Distributed State Estimation Using a Modified Partitioned Moving Horizon Strategy for Power Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
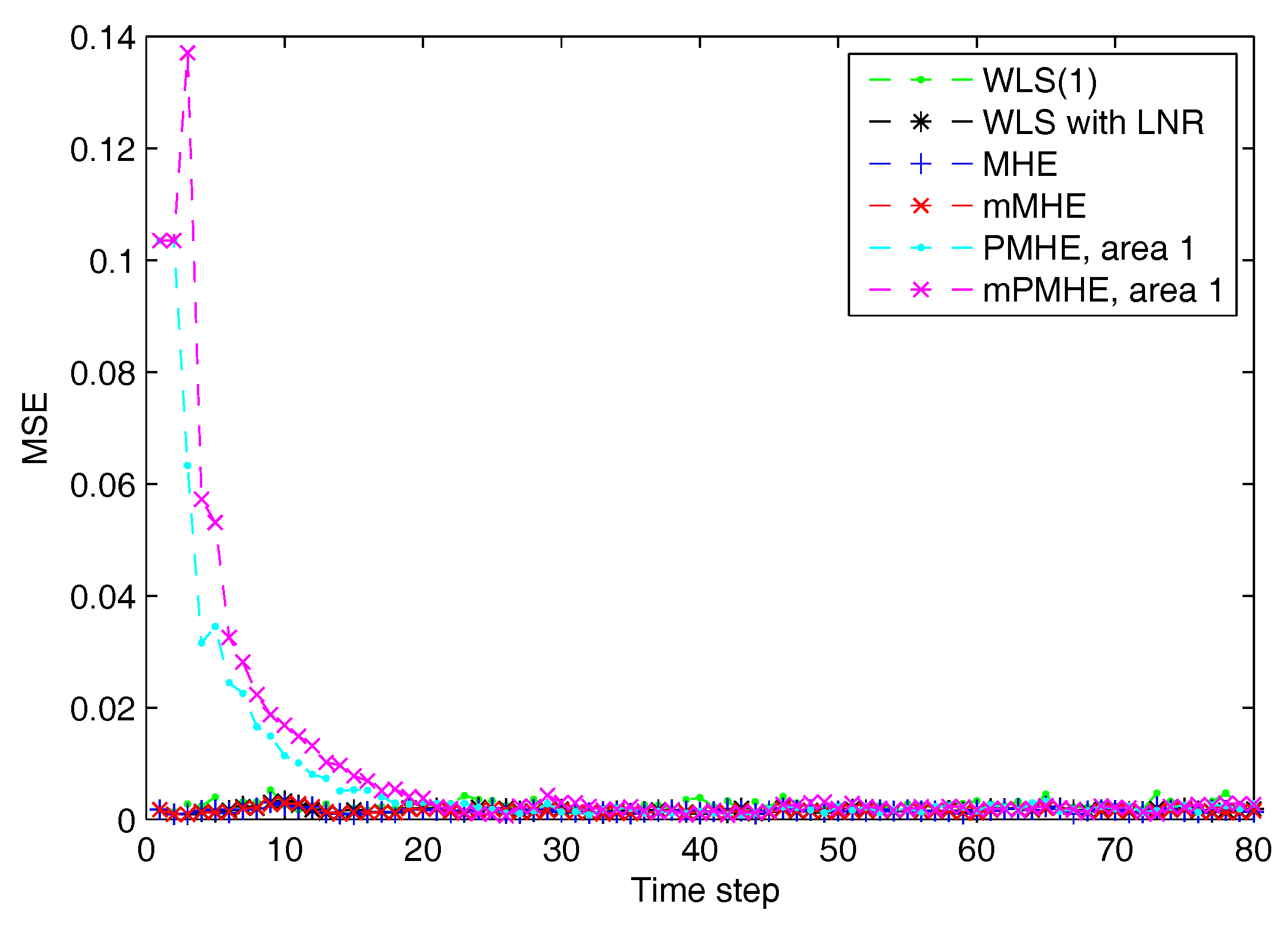
- Instead of all the states in the window estimated by PMHE, the mPMHE only estimates the state vector at the beginning of the window so it is faster than PMHE. The estimated precision of mPMHE is slightly lower than that of PMHE, but their difference is insignificant. The mPMHE achieves comparable state estimation accuracy but with a significant reduction in the overall computation load.
- It is a distributed algorithm and is suitable for large-scale PSSE. Each local area solves for its own local states by using the local measurements and the estimated results from neighboring areas, so the computation load is small. In addition, the communication load is also small because the information is exchanged among neighboring areas only.
- Constraints are taken into account during the optimization process and it is robust to outliers. Hence, good estimated results could be obtained.
2. Centralized State Estimation
2.1. Measurement Model and State Equation
2.2. Weighted Least Squares (WLS)
2.3. Moving Horizon Estimation (MHE)
2.4. Modified Moving Horizon Estimation (mMHE)
3. Modified Partitioned Moving Horizon Estimation (mPMHE)
3.1. mPMHE Problem Formulation
3.2. Update Matrices
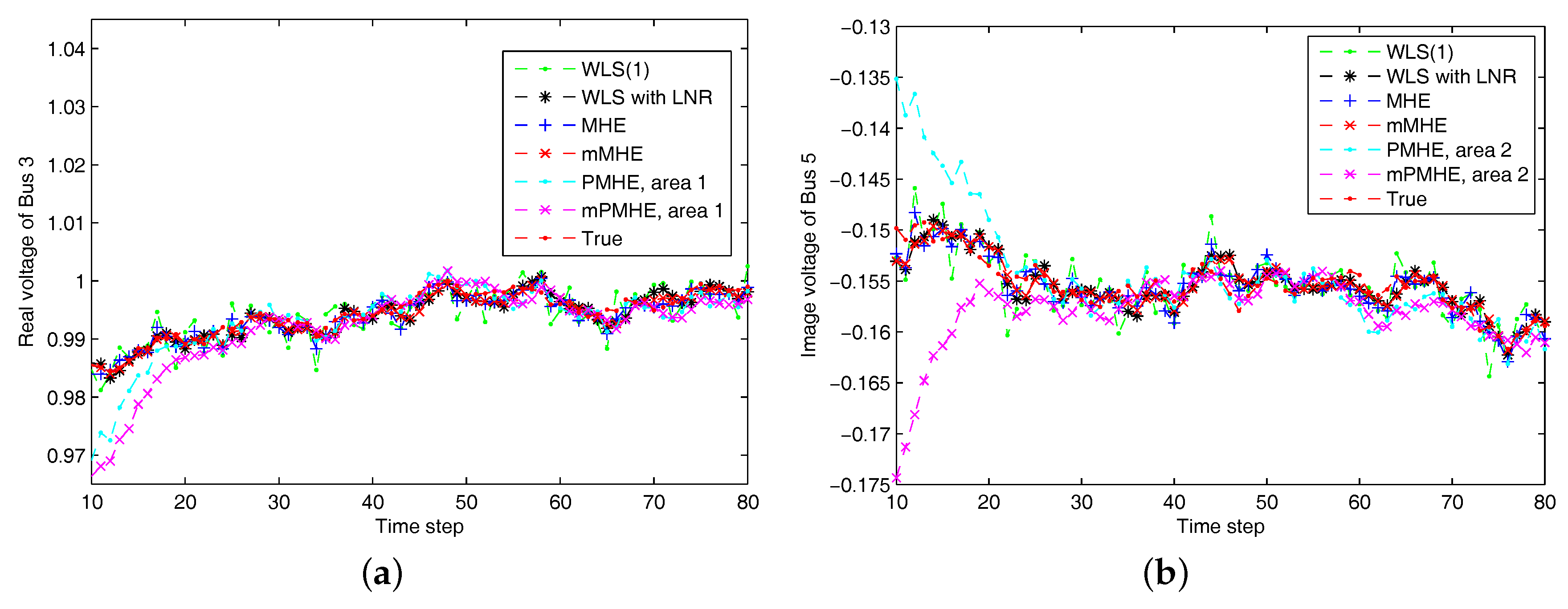
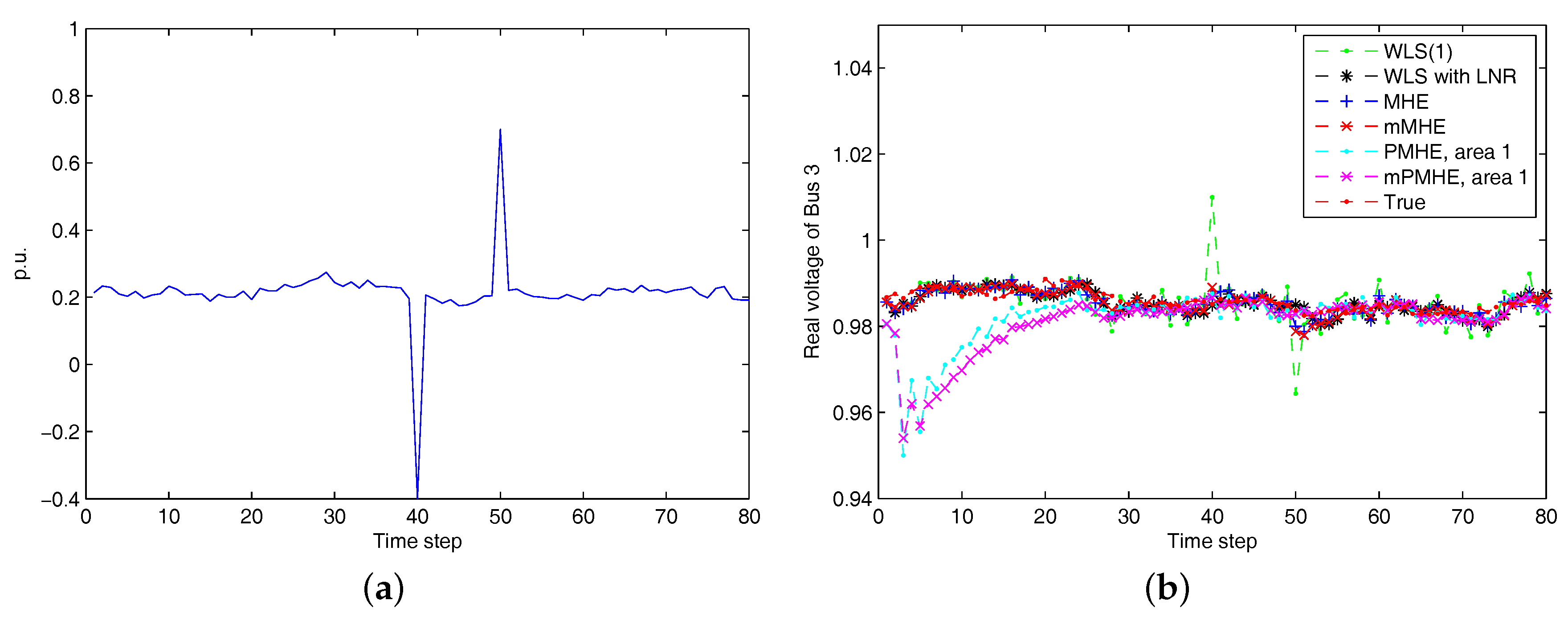
4. Simulation Results
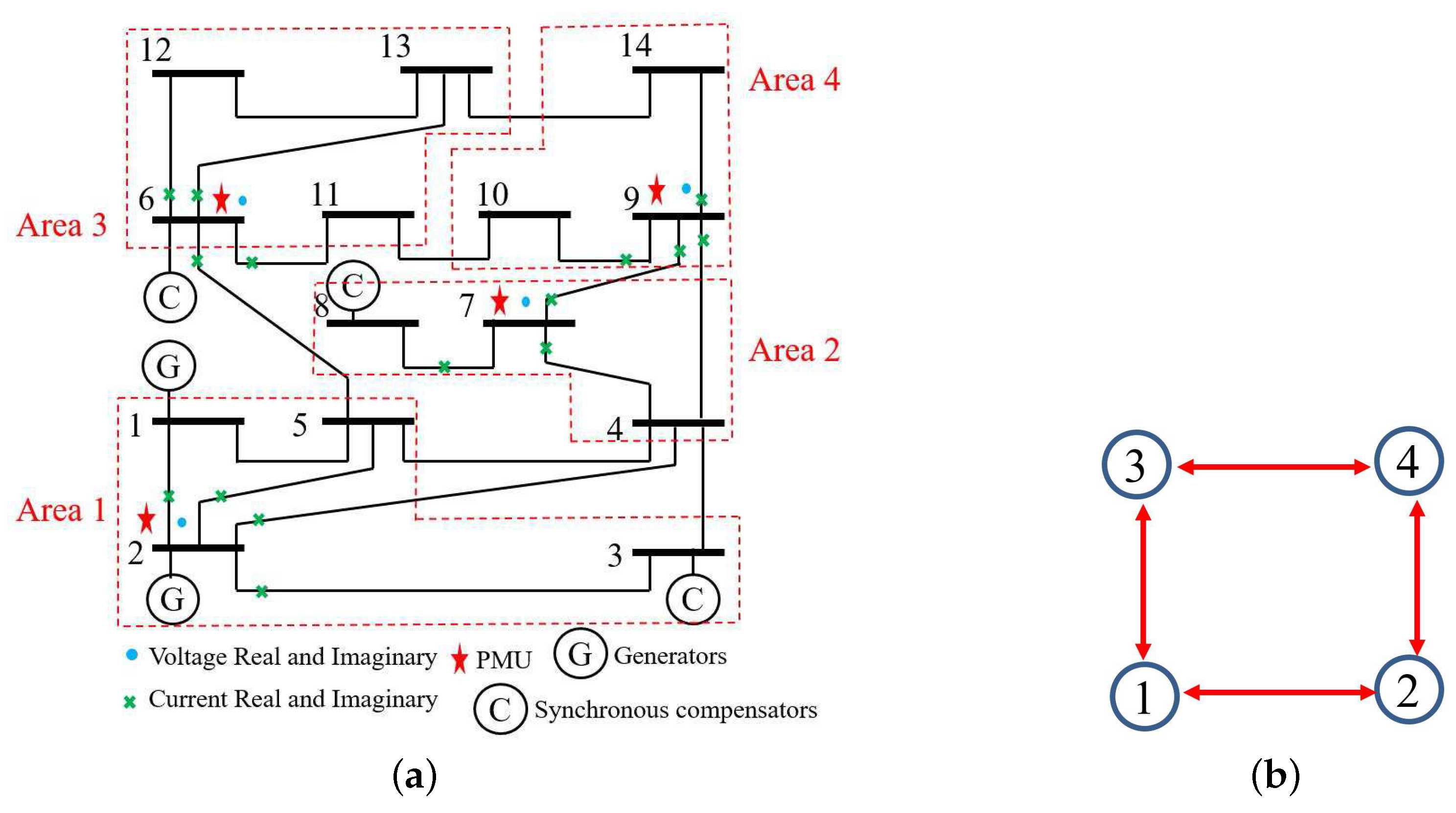
4.1. Simulations on the IEEE 14-Bus System
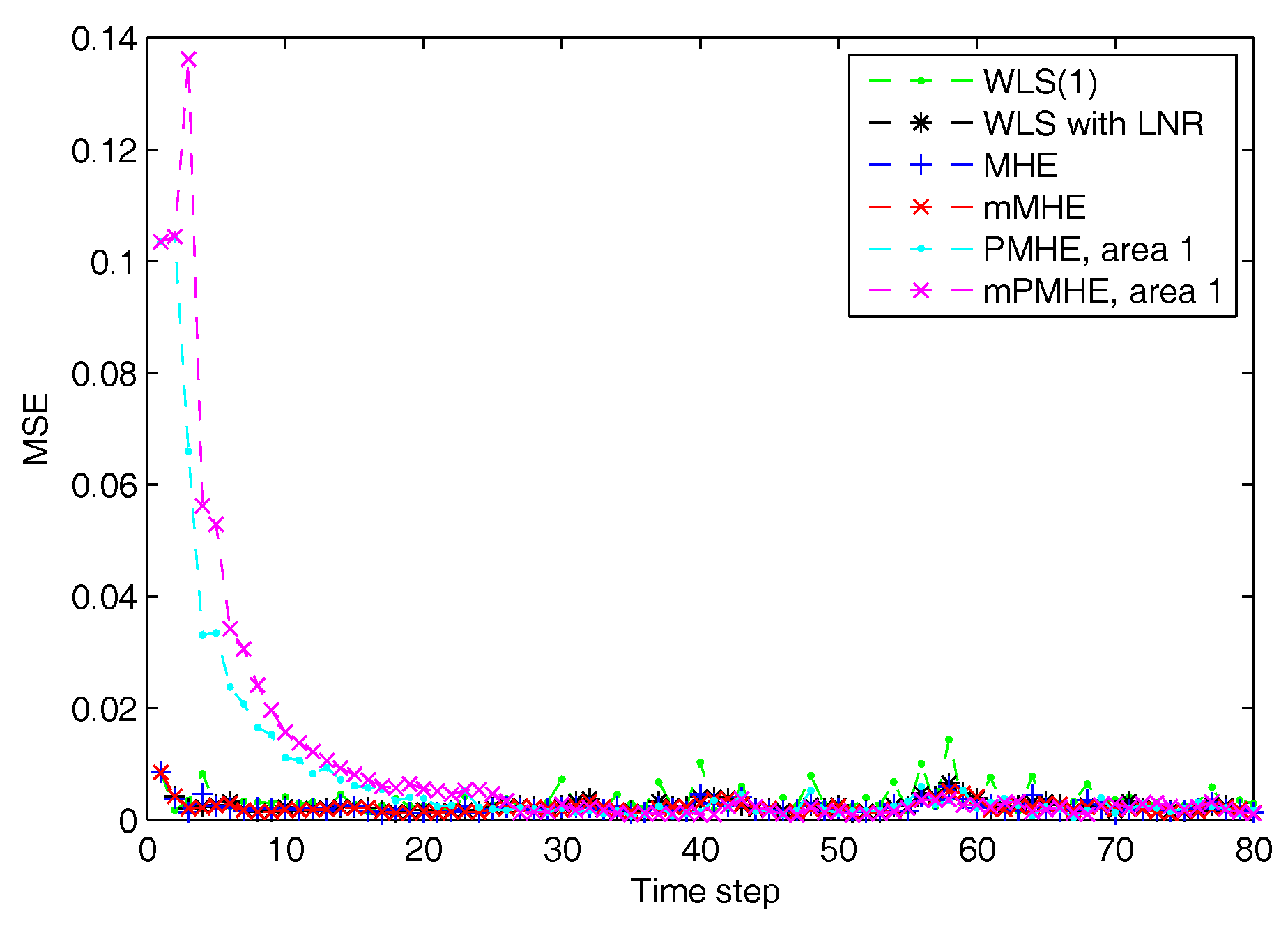
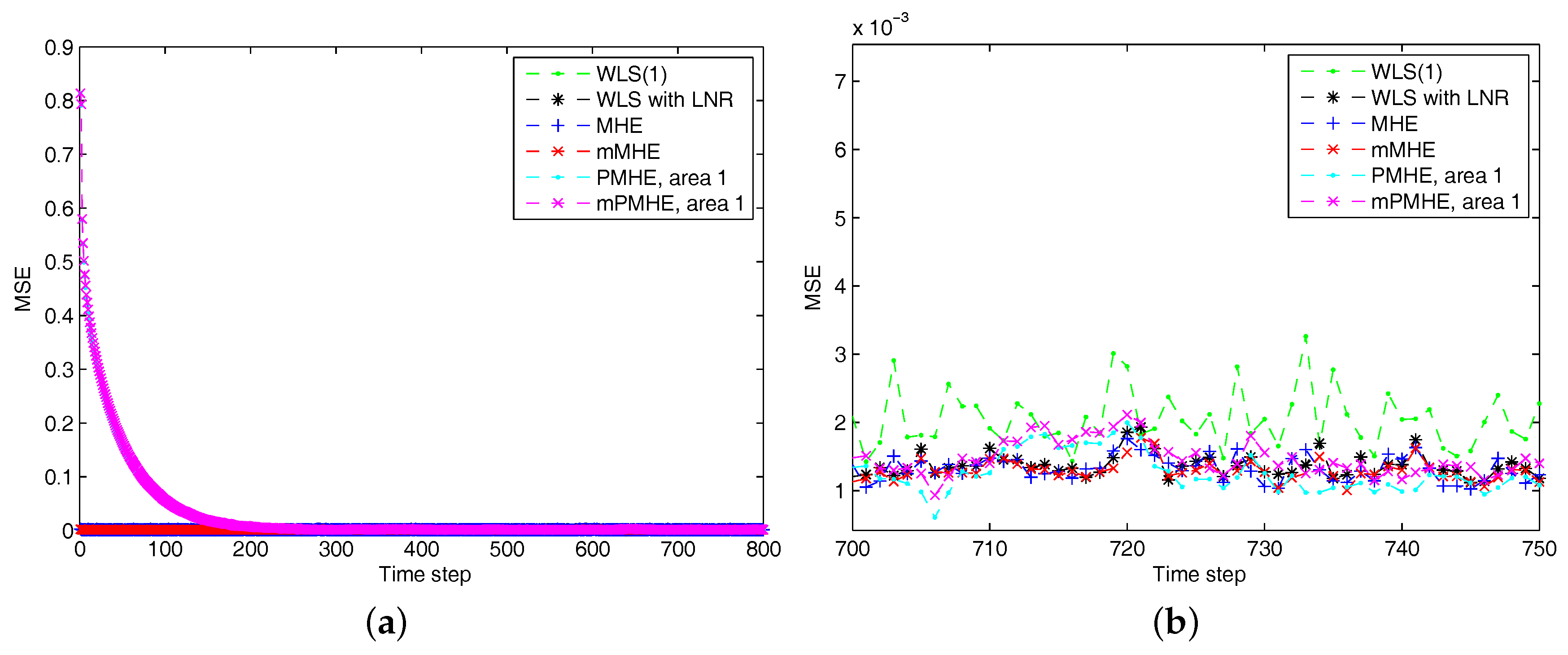
4.1.1. Redundant Observations
- The initial state vectors ; .
- The initial covariance matrices: , , .
- The noise covariances: , ; ;
- The horizon length: .
- State constraints: , , where .
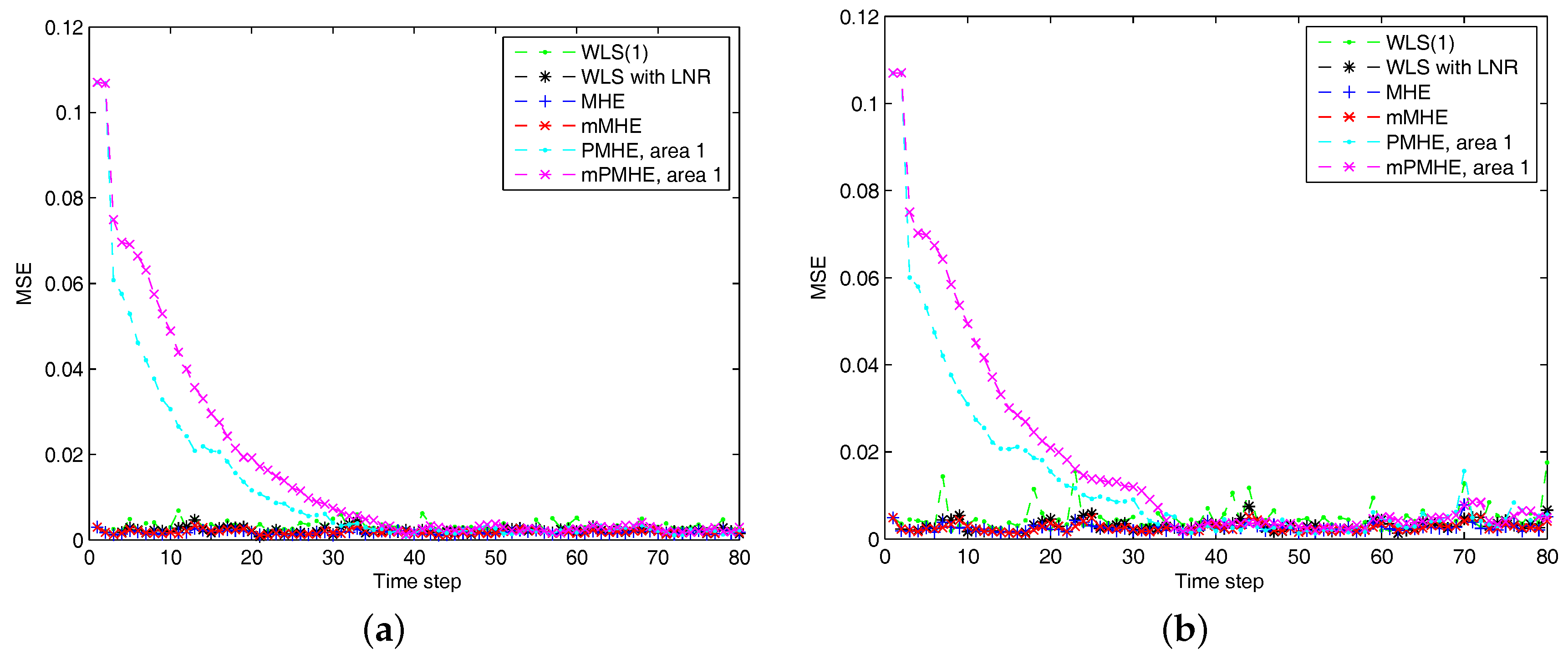
4.1.2. Full Observation with Minimum Number of PMUs
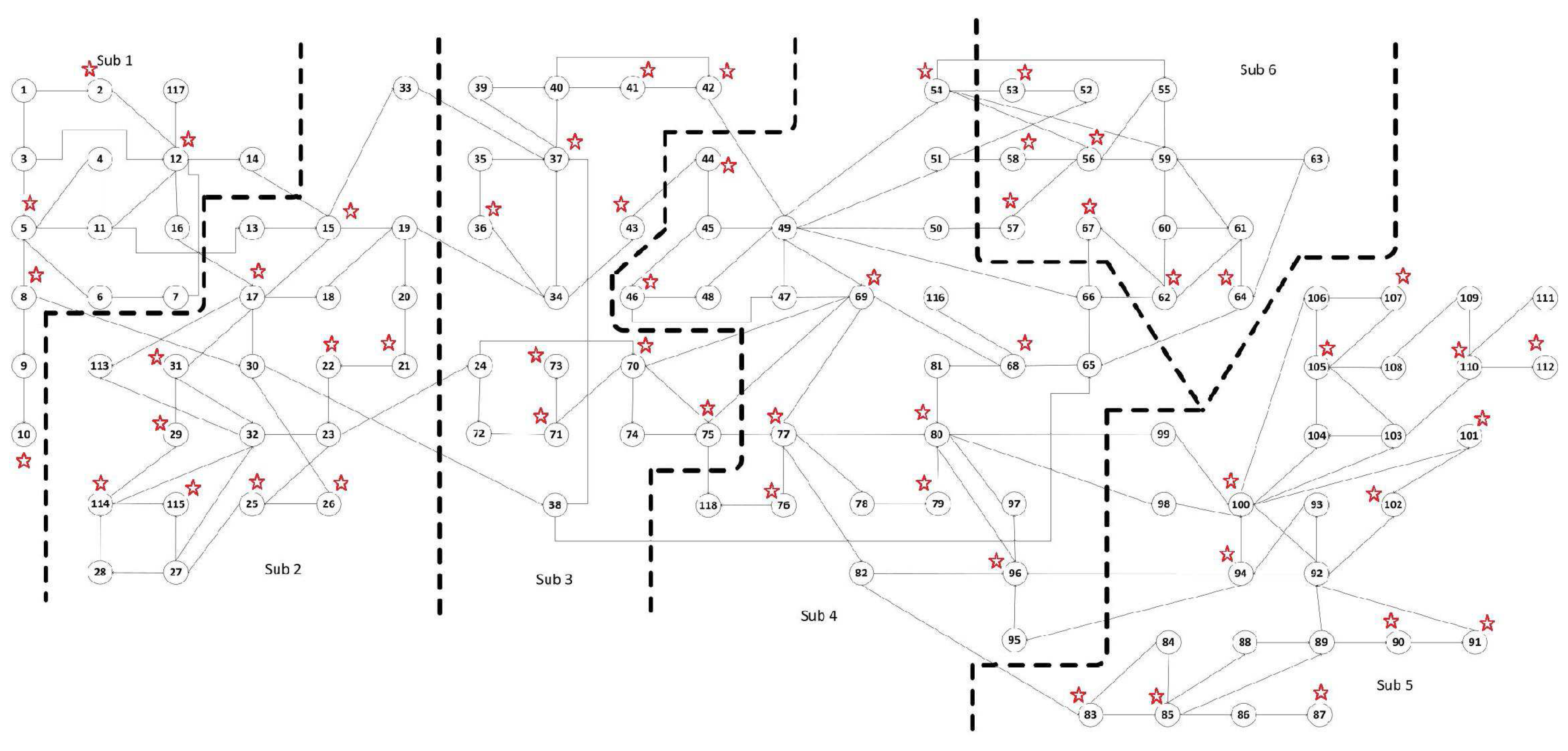
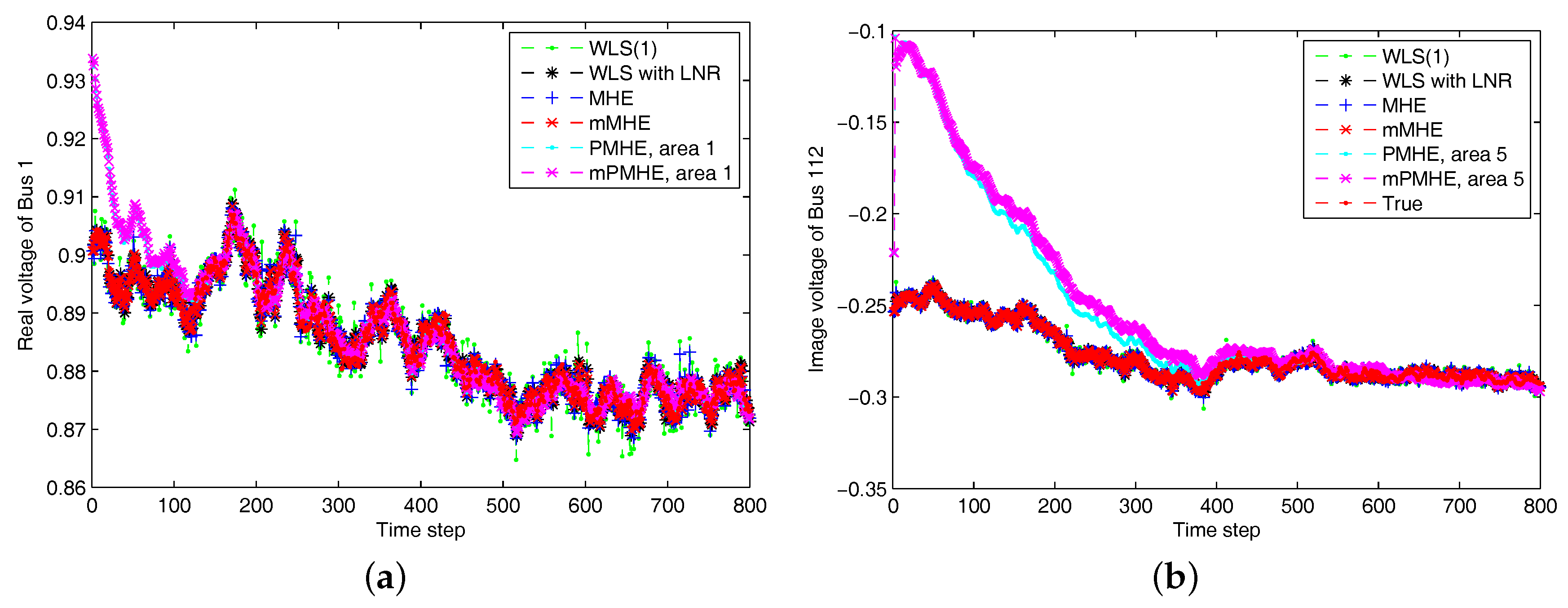
4.2. The IEEE 118-Bus System with Non-Gaussian Noise
4.2.1. Redundant Observations
- The initial state vectors ; ; ; ; ; .
- The initial covariance matrices: , , , , , .
- The noise covariances: , , , , , . ;
- The horizon length: .
- State constraints: , , where .
4.2.2. Full Observation with Minimum Number of PMUs
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| m | Number of measurements at time step k |
Number of local measurements at area i | |
| n | Number of states |
Number of local states at area i | |
| x | True state vector, |
Estimated state vector | |
True local states at area i, | |
Local state vector estimated by the PMHE at time step t | |
Real part of the voltage phasor at bus i | |
Imaginary part of the voltage phasor at bus i | |
The real part of the current measurement | |
The imaginary part of the current measurement | |
Vector of process noise at time step k | |
Process noise at local area i in the PMHE algorithm, | |
| z | Measurements from Phasor Measurement Units |
| v | Measurement noise |
The i-th measurement residual at time step k | |
The normalized measurement residual i at time step k | |
Chosen function of | |
| J | Cost function |
Probability density function of | |
| H | Measurement matrix |
Weighting factor for i-th measurement at time step k | |
Derivative of J wrt | |
Horizon length of measurements | |
| t, k | Time index |
Standard deviation of measurement noise | |
| Q | Covariance matrix of process noise |
| R | Covariance matrix of measurement noise |
| P | State covariance matrix |
Constraint set for state x |
References
- Abur, A.; Expósito, A.G. Power System State Estimation: Theory and Implementation; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Song, W.Z. Distributed power-line outage detection based on wide area measurement system. Sensors 2014, 14, 13114–13133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göl, M.; Abur, A. LAV based robust state estimation for systems measured by PMUs. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göl, M.; Abur, A. A robust PMU based three-phase state estimator using modal decoupling. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 29, 2292–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Kyriakides, E. PMU measurement uncertainty considerations in WLS state estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, V.; Lewis, T. Outliers in Statistical Data; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, M.M.; Li, L. An overview of distributed microgrid state estimation and control for smart grids. Sensors 2015, 15, 4302–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticelli, A. State Estimation in Electric Power Systems: A Generalized Approach; Springer: NewYork, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Scaglione, A. Robust decentralized state estimation and tracking for power systems via network gossiping. IEEE J. Select. Areas Commum. 2013, 31, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, M. Robust algorithm for generalized state estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 1886–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, G. A robust algorithm for power system state estimation with equality constraints. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Abur, A. Robust linear state estimation using multi-level power system models with different partitions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Manchester PowerTech, Manchester, UK, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pegoraro, P.A.; Meloni, A.; Atzori, L.; Castello, P.; Sulis, S. PMU-Based Distribution System State Estimation with Adaptive Accuracy Exploiting Local Decision Metrics and IoT Paradigm. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T. Robust state estimation for power systems via moving horizon strategy. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2017, 10, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Grover, M.A. A modified moving horizon estimator for in situ sensing of a chemical vapor deposition process. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2009, 17, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, B.; Sun, H. A distributed state estimation method for power systems incorporating linear and nonlinear models. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 64, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, K.; Wydra, M.; Ksiezopolski, B. Secure and time-aware communication of wireless sensors monitoring overhead transmission lines. Sensors 2017, 17, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Choi, D.H.; Kar, S.; Poor, H. Fully distributed state estimation for wide-area monitoring systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekatos, V.; Giannakis, G. Distributed Robust Power System State Estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wu, W.; Gomez-Exposito, A.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y. Distributed robust bilinear state estimation for power systems with nonlinear measurements. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Heng, W. Distributed point-based gaussian approximation filtering for forecasting-aided state estimation in power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 2597–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhou, D.; Tran, T.; Kastner, C.; Ling, K.V.; Tseng, K.J.; Maciejowski, J.M. Distributed moving horizon estimation for power systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power Energy Society General Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 26–30 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Terzija, V.; Valverde, G.; Cai, D.; Regulski, P.; Madani, V.; Fitch, J.; Skok, S.; Begovic, M.M.; Phadke, A. Wide-area monitoring, protection, and control of future electric power networks. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, M.; Ferrari-Trecate, G.; Scattolini, R. Moving-horizon partition-based state estimation of large-scale systems. Automatica 2010, 46, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Welch, G.; Bishop, G. Observability and estimation uncertainty analysis for PMU placement alternatives. In Proceedings of the North American Power Symposium, Arlington, TX, USA, 26–28 September 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Tan, Z.; Wiesel, A.; Nehora, A. Power system state estimation using pmus with imperfect synchronization. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 4162–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.F.; Werner, S.; Huang, J.; Kashyap, N.; Gupta, V. State estimation in electric power grids: Meeting new challenges presented by the requirements of the future grid. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.V.; Rawlings, J.B.; Lee, J.H. Constrained linear state estimation– a moving horizon approach. Automatica 2001, 37, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Rawlings, J.; Mayne, D. Constrained state estimation for nonlinear discrete-time systems: Stability and moving horizon approximations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2003, 48, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagchi, I. Power Systems Test Case Archive; Technical report; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Expósito, A.; Abur, A.; Rousseaux, P.; de la Villa Jaén, A.; Gómez-Quiles, C. On the use of PMUs in power system state estimation. In Proceedings of the 17th Power Systems Computation Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, 22–26 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hampel, F.; Ronchetti, E.; Rousseeuw, P.; Stahel, W. Robust Statistics: The Approach Based on Influence Functions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, D.G.; Lee, J.H. On the use of constraints in least squares estimation and control. Automatica 2002, 38, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, X.; Lin, Z.; Fu, M.; Sun, Y. A new distributed state estimation technique for power networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 American Control Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 17–19 June 2013; pp. 3338–3343. [Google Scholar]

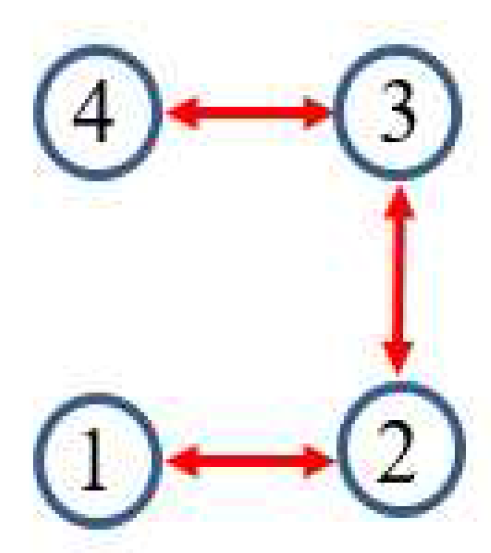

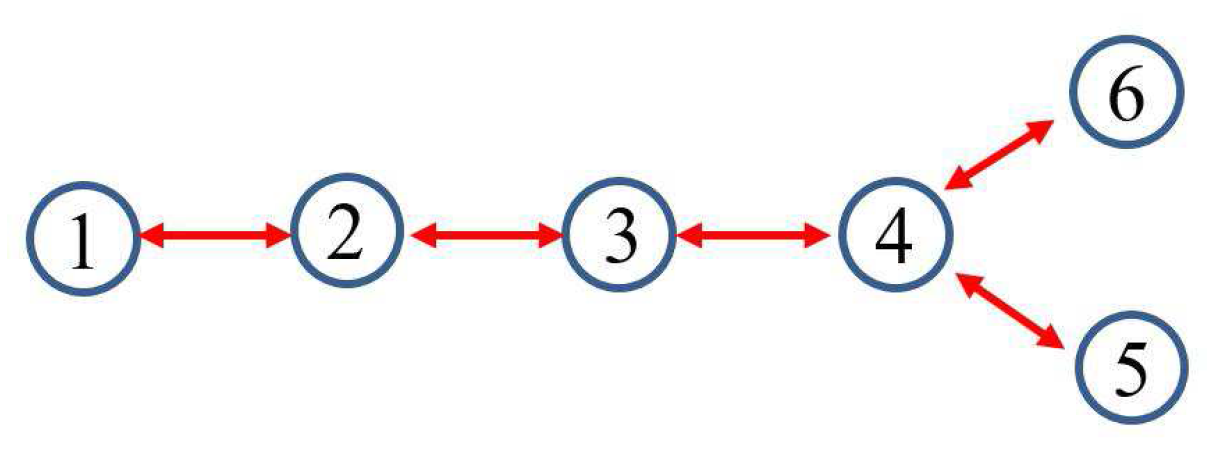

| Area | Number of Local Measurements | Measurements |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | |
| 2 | 20 | |
| 3 | 20 | |
| 4 | 8 | |
| Noise | Gaussian | Non-Gaussian | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimator | Horizon Length | AMSE | Average Time | AMSE | Average Time |
| (ms) | (ms) | ||||
| WLS | 1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | ||
| 3 | 1.6 | 1.9 | |||
| WLS with LNR | 3 | 7.7 | 14.0 | ||
| LAV | 3 | 11.3 | 12.0 | ||
| MHE | 3 | 11.8 | 15.9 | ||
| mMHE | 3 | 6.6 | 7.3 | ||
| PMHE in [24] (area 1) | 3 | 4.9 | 6.5 | ||
| PMHE in [24] (area 2) | |||||
| PMHE in [24] (area 3) | |||||
| PMHE in [24] (area 4) | |||||
| mPMHE (area 1) | 3 | 2.6 | 3.7 | ||
| mPMHE (area 2) | |||||
| mPMHE (area 3) | |||||
| mPMHE (area 4) | |||||
| Noise | Gaussian | Non-Gaussian | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimator | Horizon Length | AMSE | Average Time | AMSE | Average Time |
| (ms) | (ms) | ||||
| WLS | 1 | 3.2 | 0.2 | 5.1 | 0.2 |
| 3 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 4.1 | 0.7 | |
| WLS with LNR | 3 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 3.9 |
| LAV | 3 | 4.4 | 2.4 | 5.3 | |
| MHE | 3 | 1.7 | 5.3 | 2.1 | 7.4 |
| mMHE | 3 | 1.8 | 3.7 | 2.3 | 4.9 |
| PMHE in [24] (area 1) | 3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 2.1 | 4.3 |
| PMHE in [24] (area 2) | |||||
| PMHE in [24] (area 3) | |||||
| PMHE in [24] (area 4) | |||||
| mPMHE (area 1) | 3 | 1.8 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.8 |
| mPMHE (area 2) | |||||
| mPMHE (area 3) | |||||
| mPMHE (area 4) | |||||
| Scenarios | Redundant Observations | Observation with Minimum Number of PMUs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of PMUs | 54 | 32 | |||
| Estimator | Horizon Length | AMSE | Average Time | AMSE | Average Time |
| (ms) | (ms) | ||||
| WLS | 1 | 14 | 4.2 | 6.4 | |
| 3 | 182 | 2.6 | 59 | ||
| WLS with LNR | 3 | 302 | 2.2 | 115 | |
| LAV | 3 | 1.4 | 80 | 2.2 | 55 |
| MHE | 3 | 882 | 2.1 | 330 | |
| mMHE | 3 | 669 | 2.2 | 264 | |
| PMHE in [24] (area 1) | 3 | 55 | 2.1 | 33 | |
| PMHE in [24] (area 2) | |||||
| PMHE in [24] (area 3) | |||||
| PMHE in [24] (area 4) | |||||
| mPMHE (area 1) | 3 | 32 | 2.2 | 21 | |
| mPMHE (area 2) | |||||
| mPMHE (area 3) | |||||
| mPMHE (area 4) | |||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Foo, Y.S.E.; Ling, K.V.; Chen, X. Distributed State Estimation Using a Modified Partitioned Moving Horizon Strategy for Power Systems. Sensors 2017, 17, 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102310
Chen T, Foo YSE, Ling KV, Chen X. Distributed State Estimation Using a Modified Partitioned Moving Horizon Strategy for Power Systems. Sensors. 2017; 17(10):2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102310
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tengpeng, Yi Shyh Eddy Foo, K.V. Ling, and Xuebing Chen. 2017. "Distributed State Estimation Using a Modified Partitioned Moving Horizon Strategy for Power Systems" Sensors 17, no. 10: 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102310
APA StyleChen, T., Foo, Y. S. E., Ling, K. V., & Chen, X. (2017). Distributed State Estimation Using a Modified Partitioned Moving Horizon Strategy for Power Systems. Sensors, 17(10), 2310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102310





