Ultratrace Detection of Histamine Using a Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer-Based Voltammetric Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Polymer Synthesis
2.2. Binding Analysis
2.3. Preparation of the Sensors
2.4. General Method for Electrochemical Measurements
2.5. The Measurement of Histamine in Real Samples
3. Results
3.1. Molecularly- Imprinted Polymers for Histamine
3.1.1. Polymer Synthesis
3.1.2. Optical Batch Rebinding Experiment
3.2. MIP-CP Electrode
3.2.1. Fabrication of MIP-CP Electrode
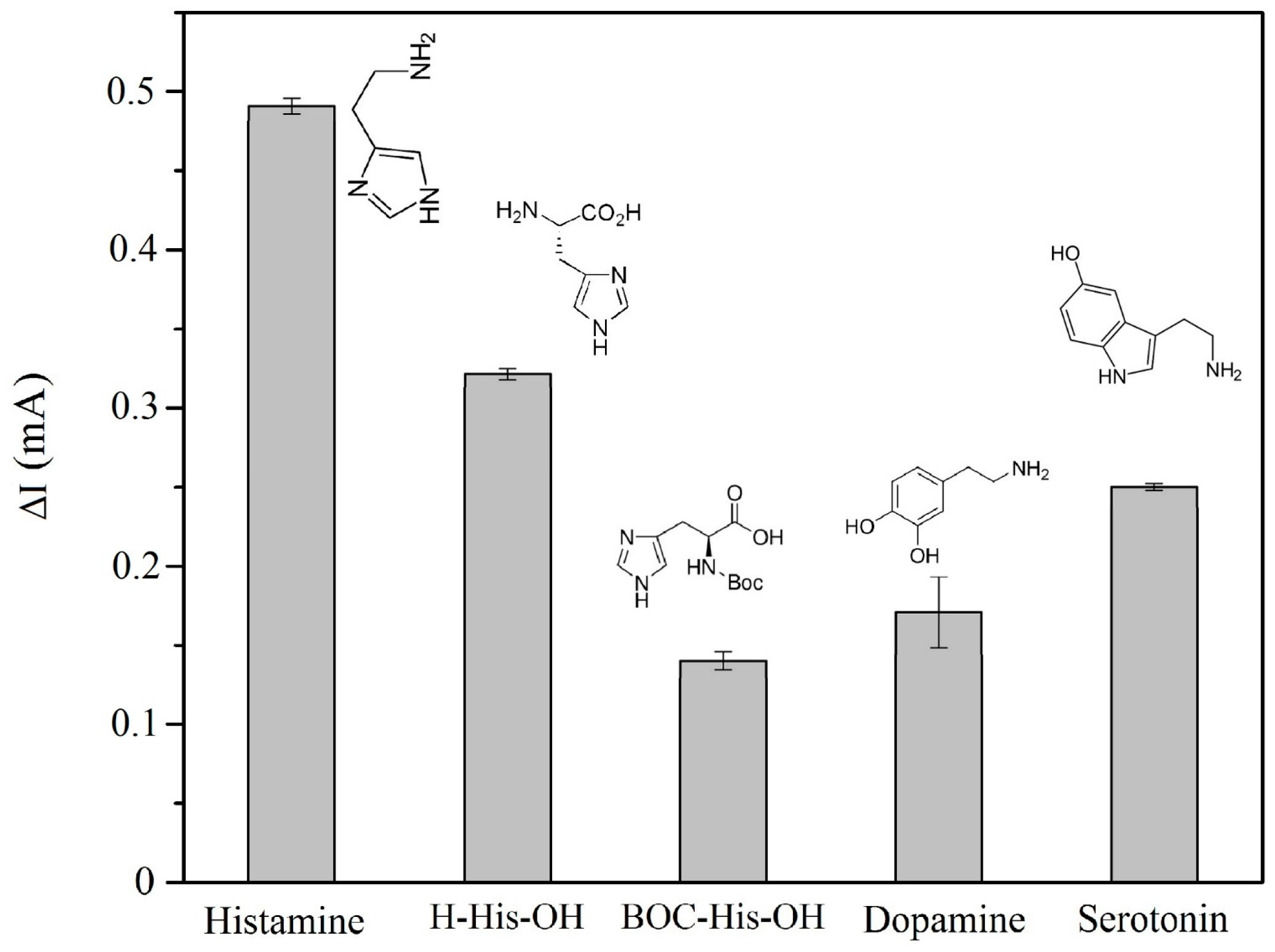
3.2.2. Selectivity of the Modified CP Electrode
3.3. Analytical Characterization
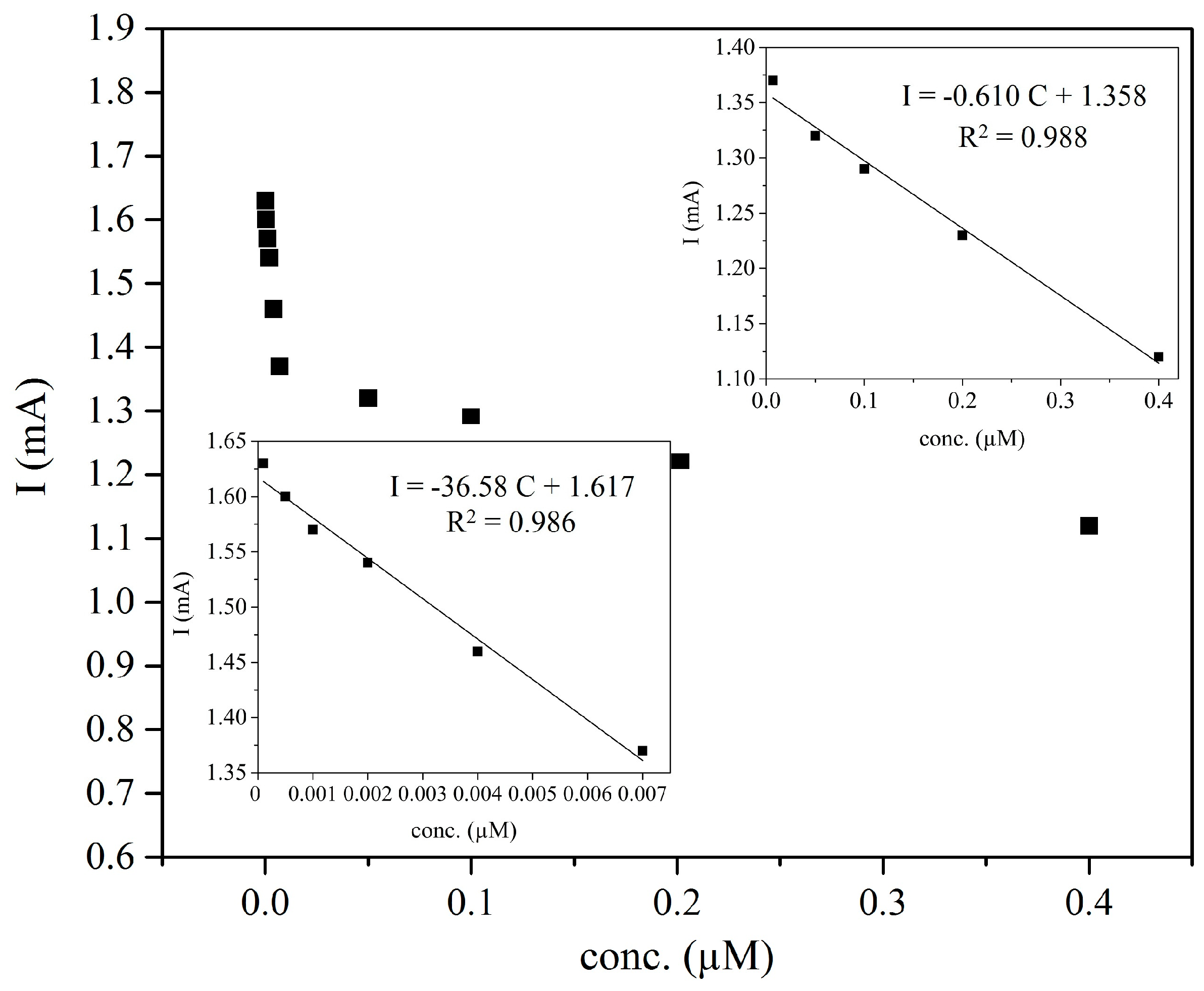
3.3.1. Calibration of the MIP-CP Electrode
3.3.2. Histamine Determination in Human Plasma
3.4. Comparison of the Developed Method and Other Previously Reported Electrochemical Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jutel, M.; Watanabe, T.; Akdis, M.; Blaser, K.; Akdis, C.A. Immune regulation by histamine. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maintz, L.; Novak, N. Histamine and histamine intolerance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.L.; Eitenmiller, R.R. Histamine food poisoning: Toxicology and clinical aspects. CRC Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1986, 17, 91–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehane, L.; Olley, J. Histamine fish poisoning revisited. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 58, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.O.; Judas, I.C.; Oliveira, M.B.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Ferreira, M.A. A GC-MS method for quantitation of histamine and other biogenic amines in beer. Chromatographia 2001, 53, S327–S331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Sato, M.; Han, Y.; Tan, Z.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakano, T. A simple and rapid method for histamine analysis in fish and fishery products by tlc determination. Food Control 2011, 22, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, E.R.; Taylor, S.L. Thin-layer chromatographic screening methods for histamine in tuna fish. J. Chromatogr. A 1978, 153, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, F.R.; Wei, C.I.; Otwell, W.S.; Sims, C.A.; Littell, R.C.; Hogle, A.D.; Marshall, M.R. Gas chromatographic analysis of histamine in mahi-mahi (coryphaena hippurus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4754–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, B.-S.; Wang, J.-T.; Choong, Y.-M. A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of histamine in fish and fish products. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-Y.; Sun, M.-X. Determination of histamine and histidine by capillary zone electrophoresis with pre-column naphthalene-2,3-dicarboxaldehyde derivatization and fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1040, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauza, T.; Blaise, A.; Daumas, F.; Cabanis, J.C. Determination of biogenic amines and their precursor amino acids in wines of the vallée du rhône by high-performance liquid chromatography with precolumn derivatization and fluorimetric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 707, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.B.; Marley, P.D. Development of an assay for histamine using automated high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. B: Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1995, 670, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, A. A review: Current analytical methods for the determination of biogenic amines in foods. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestos, C.; Loukatos, P.; Komaitis, M. Determination of biogenic amines in wines by HPLC with precolumn dansylation and fluorimetric detection. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornsdottir-Butler, K.; Bencsath, F.A.; Benner, J.R.A. Modification and single-laboratory validation of aoac official method 977.13 for histamine in seafood to improve sample throughput. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patange, S.B.; Mukundan, M.K.; Ashok Kumar, K. A simple and rapid method for colorimetric determination of histamine in fish flesh. Food Control 2005, 16, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessatti, T.L.; Fontana, J.D.; Pessatti, M.L. Spectrophotometric determination of histamine in fisheries using an enzyme immunoassay method. Meth. Mol. Biol. 2004, 268, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Cinquina, A.L.; Longo, F.; Calı̀, A.; De Santis, L.; Baccelliere, R.; Cozzani, R. Validation and comparison of analytical methods for the determination of histamine in tuna fish samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1032, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Gigirey, B.; Craven, C.; An, H. Histamine formation in albacore muscle analyzed by aoac and enzymatic methods. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, Z.S.; Mehmeti, E.; Kalcher, K.; Guzsvány, V.; Stanković, D.M. Swcnt-modified carbon paste electrode as an electrochemical sensor for histamine determination in alcoholic beverages. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2701–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, H.; Amare, M.; Tessema, M.; Admassie, S. Lignin modified glassy carbon electrode for the electrochemical determination of histamine in human urine and wine samples. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 121, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geto, A.; Tessema, M.; Admassie, S. Determination of histamine in fish muscle at multi-walled carbon nanotubes coated conducting polymer modified glassy carbon electrode. Synth. Met. 2014, 191, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Sun, D.; Tachikawa, H.; Davidson, V.L. Improved sensitivity of a histamine sensor using an engineered methylamine dehydrogenase. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keow, C.M.; Abu Bakar, F.; Salleh, A.B.; Heng, L.Y.; Wagiran, R.; Bean, L.S. An amperometric biosensor for the rapid assessment of histamine level in tiger prawn (penaeus monodon) spoilage. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1636–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, M.; Frébort, I.; Peč, P.; Galuszka, P.; Mattiasson, B.; Csöregi, E. Amine oxidase based amperometric biosensors forhistamine detection. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Takagi, K.; Kano, K.; Ikeda, T. Bioelectrocatalytic detection of histamine using quinohemoprotein amine dehydrogenase and the native electron acceptor cytochrome c-550. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Tachikawa, H.; Zhu, Z.; Davidson, V.L. Amperometric detection of histamine with a methylamine dehydrogenase polypyrrole-based sensor. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 2211–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarada, B.V.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A. Electrochemical oxidation of histamine and serotonin at highly boron-doped diamond electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbara, G.; Stanghellini, V.; De Giorgio, R.; Cremon, C.; Cottrell, G.S.; Santini, D.; Pasquinelli, G.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Grady, E.F.; Bunnett, N.W.; et al. Activated mast cells in proximity to colonic nerves correlate with abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.D. Histamine, mast cells, and the enteric nervous system in the irritable bowel syndrome, enteritis, and food allergies. Gut 2006, 55, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.Y.; Schwartz, L.B.; Curry, A.; Pesola, G.R.; Knight, R.J.; Lee, H.-S.; Bakalchuk, L.; Tenenbaum, C.; Westfal, R.E. Histamine and tryptase levels in patients with acute allergic reactions: An emergency department–based study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, J.; Li, Y.Z.; Alkhouri, H.; Blake, A.E.; Ge, Q.; Armour, C.L.; Hughes, J.M. Histamine and tryptase modulate asthmatic airway smooth muscle gm-csf and rantes release. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adlesic, M.; Verdrengh, M.; Bokarewa, M.; Dahlberg, L.; Foster, S.J.; Tarkowski, A. Histamine in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2007, 65, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Troost, F.J.; Mingels, R.H.G.; Welsch, T.; van Grinsven, B.; Vranken, T.; Ingebrandt, S.; Thoelen, R.; Cleij, T.J.; Wagner, P. Impedimetric detection of histamine in bowel fluids using synthetic receptors with ph-optimized binding characteristics. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trikka, F.A.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Ye, L.; Kyriakidis, D.A. Molecularly imprinted polymers for histamine recognition in aqueous environment. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 2113–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allender, C.J.; Richardson, C.; Woodhouse, B.; Heard, C.M.; Brain, K.R. Pharmaceutical applications for molecularly imprinted polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 195, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.; Dong, H.; Li, L. Molecular imprinting-based fluorescent chemosensor for histamine using zinc(ii)–protoporphyrin as a functional monomer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 466, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Grant, E.; Lu, X. Determination of histamine in canned tuna by molecularly imprinted polymers-surface enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 901, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Kobben, S.; Jiménez-Monroy, K.L.; Modesto, L.; Kraus, M.; Vandenryt, T.; Gaulke, A.; van Grinsven, B.; Ingebrandt, S.; Junkers, T.; et al. Thermal detection of histamine with a graphene oxide based molecularly imprinted polymer platform prepared by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horemans, F.; Alenus, J.; Bongaers, E.; Weustenraed, A.; Thoelen, R.; Duchateau, J.; Lutsen, L.; Vanderzande, D.; Wagner, P.; Cleij, T.J. MIP-based sensor platforms for the detection of histamine in the nano- and micromolar range in aqueous media. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzyk, A.; Suriyanarayanan, S.; Kutner, W.; Chitta, R.; D’Souza, F. Selective histamine piezoelectric chemosensor using a recognition film of the molecularly imprinted polymer of bis(bithiophene) derivatives. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongaers, E.; Alenus, J.; Horemans, F.; Weustenraed, A.; Lutsen, L.; Vanderzande, D.; Cleij, T.J.; Troost, F.J.; Brummer, R.J.; Wagner, P. A MIP-based biomimetic sensor for the impedimetric detection of histamine in different ph environments. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2010, 207, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellergren, B. Molecular imprinting by noncovalent interactions. Enantioselectivity and binding capacity of polymers prepared under conditions favoring the formation of template complexes. Die Makromol. Chem. 1989, 190, 2703–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M. Molecularly Imprinted Materials: Science and Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Henao-Escobar, W.; del Torno-de Román, L.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J. Dual enzymatic biosensor for simultaneous amperometric determination of histamine and putrescine. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veseli, A.; Vasjari, M.; Arbneshi, T.; Hajrizi, A.; Švorc, Ľ.; Samphao, A.; Kalcher, K. Electrochemical determination of histamine in fish sauce using heterogeneous carbon electrodes modified with rhenium(IV) oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, Z.S.; Švarc-Gajić, J.V. A simple and rapid method for histamine determination in fermented sausages by mediated chronopotentiometry. Food Control 2011, 22, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švarc-Gajić, J.; Stojanović, Z. Determination of histamine in cheese by chronopotentiometry on a thin film mercury electrode. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari-adergani, B.; Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Dinarvand, R. Ultrasensitive flow-injection electrochemical method for determination of histamine in tuna fish samples. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Polymer | Template (mmol) | MAA (mmol) | EGDMA (mmol) | Solvent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIP1 | 0.24 | 1.2 | 6 | CHCl3 |
| NIP1 | - | 1.2 | 6 | CHCl3 |
| MIP2 | 0.24 | 1.2 | 6 | MeCN |
| NIP2 | - | 1.2 | 6 | MeCN |
| Sample | Spiked (mol·L−1) | Found (mol·L−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human serum | 5.0 × 10−10 | 5.2 × 10−10 | 104 | 2.02 |
| 4.0 × 10−9 | 4.2 × 10−9 | 105 | 3.58 | |
| 2.0 × 10−7 | 1.9 × 10−7 | 95 | 3.42 |
| Method | Electrode | Linear Range (mol·L−1) | Detection Limit (mol·L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impedimetry | Polymer-coated Al | 1.2 × 10−8–2.0 × 10−9 | 2.0 × 10−9 | [42] |
| Voltammetry | Glassy carbon | 2.0 × 10−4–5.0 × 10−6 | 0.3 × 10−6 | [21] |
| Amperometry | Screen-printed | 6.0 × 10−5–8.0 × 10−6 | 8.1 × 10−6 | [45] |
| Amperometry | Heterogeneous carbon | 8.9 × 10−5–4.5 × 10−6 | 1.8 × 10−6 | [46] |
| Voltammetry | SWCNT-modified carbon paste | 7.2 × 10−4–4.5 × 10−6 | 1.3 × 10−6 | [20] |
| Chronopotentiometry | Gold | 8.9 × 10−4–1.8 × 10−5 | 2.4 × 10−6 | [28] |
| Chronopotentiometry | Glassy carbon | 8.1 × 10−4–1.8 × 10−5 | 1.2 × 10−5 | [47] |
| Amperometry | Boron-doped diamond | 8.1 × 10−3–4.5 × 10−5 | 4.0 × 10−5 | [48] |
| Voltammetry | Gold micro electrode | 4.9 × 10−8–9.9 × 10−12 | 3.1 × 10−12 | [49] |
| Voltammetry | NC/MIP/CPE | 4 × 10−7–7 × 10−9 and 7 × 10−9–10 × 10−10 | 7.4 × 10−11 | This work |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhoundian, M.; Rüter, A.; Shinde, S. Ultratrace Detection of Histamine Using a Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer-Based Voltammetric Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030645
Akhoundian M, Rüter A, Shinde S. Ultratrace Detection of Histamine Using a Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer-Based Voltammetric Sensor. Sensors. 2017; 17(3):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030645
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhoundian, Maedeh, Axel Rüter, and Sudhirkumar Shinde. 2017. "Ultratrace Detection of Histamine Using a Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer-Based Voltammetric Sensor" Sensors 17, no. 3: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030645
APA StyleAkhoundian, M., Rüter, A., & Shinde, S. (2017). Ultratrace Detection of Histamine Using a Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer-Based Voltammetric Sensor. Sensors, 17(3), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030645






