Technical Aspects and Validation of a New Biofeedback System for Measuring Lower Limb Loading in the Dynamic Situation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
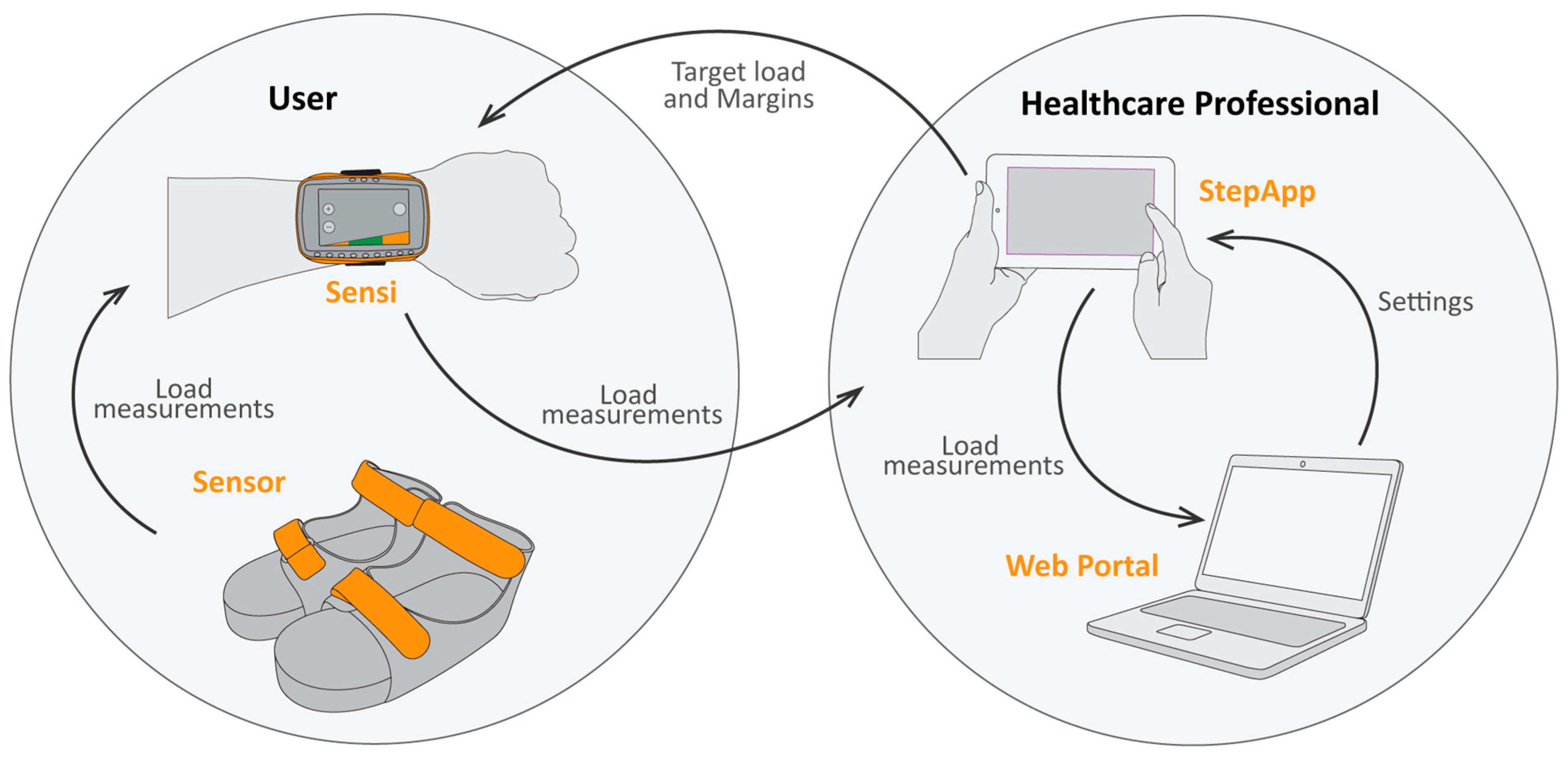
2.1. Technical Aspects of the System
2.1.1. Set-Up of the System
2.1.2. The Sensor
2.1.3. The Sandals
2.1.4. The Wrist Device
2.1.5. The Tablet
2.2. Validation of the Biofeedback System
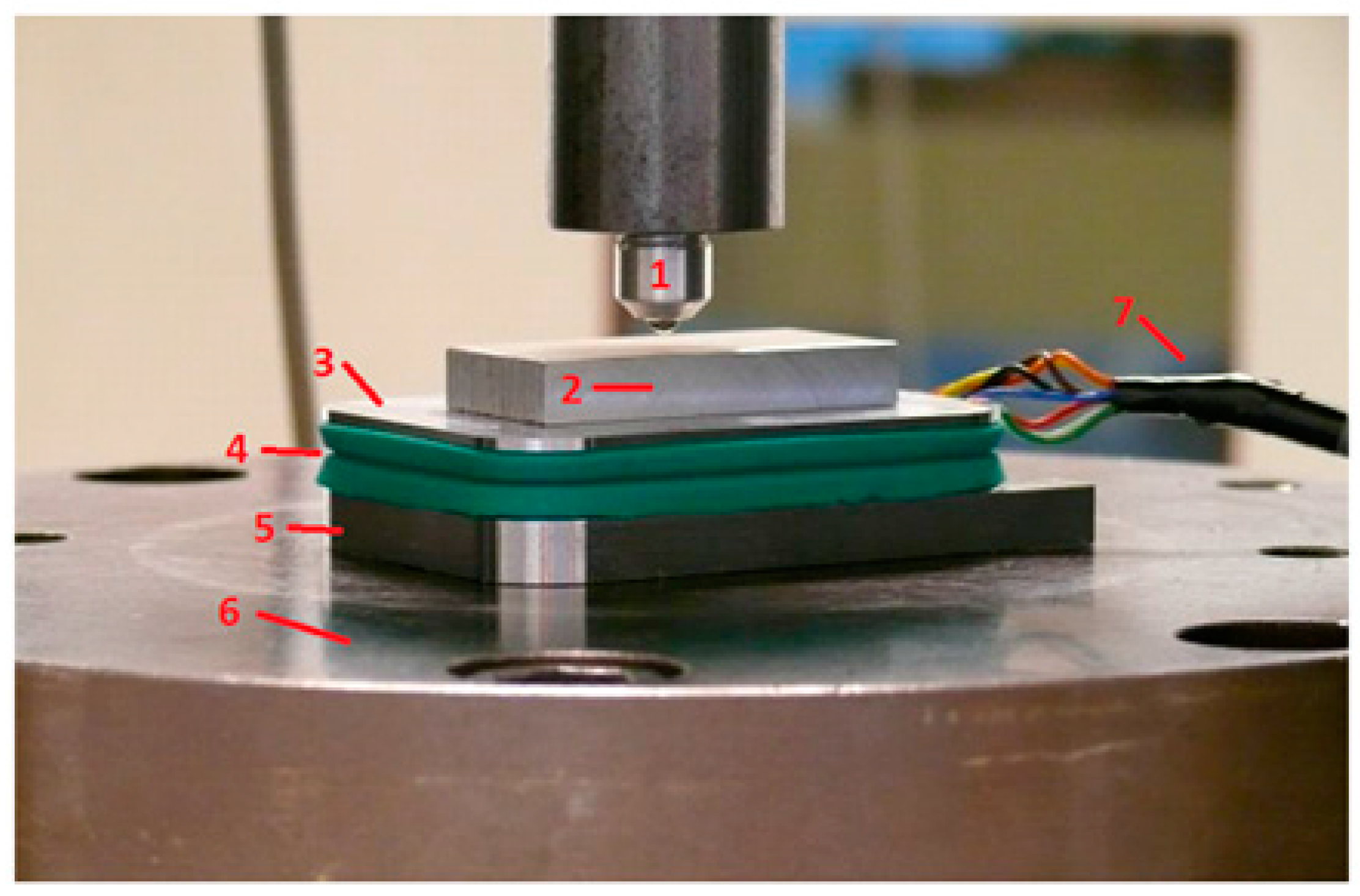
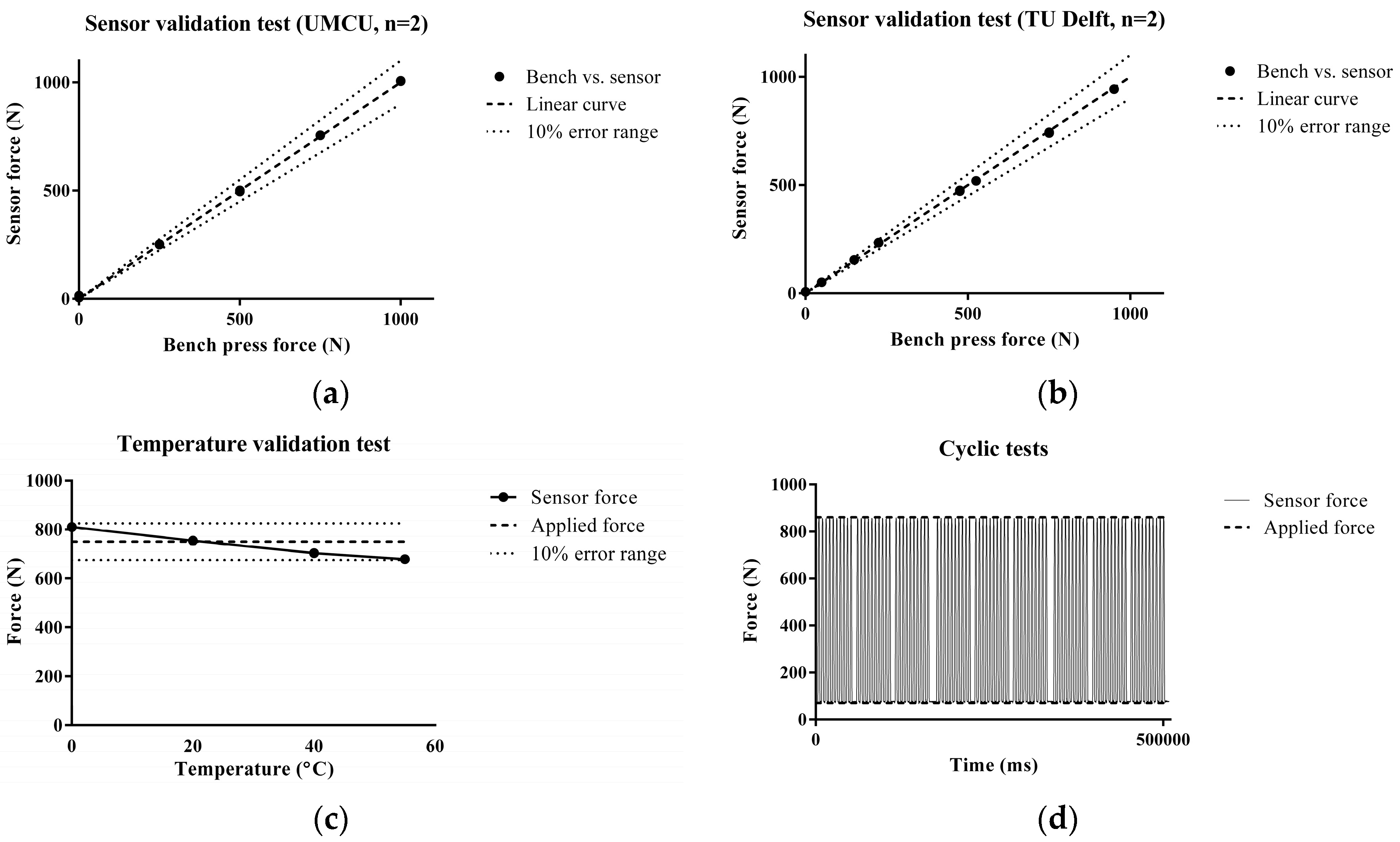
2.2.1. Static Loading
2.2.2. Dynamic Loading
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdul Razak, A.H.; Zayegh, A.; Begg, R.K.; Wahab, Y. Foot plantar pressure measurement system: A review. Sensors 2012, 12, 9884–9912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurkmans, H.L.P.; Bussmann, J.B.J.; Benda, E.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Stam, H.J. Techniques for measuring weight bearing during standing and walking. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogkamer, W.; Bruijn, S.M.; Potocanac, Z.; van Calenbergh, F.; Swinnen, S.P.; Duysens, J. Gait asymmetry during early split-belt walking is related to perception of belt speed difference. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 114, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Hidler, J. Biomechanics of overground vs. treadmill walking in healthy individuals. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, J.R.; Franz, J.R.; Jackson, K.; Dicharry, J.; Riley, P.O.; Kerrigan, D.C. A three-dimensional kinematic and kinetic comparison of overground and treadmill walking in healthy elderly subjects. Clin. Biomech. 2010, 25, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hustedt, J.W.; Blizzard, D.J.; Baumgaertner, M.R.; Leslie, M.P.; Grauer, J.N. Current advances in training orthopaedic patients to comply with partial weight-bearing instructions. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2012, 85, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Isakov, E. Gait rehabilitation: A new biofeedback device for monitoring and enhancing weight-bearing over the affected lower limb. Eur. Medicophys. 2007, 43, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, S.; Cunningham, J.L.; West, S. A comparison of vertical force and temporal parameters produced by an in-shoe pressure measuring system and a force platform. Clin. Biomech. 2001, 16, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamberg, S.J.M.; Benbasat, A.Y.; Scarborough, D.M.; Krebs, D.E.; Paradiso, J.A. Gait analysis using a shoe-integrated wireless sensor system. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2008, 12, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalfamo, P.; Moser, D.; Ghoussayni, S.; Ewins, D. Detection of gait events using an F-Scan in-shoe pressure measurement system. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernozek, T.W.; LaMott, E.E.; Dancisak, M.J. Reliability of an in-shoe pressure measurement system during treadmill walking. Foot Ankle Int. 1996, 17, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winstein, C.J.; Pohl, P.S.; Cardinale, C.; Green, A.; Scholtz, L.; Waters, C.S. Learning a partial-weight-bearing skill: Effectiveness of two forms of feedback. Phys. Ther. 1996, 76, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershko, E.; Tauber, C.; Carmeli, E. Biofeedback Versus Physiotherapy in Patients with Partial Weight-Bearing. Am. J. Orthop. 2008, 37, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, A.; Blokhuis, T.J.; Meeks, M.D.M.E.; Hermens, H.J.; Holtslag, H.R. Dynamic weight loading in older people with hip fracture. J. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 46, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.K.S.; Goonetilleke, R.S.; Cheung, Y.S.; So, G.M.Y. A flexible encapsulated MEMS pressure sensor system for biomechanical applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2001, 7, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.Z.; Gross, M.T.; Van Werkhoven, H.; Piazza, S.J.; Sawicki, G.S. Adding Stiffness to the Foot Modulates Soleus Force-Velocity Behaviour during Human Walking. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 Observed curve, ● R-Mill vs. biofeedback system.
Observed curve, ● R-Mill vs. biofeedback system.
 Observed curve, ● R-Mill vs. biofeedback system.
Observed curve, ● R-Mill vs. biofeedback system.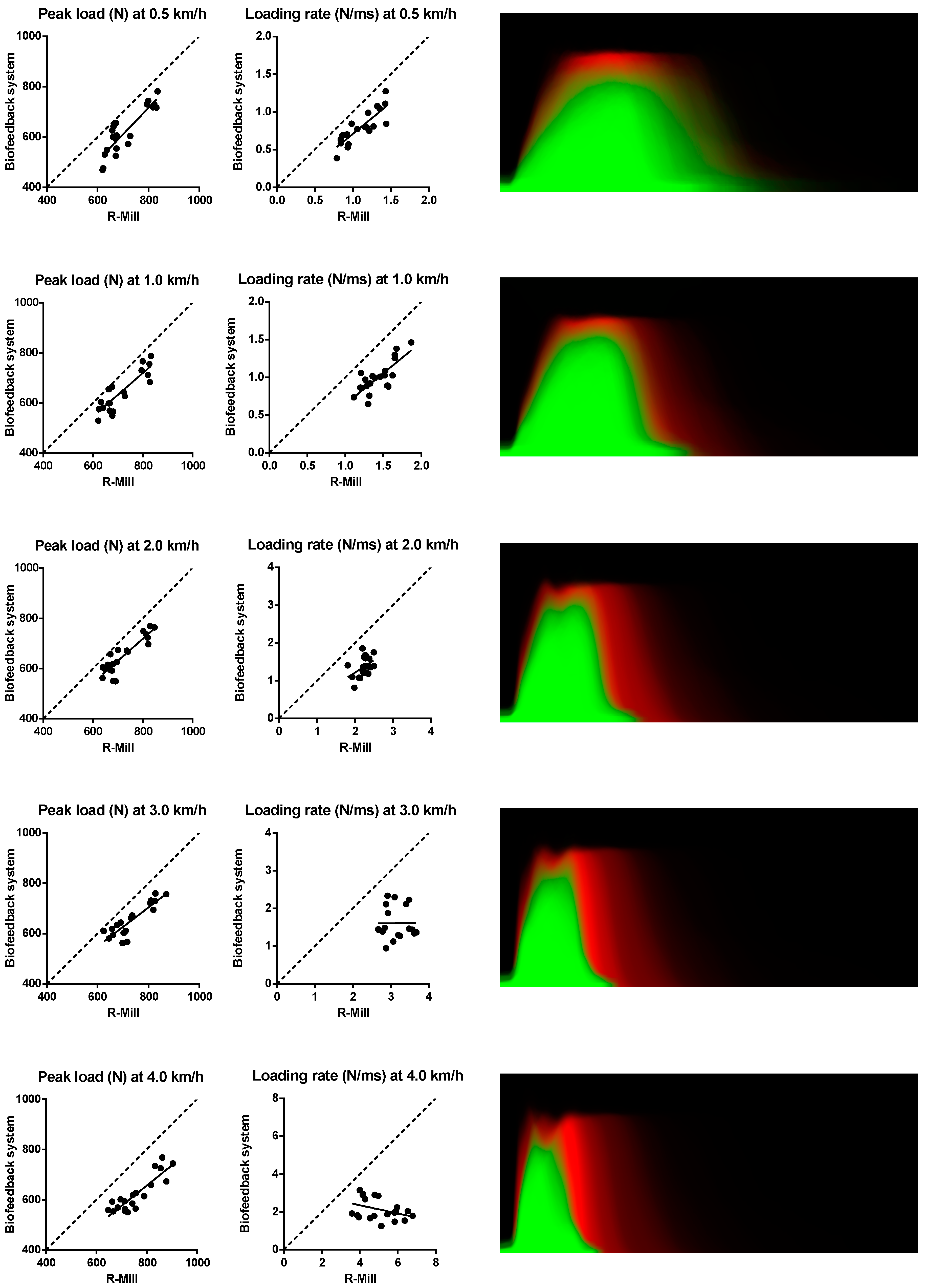
| Speed (km/h) | Relative Error (Min–Max) | Absolute Error in N (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | −0.15 (−0.05 to −0.26) | −105.9 (−34.56 to −166.5) |
| 1.0 | −0.12 (−0.04 to −0.21) | −86.15 (−25.14 to −162.7) |
| 2.0 | −0.12 (−0.04 to −0.22) | −88.73 (−29.77 to −159.5) |
| 3.0 | −0.13 (−0.05 to −0.23) | −97.77 (−30.23 to −166.5) |
| 4.0 | −0.20 (−0.13 to −0.27) | −152.2 (−86.89 to −221.3) |
| Speed (km/h) | Relative Error (Min–Max) | Absolute Error in N/ms (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | −0.29 (−0.11 to −0.51) | −0.03 (−0.01 to −0.06) |
| 1.0 | −0.31 (−0.12 to −0.50) | −0.04 (−0.02 to −0.07) |
| 2.0 | −0.38 (−0.15 to −0.59) | −0.09 (−0.03 to −0.12) |
| 3.0 | −0.48 (−0.20 to −0.67) | −0.16 (−0.06 to −0.24) |
| 4.0 | −0.57 (−0.21 to −1.27) | −0.30 (−0.09 to −0.51) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raaben, M.; Holtslag, H.R.; Augustine, R.; Van Merkerk, R.O.; Koopman, B.F.J.M.; Blokhuis, T.J. Technical Aspects and Validation of a New Biofeedback System for Measuring Lower Limb Loading in the Dynamic Situation. Sensors 2017, 17, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030658
Raaben M, Holtslag HR, Augustine R, Van Merkerk RO, Koopman BFJM, Blokhuis TJ. Technical Aspects and Validation of a New Biofeedback System for Measuring Lower Limb Loading in the Dynamic Situation. Sensors. 2017; 17(3):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030658
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaaben, Marco, Herman R. Holtslag, Robin Augustine, Rutger O. Van Merkerk, Bart F. J. M. Koopman, and Taco J. Blokhuis. 2017. "Technical Aspects and Validation of a New Biofeedback System for Measuring Lower Limb Loading in the Dynamic Situation" Sensors 17, no. 3: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030658
APA StyleRaaben, M., Holtslag, H. R., Augustine, R., Van Merkerk, R. O., Koopman, B. F. J. M., & Blokhuis, T. J. (2017). Technical Aspects and Validation of a New Biofeedback System for Measuring Lower Limb Loading in the Dynamic Situation. Sensors, 17(3), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030658








