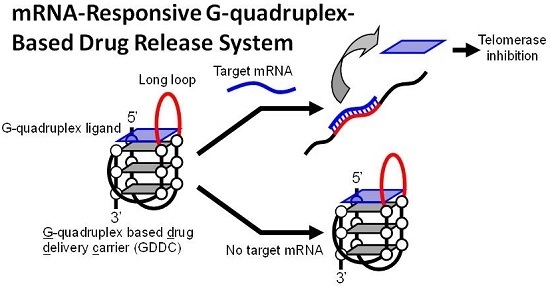
A mRNA-Responsive G-Quadruplex-Based Drug Release System
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Cell Lysate
2.3. G-quadruplex Structural Analysis
2.4. UV-Vis Spectral Analysis
2.5. Determination of the Association Constant
2.6. Two-Step TRAP Assay
2.7. Fluorescence Intensity Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
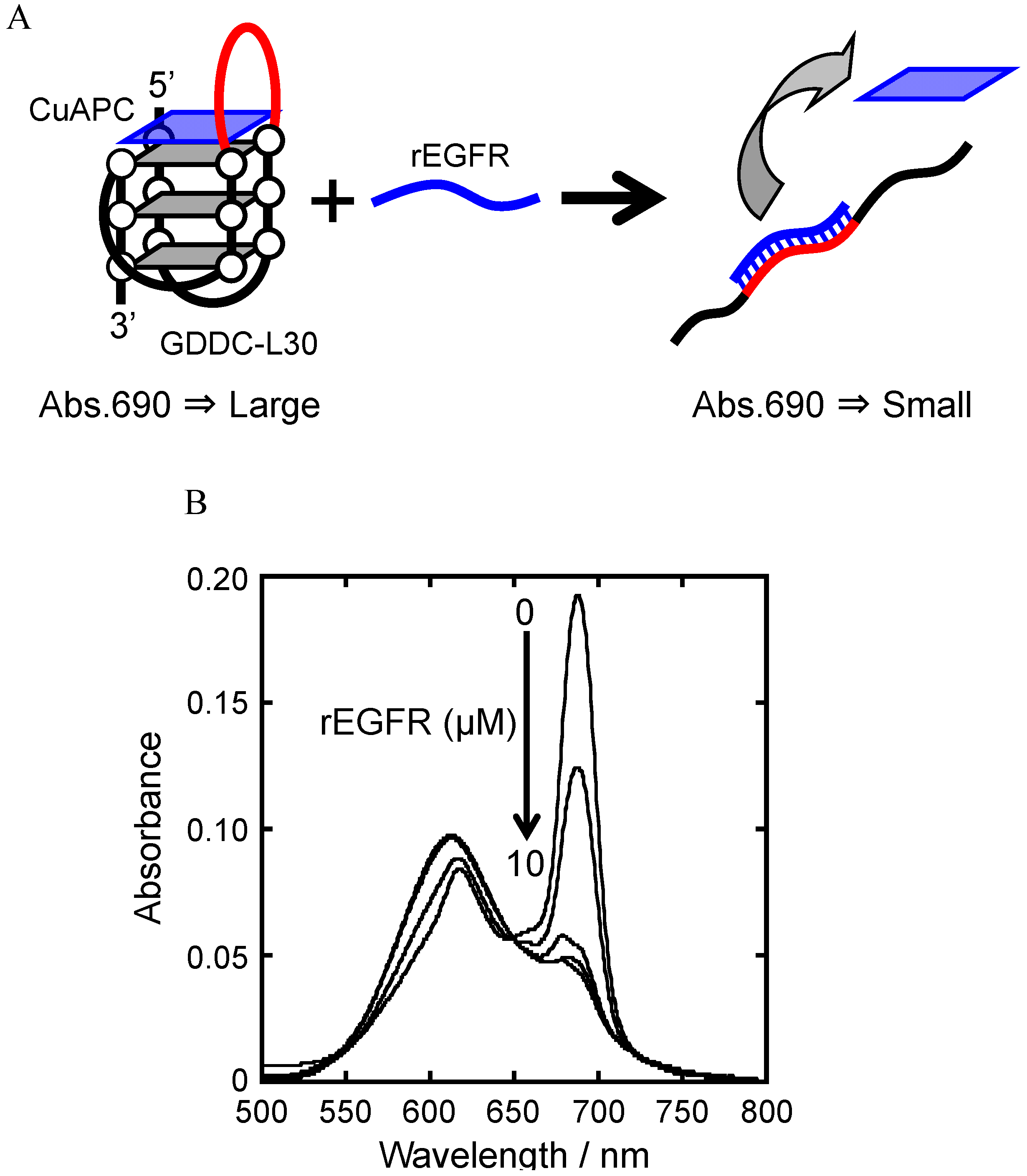
3.1. Design of GDDC
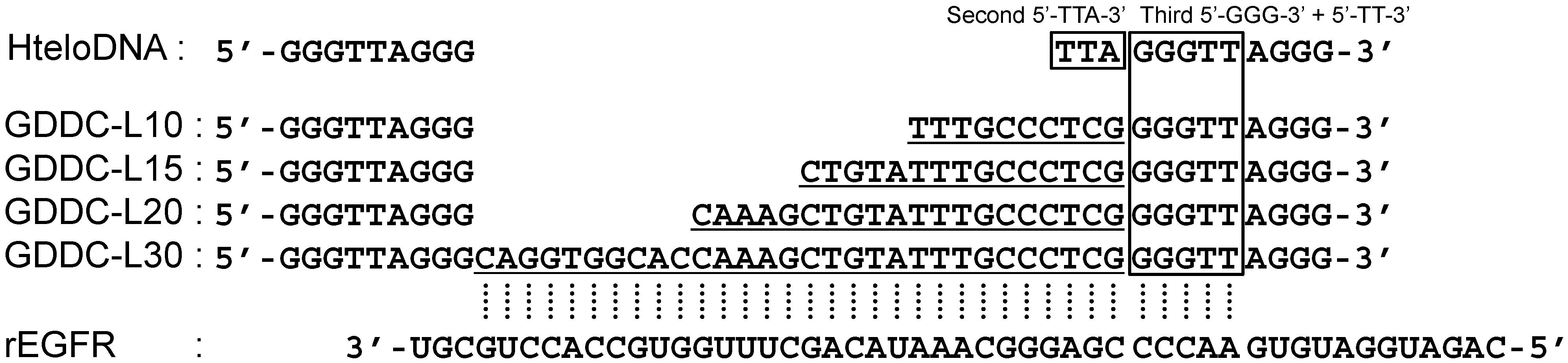
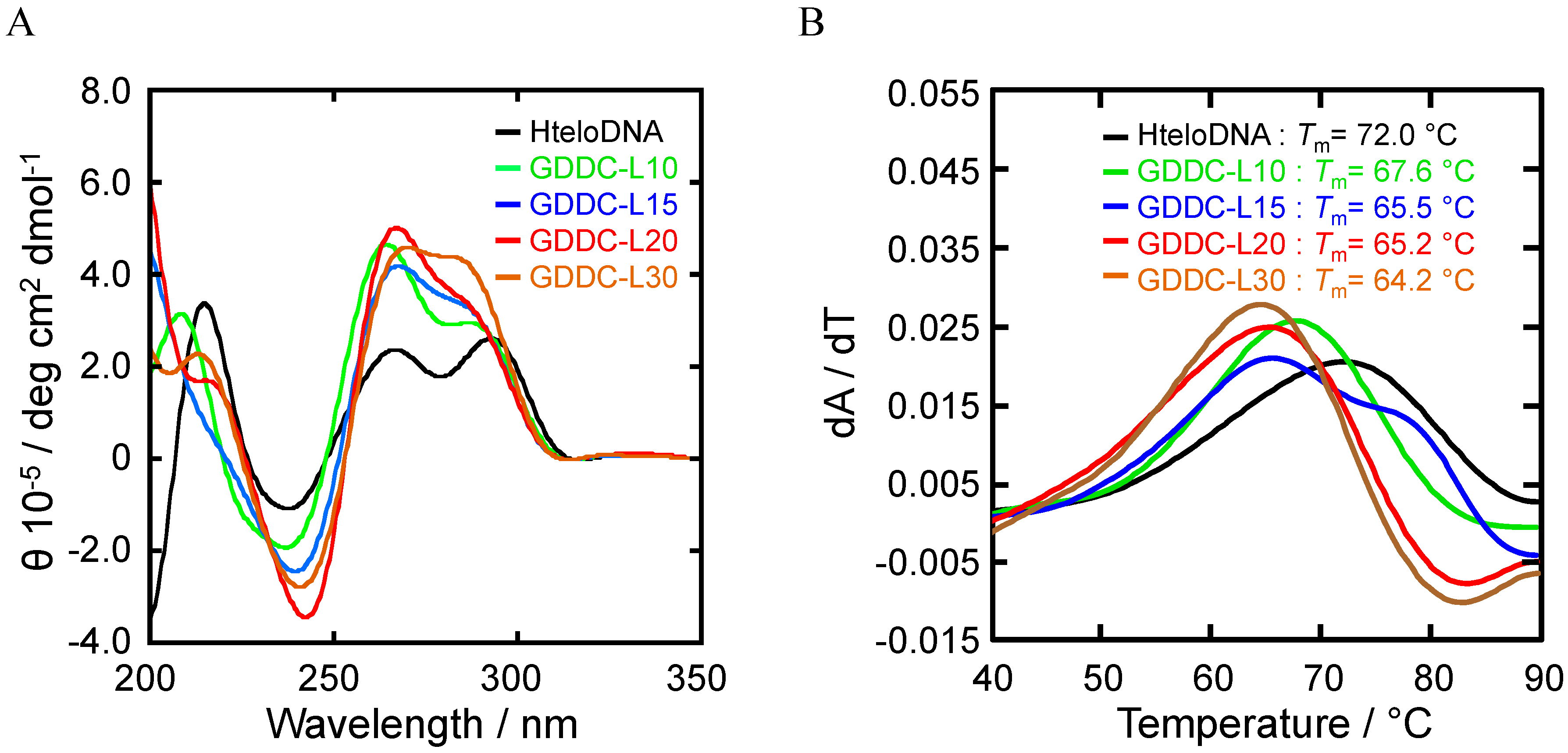
3.2. Selection of G-Quadruplex Ligand for GDDC
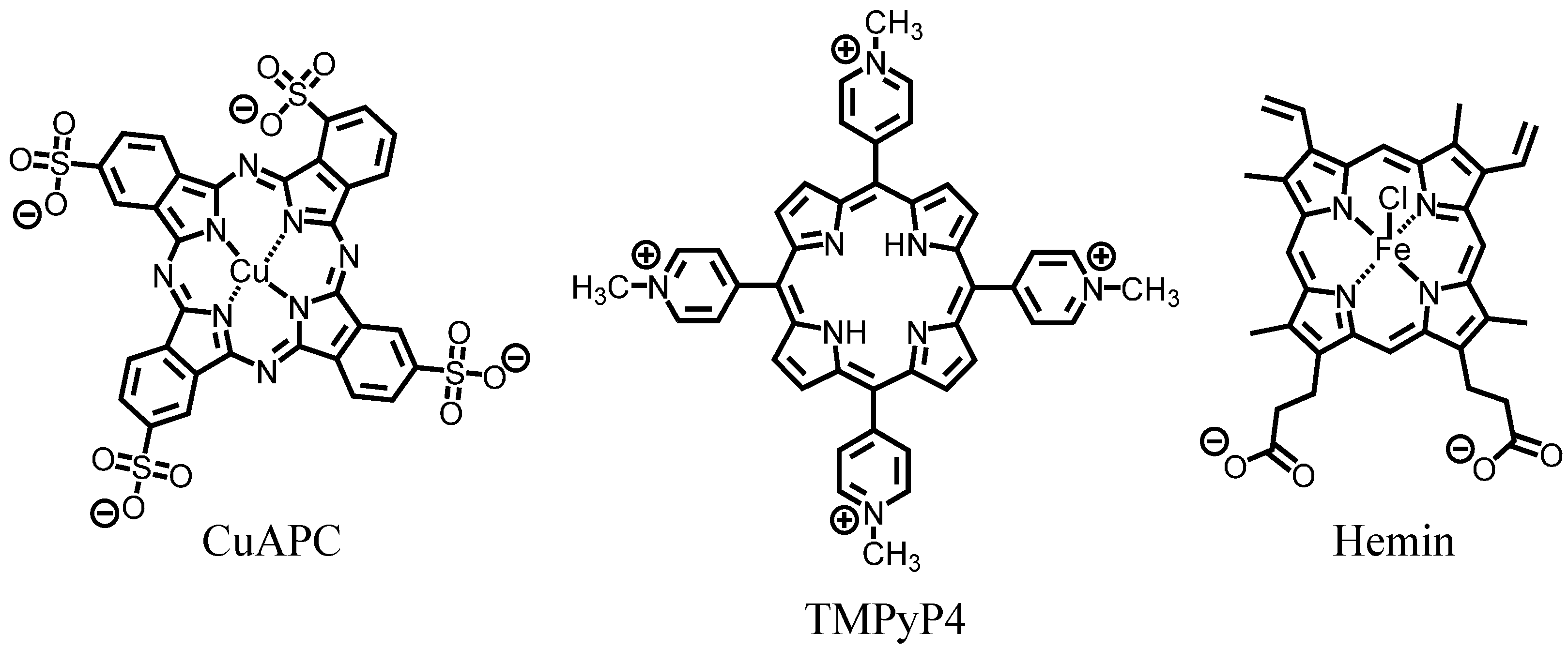
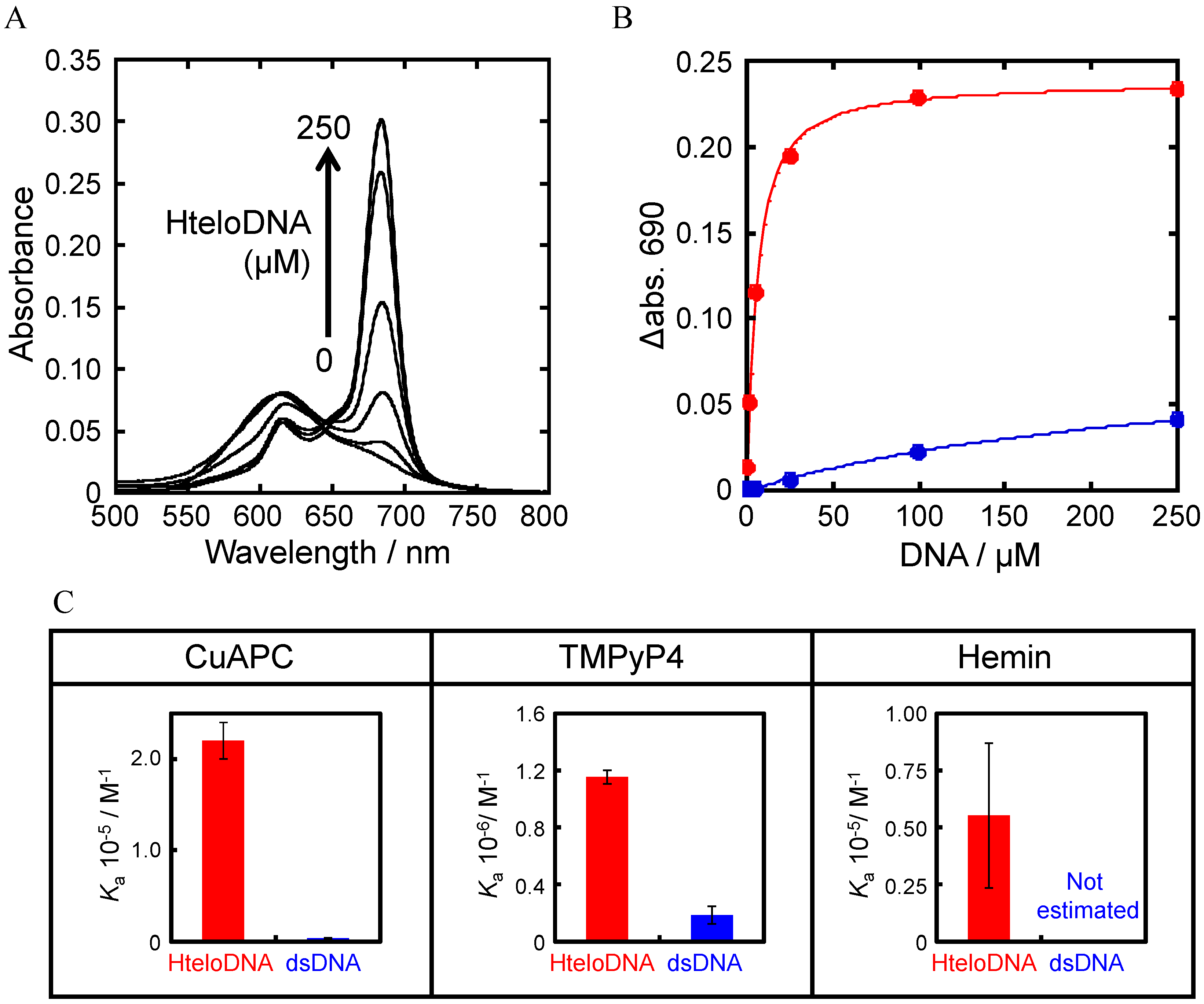
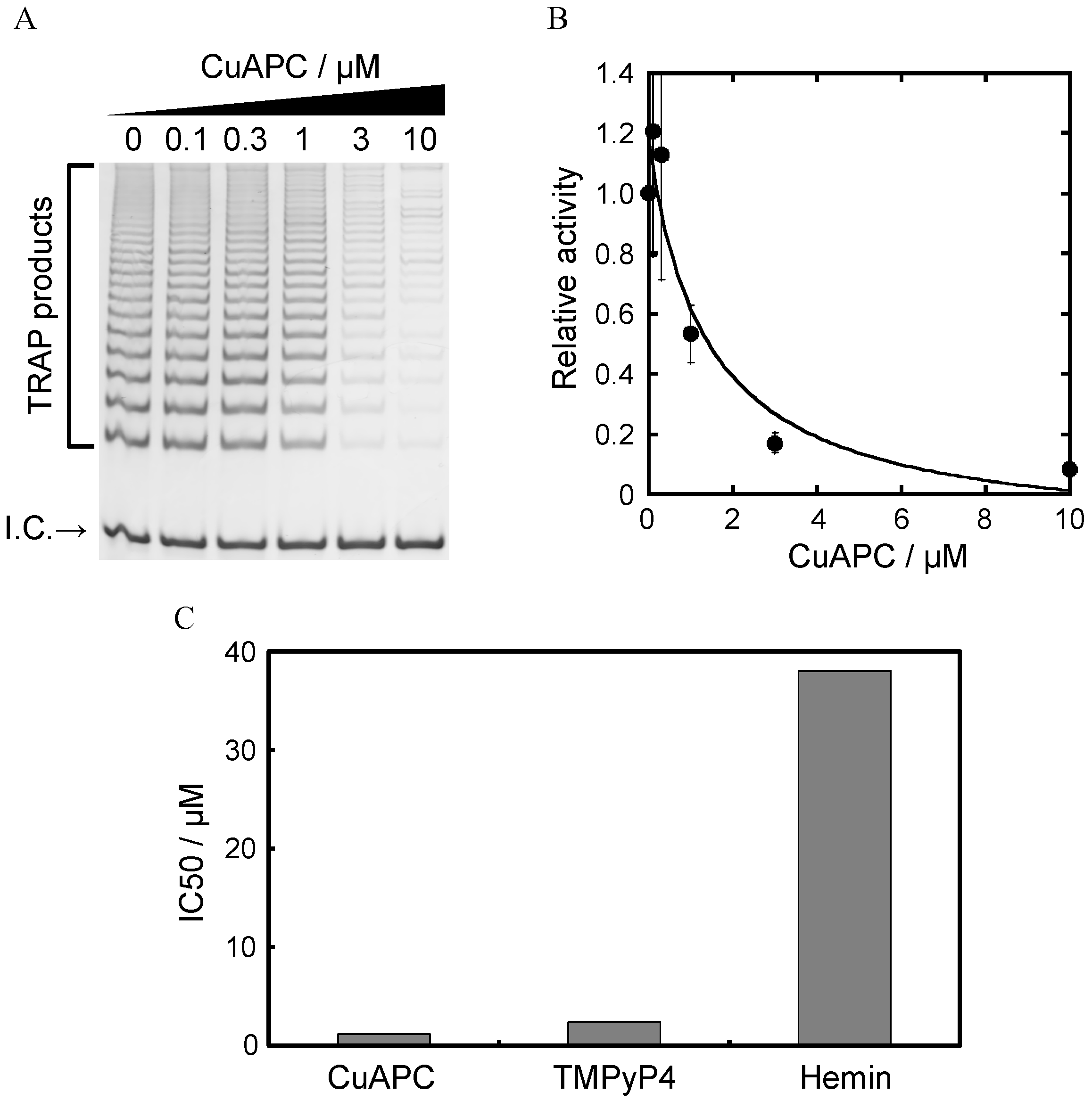
3.3. Affinity of CuAPC to GDDCs
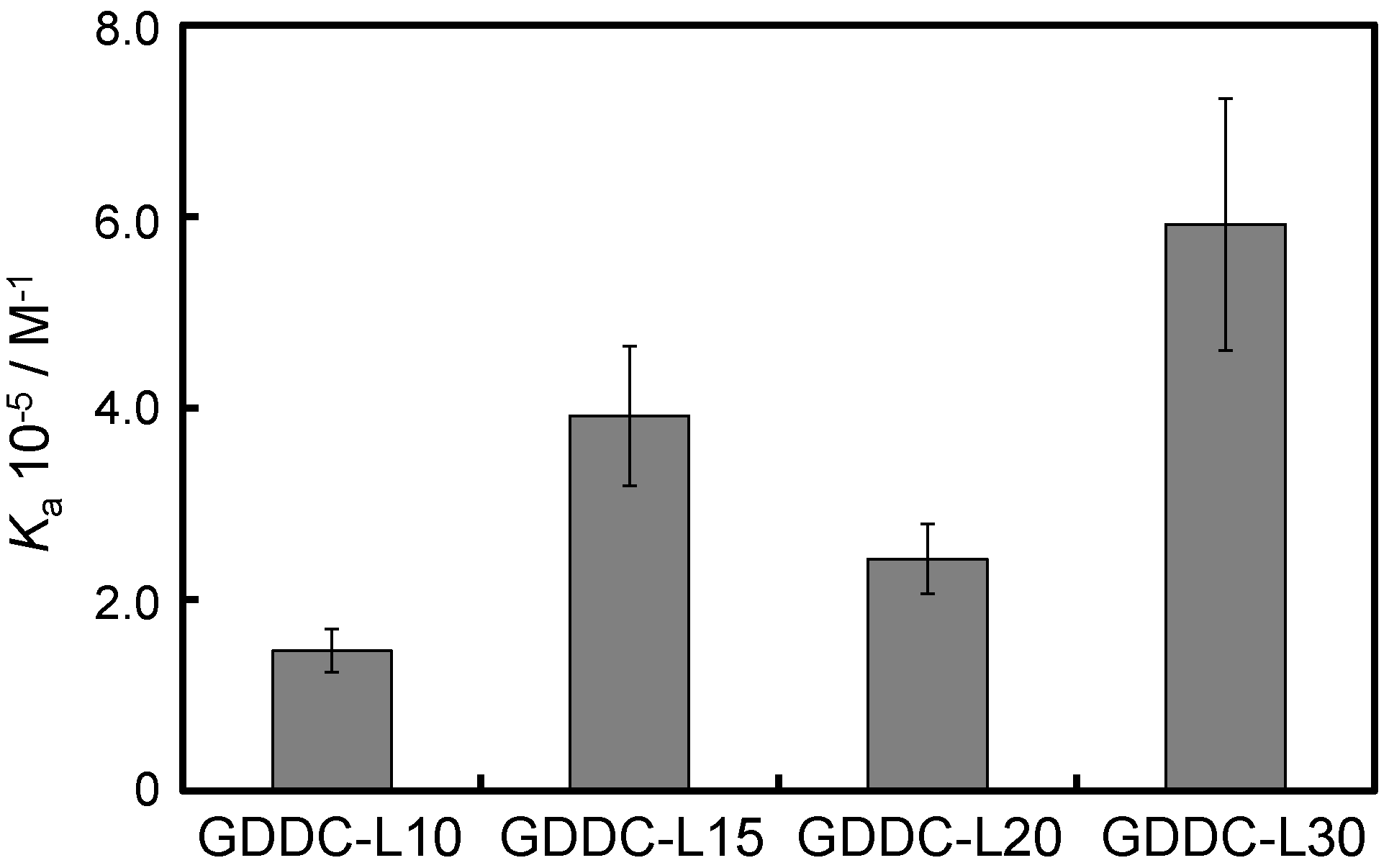
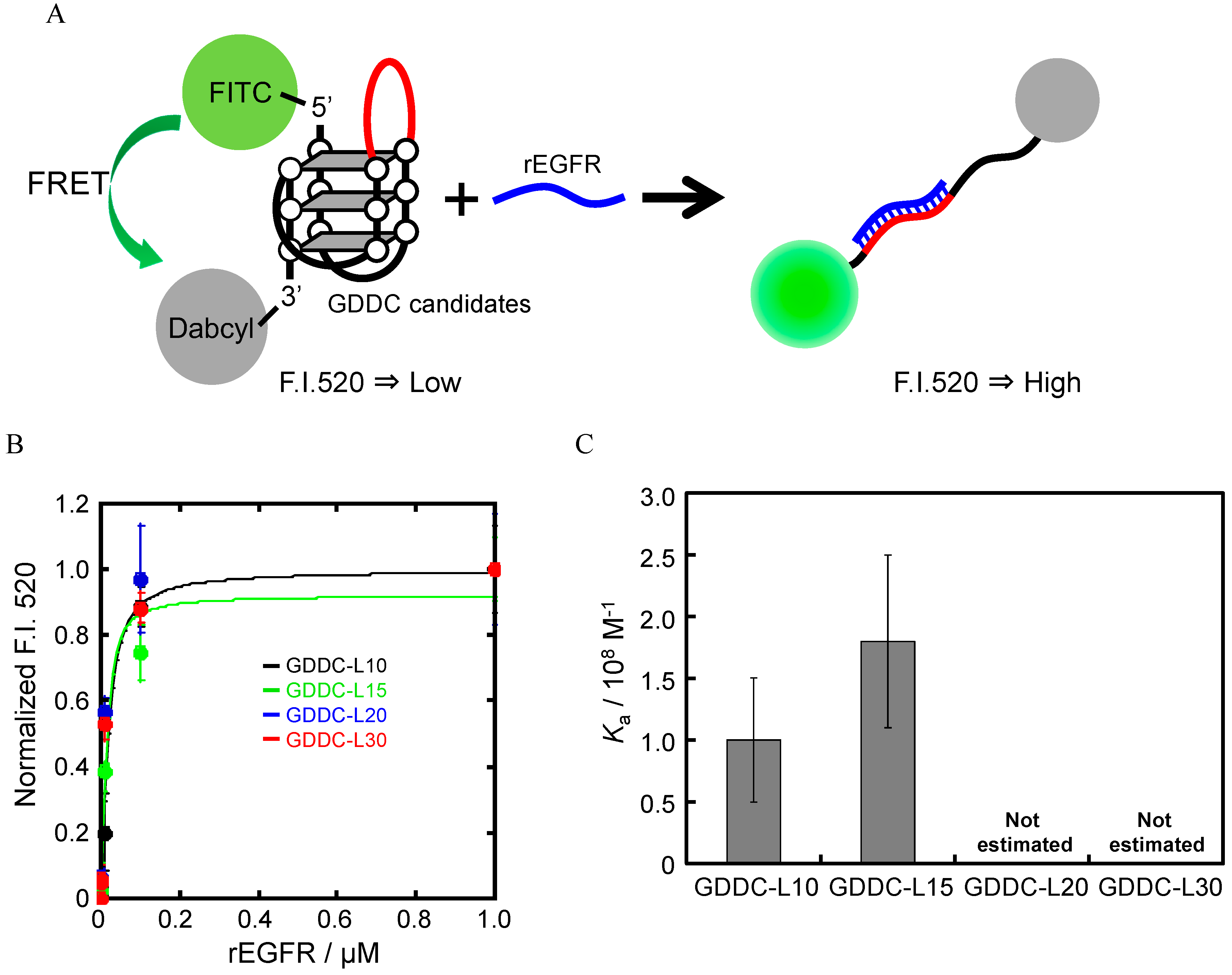
3.4. Unfolding of GDDCs by rEGFR
3.5. Release of CuAPC from GDDC-L30 in Response to rEGFR
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danhier, F.; Feron, O.; Preat, V. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: Passive and active tumor targeting of nanocarriers for anti-cancer drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofheinz, R.D.; Gnad-Vogt, S.U.; Beyer, U.; Hochhaus, A. Liposomal encapsulated anti-cancer drugs. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2005, 16, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Tjulandin, S.; Davidson, N.; Shaw, H.; Desai, N.; Bhar, P.; Hawkins, M.; O’Shaughnessy, J. Phase iii trial of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel compared with polyethylated castor oil-based paclitaxel in women with breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7794–7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, N.; Trieu, V.; Yao, Z.W.; Louie, L.; Ci, S.; Yang, A.; Tao, C.L.; De, T.; Beals, B.; Dykes, D.; et al. Increased antitumor activity, intratumor paclitaxel concentrations, and endothelial cell transport of cremophor-free, albumin-bound paclitaxel, ABI-007, compared with cremophor-based paclitaxel. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, E.; Spinelli, G.P.; Tomao, F.; Tomao, S. Albumin-bound formulation of paclitaxel (Abraxane® ABI-007) in the treatment of breast cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2009, 4, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sluis, R.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Raghunand, N.; Ballesteros, P.; Alvarez, J.; Cerdan, S.; Galons, J.P.; Gillies, R.J. In vivo imaging of extracellular pH using 1H MRSI. Magnet. Reson. Med. 1999, 41, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, R.A.; Casavola, V.; Reshkin, S.J. The role of disturbed ph dynamics and the Na+/H+ exchanger in metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahimi-Horn, M.C.; Pouyssegur, J. Oxygen, a source of life and stress. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3582–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.S.; Gillies, R.D.; Gatenby, R.A. Adaptation to hypoxia and acidosis in carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feron, O. Pyruvate into lactate and back: From the warburg effect to symbiotic energy fuel exchange in cancer cells. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 92, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.E.; Pu, F.; Huang, Z.Z.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. Stimuli-responsive controlled-release system using quadruplex dna-capped silica nanocontainers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 1638–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, Y.; Simmel, F.C. Nucleic acid based molecular devices. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3124–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaku, H.; Murashima, T.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. Specific binding of anionic porphyrin and phthalocyanine to the g-quadruplex with a variety of in vitro and in vivo applications. Molecules 2012, 17, 10586–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beissenhirtz, M.K.; Willner, I. Dna-based machines. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 3392–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bath, J.; Turberfield, A.J. DNA nanomachines. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmer, W.U.; Reuter, A.; Simmel, F.C. A DNA-based machine that can cyclically bind and release thrombin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3550–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Cheng, I.; Luo, K.Q.; Mi, Y.L. Capture and release of protein by a reversible dna-induced sol-gel transition system. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdoncle, A.; Torres, A.E.; Gosse, C.; Lacroix, L.; Vekhoff, P.; Le Saux, T.; Jullien, L.; Mergny, J.L. Quadruplex-based molecular beacons as tunable dna probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11094–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, T.M.; Lu, Y.J.; Tan, J.H.; Huang, Z.S.; Wong, K.Y.; Gu, L.Q. G-quadruplexes: Targets in anticancer drug design. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 690–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidle, S.; Parkinson, G.N. Quadruplex DNA crystal structures and drug design. Biochimie 2008, 90, 1184–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cian, A.; Lacroix, L.; Douarre, C.; Temime-Smaali, N.; Trentesaux, C.; Riou, J.F.; Mergny, J.L. Targeting telomeres and telomerase. Biochimie 2008, 90, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiades, S.N.; Abd Karim, N.H.; Suntharalingam, K.; Vilar, R. Interaction of metal complexes with g-quadruplex DNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4020–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaku, H.; Fujimoto, T.; Murashima, T.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. Phthalocyanines: A new class of g-quadruplex-ligands with many potential applications. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 6203–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Neidle, S. G-quadruplex nucleic acids as therapeutic targets. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2009, 13, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidle, S. The structures of quadruplex nucleic acids and their drug complexes. Curr. Opin. Struc. Biol. 2009, 19, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschin, M. G-quadruplex DNA structures and organic chemistry: More than one connection. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 2225–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase-activity in tetrahymena extracts. Cell 1985, 43, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, G.B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes ttaggg repeats. Cell 1989, 59, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.W.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Prowse, K.R.; Harley, C.B.; West, M.D.; Ho, P.L.C.; Coviello, G.M.; Wright, W.E.; Weinrich, S.L.; Shay, J.W. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 1994, 266, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaku, H.; Murashima, T.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. Anionic phthalocyanines targeting g-quadruplexes and inhibiting telomerase activity in the presence of excessive dna duplexes. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5740–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaku, H.; Murashima, T.; Tateishi-Karimata, H.; Nakano, S.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. Study on effects of molecular crowding on g-quadruplex-ligand binding and ligand-mediated telomerase inhibition. Methods 2013, 64, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaku, H.; Murashima, T.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. In vitro assays predictive of telomerase inhibitory effect of g-quadruplex ligands in cell nuclei. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 2605–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandis, J.R.; Tweardy, D.J. Elevated levels of transforming growth-factor-alpha and epidermal growth-factor receptor messenger-rna are early markers of carcinogenesis in head and neck-cancer. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3579–3584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Noguchi, Y.; Sugiyama, H. The new models of the human telomere d aggg(ttaggg)(3) in K+ solution. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 5584–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrus, A.; Chen, D.; Dai, J.X.; Bialis, T.; Jones, R.A.; Yang, D.Z. Human telomeric sequence forms a hybrid-type intramolecular g-quadruplex structure with mixed parallel/antiparallel strands in potassium solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, K.N.; Phan, A.T.; Kuryavyi, V.; Lacroix, L.; Patel, D.J. Structure of the human telomere in K+ solution: An intramolecular (3+1) g-quadruplex scaffold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9963–9970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheelhouse, R.T.; Sun, D.K.; Han, H.Y.; Han, F.X.G.; Hurley, L.H. Cationic porphyrins as telomerase inhibitors: The interaction of tetra-(N-methyl-4-pyridyl)porphine with quadruplex DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 3261–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travascio, P.; Bennet, A.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Sen, D. A ribozyme and a catalytic DNA with peroxidase activity: Active sites versus cofactor-binding sites. Chem. Biol. 1999, 6, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Miyoshi, D.; Kubodera, T.; Nishimura, A.; Nakai, S.; Sugimoto, N. Roles of Mg2+ in TPP-dependent riboswitch. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 2583–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergny, J.L.; Phan, A.T.; Lacroix, L. Following g-quartet formation by UV-spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1998, 435, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.Q.; Zhang, D.H.; Gu, X.B.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. Regulation of telomerase activity by the thermodynamic stability of a dna center dot rna hybrid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9034–9038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autexier, C.; Lue, N.F. The structure and function of telomerase reverse transcriptase. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 493–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theimer, C.A.; Feigon, J. Structure and function of telomerase RNA. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2006, 16, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, A.T.; Kuryavyi, V.; Gaw, H.Y.; Patel, D.J. Small-molecule interaction with a five-guanine-tract g-quadruplex structure from the human myc promoter. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.J.; Heddi, B.; Tera, M.; Iida, K.; Nagasawa, K.; Phan, A.T. Solution structure of an intramolecular (3 + 1) human telomeric G-quadruplex bound to a telomestatin derivative. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13495–13501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collie, G.W.; Sparapani, S.; Parkinson, G.N.; Neidle, S. Structural basis of telomeric RNA quadruplex—Acridine ligand recognition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2721–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzicalupi, C.; Ferraroni, M.; Bilia, A.R.; Scheggi, F.; Gratteri, P. The crystal structure of human telomeric DNA complexed with berberine: An interesting case of stacked ligand to G-tetrad ratio higher than 1:1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collie, G.W.; Promontorio, R.; Hampel, S.M.; Micco, M.; Neidle, S.; Parkinson, G.N. Structural basis for telomeric G-quadruplex targeting by naphthalene diimide ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoludis, J.M.; Miller, S.T.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Barrett, S.P.; Rablen, P.R.; Lawton, T.J.; Yatsunyk, L.A. Optimized end-stacking provides specificity of N-methyl mesoporphyrin IX for human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20446–20456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergny, J.L.; Maurizot, J.C. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer as a probe for G-quartet formation by a telomeric repeat. Chembiochem 2001, 2, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho-Pun-Cheung, A.; Bazin, H.; Gaborit, N.; Larbouret, C.; Garnero, P.; Assenat, E.; Castan, F.; Bascoul-Mollevi, C.; Ramos, J.; Ychou, M.; et al. Quantification of HER expression and dimerization in patients’ tumor samples using time-resolved Förster resonance energy transfer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaku, H.; Murashima, T.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. A mRNA-Responsive G-Quadruplex-Based Drug Release System. Sensors 2015, 15, 9388-9403. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150409388
Yaku H, Murashima T, Miyoshi D, Sugimoto N. A mRNA-Responsive G-Quadruplex-Based Drug Release System. Sensors. 2015; 15(4):9388-9403. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150409388
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaku, Hidenobu, Takashi Murashima, Daisuke Miyoshi, and Naoki Sugimoto. 2015. "A mRNA-Responsive G-Quadruplex-Based Drug Release System" Sensors 15, no. 4: 9388-9403. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150409388
APA StyleYaku, H., Murashima, T., Miyoshi, D., & Sugimoto, N. (2015). A mRNA-Responsive G-Quadruplex-Based Drug Release System. Sensors, 15(4), 9388-9403. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150409388