Spectral Analysis of Acceleration Data for Detection of Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Wireless Sensor
2.2. Subjects
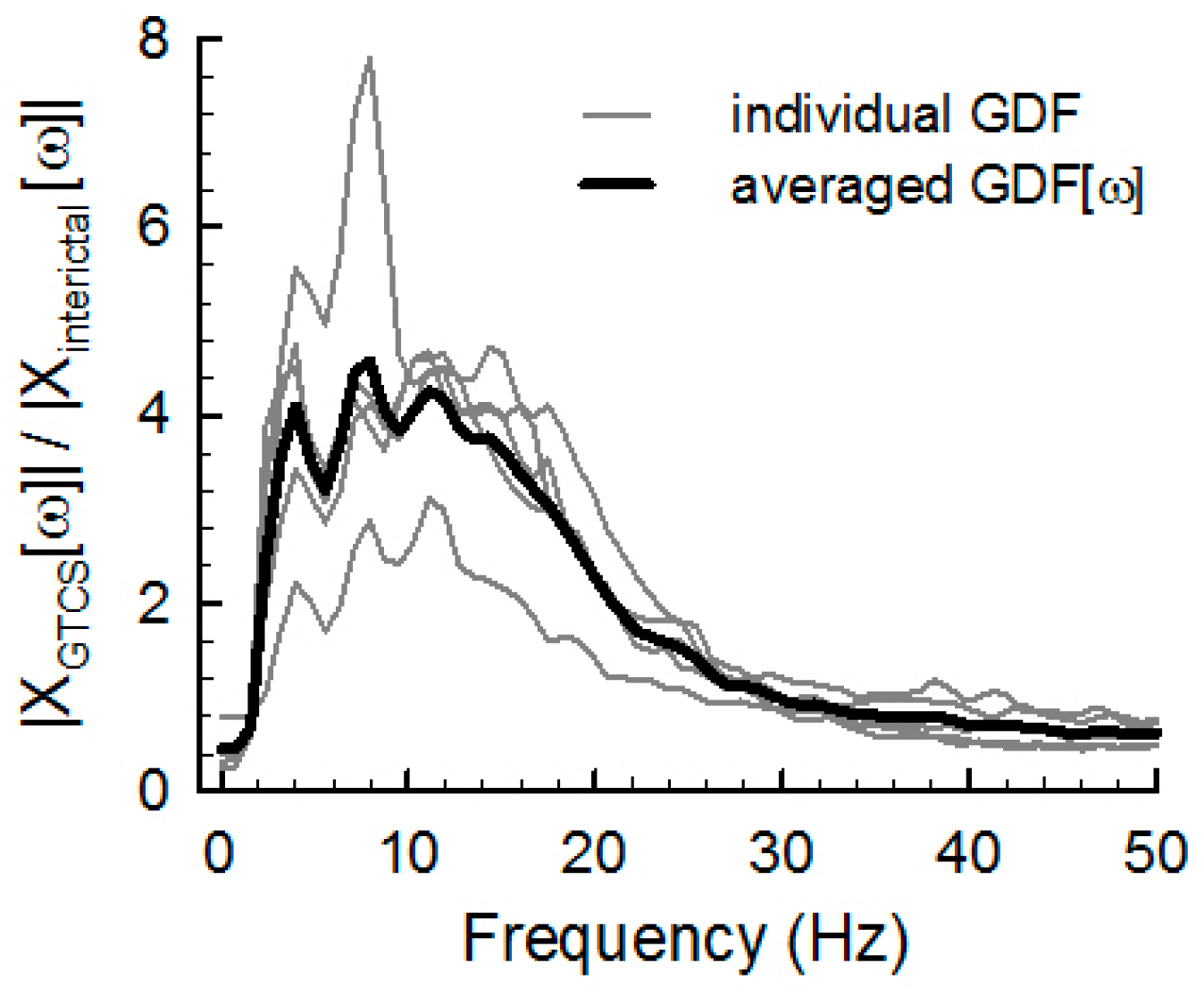
2.3. Spectral Analysis Method for ACM Data
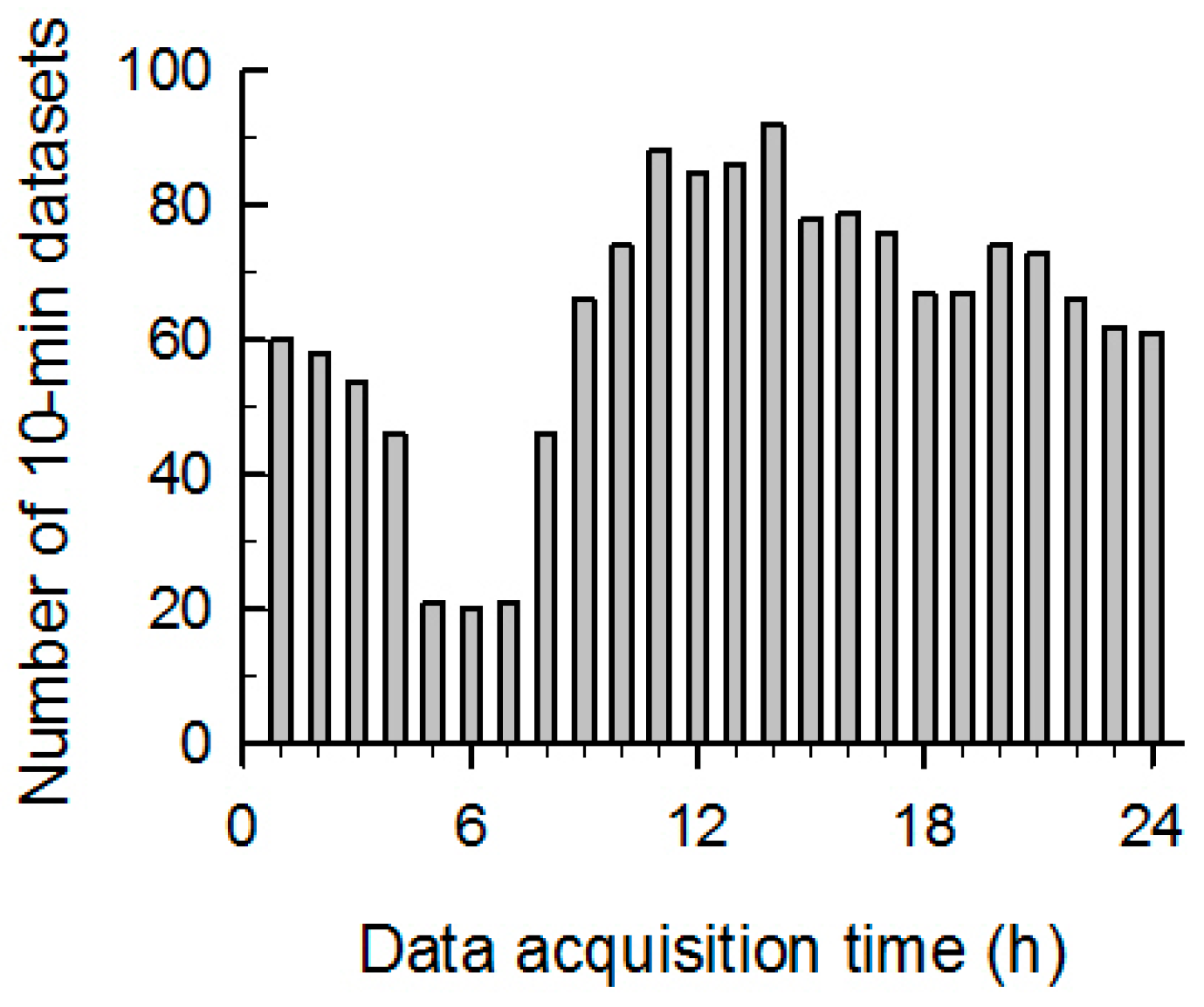
2.4. Evaluation of Spectral and Temporal Analyses
3. Results
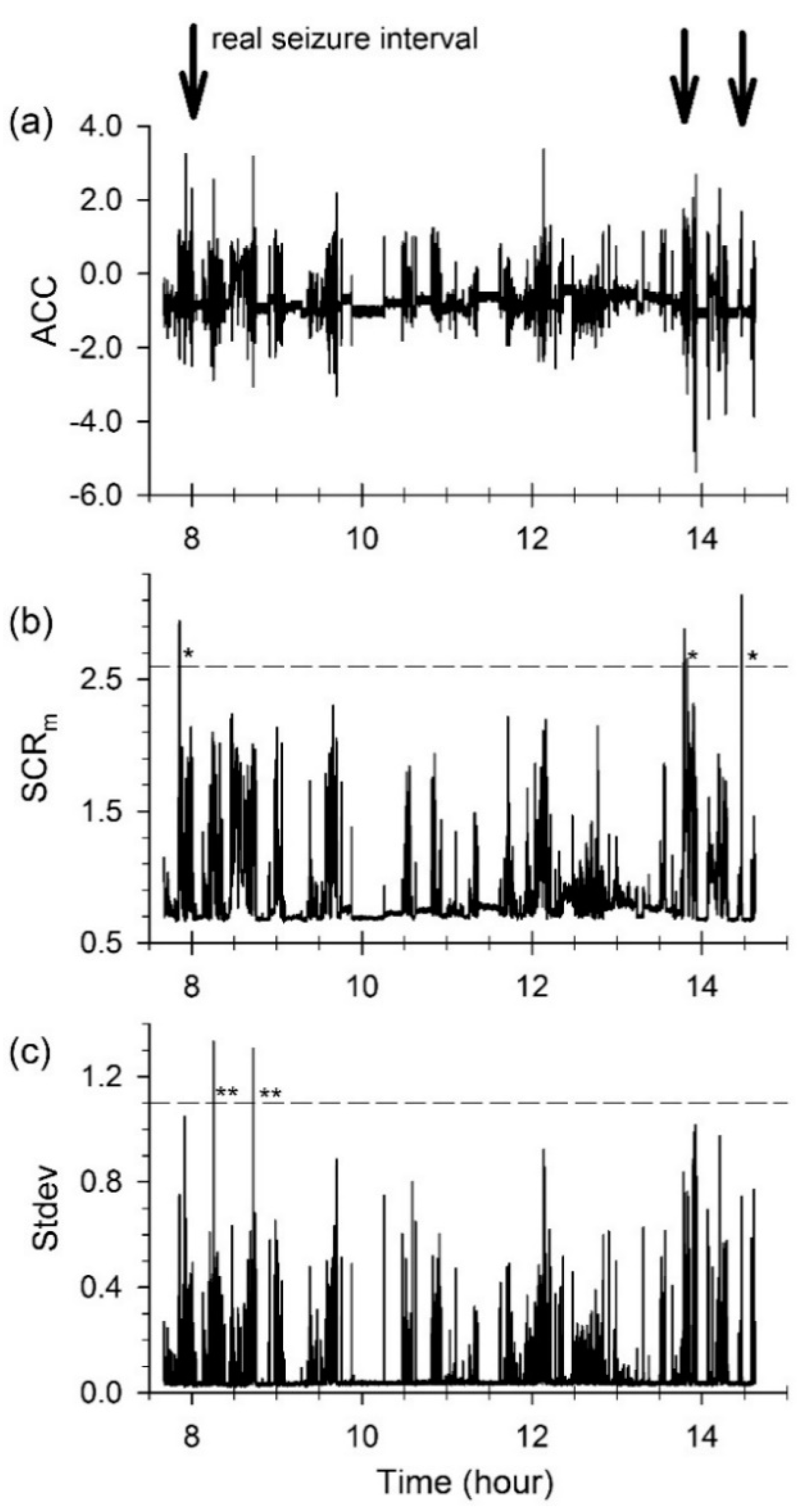
3.1. GTCS Detection
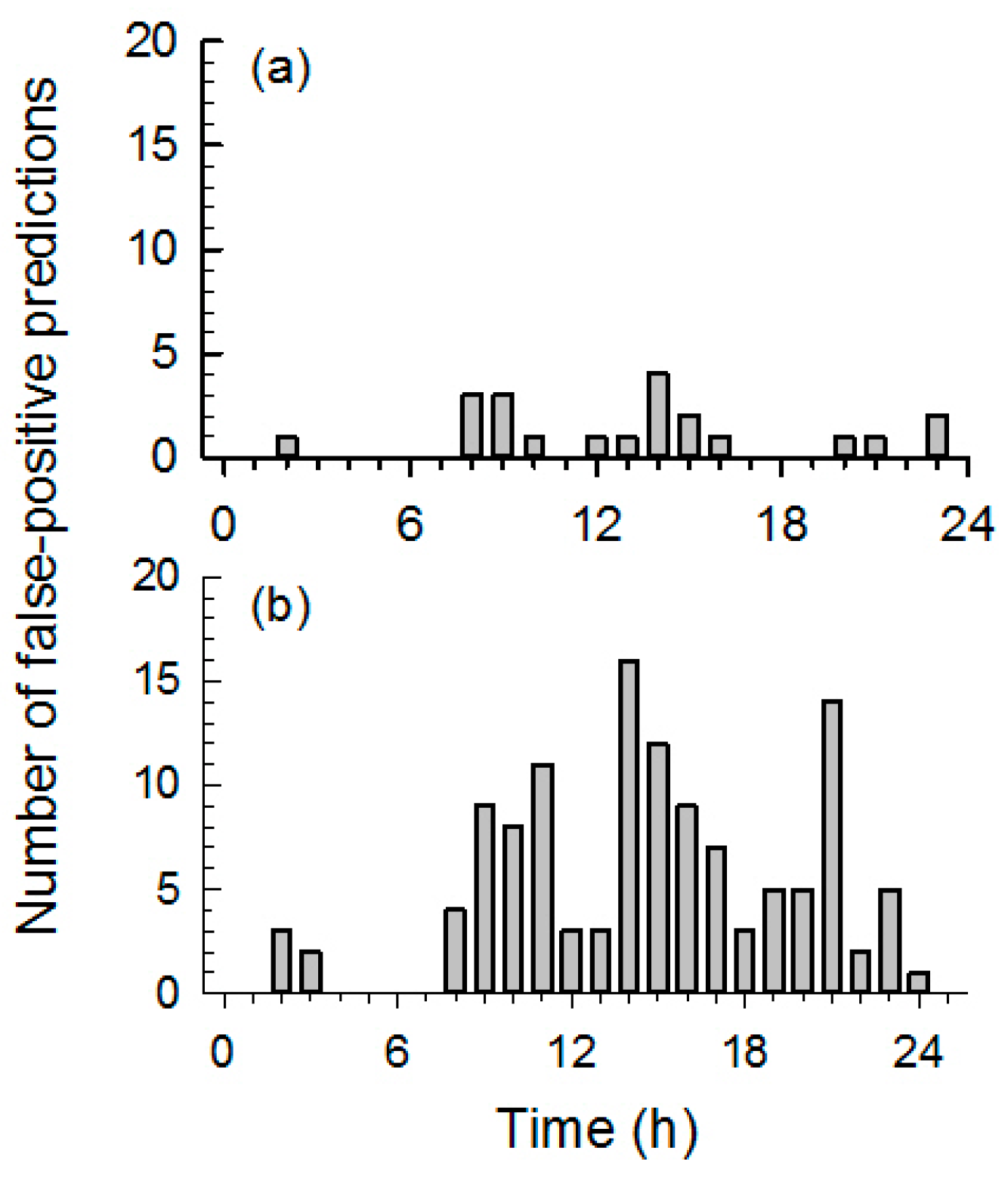
3.2. Comparison of the Spectral and Temporal Analysis Methods
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lockman, J.; Fisher, R.S.; Olson, D.M. Detection of seizure-like movements using a wrist accelerometer. Epilepsy Behav. 2011, 20, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nashef, L.; Garner, S.; Sander, J.W.; Fish, D.R.; Shorvon, S.D. Circumstances of death in sudden death in epilepsy: Interviews of bereaved relatives. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 64, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nashef, L.; Hindocha, N.; Makoff, A. Risk factors in sudden death in epilepsy (SUDEP): The quest for mechanisms. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, Y.; Nashef, L.; Sander, J.W. Case-control study of SUDEP. Neurology 2005, 64, 1131–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulc, E.; Unterberger, I.; Saboor, S.; Hilbe, J.; Ertl, M.; Ammenwerth, E.; Trinka, E.; Them, C. Measurement and quantification of generalized tonic-clonic seizures in epilepsy patients by means of accelerometry—An explorative study. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 95, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, C.; Anedo, V.; Cahill, M.; Devinsky, O. Detection norturnal convulsions: Efficacy of the MP5 monitor. Seizure 2009, 18, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, A.; Patel, S.; Chowdhury, A.R.; Welsh, M.; Pang, T.; Schachter, S.; Olaighin, G.; Bonato, P. Development of a body sensor network to detect motor patterns of epileptic seizures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 3204–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jallon, P.; Bonnet, S.; Antonakios, M.; Guillemaud, R. Detection system of motor epileptic seizures through motion analysis with 3D accelerometers. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2009, 2009, 2466–2469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.M.; Shiau, D.S.; Kern, R.T.; Chien, J.H.; Yang, M.C.; Yandora, K.A.; Valeriano, J.P.; Halford, J.J.; Sackellares, J.C. Assessment of a scalp EEG-based automated seizure detection system. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijsen, T.M.; Aarts, R.M.; Cluitmans, P.J.; Griep, P.A. Time-frequency analysis of accelerometry data for detection of myoclonic seizures. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, M.Z.; Loddenkemper, T.; Reinsberger, C.; Swenson, N.C.; Goyal, S.; Sabtala, M.C.; Madsen, J.R.; Picard, R.W. Convulsive seizure detection using a wrist-worn electrodermal activity and accelerometry biosensor. Epilepsia 2012, 53, e93–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesaei, S.; Sharafat, A.R. Real-time Detection of Precursors to Epileptic Seizures: Non-Linear Analysis of System Dynamics. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2014, 4, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ayoubian, L.; Lacoma, H.; Gotman, J. Automatic seizure detection in SEEG using high frequency activities in wavelet domain. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nijsen, T.M.; Arends, J.B.; Griep, P.A.; Cluitmans, P.J. The potential value of three-dimensional accelerometry for detection of motor seizures in severe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2005, 7, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milosevic, M.; Van de Vel, A.; Cuppens, K.; Bonroy, B.; Ceulemans, B.; Lagae, L.; Vanrumste, B.; Van Huffel, S. Feature selection methods for accelerometry-based seizure detection in children. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becq, G.; Bonnet, S.; Minotti, L.; Antonakios, M.; Guillemaud, R.; Kahane, P. Classification of epileptic motor manifestations using inertial and magnetic sensors. Comput. Biol. Med. 2011, 41, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayly, J.; Carino, J.; Petrovski, S.; Smit, M.; Fernando, D.A.; Vinton, A.; Yan, B.; Gubbi, J.R.; Palaniswami, M.S.; O’Brien, T.J. Time-frequency mapping of the rhythmic limb movements distinguishes convulsive epileptic from psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milosevic, M.; Van de Vel, A.; Bonroy, B.; Ceulemans, B.; Lagae, L.; Vanrumste, B.; Huffel, S.V. Automated Detection of Tonic-Clonic Seizures Using 3-D Accelerometry and Surface Electromyography in Pediatric Patients. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijsen, T.M.; Cluitmans, P.J.; Arends, J.B.; Griep, P.A. Detection of subtle nocturnal motor activity from 3-D accelerometry recordings in epilepsy patients. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luinge, H.J.; Veltink, P.H. Measuring orientation of human body segments using miniature gyroscopes and accelerometers. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2005, 43, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Subject | Age | Sex | Recording Time (h) | GTCS ID (Duration, s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 28 | F | 25.87 | - |
| S2 | 34 | M | 23.68 | GTCS1 (90), GTCS2 (90) |
| S3 | 18 | M | 7.33 | - |
| S4 | 39 | M | 8.41 | - |
| S5 | 13 | M | 7.02 | - |
| S6 | 50 | F | 6.95 | GTCS3 (130), GTCS4 (256), GTCS5 (89) |
| S7 | 30 | F | 37.15 | GTCS6(153) |
| S8 | 40 | F | 7.00 | - |
| S9 | 33 | M | 55.83 | - |
| S10 | 26 | F | 3.47 | - |
| S11 | 52 | M | 38.12 | GTCS7(165), GTCS8 (136), GTCS9 (108) |
| S12 | 33 | M | 25.75 | GTCS10 (119) |
| 10-Fold Case | Spectral Analysis | Temporal Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEN | FPR | SPEC | PPV | SEN | FPR | SPEC | PPV | |
| (%) | (cases/24 h) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (cases/24 h) | (%) | (%) | |
| 1 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 |
| 2 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0.9 | 99 | 50 |
| 3 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 1.9 | 99 | 33 |
| 4 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0.9 | 99 | 50 |
| 5 | 100 | 1.9 | 99 | 33 | 100 | 9.7 | 99 | 9 |
| 6 | 100 | 2.9 | 99 | 25 | 100 | 21.3 | 99 | 4 |
| 7 | 100 | 6.8 | 99 | 12 | 100 | 30.1 | 99 | 3 |
| 8 | 100 | 5.8 | 99 | 14 | 0 | 16.6 | 99 | 0 |
| 9 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 16.6 | 99 | 5 |
| 10 | 100 | 2.9 | 99 | 25 | 100 | 20.4 | 99 | 4 |
| Mean | 100 | 2.0 | 99 | 61 | 90 | 11.8 | 99 | 26 |
| Spectral Analysis | Temporal Analysis | Milosevic et al. [18] | Dalton et al. [7] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACM No. | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Feature | SCR | Stdev. | Spectral, temporal | Temporal |
| Decision 1 | Threshold | Threshold | SVM | DTW |
| No. of patients 2 | 5/12 | 5/12 | 7/56 | 5/5 |
| No. of seizures | 10 | 10 | 22 | 21 |
| Seizure type 3 | GTC | GTC | TC | C |
| Record duration | 246 h | 246 h | 1998 h | 130 h |
| Sensitivity (%) | 100 | 90 | 86 | 91 |
| FPR (case/24 h) | 2.0 | 11.8 | 3.9 | 9.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joo, H.S.; Han, S.-H.; Lee, J.; Jang, D.P.; Kang, J.K.; Woo, J. Spectral Analysis of Acceleration Data for Detection of Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures. Sensors 2017, 17, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030481
Joo HS, Han S-H, Lee J, Jang DP, Kang JK, Woo J. Spectral Analysis of Acceleration Data for Detection of Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures. Sensors. 2017; 17(3):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030481
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoo, Hyo Sung, Su-Hyun Han, Jongshill Lee, Dong Pyo Jang, Joong Koo Kang, and Jihwan Woo. 2017. "Spectral Analysis of Acceleration Data for Detection of Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures" Sensors 17, no. 3: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030481
APA StyleJoo, H. S., Han, S.-H., Lee, J., Jang, D. P., Kang, J. K., & Woo, J. (2017). Spectral Analysis of Acceleration Data for Detection of Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures. Sensors, 17(3), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030481







