The Ionospheric Scintillation Effects on the BeiDou Signal Receiver
Abstract
:1. Introduction
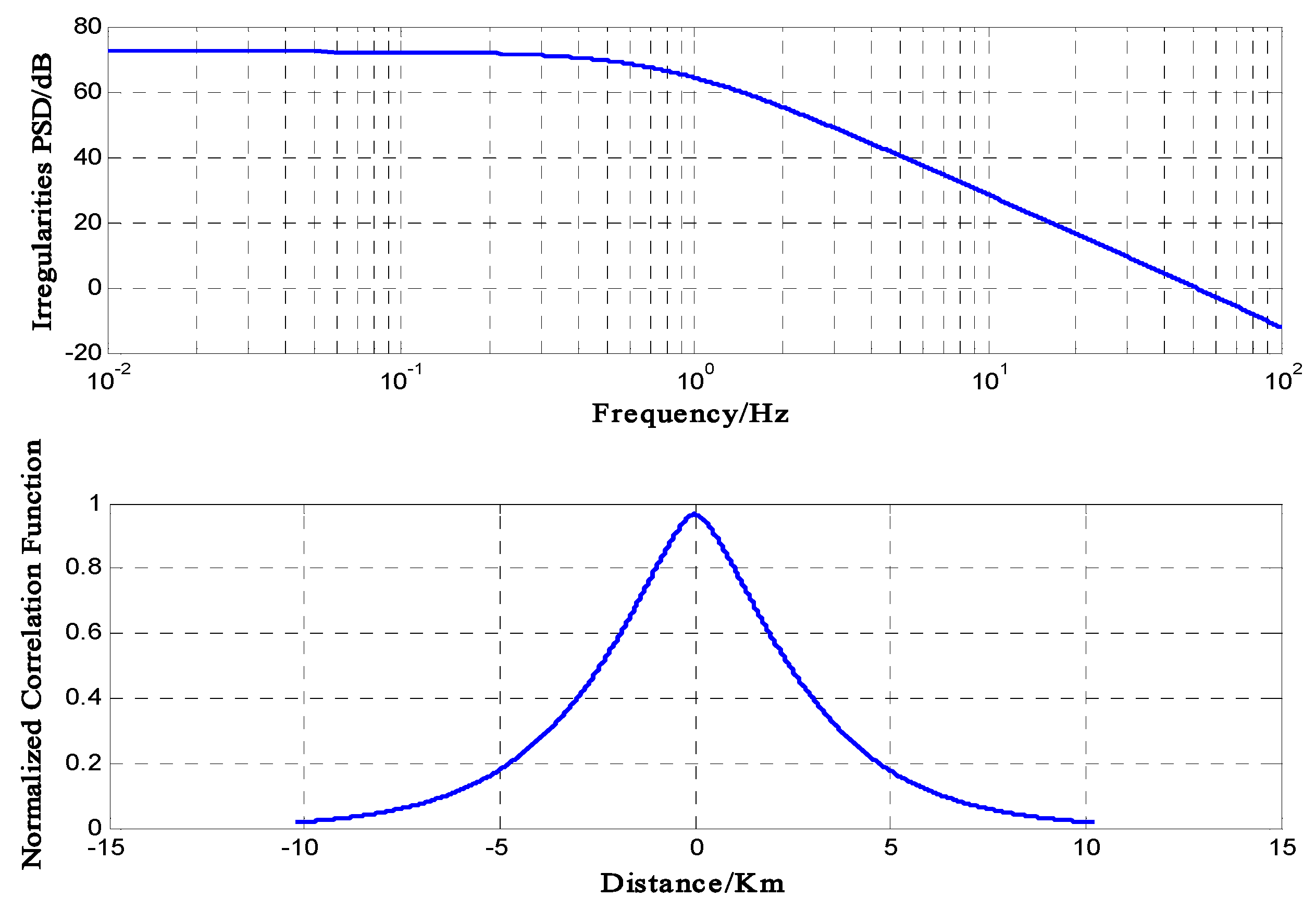
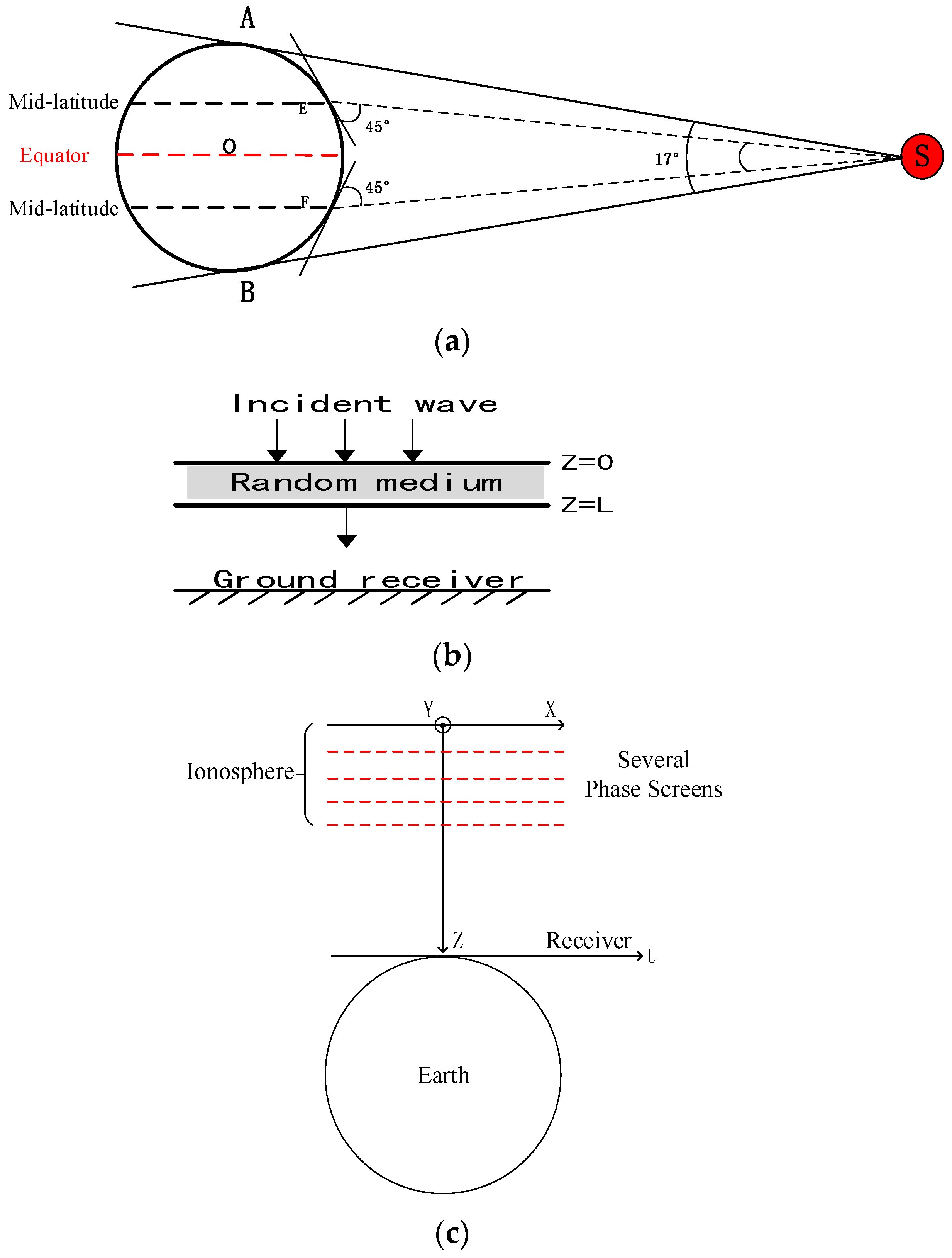
2. Inhomogeneity Characteristics
3. Solution of Signal Propagation Based on MPS Technique
3.1. Formulation
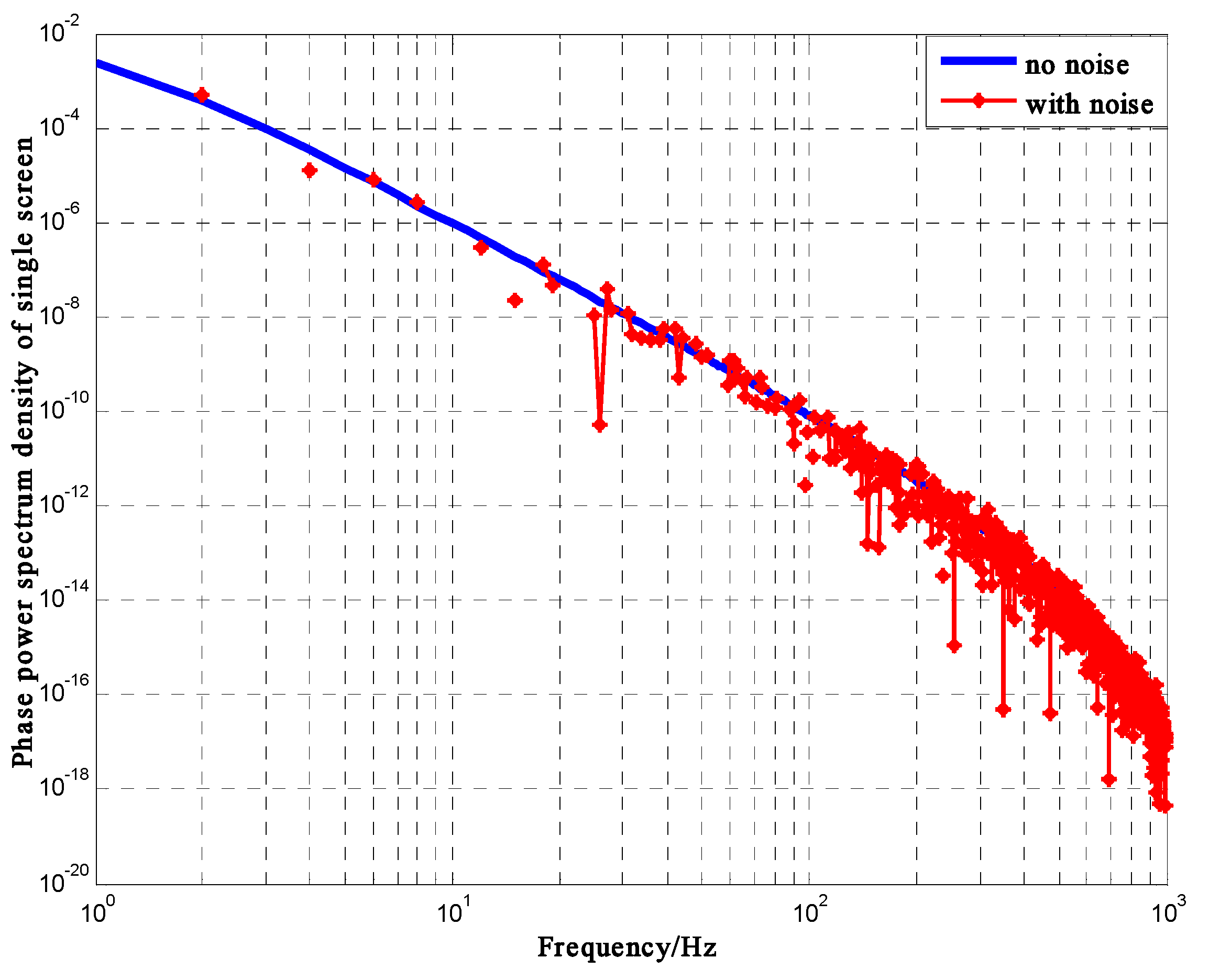
3.2. Computational Set up of Simulations
3.3. Experimental Results
4. Effect on the Acquisition Process for the BeiDou Receiver
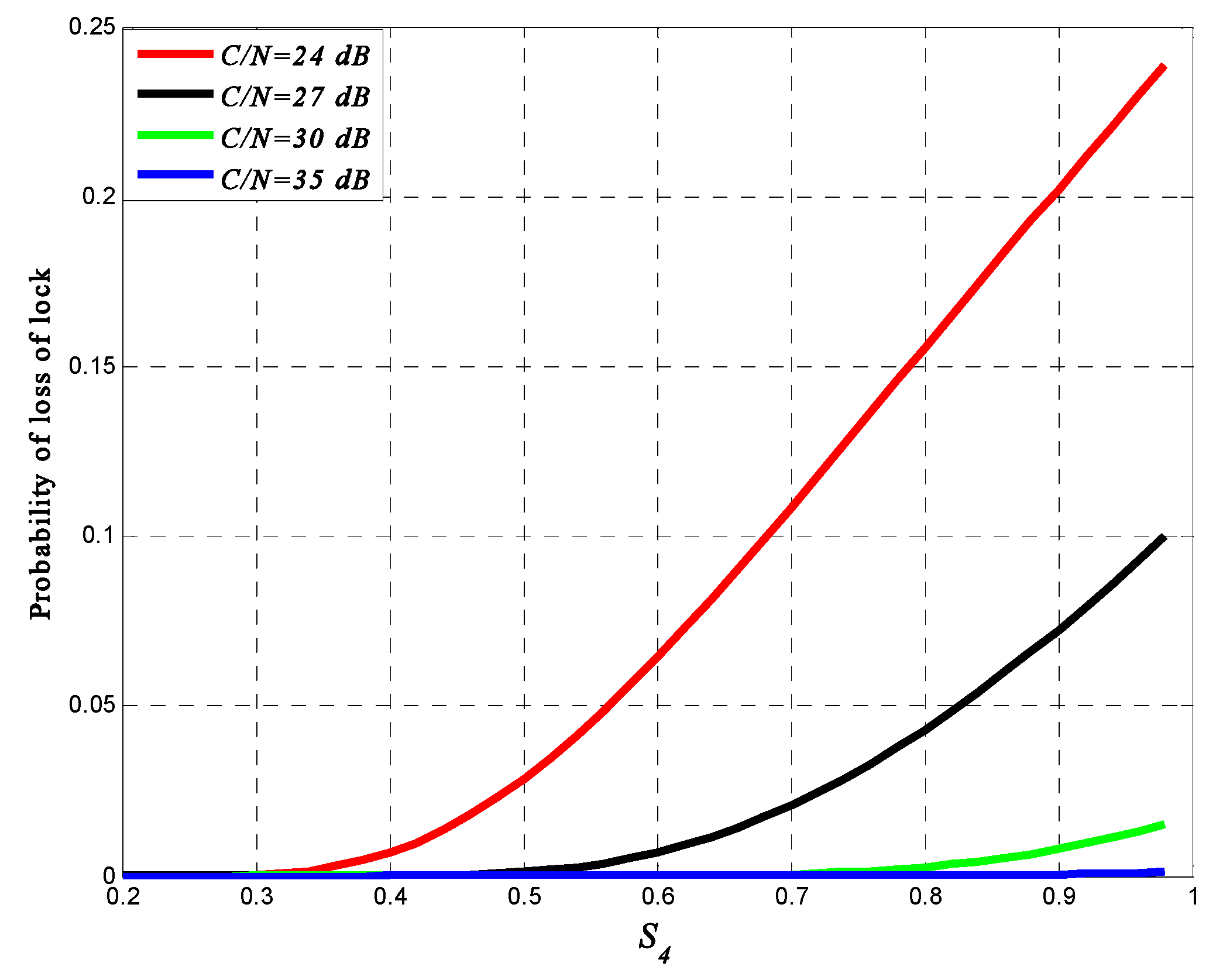
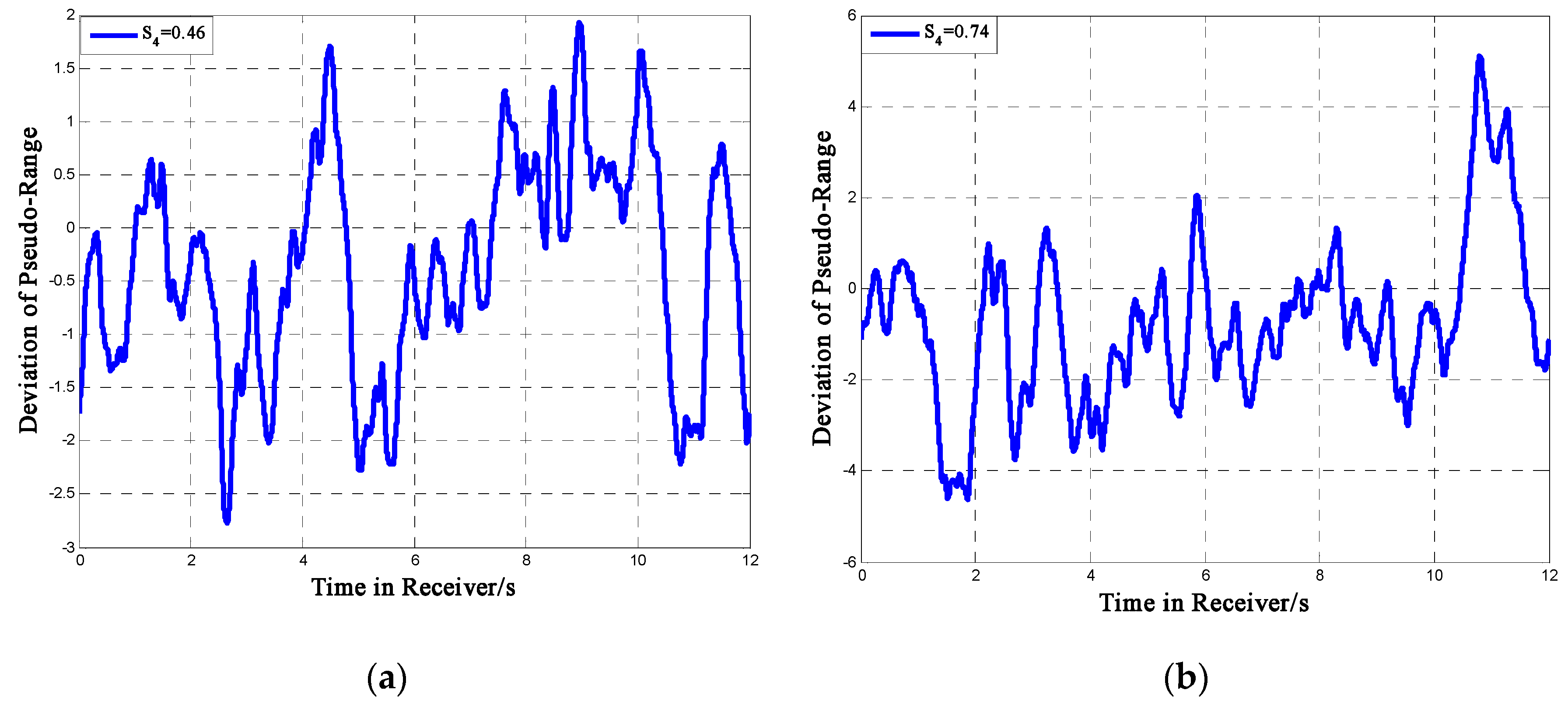
5. Effect on Tracking Process for BeiDou Receiver
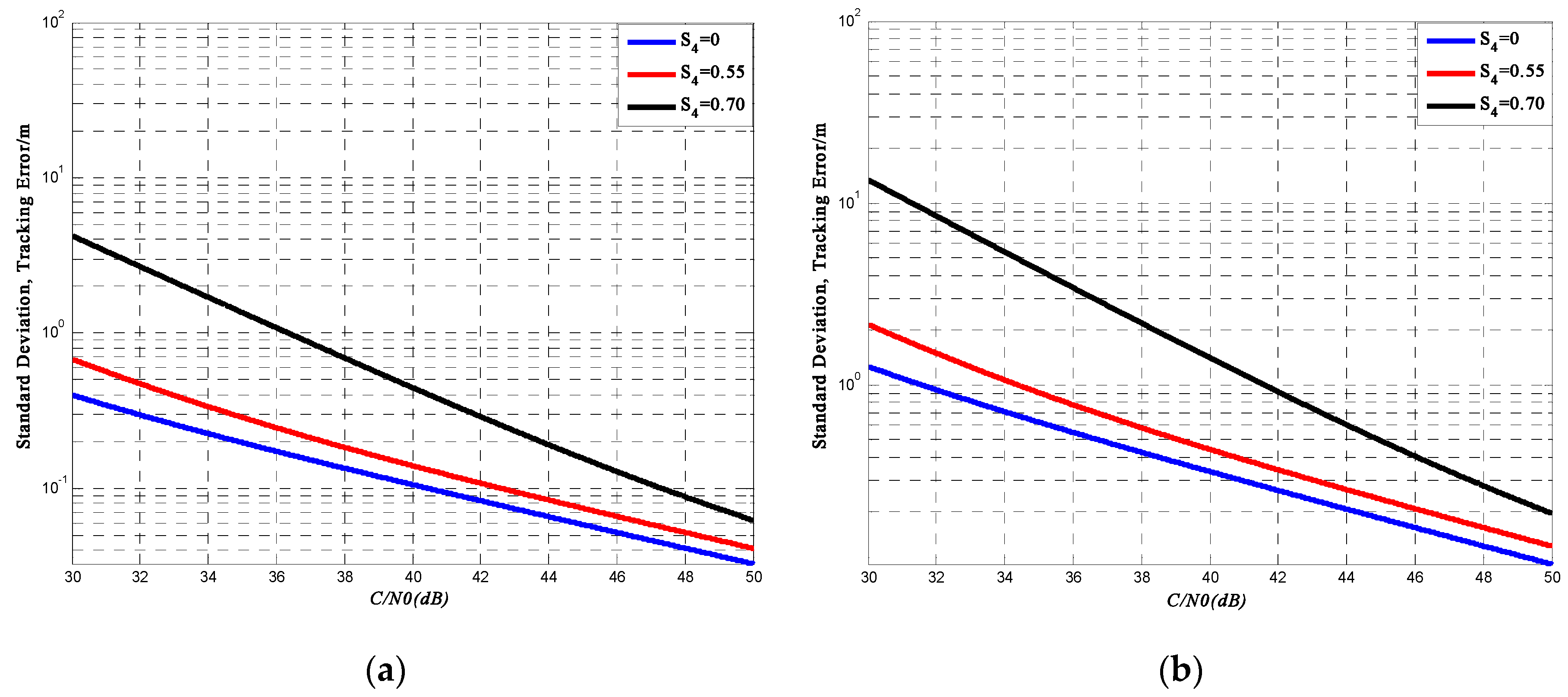
5.1. Determining PLL Variance for the BeiDou B1I Signal
5.2. Determining DLL Variance for BeiDou B1I Signal
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knight, M.; Finn, A. The Effects of ionospheric scintillations on GPS. In Proceedings of the 11th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1998), Nashville, TN, USA, 15–18 September 1998; pp. 673–685.
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ibrahim, A.S. Modeling the effects of ionosphere scintillation on GNSS aviation navigation performance. Int. J. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 9, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Strangeways, H.J.; Tiwari, R. Prediction and mitigation of ionospheric scintillation and tracking jitter for GNSS positioning. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on ELMAR, Zadar, Croatia, 25–27 September 2013; pp. 319–322.
- Zhao, Q.; Deng, H.; Zhao, H. Research on ionospheric scintillation with Beidou satellite signal. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2015, E98.B, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, D.; Zhen, W. The study of ionospheric scintillation model with satellite signal. Glob. Position Syst. 2013, 38, 13–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Conker, R.S.; El-Arini, M.B.; Hegarty, C.J.; Hsiao, T. Modeling the effects of ionospheric scintillation on GPS/Satellite-Based Augmentation System availability. Radio Sci. 2003, 38, 1-1–1-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béniguel, Y. Global Ionospheric Propagation Model (GIM): A propagation model for scintillations of transmitted signals. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 4-1–4-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béniguel, Y. Ionosphere scintillation at low and high latitudes (modelling vs. measurement). In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 17–22 April 2016.
- Ho, Y.H.; Abdullah, S.; Mokhtar, M.H. Global Positioning System (GPS) positioning errors modeling using Global Ionospheric Scintillation Model (GISM). In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Space Science & Communication, Melaka, Malaysia, 1–3 July 2013; Volume 148, pp. 33–38.
- Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; Zhou, P. Improved precise point positioning in the presence of ionospheric scintillation. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vani, B.C.; Shimabukuro, M.H.; Monico, J.F.G. Visual exploration and analysis of ionospheric scintillation monitoring data: The ISMR query tool. Comput. Geosci. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veettil, S.V.; Marcio, A.; Biagio, F.; Zeynep, E.; Craig, H.; De Franceschi, G.; Alfonsi, L.; Spogli, L.; Vincenzo, R.; Bruno, B.; et al. Tackling ionospheric scintillation threat to GNSS in Latin America. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2011, 1, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Rino, C.L. A power law phase screen model for ionospheric scintillation. I—Weak scatter. II—Strong scatter. Radio Sci. 1979, 14, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepp, D.L. Multiple phase-screen calculation of the temporal behavior of stochastic waves. Proc. IEEE 1983, 71, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, C.S.; Groves, K.M.; Caton, R.G.; Rino, C.L.; Straus, P.R. Multiple phase screen modeling of ionospheric scintillation along radio occultation raypaths. Radio Sci. 2011, 46, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.B.; Bust, G.S.; Clauer, C.R.; Rino, C.L.; Carrano, C.S. Satellite-beacon Ionospheric-scintillation Global Model of the upper Atmosphere (SIGMA) I: High-latitude sensitivity study of the model parameters. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 4026–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.B.; Bust, G.S.; Clauer, C.R.; Scales, W.A.; Frissell, N.A.; Ruohoniemi, J.M.; Spogli, L.; Mitchell, C.; Weatherwax, A.T. Satellite-beacon Ionospheric-scintillation Global Model of the upper Atmosphere (SIGMA) II: Inverse modeling with high-latitude observations to deduce irregularity physics. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 9188–9203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.C.; Liu, C.H. An investigation of temporal moments of stochastic waves. Radio Sci. 1977, 12, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.C.; Liu, C.H. Radio wave scintillations in the ionosphere. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 324–360. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Phelps, A.D.R.; Sagalyn, R.C. In Situ Measurement of the Structure and Spectral Characteristics of Small Scale F Region Ionospheric Irregularities. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2007, 47, 623–625. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Rastogi, R.G. Amplitude scintillations during the early and late phases of evolution of irregularities in the nighttime equatorial ionosphere. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, D.G. Power spectra of ionospheric scintillations. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1974, 36, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarskii, V.I. The Effects of the Turbulent Atmosphere on Wave Propagation; Israel Program for Science Translations: Jerusalem, Israel, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe, J.A. Some Aspects of Diffraction Theory and their Application to the Ionosphere. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2002, 19, 188–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document-Open Service Signal; version 2.0; China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 1–9.
- Kaplan, E.D.; Hegarty, C. Understanding GPS: Principles and Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Gao, Y.; Long, T. Four-way signal processing carrier phase lock loop in ionosphere scintillation environment. Beijing Ligong Daxue Xuebao/Trans. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2014, 34, 322–326. [Google Scholar]
- Conker, R.S.; El-Arini, M.B.; Hegarty, C.J.; Hsiao, T. Modeling the Effects of Ionospheric Scintillation on GPS/SBAS Availability. In Proceedings of the Iain World Congress & Annual Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 26–29 June 2000; Volume 38, pp. 563–576.







| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier Frequency (MHz) | 1561.098 |
| Ionosphere Altitude (km) | 200–400 |
| Power Law Index p | 4 |
| False Alarm Probability | 10−6 |
| Classical Electron Radius (m) | 2.818 × 10−15 |
| Code Rate of BeiDouB1I Signal (Mbps) | 2.046 |
| Sample Points | 6000 |
| Sampling Frequency | 500 |
| Outer Scale (m) | 5000 |
| Inner Scale (m) | 15 |
| Distance Between two Adjacent Screens (m) | 5000 |
| Average Electron Density | 9 × 1011 |
| Computer Language | Matlab |
| Location of Receiver | N18°, E109° |
|---|---|
| Date (GMT + 0800) | 21 March 2016 |
| Time period (GMT + 0800) | 07:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. |
| Positioning Satellites | Three MEO and one IGSO |
| Time Sampling Interval | 60 s |
| Positioning Method | Single Point Positioning |
| Satellite Clock Error | 0 |
| Coordinate System | J2000 |
| Total Sample Points | 181 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Zhao, H.; Feng, W. The Ionospheric Scintillation Effects on the BeiDou Signal Receiver. Sensors 2016, 16, 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111883
He Z, Zhao H, Feng W. The Ionospheric Scintillation Effects on the BeiDou Signal Receiver. Sensors. 2016; 16(11):1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111883
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhijun, Hongbo Zhao, and Wenquan Feng. 2016. "The Ionospheric Scintillation Effects on the BeiDou Signal Receiver" Sensors 16, no. 11: 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111883
APA StyleHe, Z., Zhao, H., & Feng, W. (2016). The Ionospheric Scintillation Effects on the BeiDou Signal Receiver. Sensors, 16(11), 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111883







