Tip Pressure on Semicircular Specimens in Tapping Mode Atomic Force Microscopy in Viscous Fluid Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
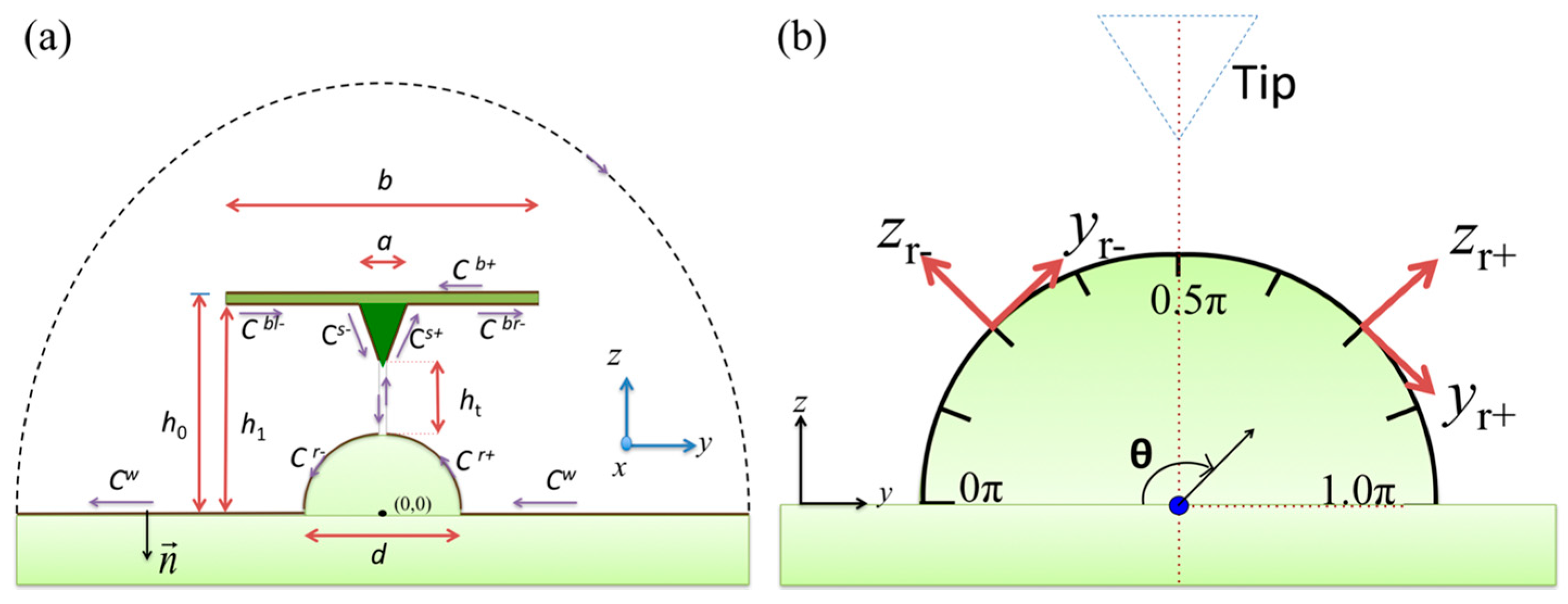
2.1. Mathematical Model
2.2. Numerical Calculation
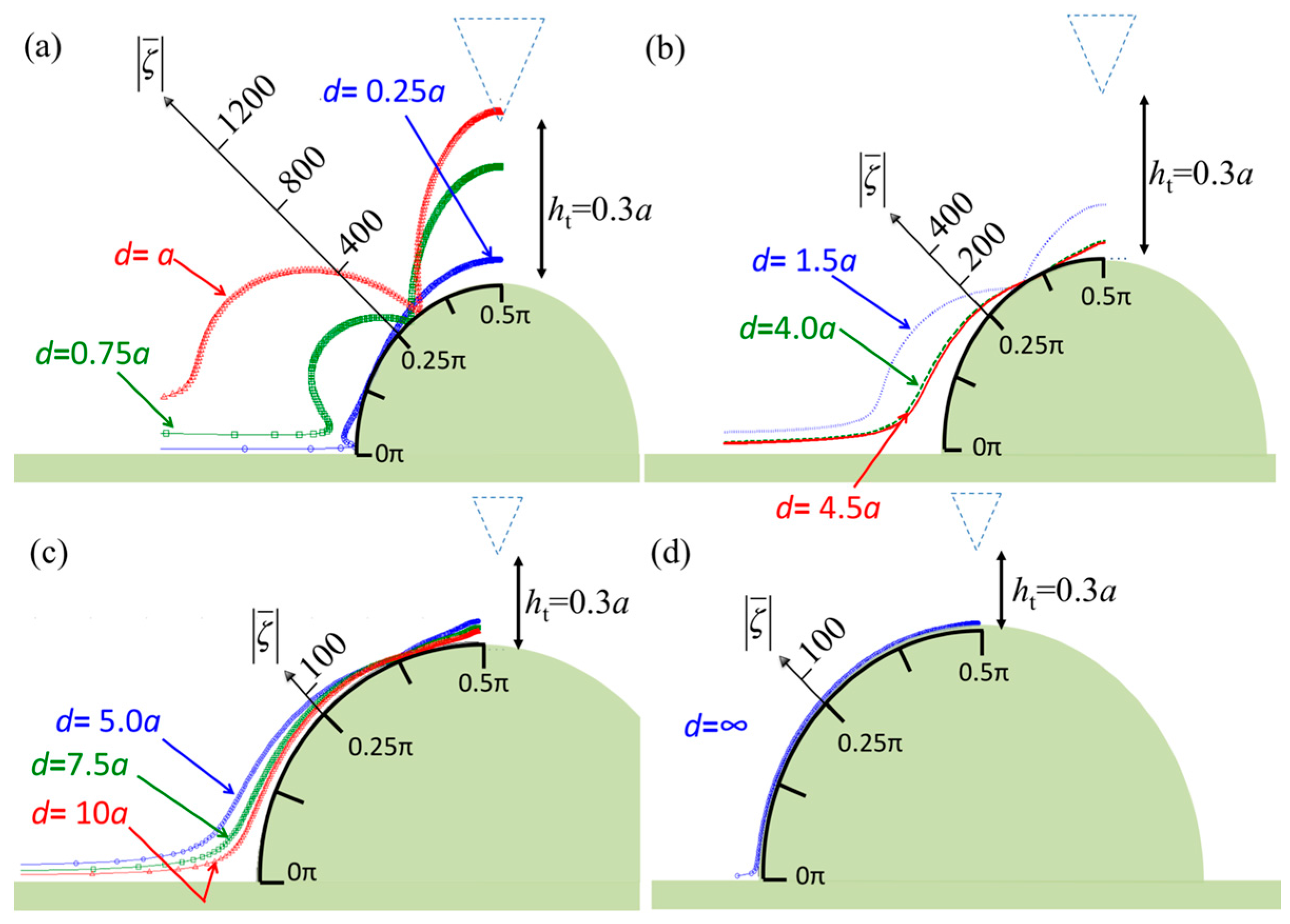
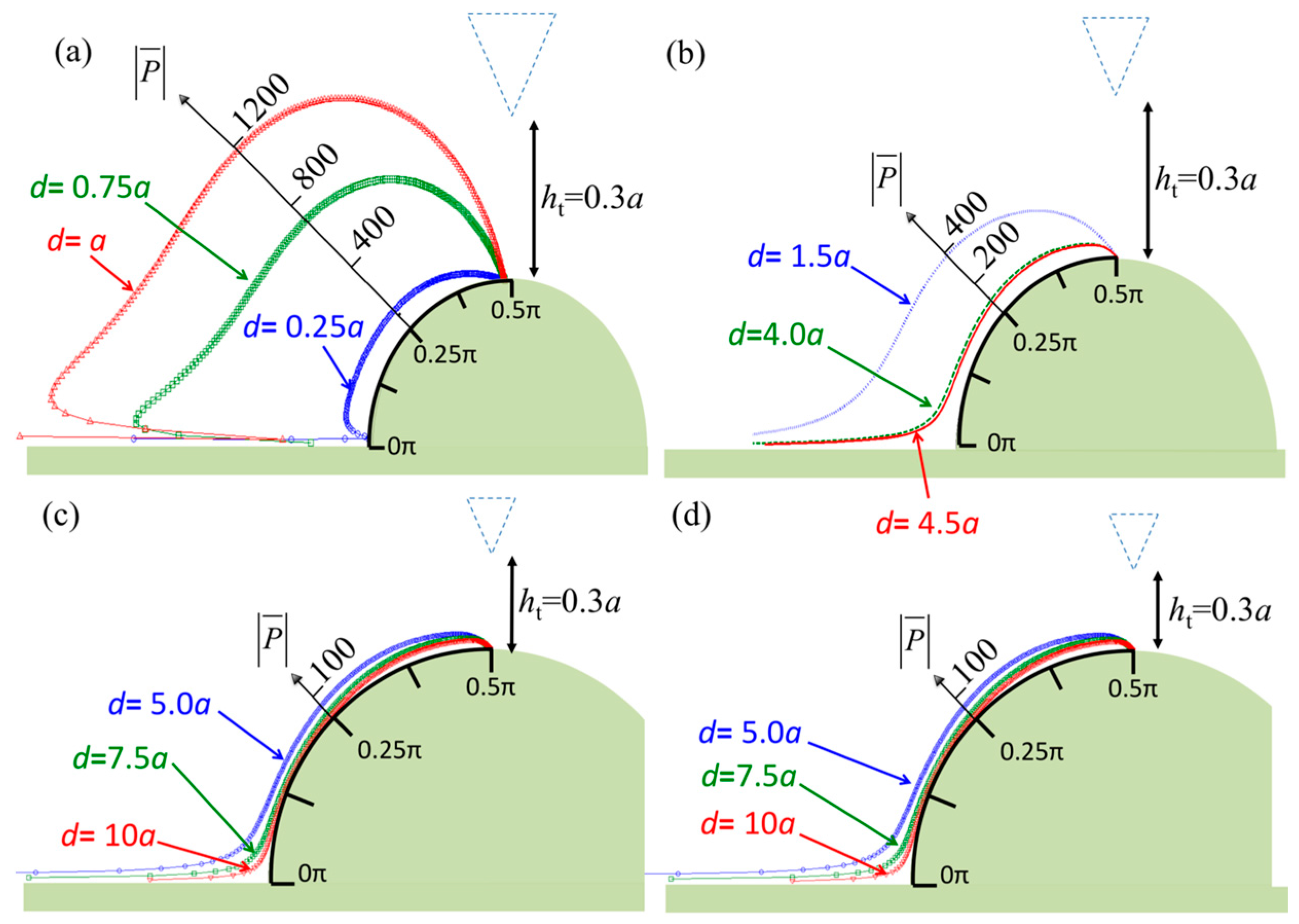
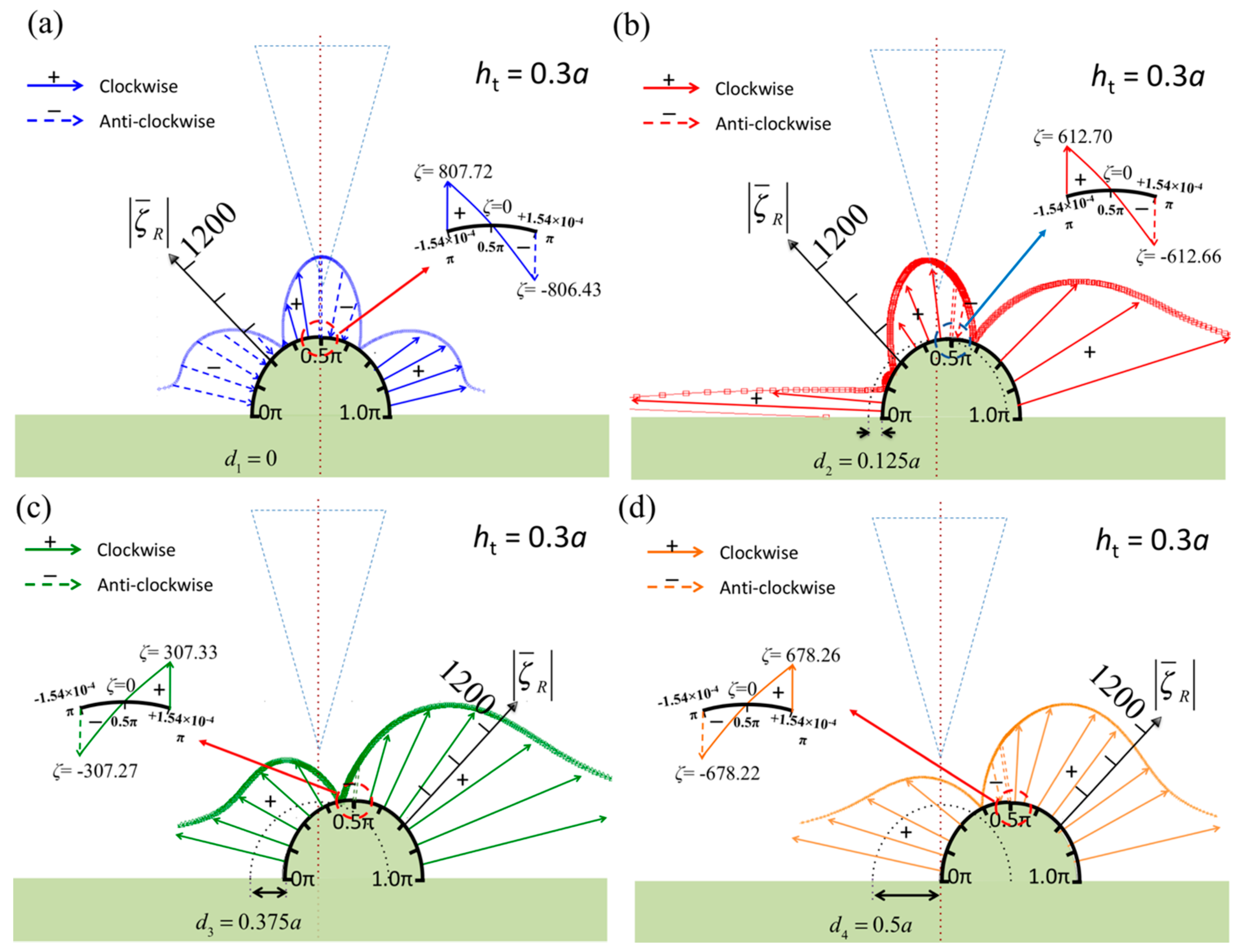
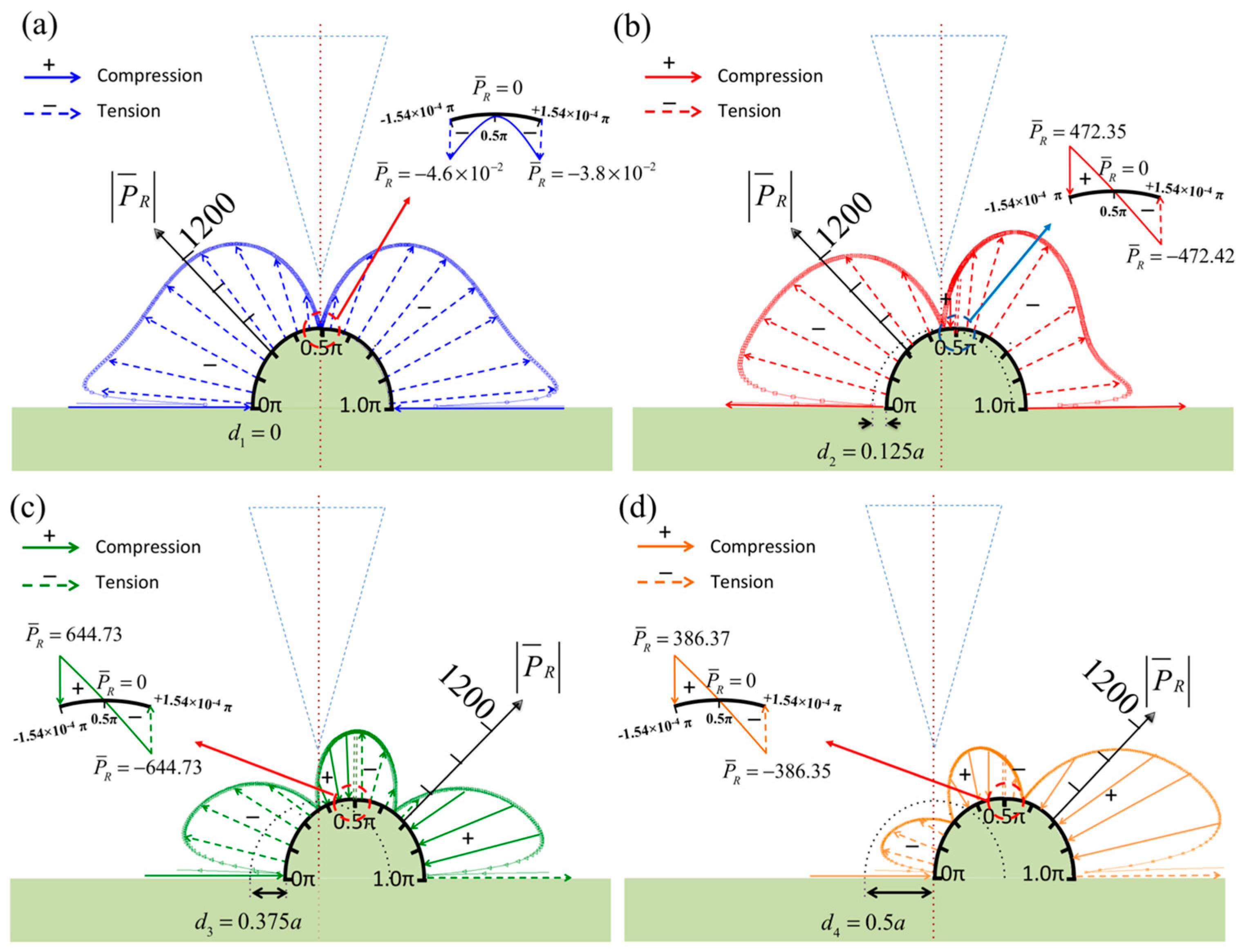
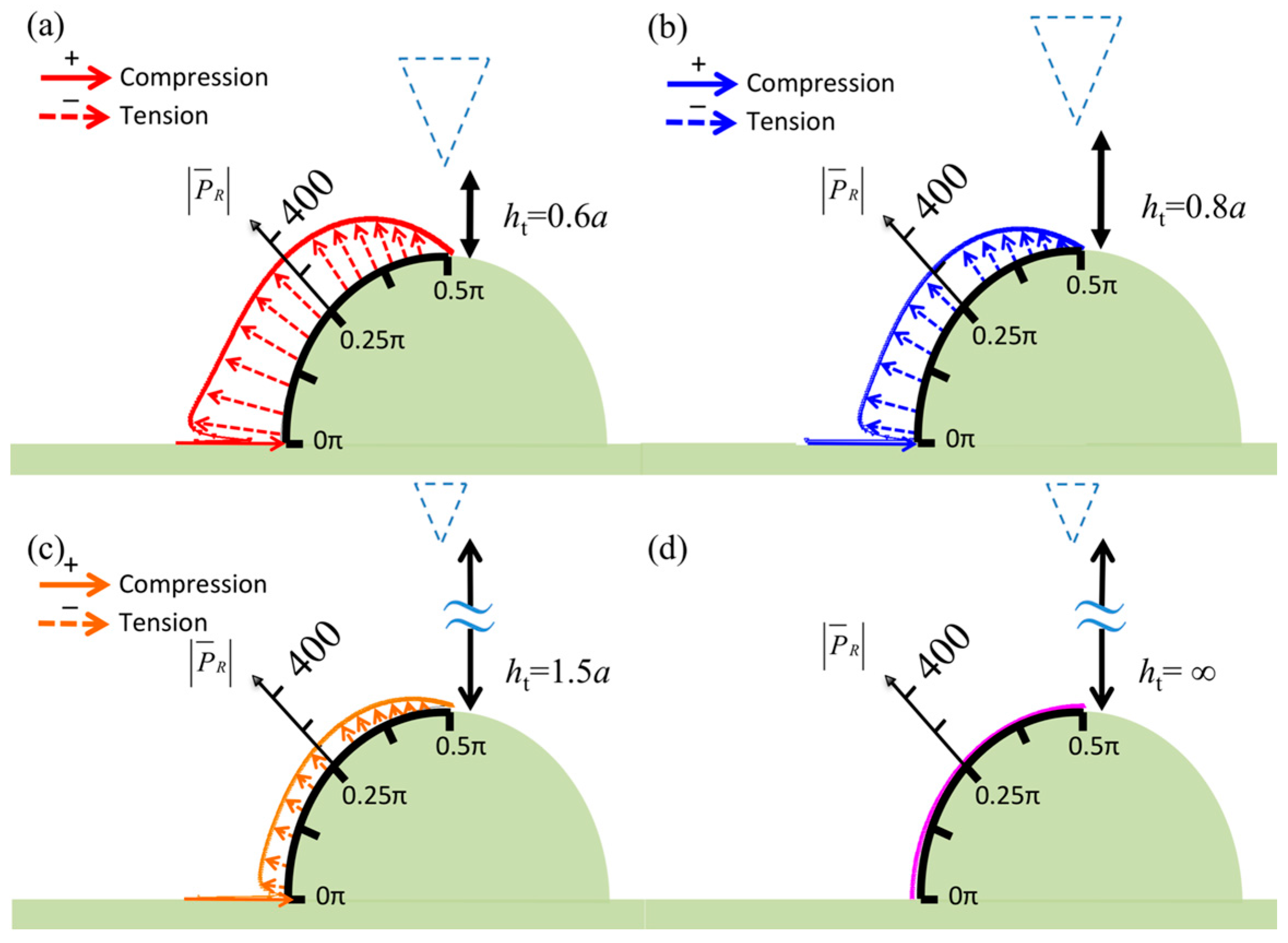
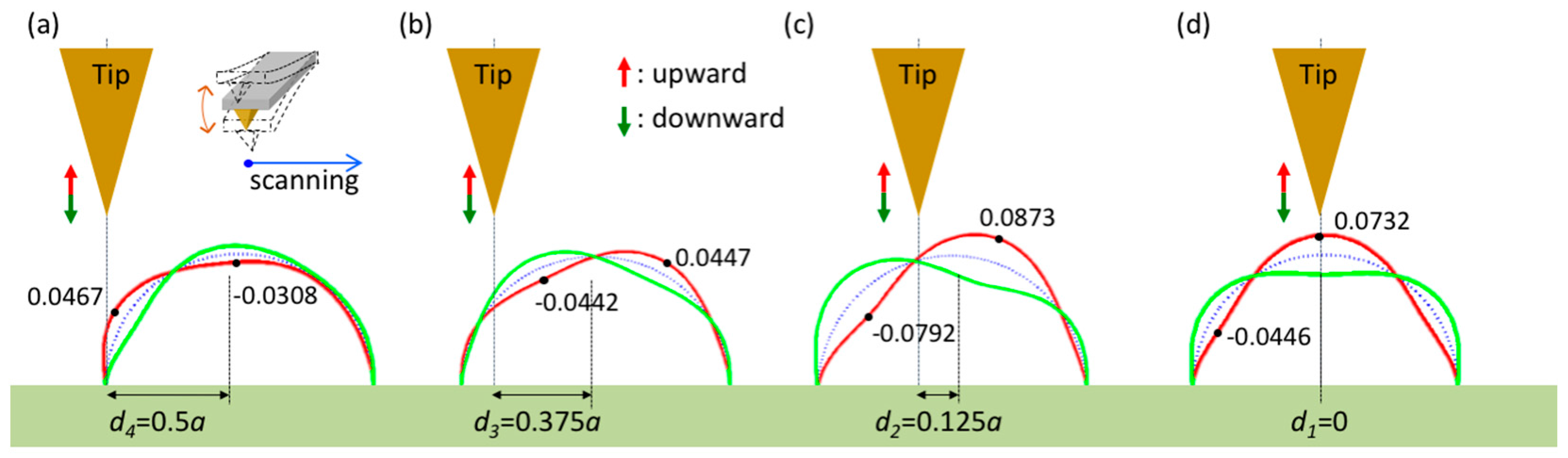
3. Numerical Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Wall | Specimen | Beam | Tip | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cw+ | Cw− | Cr+ | Cr− | Cb+ | Cbl− | Cbr− | Cs+ | Cs− | |
| Y | y′ | y′ | y’ | y’ | y’ | ||||
| Z | 0 | 0 | ×sin β | ×sin (γ-90°) | h0 | h1 | h1 | ×sin θ | ×sin (α-90°) |
Appendix B
References
- Basak, S.; Raman, A.; Garimella, S.V. Hydrodynamic loading of microcantilevers vibrating in viscous fluids. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 114906. [Google Scholar]
- Woolley, A.T.; Cheung, C.L.; Hafner, J.H.; Lieber, C.M. Structure biology with carbon nanotube AFM probes. Cell Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, R193–R204. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Carrasco, C.; de Pablo, P.J.; Gomez-Herrero, J.; Raman, A. Unmasking imaging forces on soft biological samples in liquids when using dynamic atomic force microscopy: A case study on viral capsids. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 2520–2528. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.X.; Liu, R.P.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.K.; Fan, C.Z. Distorted surface topography observed by atomic force microscopy. Measurement 2006, 39, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, P.J. Frequency function in atomic force microscopy applied to a liquid environment. Sensors 2014, 14, 9369–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, C.P.; Sader, J.E. Small amplitude oscillations of a thin beam immersed in a viscous fluid near a solid surface. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, R.C.; Jana, A.; Raman, A. Hydrodynamic loading of microcantilevers oscillating near rigid walls. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janovjak, H.; Struckmeier, J.; Muller, D.J. Hydrodynamic effects in fast AFM single-molecule force measurements. Eur. Biophys. J. 2005, 34, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, H.J.; Shih, P.J. Tip effect of the tapping mode of atomic force microscope in viscous fluid environments. Sensors 2015, 15, 18381–18401. [Google Scholar]
- Walczyk, W.; Hain, N.; Schonherr, H. Hydrodynamic effects of the tip movement on surface nanobubbles: A combined tapping mode, lift mode and force volume mode AFM study. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 5945–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kang, S.K.; Choi, I.; Lee, J.; Yi, J. Dependence of image distortion in a liquid-cell atomic force microscope on fluidic properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 173121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, H.V.; Perrino, A.P.; Garcia, R. Peak forces in high-resolution imaging of soft matter in liquid. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3198–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, C.; Allen, M.; Elings, V.; Engel, A.; Muller, D.J. Tapping-mode atomic force microscopy produces faithful high-resolution images of protein surfaces. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medalsy, I.D.; Muller, D.J. Nanomechanical properties of proteins and membranes depend on loading rate and electrostatic interactions. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2642–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichare, S.; Inamdar, M.M.; Sen, S. Influence of cell spreading and contractility on stiffness measurements using AFM. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10464–10471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.S.; Lee, G.Y.; Ong, C.N.; Lim, C.T. AFM indentation study of breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, E.O. Calculation of unsteady flows due to small motions of cylinders in a viscous fluid. J. Eng. Math. 1969, 3, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sader, J.E.; Green, P. Small amplitude oscillations of a thin beam immersed in a viscous fluid near a solid surface. AIP Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 073102. [Google Scholar]
- Sader, J.E. Frequency response of cantilever beams immersed in viscous fluids with applications to the atomic force microscope. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sader, J.E.; Chon, J.W.M. Calibration of rectangular atomic force microscope cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1999, 70, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.P.; Sader, J.E. Torsional frequency response of cantilever beams immersed in viscous fluids with applications to the atomic force microscope. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 6262–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.P.; Lioe, H.; Cleveland, J.P.; Proksch, R.; Mulvaney, P.; Sader, J.E. Normal and torsional spring constants of atomic force microscope cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 75, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, D.E. Characteristics of fracture during the approach process and wear mechanism of a silicon AFM tip. Ultramicroscopy 2005, 102, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, T.G.; Starodubtseva, M.N.; Yegorenkov, N.I.; Chizhik, S.A.; Zhdanov, R.I. Atomic force microscopy probing of cell elasticity. Micron 2007, 38, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shih, H.-J.; Dai, C.-L.; Shih, P.-J. Tip Pressure on Semicircular Specimens in Tapping Mode Atomic Force Microscopy in Viscous Fluid Environments. Sensors 2017, 17, 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102182
Shih H-J, Dai C-L, Shih P-J. Tip Pressure on Semicircular Specimens in Tapping Mode Atomic Force Microscopy in Viscous Fluid Environments. Sensors. 2017; 17(10):2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102182
Chicago/Turabian StyleShih, Hua-Ju, Ching-Liang Dai, and Po-Jen Shih. 2017. "Tip Pressure on Semicircular Specimens in Tapping Mode Atomic Force Microscopy in Viscous Fluid Environments" Sensors 17, no. 10: 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102182
APA StyleShih, H.-J., Dai, C.-L., & Shih, P.-J. (2017). Tip Pressure on Semicircular Specimens in Tapping Mode Atomic Force Microscopy in Viscous Fluid Environments. Sensors, 17(10), 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102182




