A Fair Contention Access Scheme for Low-Priority Traffic in Wireless Body Area Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Priority-Based MAC Protocols
3. IEEE 802.15.4 MAC and PA-MAC Overview
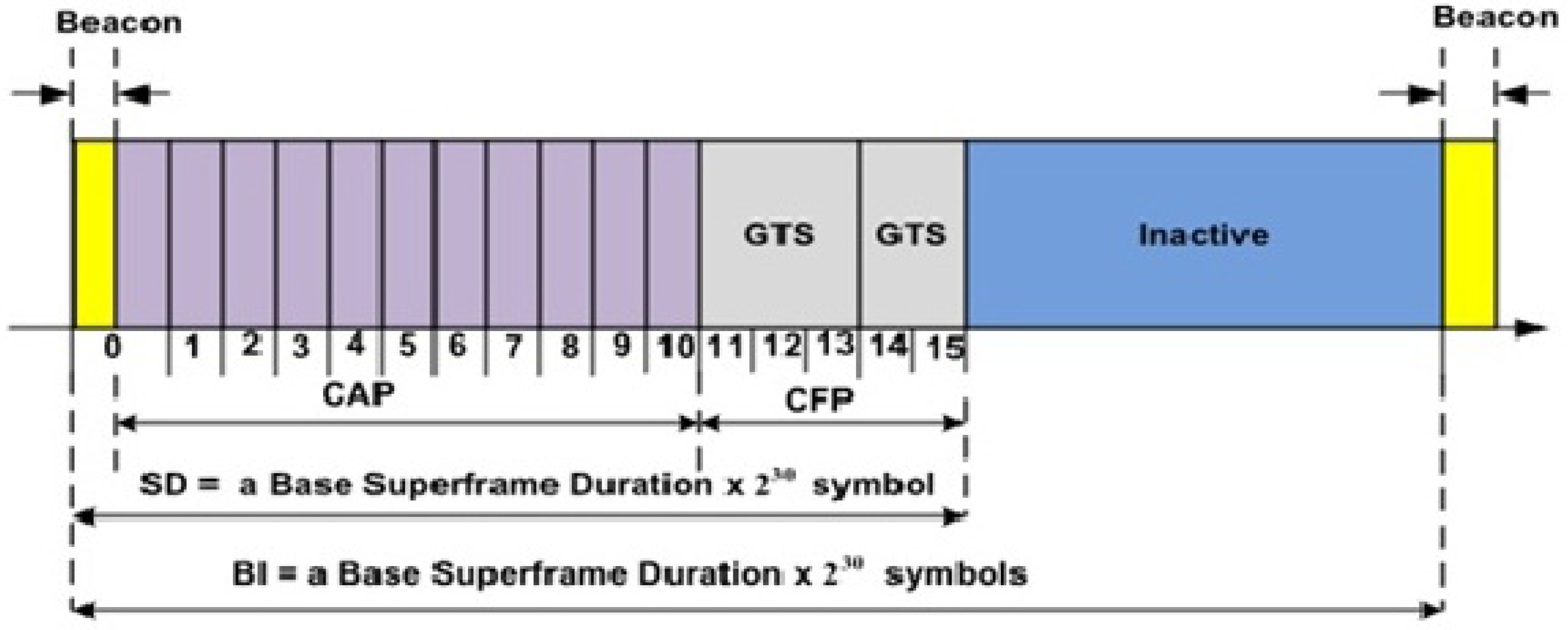
3.1. IEEE 802.15.4 MAC
- Non beacon-enabled mode based on un-slotted CSMA/CA
- Beacon-enabled mode, where sensor nodes receive periodic beacon frames from the coordinator to synchronize with the coordinator.
- Whenever a node has data to transmit, the transfer is initiated by the coordinator.
- If a coordinator has data to transmit, the transfer is still initiated by the coordinator.
3.2. PA-MAC
4. Traffic-Adaptive Priority-Based MAC (TAP-MAC) Design and Operation
4.1. TAP-MAC Design and Operation
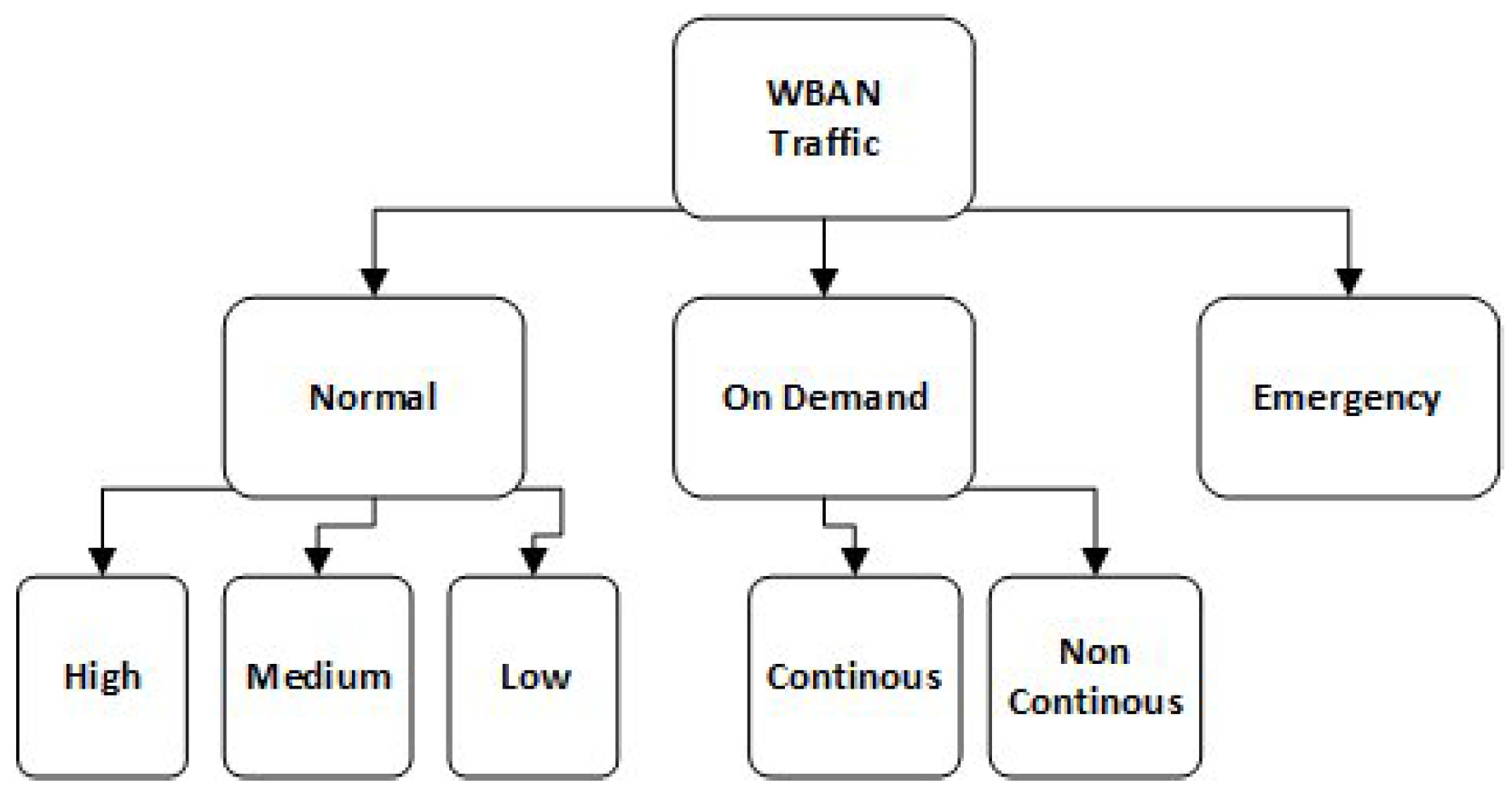
4.1.1. Traffic Classification
4.1.2. Traffic Prioritization
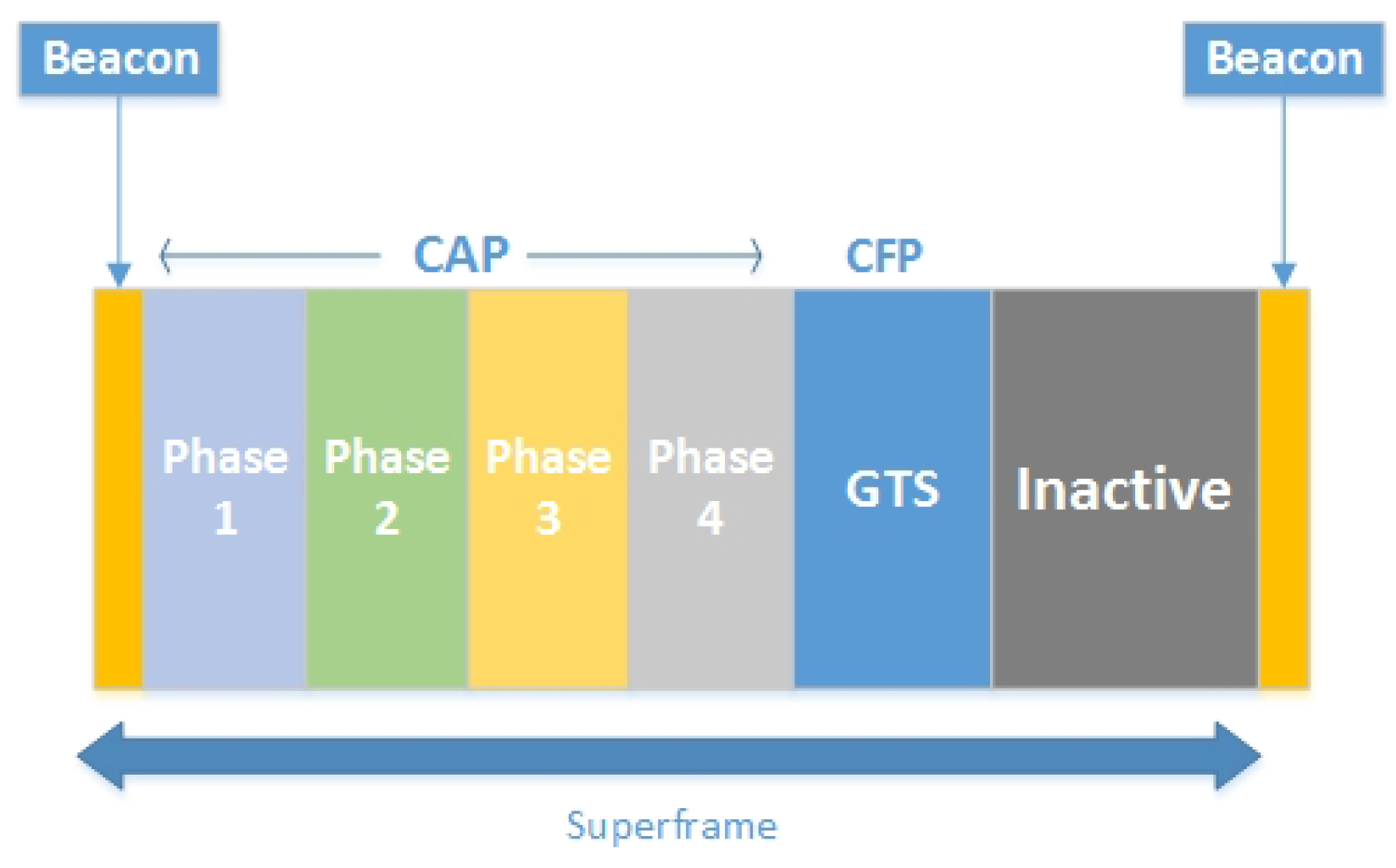
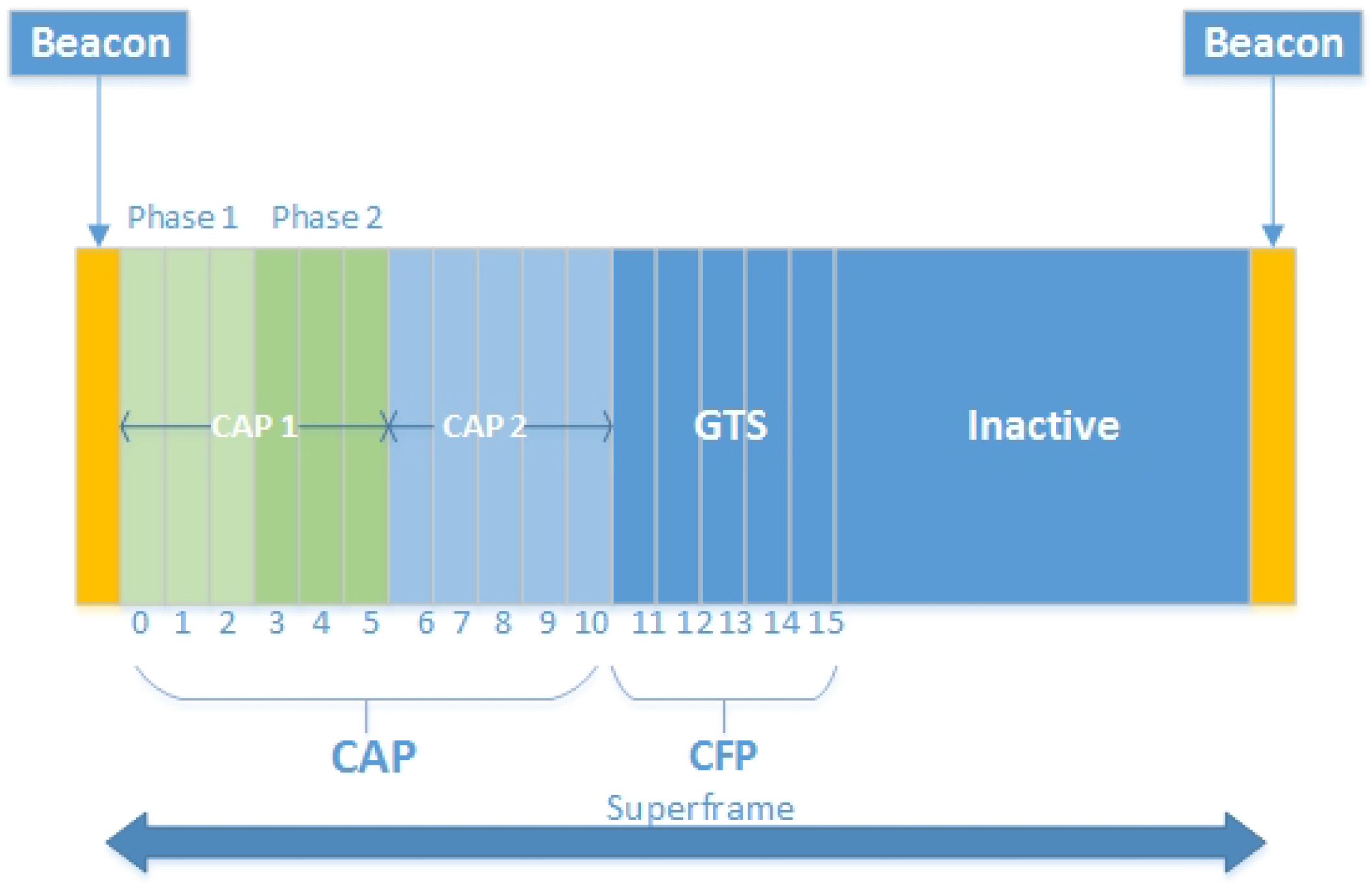
4.1.3. Dynamic CAP Adjustment
| Algorithm 1: Computes and based on traffic conditions. |
 |
| Algorithm 2: Computes sub-phases of and for . |
 |
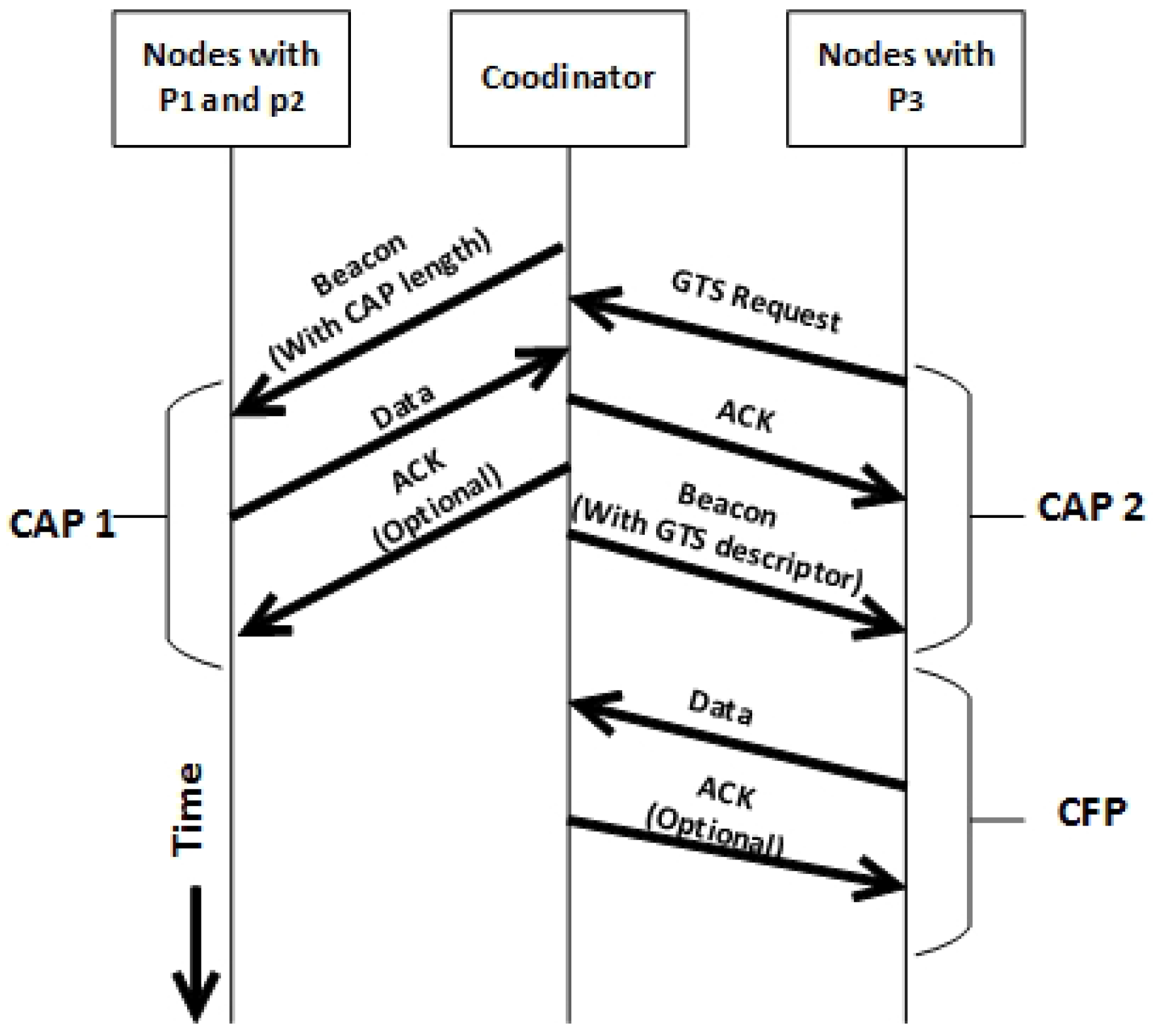
4.1.4. TAP-MAC Superframe Structure
4.1.5. Channels in TAP-MAC
4.1.6. TAP-MAC Data Transfer
5. TAP-MAC Performance Evaluation
5.1. Simulation Environment
5.2. Simulation Scenarios
5.2.1. Scenario 1
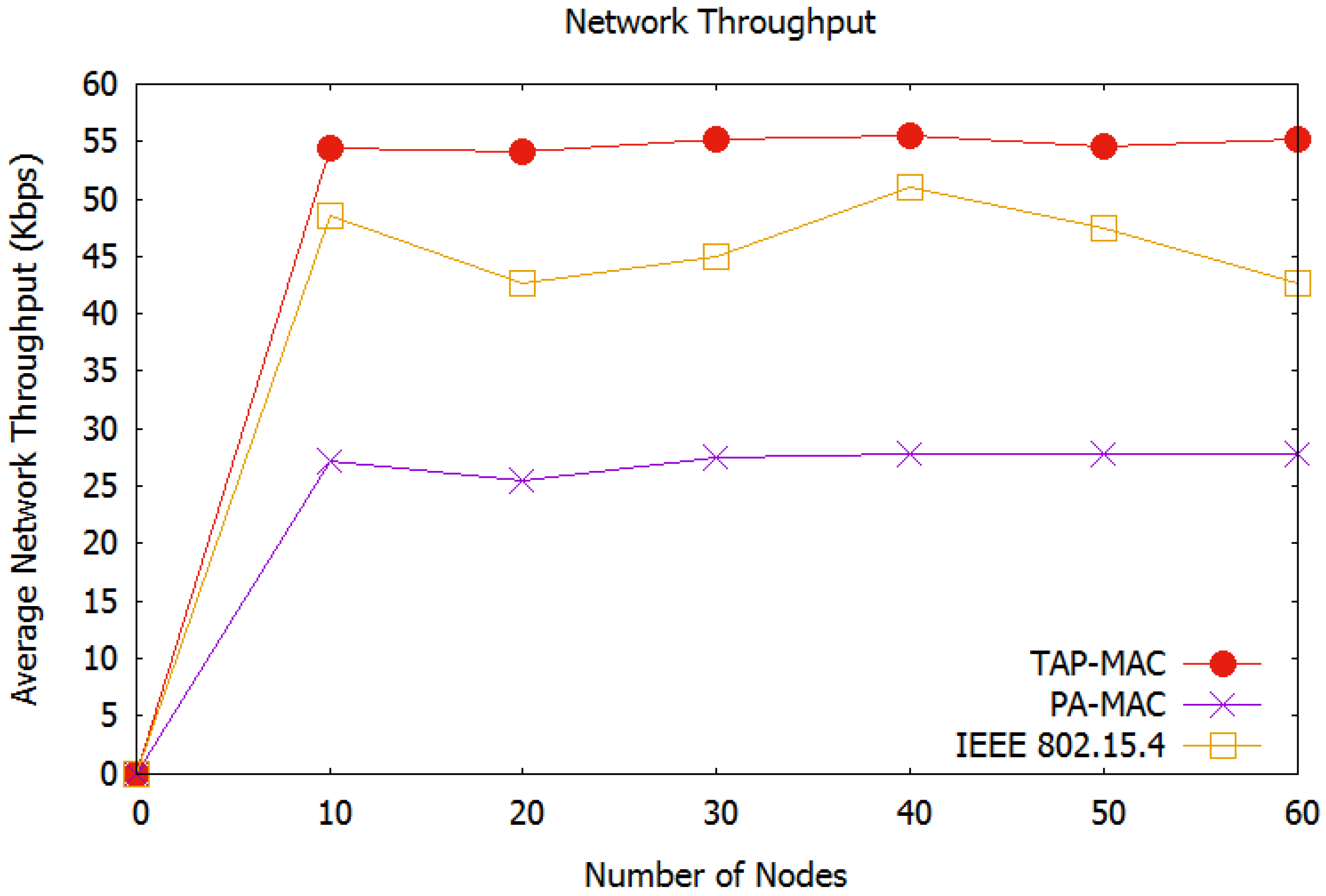
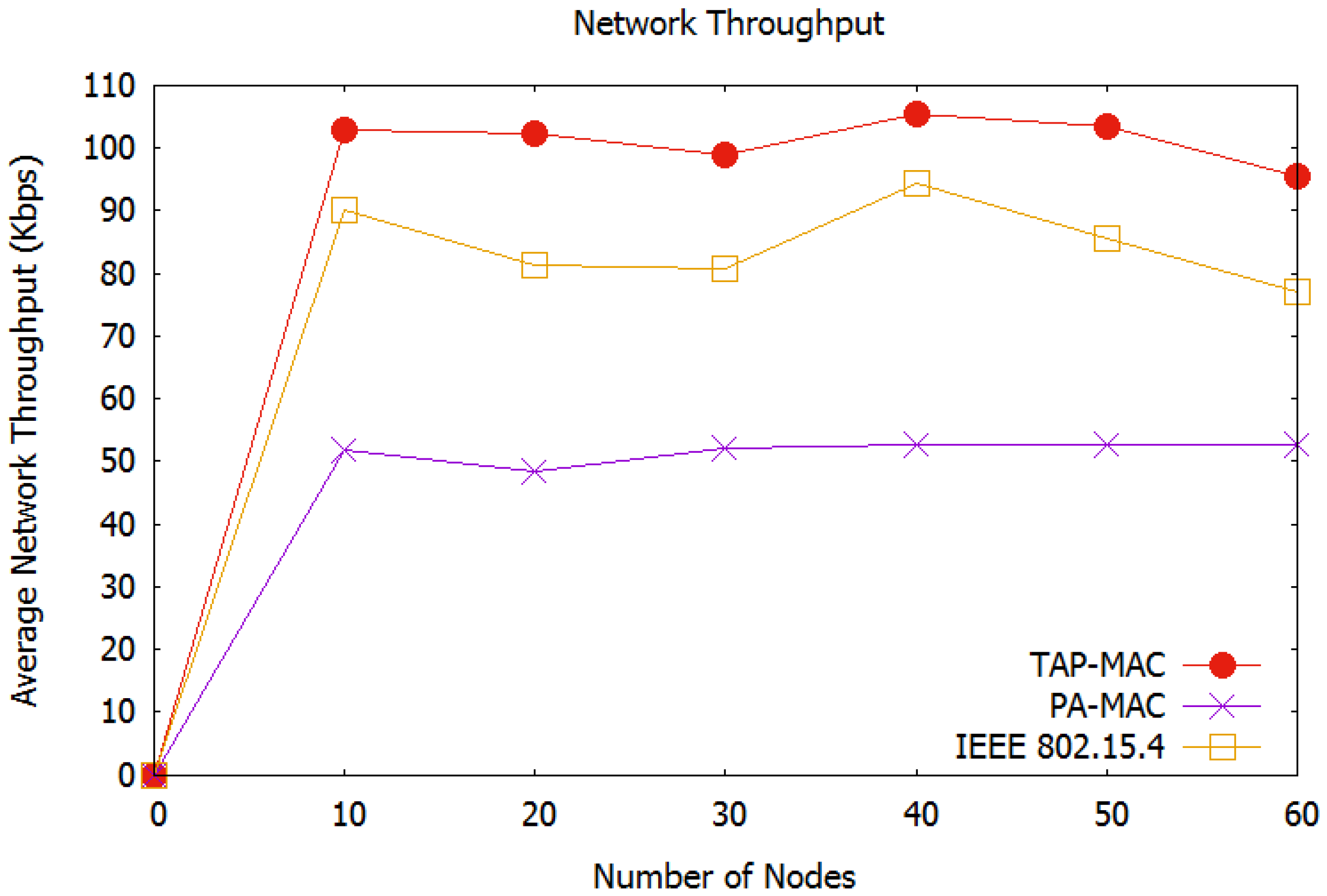
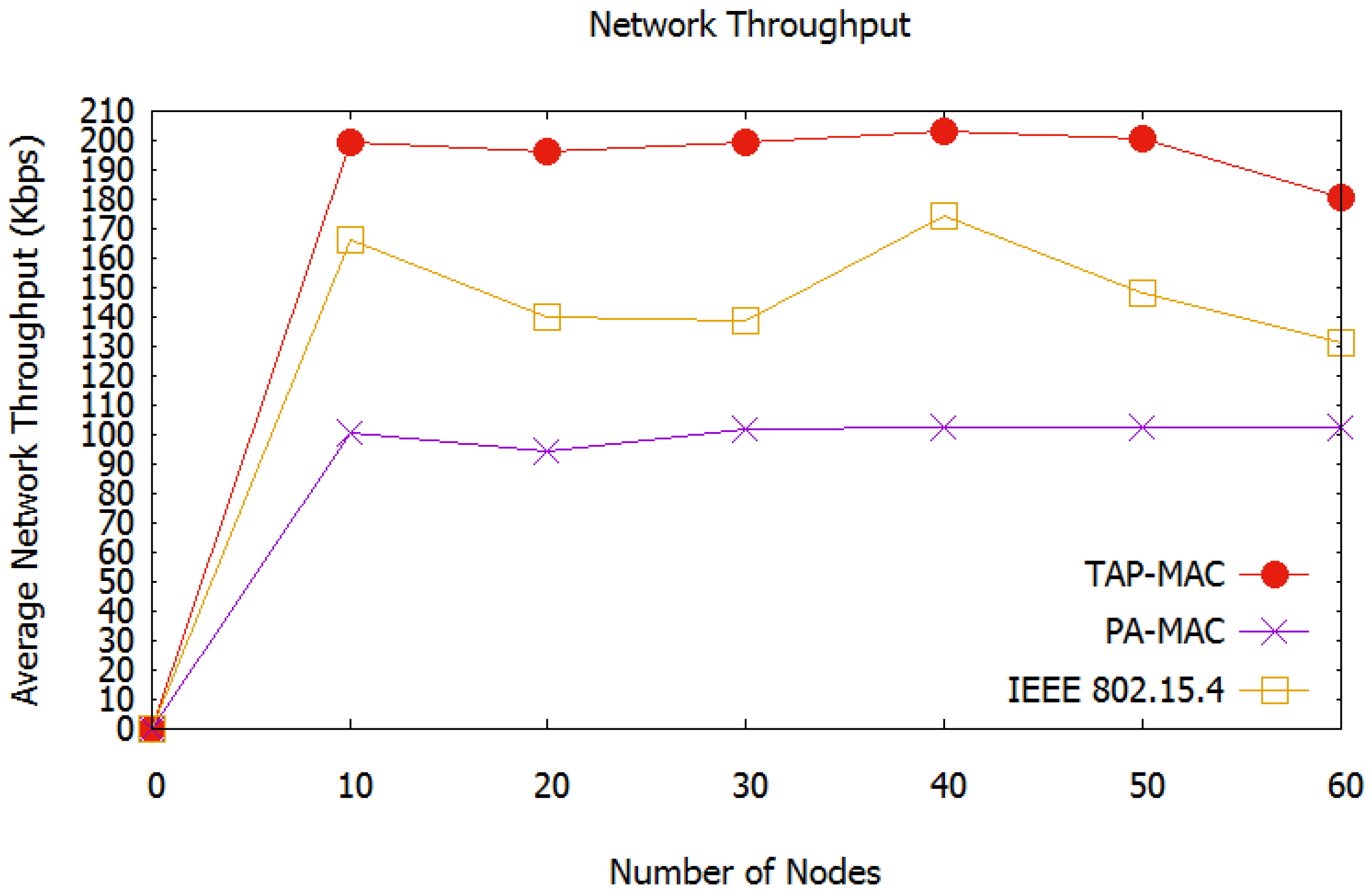
Average Network Throughput
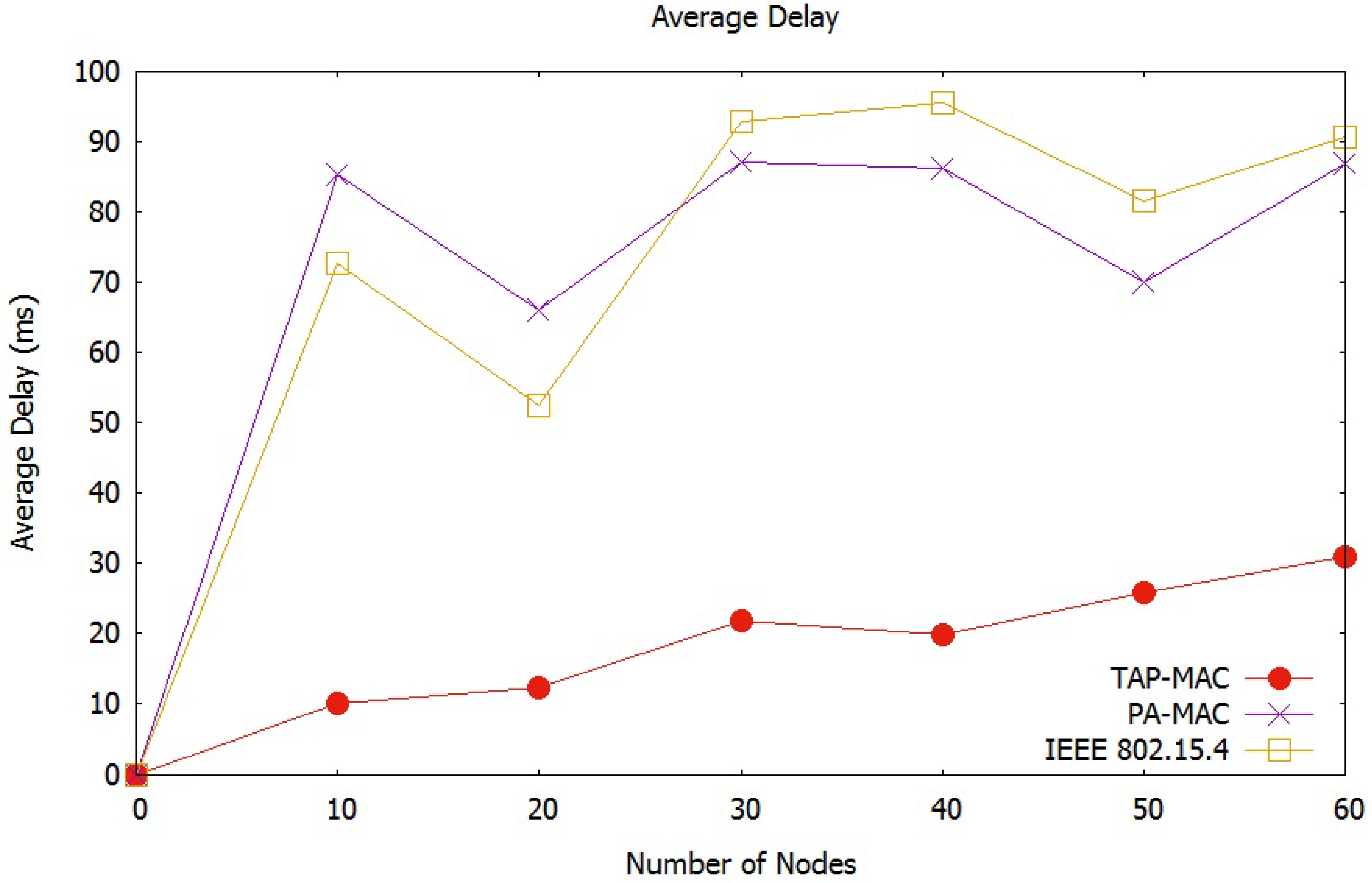
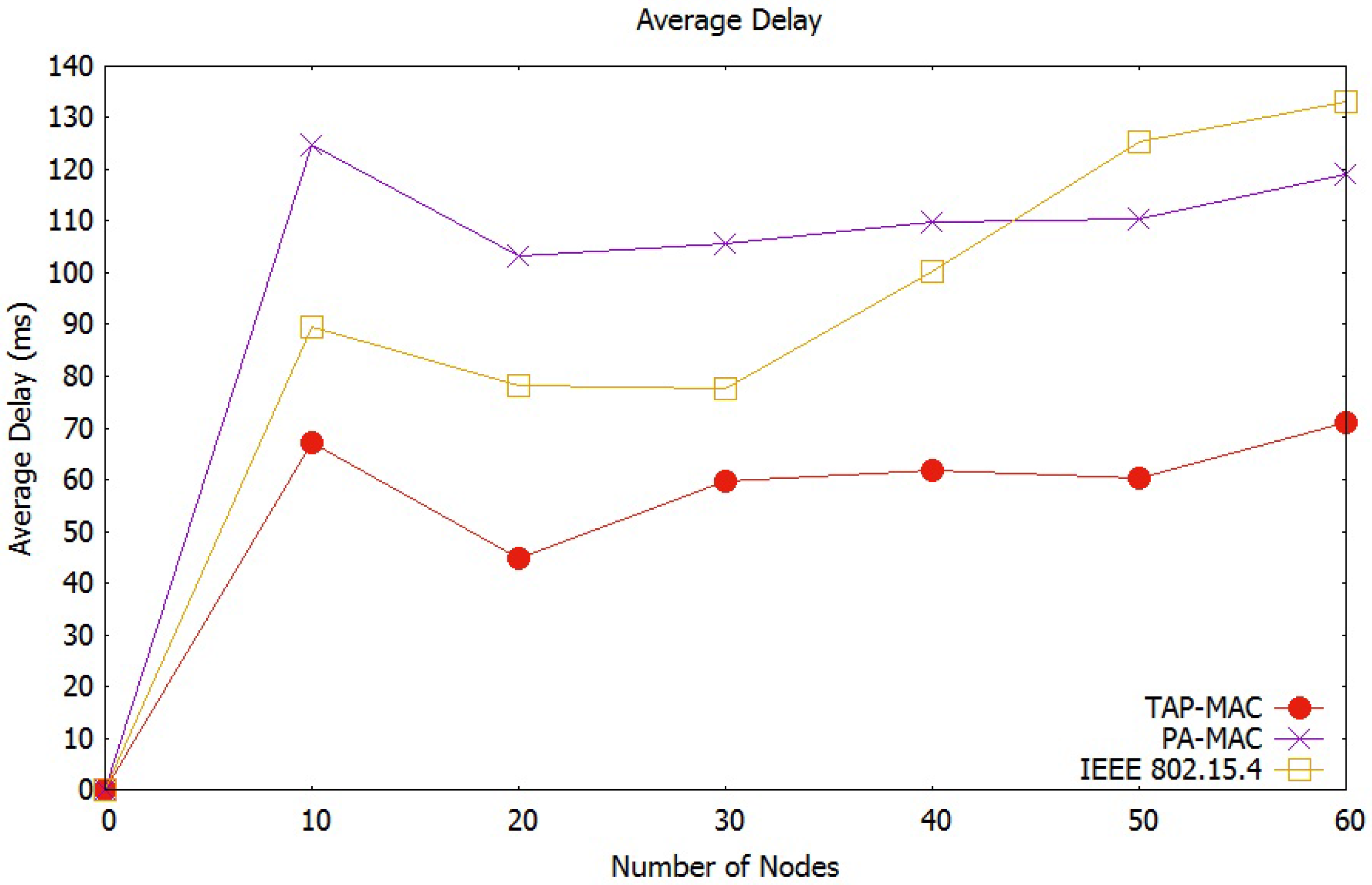
Average Network Delay
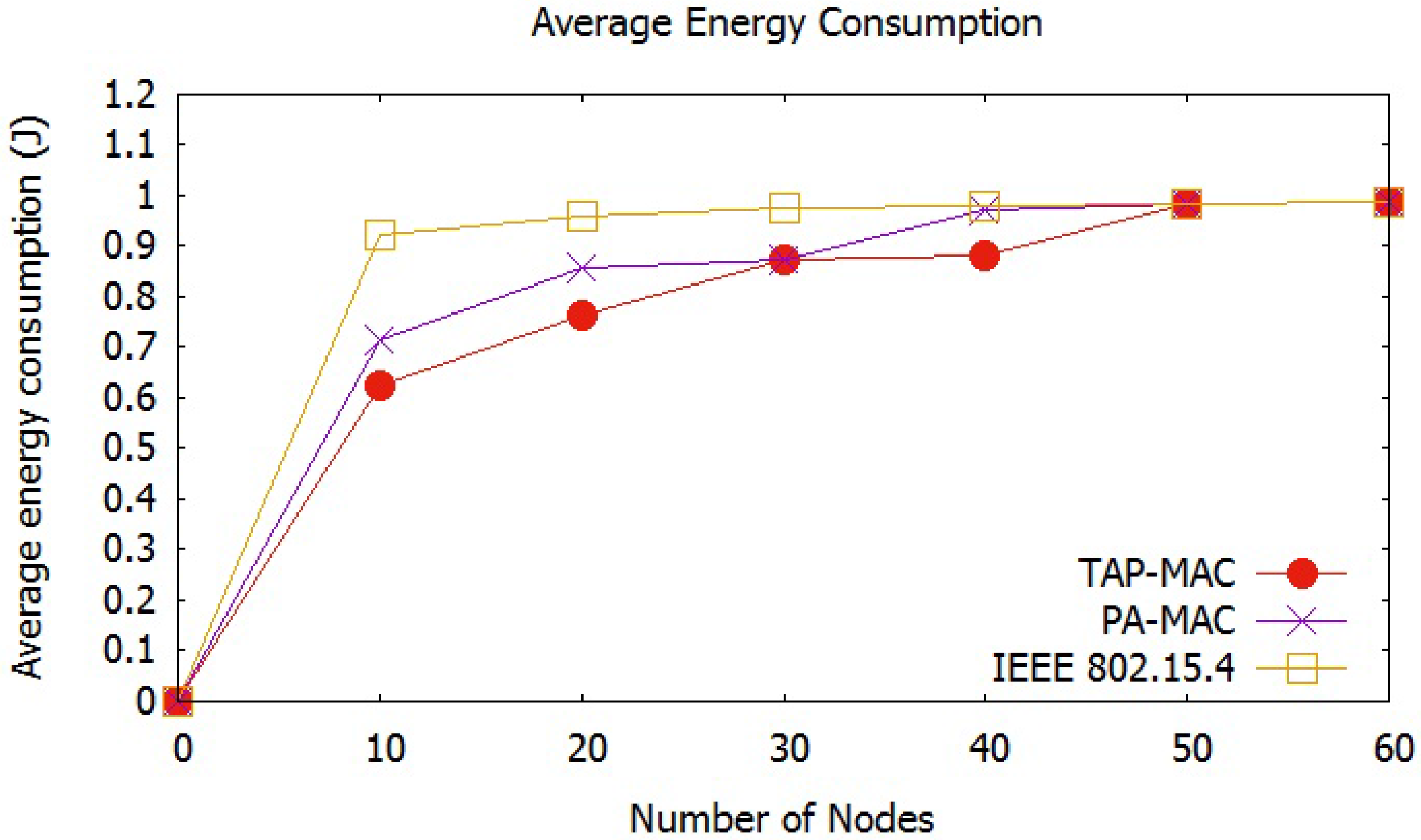
Average Energy Consumption
5.2.2. Scenario 2
Average Network Throughput
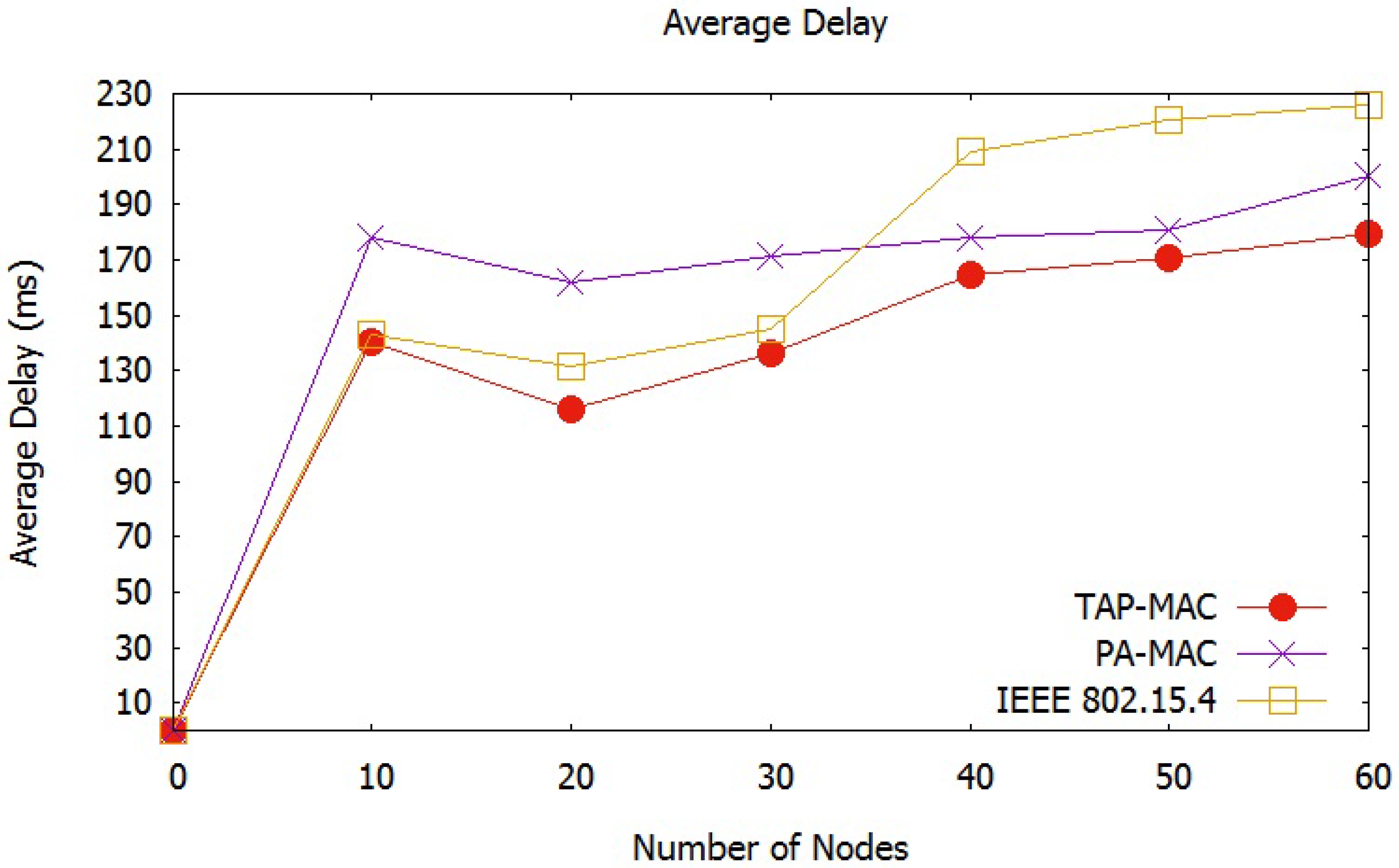
Average Network Delay
Average Energy Consumption
5.2.3. Scenario 3
Average Network Throughput
Average Network Delay
Average Energy Consumption
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEEE Standard. 802.15.4: Low-Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks (LR-WPANs); IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Victor, L.; Cupid, C. Enabling technologies for wireless body area networks: A survey and outlook. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2009, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortino, F.; Giannantonio, R.; Gravina, R.; Kuryloski, P.; Jafari, R. Enabling Effective Programming and Flexible Management of Efficient Body Sensor Network Applications. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2013, 43, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, R.; Alinia, P.; Ghasemzadeh, H.; Fortino, G. Multi-sensor fusion in body sensor networks: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Inf. Fusion 2017, 35, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassaghi, S.; Abolhasan, M.; Lipman, J.; Smith, D.; Jamalipour, A. Wireless Body Area Network: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1658–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Chen, M.; Kwak, K.S. Throughput and Delay Analysis of IEEE 802.15.6-based CSMA/CA protocol. J. Med. Syst. 2012, 36, 3875–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, E.; Gorday, P.; Hester, L.; Gutierrez, J.A.; Naeve, M.; Heile, B.; Bahl, B. Home networking with IEEE 802.15.4: A developing standard for low-rate wireless personal area networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2002, 8, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Moh, S. A Priority-Based Adaptive MAC Protocol for Wireless Body Area Networks. Sensors 2016, 16, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Imran, M.; Alnuem, M. A Hybrid and Secure Priority-Guaranteed MAC Protocol for Wireless Body Area Network. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dolmans, G. A new priority-guaranteed MAC protocol for emerging body area networks. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Communications, Cannes/La Bocca, France, 23–29 August 2009; pp. 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.J.; Xie, Y.; Yi, Q. An All Dynamic Mac Protocol for Wireless Body Area Network. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Shanghai, China, 21–23 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Shen, B.; Islam, M.; Khan, P.; Saleem, S.; KwakAn, K.S. A study of MAC protocols for WBANs. Sensors 2010, 10, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Higgins, H.; Braem, B.; Latre, B.; Blondia, C.; Moerman, I.; Saleem, S.; Rahman, Z.; Kwak, K.S. A comprehensive survey of wireless body area networks on PHY, MAC, and network layers solutions. J. Med. Syst. 2012, 3, 1065–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.F.G.; Dutkiewicz, E. BodyMAC: Energy efficient TDMA-based MAC protocol for Wireless Body Area Networks. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technology, Icheon, Korea, 28–30 September 2009; pp. 1455–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Elhadj, H.; Elias, J.; Chaari, L.; Kamoun, L. A priority-based Cross Layer Routing Protocol for healthcare applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th Annual IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, I.; Alam, N.; Razzaque, M.; Hassan, M.; Alamri, A. Traffic priority and load adaptive MAC protocol for QoS provisioning in body sensor networks. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Hong, S.; Lee, S.; Bang, Y. ATLAS: A traffic load aware sensor MAC design for collaborative body area sensor networks. Sensors 2011, 11, 11560–11580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberola, R.; Pesch, D. Duty cycle learning algorithm (DCLA) for IEEE 802.15.4 beacon-enabled wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2012, 10, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Balasingham, I. Performance analysis of the IEEE 802.15.4 based ECG monitoring network. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 30 May–1 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, F.; Li, J.; Hao, R.; Kong, X.; Gao, R. Service Differentiated and Adaptive CSMA/CA over IEEE 802.15.4 for Cyber-Physical Systems. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espina, J.; Falck, T.; Muehlsteff, J.; Aubert, X. Wireless Body Sensor Network for Continuous Cuff-less Blood Pressure Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE/EMBS International Summer School on Medical Devices and Biosensors, Cambridge, MA, USA, 4–6 September 2006; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Ha, J.; Jeon, J.; Kim, D.; Kwon, W. ECAP: A Bursty Traffic Adaptation Algorithm for IEEE 802.15.4 Beacon-Enabled Networks. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, Dublin, Ireland, 22–25 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Tan, J. Heartbeat-driven medium-access control for body sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.H.; Yundra, E.; Wu, H.K.; Udin Harun, M. Analysis of superframe duration adjustment scheme for IEEE 802.15.4 networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 Seventh International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks, Sapporo, Japan, 7–10 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Hao, B.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. A novel medium access control protocol with low delay and traffic adaptivity for wireless body area networks. J. Med. Syst. 2011, 35, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Cho, J. A novel priority-based channel access algorithm for contention-based MAC protocol in WBANs. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 20–22 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sheraz, A.; Khan, W.U.; Ullah, S.; Naeem, F.; Ullah, S.I.; Salam, A. A Comparative Analysis of Energy Efficient Medium Access Control Protocols for Wireless Body Area Networks. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. 2016, 14, 758–764. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, C.H.S.; Ghamri-Doudane, Y.; Lohier, S. A duty cycle self-adaptation algorithm for the 802.15.4 wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the Global Information Infrastructure Symposium, Trento, Italy, 28–31 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, J.; Aedo, J.; Rivera, F. Continuous, non-invasive and cuff-free blood pressure monitoring system. In Proceedings of the Andean Region International Conference, Cuenca, Ecuador, 7–9 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE 802.15 WPAN Task Group 6 Body Area Networks (BAN). Available online: http://www.ieee802.org/15/pub/TG6.html (accessed on 20 February 2016).
- Chen, Z.; Lin, C.; Wen, H.; Yin, H. An Analytical Model for Evaluating IEEE 802.15.4 CSMA/CA protocol in Low-rate wireless application Model. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 21–23 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bossche, A.V.D.; Val, T.; Campo, E. Prototyping and performance analysis of a QoS MAC layer for industrial wireless network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fieldbuses and Networks in Industrial and Embedded Systems 2007, Toulouse, France, 7–9 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, D.; Lee, T.T. Throughput stability and energy consumption of IEEE 802.15.4 beacon-enabled mode. In Proceedings of the 2012 21st Annual Wireless and Optical Communications Conference, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 19–21 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, M.; Trsek, H.; Graeser, O.; Jasperneite, J. Performance Investigation and Optimization of IEEE 802.15.4 for IndustrialWireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, Hamburg, Germany, 15–18 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Tang, Z.; Chen, H.H.; Zhang, Q. An accurate and scalable analytical model for IEEE 802.15.4 slotted CSMA/CA networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 8, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, C.; Verdone, R. Performance analysis of IEEE 802.15.4 non beacon-enabled mode. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 3480–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, V.; Obraczka, K.; Garcia-Luna-Aceves, J.J. Energy-efficient collision-free medium access control for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5–7 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, P.K.; Yin, D.; Lee, T.T. Analysis of non-persistent CSMA protocols with exponential backoff scheduling. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2011, 59, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S.; Dahal, S.; Shin, S. Does the IEEE 802.15.4 MAC Protocol Work Well in Wireless Body Area Networks. J. Adv. Comput. Netw. 2016, 4, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.S.W.; Nguyen, G.; Walrand, J. Practical Synchronization Techniques for Multi-Channel MAC. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 23–29 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly, R. IEEE standards for physical and data communications. Biomed. Instrum. Technol. 2003, 30, 172–175. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Paulus, R.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Kumar, M. Analysis of energy model and Performance of IEEE 802.15.4 WSNs under Different Duty Cycle. J. Electron. Commun. Eng. 2014, 9, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.J.; Hong, S.H.; Moon, S.P.; Chang, T.G.; Cho, H. Segmentized clear channel assessment for IEEE 802.15.4 networks. Sensors 2016, 16, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, S.; Deligiannis, N.; Surace, R.; Loscrì, V. Decentralized Time-Synchronized Channel Swapping for Ad Hoc Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 8538–8553. [Google Scholar]
- Galzarano, S.; Liotta, A.; Fortino, G. QL-MAC: A Q-Learning Based MAC for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing, Vietri sul Mare, Italy, 18–20 December 2013. [Google Scholar]



| Traffic | Priority Level | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency traffic | (Highest) | Emergency alarm signals |
| On-demand traffic | (Medium) | Continuous/non-continuous medical signals (EEG, EMG, blood pressure, temperature) |
| Normal traffic | (Lowest) | Audio/video/data |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Data rate | 250 Kbps |
| Frequency | GHz |
| Symbol rate | ksymbols/s |
| Superframe duration | 122.88 ms |
| Transition time | 192 s |
| aUnitBackoff period | 20 symbols |
| macMaxCSMABackoffs | 5 |
| macMinBE | 3 |
| macMaxBE | 5 |
| Initial energy | 1 Joule |
| Transmission power consumption | 12.3 mA |
| Reception power consumption | 14 mA |
| Idle power consumption | 0.4 mA |
| Traffic type | CBR |
| Clear channel assessment | 8 symbols |
| Beacon size | 40 bytes |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henna, S.; Sajeel, M.; Bashir, F.; Asfand-e-yar, M.; Tauqir, M. A Fair Contention Access Scheme for Low-Priority Traffic in Wireless Body Area Networks. Sensors 2017, 17, 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17091931
Henna S, Sajeel M, Bashir F, Asfand-e-yar M, Tauqir M. A Fair Contention Access Scheme for Low-Priority Traffic in Wireless Body Area Networks. Sensors. 2017; 17(9):1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17091931
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenna, Shagufta, Muhammad Sajeel, Faisal Bashir, Muhammad Asfand-e-yar, and Muhammad Tauqir. 2017. "A Fair Contention Access Scheme for Low-Priority Traffic in Wireless Body Area Networks" Sensors 17, no. 9: 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17091931
APA StyleHenna, S., Sajeel, M., Bashir, F., Asfand-e-yar, M., & Tauqir, M. (2017). A Fair Contention Access Scheme for Low-Priority Traffic in Wireless Body Area Networks. Sensors, 17(9), 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17091931





