Infrastructure-Less Indoor Localization Using the Microphone, Magnetometer and Light Sensor of a Smartphone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Indoor Location Estimation Methodology
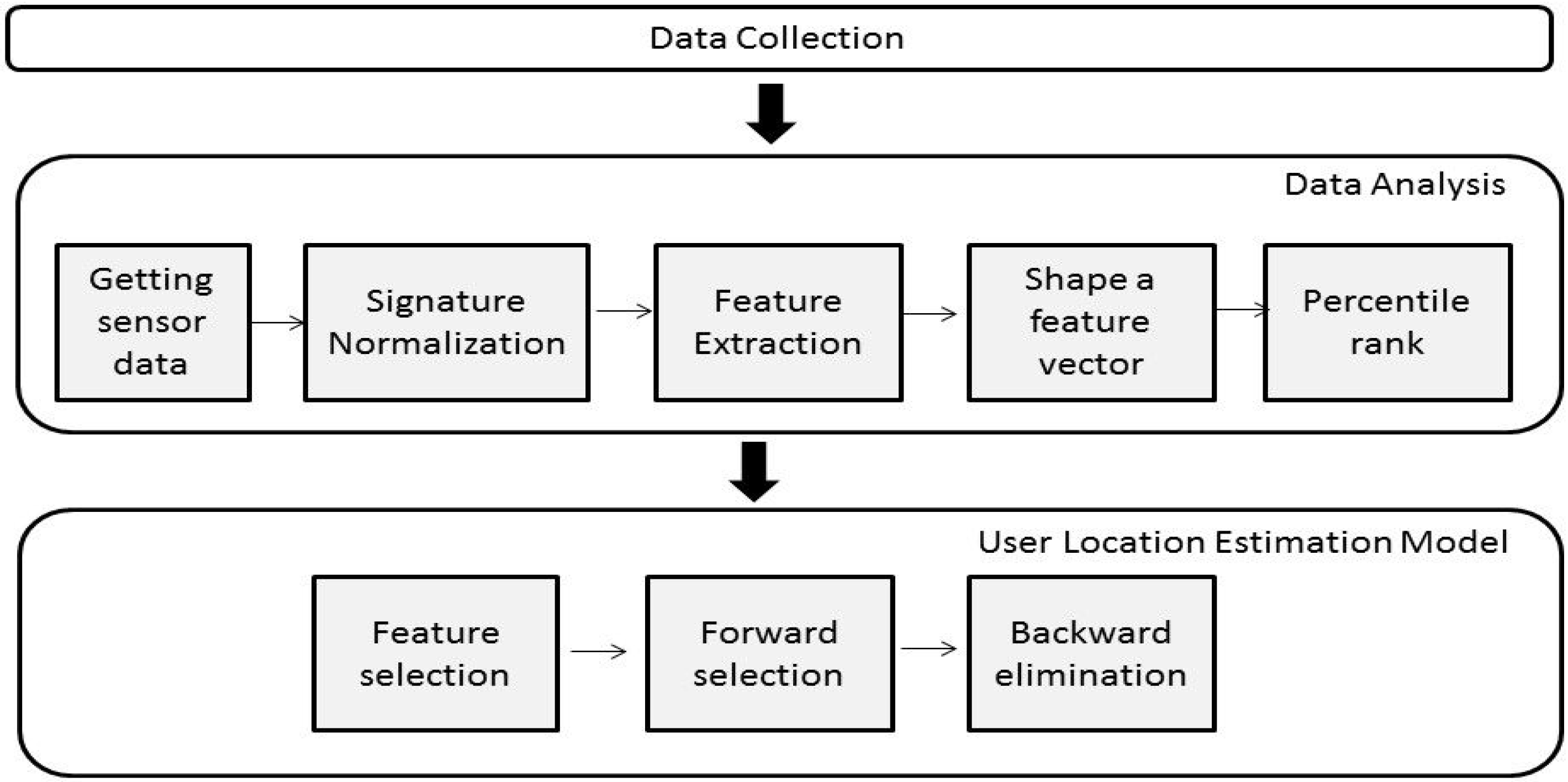
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Data Analysis
| Features | Temporal Domain | Spectral Domain |
|---|---|---|
| Kurtosis | * | * |
| Mean | * | * |
| Median | * | * |
| Standard Deviation | * | * |
| Variance | * | * |
| Coefficient of Variation (CV) | * | * |
| Inverse CV | * | * |
| 1,5,25,50,75,95,99 100-Quantile | * | * |
| Trimmed Mean | * | * |
| Shannon Entropy | * | |
| Slope | * | |
| Spectral Flatness | * | |
| Spectral Centroid | * | |
| Skewness | * | |
| 1–10 Spectrum Components | * |
2.3. User’s Location Estimation Model
- From a random selection of subsets from a population, the chromosomes are defined as variable subsets of a given size.
- The capability of each chromosome is assessed for its ability to predict a dependent variable and has a certain level of accuracy.
- The natural selection process, progressive improvement of the chromosome population, is driven by a number of operators: selection, mutation and crossover.
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Local Test Environment
3.2. Test Data Collection
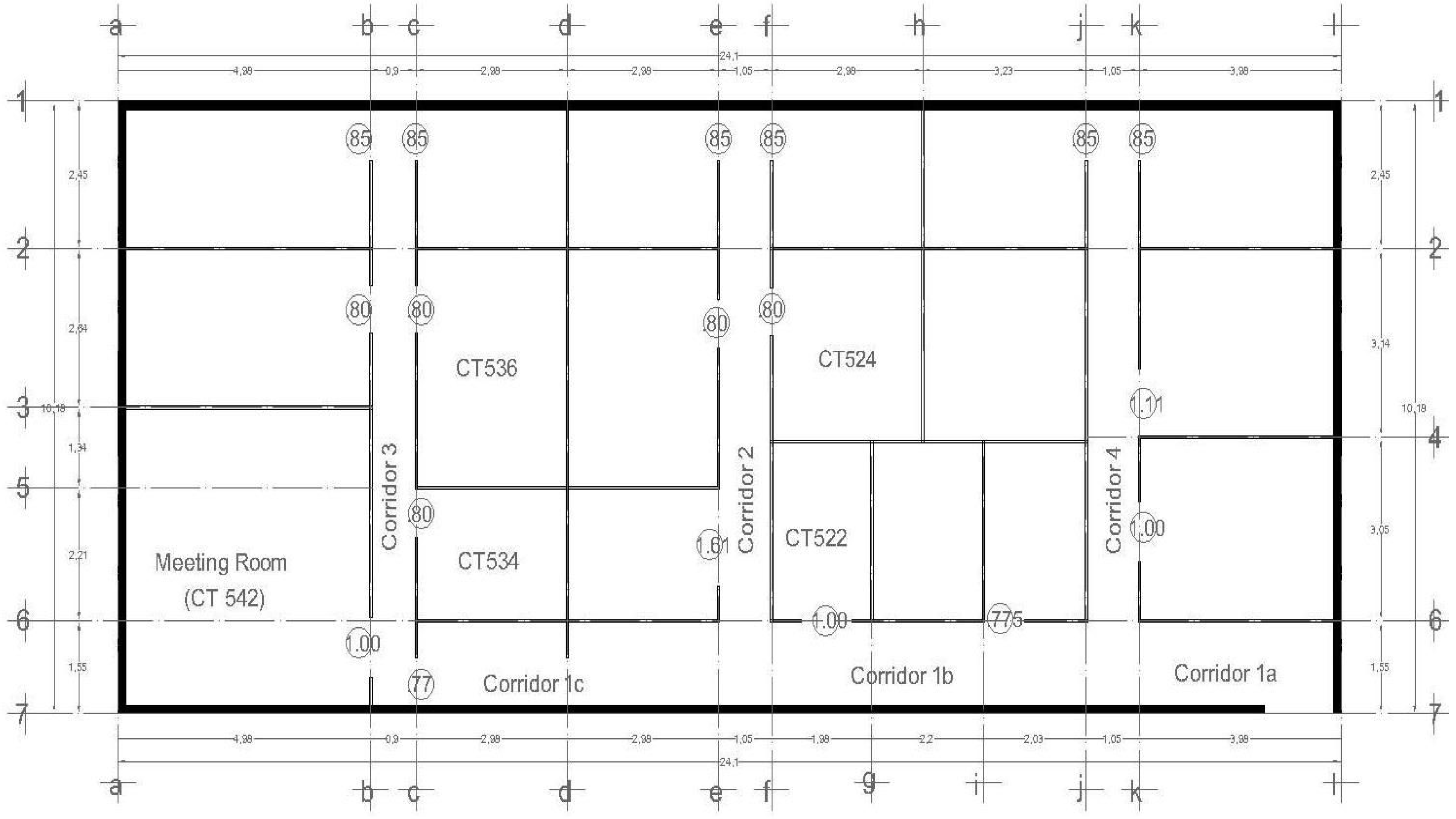
3.3. Software Requirements
3.4. Getting the Classification Models from the Information Sources
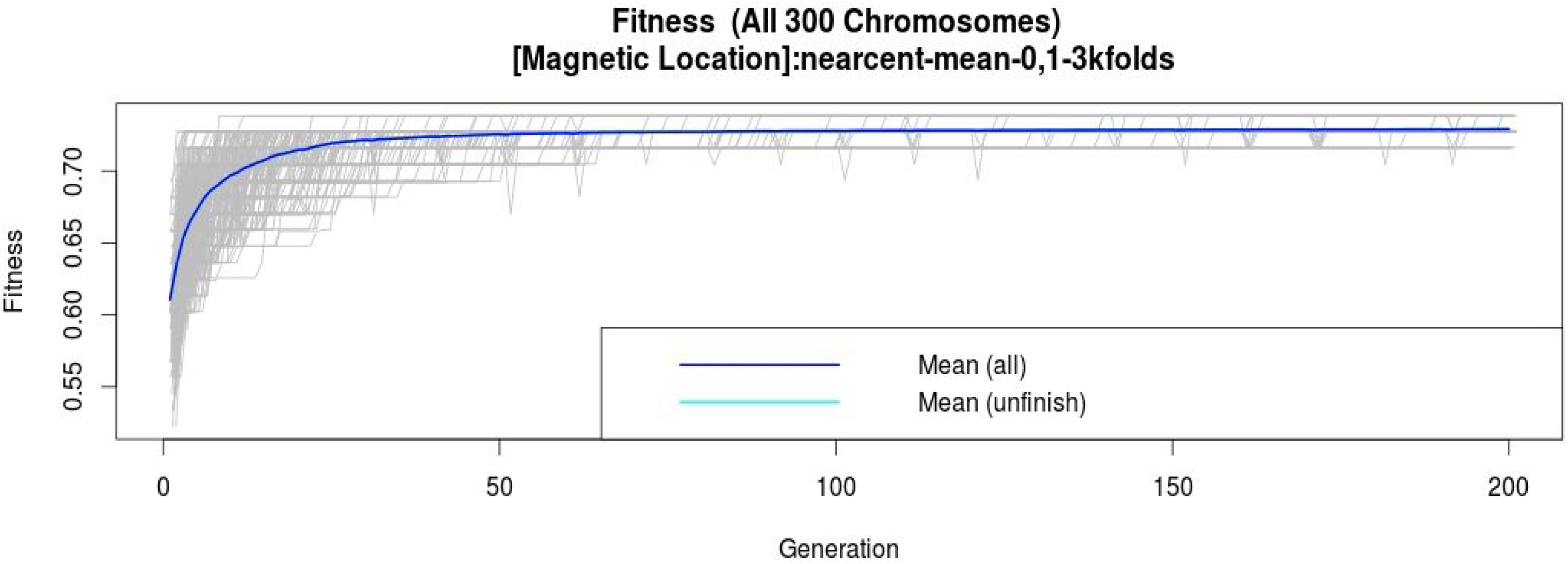
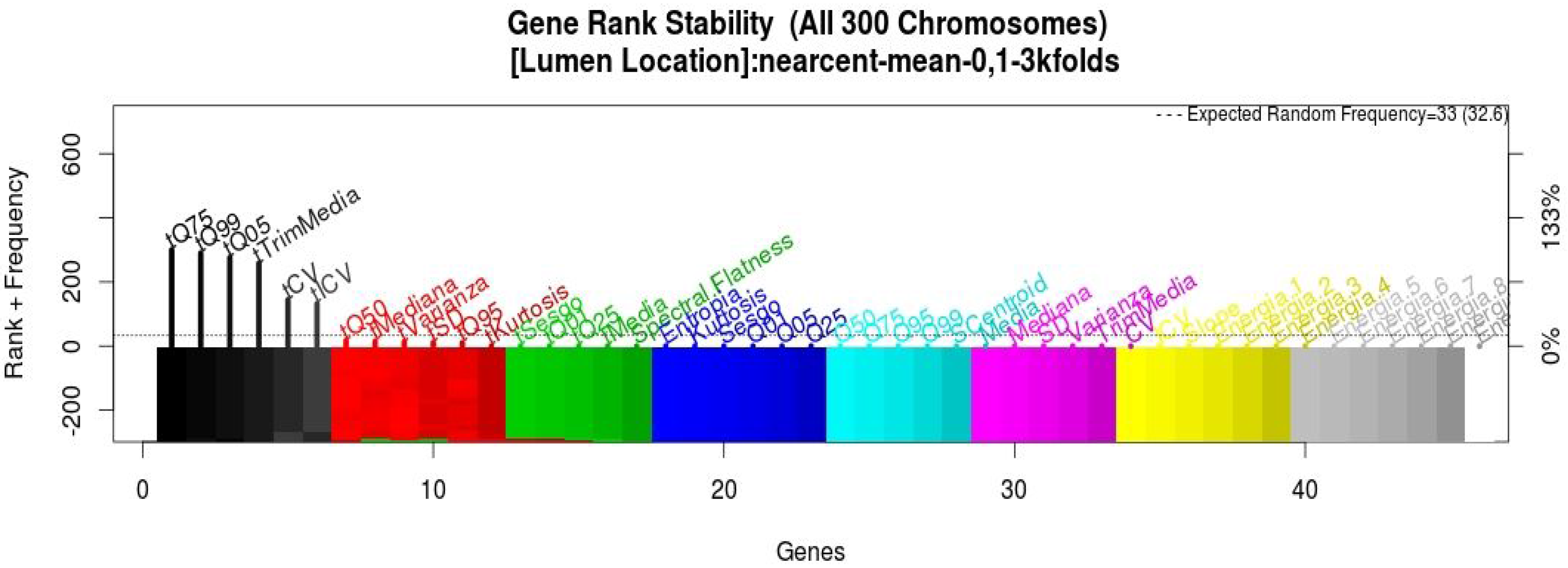
| Sensor/Device | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Field Sensor | 0.7246683 | 0.9704668 |
| Light Sensor | 0.7059034 | 0.9705903 |
| Microphone Device | 0.7567806 | 0.9756781 |
| Sensor/Device | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic- Field Sensor | 0.7580685 | 0.9758069 |
| Light Sensor | 0.7030924 | 0.9703092 |
| Microphone Device | 0.776298 | 0.9776298 |
3.5. Signal Information Fusion

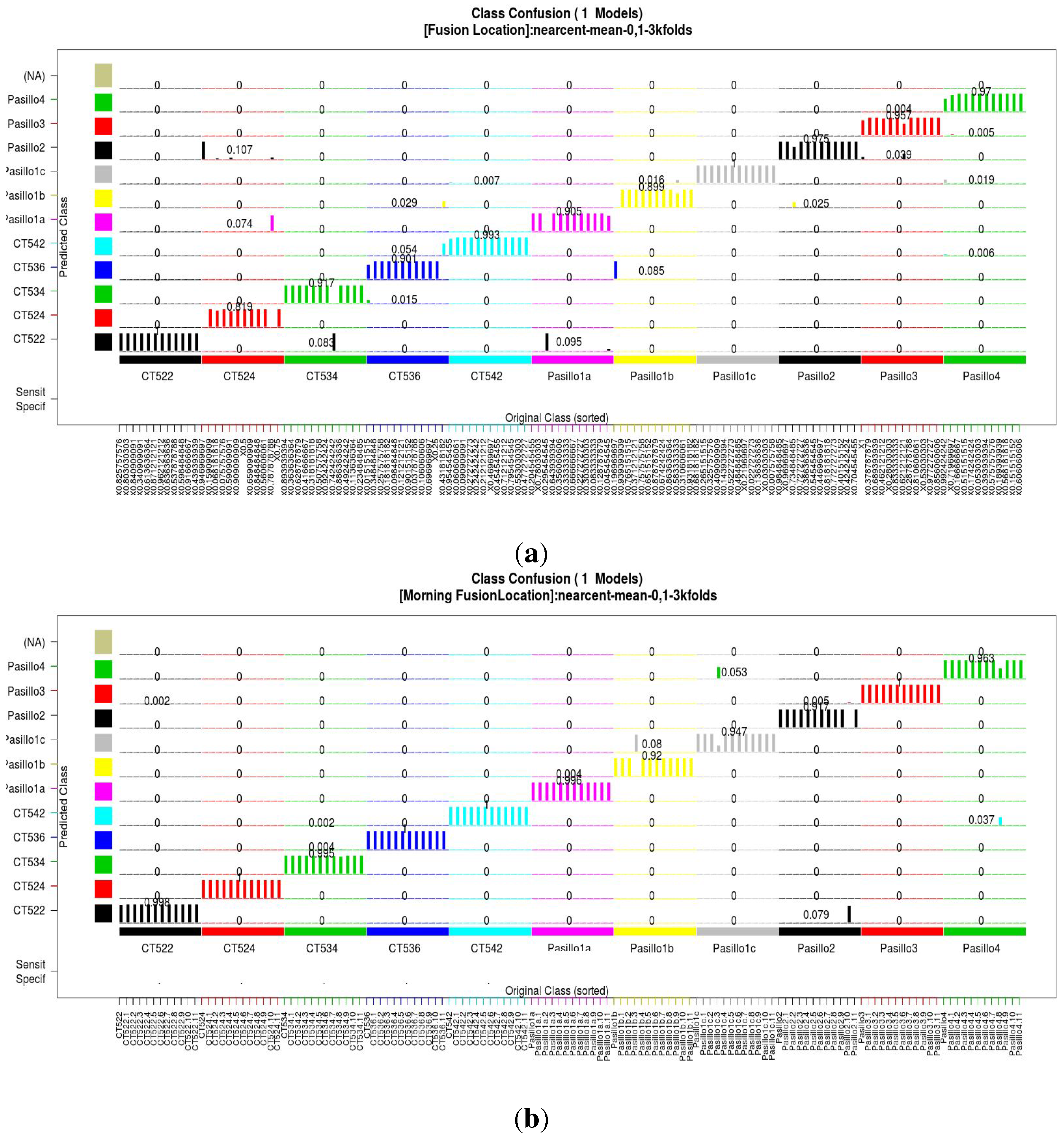
| Season Dataset | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| Summer Dataset | 0.9396806 | 0.9939681 |
| Winter Dataset | 0.9760147 | 0.9976015 |
| Approach | Features | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| Best Chromosome | 5 | 0.889 |
| Nearest Centroid | 136 | 0.920 |
| Maximum Likelihood Classification | 136 | 0.926 |
| K-Nearest Neighbors | 136 | 0.931 |
| Random Forest | 136 | 0.934 |
| Our Approach | 6 | 0.955 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schilit, B.; Adams, N.; Want, R. Context-aware computing applications. In Proceedings of the 1994 First Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications (WMCSA ’94), Washington, CO, USA, 8–9 December, 1994.
- Gu, Y.; Lo, A.; Niemegeers, I. A survey of indoor positioning systems for wireless personal networks. IEEE Commun. Surveys Tutor. 2009, 11, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Darabi, H.; Banerjee, P.; Liu, J. Survey of wireless indoor positioning techniques and systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C: Appl. Rev. 2007, 37, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautz, R. Overview of current indoor positioning systems. Geod. Kartogr. 2009, 35, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniukevic, A.; Sabonis, D.; Jensen, C.S.; Lu, H. Improving wi-fi based indoor positioning using bluetooth add-ons. In Proceedings of the 2011 12th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM), Lulea, Sweden, 6–9 June 2011.
- Galvan T., C.E.; Galvan-Tejada, I.; Sandoval, E. I.; Brena, R. Wifi bluetooth based combined positioning algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2012, 35, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Want, R.; Hopper, A.; Falcao, V.; Gibbons, J. The active badge location system. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 1992, 10, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.; Jones, A.; Hopper, A. A new location technique for the active office. IEEE Pers. Commun. 1997, 4, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyantha, N.B.; Chakraborty, A.; Balakrishnan, H. The cricket location-support system. In Proceedings of the 6th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Boston, MA, USA, 6–11 August 2000.
- Ni, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Lau, Y.C.; Patil, A.P. Landmarc: Indoor location sensing using active rfid. Wirel. Netw. 2004, 10, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.; Lemelson, H.; Farber, A.; Effelsberg, W. Bluepos: Positioning with bluetooth. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing (WISP 2009), Budapest, Hungary, 26–28 August 2009.
- Schweinzer, H.; Syafrudin, M. Losnus: An ultrasonic system enabling high accuracy and secure tdoa locating of numerous devices. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010.
- Noh, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Lee, U.; Vij, P.; Joy, J.; Gerla, M. Clips: Infrastructure-free collaborative indoor positioning scheme for time-critical team operations. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), San Diego, CA, USA, 18–22 March 2013; pp. 172–178.
- Han, J.; Owusu, E.; Nguyen, L.T.; Perrig, A.; Zhang, J. Accomplice: Location inference using accelerometers on smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2012 Fourth International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), Bangalore, India, 3–7 January 2012.
- Kim, S.E.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, J.; Kim, E.S. Indoor positioning system using geomagnetic anomalies for smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sydney, Australia, 13–15 November 2012.
- Li, F.; Zhao, C.; Ding, G.; Gong, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, F. A reliable and accurate indoor localization method using phone inertial sensors. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–8 September 2012.
- Pratama, A.R.; Widyawan; Hidayat, R. Smartphone-based pedestrian dead reckoning as an indoor positioning system. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on System Engineering and Technology (ICSET), Bandung, West Java, Indonesia, 11–12 September 2012; pp. 1–6.
- Werner, M.; Kessel, M.; Marouane, C. Indoor positioning using smartphone camera. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Guimarães, Portugal, 21–23 September 2011.
- Mulloni, A.; Wagner, D.; Barakonyi, I.; Schmalstieg, D. Indoor positioning and navigation with camera phones. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2009, 8, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storms, W.; Shockley, J.; Raquet, J. Magnetic field navigation in an indoor environment. In Proceedings of the Ubiquitous Positioning Indoor Navigation and Location Based Service (UPINLBS), Kirkkonummi, Finland, 14–15 October 2010.
- Bilke, A.; Sieck, J. Using the magnetic field for indoor localisation on a mobile phone. Lect. Notes Geoinform. Cartogr. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizyan, M.; Constandache, I.; Choudhury, R.R. Surroundsense: Mobile phone localization via ambience fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Beijing, China, 20–25 September 2009.
- Galván-Tejada, C.E.; García-Vázquez, J.P.; Brena, R.F. Magnetic field feature extraction and selection for indoor location estimation. Sensors 2014, 14, 11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozick, B.; Subbu, K.P.; Dantu, R.; Maeshiro, T. Magnetic maps for indoor navigation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 3883–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, F. A sufficient condition for pooling data. Synthese 2008, 163, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, G.; Longari, M.; Pollastri, E. Musical instrument timbres classification with spectral features. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal Process. 2003, 2003, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Pavlidis, T. Segmentation by texture using a co-occurrence matrix and a split-and-merge algorithm. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1979, 10, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I.H. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrou, T.; Kudumakis, P.; Speller, R.; Sandler, M.; Linney, A. Classification of audio signals using statistical features on time and wavelet transform domains. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–15 May 1998.
- Indyk, P.; Motwani, R. Approximate nearest neighbors: Towards removing the curse of dimensionality. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Dallas, TX, USA, 24–26 May 1998.
- Torteya, A.M.; Tamez Peña, J.G.; Treviño Alvarado, V.M. Multivariate predictors of clinically relevant cognitive decay: A wide association study using available data from adni. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2012, 8, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, V.; Falciani, F. Galgo: An R package for multivariate variable selection using genetic algorithms. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1154–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Donahoe, M.; Schmandt, C.; Kim, I.-J.; Razavai, P.; Wiseman, M. Indoor location sensing using geo-magnetism. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Bethesda, MD, USA, 28 June–1 July 2011.
- Laoudias, C.; Zeinalipour-Yazti, D.; Panayiotou, C.G. Crowdsourced indoor localization for diverse devices through radiomap fusion. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Montbeliard-Belfort, France, 28–31 October 2013.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galván-Tejada, C.E.; García-Vázquez, J.P.; Galván-Tejada, J.I.; Delgado-Contreras, J.R.; Brena, R.F. Infrastructure-Less Indoor Localization Using the Microphone, Magnetometer and Light Sensor of a Smartphone. Sensors 2015, 15, 20355-20372. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150820355
Galván-Tejada CE, García-Vázquez JP, Galván-Tejada JI, Delgado-Contreras JR, Brena RF. Infrastructure-Less Indoor Localization Using the Microphone, Magnetometer and Light Sensor of a Smartphone. Sensors. 2015; 15(8):20355-20372. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150820355
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalván-Tejada, Carlos E., Juan Pablo García-Vázquez, Jorge I. Galván-Tejada, J. Rubén Delgado-Contreras, and Ramon F. Brena. 2015. "Infrastructure-Less Indoor Localization Using the Microphone, Magnetometer and Light Sensor of a Smartphone" Sensors 15, no. 8: 20355-20372. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150820355
APA StyleGalván-Tejada, C. E., García-Vázquez, J. P., Galván-Tejada, J. I., Delgado-Contreras, J. R., & Brena, R. F. (2015). Infrastructure-Less Indoor Localization Using the Microphone, Magnetometer and Light Sensor of a Smartphone. Sensors, 15(8), 20355-20372. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150820355









