge the two sets of data and use the merged data to indicate air quality. Inevitably, the authentic data from the victim sensor are “polluted” by the fake data.
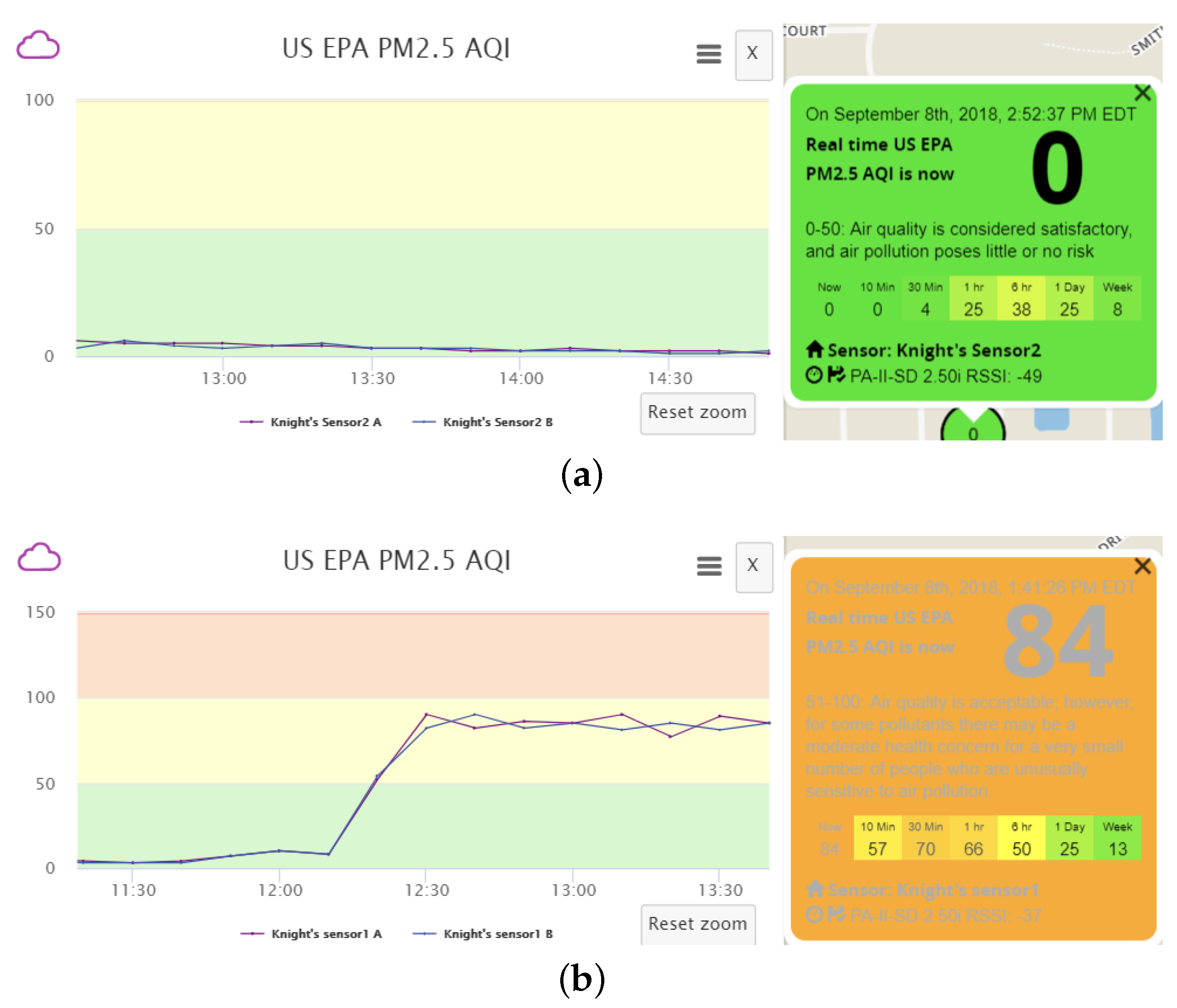
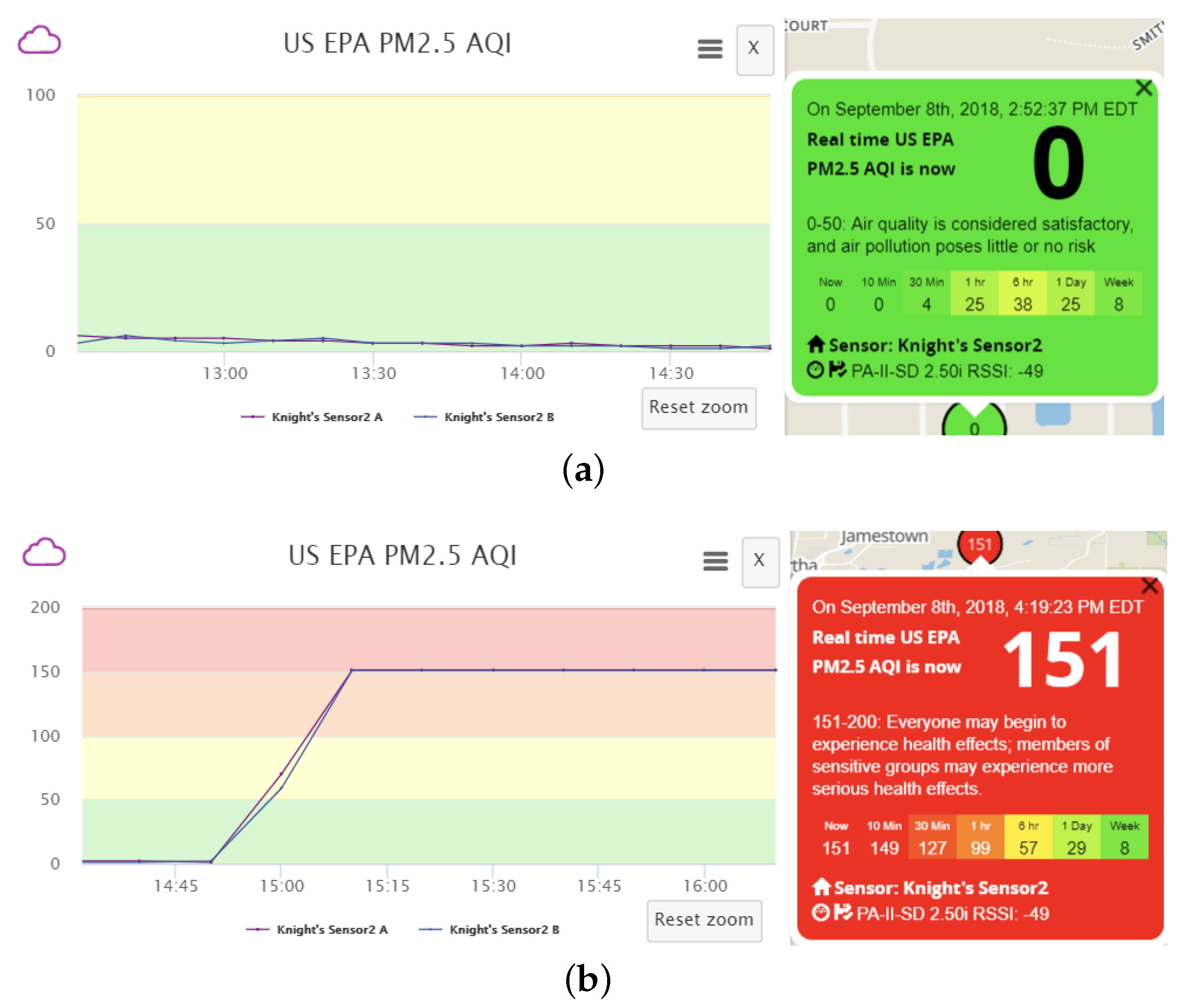
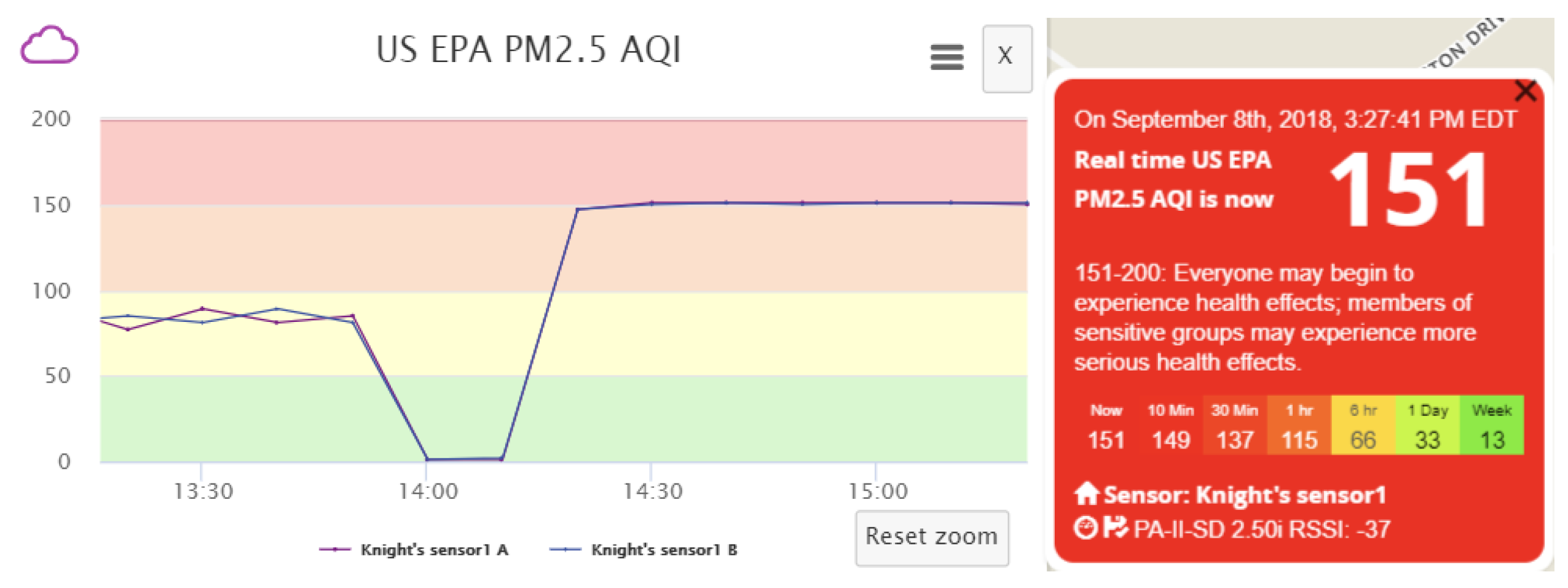
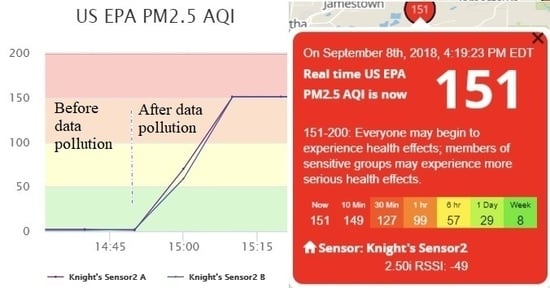
In addition, we can vary the data transmission frequency of counterfeit sensor data to better suppress authentic data, to conceal malicious activities from the owners of the victim sensor and the servers, and to achieve a desired level of air pollution. We find that each of the two channels within a real sensor transmits data at an interval of approximately 80 s. If our fake sensor also sends counterfeit data every 80 s, the a.com servers would receive both authentic and fabricated sensor data at the same frequency, and the two data sets will be averaged. The resulting effect of data pollution, taking the AQI calculated based on measured PM2.5 as an example, is shown in
Figure 6. One can observe two phenomena: Firstly, the polluted data presents many ups and downs. This fluctuation is the result of averaging the received real and fake measurements within each 10-min period. When the fake data sending frequency is relatively low, it is likely that the number of received fake data samples varies slightly between different periods. Meanwhile, the fake data is usually much larger (or smaller) than the real data. Hence, receiving even one more fake message may lead to apparent fluctuation in the averaged result. For the real measurements, slight fluctuation exists as well due to natural variations of pollutant concentrations in the ambient environment. Therefore, the polluted data fluctuation is actually the combined result of the variations in real data and the instability caused by received fake data. Secondly, the AQI is not the intended value, which should be 151, as suggested by the fabricated message, due to average of both authentic and fabricated data. Such phenomena, especially the data fluctuation, could raise the possibility of detection by the sensor owner or the a.com system. It is of great interest to better understand the phenomena and whether optimization procedures can be performed to reduce data fluctuation, to better suppress authentic sensor data, and to achieve a desired level of AQI.
After significant efforts in analyzing the phenomena, we arrive at the following explanation: the graphical representation of the AQI value on the a.com Map is calculated using averaged PM2.5 measurement data in the past 10 min. Numerical presentation of the AQI value follows the same computation methodology but with a varied interval.
Therefore, an attacker may want to adjust the data update frequency of the fake sensor so that the AQI can be manipulated to the desired value. Here, we define the following notations: (1) the update interval of the visualized data on map as
, where
min
s; (2) the real sensor and fake sensor data update intervals as
and
respectively, where
s and
is to be determined; (3) the real PM2.5 measurement (assuming constant during pollution) and fabricated PM2.5 measurement as
and
respectively; (4) with respect to the targeted AQI, the corresponding range of PM2.5 pollutant measurement as
(obtainable via the United States EPA AQI calculation table [
38]). Here, only
and
are controllable variables, and all others are given. Therefore, we define three problems for pollution methodology optimization as follows and also present the sketchy solution methodologies for these three problems.
Problem I: Under what values of and can the visualized AQI be the same as the targeted AQI?
Solution. To ensure the displayed AQI value is the same as desired, a necessary and sufficient condition is to select proper
and
(
) such that the average of all received PM2.5 measurements during each update interval is located within the range
. This can be mathematically formulated as the following inequality.
■
Since smaller values of are equivalent to higher message transmitting frequencies, the adversary may want to know a minimum required number of messages, which corresponds to the maximum value of , for a given , to ensure the targeted AQI can be achieved. This can be formulated as Problem II.
Problem II: For a given , what is the maximum applicable value of ?
Solution. This can be viewed as an optimization problem:
Subject to:
Therefore, we can derive the maximum value of
(denoted as
) for different cases as presented by Equation (
4):
■
Deductions here are assuming a suitable value of . Certainly, requirements exist when selecting value of to make data pollution action practical. In this work, when , we opt to choose ; and when , we opt to choose . This conservative yet clear choice satisfies all requirements of , and more importantly, it additionally grants that we can send fabricated messages as frequently as we want (i.e., can be selected for as close to 0 as we want, so long as it is less than , targeted AQI still can be achieved). Such freedom enables the choice of any adequately desired higher fake data frequency, which can thus help to alleviate fake data receiving instability and better suppress real data and its variations, so that a better pollution result with much less fluctuation can be achieved. The case when is trivial since no fabricated message is needed for pollution in this situation.
Furthermore, we empirically consider the possibility of deciding a uniform for parallel multiple sensor data pollution, in which identical targeted AQI and a proper are used for polluting all victim sensors in parallel. This is expressed in Problem III.
Problem III: What is the uniform when multiple sensors are being polluted simultaneously?
Solution. Denote this uniform maximum fake sensor data update interval as . We assume the number of sensors being polluted simultaneously is n. The corresponding real PM2.5 measurements for these sensors are , , …, . Without loss of generality, we assume these n values are all in an increasing order, and among these n values, the first values , …, are less than ; values , …, are in between and ; and remaining values , …, are greater than , where . This assumption is general and can always be achieved by reordering all sensors.
Since sensors in position
through
do not have any requirement on
, we exclude them from the later portion of the solution. For the rest of the sensors, we denote corresponding
for sensor
i as
,
, and
.
can be expressed as:
where
and
. By Equation (
4),
That is, when launching multiple sensor pollution attacks simultaneously, a suitable uniform exists, and is only possibly affected by the smallest and largest real PM2.5 readings among all sensors. ■