A Stretchable Electromagnetic Absorber Fabricated Using Screen Printing Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
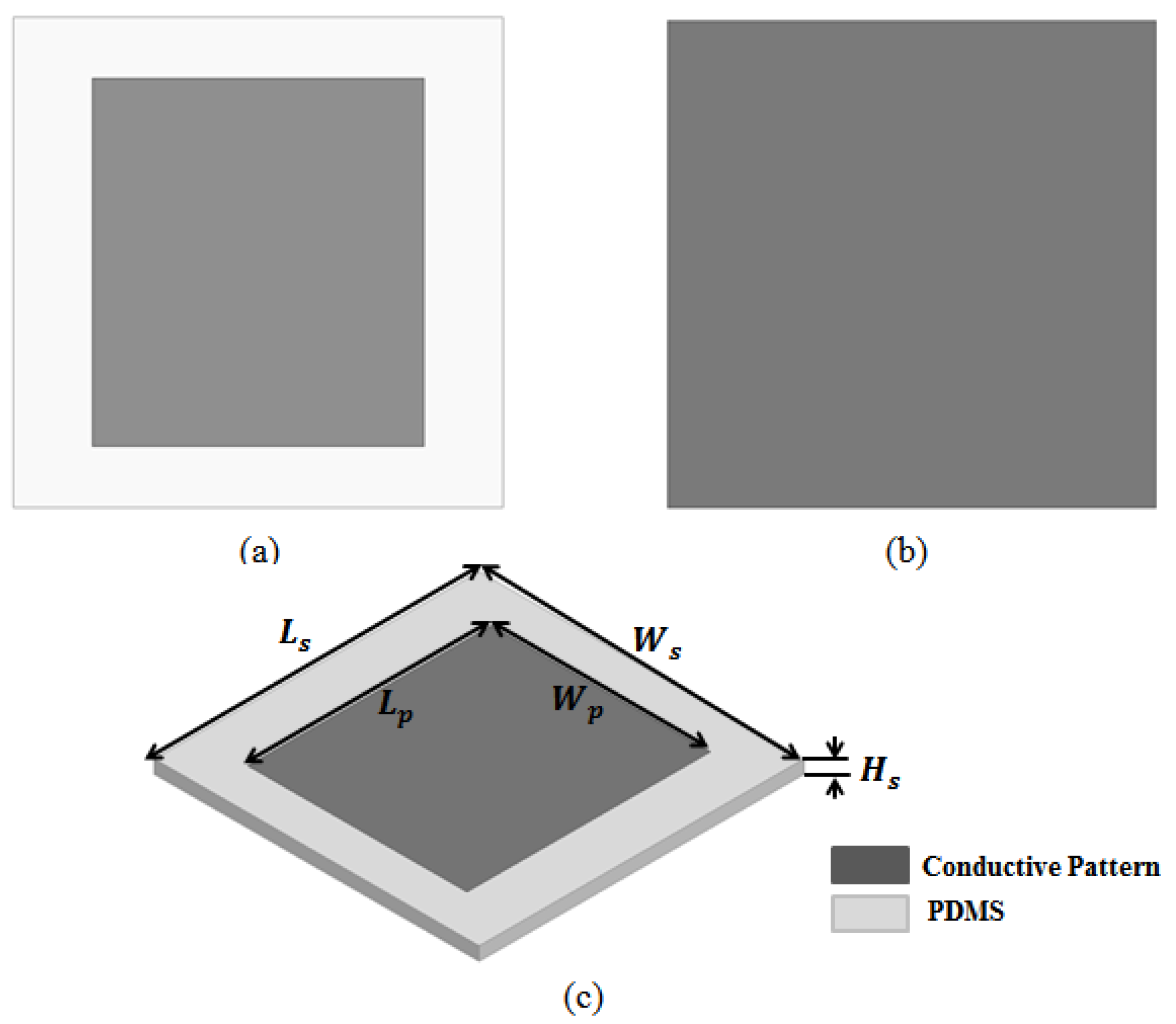
2. Absorber Design
3. Fabrication Processes
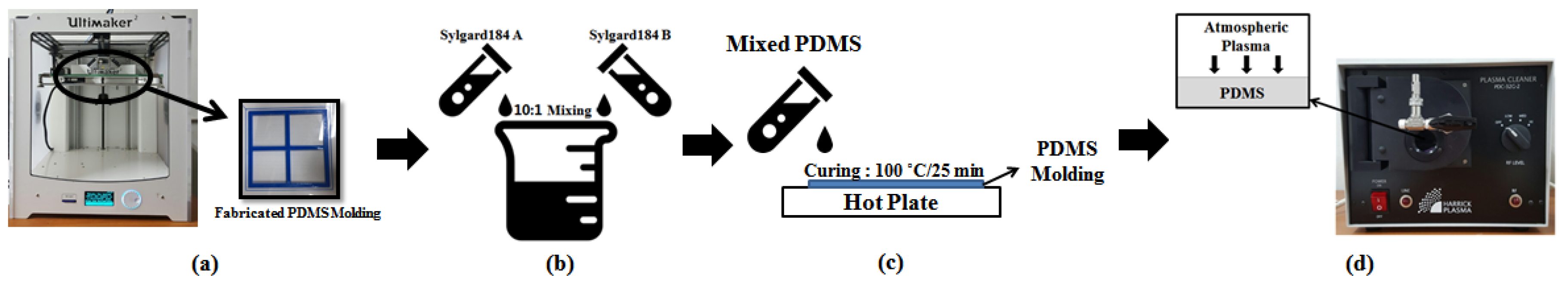
3.1. PDMS Fabrication
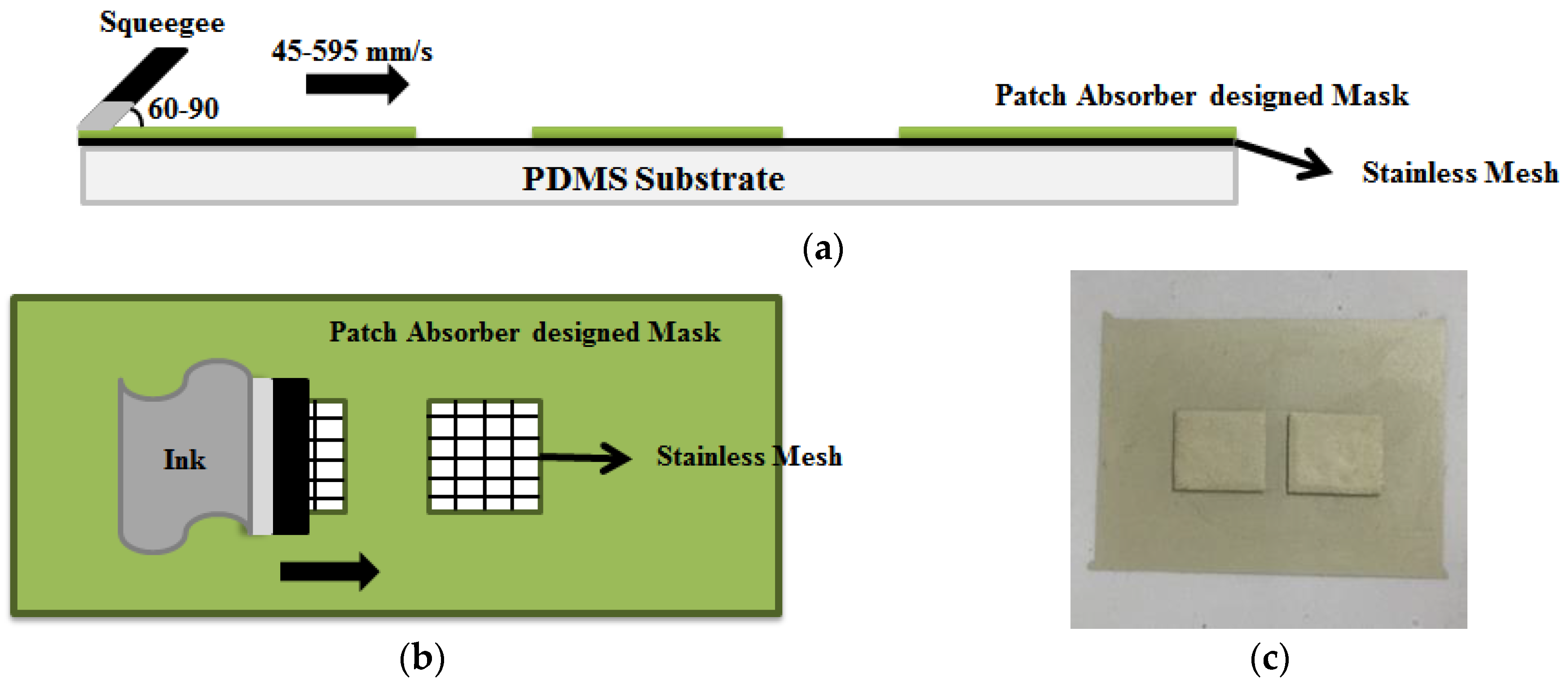
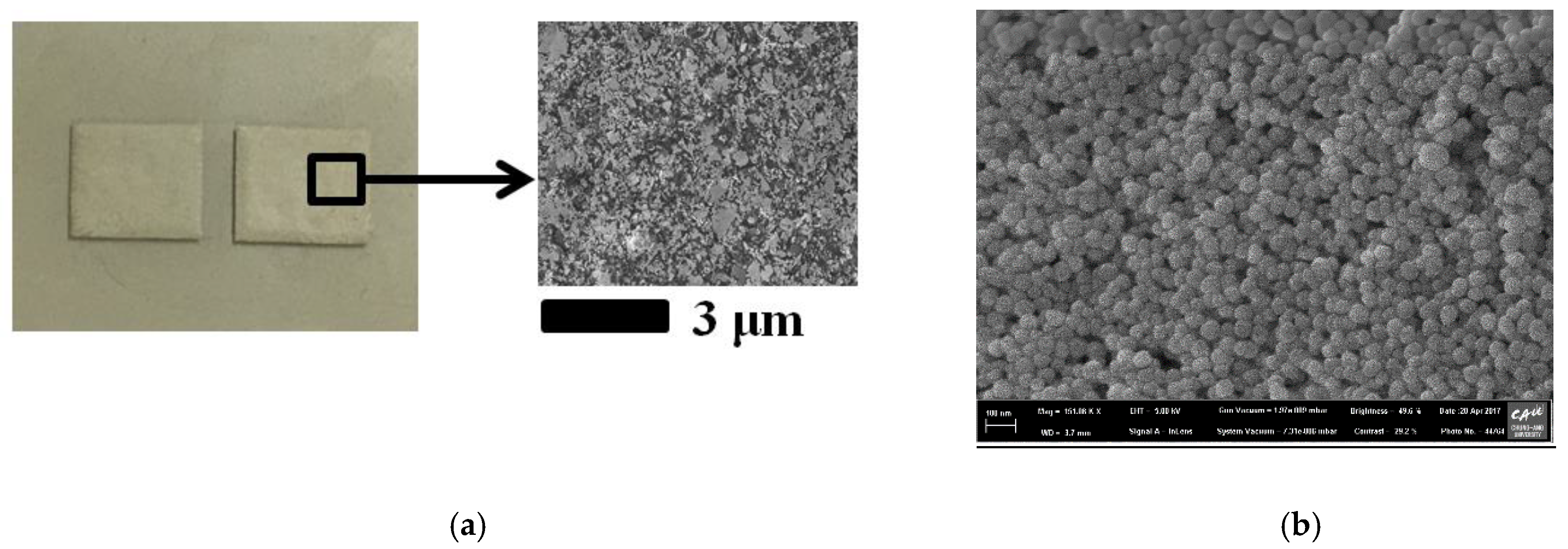
3.2. Screen Printing Process
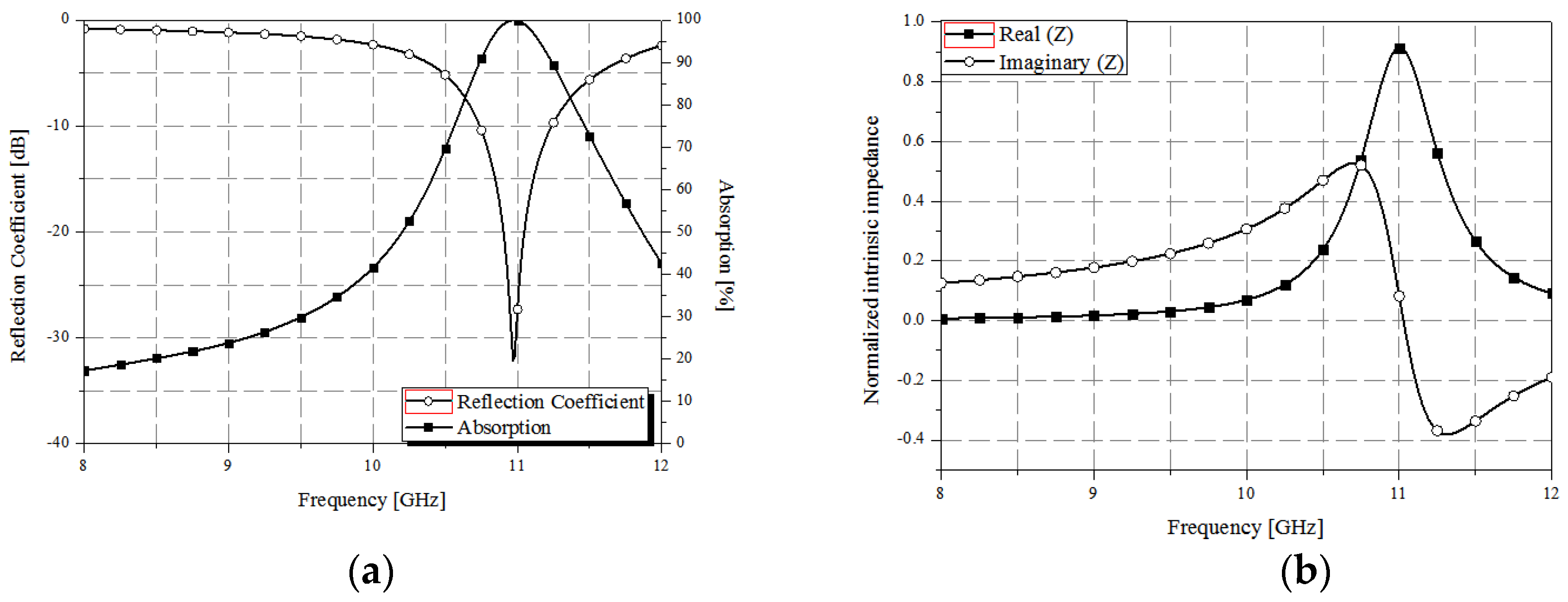
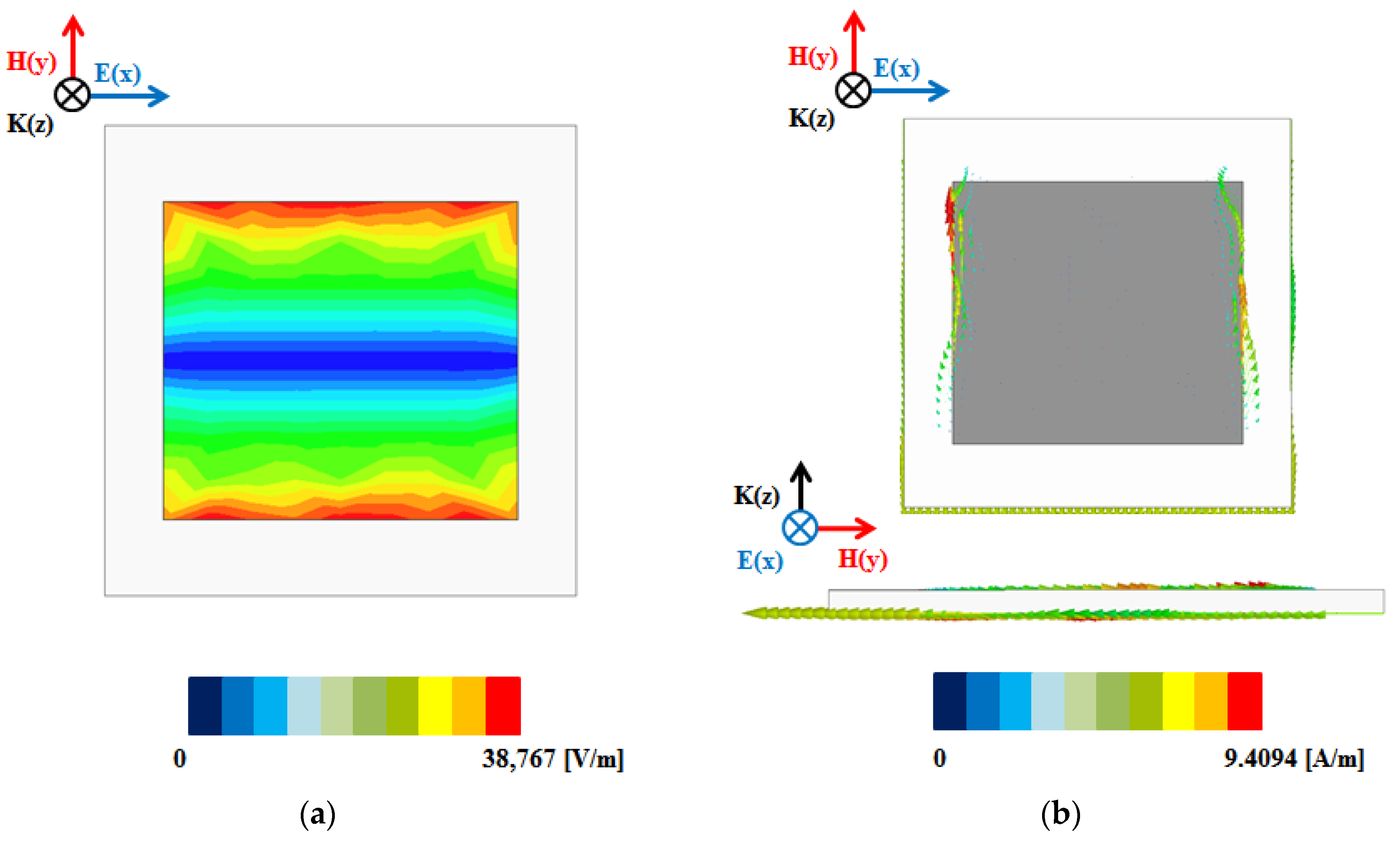
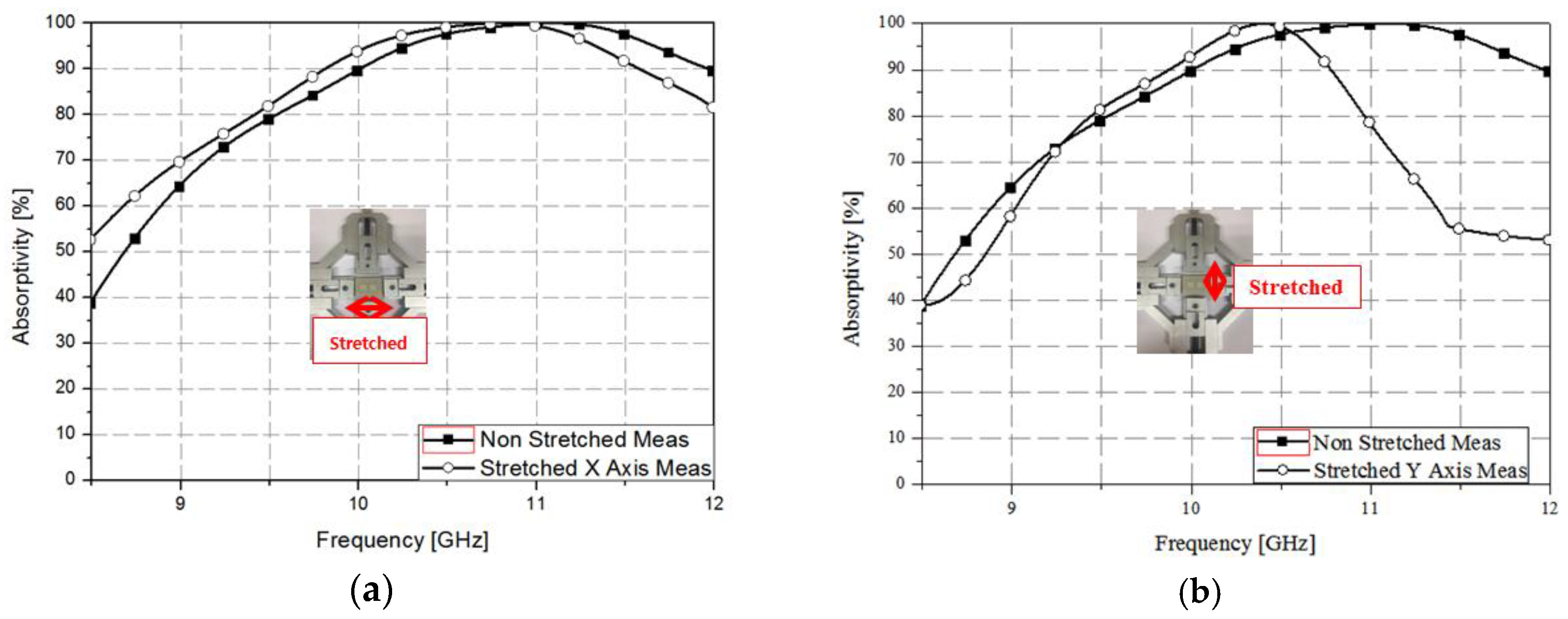
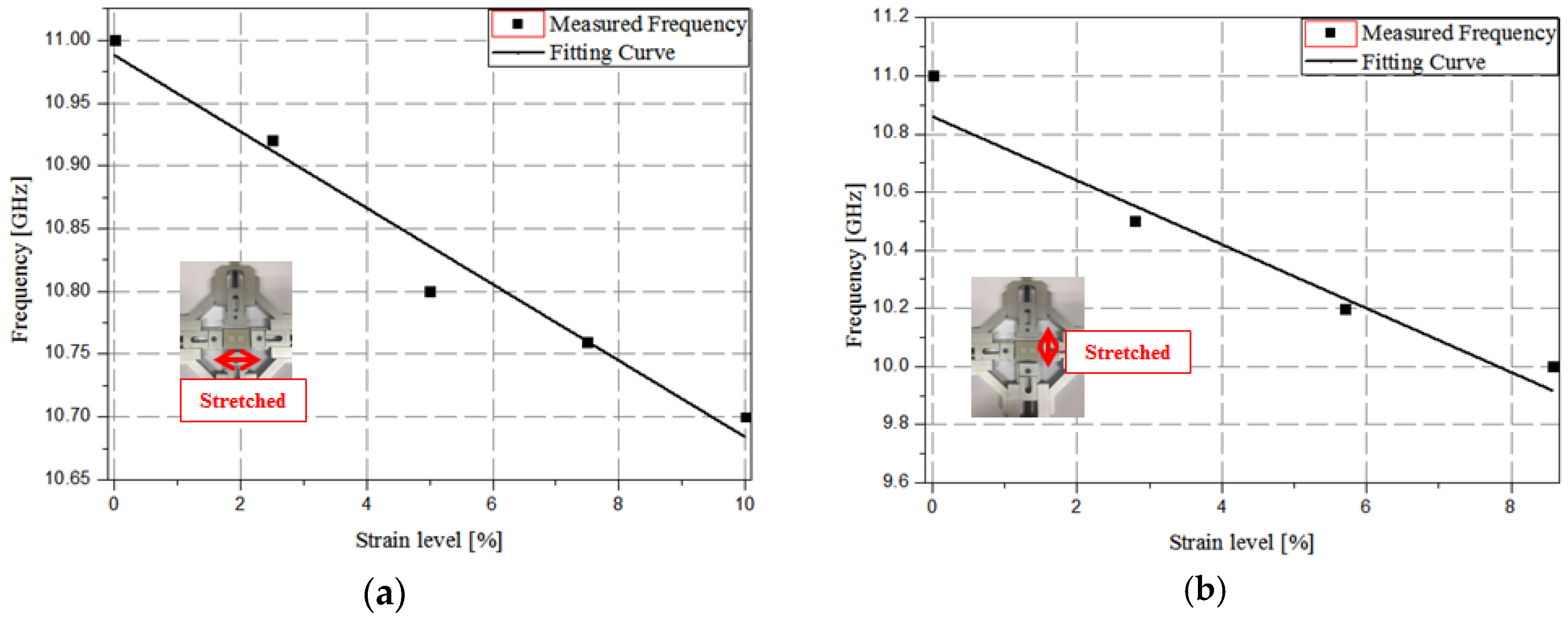
4. Measurement Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schurig, D.; Mock, J.J.; Justice, B.J.; Cummer, S.A.; Pendry, J.B.; Starr, A.F.; Smith, D.R. Metamaterial electromagnetic cloak at microwave frequencies. Science 2006, 314, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsome, W.T.; Goldberg, M.E.; Maunsell, J.H.R.; Buneo, C.A.; Duncan, J.; Cave, K.R.; Franzel, S.L.; Miller, E.K.; Duncan, J.; Desimone, R.; et al. Sub-diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver superlens. Science 2005, 1783, 534–537. [Google Scholar]
- Boyko, S.N.; Kukharenko, A.S.; Yaskin, Y.S. EBG Metamaterial ground plane for mitigation of multipath signals in GNSS sntenna. J. Elecromagn. Eng. Sci. 2015, 15, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lee, B. Design of thin RC absorbers using a silver nanowire resistive screen. J. Elecromagn. Eng. Sci. 2016, 16, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.T.; Padilla, W.J.; Zide, J.M.O.; Gossard, A.C.; Taylor, A.J.; Averitt, R.D. Active terahertz metamaterial devices. Nature 2006, 444, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.X.; Wang, G.M.; Qi, M.Q. A miniaturized triple-band metamaterial antenna with radiation pattern selectivity and polarization diversity. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 137, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, N.I.; Sajuyigbe, S.; Mock, J.J.; Smith, D.R.; Padilla, W.J. Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Yoon, Y.-H.; Jo, K.-J.; Jung, G.-B.; An, C.-C. Effects of sheet thickness on the electromagnetic wave absorbing characterization of Li 0.375 Ni 0.375 Zn 0.25 -ferrite composite as a radiation absorbent Material. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2016, 16, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Choi, J.; Kim, S.S. Wide bandwidth pyramidal absorbers of granular ferrite and carbonyl iron powders. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2000, 36, 3272–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, K.; Inui, T. Electromagnetic wave absorber using ferrite absorbing material dispersed with short metal fibers. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1984, 20, 1261–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, D.; Lim, S. Frequency-tunable metamaterial absorber using a varactor-loaded fishnet-like resonator. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 4113–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.B.; Zhou, P.H.; Lu, H.P.; Xu, Y.Q.; Liang, D.F.; Deng, L.J. Resistance selection of high impedance surface absorbers for perfect and broadband absorption. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.A. Frequency selective radome with wideband absorbing properties. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.; Lim, S. Polarization-independent and ultrawideband metamaterial absorber using a hexagonal artificial impedance surface and a resistor-capacitor layer. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 2652–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Shrekenhamer, D.; Chen, W.C.; Padilla, W.J. Liquid crystal tunable metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Feng, N.; Wang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Huang, S.; Bi, K. Magnetically tunable metamaterial perfect absorber. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, M.K.; Javaheri, M.; Zillohu, A.U.; El-Khozondar, H.J.; Bawa’aneh, M.S.; Lavrinenko, A.; Faupel, F.; Elbahri, M. Photo-driven super absorber as an active metamaterial with a tunable molecular-plasmonic coupling. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Strikwerda, A.C.; Fan, K.; Padilla, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Averitt, R.D. MEMS based structurally tunable metamaterials at terahertz frequencies. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2011, 32, 580–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, J.; Qi, M.Q.; Jiang, W.X.; Cui, T.J. A tunable metamaterial absorber using varactor diodes. New J. Phys. 2013, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Sonkusale, S. Microwave diode switchable metamaterial reflector/absorber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.; Lim, S. Stretchable complementary split ring resonator (CSRR)-based radio frequency (RF) sensor for strain direction and level detection. Sensors 2016, 16, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, D.; Lim, S. A fluidically tunable metasurface absorber for flexible large-scale wireless ethanol sensor applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, D.; Lim, S. Wideband-switchable metamaterial absorber using injected liquid metal. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Feng, S.; Qiu, K.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, J. Mechanically stretchable and tunable metamaterial absorber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 091907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melik, R.; Unal, E.; Perkgoz, N.K.; Puttlitz, C.; Demir, H.V.; Melik, R.; Unal, E.; Perkgoz, N.K.; Puttlitz, C. Flexible metamaterials for wireless strain sensing flexible metamaterials for wireless strain sensing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 181105, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Melik, R.; Member, S.; Unal, E.; Perkgoz, N.K.; Santoni, B.; Kamstock, D.; Puttlitz, C.; Demir, H.V. Nested metamaterials for wireless strain sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2010, 16, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surapaneni, R.; Xie, Y.; Park, K.; Mastrangelo, C. Microfabrication of flexible self-repairing ground reaction sensor with liquid metal electrodes. Procedia Eng. 2011, 25, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Park, I. Carbon nanotubes-ecoflex nanocomposite for strain sensing with ultra-high stretchability. In Proceedings of the 28th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Estoril, Portugal, 18–22 January 2015; pp. 744–747. [Google Scholar]
- San-Miguel, A.; Lu, H. Microfluidics as a tool for C. elegans research. WormBook 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Abe, T.; Esashi, M. Deep reactive ion etching of Pyrex glass using SF6 plasma. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 87, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, B.; Verma, R.D.; Samadhiya, A. Design of rectangular microstrip patch antenna incorporated with innovative metamaterial structure for dual band operation and amelioration in patch antenna parameters with negative µ and ε. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2012, 1, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.L.; Drayton, R.F. A CPW T-resonator technique for electrical characterization of microwave substrates. In Proceedings of the 57th IEEE ARFTG Conference, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–25 May 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lätti, K.P.; Kettunen, M.; Strom, J.P.; Silventoinen, P. A review of microstrip T-resonator method in determining the dielectric properties of printed circuit board materials. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khondoker, M.A.H.; Sameoto, D. Fabrication methods and applications of microstructured gallium based liquid metal alloys. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 093001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahzadeh, S.; Forooraghi, K.; Atlasbaf, Z. A polarization-insensitive metamaterial absorber with a broad angular band. In Proceedings of the 20th IEEE Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Tehran, Iran, 15–17 May 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, J.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J. Design of a metamaterial absorber for ISM applications. J. Elecromagn. Eng. Sci. 2013, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, K.; Mashimo, Y.; Koyama, Y.; Fockenberg, C.; Nakashima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Li, J.; Chen, Y. 3D printing of soft lithography mold for rapid production of polydimethylsiloxane-based microfluidic devices for cell stimulation with concentration gradients. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Li, X.; Kim, C.; Hashimoto, M.; Wiley, B.J.; Ham, D.; Whitesides, G.M. Stretchable microfluidic radiofrequency antennas. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2749–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-Y.; Liao, Y.-C. Adhesive stretchable printed conductive thin film patterns on PDMS surface with an atmospheric plasma treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11868–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auyeung, R.C.Y.; Kim, H.; Mathews, S.A.; Piqué, A. Laser direct-write of metallic nanoparticle inks. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2007, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.; Lim, S. A Stretchable Electromagnetic Absorber Fabricated Using Screen Printing Technology. Sensors 2017, 17, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051175
Jeong H, Lim S. A Stretchable Electromagnetic Absorber Fabricated Using Screen Printing Technology. Sensors. 2017; 17(5):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051175
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Heijun, and Sungjoon Lim. 2017. "A Stretchable Electromagnetic Absorber Fabricated Using Screen Printing Technology" Sensors 17, no. 5: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051175
APA StyleJeong, H., & Lim, S. (2017). A Stretchable Electromagnetic Absorber Fabricated Using Screen Printing Technology. Sensors, 17(5), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051175






