Fisheye-Based Method for GPS Localization Improvement in Unknown Semi-Obstructed Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
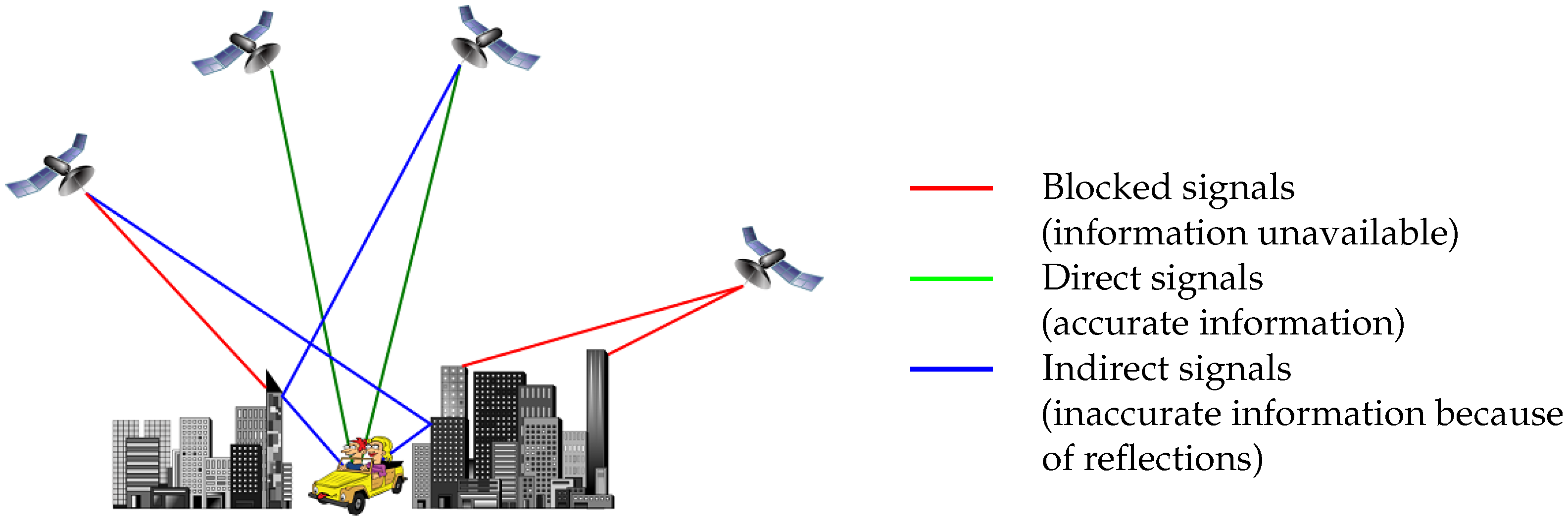
1.1. Principle of GNSS Localization
- a signal is delayed in different Earth’s atmosphere layers (especially the ionosphere and troposphere) [1] (pp. 247–250);
- in semi-obstructed area, a signal may be received after multiple reflections on the structures, and even worse, it may be received several times by multipath effect [1] (pp. 254–257).
1.2. Multipath Effect
1.3. State-of-the-Art of NLOS Correction Methods
- Authors aiming to detect NLOS signals without correcting pseudorange delays:
- -
- Most of the time they only exclude NLOS signals for position computation;
- -
- Some of them use the NLOS information inside specific procedures.
- Authors trying to correct pseudorange delays;
- And authors applying a different strategy, consisting in testing and validating many positions in a 3D model of the area.
1.3.1. NLOS Signals Detection and Exclusion
1.3.2. NLOS Signals Filtering
- Smoothing using NLOS information:
- Weighting of NLOS data:In [5], Tay and Marais weight the contribution of NLOS signals in the position computation according to the CN0. NLOS satellites are identified using the fisheye vision-based method described in [35]. Results seem better than a simple NLOS exclusion, in terms of accuracy and without loss of availability. For presented sequence, position error is reduced from 15 m to approximately 4 m.
- Shadow-matching:This method is used in [13]. The principle consists in testing a grid of candidates positions around the initial GNSS position that is computed. For each satellite, the aim is to use the 3D model and ray-tracing to describe areas where the satellite might be LOS, NLOS or totally blocked. The test is done by correlating the state of each satellite in the model with CN0 measurements of the reality. The candidate position with the best score is considered as the final estimated position.
1.3.3. NLOS Pseudoranges Correction
- multipath effect (a signal is received more than once)
- signal reflection (weaker signal)
- signal diffraction and diffusion (signal very weak, occurs when it passes through vegetation or reaches an edge)
1.4. NLOS Detection Methods Based on Vision
1.5. Bibliography on Calibration
- Cameras calibration
- Matching for 3D scene reconstruction
1.5.1. Pattern-Based Calibration
1.5.2. Self-Calibration
1.6. Works on Matching for 3D Scene Reconstruction
1.6.1. Sparse Matching Methods
1.6.2. Dense Matching Methods
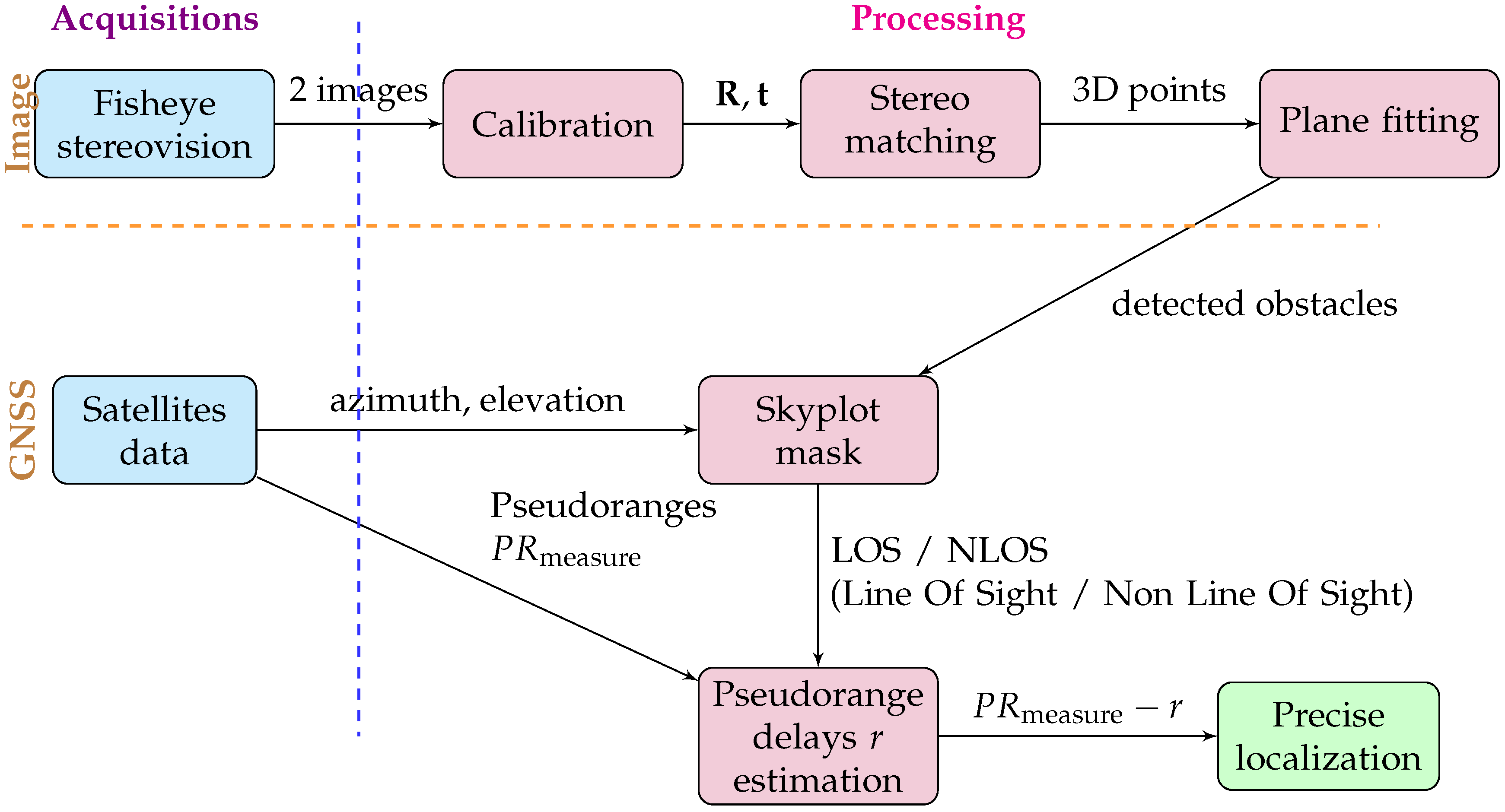
1.7. Paper Presentation
- Generation of the 3D model is a step for the PR delay estimation and the GNSS fix computation, whereas SLAM computes and refine simultaneously local mapping and localization within a unique problem formulation;
- In presented works the localization concerns improvement of GPS accuracy, and not the visual-based positioning in the local mapping;
- GNSS positioning is the output of our procedure, and can be, as well as SLAM, an input among others for visual and inertial navigation;
- Hence, both methods can be combined.
2. True-Scale 3D Modelling for the Proposed Method
- Data must be updated as often as possible.
- Re-positioning in the 3D model is difficult as the receiver is not well-localised in the true world.
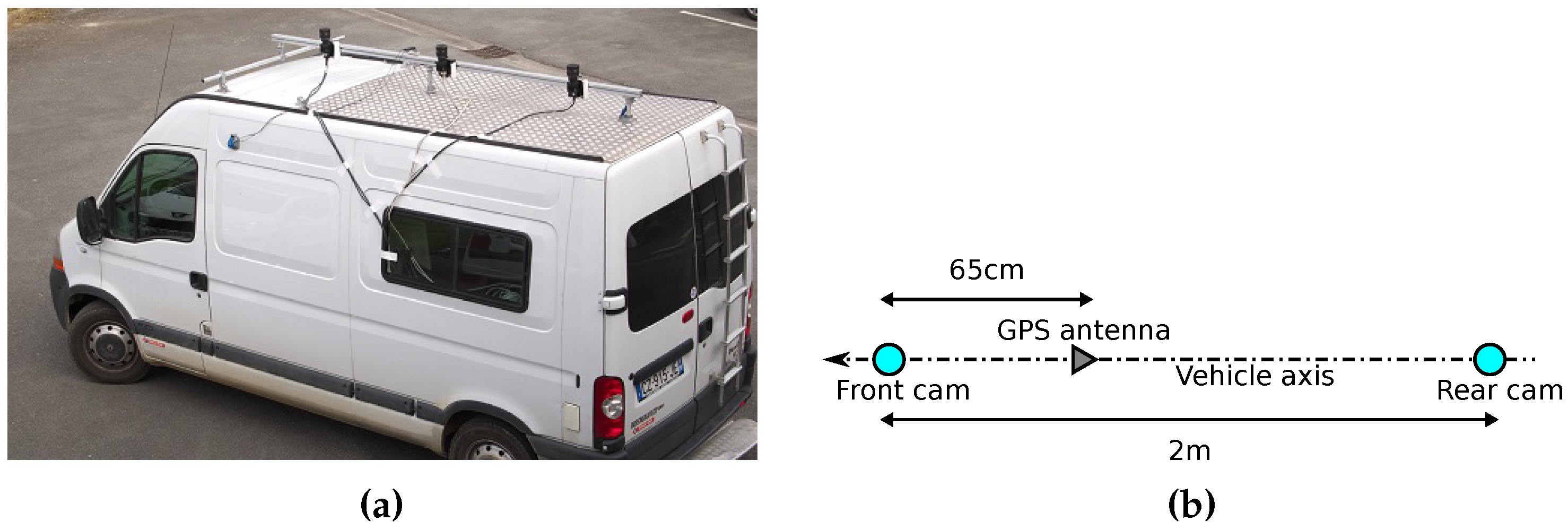
2.1. Sample Scenes and Configuration
- Cap3/0900, sequence duration = 29 s, Geographic North = 318°, before the junction between rue Saint André and rue de la Halle
- Cap4/1560, sequence duration = 32 s, Geographic North = 115°, before the junction between rue Esquermoise and rue de Thiers
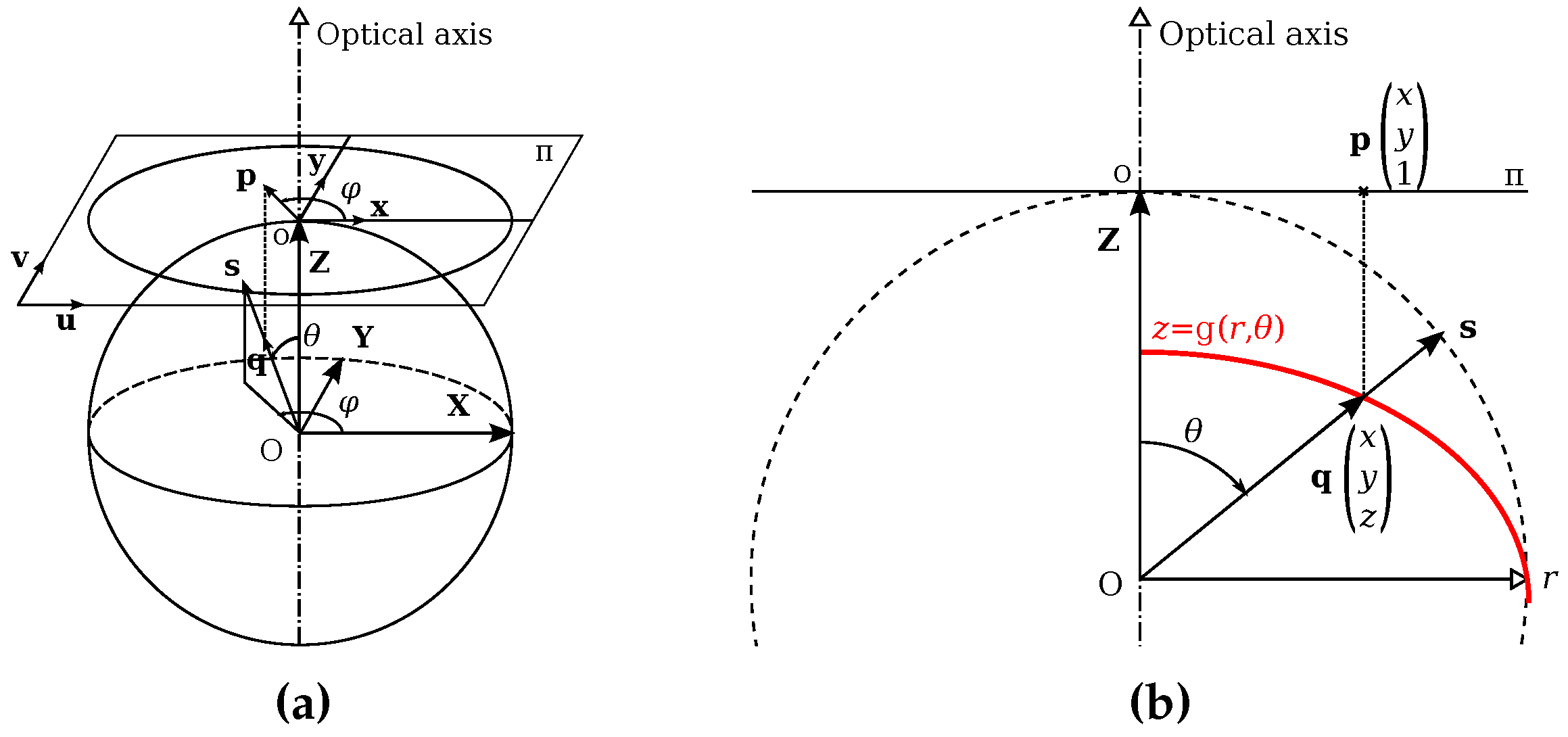
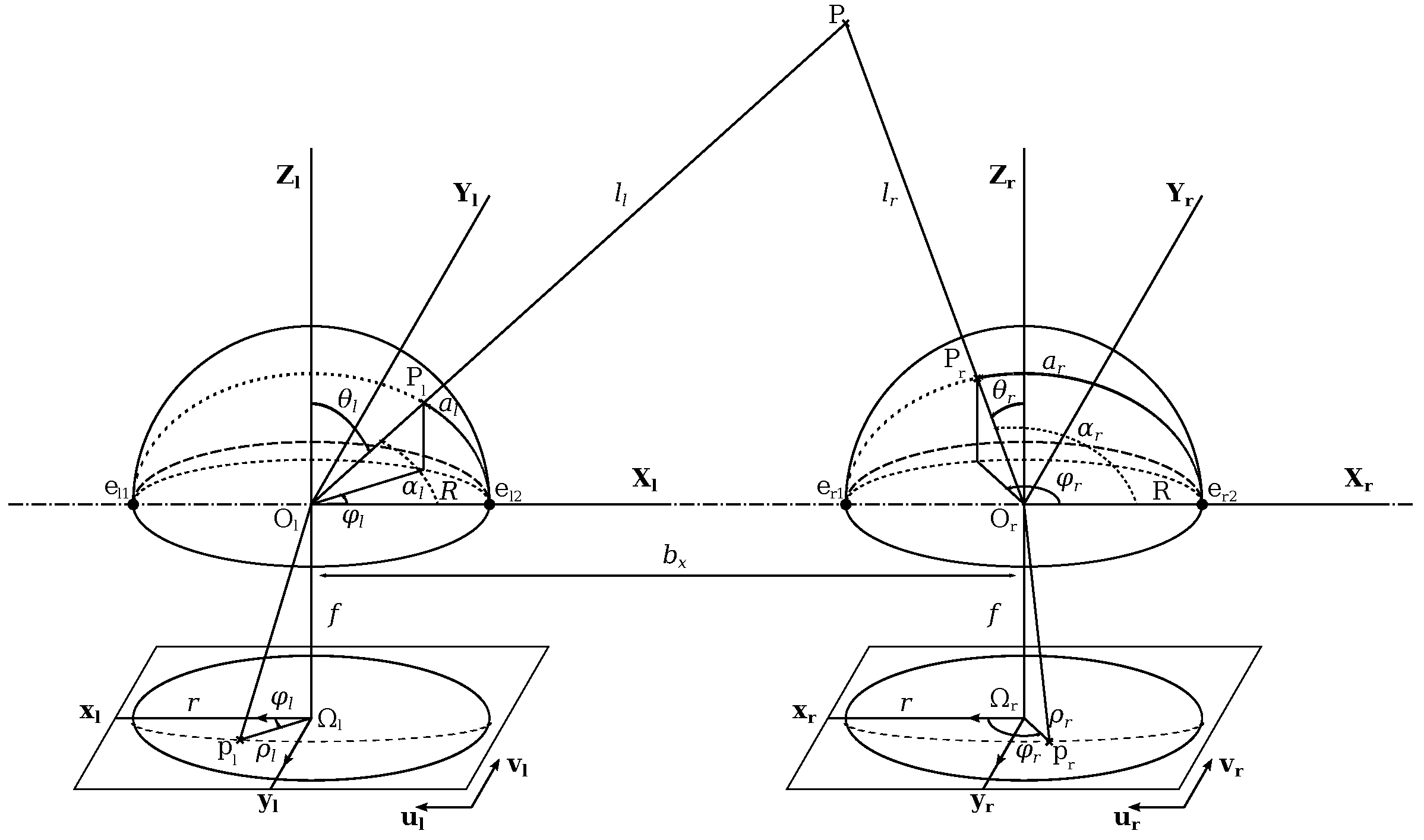
2.2. Fisheye Projection Model
- Calibration is done to know intrinsic camera parameters and extrinsic parameters between two points of view;
- A matching step is applied according to stereovision principles and the epipolar geometry for spherical model cameras;
- The point cloud is processed to extract semantic information and to identify structures like walls.
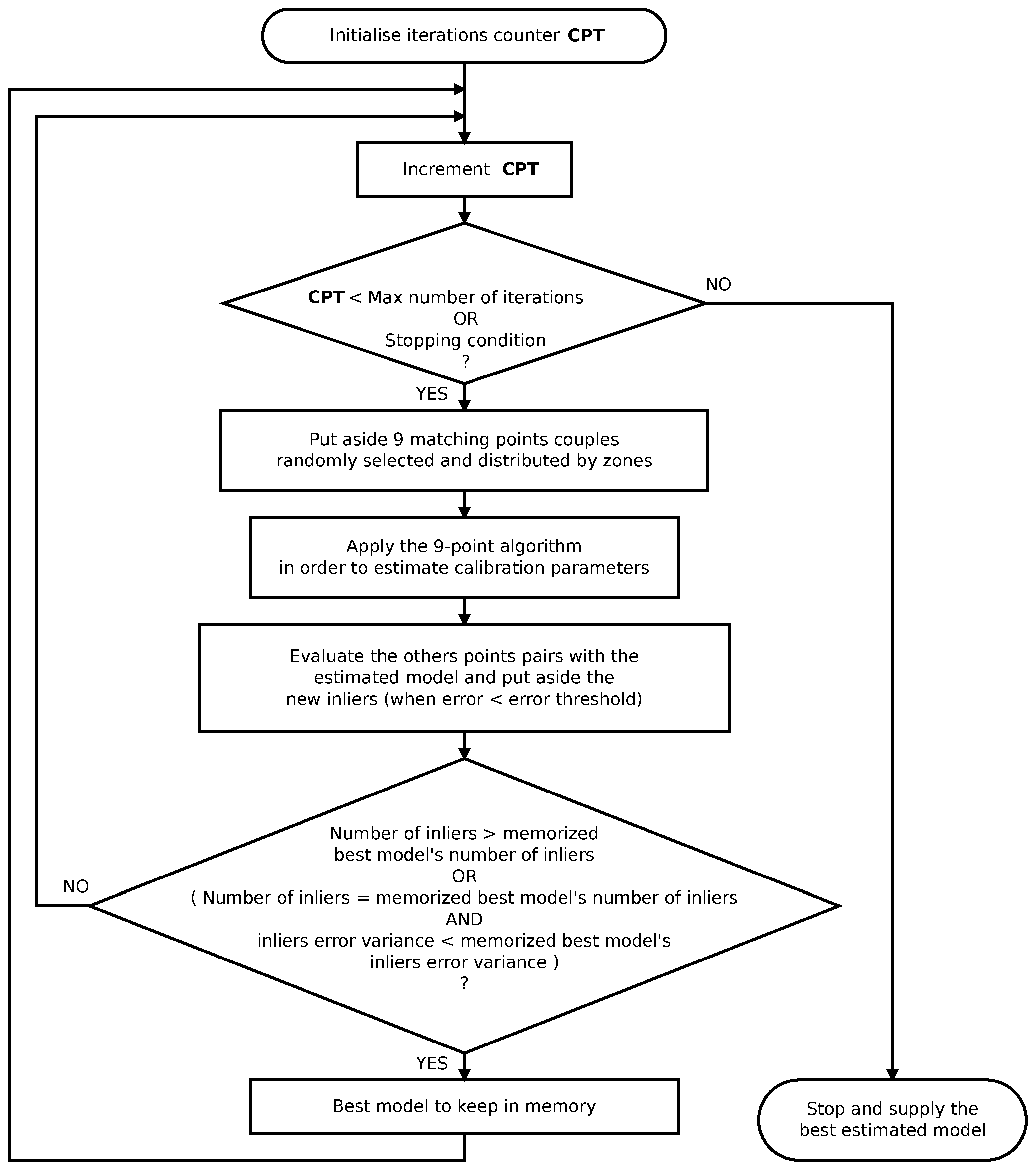
2.3. Self-Calibration
- to estimate model parameters linking every scene point P to its projection p in the image;
- to find parameters needed for the computation of conjugate epipolar curves from which the matching process is assessed.
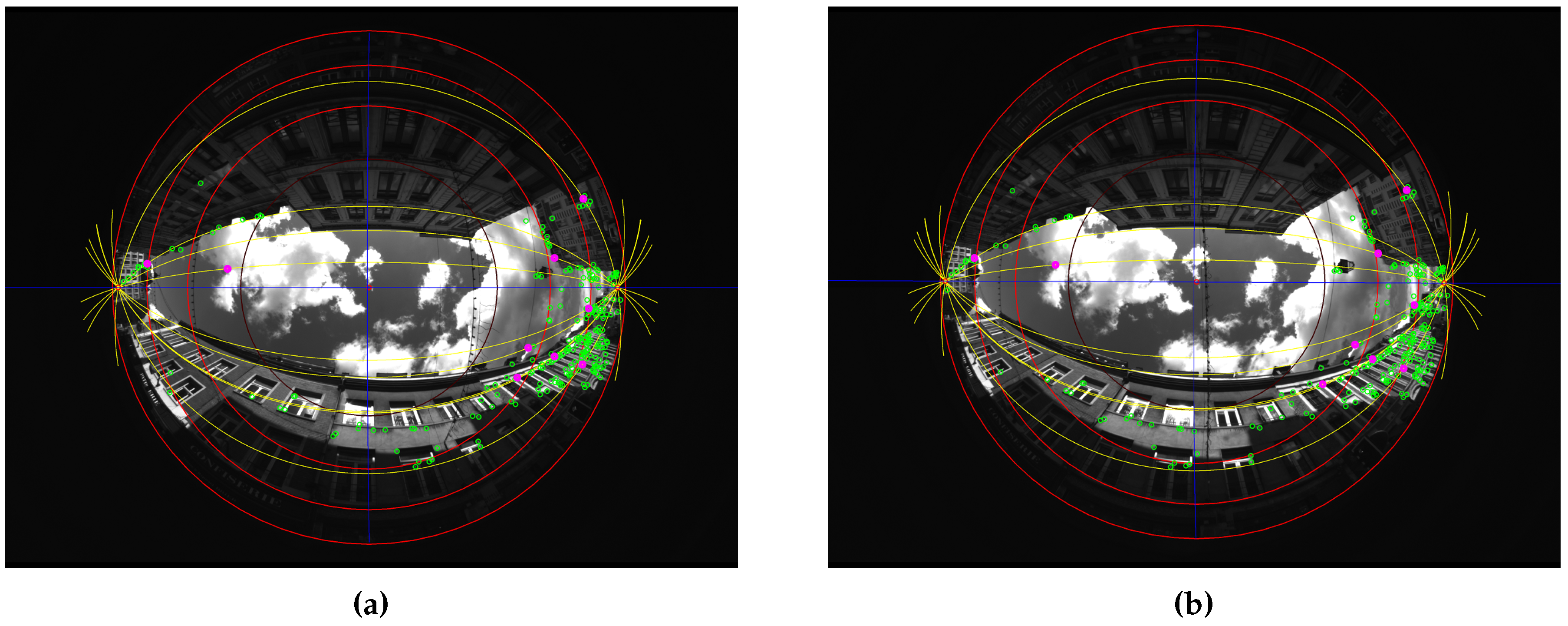
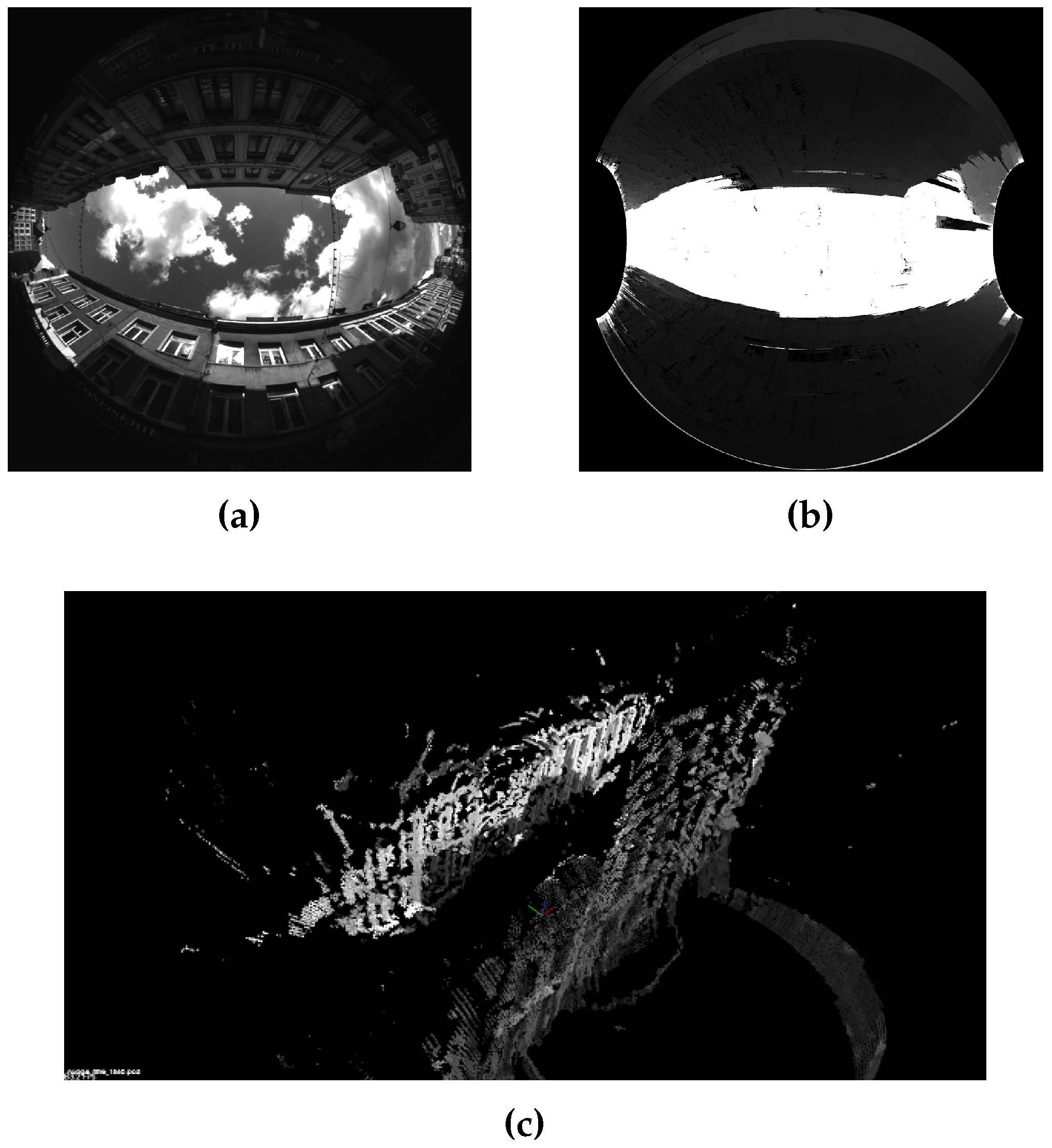
2.4. Stereo Matching and 3D Scene Generation
2.5. Plane Extraction and Evaluation
- a 2D histogram in the plane, following the direction,
- an elevation map.
- 1 pixel dilation and erosion (closing), to fill holes in the imprint;
- Binary thresholding;
- Thinning of Zhang and Suen [51] in order to avoid the detection of overlapping segments.
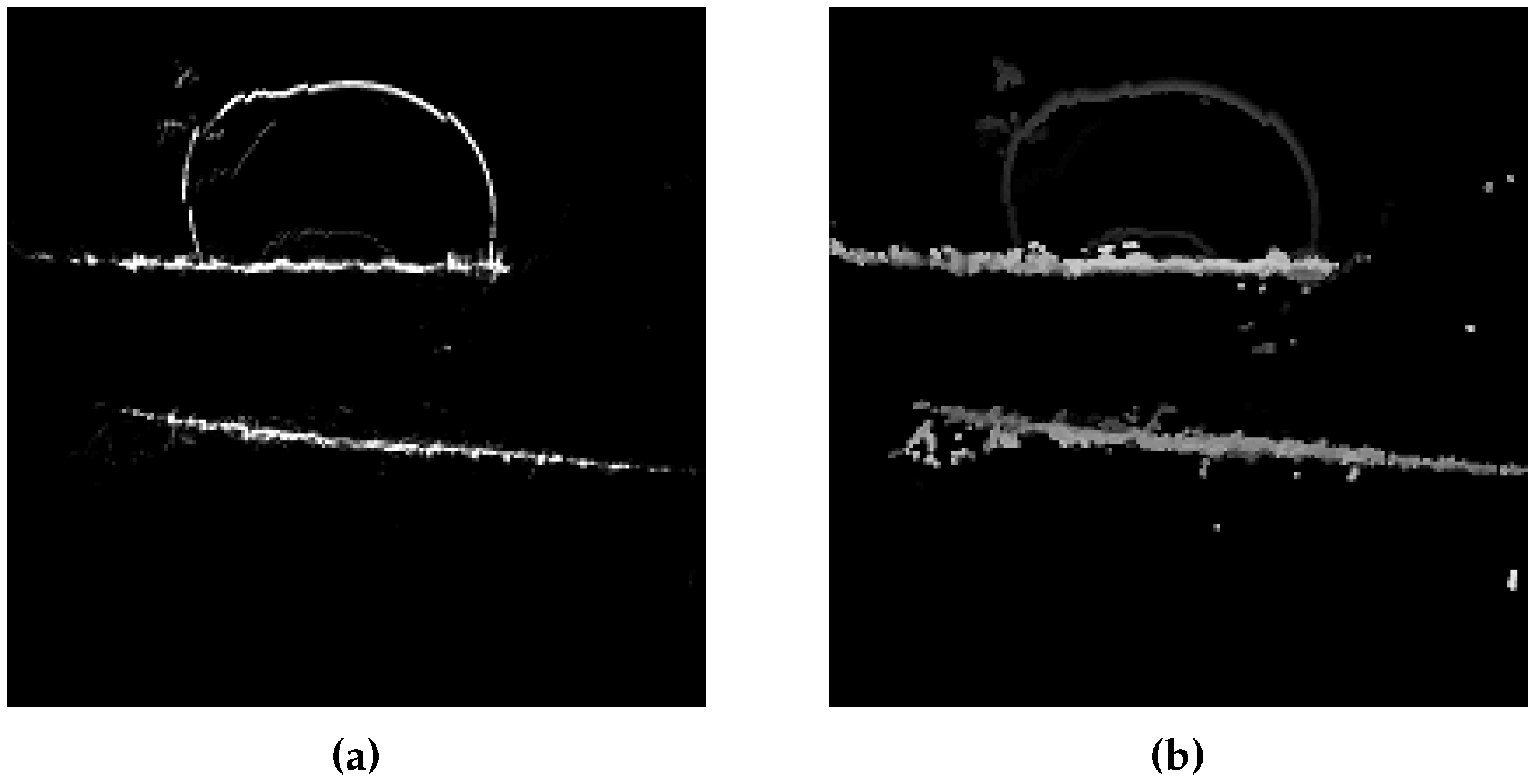
- Ground prints and detected segments;
- Projection of top points in the fisheye view;
- Projection of extracted planes in the fisheye view.
- Street width estimated from extracted planes (Width between the structures’ planes facing along the street).
3. GNSS Positioning Improvement Based on Generated 3D Model
- Detection of NLOS signals;
- Estimation of NLOS pseudoranges delay;
- Position computation replacing NLOS pseudoranges by corrected ones if available.
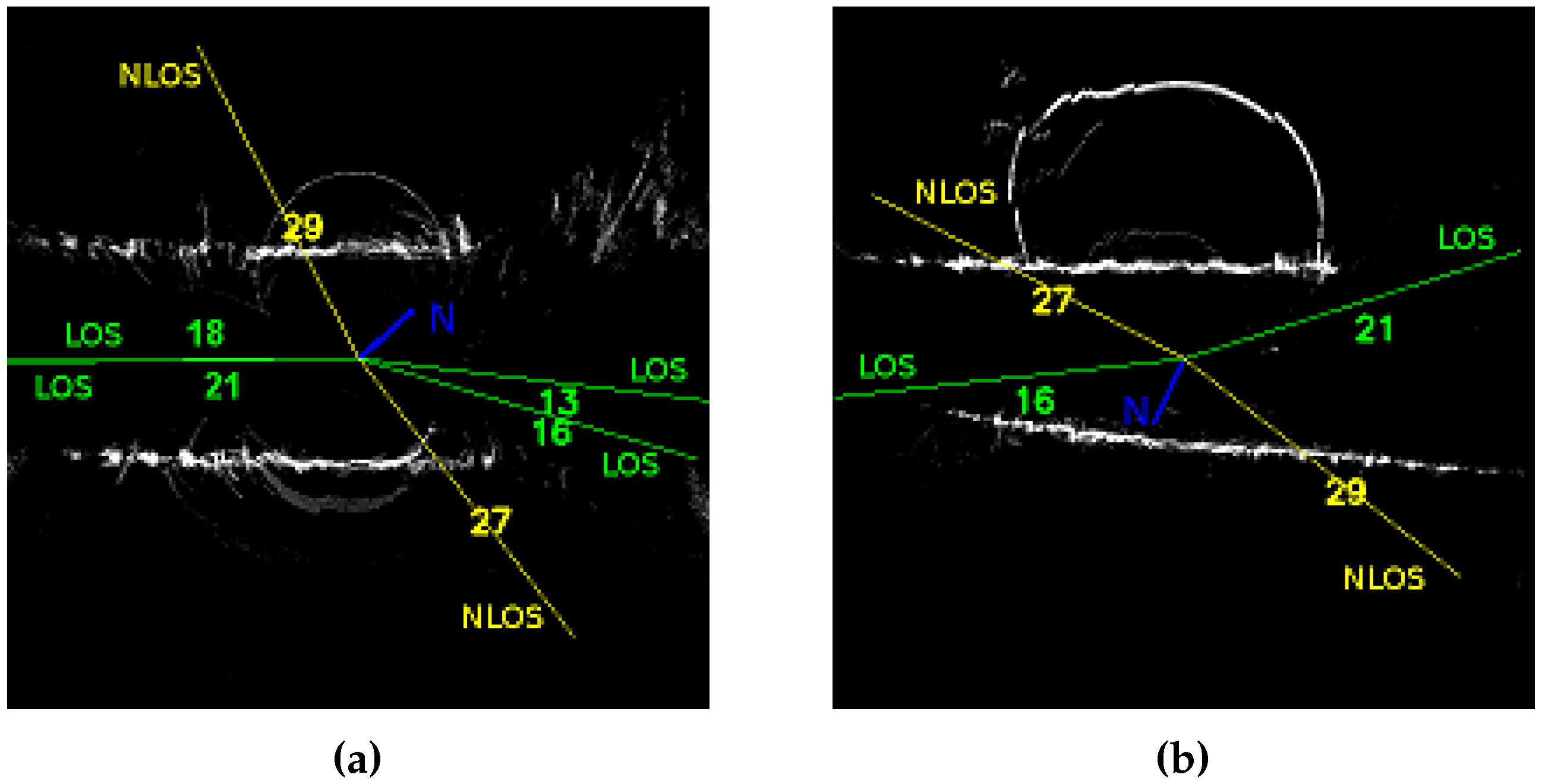
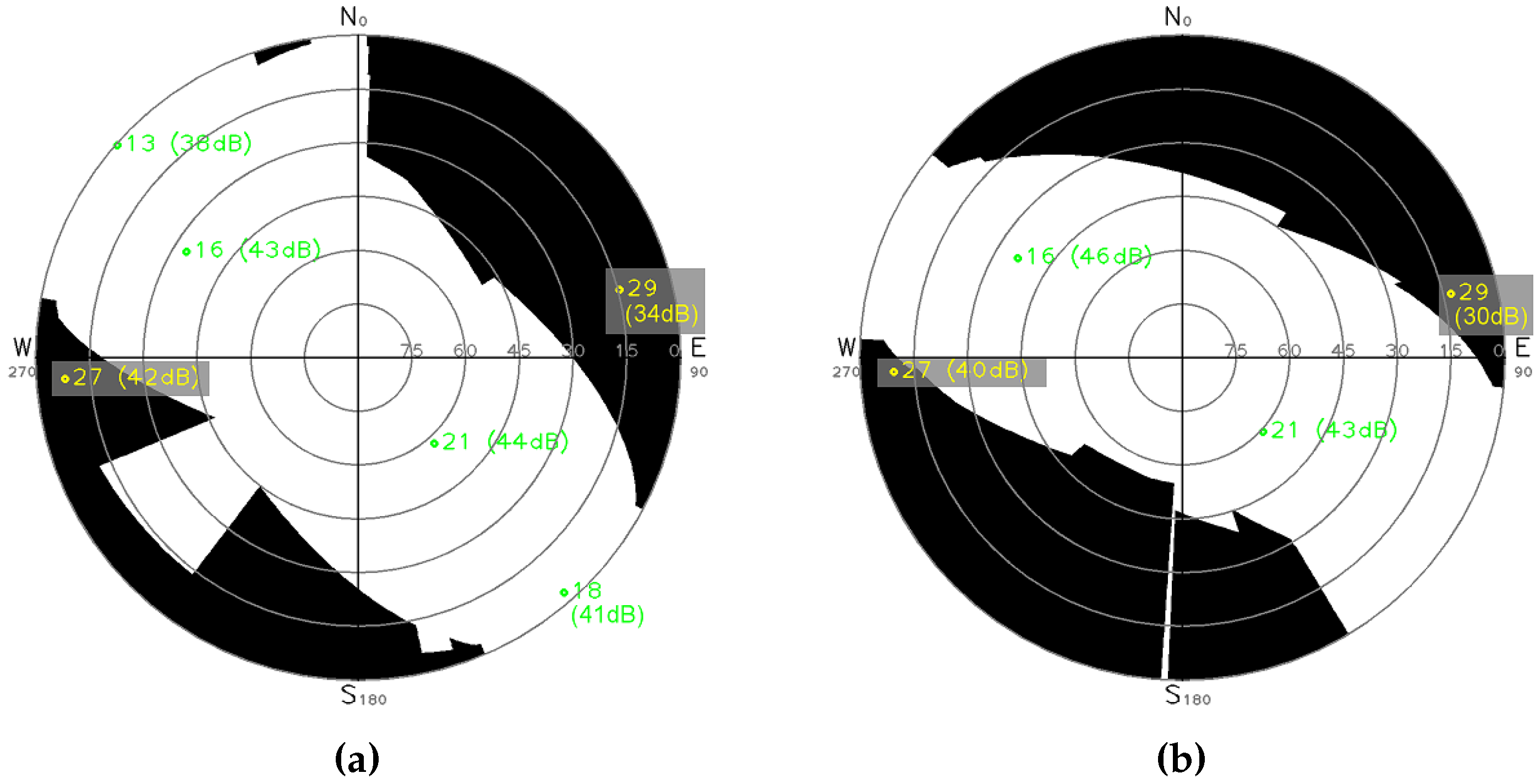
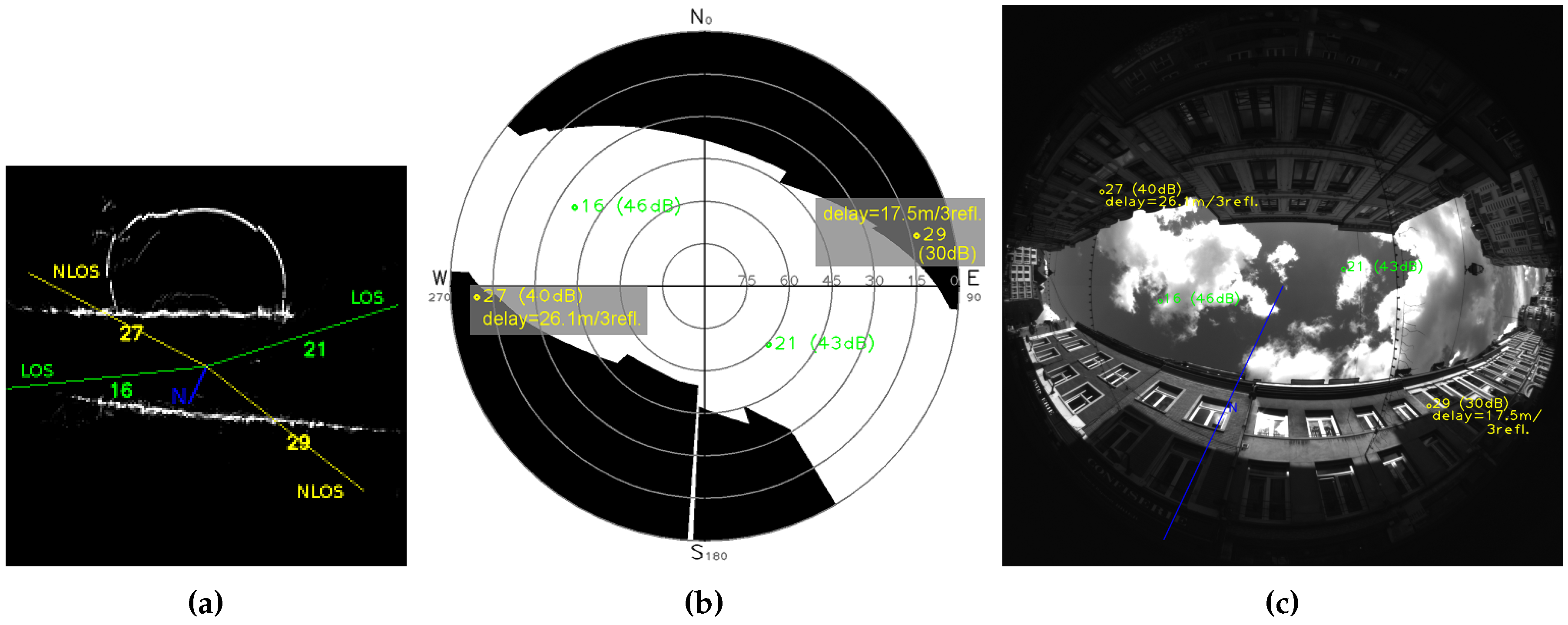
3.1. Generation of Visibility Masks
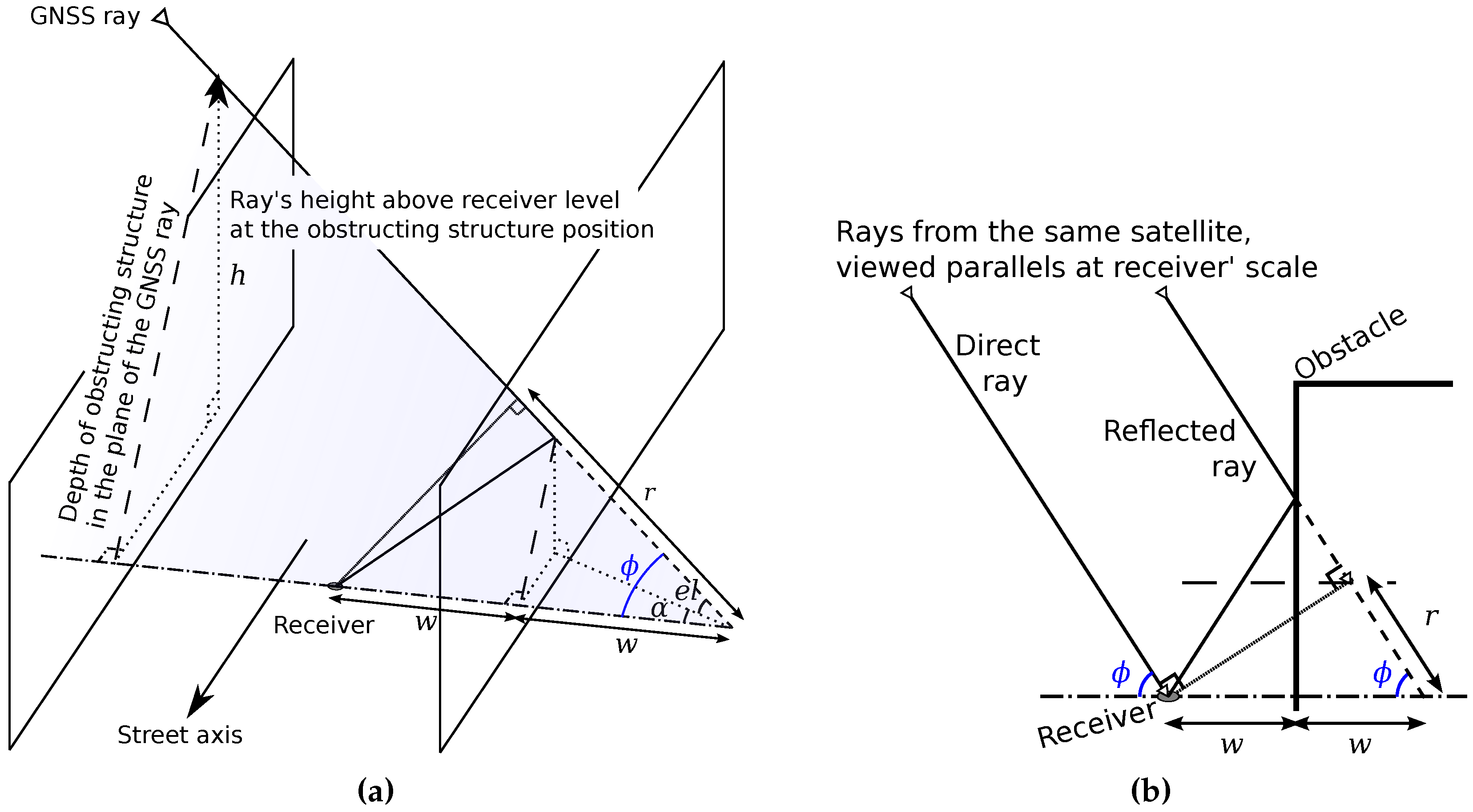
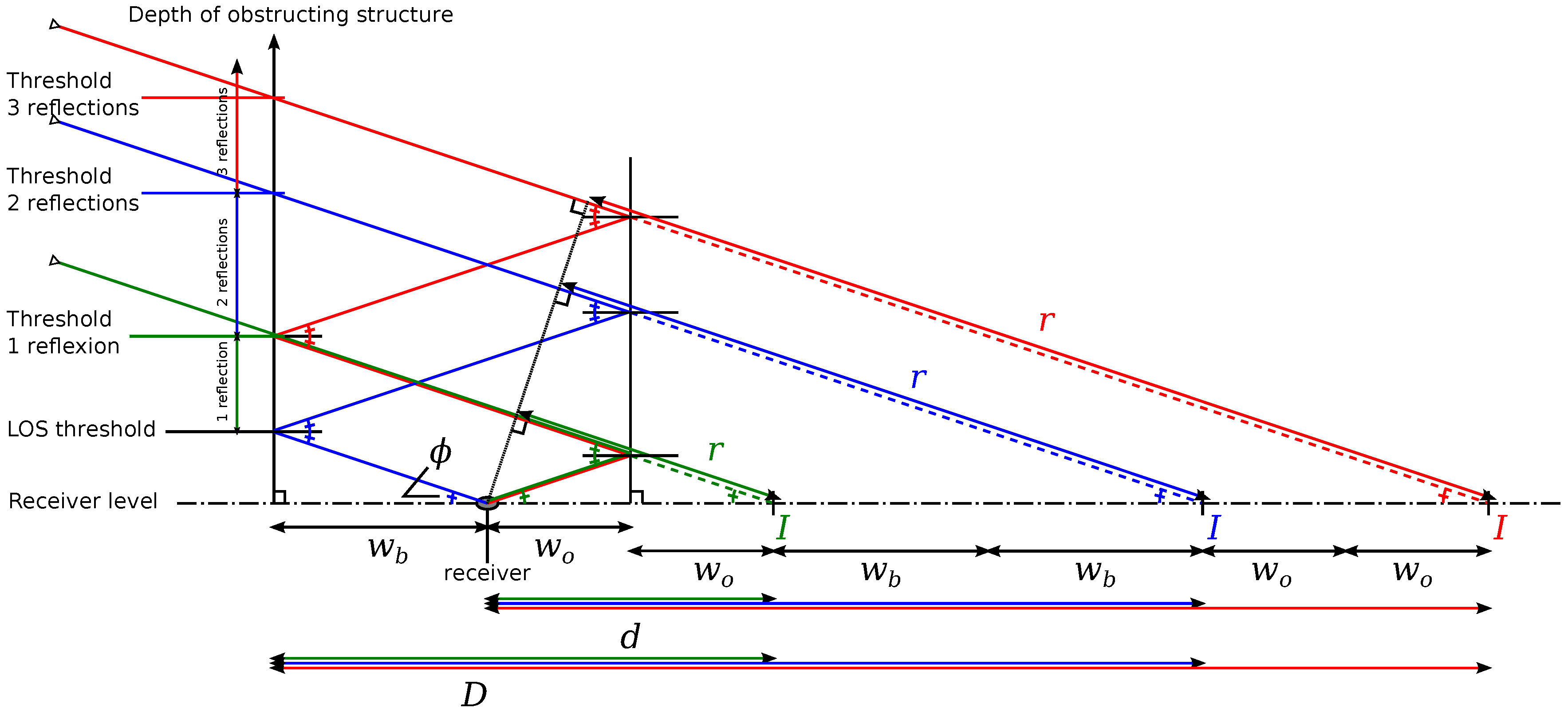
3.2. Delay Estimation with a 3 Reflections Model
- To extract the planes from the 3D point cloud and generate a visibility mask at receiver’s position;
- To detect LOS and NLOS satellites with the visibility mask;
- To measure structures distances on both street sides according to the “urban trench” model;
- For NLOS satellites, to measure the height of blocking structure and estimate the delay r in order to compute .
4. Evaluation of GPS Localization with Proposed Method
4.1. Validation Procedure
4.2. Metrics
- availability rate for 4 satellites (in percent);
- average error (euclidean distance) compared to the truth position (in metres);
- standard deviation (in metres).
- NLOS exclusion;
- delay estimation for 1 reflection;
- delay estimation for 1 to 3 reflections,
- CN0 threshold: let be the threshold value, is assumed NLOS a satellite whose CN0 < otherwise it is LOS, to do for dBHz;
- proposed visibility mask obtained thanks to the generated 3D model.
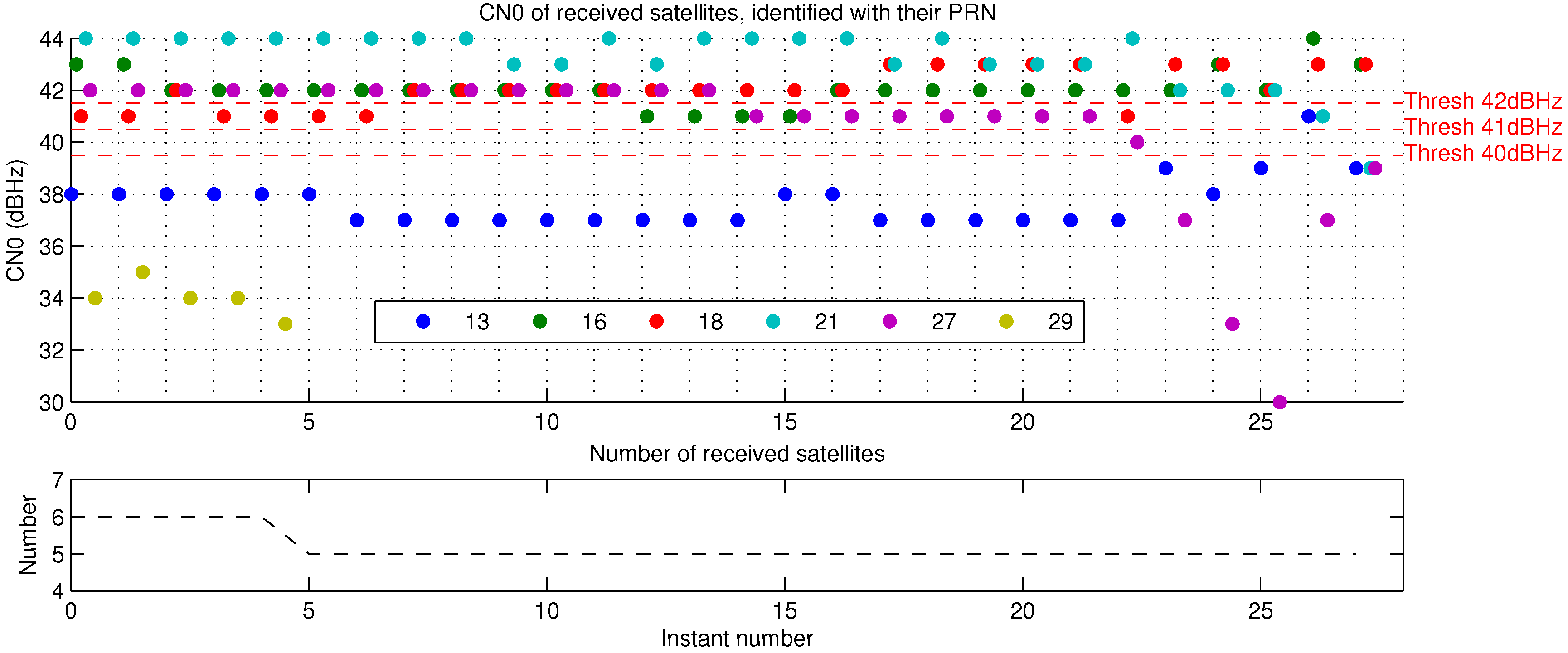
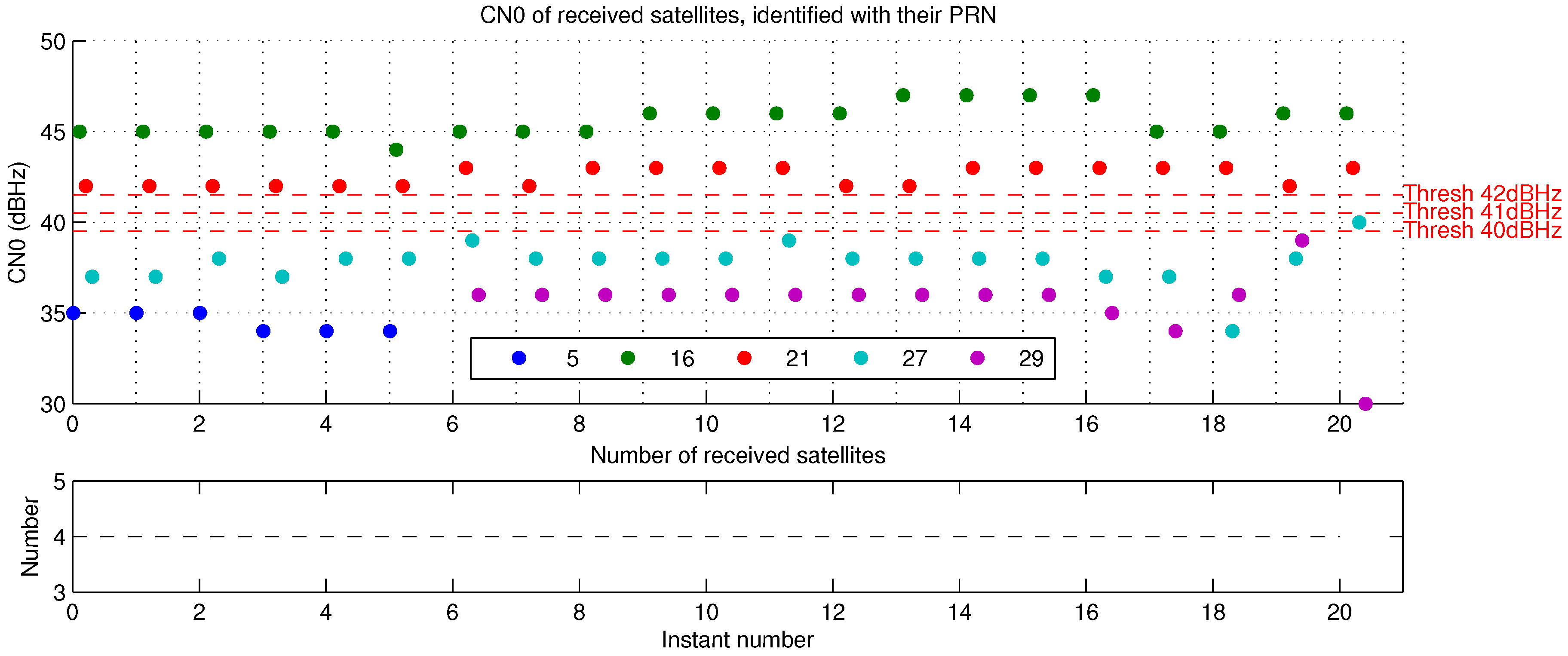
4.3. Results
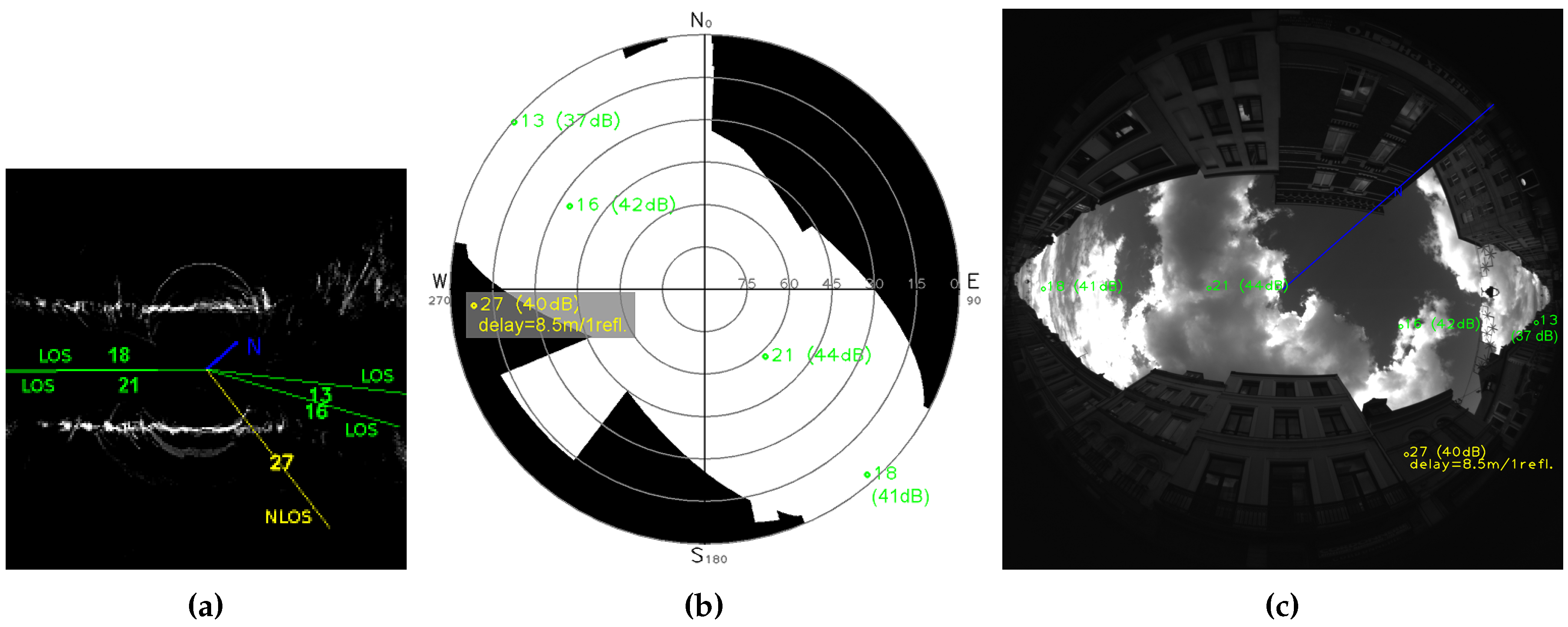
- 40 dBHz, only satellite PRN 13 is detected NLOS;
- 41 dBHz, satellites PRN 13 and 27 are detected NLOS, it might be the best CN0 threshold result for this instant;
- 42 dBHz, satellites PRN 13, 27 and 18 (41 dBHz) are detected NLOS, detection of PRN 18 is a false detection as can be shown thanks to Figure 19.
5. Conclusions
- A correction instead of a rejection of NLOS, does not imply loss of service availability;
- No environment data to store;
- No updates of embedded data to do, because the structure of the environment is updated on line;
- No re-positioning problem in the 3D model, because the reference position is known thanks to the 3D model built around it.
5.1. Perspectives
- To develop a real-time implementation of the procedure;
- To extend the reflection model to a reflection and diffraction model;
- To experiment with more than one GNSS constellation (currently only GPS);
- To use a configuration with very precise data synchronisation (≪ 1 ms) in order to evaluate the method with synchronised GPS RTK truth and in dynamic situations;
- To detect vegetation for a specific diffraction model;
- To improve the plane extraction to be more accurate in height boundaries.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CN0 | Carrier-to-receiver Noise density |
| DGNSS | Differential Global Navigation Satellite System |
| DOP | Dilution Of Precision |
| EKF | Extended Kalman Filter |
| ENU | East North Up |
| GDOP | Geometrical Dilution Of Precision |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| HDOP | Horizontal Dilution Of Precision |
| HMRF-EM | Hidden Markov Random Fields Expectation-Maximization |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| LOS | Line Of Sight |
| NLOS | Non Line Of Sight |
| PR | PseudoRange |
| PRN | PseudoRandom Noise number |
| RAIM FDE | Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring, Fault Detection and Exclusion |
| RANSAC | RANdom SAmple Consensus |
| RMS | Root Mean Square |
| RTK | Real Time Kinematic |
| SIFT | Scale-Invariant Feature Transform |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization And Mapping |
| WGS84 | World Geodetic System 1984 |
References
- Groves, P.D. Principles of GNSS, Inertial, and Multisensor Integrated Navigation Systems; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Marais, J. Localisation de Mobiles Terrestres par Satellites: Mise en Oeuvre D’outils Permettant L’analyse de L’influence des Conditions de Propagation et des Effets de Masques sur la Disponibilité du Service Offert. Ph.D. Thesis, Sciences et Technologies, Université Lille1, Villeneuve-d’Ascq, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Viandier, N. Modélisation et Utilisation des Erreurs de Pseudodistances GNSS en Environnement Transport Pour L’amélioration des Performances de Localisation. PhD Thesis, Ecole Centrale de Lille, Villeneuve-d’Ascq, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marais, J.; Meurie, C.; Attia, D.; Ruichek, Y.; Flancquart, A. Toward accurate localization in guided transport: Combining GNSS data and imaging information. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2014, 43, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.; Marais, J. Weighting models for GPS Pseudorange observations for land transportation in urban canyons. In Proceedings of the 6th European Workshop on GNSS Signals and Signal Processing, Neubiberg, Germany, 5–6 December 2013; p. 4.
- Suzuki, T.; Kubo, N. N-LOS GNSS signal detection using fish-eye camera for vehicle navigation in urban environments. In Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2014), Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 2014; pp. 1897–1906.
- Gakne, P.V.; Petovello, M. Assessing image segmentation algorithms for sky identification in GNSS. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Banff, AB, Canada, 13–16 October 2015; pp. 1–7.
- Sanromà Sánchez, J.; Gerhmann, A.; Thevenon, P.; Brocard, P.; Ben Afia, A.; Julien, O. Use of a FishEye Camera for GNSS NLOS Exclusion and Characterization in Urban Environments. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, Monterey, CA, USA, 25–28 January 2016.
- Obst, M.; Bauer, S.; Wanielik, G. Urban multipath detection and mitigation with dynamic 3D maps for reliable land vehicle localization. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ION Position Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Myrtle Beach, SC, USA, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 685–691.
- Bourdeau, A.; Sahmoudi, M.; Tourneret, J.Y. Constructive use of GNSS NLOS-multipath: Augmenting the navigation Kalman filter with a 3D model of the environment. In Proceedings of the 2012 15th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Singapore, 9–12 July 2012; pp. 2271–2276.
- Sahmoudi, M.; Bourdeau, A.; Tourneret, J.Y. Deep fusion of vector tracking GNSS receivers and a 3D city model for robust positioning in urban canyons with NLOS signals. In Proceedings of the 2014 7th ESA Workshop on Satellite Navigation Technologies and European Workshop on GNSS Signals and Signal Processing (NAVITEC), Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 3–5 December 2014; pp. 1–7.
- Peyret, F.; Bétaille, D.; Carolina, P.; Toledo-Moreo, R.; Gomez-Skarmeta, A.; Ortiz, M. GNSS Autonomous Localization: NLOS Satellite Detection Based on 3-D Maps. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2014, 21, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, P.D.; Wang, L.; Adjrad, M.; Ellul, C. GNSS Shadow Matching: The Challenges Ahead. In Proceedings of the 28th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2015), Tampa, FL, USA, 14–18 September 2015; pp. 2421–2443.
- Miura, S.; Hsu, L.T.; Chen, F.; Kamijo, S. GPS Error Correction With Pseudorange Evaluation Using Three-Dimensional Maps. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 16, 3104–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.T.; Gu, Y.; Kamijo, S. NLOS Correction/Exclusion for GNSS Measurement Using RAIM and City Building Models. Sensors 2015, 15, 17329–17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sato, Y.; Oishi, T.; Ikeuchi, K. Identifying Reflected GPS Signals and Improving Position Estimation Using 3D Map Simultaneously Built with Laser Range Scanner; Technical Report; Computer Vision Laboratory, Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Marais, J.; Berbineau, M.; Nahimana, D.F. Effect of alternate path on satellite positioning accuracy in an urban environment. In Proceedings of the International Communications Satellite Systems Conference (ICSSC), Rome, Italy, 26–30 September 2005; p. 12.
- Ercek, R.; De Doncker, P.; Grenez, F. Study of Pseudo-Range Error due to Non-Line-of-Sight-Multipath in Urban Canyons. In Proceedings of the 18th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS ’05), Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2005.
- Bétaille, D.; Peyret, F.; Ortiz, M. How to enhance accuracy and integrity of satellite positioning for mobility pricing in cities: The Urban Trench method. In Proceedings of the Transport Research Arena 2014, Paris, France, 14–17 April 2014.
- Gehrig, S.K.; Rabe, C.; Krüger, L. 6D Vision Goes Fisheye for Intersection Assistance. In Proceedings of the Canadian Conference on Computer and Robot Vision, Windsor, ON, Canada, 28–30 May 2008; pp. 34–41.
- Li, S. Binocular Spherical Stereo. IEEE Trans. Iintell. Transp. Syst. 2008, 9, 589–600. [Google Scholar]
- Ragot, N. Conception d’un Capteur de Stéréovision Omnidirectionnelle: Architecture, Étalonnage et Applications À la Reconstruction de Scènes 3D. Ph.D. Thesis, École Doctorale Sciences Physiques, Mathématiques et de l’Information pour l’Ingénieur, Université de Rouen, Institut de Recherche en Systèmes Electroniques EMbarqués, Saint-Etienne du Rouvray, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- BOSS Project—On Board Wireless Secured Video Surveillance. 2009. Available online: http://www.multitel.be/BOSS/ (accessed on 18 12 2015).
- Mičušìk, B. Two-View Geometry of Omnidirectional Cameras. Ph.D. Thesis, Czech Technical University, Prague, Czech Republic, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, C.; Stewenius, H. A Nine-point Algorithm for Estimating Para-Catadioptric Fundamental Matrices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR ’07), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8.
- Lhuillier, M.; Quan, L. Reconstruction quasi-dense et modèles 3D à partir d’une séquence d’images. In Proceedings of the Congrès AFRIF-AFIA Reconnaissance des Formes et Intelligence Artificielle, Toulouse, France, 2004; pp. 895–904. (In French)
- Nieradka, G.; Butkiewicz, B. Features stereo matching based on fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the International Fuzzy Systems Association—European Society for Fuzzy Logic and Technology (IFSA-EUSFLAT), Lisbon, Portugal, 20–24 July 2009.
- Fabbri, R.; Kimia, B. 3D Curve Sketch: Flexible Curve-Based Stereo Reconstruction and Calibration. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010.
- Lee, S.H.; Kanatsugu, Y.; Park, J.I. MAP-Based Stochastic Diffusion for Stereo Matching and Line Fields Estimation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 47, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstmann, S.; Kanou, Y.; Ohya, J.; Thuering, S.; Schmitt, A. Real-Time Stereo by using Dynamic Programming. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004.
- Deng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Lin, X.; Tang, X. A Symmetric Patch-Based Correspondence Model for Occlusion Handling. In Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE International Conference on Association for Computer Vision, Beijing, China, 17–21 October 2005; pp. 316–1322.
- Ruichek, Y. Perception de L’environnement par Stéréovision, Application à la Sécurité Dans les Systèmes de Transports Terrestres; Habilitation à Diriger des Recherches; Université des Sciences et Technologies de Lille: Villeneuve-d’Ascq, France, 2005. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.P.; Yeung, S.K.; Jia, J.; Tang, C.K. Quasi-Dense 3D Reconstruction using Tensor-based Multiview Stereo. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010.
- Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, W.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Gong, X. Real-time stereo vision system using adaptive weight cost aggregation approach. EURASIP J. Image. Video Process. 2011, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, D. Segmentation D’images par Combinaison Adaptative Couleur-Texture et Classification de Pixels : Applications à la Caractérisation de L’environnement de Réception de Signaux GNSS. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Technologie de Belfort-Montbéliard, Belfort, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cannelle, B.; Paparoditis, N.; Pierrot-Deseilligny, M.; Papelard, J.P. Off-line vs. On-line Calibration of a Panoramic-Based Mobile Mapping System. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Melbourne, Australia, 25 August–1 September 2012; Volume I-3.
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chum, O. Two-View Geometry Estimation by Random Sample and Consensus. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of the Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University, Prague, Czech Republic, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lemonde, V. Stéréovision Embarquée Sur véhicule: De L’auto-Calibrage à la Détection D’obstacles. PhD Thesis, INSA de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, J. Construction de modèles 3D à partir de données vidéo fisheye—Application à la localisation en milieu urbain. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Technologie de Belfort-Montbéliard, Institut Français des Sciences et Technologies des Transports de l’Aménagement et des Réseaux, Villeneuve-d’Ascq, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Baselgia, C. Fast Camera Motion Estimation for Visual Navigation. Master’s Thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chambon, S. Mise en Correspondance StéRéOscopique D’images Couleur en Présence D’occultations. Ph.D. Thesis, École Doctorale Informatique et Télécommunications, Université Paul Sabatier—Toulouse III, Institut de Recherche en Informatique de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardós, J.D. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, D.; Engel, J.; Cremers, D. Large-Scale Direct SLAM for Omnidirectional Cameras. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015.
- Indelman, V.; Williams, S.; Kaess, M.; Dellaert, F. Information fusion in navigation systems via factor graph based incremental smoothing. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, J.; Ambellouis, S.; Ruichek, Y. Equisolid fisheye stereovision calibration and point cloud computation. In Proceedings of the 2013 ISPRS-SSG Conference on Serving Society with Geoinformatics, Antalya, Turkey, 11–17 November 2013; p. 6.
- Moreau, J.; Ambellouis, S.; Ruichek, Y. 3D Reconstruction of Urban Environments Based on Fisheye Stereovision. In Proceedings of the 2012 Eighth International Conference on Signal Image Technology and Internet Based Systems (SITIS), Naples, Italy, 25–29 November 2012; pp. 36–41.
- Illingworth, J.; Kittler, J. A survey of the hough transform. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1988, 44, 87–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matas, J.; Galambos, C.; Kittler, J. Robust Detection of Lines Using the Progressive Probabilistic Hough Transform. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2000, 78, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Suen, C.Y. A Fast Parallel Algorithm for Thinning Digital Patterns. Commun. ACM 1984, 27, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, D.; Behnke, S. Approximate Triangulation and Region Growing for Efficient Segmentation and Smoothing of Range Images. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2014, 62, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, R.B. Dilution of Precision; GPS World: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1999; pp. 52–59. [Google Scholar]



| Topic | Sub-Topic | References |
|---|---|---|
| NLOS detection | CN0 threshold | [2,3,4] |
| Vision segmentation | [5,6,7,8] | |
| Recorded 3D data | [9,10,11,12,13,14,15] | |
| Online 3D data | [16] (lidar) | |
| Positioning considering LOS/NLOS status | NLOS rejection | [4,6,7,9,12,16] |
| LOS/NLOS weighting | [5] | |
| LOS/NLOS Kalman filter | [10,11] | |
| Shadow matching | [13] | |
| PR delay correction | Local reflections | [3,17,18,19] |
| Local diffractions | [3,18] | |
| Multipath | [3,18] | |
| Delay simulation at candidates positions | [14,15] | |
| Estimator based on measures | [8] | |
| Omnidirectional vision calibration | Pattern | [20,21,22,23] |
| Self-calibration | [24,25] | |
| Stereo matching | Sparse | [26,27,28] |
| Dense | [29,30,31,32,33,34] |
| Scene | Maps and Projections | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2D Segments | Top Points | Planes | |
| Cap3/0900 | 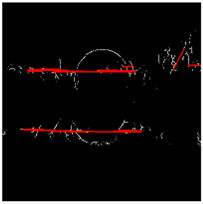 |  | 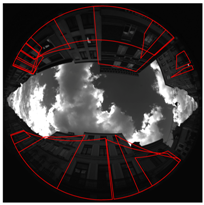 |
| Cap4/1560 | 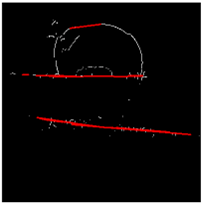 |  |  |
| Scene | True Width | Trench Measure | Difference (Accuracy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cap3/0900 | 12.3 m | 12.35 m | 0.05 m |
| Cap4/1560 | 9.5 m | 10.52 m | 1.02 m |
| Reflections | Delay | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| ∞ | ⩾ 3 |
| Correction | LOS and NLOS Distinction Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 dBHz | CN0 Threshold 41 dBHz | 42 dBHz | Proposed Visibility Mask | |
| Without | 2D positioning = 22.73 m; Standard deviation = 7.31 m | |||
| NLOS rejection | Avail = 85.71% | Avail = 82.14% | Avail = 21.43% | Avail = 100% |
| = 61.77 m | = 61.83 m | = 63.35 m | = 98.73 m | |
| Std dev = 3.21 m | Std dev = 3.27 m | Std dev = 2.51 m | Std dev = 17.78 m | |
| 1 reflection | = 21.34 m | = 20.84 m | = 16.96 m | = 12.64 m |
| Std dev = 9.52 m | Std dev = 9.47 m | Std dev = 8.45 m | Std dev = 1.80 m | |
| 1 to 3 reflections | = 22.69 m | = 22.19 m | = 18.60 m | = 11.50 m |
| Std dev = 11.59 m | Std dev = 11.49 m | Std dev = 10.19 m | Std dev = 3.13 m | |
| Correction | LOS and NLOS Distinction Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 dBHz | CN0 Threshold 41 dBHz | 42 dBHz | Proposed Visibility Mask | |
| Without | 2D positioning = 16.70 m; Standard deviation = 3.63 m | |||
| NLOS rejection | Avail = 0% | Avail = 0% | Avail = 0% | Avail = 0% |
| = N/A | = N/A | = N/A | = N/A | |
| Std dev = N/A | Std dev = N/A | Std dev = N/A | Std dev = N/A | |
| 1 reflection | = 12.85 m | = 12.47 m | = 12.47 m | = 12.47 m |
| Std dev = 4.65 m | Std dev = 3.58 m | Std dev = 3.58 m | Std dev = 3.58 m | |
| 1 to 3 reflections | = 7.49 m | = 6.38 m | = 6.38 m | = 6.38 m |
| Std dev = 6.74 m | Std dev = 2.20 m | Std dev = 2.20 m | Std dev = 2.20 m | |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreau, J.; Ambellouis, S.; Ruichek, Y. Fisheye-Based Method for GPS Localization Improvement in Unknown Semi-Obstructed Areas. Sensors 2017, 17, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010119
Moreau J, Ambellouis S, Ruichek Y. Fisheye-Based Method for GPS Localization Improvement in Unknown Semi-Obstructed Areas. Sensors. 2017; 17(1):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010119
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreau, Julien, Sébastien Ambellouis, and Yassine Ruichek. 2017. "Fisheye-Based Method for GPS Localization Improvement in Unknown Semi-Obstructed Areas" Sensors 17, no. 1: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010119
APA StyleMoreau, J., Ambellouis, S., & Ruichek, Y. (2017). Fisheye-Based Method for GPS Localization Improvement in Unknown Semi-Obstructed Areas. Sensors, 17(1), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010119






