A Novel Gradient Vector Flow Snake Model Based on Convex Function for Infrared Image Segmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Background
2.1. Traditional Snakes Model
- It is very sensitive to the location of the initial contour. During the practical segmentation process, the initial location of the contour must be manually put near the image edge of interest, resulting in poor interactivity.
- It is prone to converge towards the false edge near the object, and is not robust to the noise.
- Its convergence performance is poor for the object contour with sunken regions.
2.2. The GVF Snakes Model
2.3. An Improved GVF Snakes Model
2.3.1. GGVF Snakes Model
2.3.2. NGVF Snakes and NBGVF Snakes
3. Algorithm Improvement
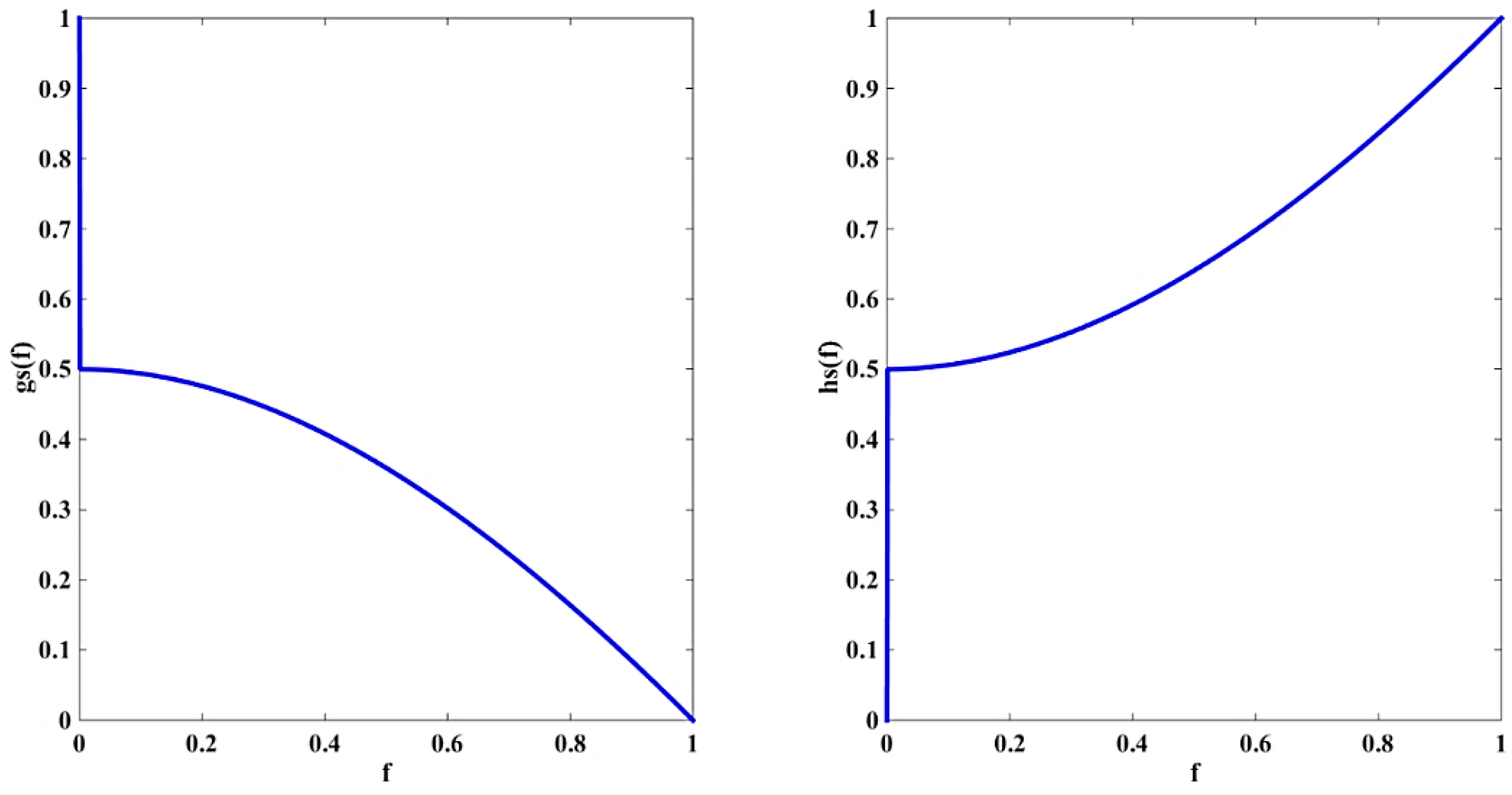
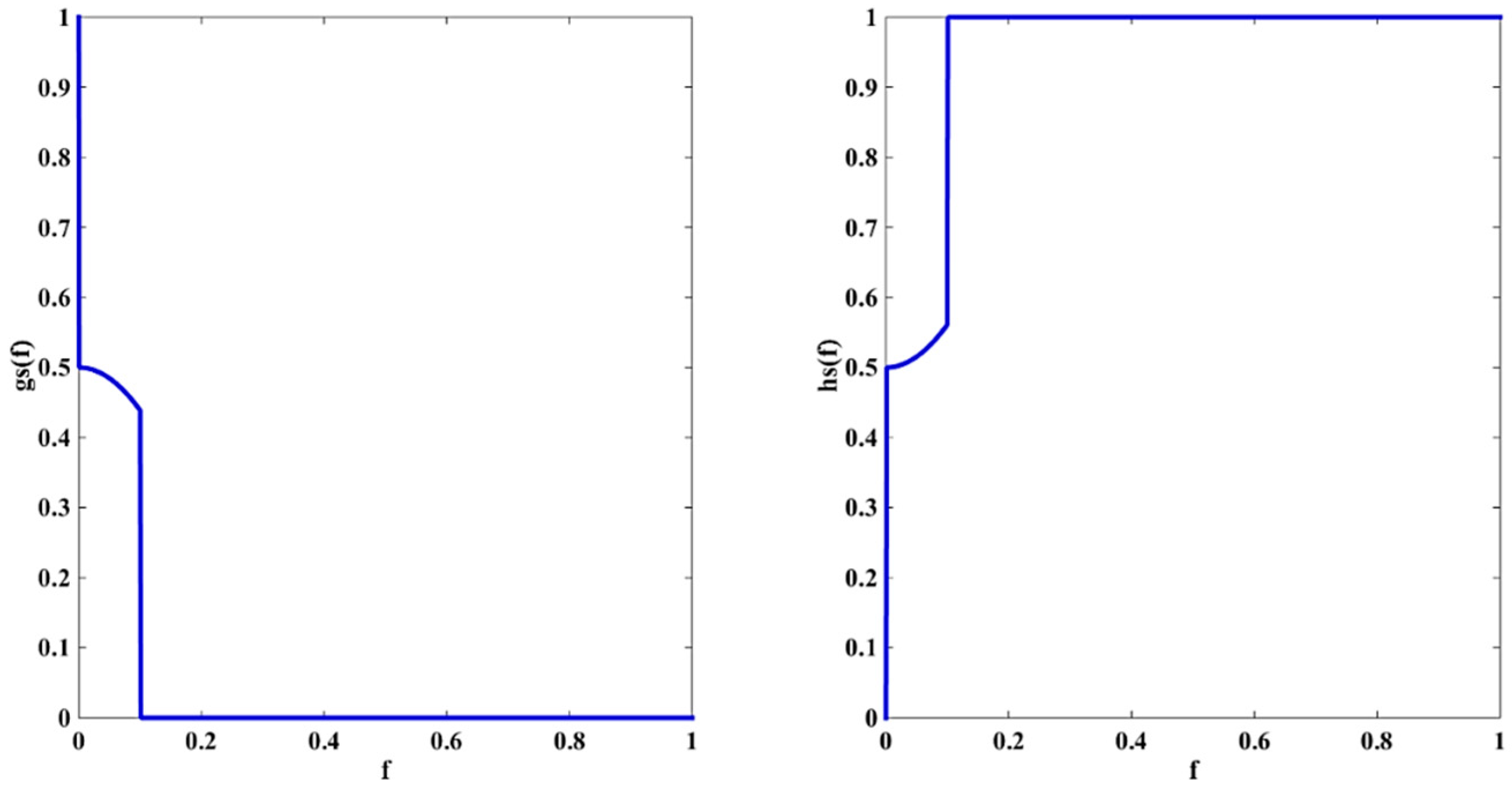
3.1. Improved Version of the GVF Model
3.2. Numerical Implementation
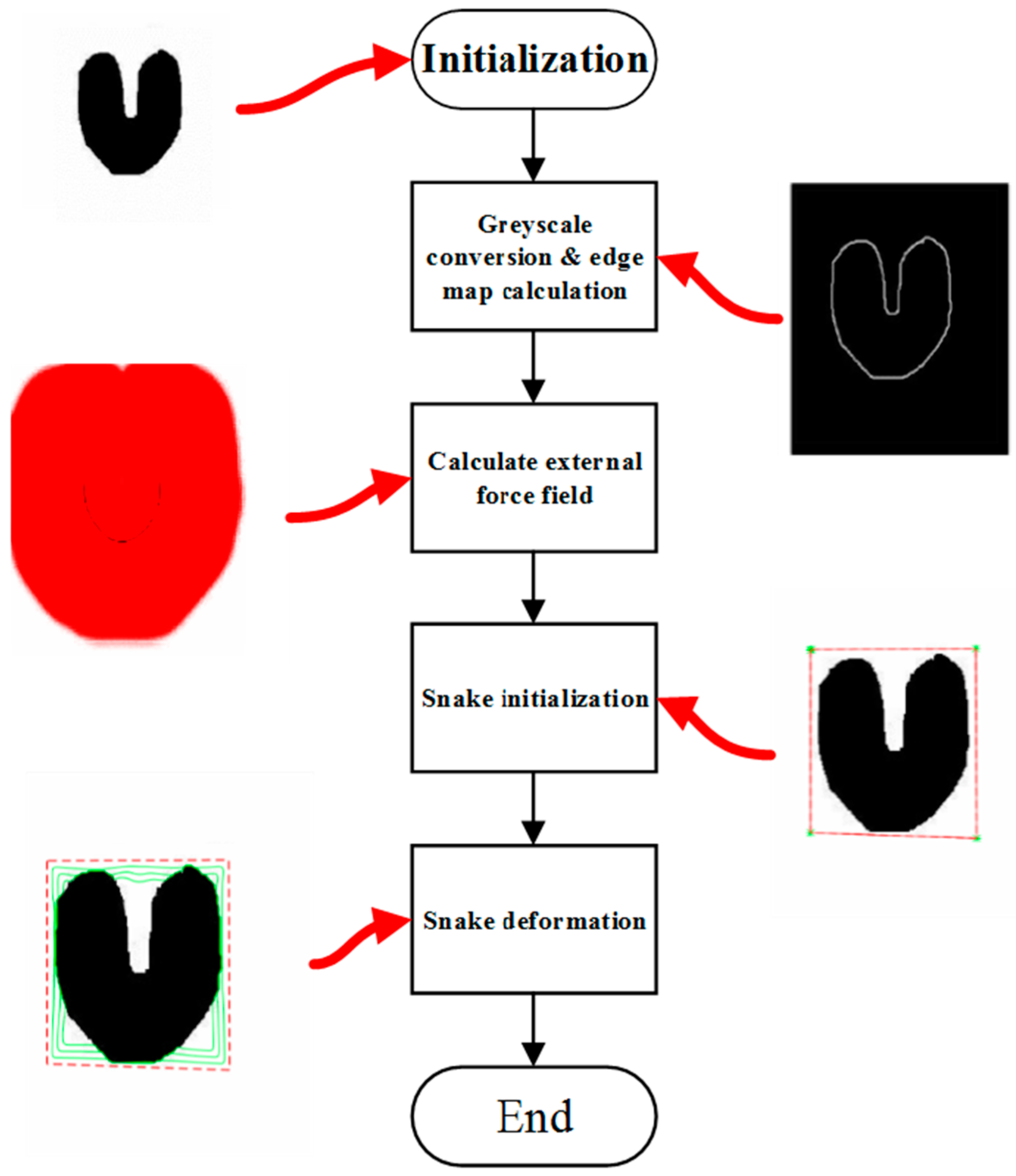
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
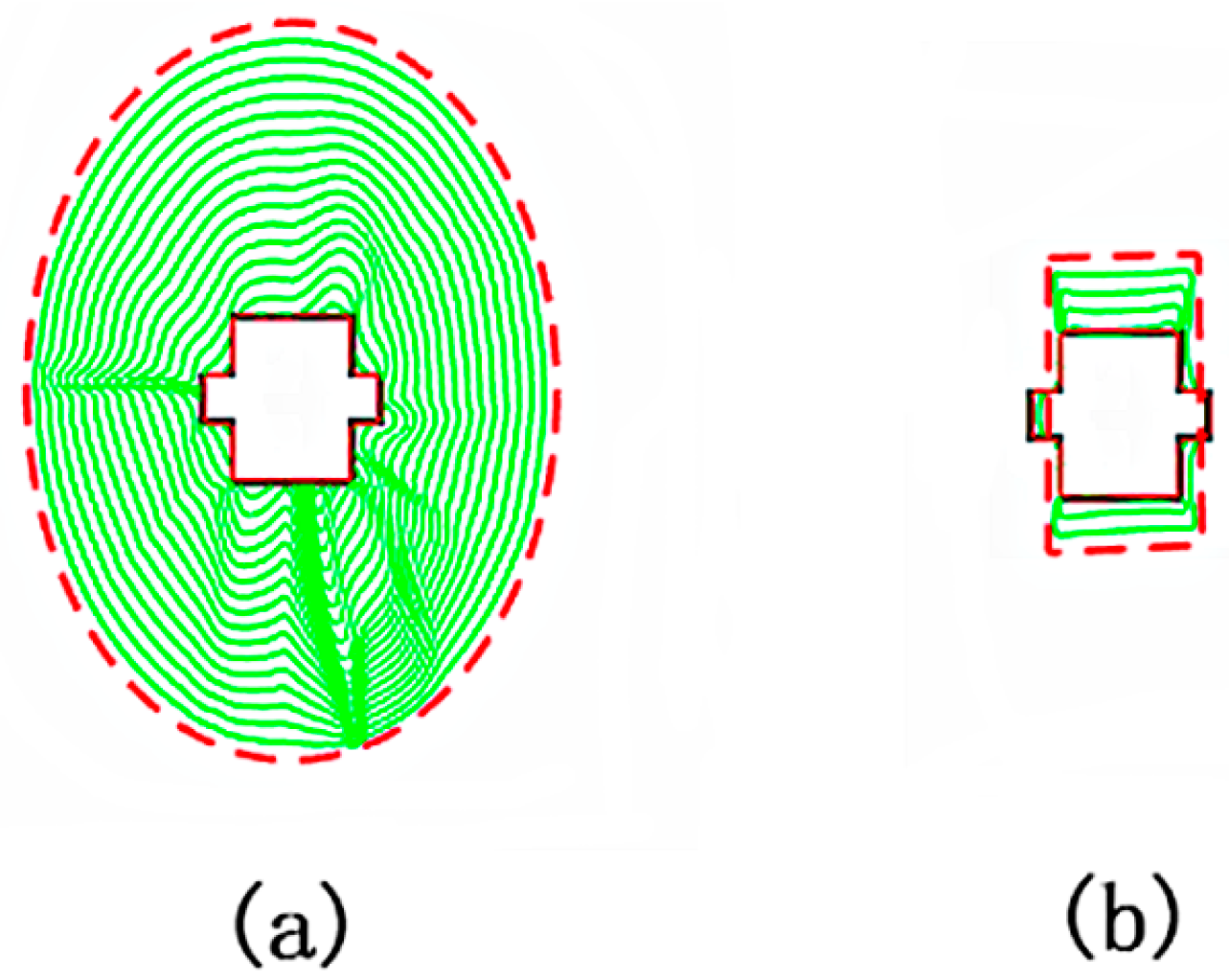
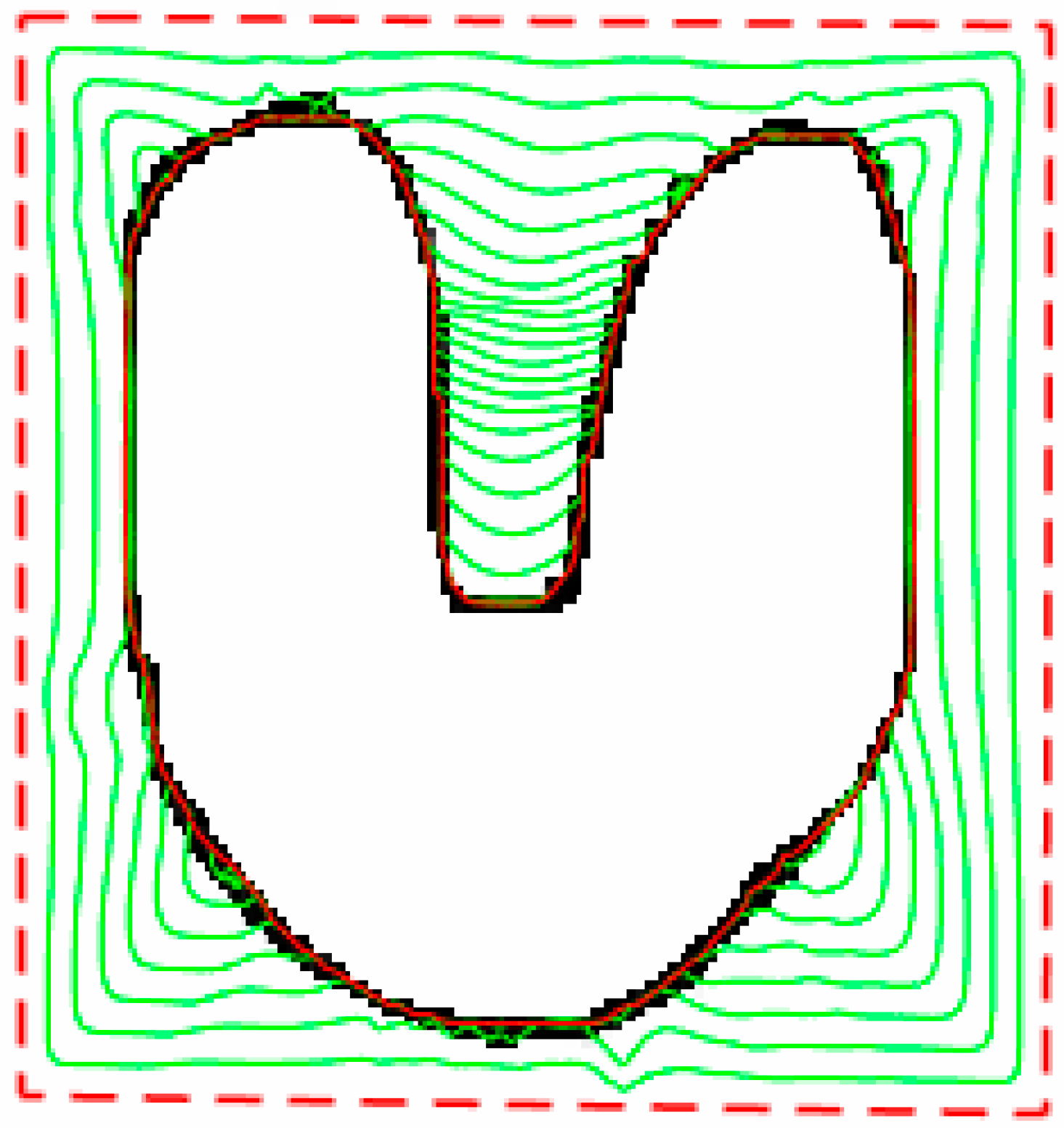
4.1. Catching Range, Convergence for Convex and Concave Planes and Insensitivity to Initial Contours
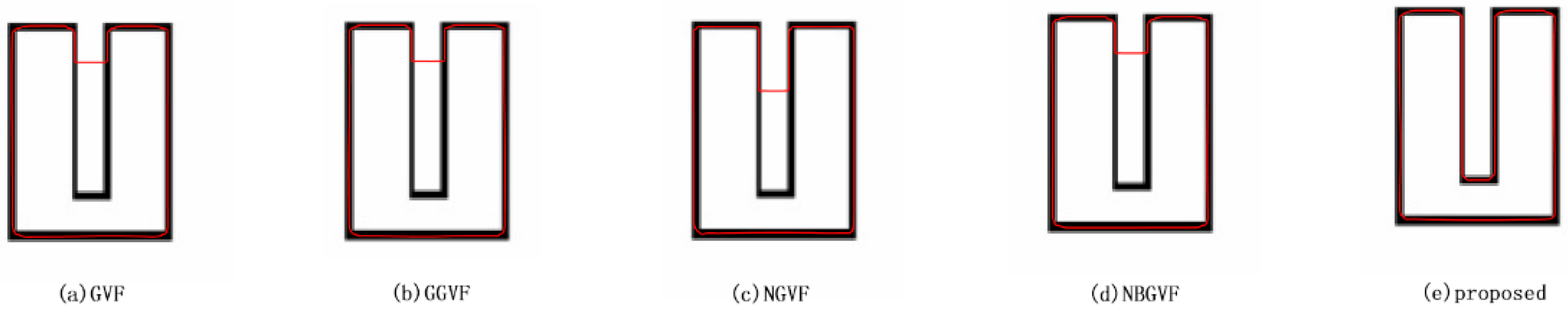
4.2. Convergence for Long Narrow Edges
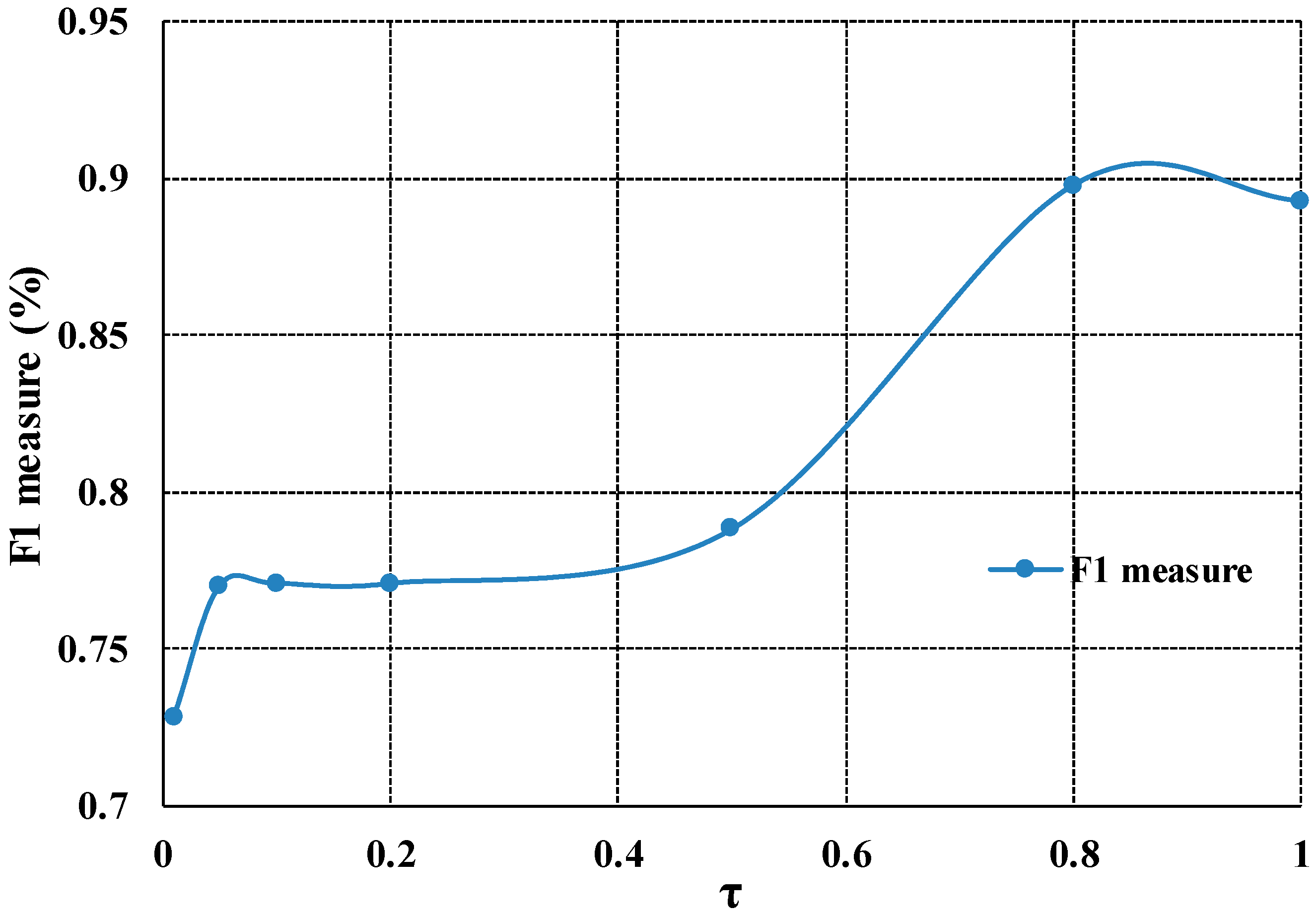
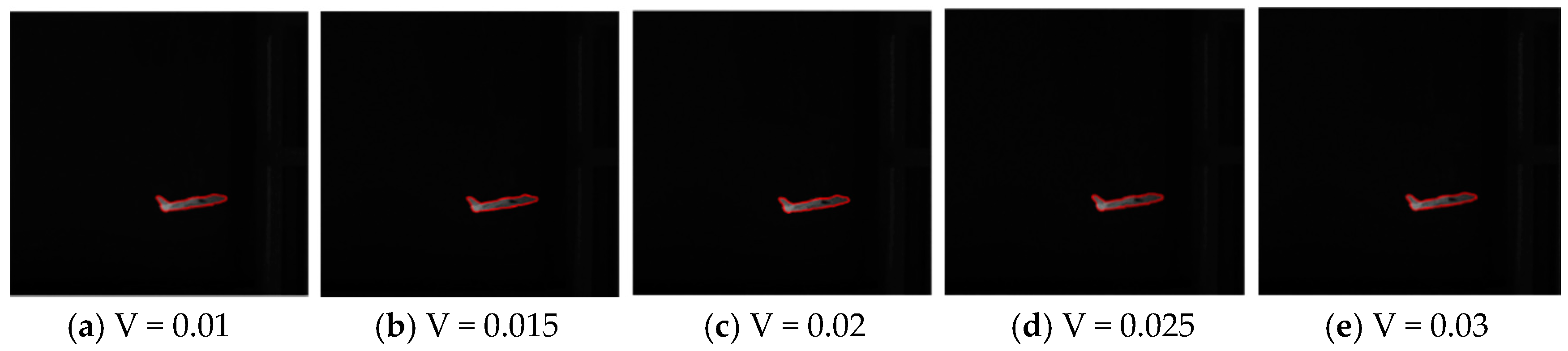
4.3. Parameter Settings Sensitivity
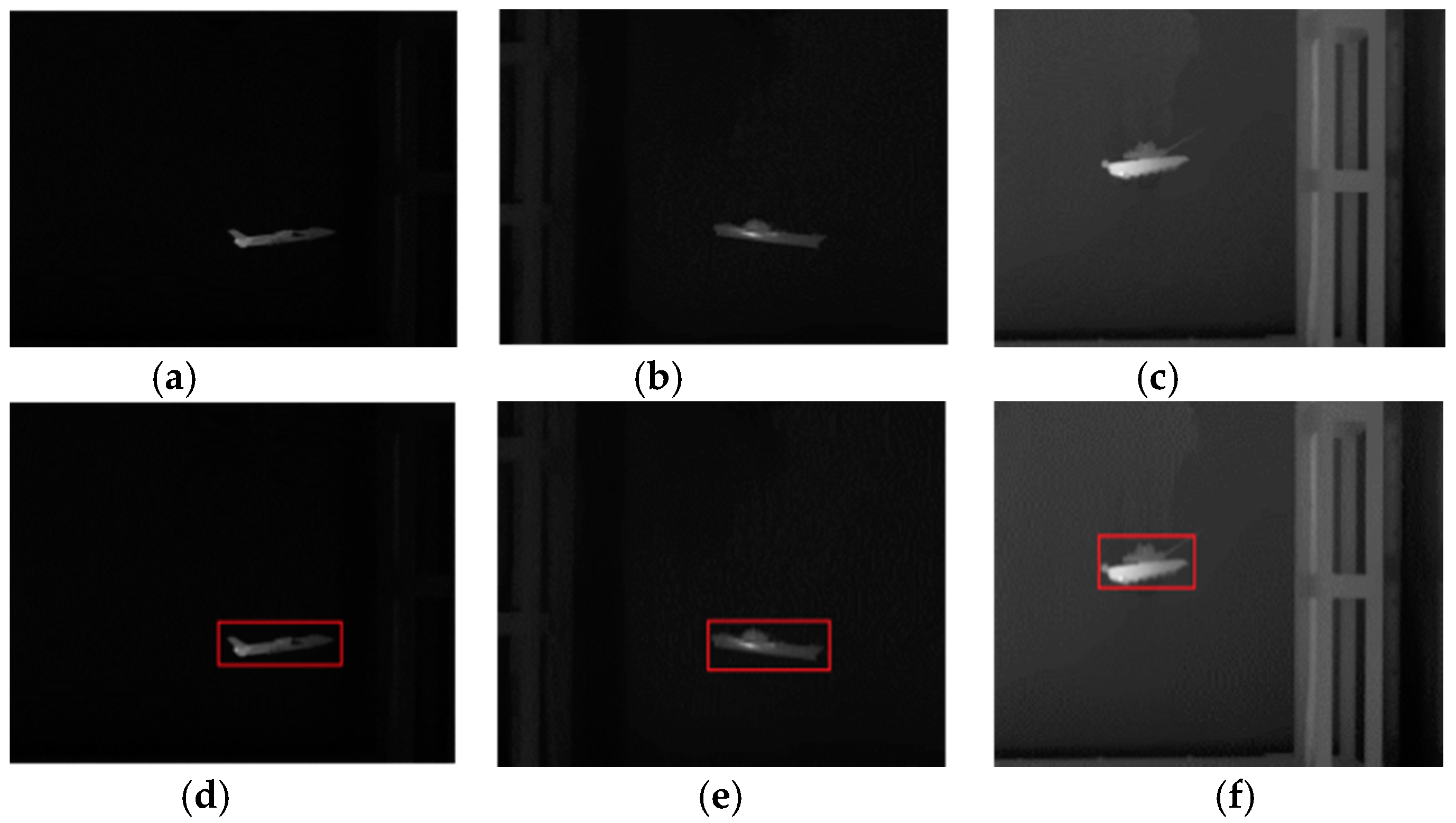
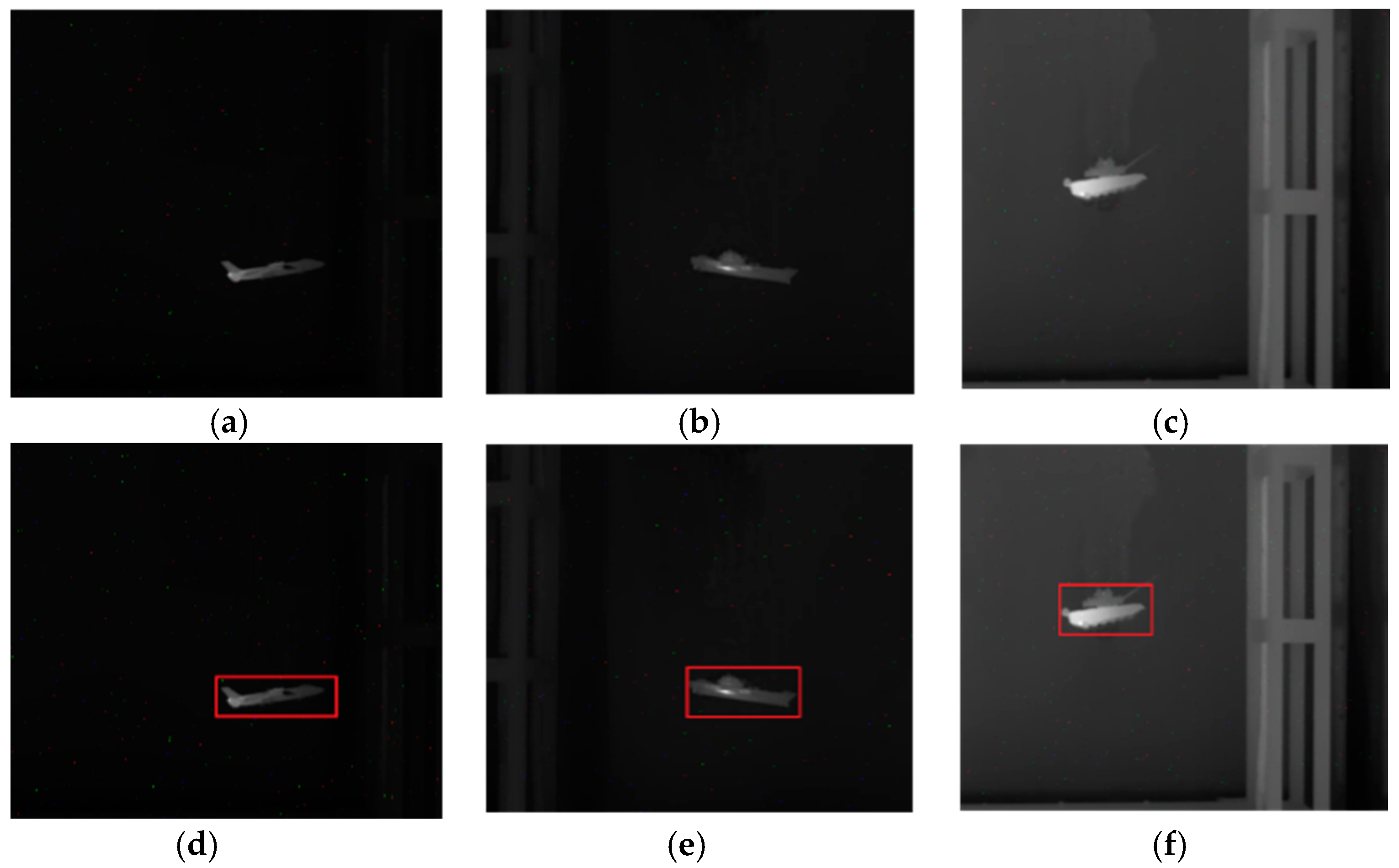
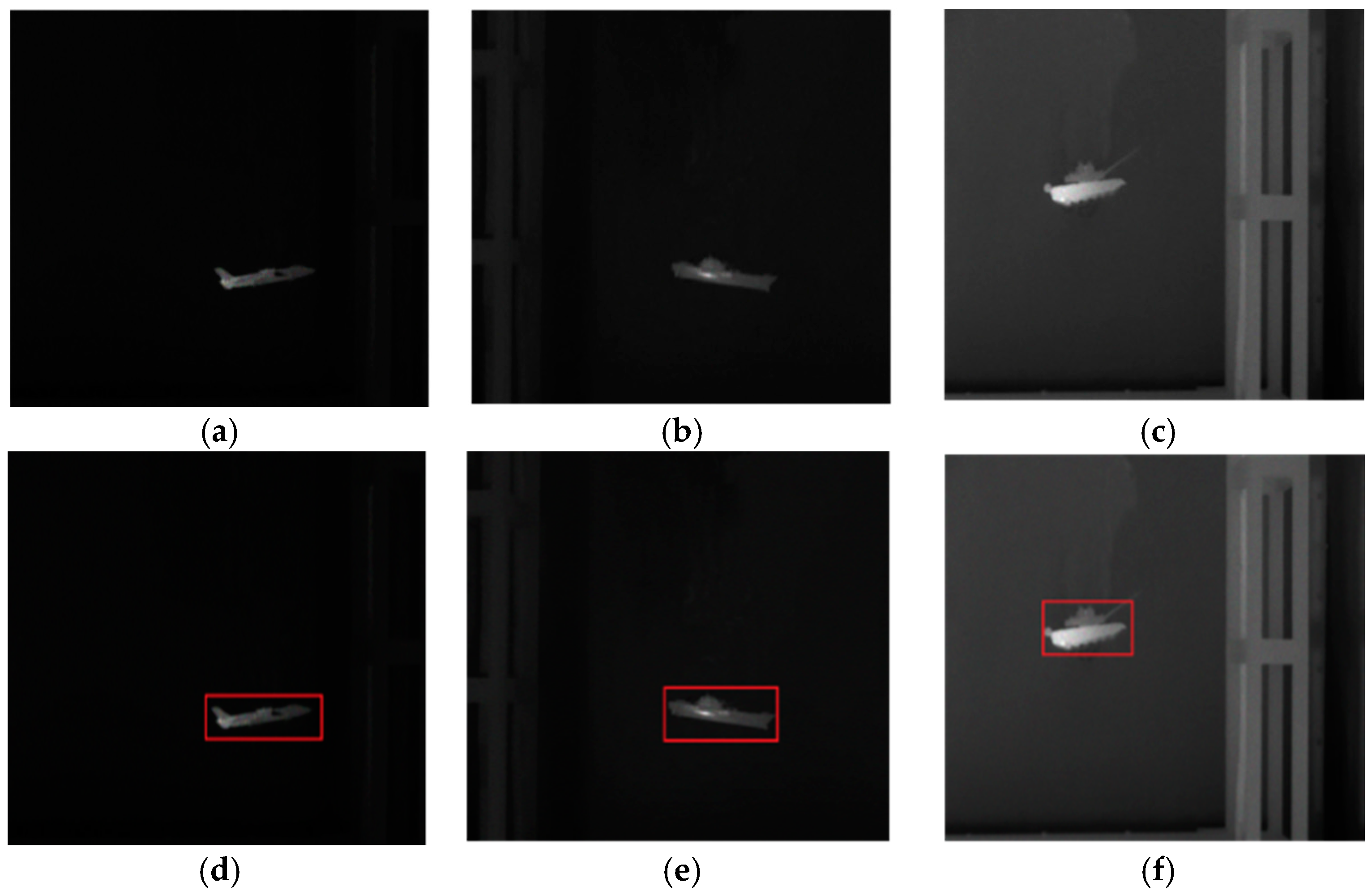
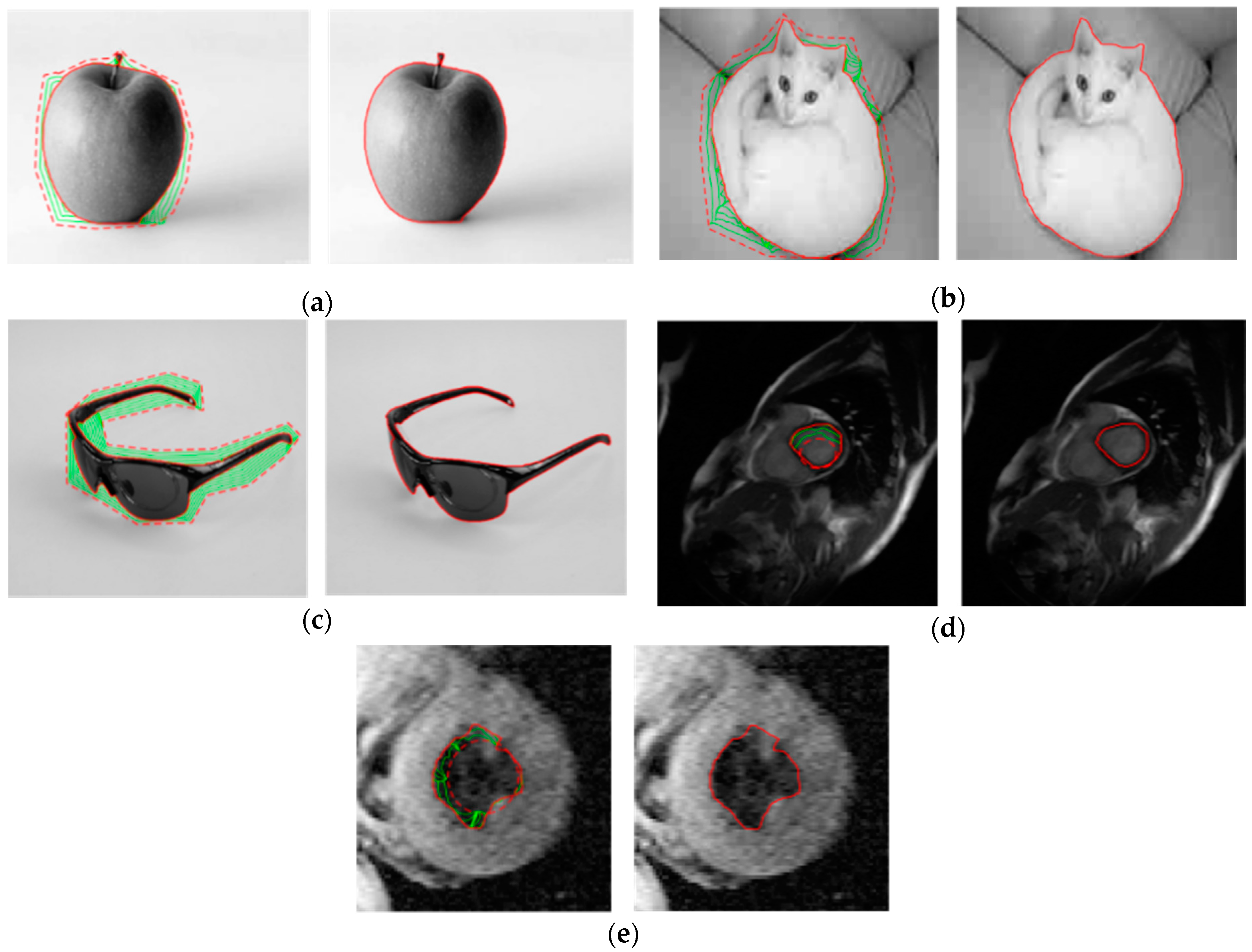
4.4. Segmentation Results for Common Real-World Infrared Images
4.5. Segmentation Results of Noise-Corrupted Infrared Images
4.6. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, S.; Gao, R. A novel generalized gradient vector flow snake model using minimal surface and component-normalized method for medical image segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2016, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, N.; Acton, S.T.; Ley, K. Tracking leukocytes in vivo with shape and size constrained active contours. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2002, 21, 1222–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, A.R.; Mukherjee, D.P.; Acton, S.T. Constraining active contour evolution via Lie Groups of transformation. IEEE Trans. Imag. Process. 2004, 6, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Y.; Gong, Y. Active contour model based on local and global intensity information for medical image segmentation. Neurocomputing 2016, 186, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciecholewski, M. An edge-based active contour model using an inflation/deflation force with a damping coefficient. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 44, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Tian, H. Generalized gradient vector flow for snakes: New observations, analysis, and improvement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2013, 23, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y. Adaptive diffusion flow active contours for image segmentation. Comput. Vis. Imag. Underst. 2013, 117, 1421–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, P.; Ju, Y.; Wang, C. A new active contour model based on distance-weighted potential field. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 1729–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, W.; Qu, F. Guide filter-based gradient vector flow module for infrared image segmentation. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 9809–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; An, J.; Liu, Z. A novel edge detection algorithm based on global minimization active contour model for oil slick infrared aerial image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhou, H.; Shao, Y. An improved Chan-Vese model by regional fitting for infrared image segementation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 74, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalooshi, F.A.; Krieger, E.; Sidike, P.; Asari, V.K. Efficient thermal image segmentation through integration of nonlinear enhancement with unsupervised active contour model. Opt. Pattern Recognit. XXVI 94770C 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Yan, L. Fast hybrid fitting energy-based active contour model for target detection. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2011, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Paragios, N.; Deriche, R. Geodesic active regions and level set methods for motion estimation and tracking. Comput. Vis. Imag. Underst. 2005, 97, 259–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Freedman, D. Tracking objects using density matching and shape priors. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; pp. 1056–1062.
- Jalba, A.; Wikinson, M.; Roerdink, J. CPM: A deformable model for shape recovery and segmentation based on charged particles. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 1320–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, M.; Witkin, A.; Terzopoulos, D. Snakes: Active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1988, 1, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Prince, J. Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans. Imag. Process. 2002, 7, 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Prince, J. Generalized gradient vector flow external forces for active contours. Signal Process. 1998, 71, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Wu, C.; Liu, S.; Yang, S. NGVF: An improved external force field for active contour model. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2007, 28, 58–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.; Lu, S. Image segmentation using active contours with normally biased GVF external force. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 2010, 17, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, R. A novel snake model using new multi-step decision model for complex image segmentation. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2016, 51, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselles, V.; Kimmel, R.; Sapiro, G. Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. 1997, 22, 61–79. [Google Scholar]
- Santarelli, M.F.; Positano, V.; Michelassi, C.; Lombardi, M.; Landini, L. Automated cardiac MR image segmentation: Theory and measurement valuation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2003, 25, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Masterson, K.; Valle, J.P. Comparative evaluation of active contour model extensions for automated cardiac MR image segmentation by regional error assessment. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2007, 20, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Mirmehdi, M. MAC: Magnetostatic active contour model. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Mirmehdi, M. RAGS: Region-aided geometric snake. IEEE Trans. Imag. Process. 2004, 13, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Song, H.; Zhang, L. Active contours driven by local image fitting energy. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsamea, M.; Gnecco, G.; Gaber, M. An efficient self-organizing active contour model for image segmentation. Neurocomputing 2015, 149, 820–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
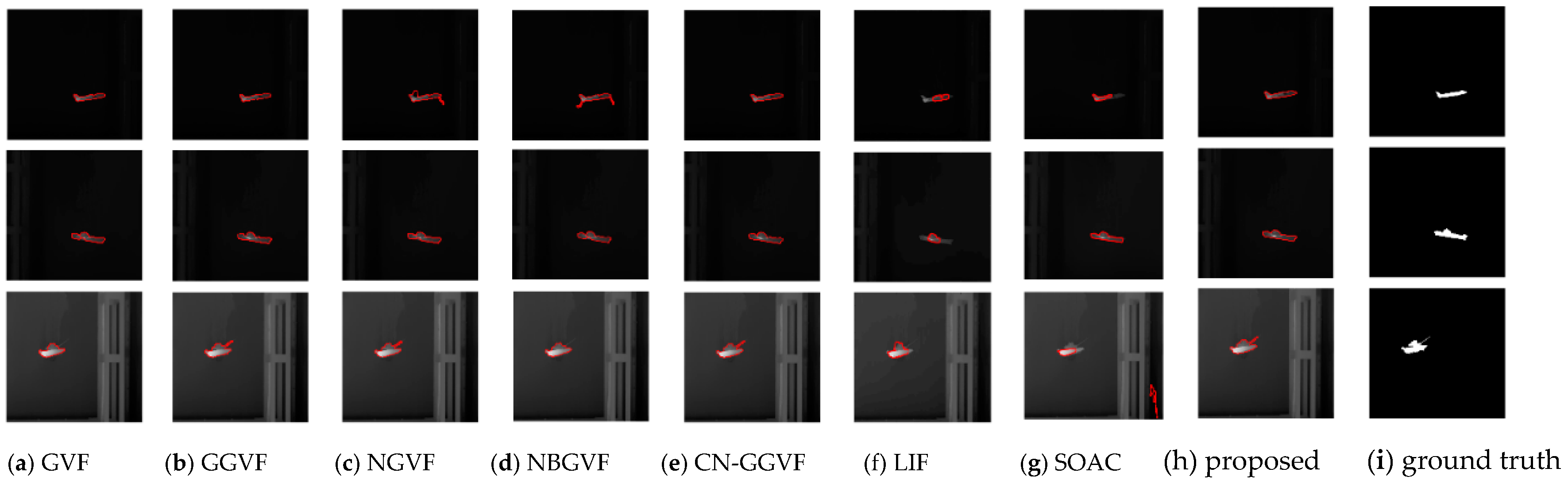

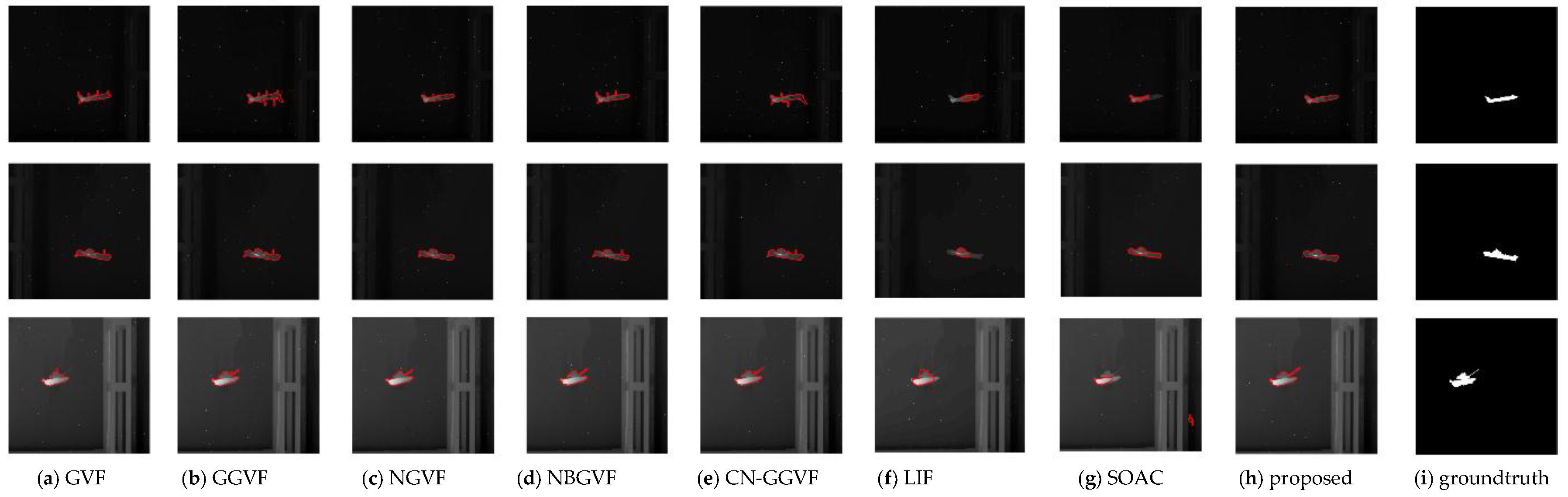
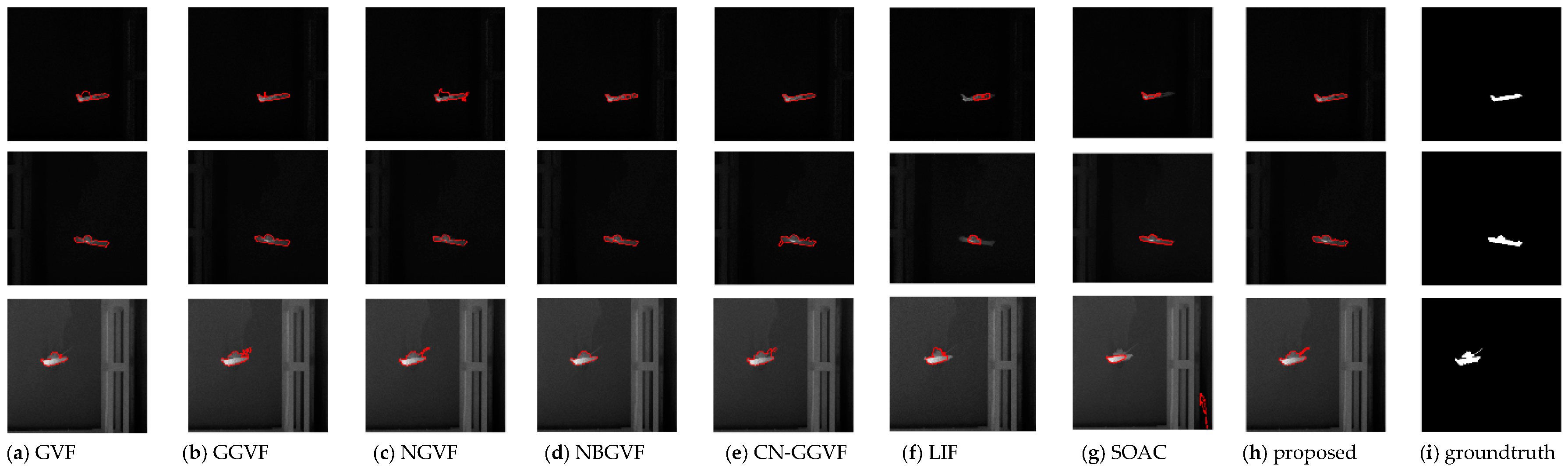
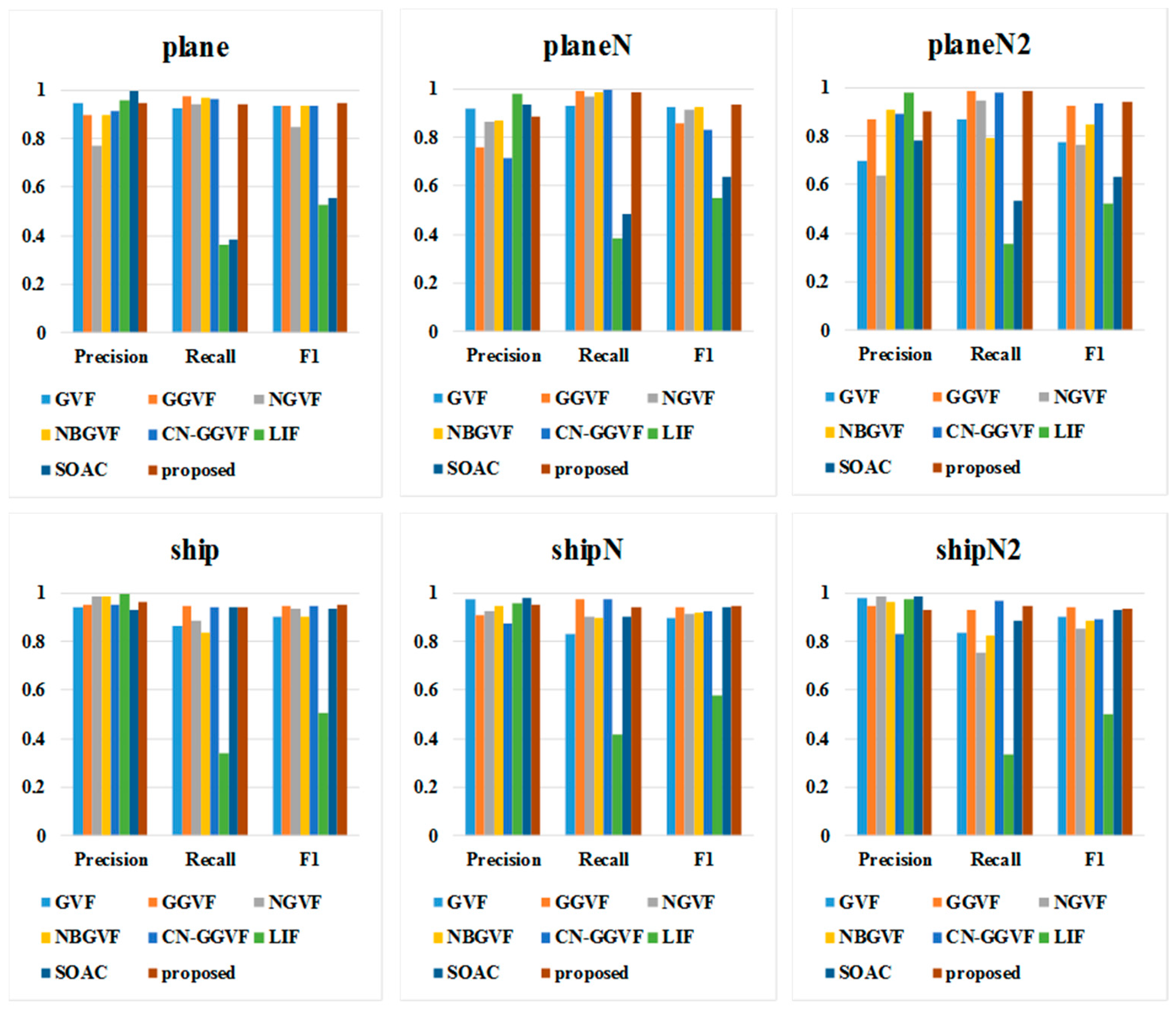
| GVF | GGVF | NGVF | NBGVF | CN-GGVF | LIF | SOAC | Proposed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plane | Precision | 0.9475 | 0.8958 | 0.7723 | 0.8984 | 0.914 | 0.955 | 0.9948 | 0.9484 |
| Recall | 0.9246 | 0.9759 | 0.9407 | 0.9688 | 0.9618 | 0.3628 | 0.3829 | 0.9427 | |
| F1 | 0.9359 | 0.9341 | 0.8482 | 0.9323 | 0.9373 | 0.5259 | 0.553 | 0.9456 | |
| ship | Precision | 0.9398 | 0.9497 | 0.9859 | 0.9835 | 0.9494 | 0.9961 | 0.9269 | 0.9597 |
| Recall | 0.8645 | 0.9453 | 0.8858 | 0.8331 | 0.9399 | 0.3391 | 0.9399 | 0.9386 | |
| F1 | 0.9006 | 0.9475 | 0.9332 | 0.9021 | 0.9446 | 0.506 | 0.9334 | 0.949 | |
| tank | Precision | 0.925 | 0.8972 | 0.8993 | 0.8929 | 0.8846 | 0.8625 | 0.6616 | 0.9122 |
| Recall | 0.8621 | 0.9549 | 0.9116 | 0.8868 | 0.9295 | 0.7073 | 0.3389 | 0.9505 | |
| F1 | 0.8924 | 0.9251 | 0.9054 | 0.8899 | 0.9065 | 0.7772 | 0.4482 | 0.931 |
| GVF | GGVF | NGVF | NBGVF | CN-GGVF | SOAC | LIF | Proposed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| planeN | Precision | 0.9177 | 0.7606 | 0.8643 | 0.8705 | 0.7147 | 0.9337 | 0.9769 | 0.8861 |
| Recall | 0.9296 | 0.9899 | 0.9668 | 0.9859 | 0.996 | 0.4814 | 0.3819 | 0.9849 | |
| F1 | 0.9236 | 0.8603 | 0.9127 | 0.9246 | 0.8322 | 0.6353 | 0.5491 | 0.9329 | |
| shipN | Precision | 0.9756 | 0.9097 | 0.9262 | 0.944 | 0.8767 | 0.9798 | 0.9555 | 0.9527 |
| Recall | 0.8284 | 0.9753 | 0.9045 | 0.8963 | 0.9733 | 0.9045 | 0.4159 | 0.9406 | |
| F1 | 0.896 | 0.9414 | 0.9152 | 0.9195 | 0.9225 | 0.9406 | 0.5795 | 0.9466 | |
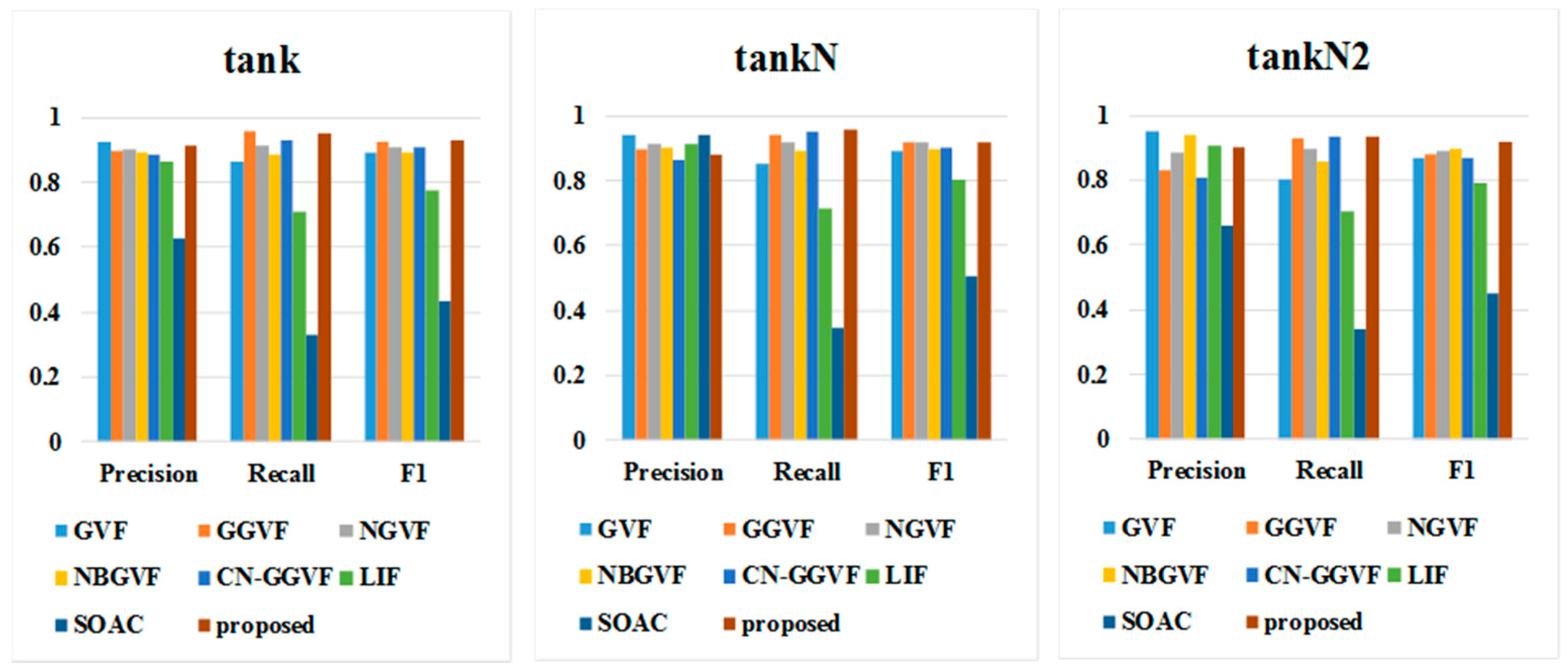
| tankN | Precision | 0.9381 | 0.8944 | 0.9145 | 0.9027 | 0.8607 | 0.9407 | 0.9104 | 0.8815 |
| Recall | 0.8528 | 0.9431 | 0.9196 | 0.8893 | 0.9518 | 0.3432 | 0.7168 | 0.9567 | |
| F1 | 0.8934 | 0.9181 | 0.9171 | 0.896 | 0.904 | 0.5029 | 0.8021 | 0.9176 |
| GVF | GGVF | NGVF | NBGVF | CN-GGVF | SOAC | LIF | Proposed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| planeN2 | Precision | 0.6992 | 0.8713 | 0.6366 | 0.9076 | 0.8928 | 0.7794 | 0.978 | 0.9026 |
| Recall | 0.8714 | 0.9869 | 0.9477 | 0.793 | 0.9789 | 0.5327 | 0.3568 | 0.9869 | |
| F1 | 0.7758 | 0.9255 | 0.7616 | 0.8464 | 0.9338 | 0.6328 | 0.5228 | 0.9429 | |
| shipN2 | Precision | 0.9805 | 0.9455 | 0.987 | 0.9598 | 0.8277 | 0.9852 | 0.9711 | 0.9277 |
| Recall | 0.8336 | 0.9317 | 0.7533 | 0.8223 | 0.9662 | 0.884 | 0.3342 | 0.9443 | |
| F1 | 0.9011 | 0.9385 | 0.8545 | 0.8857 | 0.8887 | 0.9318 | 0.4973 | 0.9359 | |
| tankN2 | Precision | 0.9487 | 0.8297 | 0.8835 | 0.9383 | 0.8086 | 0.6616 | 0.9082 | 0.9037 |
| Recall | 0.8002 | 0.9307 | 0.8955 | 0.8565 | 0.9326 | 0.3389 | 0.7038 | 0.9338 | |
| F1 | 0.8682 | 0.8773 | 0.8894 | 0.8956 | 0.8662 | 0.4482 | 0.793 | 0.9185 |
| GVF | GGVF | NGVF | NBGVF | CN-GGVF | LIF | SOAC | Proposed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average CPU Time (s) | 81.131 | 84.074 | 93.401 | 88.699 | 86.297 | 184.065 | 117.122 | 79.561 |
| Number of Iterations | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 300 | 200 | 100 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, Q. A Novel Gradient Vector Flow Snake Model Based on Convex Function for Infrared Image Segmentation. Sensors 2016, 16, 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101756
Zhang R, Zhu S, Zhou Q. A Novel Gradient Vector Flow Snake Model Based on Convex Function for Infrared Image Segmentation. Sensors. 2016; 16(10):1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101756
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui, Shiping Zhu, and Qin Zhou. 2016. "A Novel Gradient Vector Flow Snake Model Based on Convex Function for Infrared Image Segmentation" Sensors 16, no. 10: 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101756
APA StyleZhang, R., Zhu, S., & Zhou, Q. (2016). A Novel Gradient Vector Flow Snake Model Based on Convex Function for Infrared Image Segmentation. Sensors, 16(10), 1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101756





