Leveraging Two Kinect Sensors for Accurate Full-Body Motion Capture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview
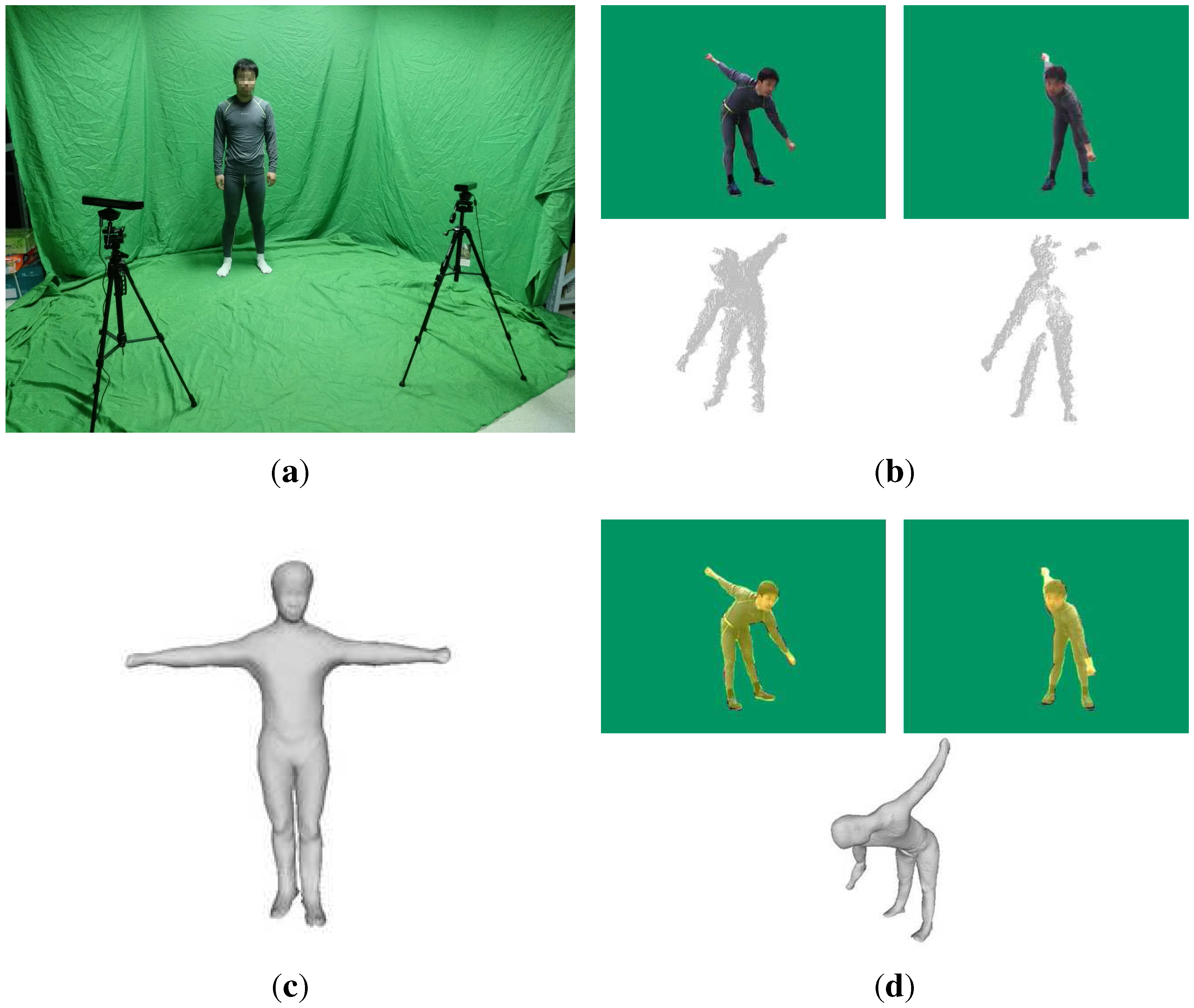
3. Motion Capture
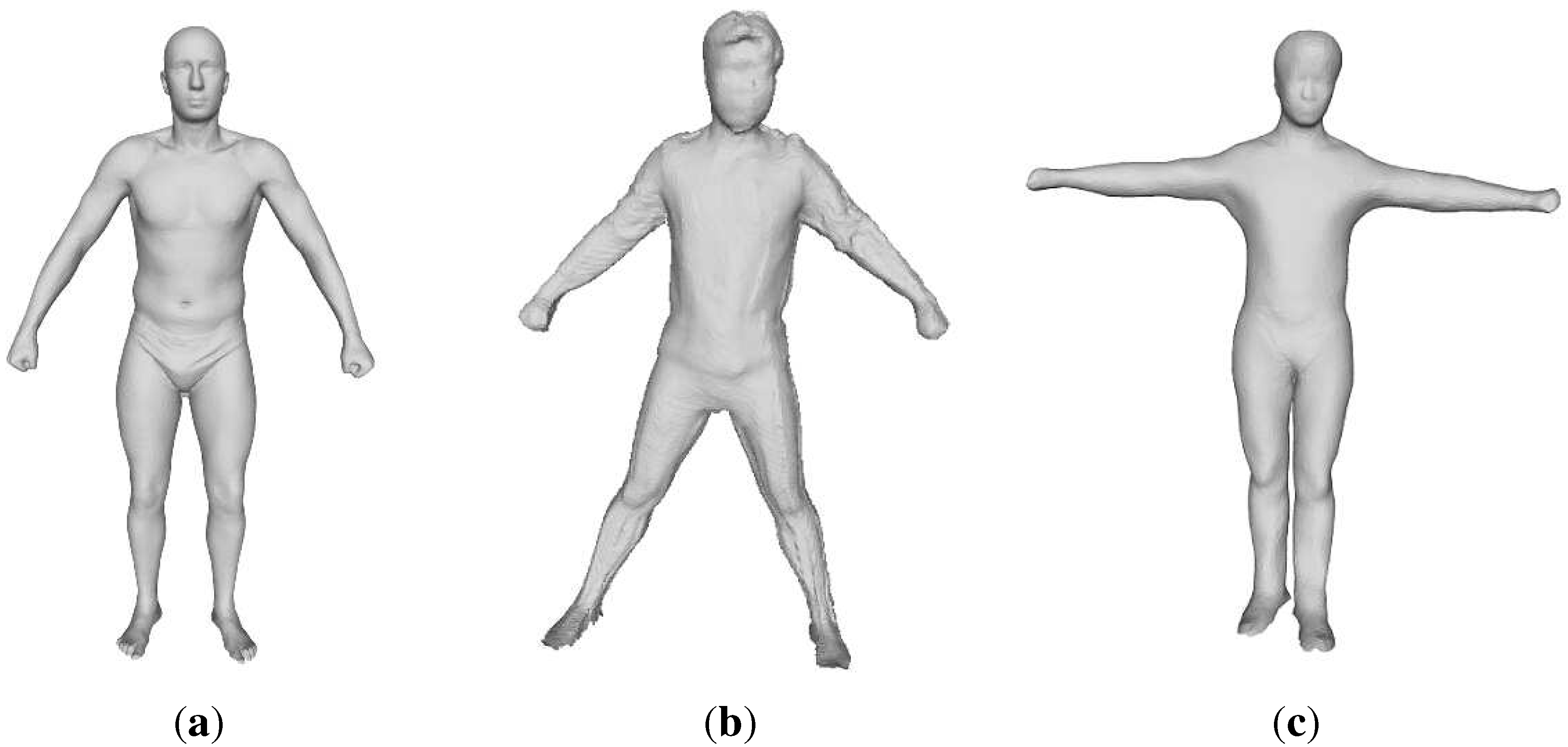
3.1. Full-Body Shape Modeling
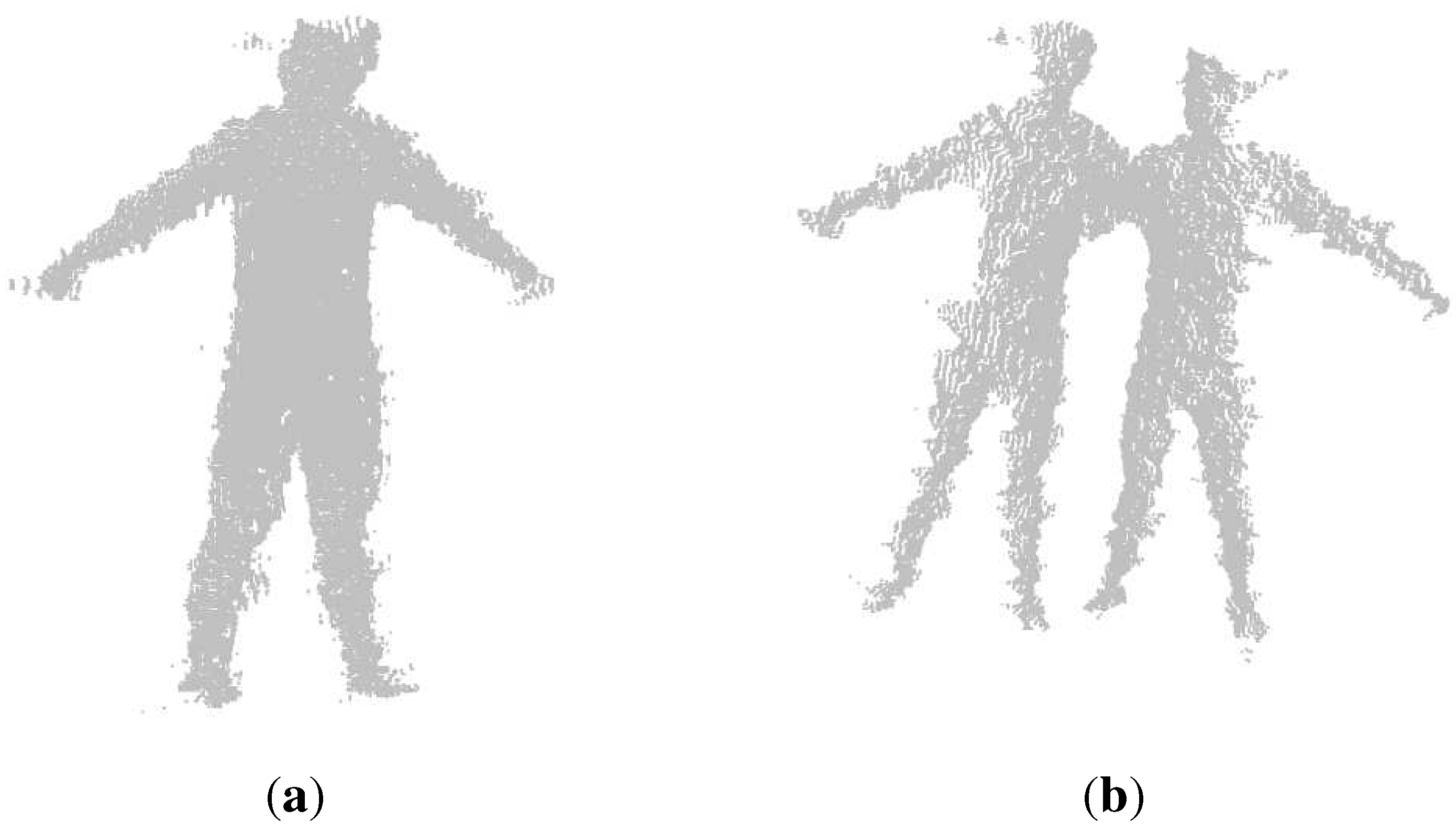
3.2. Point Cloud Registration
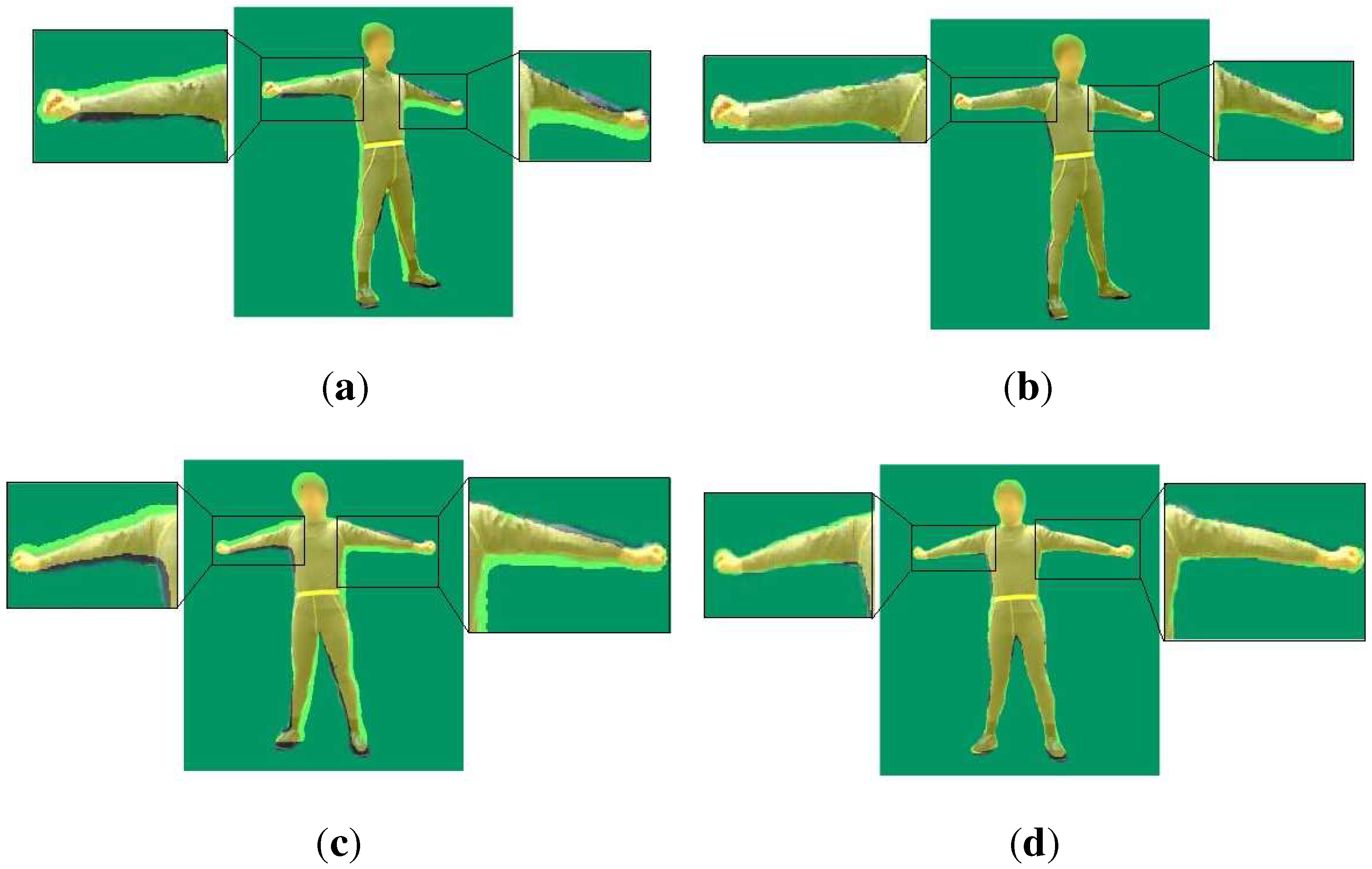
3.3. Pose Tracking
3.3.1. Temporal Term
| Left Camera | Right Camera | |
|---|---|---|
| Coincidence ratio without temporal term | 87.51% | 88.39% |
| Coincidence ratio with linear prediction | 86.48% | 87.43% |
| Coincidence ratio with quadratic prediction | 90.54% | 91.68% |
3.3.2. Optimization
3.4. Failure Detection
- : The pixels belong to both the observed and the rendered map, and the difference of the depth value is less than 5 cm
- : The pixels belong to both the observed and the rendered map, but the difference of the depth value is more than 5 cm
- : The pixels belong to the rendered depth map, but do not belong to the observed depth map.
- : The pixels belong to the observed depth map, but do not belong to the rendered depth.
- The proportion of the effective area is less than a threshold, which is experimentally set to 15%.
- Any term of the reconstructed pose parameters comes to an unreasonable result. In other words, an unreasonable result means that the rotation direction or angle comes to an impossible result, for example the rotation angle of the arm is less than 0.
4. Results and Discussion

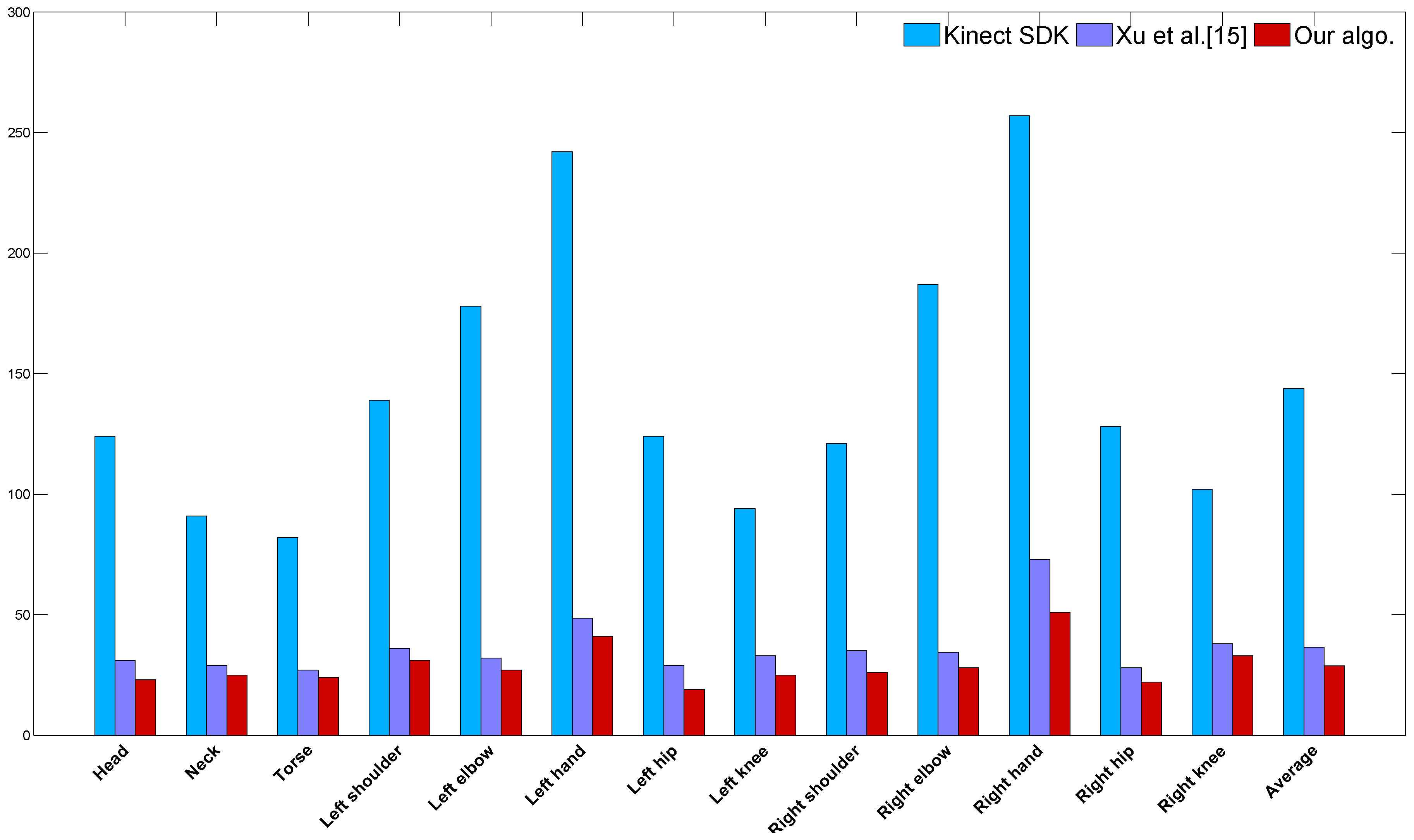
4.1. Comparison against Kinect
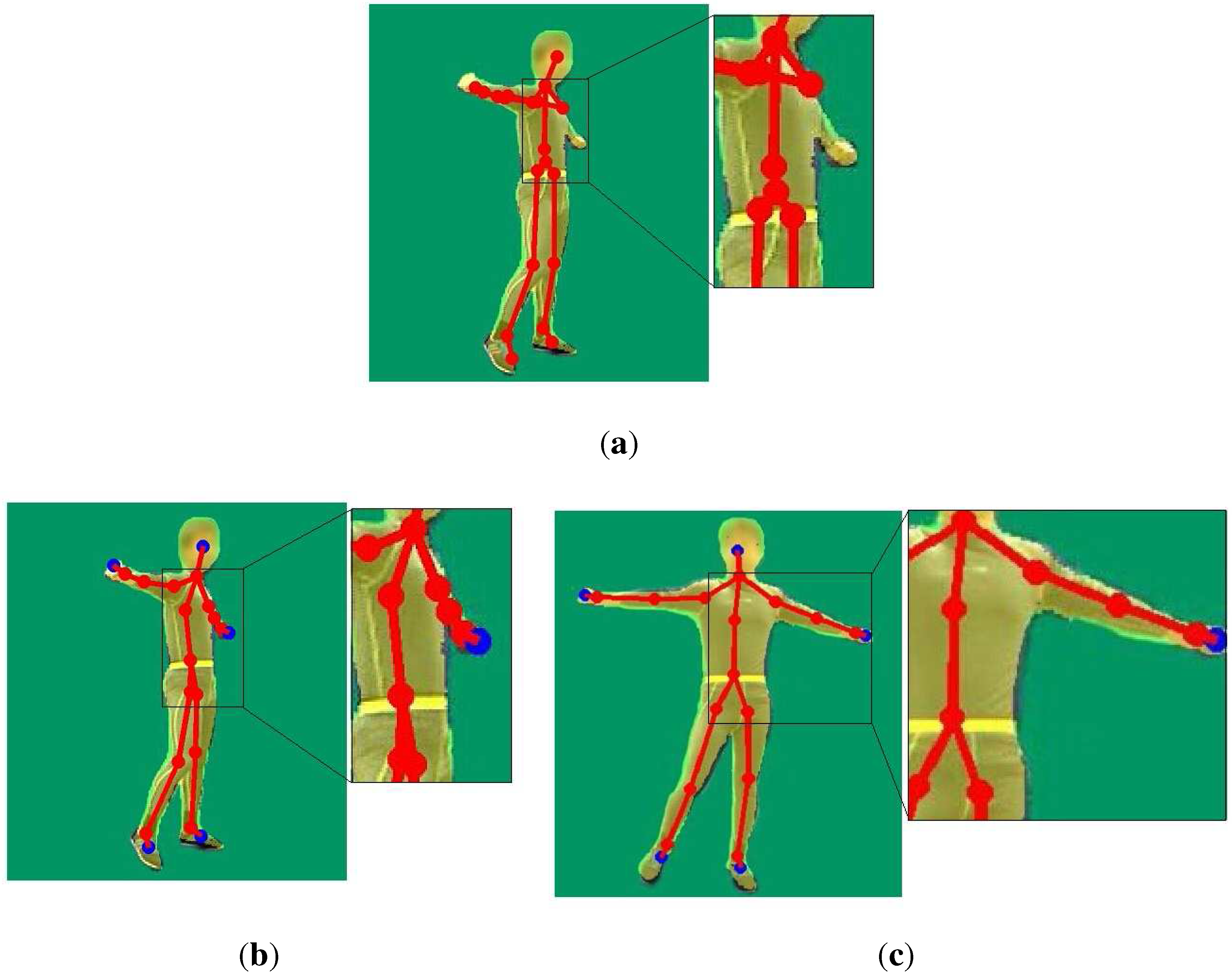
4.2. Comparison against Motion Capture Using a Single Depth Camera
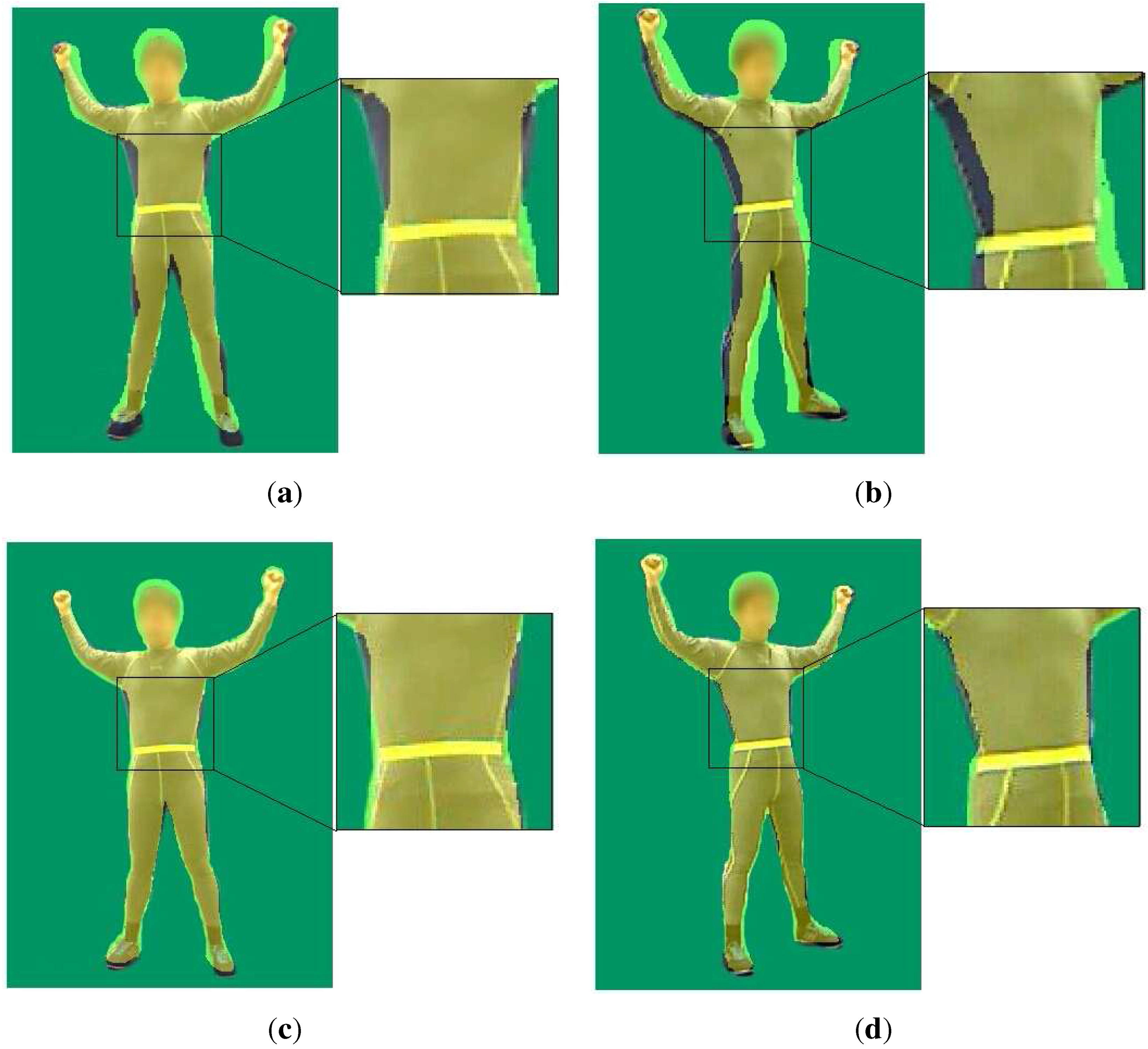

| Left Camera | Right Camera | |
|---|---|---|
| Proportion of the effective region of [15] | 86.35% | 87.73% |
| Proportion of the effective region of our method | 89.72% | 90.86% |
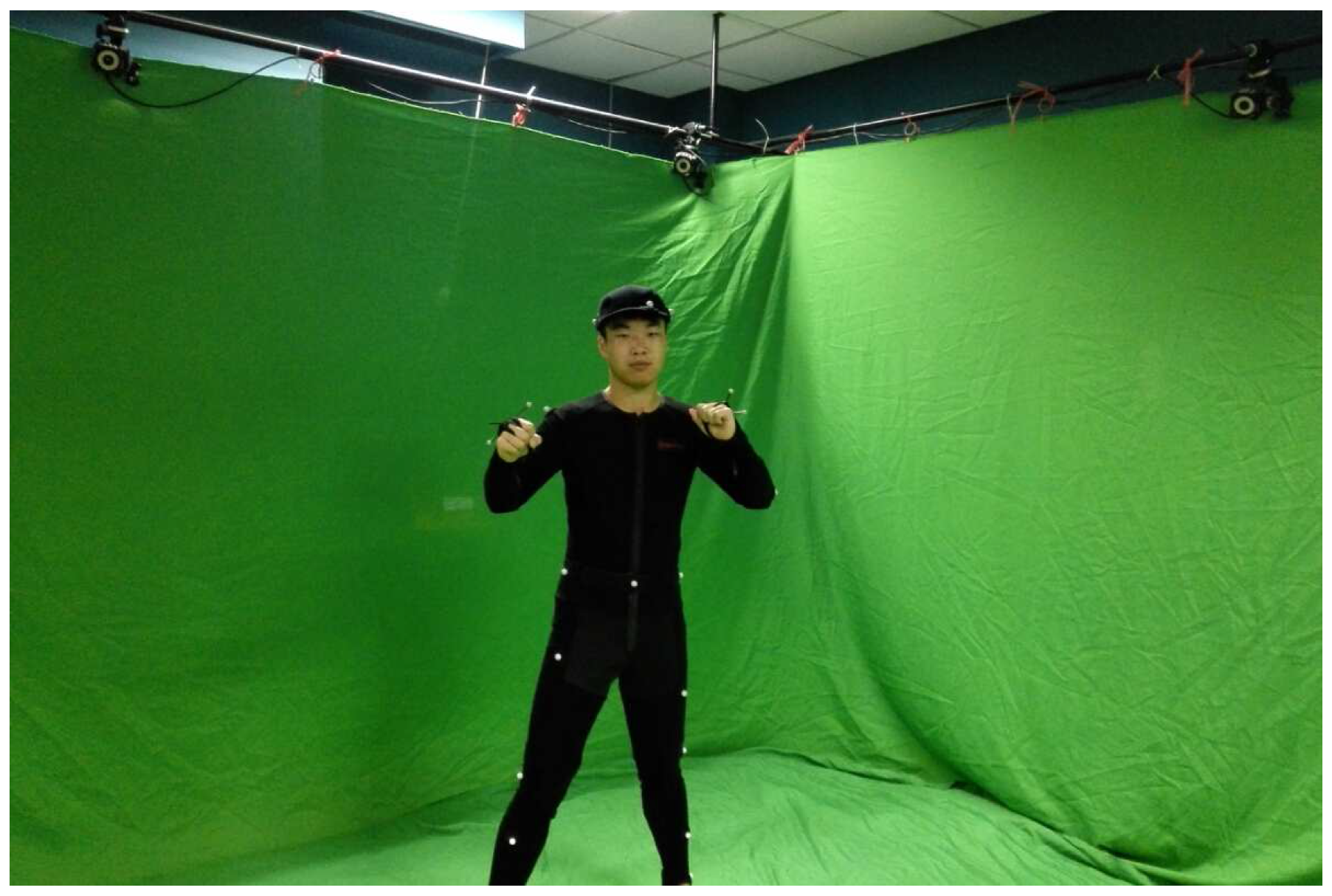
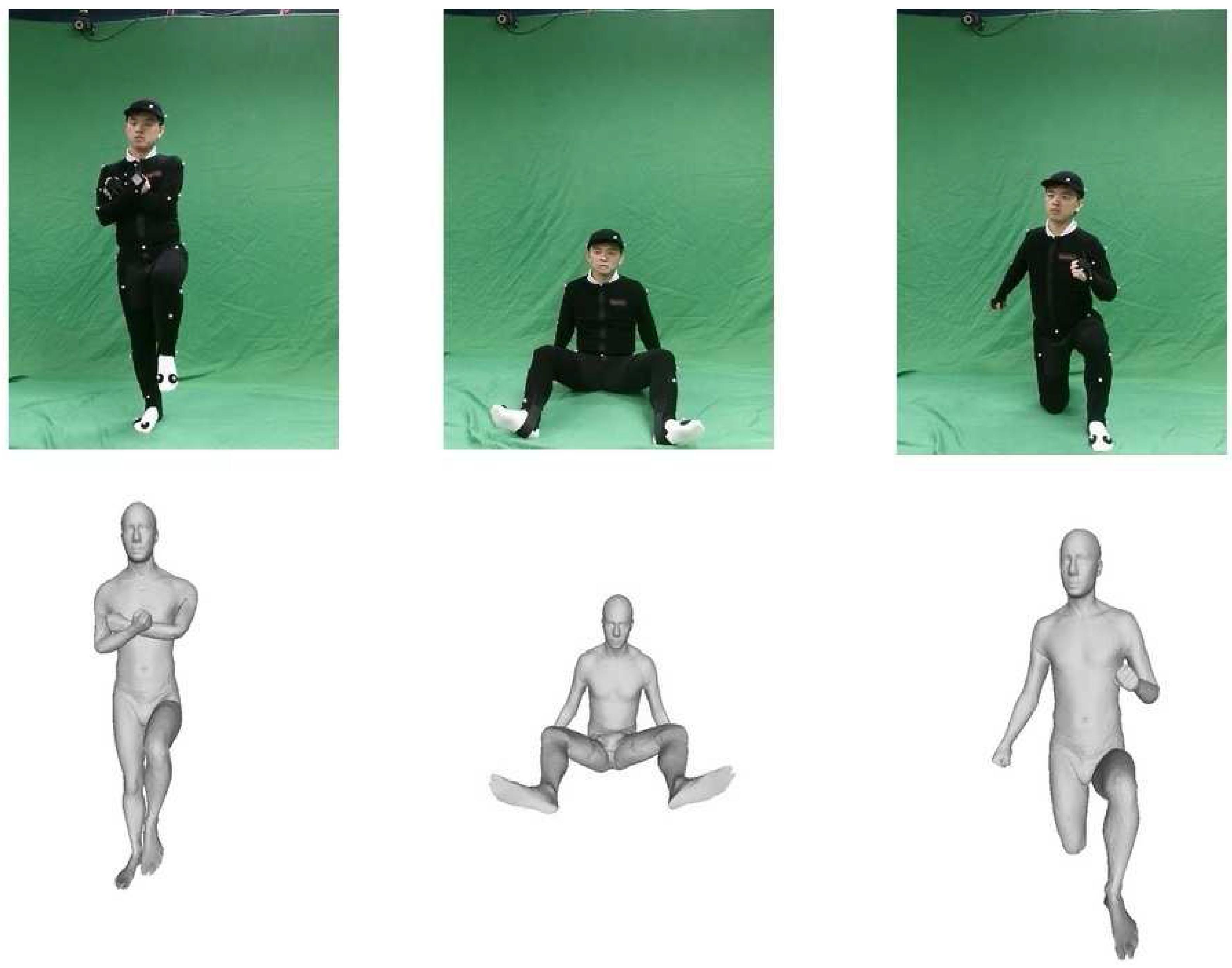
4.3. Comparison against OptiTrack
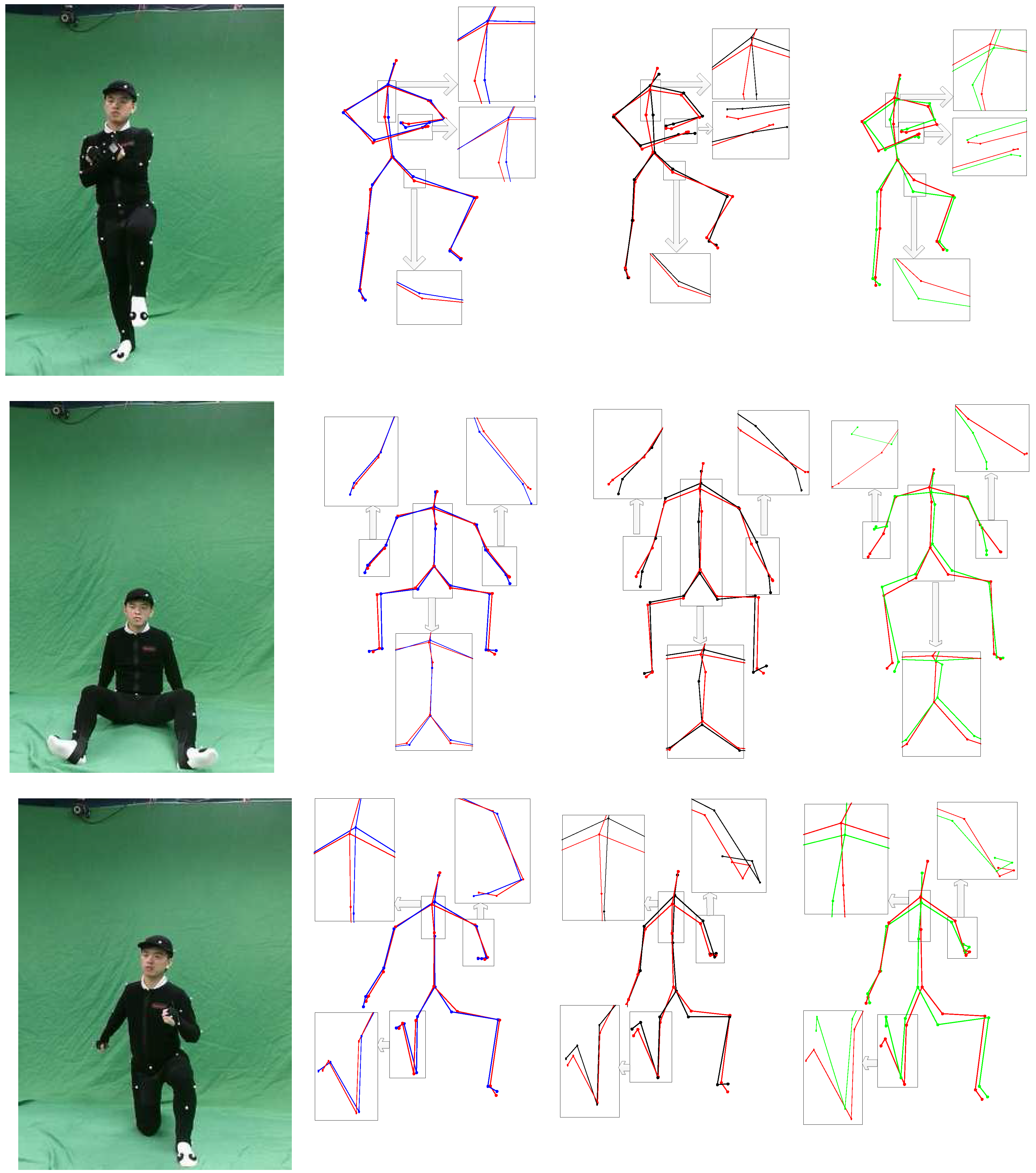
4.4. Evaluation of Algorithm Complexity and System Robustness
4.4.1. Complexity Analysis
4.4.2. Tracking Failure Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moeslund, T.B.; Hilton, A.; Krüger, V. A Survey of Advances in Vision-Based Human Motion Capture and Analysis. Comp. Vis. Image Uud. 2006, 104, 90–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicon System 2014. Available online: http://www.vicon.com/ (accessed on 6 August 2013).
- Xsens 2014. Available online: http://www.xsens.com/ (accessed on 6 August 2013).
- Ascension 2014. Available online: http://www.ascension-tech.com/ (accessed on 6 August 2013).
- De Aguiar, E.; Stoll, C.; Theobalt, C.; Ahmed, N.; Seidel, H.P.; Thrun, S. Performance Capture from Sparse Multi-view Video. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Stoll, C.; Gall, J.; Seidel, H.P.; Theobalt, C. Markerless Motion Capture of Interacting Characters using Multi-View Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1249–1256.
- Stoll, C.; Hasler, N.; Gall, J.; Seidel, H.; Theobalt, C. Fast Articulated Motion Tracking using a Sums of Gaussians Body Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 951–958.
- Straka, M.; Hauswiesner, S.; Ruther, M.; Bischof, H. Rapid Skin: Estimating the 3D Human Pose and Shape in Real-Time. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on 3D Imaging, Modeling, Processing, Visualization and Transmission, ETH Zürich, Switzerland, 13–15 October 2012; pp. 41–48.
- Khoshelham, K.; Elberink, S.O. Accuracy and Resolution of Kinect Depth Data for Indoor Mapping Applications. Sensors 2012, 12, 1437–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, R.; Ren, L.; Pollefeys, M. Accurate 3D Pose Estimation from a Single Depth Image. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 731–738.
- Weiss, A.; Hirshberg, D.; Black, M.J. Home 3D Body Scans from Noisy Image and Range Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 1951–1958.
- Shotton, J.; Sharp, T.; Kipman, A.; Fitzgibbon, A.; Finocchio, M.; Blake, A.; Cook, M.; Moore, R. Real-Time Human Pose Recognition in Parts from Single Depth Images. Commun. ACM 2013, 56, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grest, D.; Krüger, V.; Koch, R. Single view motion tracking by depth and silhouette information. In Image Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, German, 2007; pp. 719–729. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, P.; Chai, J. Accurate Realtime Full-Body Motion Capture using a Single Depth Camera. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, S. Measuring Accurate Body Parameters of Dressed Humans with Large-Scale Motion Using a Kinect Sensor. Sensors 2013, 13, 11362–11384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguelov, D.; Srinivasan, P.; Koller, D.; Thrun, S.; Rodgers, J.; Davis, J. SCAPE: Shape Completion and Animation of PEople. ACM Trans. Graph. 2005, 24, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Deng, K.; Bai, X.; Leyvand, T.; Guo, B.; Tu, Z. Exemplar-based human action pose correction and tagging. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 1784–1791.
- Shen, W.; Deng, K.; Bai, X.; Leyvand, T.; Guo, B.; Tu, Z. Exemplar-based human action pose correction. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Lei, R.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, Z. Regularity Guaranteed Human Pose Correction. In Computer Vision—ACCV 2014; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 242–256. [Google Scholar]
- Microsoft Kinect API for Windows. 2012. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/kinectforwindows/ (accessed on 3 May 2013).
- Essmaeel, K.; Gallo, L.; Damiani, E.; de Pietro, G.; Dipanda, A. Temporal denoising of kinect depth data. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Signal Image Technology and Internet Based Systems (SITIS), Naples, Italy, 25–29 November 2012; pp. 47–52.
- Allen, B.; Curless, B.; Popović, Z. The space of human body shapes: Reconstruction and parameterization from range scans. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2003, 22, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sidan, D.; Davis, J.; Yang, R. Semantic Parametric Reshaping of Human Body Models. In Proceedings of the 2014 2nd International Conference on 3D Vision, Tokyo, Japan, 8–11 December 2014; pp. 41–48.
- Hasler, N.; Stoll, C.; Sunkel, M.; Rosenhahn, B.; Seidel, H.P. A Statistical Model of Human Pose and Body Shape. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the European Association for Computer Graphics, Munich, Germany, 3 April 2009; pp. 337–346.
- Desbrun, M.; Meyer, M.; Schröder, P.; Barr, A.H. Implicit Fairing of Irregular Meshes using Diffusion and Curvature Flow. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 8–13 August 1999; pp. 317–324.
- Berger, K.; Ruhl, K.; Schroeder, Y.; Bruemmer, C.; Scholz, A.; Magnor, M.A. Markerless Motion Capture Using Multiple Color-Depth Sensors. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Vision, Modeling, and Visualization, Berlin, German, 4–6 October 2011; pp. 317–324.
- Auvinet, E.; Meunier, J.; Multon, F. Multiple depth cameras calibration and body volume reconstruction for gait analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2012 11th International Conference on Information Science, Signal Processing and their Applications (ISSPA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 2–5 July 2012; pp. 478–483.
- Gauvain, J.L.; Lee, C.H. Maximum a Posteriori Estimation for Multivariate Gaussian Mixture Observations of Markov chains. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 1994, 2, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myronenko, A.; Song, X. Point Set Registration: Coherent Point Drift. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 2262–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.; Matthews, I. Lucas-Kanade 20 Years on: A Unifying Framework. Int. J. Comp. Vis. 2004, 56, 221–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Du, S. Leveraging Two Kinect Sensors for Accurate Full-Body Motion Capture. Sensors 2015, 15, 24297-24317. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150924297
Gao Z, Yu Y, Zhou Y, Du S. Leveraging Two Kinect Sensors for Accurate Full-Body Motion Capture. Sensors. 2015; 15(9):24297-24317. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150924297
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zhiquan, Yao Yu, Yu Zhou, and Sidan Du. 2015. "Leveraging Two Kinect Sensors for Accurate Full-Body Motion Capture" Sensors 15, no. 9: 24297-24317. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150924297
APA StyleGao, Z., Yu, Y., Zhou, Y., & Du, S. (2015). Leveraging Two Kinect Sensors for Accurate Full-Body Motion Capture. Sensors, 15(9), 24297-24317. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150924297





