Label-Free Time-Gated Luminescent Detection Method for the Nucleotides with Varying Phosphate Content
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Probe 1 Selection
2.4. Label-Free K-Ras Activity Assays
2.5. QRET-Based Control Assay for GTPase Cycling and GTP Association Monitoring
2.6. Label-Free Apyrase ATPase Activity Monitoring
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
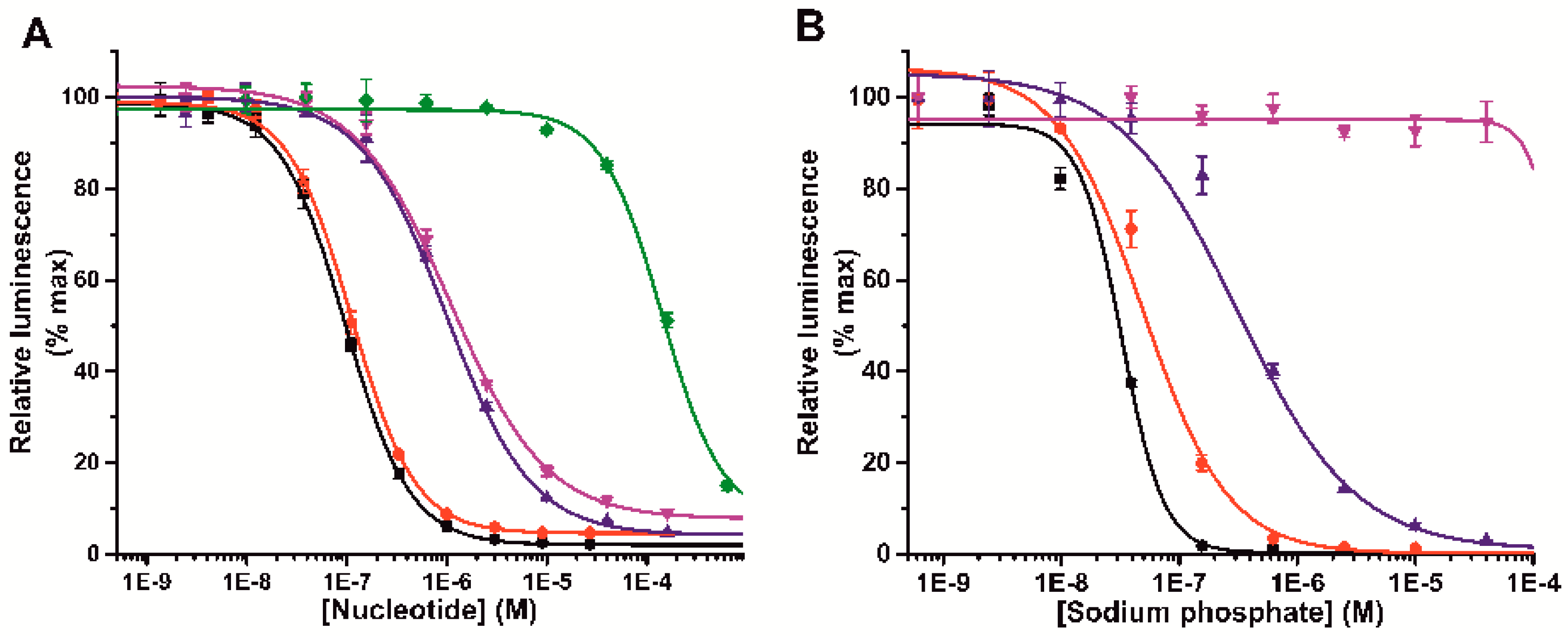
3.1. Label-Free Terbium(III)-Probe Enables Nanomolar Detection of Phosphate-Containing Molecules
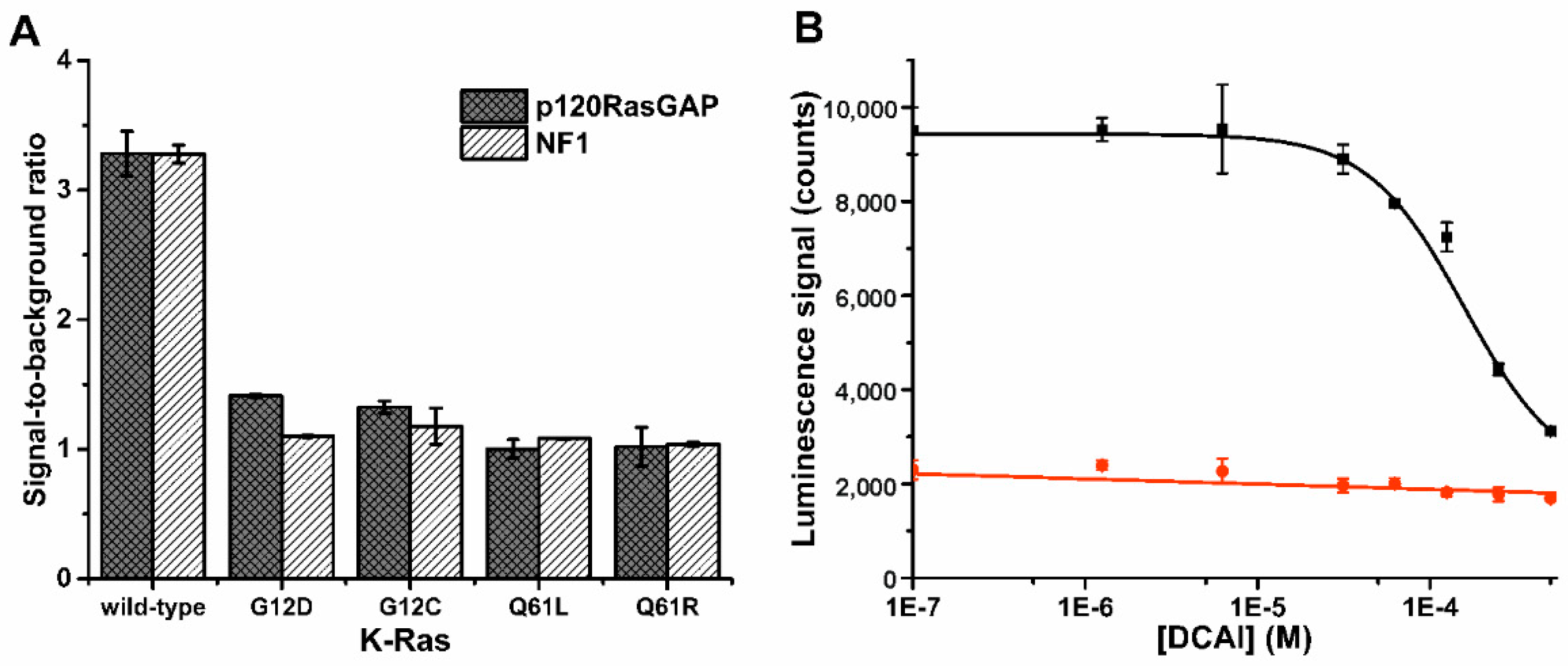
3.2. K-Ras Functionality Can Be Monitored at Nanomolar Sensitivity Similar to the Control Assay
3.3. Probe 1 Enables Nucleotide Triphosphate Hydrolysis Monitoring to Di- and Further to Nucleotide Monophosphates
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Exton, J.H. Cell signalling through guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) and phospholipases. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 243, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khakh, B.S.; Burnstock, G. The double life of ATP. Sci. Am. 2009, 301, 84–90, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firoz, A.; Malik, A.; Joplin, K.H.; Ahmad, Z.; Jha, V.; Ahmad, S. Residue propensities, discrimination and binding site prediction of adenine and guanine phosphates. BMC Biochem. 2011, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dwyer, P.J.; King, S.A.; Hoth, D.F.; Leyland-Jones, B. Role of thymidine in biochemical modulation: A review. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 3911–3919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lecca, D.; Ceruti, S. Uracil nucleotides: From metabolic intermediates to neuroprotection and neuroinflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Singh, N.J.; Lim, J.; Pan, J.; Kim, H.N.; Park, S.; Kim, K.S.; Yoon, J. Unique sandwich stacking of pyrene-adenine-pyrene for selective and ratiometric fluorescent sensing of ATP at physiological pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15528–15533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, S.; Fukuda, M.; Tamura, T.; Sakaguchi, R.; Nakata, E.; Morii, T. Simultaneous detection of ATP and GTP by covalently linked fluorescent ribonucleopeptide sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.; Lim, H.S.; Ma, Q.; Gao, Z. Optical aptasensors for adenosine triphosphate. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1683–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlyntseva, S.V.; Bazel, Y.R.; Vishnikin, A.B.; Andruch, V.J. Methods for the determination of adenosine triphosphate and other adenine nucleotides. J. Anal. Chem. 2009, 64, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensors for detection of nucleotides, FAD and NADH: Highlighted research during 2004–2010. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2222–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comley, J. Kinase screening and profiling-spoilt for choice. Drug Discov. World 2006, 7, 27–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmilä, I.; Dakubu, S.; Mukkala, V.-M.; Siitari, H.; Lövgren, T. Europium as a label in time-resolved immunofluorometric assays. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 137, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Li, M.; Ehlers, M.; Schmuck, C. A metal-free fluorescence turn-on molecular probe for detection of nucleoside triphosphates. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-H.; Yuan, W.-T.; Zhu, C.-Q.; Xu, J.-G. Species-differentiable sensing of phosphate-containing anions in neutral aqueous solution based on coordinatively unsaturated lanthanide complex probes. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 331, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, F.; Miao, Y.; Jiang, C. Determination of adenosine disodium triphosphate (ATP) using oxytetracycline-Eu3+ as a fluorescence probe by spectrofluorimetry. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 61, 2891–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, X.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Su, B. The fluorescence enhancement effect of Tb–Gd–adenosine triphosphate–phen system and its analytical application. Talanta 2005, 65, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, E.A.; Chang, J.Y.; Rosenfield, A.H.; Pierre, V.C. A selective luminescent probe for the direct time-gated detection of adenosine triphosphate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16099–16102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. Fluorogenic and chromogenic chemosensors and reagents for anions. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4419–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Härmä, H.; Rozwandowicz-Jansen, A.; Martikkala, E.; Frang, H.; Hemmilä, I.; Sahlberg, N.; Fey, V.; Perälä, M.; Hänninen, P. A new simple cell-based homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence QRET technique for receptor-ligand interaction screening. J. Biomol. Screen. 2009, 14, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martikkala, E.; Rozwandowicz-Jansen, A.; Hänninen, P.; Petäjä-Repo, U.; Härmä, H. A homogeneous single-label time-resolved fluorescence cAMP assay. J. Biomol. Screen. 2011, 16, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martikkala, E.; Veltel, S.; Kirjavainen, J.; Rozwandowicz-Jansen, A.; Lamminmäki, U.; Hänninen, P.; Härmä, H. Homogeneous single-label biochemical Ras activation assay using time-resolved luminescence. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9230–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopra, K.; Ligabue, A.; Wang, Q.; Syrjänpää, M.; Blaževitš, O.; van Adrichem, A.J.; Hänninen, P.; Veltel, S.; Abankwa, D.; Härmä, H. A homogeneous quenching resonance energy transfer assay for the kinetic analysis of the GTPase nucleotide exchange reaction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4147–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopra, K.; van Adrichem, A.J.; Salo-Ahen, O.M.H.; Peltonen, J.; Wennerberg, K.; Härmä, H. High-throughput dual screening method for Ras activities and inhibitors. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4508–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopra, K.; Rozwandowicz-Jansen, A.; Syrjänpää, M.; Blaževitš, O.; Ligabue, A.; Veltel, S.; Lamminmäki, U.; Abankwa, D.; Härmä, H. GTP-specific fab fragment-based GTPase activity assay. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3527–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karhunen, U.; Jaakkola, L.; Wang, Q.; Lamminmäki, U.; Soukka, T. Luminescence switching by hybridization-directed mixed lanthanide complex formation. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.B.; Wang, D.Y.; Guo, X.Q.; Xu, J.G. Studies on the mechanism of fluorescence quenching of Tb3+-tiron complex by nucleotides, polynucleotides and nucleic acids. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 1997, 18, 691–695. [Google Scholar]
- Vigil, D.; Cherfils, J.; Rossman, K.L.; Der, C.J. Ras superfamily GEFs and GAPs: Validated and tractable targets for cancer therapy? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Medarde, A.; Santos, E. Ras in cancer and developmental diseases. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, T.; Garrenton, L.S.; Oh, A.; Pitts, K.; Anderson, D.J.; Skelton, N.J.; Fauber, B.P.; Pan, B.; Malek, S.; Stokoe, D.; et al. Small-molecule ligands bind to a distinct pocket in Ras and inhibit SOS-mediated nucleotide exchange activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5299–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.M.; Hicks-Berger, C.A.; Kim, S.; Kirley, T.L. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a soluble calcium-activated nucleotidase, a human enzyme belonging to a new family of extracellular nucleotidases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 406, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettlun, A.M.; Uribe, L.; Calvo, V.; Silva, S.; Rivera, J.; Mancilla, M.; Antonieta, M.; Valenzuela, M.A.; Traverso-Cori, A. Properties of two apyrases from Solanum tuberosum. Phytochemistry 1982, 21, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettlun, A.M.; Espinosa, V.; García, L.; Valenzuela, M.A. Potato tuber isoapyrases: Substrate specificity, affinity labeling, and proteolytic susceptibility. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Method | Detection | Reaction | Assay Buffer | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTPase cycling assay | Probe 1: 7.5 µM antenna 1, 7.5 nM Tb(III)-N1 QRET: 7.5 nM Eu(III)-GTP, 12 nM 2A4GTP Fab, 1.8 µM MT2 | 200 nM K-Ras, 200 nM SOScat, 100 nM GAP (p120RasGAP or NF1), 1.5 µM GTP | Buffer 1: 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Triton-X 100, 0.005% γ-globulins | Probe 1: 330/545 nm Tb(III)-luminescence (10 µL) QRET: 340/615 nm Eu(III)-luminescence (10 µL) |
| GTP association assay | Probe 1: 7.5 µM antenna 1, 7.5 nM Tb(III)-N1 QRET: 10 nM Eu(III)-GTP, 1.5 µM MT2 | 500 nM K-Ras, 250 nM SOScat, 500 nM GTP 200 nM K-Ras, 200 nM SOScat, | Buffer 1: 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Triton-X 100, 0.005% γ-globulins | Probe 1: 330/545 nm Tb(III)-luminescence (10 µL) QRET: 340/615 nm Eu(III)-luminescence (10 µL) |
| Apyrase assay | Probe 1: 7.5 µM antenna 1, 7.5 nM Tb(III)-N1 | 50 µU apyrase, 1–10 µM ATP | Buffer 2: 20 mM HEPES, pH 6.5, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CaCl2, 0.01% Triton-X 100, 0.005% γ-globulins | Probe 1: 330/545 nm Tb(III)-luminescence (10 µL) |
| Anion Species | EC50 (nM) | LOD (nM) | Linear Range (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATP | 107 ± 0.5 | 15.7 ± 3.0 | 0.02–5 |
| GTP | 97 ± 0.4 | 18.2 ± 2.5 | 0.02–10 |
| CTP | 17 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 1.5 | 0.01–1 |
| ITP | 155 ± 0.4 | 43.6 ± 5.7 | 0.02–10 |
| UTP | 164 ± 0.7 | 28.2 ± 4.4 | n.c. |
| AMP-PNP | 73 ± 0.6 | 8.6 ± 3.9 | n.c. |
| ADP | 1170 ± 70 | 161 ± 48 | 0.2–150 |
| GDP | 1110 ± 60 | 197 ± 42 | 0.2–100 |
| UDP | 1540 ± 70 | 165 ± 36 | 0.2–150 |
| GMP | 16,800 ± 3900 | n.c. | n.c. |
| (NaPO3)n | 33 ± 0.2 | 13.6 ± 7.2 | n.c. |
| (NaPO3)3 | 60 ± 0.4 | 15.5 ± 2.6 | n.c. |
| (NaPO3)2 | 432 ± 3 | 69.3 ± 20.2 | n.c. |
| Na2HPO4 | >250 | n.c. | n.c. |
| cGMP | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| cAMP | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopra, K.; Seppälä, T.; Rabara, D.; Abreu-Blanco, M.; Kulmala, S.; Holderfield, M.; Härmä, H. Label-Free Time-Gated Luminescent Detection Method for the Nucleotides with Varying Phosphate Content. Sensors 2018, 18, 3989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113989
Kopra K, Seppälä T, Rabara D, Abreu-Blanco M, Kulmala S, Holderfield M, Härmä H. Label-Free Time-Gated Luminescent Detection Method for the Nucleotides with Varying Phosphate Content. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113989
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopra, Kari, Tanja Seppälä, Dana Rabara, Maria Abreu-Blanco, Sakari Kulmala, Matthew Holderfield, and Harri Härmä. 2018. "Label-Free Time-Gated Luminescent Detection Method for the Nucleotides with Varying Phosphate Content" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113989
APA StyleKopra, K., Seppälä, T., Rabara, D., Abreu-Blanco, M., Kulmala, S., Holderfield, M., & Härmä, H. (2018). Label-Free Time-Gated Luminescent Detection Method for the Nucleotides with Varying Phosphate Content. Sensors, 18(11), 3989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113989





