Water Quality Sensing and Spatio-Temporal Monitoring Structure with Autocorrelation Kernel Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Data
2.2. Sensors Description and Measurement Process
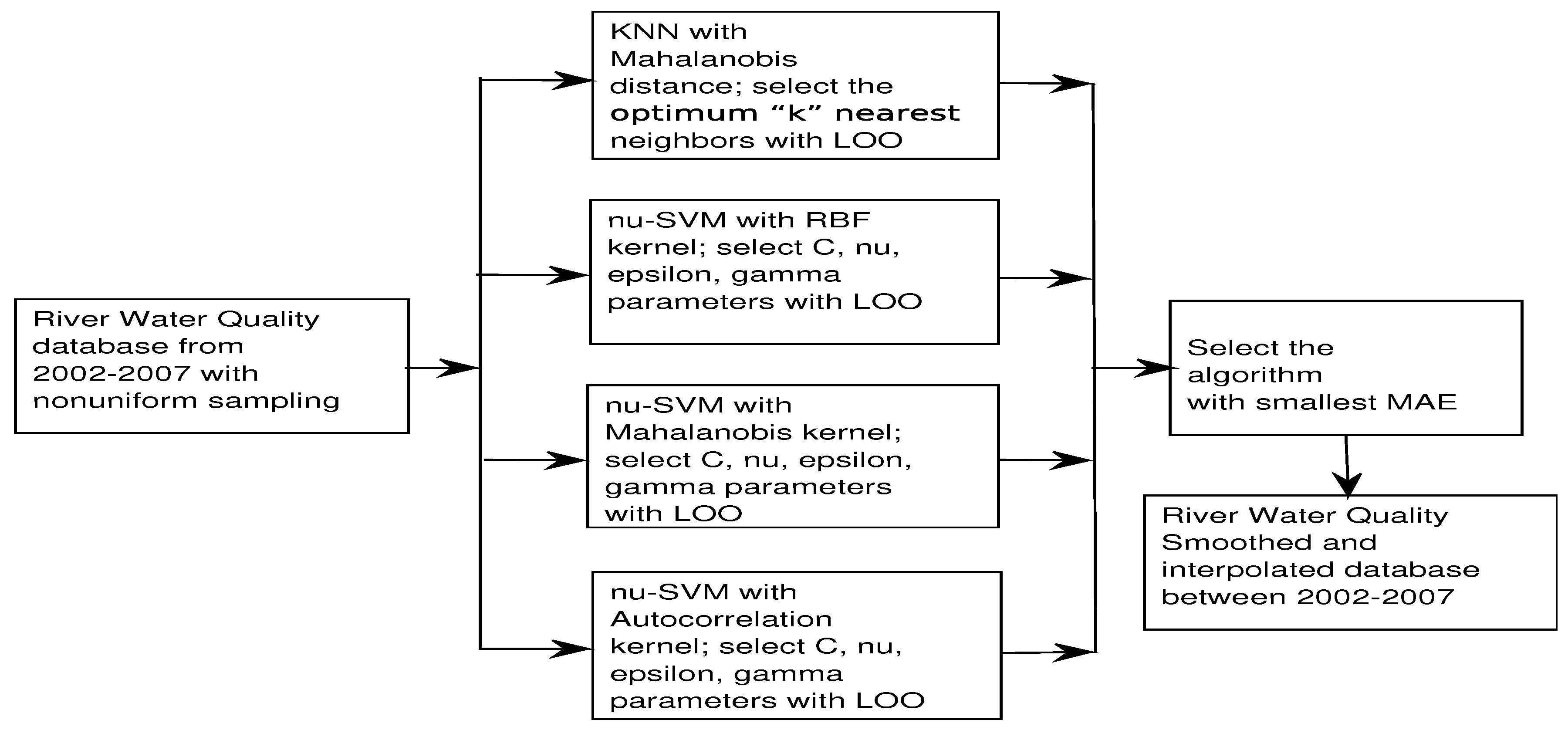
2.3. Conventional Algorithms and Spatio-Temporal Interpolation
2.4. Support Vector Regression and Autocorrelation Kernel
3. Results
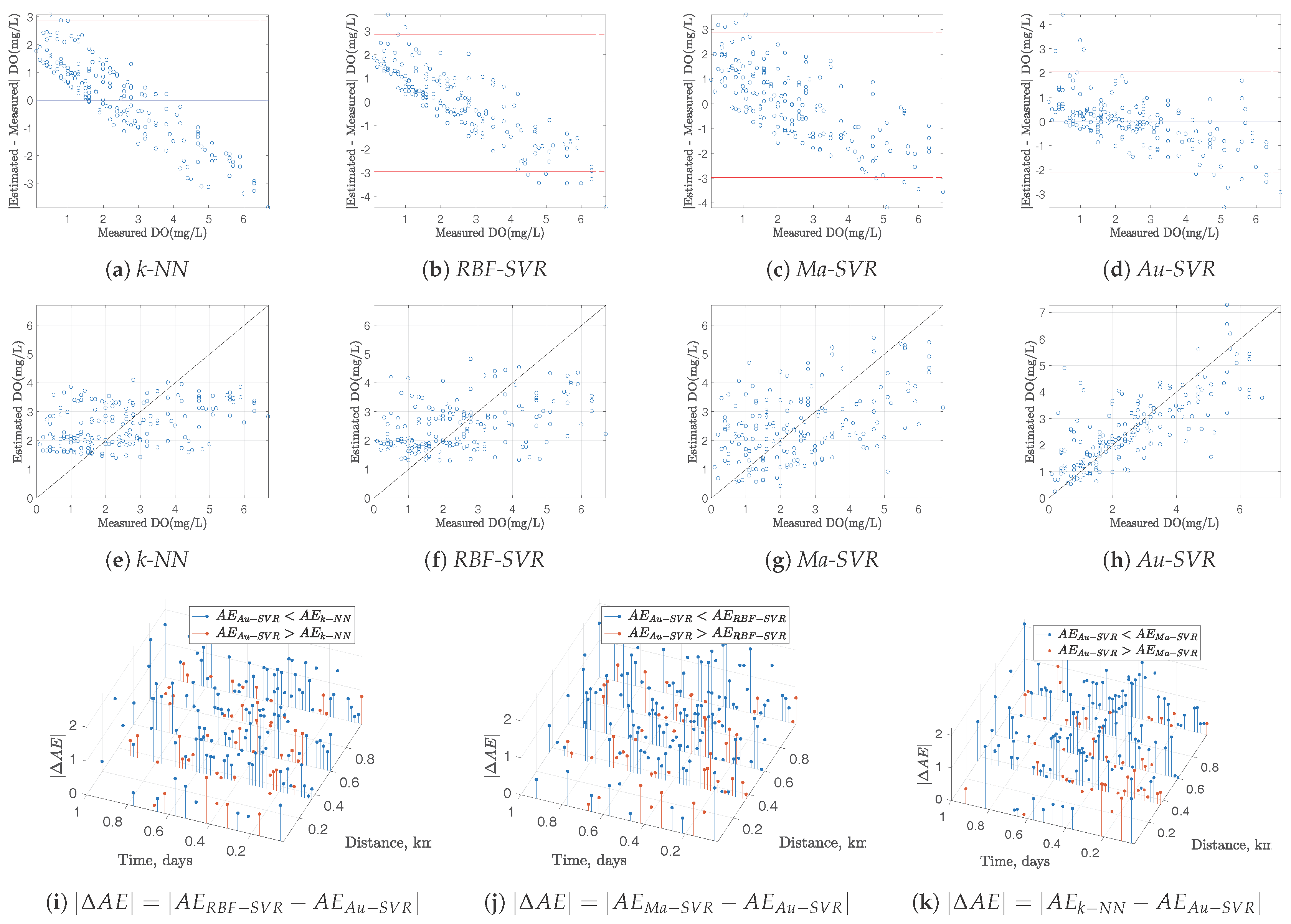
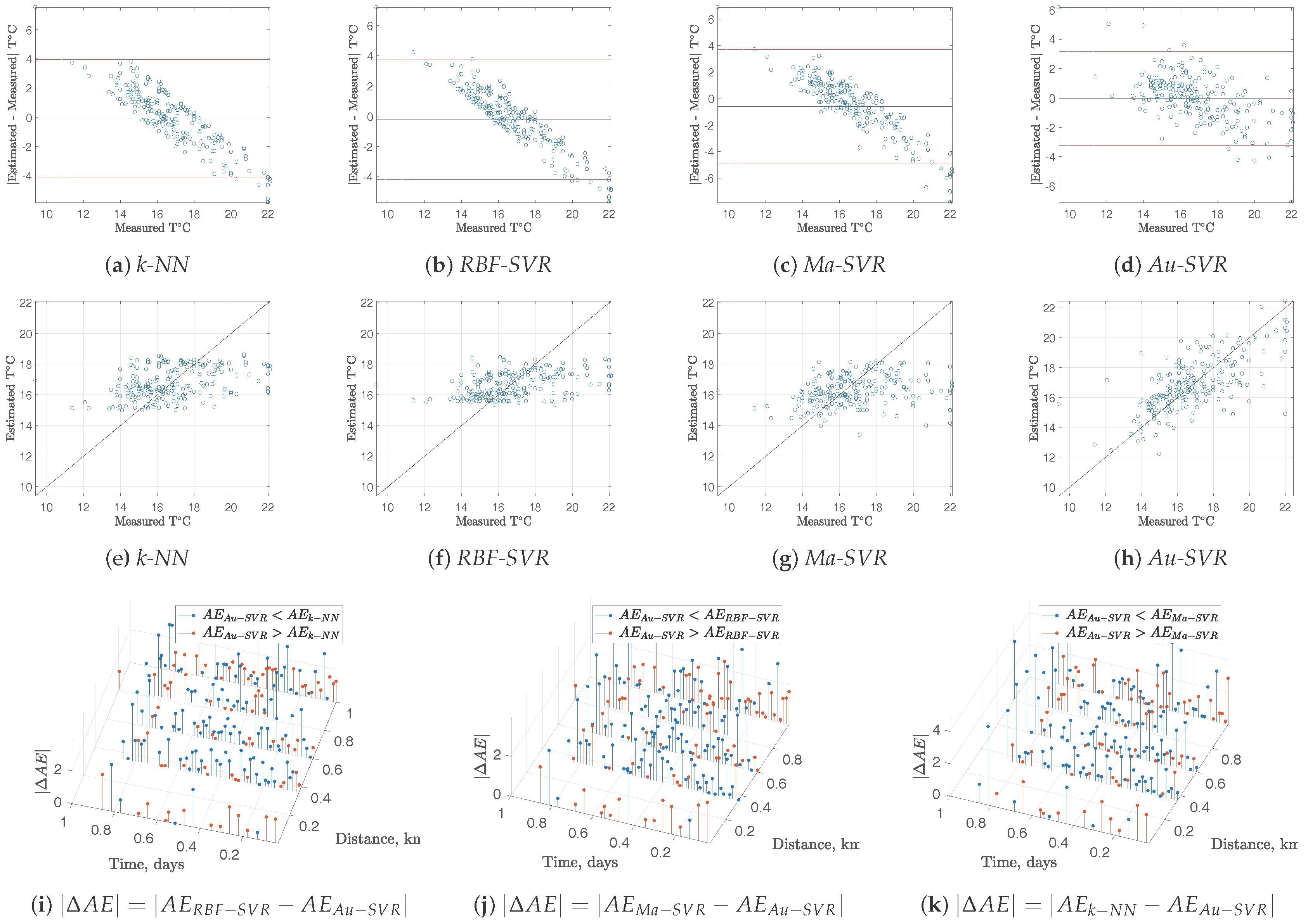
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Interpolation Performance
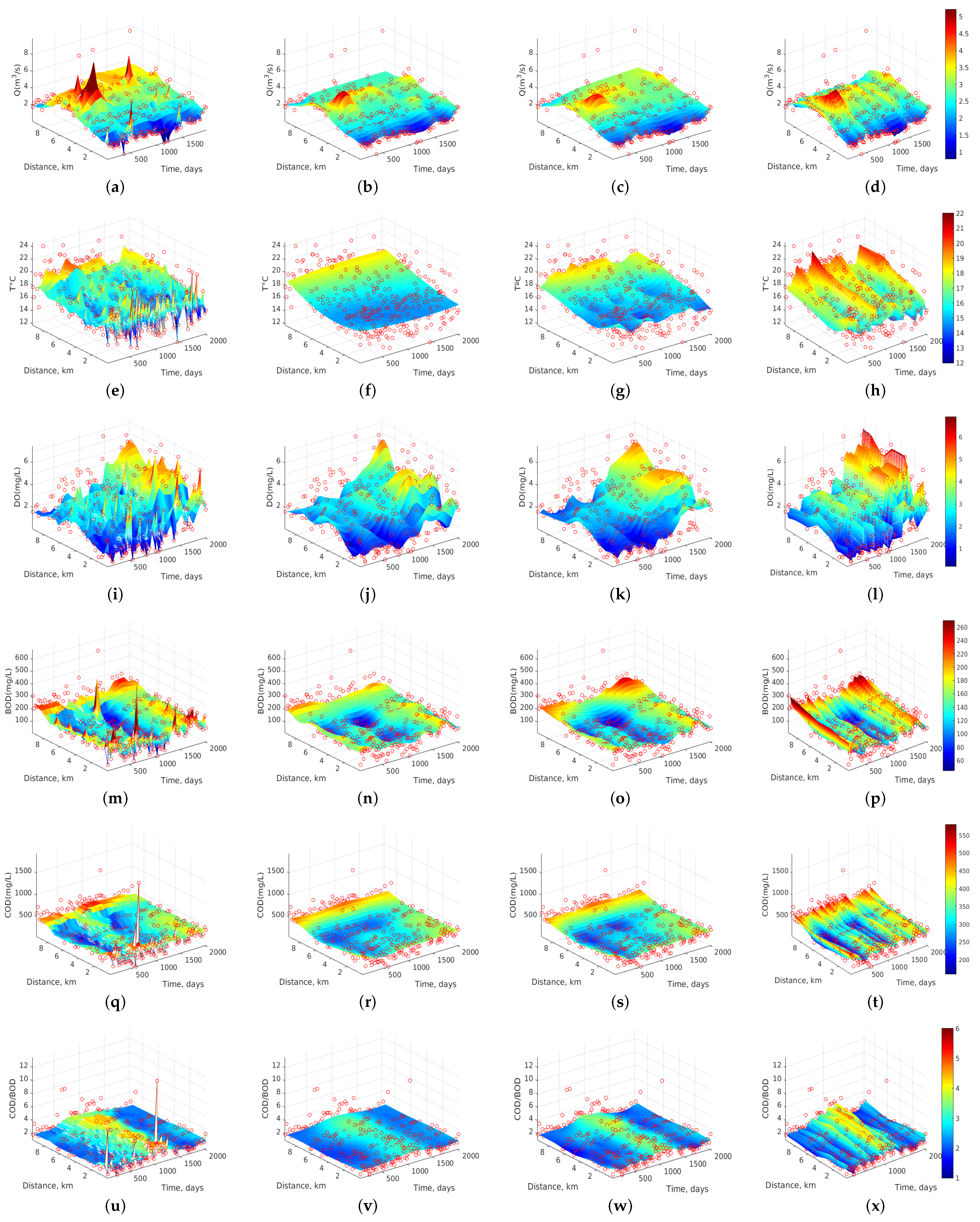
3.2. Dynamics Analysis of Water Quality Measurements
- If COD/BOD ≤ 2.5, then the organic matter is very degradable.
- If COD/BOD ∈ (2.5, 5), then the organic matter is moderately degradable.
- If COD/BOD ≥ 5, then the organic matter is little degradable.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Luo, P.; Nover, D.; Sahu, N.; Yamashiki, Y. Spatiotemporal evaluation of water quality incidents in Japan between 1996 and 2007. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Nover, D.; Yang, G.; Chen, W.; Meng, H.; Zou, S.; Liu, C. Water Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Identification of the Eastern Poyang Lake Basin Using Multivariate Statistical Methods. Sustainability 2016, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbutt, T. Principles of Water Quality Control, 5th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1998; pp. 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Taalohi, M.; Tabatabaee, H. Predicting Bar Dam Water Quality using Neural-Fuzzy Inference System. Indian J. Fundam. Appl. Life Sci. 2014, 4, 630–636. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuiykov, S. Solid-state sensors monitoring parameters of water quality for the next generation of wireless sensor networks. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 161, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaíno, I.P.; Carrera, E.V.; Sanromán-Junquera, M.; Muñoz-Romero, S.; Rojo-Alvarez, J.L.; Cumbal, L.H. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Water Quality Parameters in Machángara River with Nonuniform Interpolation Methods. Water 2016, 8, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figuera, C.; Barquero-Pérez, O.; Rojo-Álvarez, J.L.; Martínez-Ramón, M.; Guerrero-Curieses, A.; Caamaño, A.J. Spectrally adapted Mercer kernels for support vector nonuniform interpolation. Signal Process. 2014, 94, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, B.; Fokoué, E.; Zhang, H.H. Principles and Theory for Data Mining and Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 304–310. [Google Scholar]
- Empresa Pública Metropolitana de Agua Potable Quito. Estudios de Factibilidad y Diseños Definitivos del Plan de Descontaminación de los Ríos de Quito Informe No.1 “Revisión de la Información Existente y Diagnóstico”; Technical Report; Empresa Pública Metropolitana de Agua Potable Quito: Quito, Ecuador, 2009.
- Municipio del Distrito Metropolitano de Quito. Plan de Desarrollo 2012–2022. Consejo Metropolitano de Planificación. Quito, Ecuador; Technical Report; Municipio del Distrito Metropolitano de Quito: Quito, Ecuador, 2011; pp. 14–26.
- Eaton, A.; Clesceri, L. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Empresa Pública Metropolitana de Agua Potable Quito. Estudios de Factibilidad y Diseños Definitivos del Plan de Descontaminación de los Ríos de Quito Informe No.2 “Informe de Caracterización de las Descargas Industriales y Bases de Diseño”; Technical Report; Empresa Pública Metropolitana de Agua Potable Quito: Quito, Ecuador, 2009.
- Karl, S.; Truong, Q. An Adaptable k-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm for MMSE Image Interpolation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Shepard, D. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM National Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–29 August 1968; pp. 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Soguero-Ruiz, C.; Guerrero-Curieses, A.; Palancar, F.J.; Bermejo, J.; Antoranz, J.C.; Rojo-Álvarez, J.L. Autocorrelation Kernel Support Vector Machines for Doppler Ultrasound M-Mode Images Denoising. In Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-García, B.; Sanromán-Junquera, M.; Guerrero-Curieses, A.; Trenor, B.; García-Alberola, A.; Rojo-Álvarez, J.L. Non-uniform Interpolation of Cardiac Navigation Maps Using Support Vector Machines with Autocorrelation Kernel. In Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, W.W. Machine Learning Methods in the Environmental Sciences; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 196–198. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. Training ν-Support Vector Regression: Theory and Algorithms. Neural Comput. 2002, 14, 1959–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, R.; Zhang, B. Autocorrelation Kernel Functions for Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Natural Computation, Haikou, China, 24–27 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V. Statistical Learning Theory; Adaptive and Learning Systems for Signal Processing, Communications, and Control; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, J.; Altman, D. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.M.; Shin, J.K.; Hur, J. Estimating the Biodegradability of Treated Sewage Samples Using Synchronous Fluorescence Spectra. Sensors 2011, 11, 7382–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, I.; Betancourt, J. Guía Sobre Tratamientos de Aguas Residuales Urbanas Para Pequeños Núcleos de Población. Mejora de la Calidad de los Efluentes, 1st ed.; Daute DiseñO, S.L.: Las Palmas, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Navarro, F.F.; Stilianova-Stoytcheva, M.; Renteria-Gutierrez, L.; Belanche-Muñoz, L.; Flores-Ríos, B.; Ibarra-Esquer, J. Glucose Oxidase Biosensor Modeling and Predictors Optimization by Machine Learning Methods. Sensors 2016, 16, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susanto, F.; de Souza, P.; He, J. Spatiotemporal Interpolation for Environmental Modeling. Sensors 2016, 16, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, W.; Gu, S.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Spatio temporal dynamic of nutrients in the upper Han River basin, China. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, M.; Herrera, S.; Solé, D.; García-Calvo, E.; Fernández-Alba, A. Spatio temporal evaluation of organic contaminants and their transformation products along a river basin affected by urban, agricultural and industrial pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 420, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Blasio, G.; Quesada-Arencibia, A.; García, C.R.; Molina-Gil, J.M.; Caballero-Gil, C. Study on an Indoor Positioning System for Harsh Environments Based on Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Low Energy. Sensors 2017, 17, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitola, J.; Pozo, F.; Tibaduiza, D.A.; Anaya, M. A Sensor Data Fusion System Based on k-Nearest Neighbor Pattern Classification for Structural Health Monitoring Applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 417. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y. Intelligent Diagnosis Method for Rotating Machinery Using Dictionary Learning and Singular Value Decomposition. Sensors 2017, 17, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Z. Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning Methods for Leaf Area Index Retrieval from Time-Series MODIS Reflectance Data. Sensors 2017, 17, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.C.M.; Shiu, Y.S. A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning with WorldView-2 Pan-Sharpened Imagery for Tea Crop Mapping. Sensors 2016, 16, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
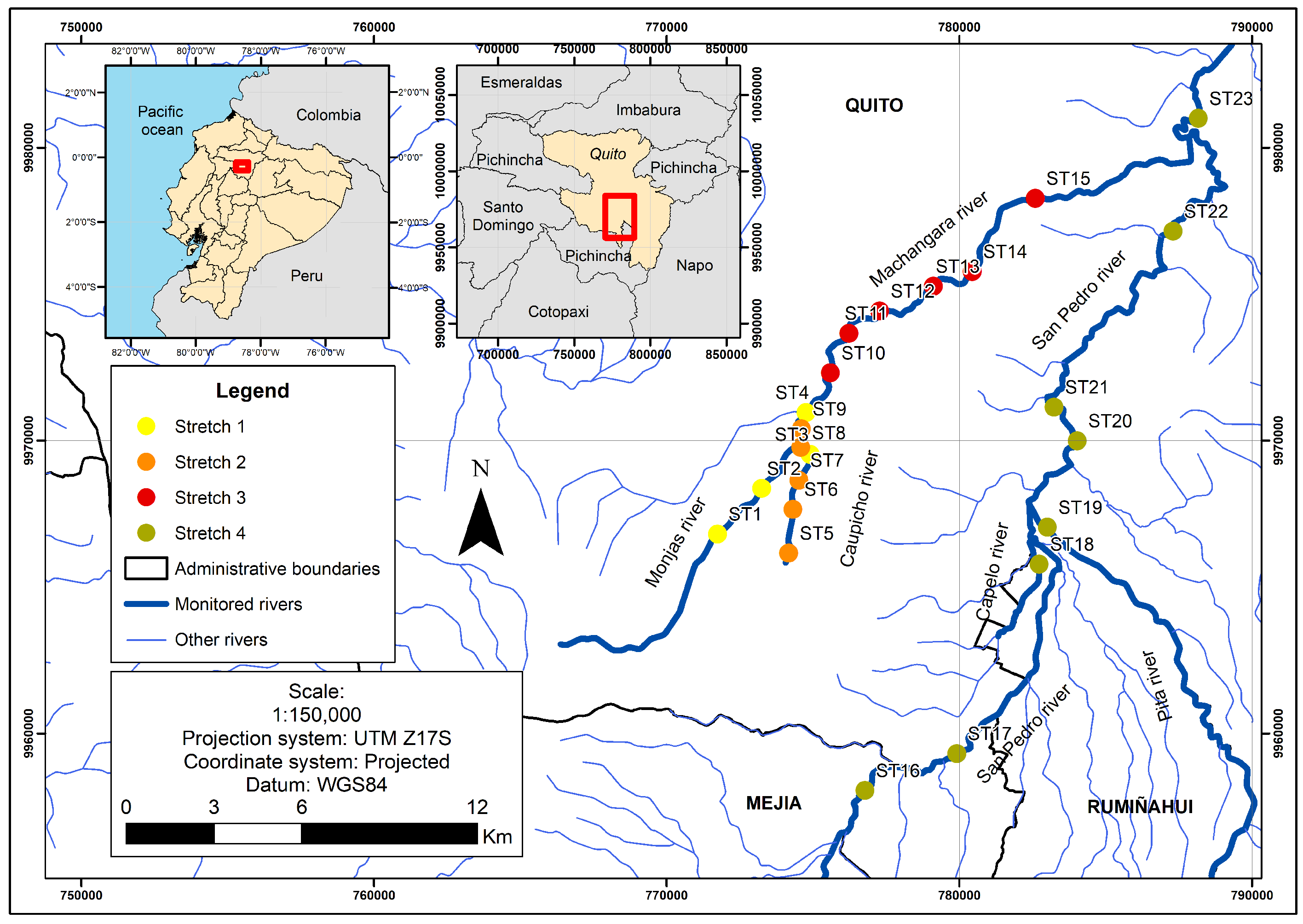


| Studied Stretch | Station Number | Station Name | Code | d (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stretch 1 | ST1 | Q. Shanshayacu | 1.02 | 0.00 |
| ST2 | Q. Ortega | 1.04 | 1.30 | |
| ST3 | R. Mch. Quimiag | 1.07 | 4.27 | |
| ST4 | R. Mch. Quito Sur | 2.05 | 5.54 | |
| Stretch 2 | ST5 | R. Mch. Caupichu | 2.01 | 0.00 |
| ST6 | R. Mch. Oleoducto | 2.02 | 1.89 | |
| ST7 | R. Mch. La Lucha | 2.03 | 3.15 | |
| ST8 | R. Mch. Fosforera | 2.04 | 4.27 | |
| ST9 | R. Mch. Quito Sur | 2.05 | 5.25 | |
| Stretch 3 | ST10 | R. Mch. El Recreo | 2.07 | 0.00 |
| ST11 | R. Mch. Villaflora | 2.08 | 1.75 | |
| ST12 | R. Mch. El Sena | 2.09 | 2.75 | |
| ST13 | R. Mch. El Trébol | 2.10 | 4.91 | |
| ST14 | R. Mch. Las Orquídeas | 2.11 | 6.31 | |
| ST15 | Q. El Batán | 1.09 | 9.49 | |
| Stretch 4 | ST16 | R. SP. Trópico | 4.02 | 0.00 |
| ST17 | R. SP Amaguaña | 4.03 | 2.98 | |
| ST18 | R. SP Capelo | 4.04 | 11.12 | |
| ST19 | R. SP Triángulo | 4.06 | 12.55 | |
| ST20 | R. SP Guangopolo | 4.07 | 16.09 | |
| ST21 | R. SP Guangopolo canal | 4.09 | 17.23 | |
| ST22 | R. SP Cumbaya Cerv. | 4.10 | 24.34 | |
| ST23 | R. SP AJ Machángara | 4.13 | 28.42 |
| Parameter | Acronym | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Flow rate | Q | m/s |
| Temperature | T | C |
| Dissolved Oxygen | DO | mg/L |
| Chemical Oxygen Demand | COD | mg/L |
| Biochemical Oxygen Demand | BOD | mg/L |
| COD/BOD ratio | COD/BOD | – |
| Stretch | Variable | N. Meas. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stretch 1 | Q | 177 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| T | 177 | 1.52 | 1.29 | 1.31 | 1.27 | |
| DO | 177 | 1.02 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.81 | |
| BOD | 177 | 124.54 | 105.99 | 108.65 | 105.3 | |
| COD | 177 | 283.75 | 244.81 | 246.28 | 238.6 | |
| COD/BOD | 177 | 0.68 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.54 | |
| Stretch 2 | Q | 212 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.13 |
| T | 212 | 1.58 | 1.54 | 1.59 | 1.20 | |
| DO | 212 | 1.18 | 1.17 | 1.15 | 0.75 | |
| BOD | 212 | 38.41 | 37.96 | 37.52 | 30.38 | |
| COD | 212 | 92.69 | 88.86 | 86.77 | 77.44 | |
| COD/BOD | 212 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.73 | |
| Stretch 3 | Q | 306 | 0.58 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.48 |
| T | 393 | 1.88 | 1.50 | 1.51 | 1.38 | |
| DO | 329 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 0.74 | |
| BOD | 396 | 49.14 | 40.96 | 40.15 | 36.19 | |
| COD | 396 | 114.96 | 94.82 | 94.24 | 83.56 | |
| COD/BOD | 396 | 0.79 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.55 | |
| Stretch 4 | Q | 303 | 1.07 | 1.05 | 0.96 | 0.90 |
| T | 303 | 1.90 | 1.76 | 1.76 | 1.30 | |
| DO | 303 | 0.93 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.71 | |
| BOD | 303 | 12.02 | 10.89 | 10.89 | 7.63 | |
| COD | 303 | 38.34 | 32.48 | 32.23 | 24.30 | |
| COD/BOD | 303 | 2.01 | 1.74 | 1.74 | 1.12 | |
| Average | 32.13 | 28.02 | 28.02 | 25.67 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vizcaíno, I.P.; Carrera, E.V.; Muñoz-Romero, S.; Cumbal, L.H.; Rojo-Álvarez, J.L. Water Quality Sensing and Spatio-Temporal Monitoring Structure with Autocorrelation Kernel Methods. Sensors 2017, 17, 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102357
Vizcaíno IP, Carrera EV, Muñoz-Romero S, Cumbal LH, Rojo-Álvarez JL. Water Quality Sensing and Spatio-Temporal Monitoring Structure with Autocorrelation Kernel Methods. Sensors. 2017; 17(10):2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102357
Chicago/Turabian StyleVizcaíno, Iván P., Enrique V. Carrera, Sergio Muñoz-Romero, Luis H. Cumbal, and José Luis Rojo-Álvarez. 2017. "Water Quality Sensing and Spatio-Temporal Monitoring Structure with Autocorrelation Kernel Methods" Sensors 17, no. 10: 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102357
APA StyleVizcaíno, I. P., Carrera, E. V., Muñoz-Romero, S., Cumbal, L. H., & Rojo-Álvarez, J. L. (2017). Water Quality Sensing and Spatio-Temporal Monitoring Structure with Autocorrelation Kernel Methods. Sensors, 17(10), 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102357







