Theoretical and Experimental: The Synthetic and Anion-Binding Properties of Tripodal Salicylaldehyde Derivatives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus
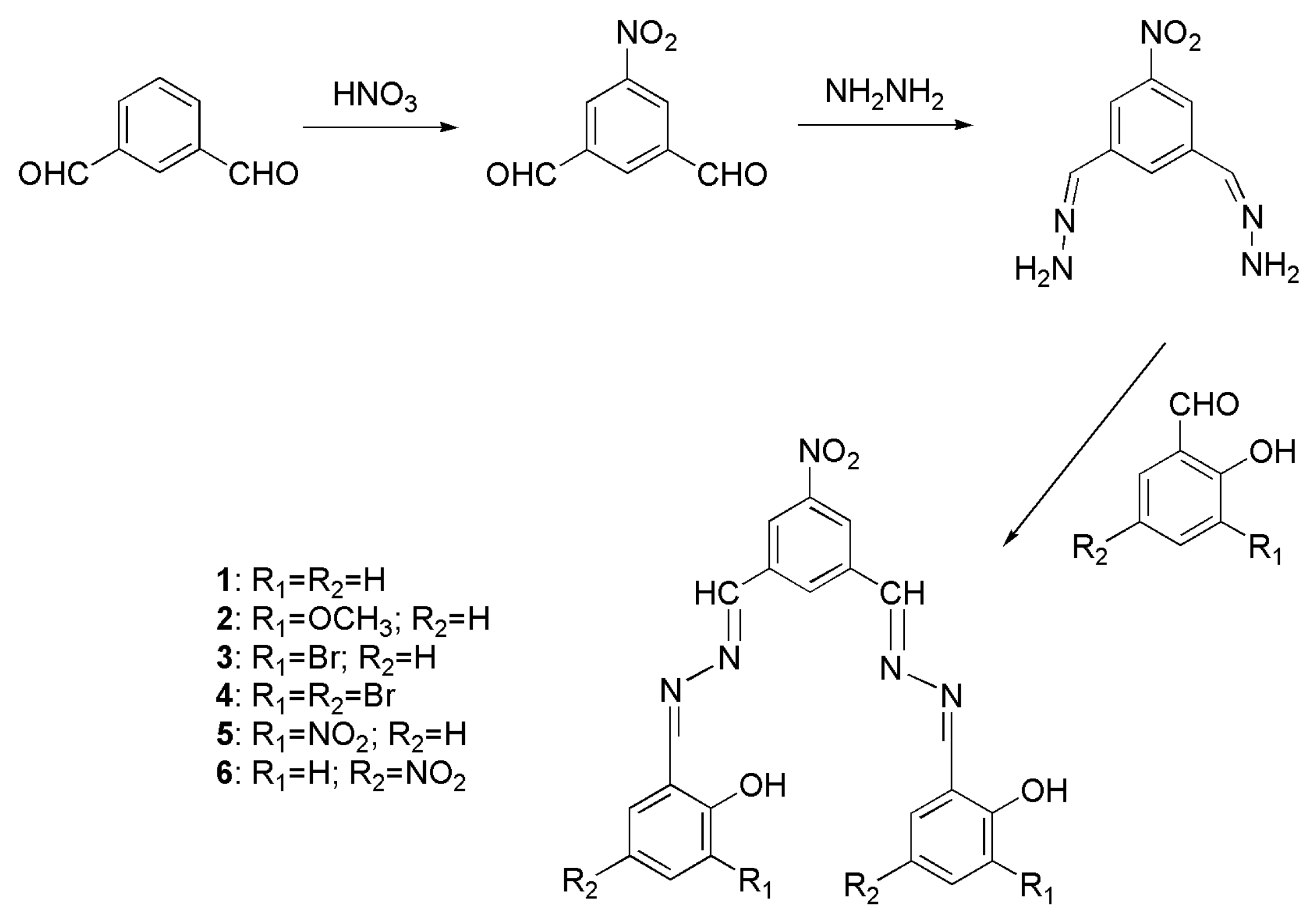
2.3. Synthesis
5-Nitro-1,3-dialdehydebenzene [33]
5-Nitro-1,3-dimethylenehydrazine-benzene
2.4. Preparation of Nanomaterials
3. Results and Discussion
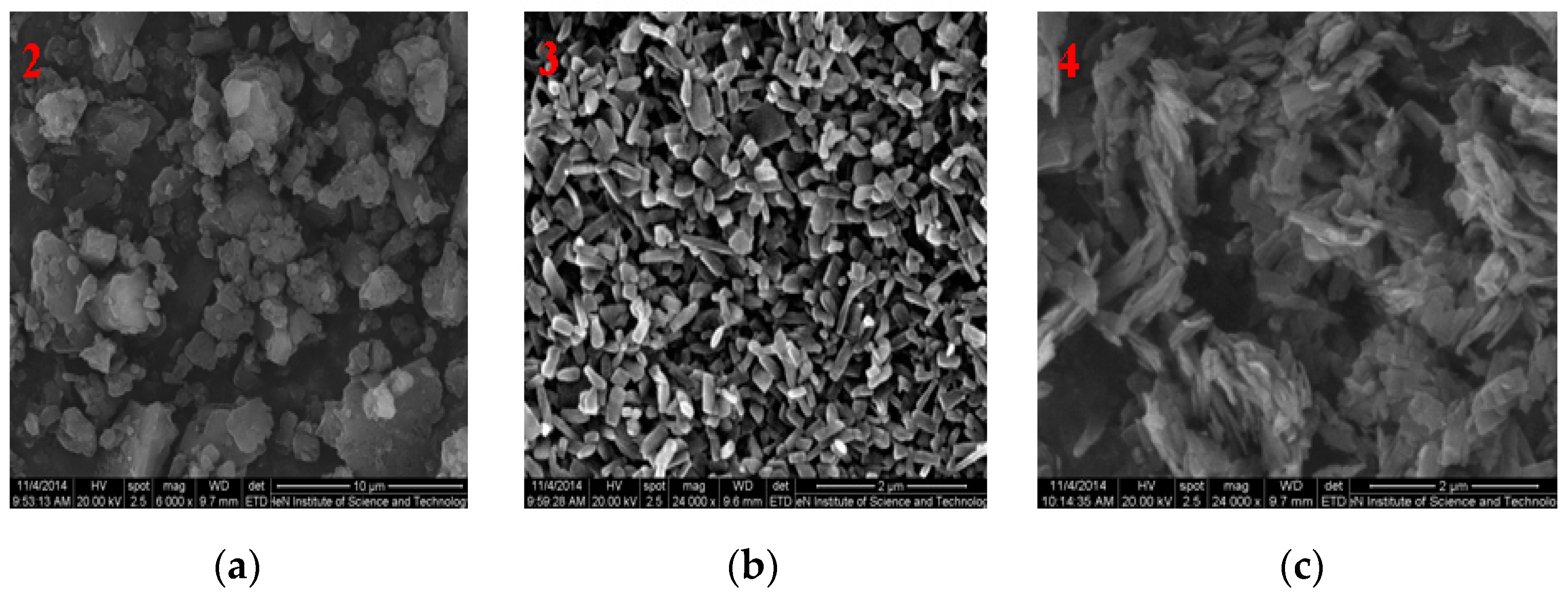
3.1. SEM Images of Nanomaterials
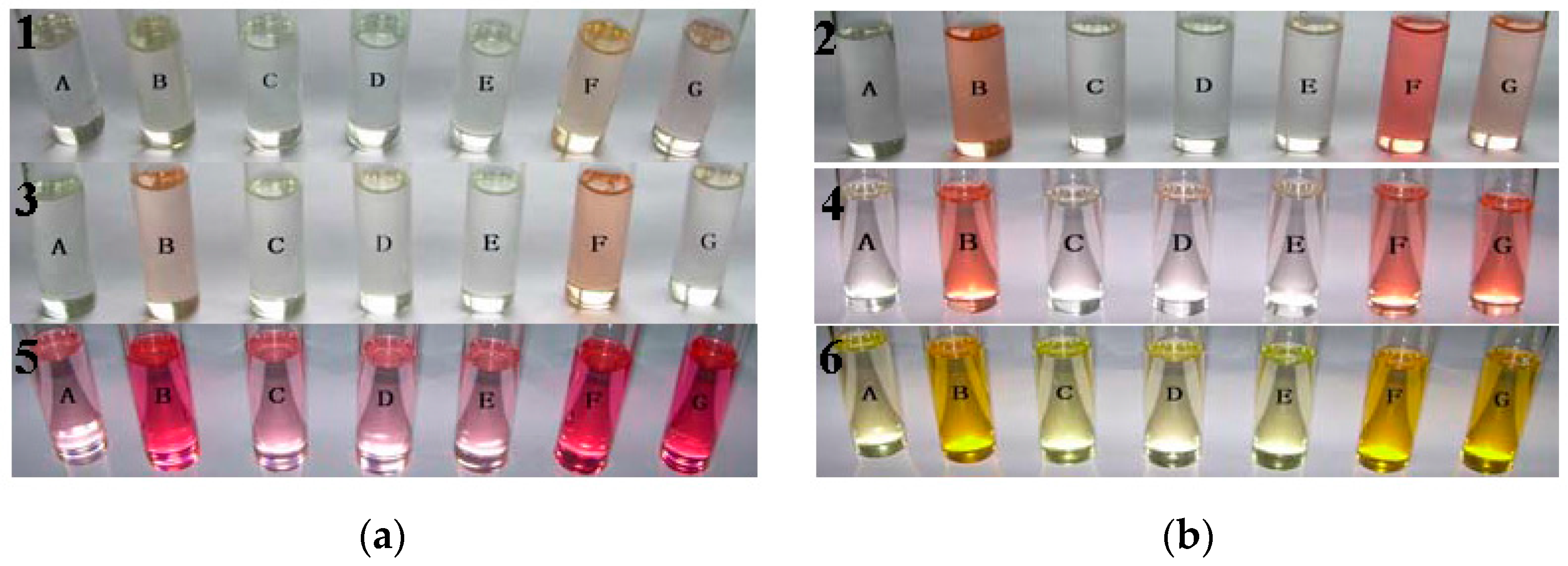
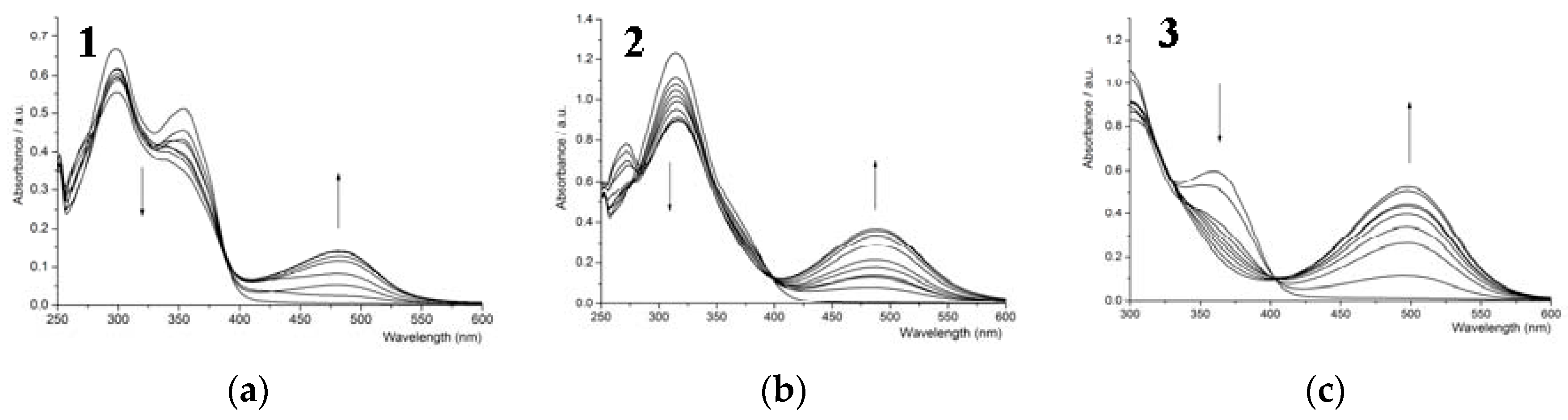
3.2. UV-Vis Titration
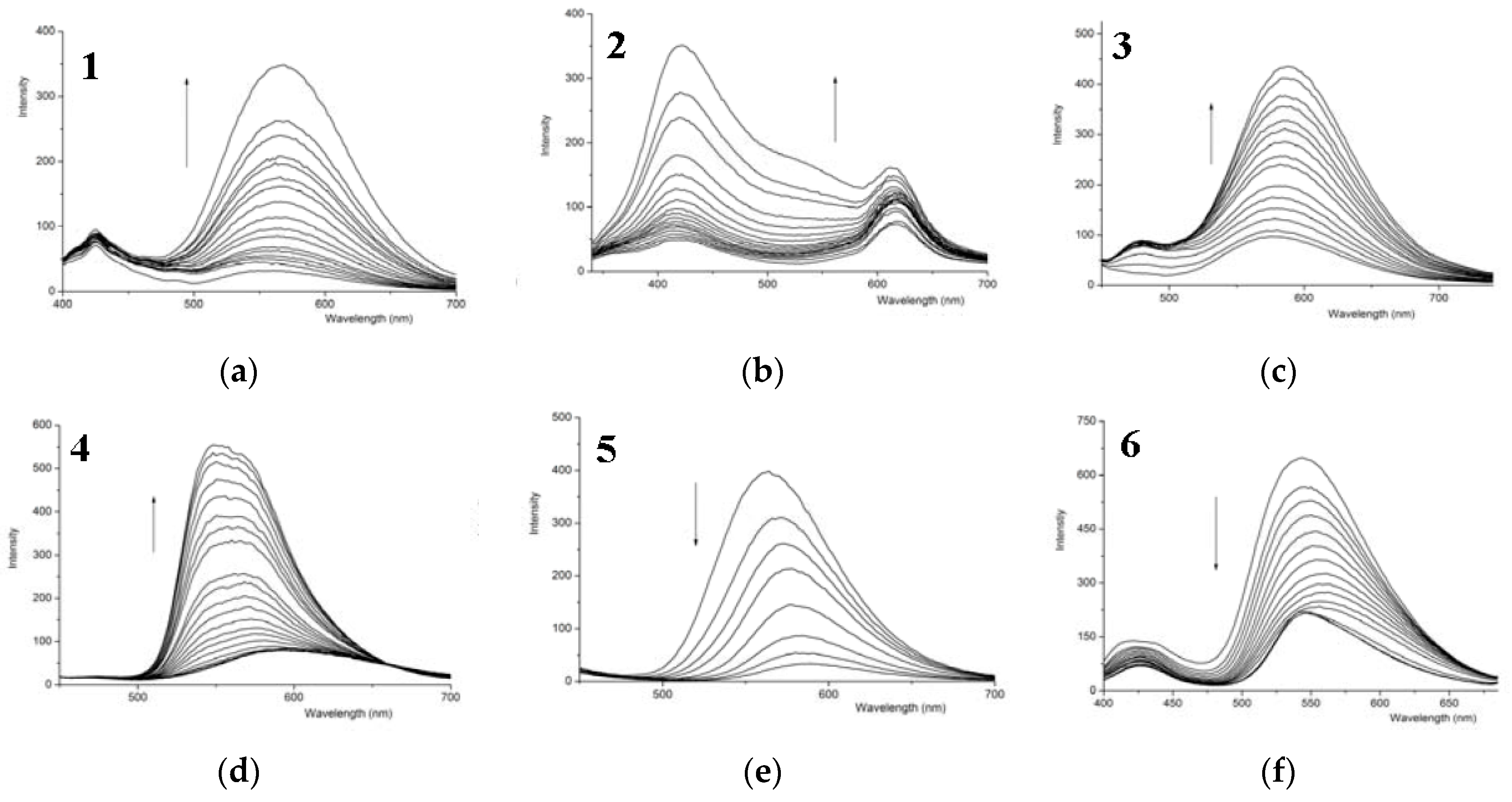
3.3. Fluorescence
3.4. Binding Constant
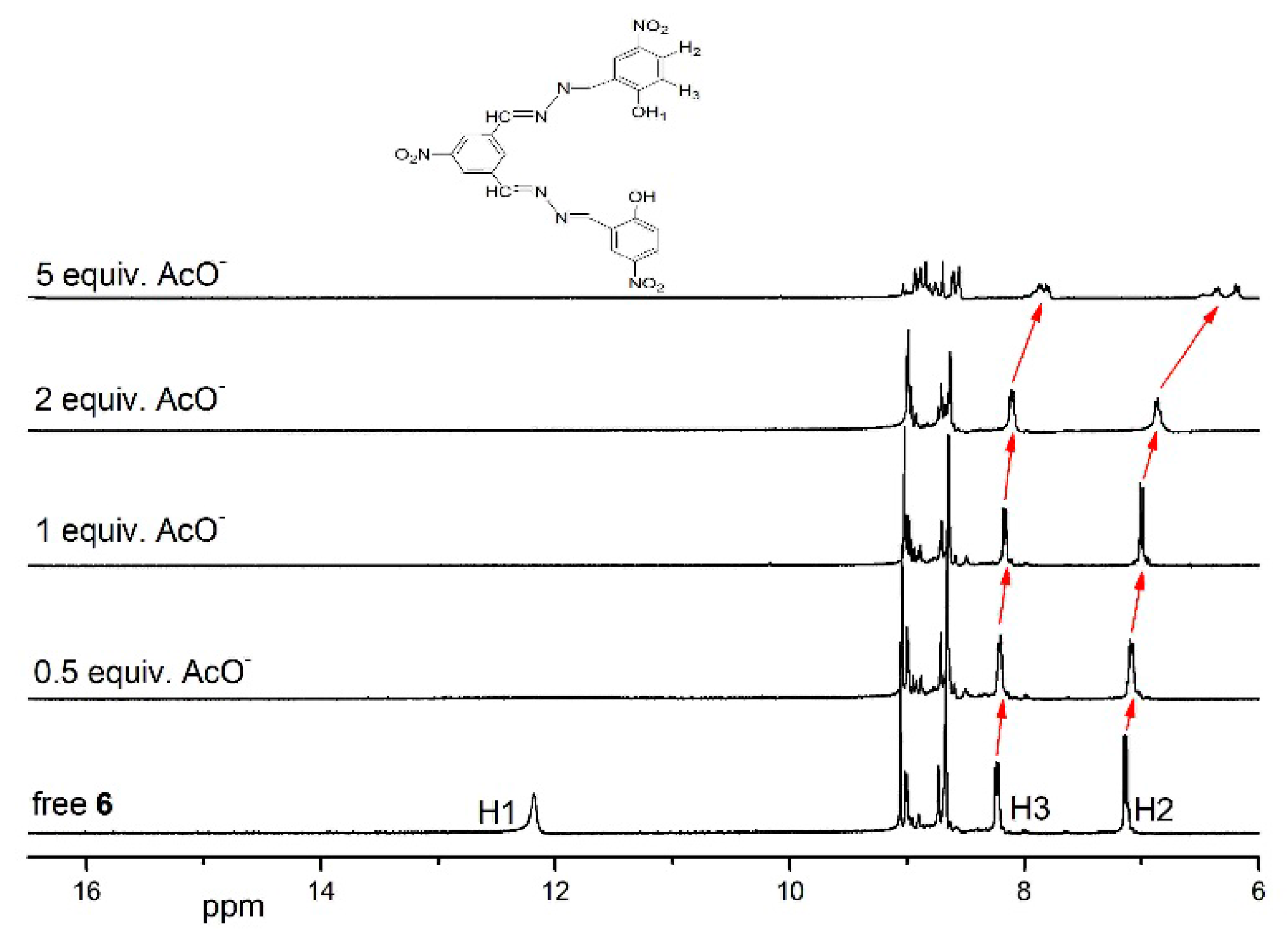
3.5. 1HNMR Titration
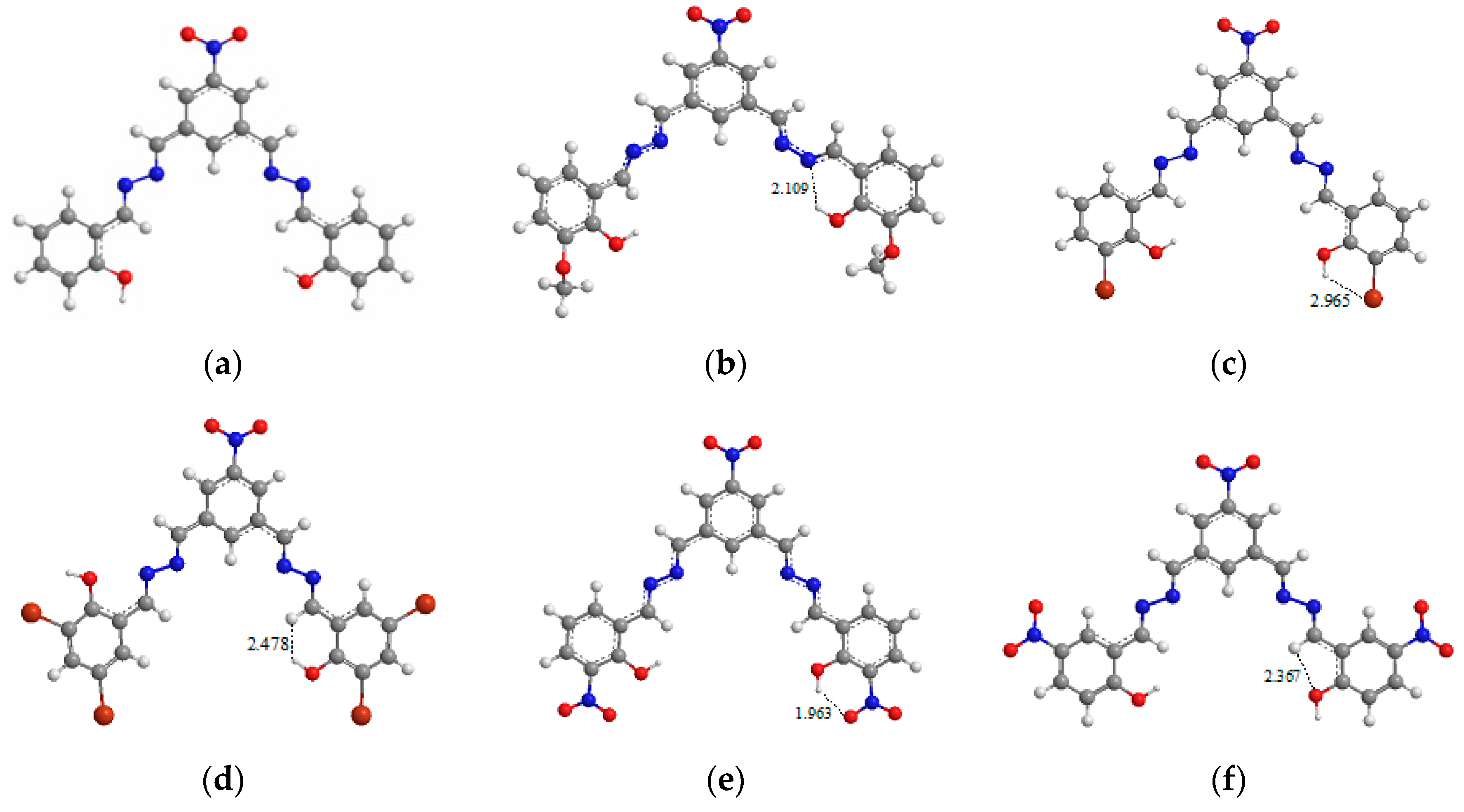
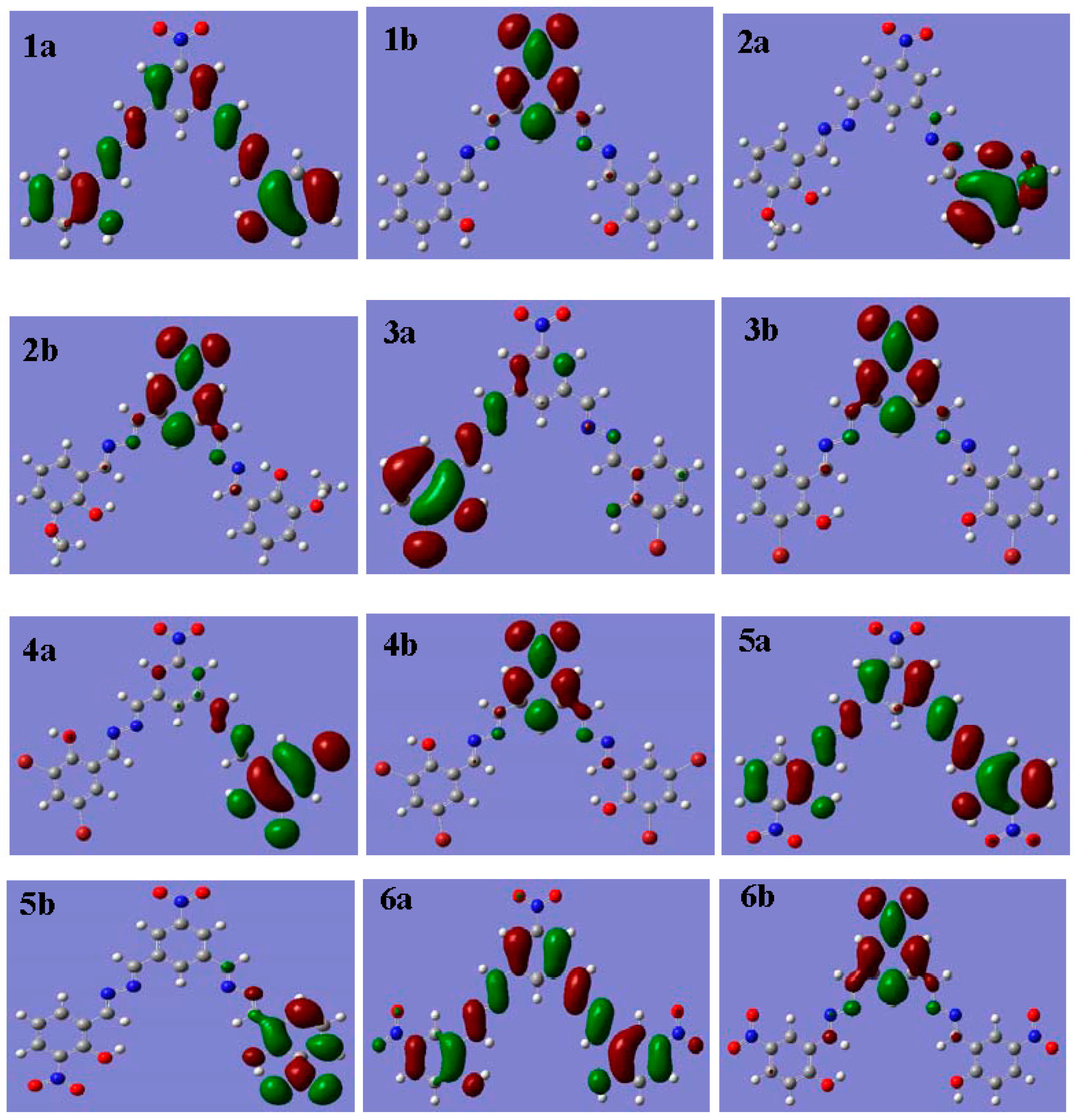
3.6. Theoretical Investigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González Mdel, C.; Otón, F.; Espinosa, A.; Tárraga, A.; Molina, P. Tris (triazole) tripodal receptors as selective probes for citrate anion recognition and multichannel transition and heavy metal cation sensing. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velu, R.; Ramakrishnan, V.T.; Ramamurthy, P. Selective fluoride ion recognition by a thiourea based receptor linked acridinedione functionalized gold nanoparticles. J. Photoch. Photobiolo. A Chem. 2011, 217, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Hwang, I.-J.; Gwon, S.-Y.; Burkinshaw, S.M.; Son, Y.-A. An anion sensor based on the displacement of 2,6-dichlorophenol-indo-o-cresol sodium salt from a water-soluble tetrasulfonated calix[4]arene. Dyes Pigment. 2011, 88, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, K. Gels based on anion recognition between triurea receptor and phosphate anion. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cametti, M.; Rissanen, K. Highlights on contemporary recognition and sensing of fluoride anion in solution and in the solid state. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2016–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodo, E.; Ciavardini, A.; Dalla Cort, A.; Giannicchi, I.; Yafteh Mihan, F.; Fornarini, S.; Vasile, S.; Scuderi, D.; Piccirillo, S. Anion recognition by uranyl-salophen derivatives as probed by infrared multiple photon dissociation spectroscopy and ab initio modeling. Chemistry 2014, 20, 11783–11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.F.; Wang, Y.L.; Wei, X.F.; Fu, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Xu, X.F. Synthesis and binding ability of molecular probes based on a phenanthroline derivative: Theory and experiment. Molecules 2013, 18, 14840–14848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Q.; Shi, B.B.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wei, T.B. Fluorescent “turn-on” detecting CN− by nucleophilic addition induced schiff-base hydrolysis. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 141, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornes, S.P.; Davies, C.H.; Blyghton, D.; Sambrook, M.R.; Beer, P.D. Contrasting anion recognition behaviour exhibited by halogen and hydrogen bonding rotaxane hosts. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 2582–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, P.A. Anion and ion-pair receptor chemistry: highlights from 2000 to 2001. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 240, 191–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.W.; Mustoe, C.L.; White, N.G.; Brown, A.; Thompson, A.L.; Kennepohl, P.; Beer, P.D. Evidence for halogen bond covalency in acyclic and interlocked halogen-bonding receptor anion recognition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Kim, S.K.; Yoon, J. Revisit to imidazolium receptors for the recognition of anions: Highlighted research during 2006–2009. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomich, J.M.; Wallace, D.; Henderson, K.; Mitchell, K.E.; Radke, G.; Brandt, T.; Amber, C.A.; Scott, A.; Ganthan, J.; Sullivan, L.; et al. Aqueous solubilization of transmembrane peptide sequences with retention of membrane insertion and function. Biophys. J. 1998, 74, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Llinares, J.M.; Powell, D.; Bowman-James, K. Multiple hydrogen bond stabilization of a sandwich complex of sulfate between two macrocyclic tetraamides. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 2936–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szumna, A.; Jurczak, J. A new macrocyclic polylactam-type neutral receptor for anions—Structural aspects of anion recognition. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 21, 4031–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, P.D.; Szemes, F.; Balzani, V.; Salà, C.M.; Drew, M.G.B.; Dent, S.W.; Maestri, M. Anion selective recognition and sensing by novel macrocyclic rransition metal receptor systems. 1H-NMR, electrochemical, and photophysical investigations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 11864–11875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessler, J.L.; Cho, D.G.; Lynch, V. Diindolylquinoxalines: Effective indole-based receptors for phosphate anion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16518–16519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, P.A.; Fyfe, J.A.; Clair St, M.H.; Weinhold, K.; Rideout, J.L.; Freeman, G.A. Phosphorylation of 3’-azido-3’-deoxythymidine and selective interaction of the 5’-triphosphate with human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8333–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Král, V.; Sessler, J.L. Molecular recognition via base-pairing and phosphate chelation. Ditopic and tritopic sapphyrin-based receptors for the recognition and transport of nucleotide monophosphates. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojida, A.; Mito-oka, Y.; Sada, K.; Hamachi, I. Molecular recognition and fluorescence sensing of monophosphorylated peptides in aqueous solution by bis (zinc (II)-dipicolylamine)-based artificial receptors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2454–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, P.A. A phenylhydrazone-based indole receptor for sensing acetate. Chem. Commun. 2005, 30, 3761–3772. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.W.; Singh, N.; Jang, D.O. Benzimidazole and thiourea conjugated fluorescent hybrid receptor for selective recognition of PO43−. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Lin, H.; Shang, X.F.; Chen, H.M.; Lin, H.K. A novel neutral receptor for selective recognition of H2PO4−. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 59, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez Blanco, J.L.; Bootello, P.; Benito, J.M.; Ortiz Mellet, C.; Garcia Fernandez, J.M. Urea-, thiourea-, and guanidine-linked glycooligomers as phosphate binders in water. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 5136–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnlaugsson, T.; Glynn, M.; Tocci, G.M.; Kruger, P.E.; Pfeffer, F.M. Anion recognition and sensing in organic and aqueous media using luminescent and colorimetric sensors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 3094–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Dai, S.; Wang, L. Optical aptasensors for quantitative detection of small biomolecules: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, V.; Esteban-Gomez, D.; Fabbrizzi, L.; Licchelli, M. What anions do to NH-containing receptors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.S.; Chen, X.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J. Recent progress in luminescent and colorimetric chemosensors for detection of thiols. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6019–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyabu, R.; Anzenbacher, P. 1,3-Indane-based chromogenic calixpyrroles with push-pull chromophores: Synthesis and anion sensing. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Lin, H.; Shao, J.; Cai, Z.S.; Lin, H.K. A phenylhydrazone-based indole receptor for sensing acetate. Talanta 2008, 74, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Shi, M.; Li, F.Y.; Fang, Q.; Yi, T.; Huang, C.H. Highly selective two-photon chemosensors for fluoride derived from organic boranes. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 5481–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.H.; Ou, S.J.; Duan, C.Y.; Zhang, B.G.; Bai, Z.P. Naked-eye detection of fluoride ion in water: A remarkably selective easy-to-prepare test paper. Chem. Commun. 2006, 6, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.G.; Duan, C.Y.; Zhang, B.G.; Bai, Z.P. A highly selective chromo- and fluorogenic dual responding fluoride sensor: Naked-eye detection of F− ion in natural water via a test paper. Dalton Trans. 2006, 30, 3678–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.H.; Yoon, J. A highly selective fluorescent chemosensor for dihydrogen phosphate via unique excimer formation and PET mechanism. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 3797–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.S.; Neckers, D.C. Photochemistry of azobenzene-containing polymers. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, J.; Fujiwara, T.; Ogawa, K. Crucial role of fluorescence in the solid-state thermochromism of salicylideneanilines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 16216–16221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Han, B.H.; Zhang, H.Y. Spectroscopic studies on molecular recognition of modified cyclodextrins. Curr. Org. Chem. 2004, 8, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; You, C.C.; Zhang, H.Y. Supramolecular Chemistry; Nankai University Publication: Tianjin, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bourson, J.; Pouget, J.; Valeur, B. Ion-responsive fluorescent compounds. 4. Effect of cation binding on the photophysical properties of a coumarin linked to monoaza-and diaza-crown ethers. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 4552–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonizzoni, M.; Fabbrizzi, L.; Taglietti, A.; Tiengo, F. (Benzylideneamino) thioureas—Chromogenic interactions with anions and N-H deprotonation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 16, 3567–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Montgomery, J.A., Jr. Software for Computational Chemistry; Gaussian, Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.; Musson, A.; De Boos, G. Superior methodology for the nitrate ion of simple aromatic compounds. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1996, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zou, K.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, S.T. Single-crystal nanoribbons, nanotubes, and nanowires from intramolecular charge-transfer organic molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3527–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.H.; Yu, J.; Padmanadan, G.; Ramakrishanan, S.; Barbara, P.F. Spatial confinement of excition transfer and the role of conformational order in organic nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Anions a | AcO− | H2PO4− | F− | Cl− (Br−, I−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ks (1) | (9.56 ± 0.05) × 103 | (4.11 ± 0.14) × 102 | (2.31 ± 0.03) × 104 | ND b |
| Ks (2) | (1.28 ± 0.06) × 103 | (1.18 ± 0.01) × 103 | (2.45 ± 0.04) × 104 | ND |
| Ks (3) | (2.76 ± 0.03) × 104 | (2.33 ± 0.02) × 103 | (1.60 ± 0.04) × 104 | ND |
| Ks (4) | (5.65 ± 0.08) × 104 | (4.35 ± 0.02) × 104 | (4.10 ± 0.10) × 104 | ND |
| Ks (5) | (6.48 ± 0.11) × 104 | (5.67 ± 0.08) × 104 | (3.35 ± 0.05) × 104 | ND |
| Ks (6) | (8.49 ± 0.19) × 104 | (6.07 ± 0.07) × 104 | (4.69 ± 0.12) × 104 | ND |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.-J.; Zhang, L.-R. Theoretical and Experimental: The Synthetic and Anion-Binding Properties of Tripodal Salicylaldehyde Derivatives. Sensors 2016, 16, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050733
Xu Z-J, Zhang L-R. Theoretical and Experimental: The Synthetic and Anion-Binding Properties of Tripodal Salicylaldehyde Derivatives. Sensors. 2016; 16(5):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050733
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhong-Jie, and Li-Rong Zhang. 2016. "Theoretical and Experimental: The Synthetic and Anion-Binding Properties of Tripodal Salicylaldehyde Derivatives" Sensors 16, no. 5: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050733
APA StyleXu, Z.-J., & Zhang, L.-R. (2016). Theoretical and Experimental: The Synthetic and Anion-Binding Properties of Tripodal Salicylaldehyde Derivatives. Sensors, 16(5), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050733






