A Multi-Channel Method for Retrieving Surface Temperature for High-Emissivity Surfaces from Hyperspectral Thermal Infrared Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodological Development
2.1. Physical Base of the Method
2.2. Data for Simulation

2.3. Determination of Centre Wavenumbers of Channel i (i = [1,p]) and Coefficients wi (i = [0,p])
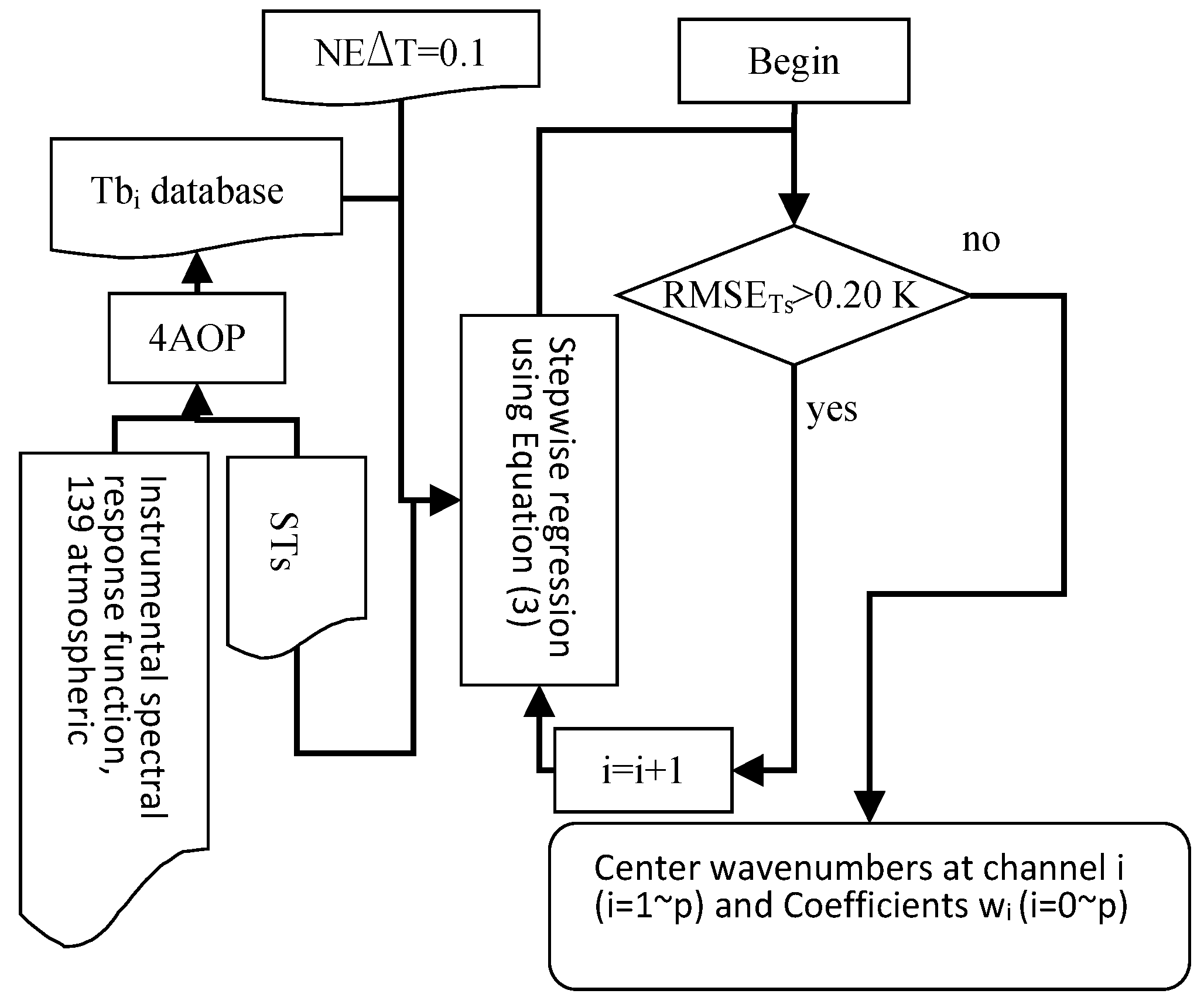
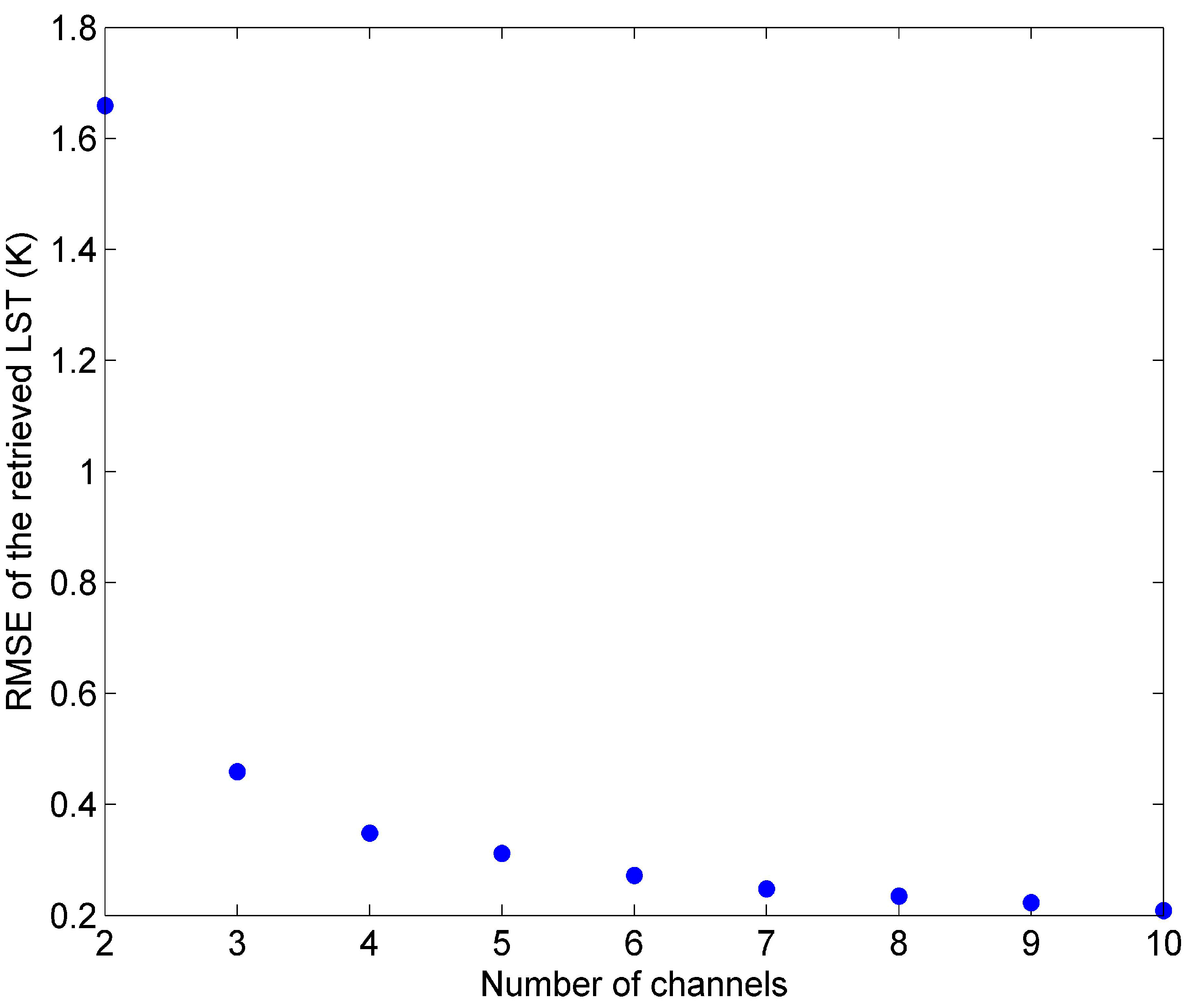
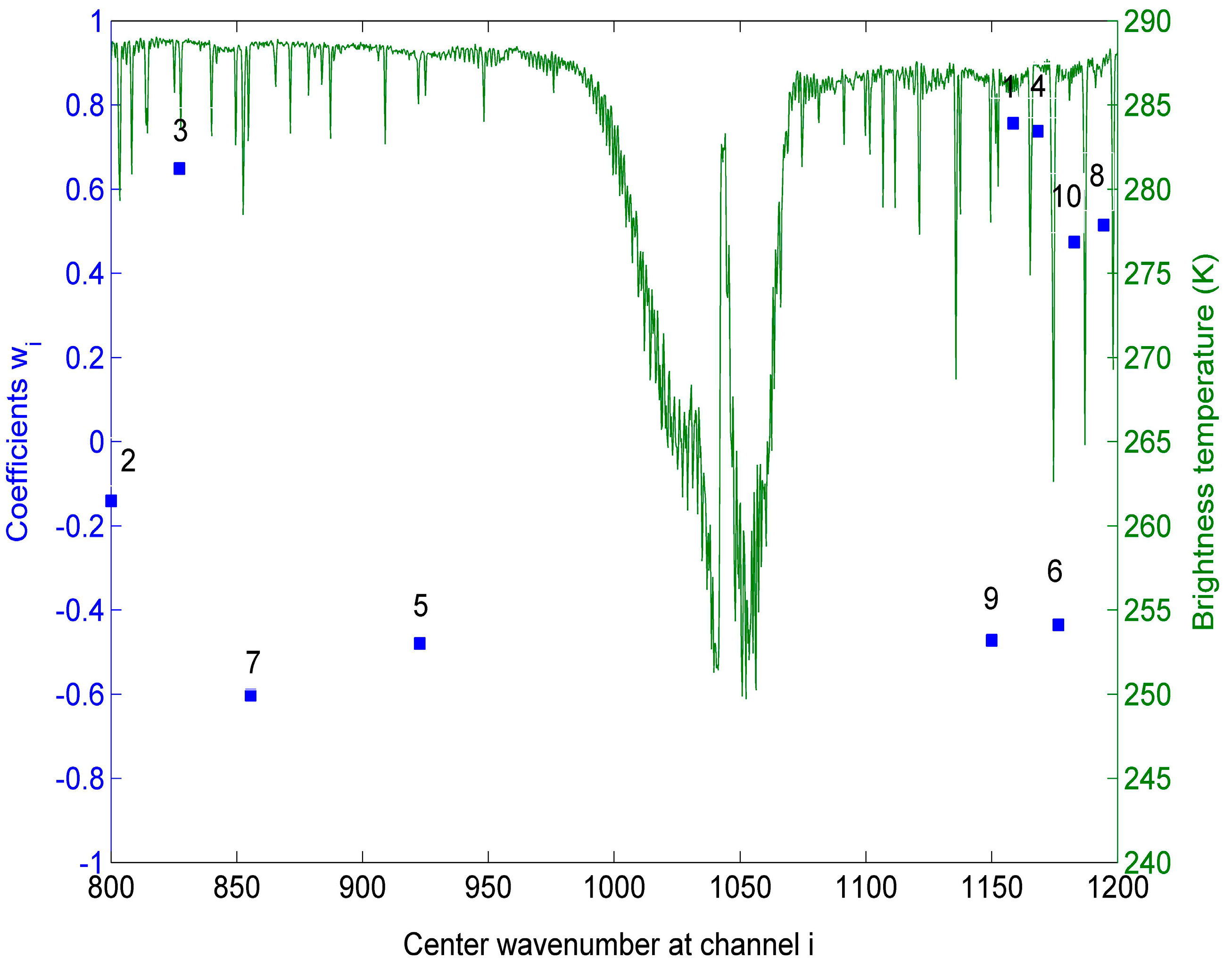
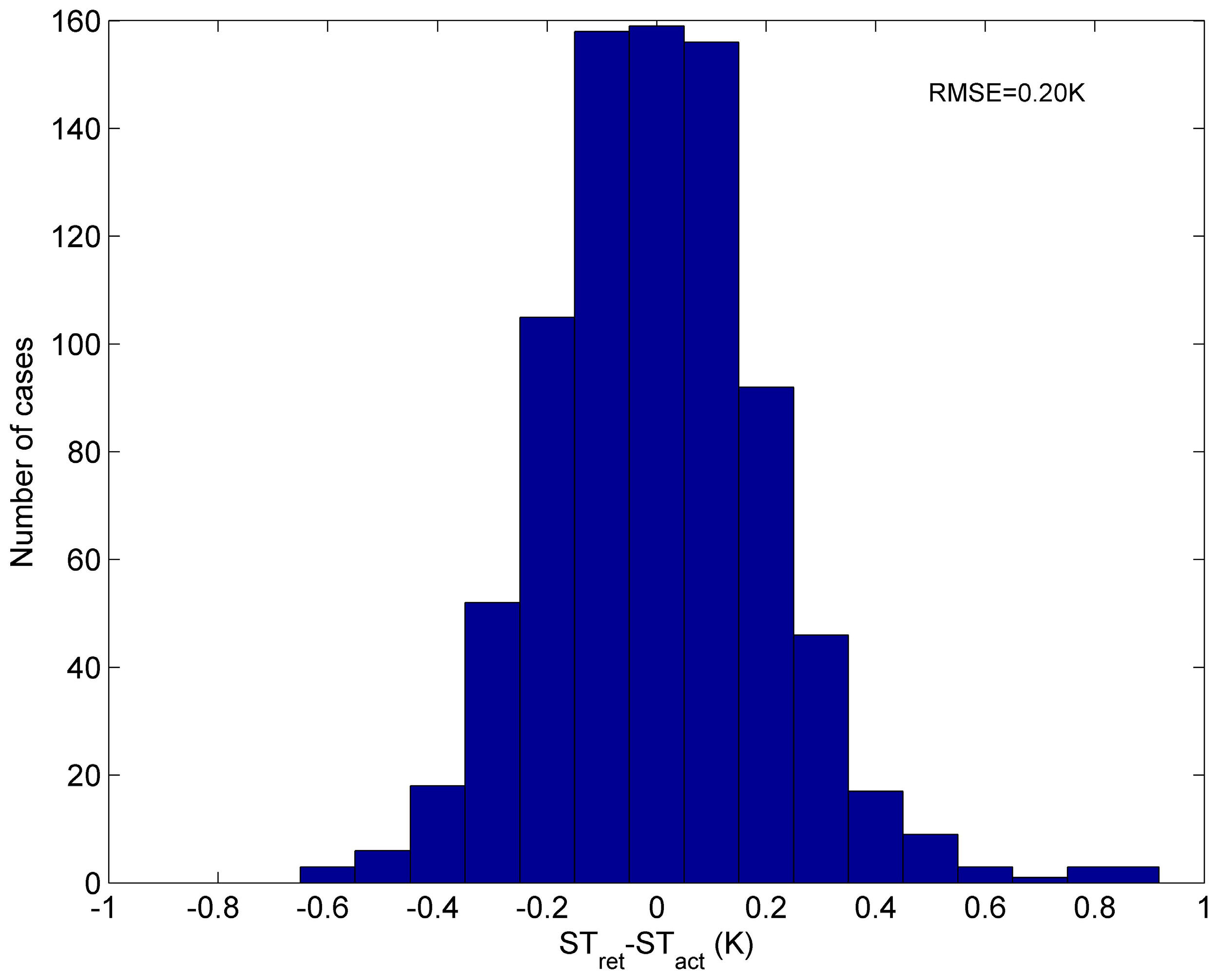
3. Evaluation of the Method
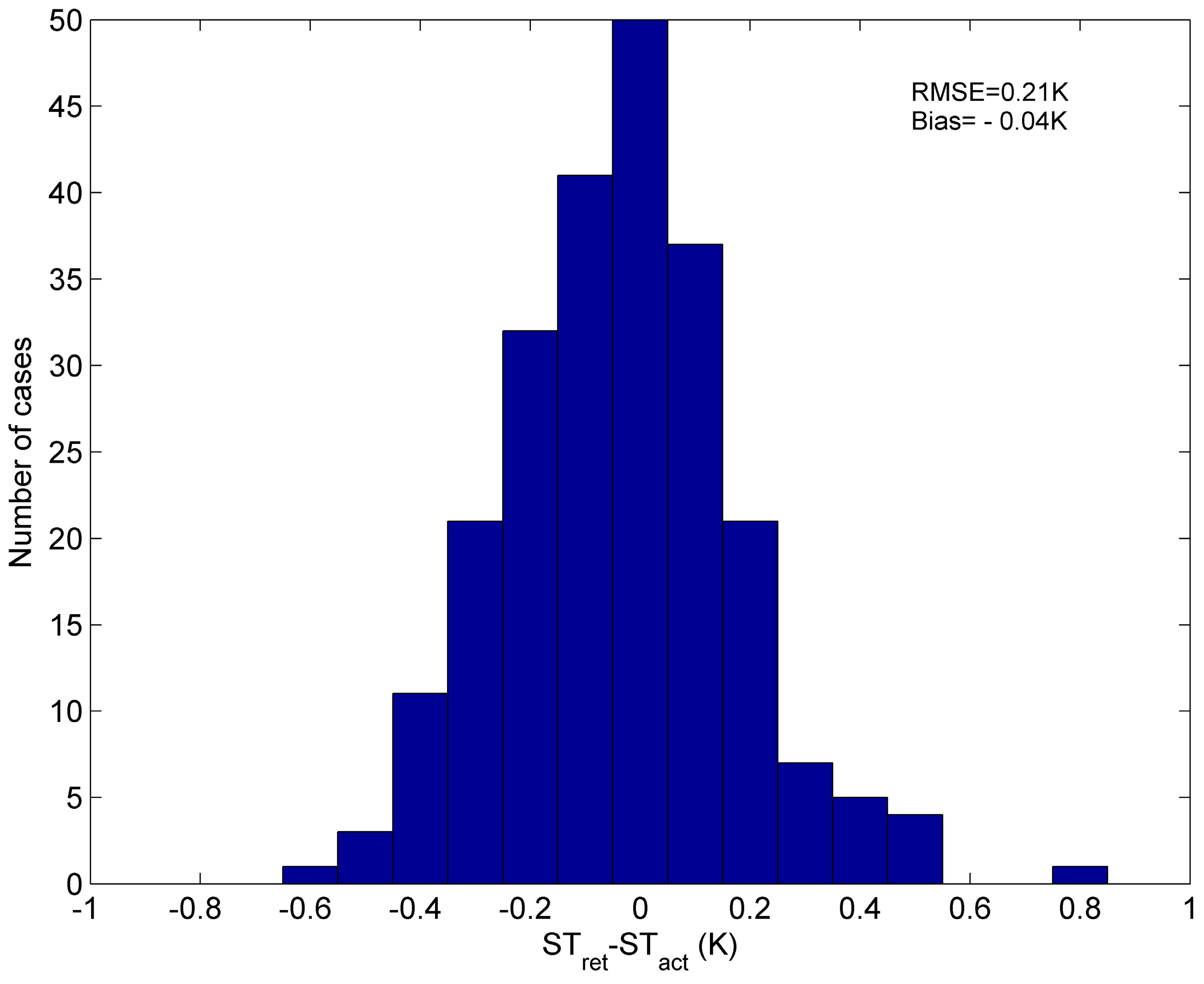
4. Sensitivity Analysis of the Method
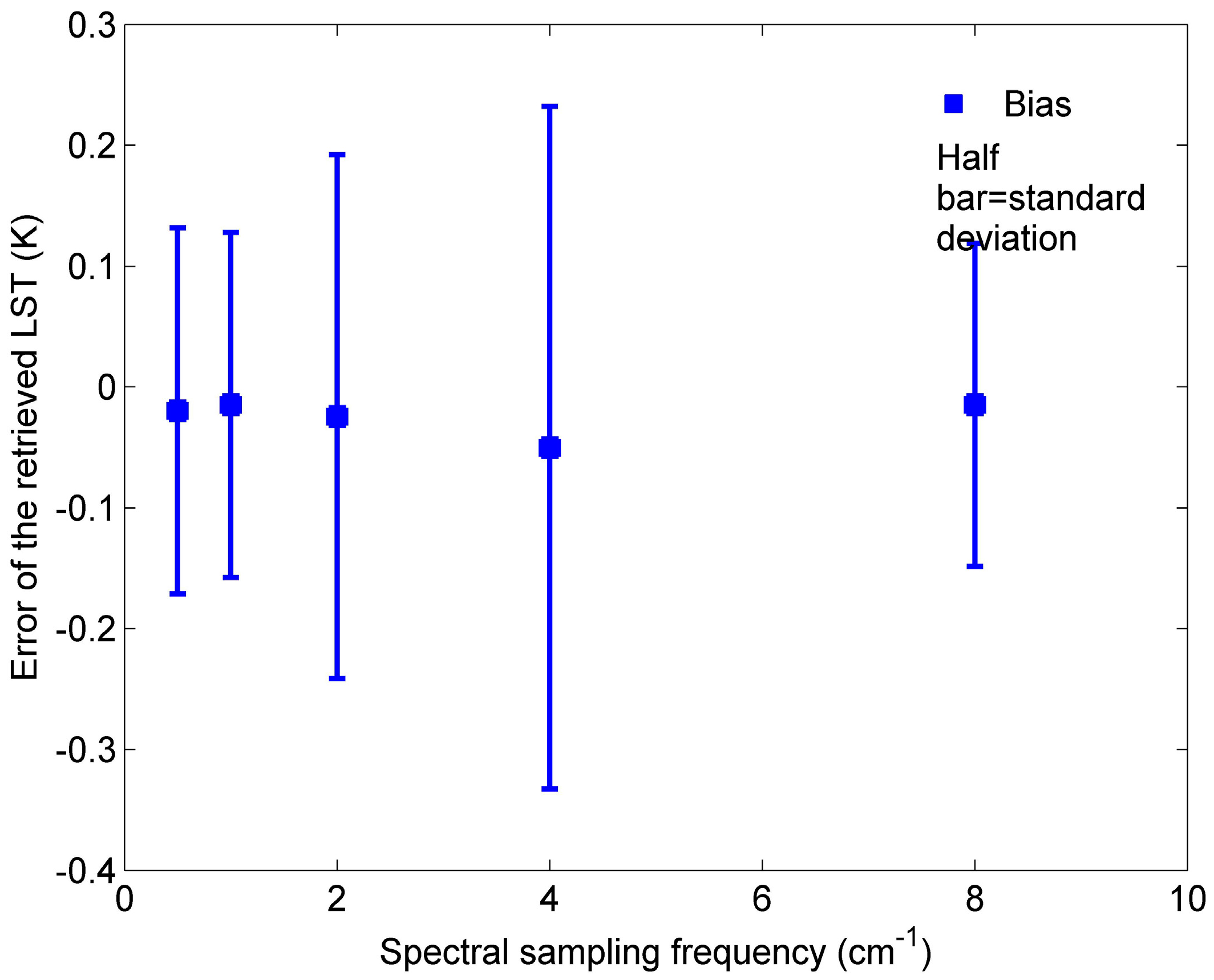
4.1. Sensitivity to Spectral Sampling Frequency
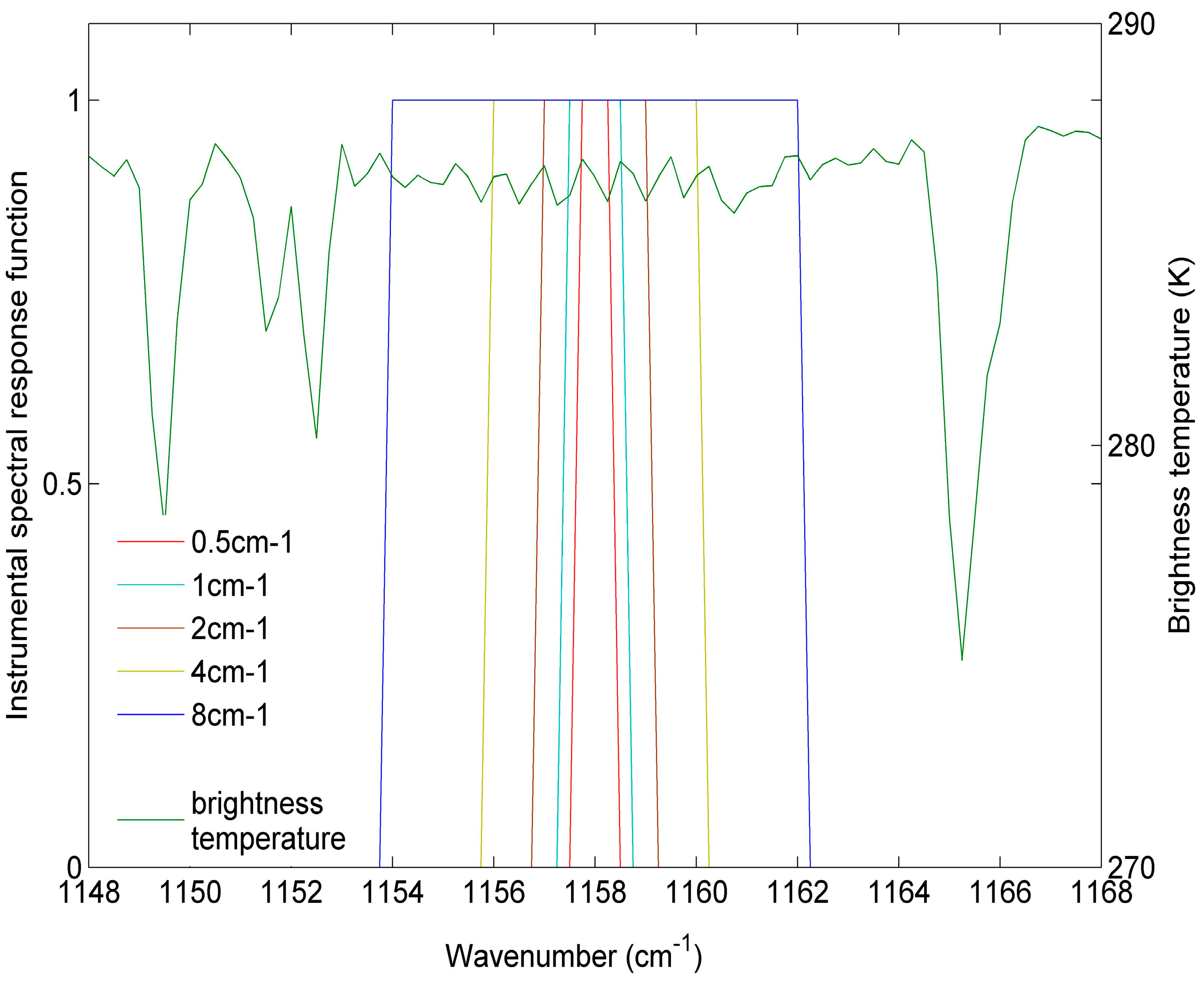
| Spectral Sampling Frequency (cm−1) | w0 | w1 | w2 | w3 | w4 | w5 | w6 | w7 | w8 | w9 | w10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | −0.435 | 0.688 | 0.025 | 0.788 | 0.877 | −0.535 | −0.516 | −0.795 | 0.575 | −0.609 | 0.504 |
| 1 | 0.676 | 0.614 | 0.132 | 1.126 | 1.050 | −0.693 | −0.624 | −1.170 | 0.586 | −0.603 | 0.579 |
| 2 | −0.372 | 0.738 | −0.148 | 2.249 | 0.939 | −2.158 | −1.210 | −1.339 | 0.953 | 0.259 | 0.720 |
| 4 | −0.080 | 0.531 | 1.555 | −0.102 | 3.360 | −3.164 | −1.772 | 0.197 | 0.053 | 0.089 | 0.257 |
| 8 | 1.083 | 2.833 | 0.931 | −1.686 | 2.256 | −1.431 | −2.140 | 1.996 | 0.683 | −2.549 | 0.102 |
4.2. Sensitivity to Instrumental Noise

5. Application to Satellite Data

5.1. Data for This Application
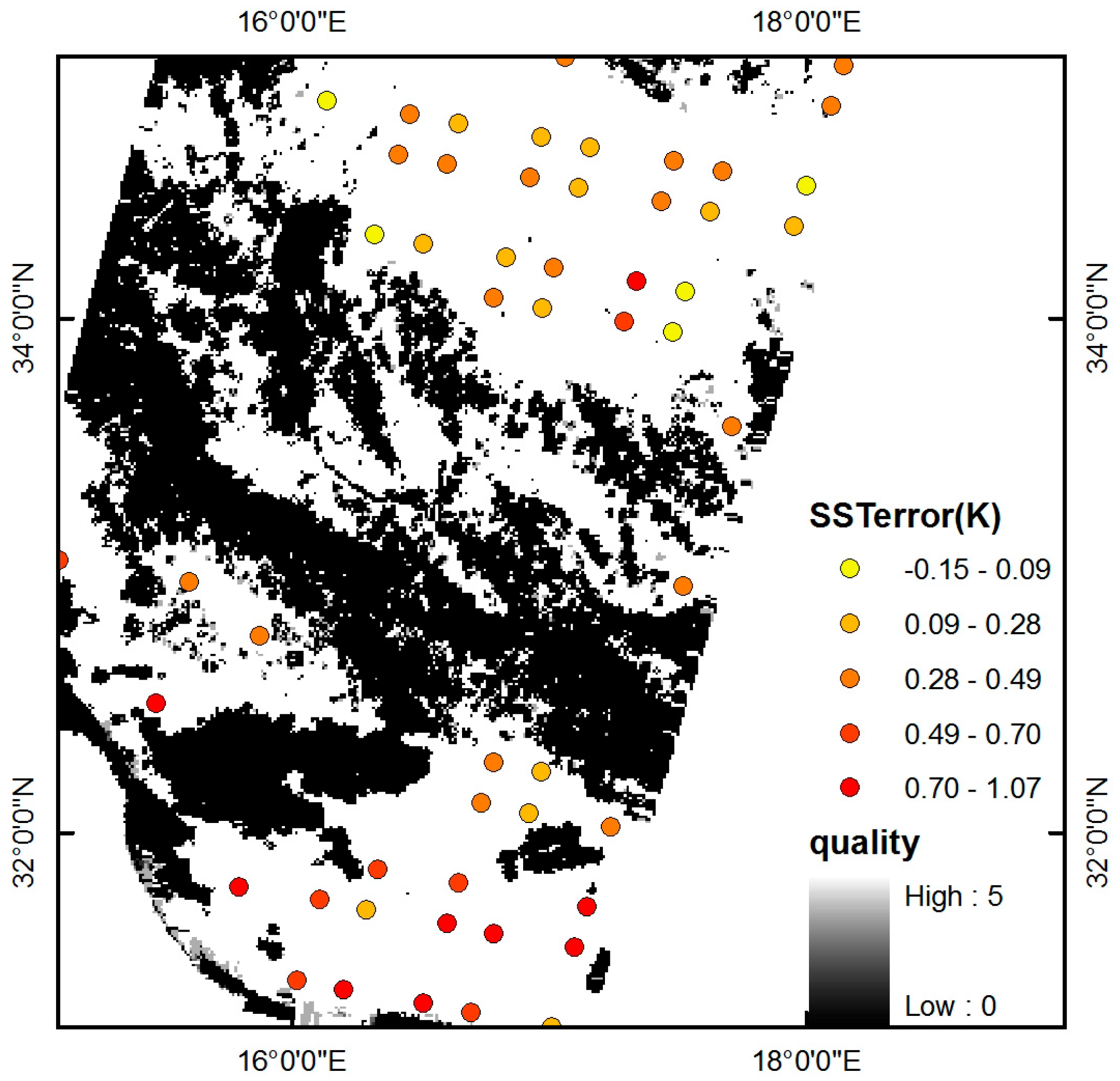
5.2. Application to the Mediterranean Sea
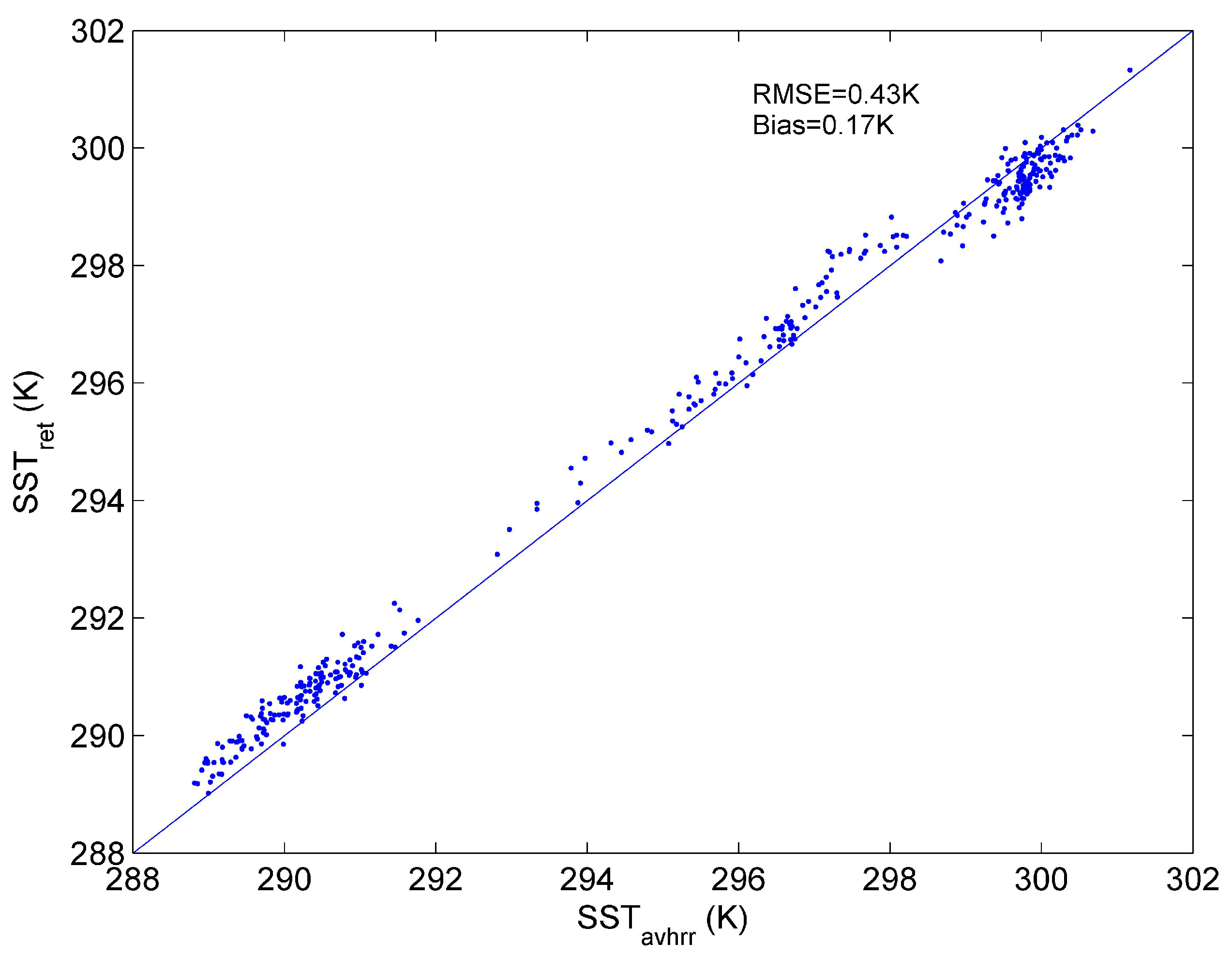
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- ST can be retrieved by our method from independent simulation data with RMSE of 0.21 K, using only 10 HypTIR measurements. This method is very accurate and promising.
- (2)
- The coefficients wi of the method are dependent on a spectral sampling frequency. Nevertheless, ST of high-emissivity surfaces can still be retrieved accurately when the coefficients are refitted for each spectral sampling frequency.
- (3)
- The impact of instrumental noise is not significant: the accuracy of the retrieved ST is of the order of magnitude of the instrumental noise.
- (4)
- In comparison with the AVHRR SST product, ST of high-emissivity surfaces can be retrieved from satellite data with a RMSE of 0.43 K. The performance of our method is good for retrieving ST for high-emissivity surfaces from satellite data.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Marshall, J.; Jung, J.; Derber, J.; Chahine, M.; Treadon, R.; Lord, S.J.; Goldberg, M.; Wolf, W.; Liu, H.C.; Joiner, J.; et al. Improving global analysis and forecasting with airs. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Li, Z.-L.; Stoll, M.P. Impact of the atmospheric transmittance and total water vapor content in the algorithms for estimating satellite sea surface temperatures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonooka, H. Accurate atmospheric correction of ASTER thermal infrared imagery using the WVS method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2778–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.; Gottsche, F.M.; Olesen, F.S.; Fischer, H. Land surface temperature and emissivity estimation from passive sensor data: Theory and practice-current trends. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2563–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, S.J.; Gabell, A.R.; Green, A.A.; Kealy, P.S. A comparison of techniques for extracting emissivity information from thermal infrared data for geologic studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 42, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillin, L.M. Estimation of sea surface temperatures from two infrared window measurements with different absorption. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 5113–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.L.; Pinker, R.T. Estimation of land surface temperature from a geostationary operational environmental satellite (GOES-8). J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Pinker, R.T. Implementation of GOES-based land surface temperature diurnal cycle to AVHRR. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 3975–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Pinker, R.T. Retrieval of surface temperature from the msg-seviri observations: Part I. Methodology. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5255–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedin, A.; Scott, N.A.; Berroir, A. A single-channel, double-viewing angle method for sea-surface temperature determination from coincident meteosat and TIROS-N radiometric measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1982, 21, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Li, Z.-L. A physics-based algorithm for retrieving land-surface emissivity and temperature from eos/modis data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 980–996. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, A.; Rokugawa, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Cothern, J.S.; Hook, S.; Kahle, A.B. A temperature and emissivity separation algorithm for advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (aster) images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Schmit, T.J.; Zhou, L.; Goldberg, M.D. Land surface emissivity from high temporal resolution geostationary infrared imager radiances: Methodology and simulation studies. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiello, G.; Serio, C.; de Feis, I.; Amoroso, M.; Venafra, S.; Trigo, I.F.; Watts, P. Kalman filter physical retrieval of surface emissivity and temperature from geostationary infrared radiances. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3613–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.L.; Wan, Z.; Moeller, C.C.; Menzel, W.P.; Gumley, L.E.; Zhang, Y.L. Retrieval of geophysical parameters from moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer thermal infrared data: Evaluation of a two-step physical algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 3537–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.L.; Wan, Z.; Moeller, C.C.; Menzel, W.P.; Gumley, L.E. Simultaneous retrieval of atmospheric profiles, land-surface temperature, and surface emissivity from moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer thermal infrared data: Extension of a two-step physical algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C. Land surface temperature retrieval from thermal infrared data: An assessment in the context of the Surface Processes and Ecosystem Changes through Response Analysis (SPECTRA) mission. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Li, Z.-L. Radiance-based validation of the V5 MODIS land-surface temperature product. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5373–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.; Abbott, E.A.; Gilson, L.; Hulley, G.; Jimenez-Munoz, J.-C.; Sobrino, J.A. Residual errors in aster temperature and emissivity standard products AST08 and AST05. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3681–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susskind, J.; Barnet, C.D.; Blaisdell, J.M. Retrieval of atmospheric and surface parameters from AIRS/AMSU/HSB data in the presence of clouds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 390–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, F.; Armante, R.; August, T.; Barnet, C.; Bouchard, A.; Camy-Peyret, C.; Zhou, D. Hyperspectral Earth Observation from IASI: Five Years of Accomplishments. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2012, 93, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, H.J. The cross-track infrared sounder (CrIS): A sensor for operational meteorological remote sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS’01), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; Volume 3, pp. 1341–1343.
- Schlussel, P.; Goldberg, M. Retrieval of atmospheric temperature and water vapour from iasi measurements in partly cloudy situations. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 29, 1703–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Will See the Launch of Six New Satellites from 2019. Available online: http://www.eumetsat.int/website/home/Satellites/FutureSatellites/MeteosatThirdGeneration/index.html (accessed on 20 December 2014).
- Zhou, D.K.; Smith, W.L.; Li, J.; Howell, H.B.; Cantwell, G.W.; Larar, A.M.; Knuteson, R.O.; Tobin, D.C.; Revercomb, H.E.; Mango, S.A. Thermodynamic product retrieval methodology and validation for NAST-I. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 6957–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, M.D.; Qu, Y.N.; McMillin, L.M.; Wolf, W.; Zhou, L.H.; Divakarla, M. Airs near-real-time products and algorithms in support of operational numerical weather prediction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, E.; Thapliyal, P.; Guan, L.; Huang, H.-L.; Li, J.; Borbas, E.; Baggett, K. International modis and airs processing package: Airs products and applications. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.K.; Larar, A.M.; Liu, X.; Smith, W.L.; Strow, L.L.; Yang, P.; Schluessel, P.; Calbet, X. Global land surface emissivity retrieved from satellite ultraspectral ir measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, F.; Chedin, A.; Scott, N.A.; Rossow, W.B. A regularized neural net approach for retrieval of atmospheric and surface temperatures with the iasi instrument. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2002, 41, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Zeng, F.; Li, C. Retrieval of atmospheric and land surface parameters from satellite-based thermal infrared hyperspectral data using a neural network technique. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3485–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pequignot, E.; Chedin, A.; Scott, N.A. Infrared continental surface emissivity spectra retrieved from airs hyperspectral sensor. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Aires, F.; Prigent, C.; Trigo, I.F.; Bernardo, F. An innovative physical scheme to retrieve simultaneously surface temperature and emissivities using high spectral infrared observations from IASI. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, C.D. Retrieval of atmospheric temperature and composition from remote measurements of thermal radiation. Rev. Geophys. 1976, 14, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Weisz, E.; Zhou, D.K. Physical retrieval of surface emissivity spectrum from hyperspectral infrared radiances. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N. Simultaneous Retrieval of Land Surface Temperature, Emissivity and Atmospheric Profiles from Hyperspectral Thermal Infrared Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 22 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Masiello, G.; Serio, C. Simultaneous physical retrieval of surface emissivity spectrum and atmospheric parameters from infrared atmospheric sounder interferometer spectral radiances. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2428–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chedin, A.; Scott, N.A.; Wahiche, C.; Moulinier, P. The improved initialization inversion method: A high resolution physical method for temperature retrievals from satellites of the TIROS-N series. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1985, 24, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, F.; Cheruy, F.; Scott, N.; Chedin, A. A neural network approach for a fast and accurate computation of a longwave radiative budget. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1998, 37, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galve, J.A.; Coll, C.; Caselles, V.; Valor, E. An atmospheric radiosounding database for generating land surface temperature algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, N.; Chedin, A. A fast line-by-line method for atmospheric absorption computations: The automatized atmospheric absorption atlas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1981, 20, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reference Documentation, Software Version 4AOP2012 v1.0. Available online: http://4aop.noveltis.com/sites/4aop.noveltis.loc/files/NOV-3049-NT-1178v4.3.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2015).
- Aires, F.; Rossow, W.B.; Scott, N.A.; Chedin, A. Remote sensing from the infrared atmospheric sounding interferometer instrument. 1. Compression, denoising, and first-guess retrieval algorithms. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ouyang, X.; Li, Z.-L.; Jiang, X.; Ma, L. An atmospheric correction method for remotely sensed hyperspectral thermal infrared data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium 2009 (IGARSS 2009), Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 3, pp. 677–680.
- Le Borgne, P.; Legendre, G.; Marsouin, A. Operational sst retrieval from MetOp/AVHRR. In Proceedings of the 2007 EUMETSAT Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–28 September 2007.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, X.; Labed, J.; Zhou, G.; Shao, K.; Li, Z.-L. A Multi-Channel Method for Retrieving Surface Temperature for High-Emissivity Surfaces from Hyperspectral Thermal Infrared Images. Sensors 2015, 15, 13406-13423. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150613406
Zhong X, Labed J, Zhou G, Shao K, Li Z-L. A Multi-Channel Method for Retrieving Surface Temperature for High-Emissivity Surfaces from Hyperspectral Thermal Infrared Images. Sensors. 2015; 15(6):13406-13423. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150613406
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Xinke, Jelila Labed, Guoqing Zhou, Kun Shao, and Zhao-Liang Li. 2015. "A Multi-Channel Method for Retrieving Surface Temperature for High-Emissivity Surfaces from Hyperspectral Thermal Infrared Images" Sensors 15, no. 6: 13406-13423. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150613406
APA StyleZhong, X., Labed, J., Zhou, G., Shao, K., & Li, Z.-L. (2015). A Multi-Channel Method for Retrieving Surface Temperature for High-Emissivity Surfaces from Hyperspectral Thermal Infrared Images. Sensors, 15(6), 13406-13423. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150613406






