RF-Based Location Using Interpolation Functions to Reduce Fingerprint Mapping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Interpolation Methods
- The Euclidean distance linear basis function.
- The multiquadratic function.
- The thin plate spline function.
- Polyharmonic spline functions.
4. Proposed RF-Based Localization
4.1. Methodology
4.2. Proposals for Improving the Location
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Case Study and Configuration
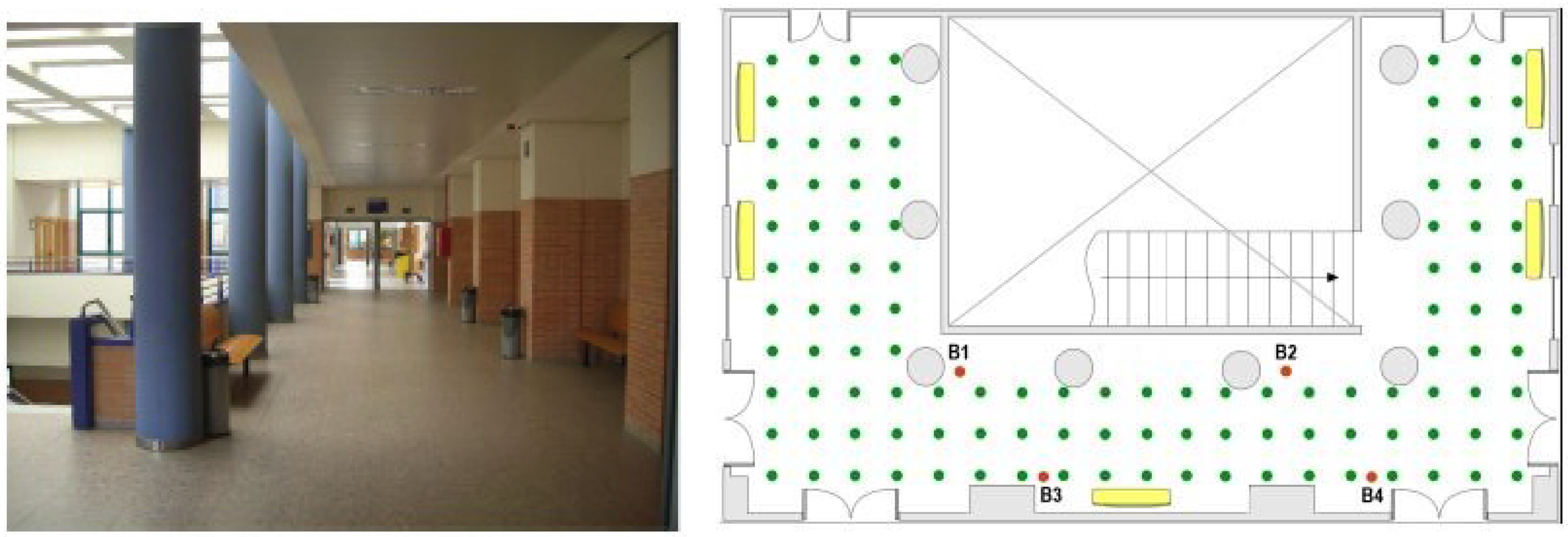
5.2. Analysis of the Database Interpolation
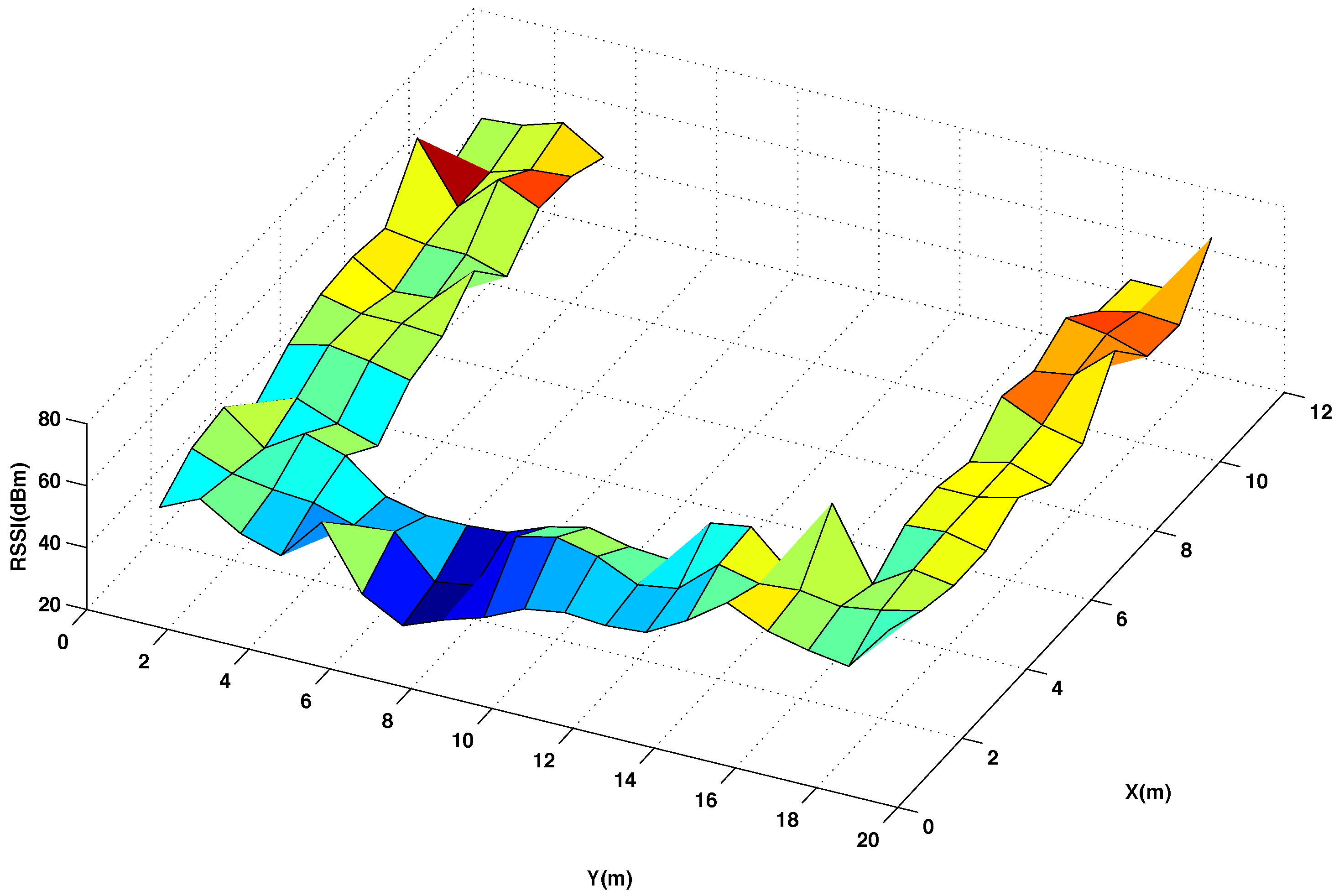
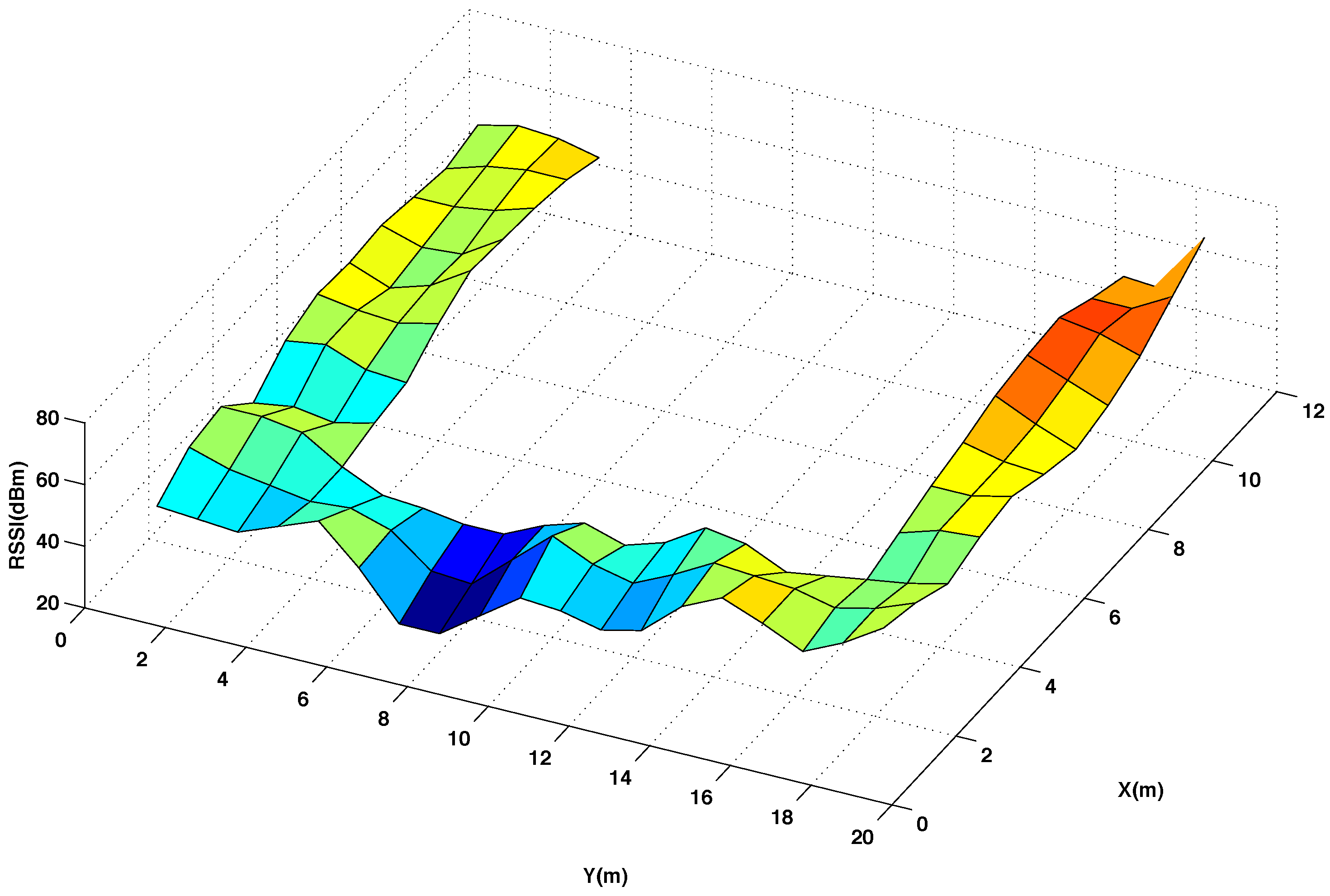
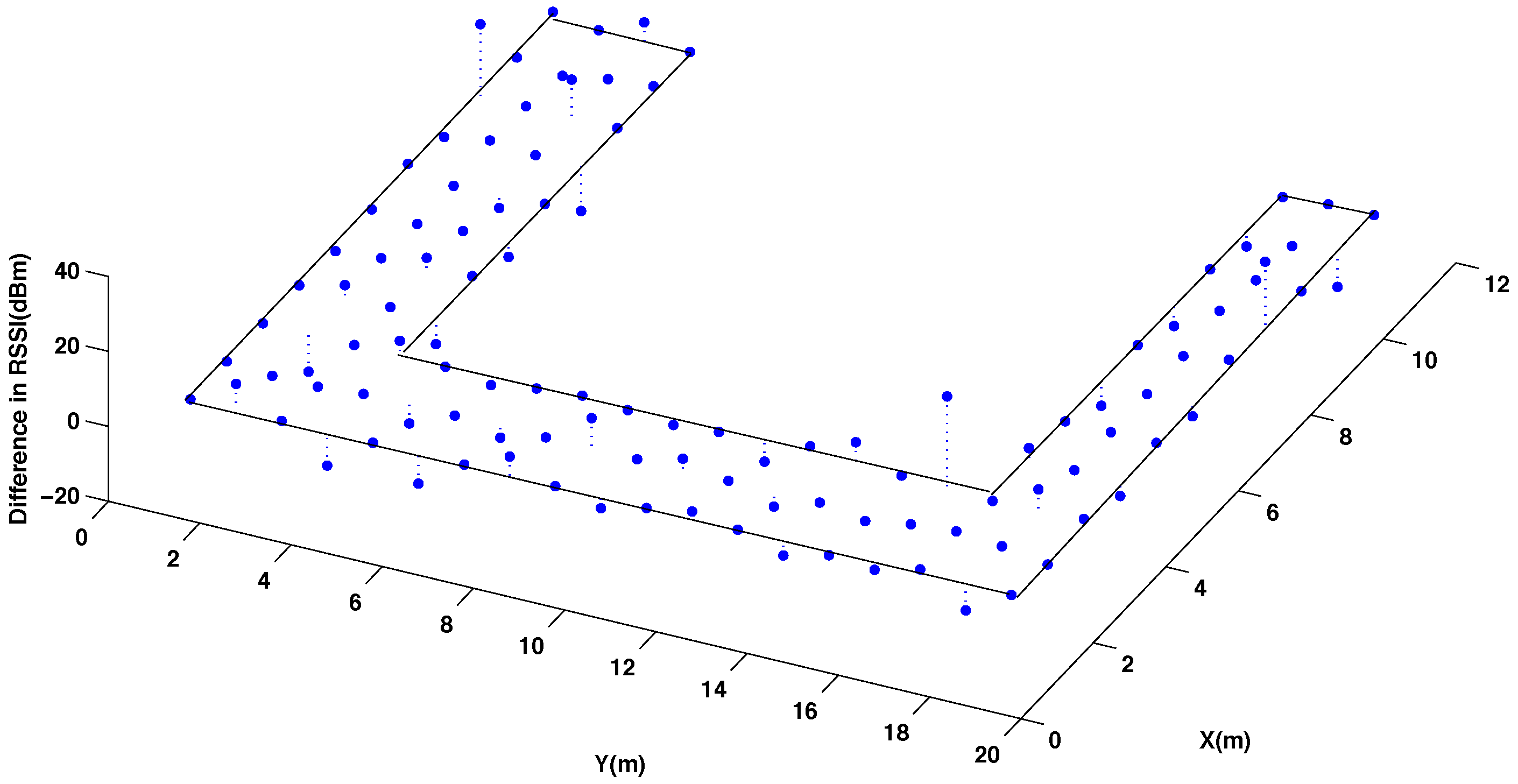
| Thin | Euclidean | Multiquadratic | Polyharmonic (n = 4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difference in RSSI values (in %) | 6.30 % | 7.80% | 7.80% | 9.80% |
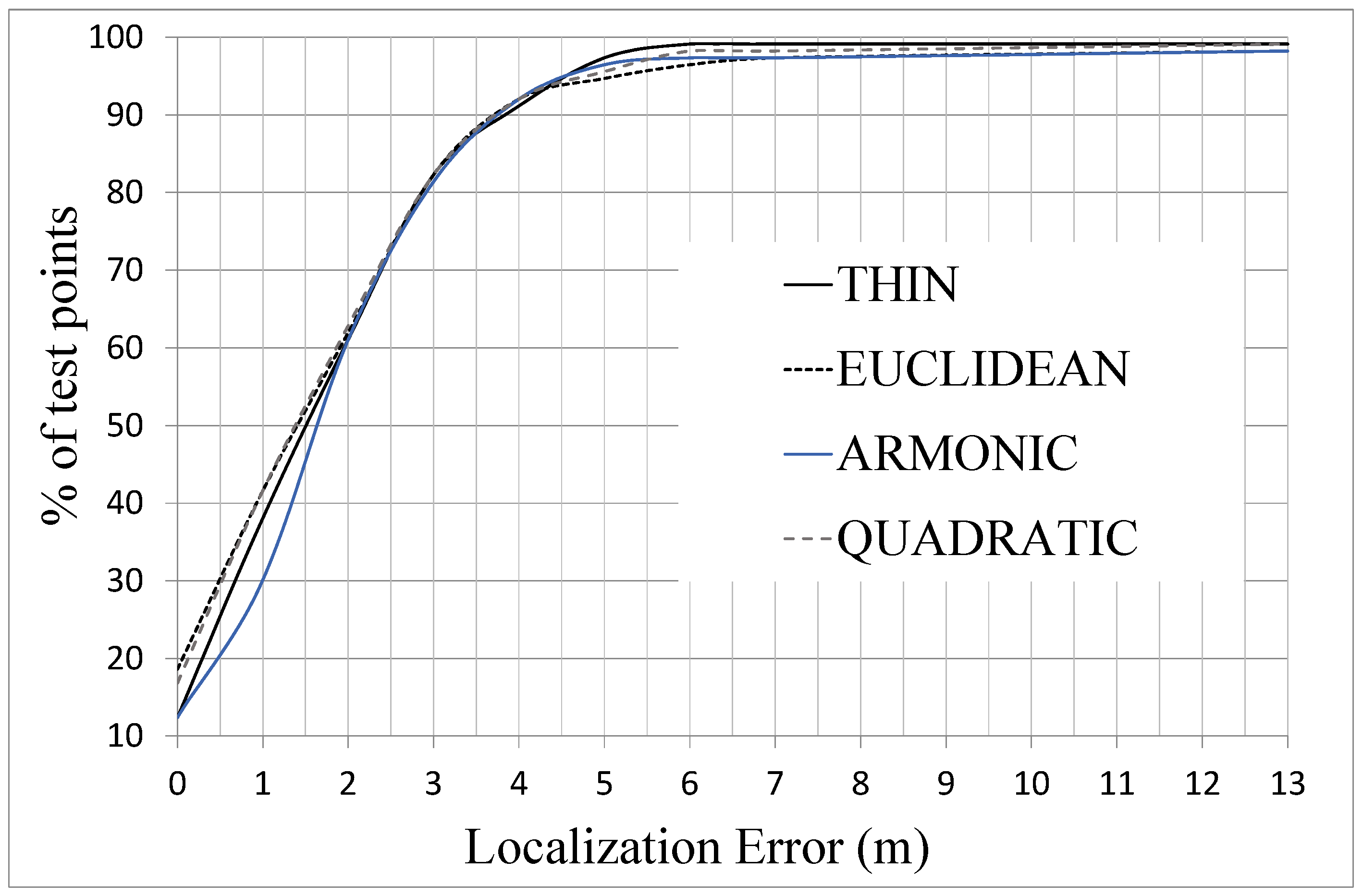
5.3. Analysis of Location Accuracy
- 100% of experimental reference points and without any interpolated point, this case produces an average location error of 2.02 m with an standard deviation of 1.88 m,
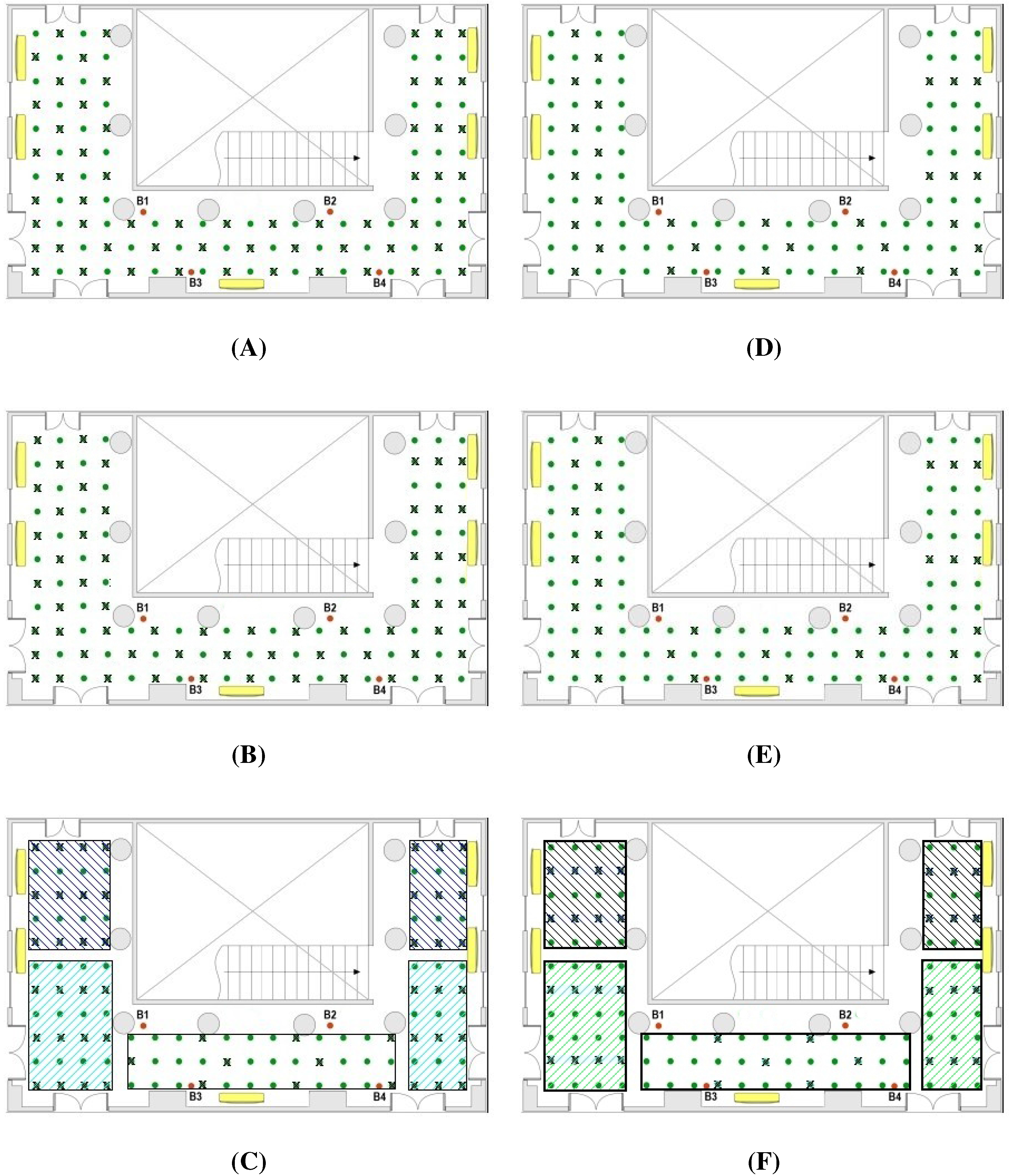
- 50% of the experimental reference points and the other 50% interpolated in three cases: case A with a configuration shown in the scheme of Figure 2A; case B, complementary of case A; and case C, choosing the reference points by zones according to their distance to beacons (Figure 2C). The main difference between the A and B distributions is that in the former most of the points blocked by obstacles in their line of sight to the beacons are included as reference points. In contrast, the B distribution includes hardly any blocked point and they are inserted in the database as interpolated points.
| Thin | Eucl | Multiqua | Polyhar n = 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| case A (50%) | mean error (m) | 2.02 | 2.09 | 2.12 | 2.22 |
| standard deviation (m) | 1.90 | 2.51 | 2.27 | 2.42 | |
| case B (50%) | mean error (m) | 2.50 | 2.38 | 2.52 | 3.10 |
| standard deviation (m) | 2.60 | 2.53 | 2.66 | 3.25 | |
| case C (50%) | mean error (m) | 2.16 | 2.28 | 2.42 | 2.53 |
| standard deviation (m) | 2.06 | 2.18 | 2.40 | 2.55 | |
| case D (25%) | mean error (m) | 3.04 | 3.12 | 3.26 | 3.34 |
| standard deviation (m) | 3.18 | 3.25 | 3.45 | 3.59 | |
| case E (25%) | mean error (m) | 2.98 | 3.06 | 3.22 | 3.52 |
| standard deviation (m) | 2.63 | 3.16 | 3.21 | 3.56 | |
| case F (25%) | mean error (m) | 3.18 | 3.33 | 3.42 | 3.56 |
| standard deviation (m) | 3.26 | 3.42 | 3.53 | 3.66 |
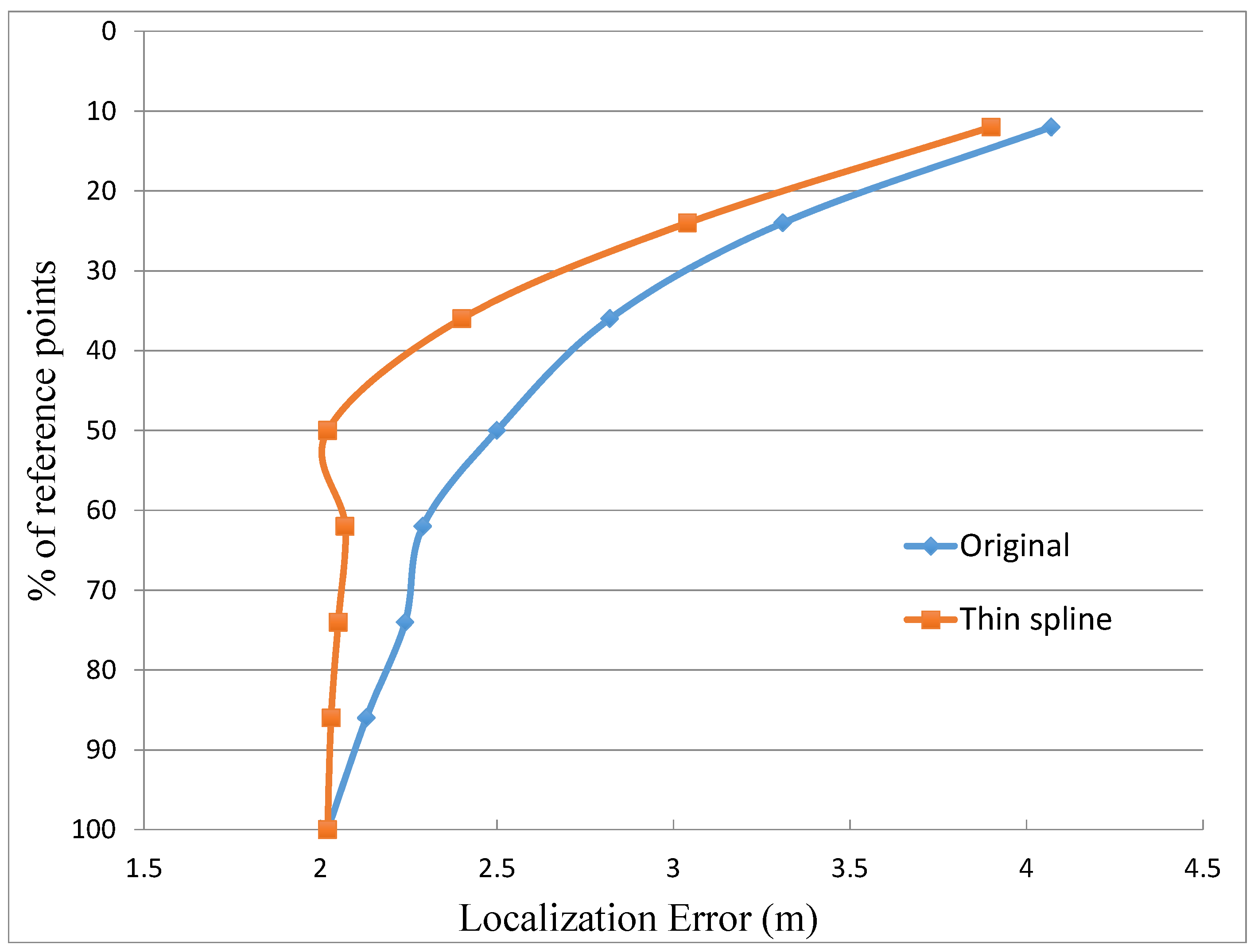
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pace, S.; Frost, G.; Lachow, I.; Frelinger, D.; Fossum, D.; Wassem, D.; Pinto, M. The Global Positioning System, Chapter 1: GPS History, Chronology and Bugets; RAND Corporation: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 237–270. [Google Scholar]
- Texas Instruments CC2431. System-on-Chip for 2.4 GHz ZigBee/IEEE 802.15.4 with Location Engine. Available online: http://www.ti.com.cn/cn/lit/ds/symlink/cc2431.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2015).
- Song, Z.; Jiang, G.; Huang, C. A Survey on Indoor Positioning Technologies. In Theoretical and Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Darabi, H.; Banerjee, P.; Liu, J. Survey of wireless indoor positioning techniques and systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Appl. Rev. 2007, 37, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Chen, J.; Guo, W.; Liu, K. Signal processing techniques in network-aided positioning: A survey of state-of-the-art positioning designs. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Lo, A.; Niemegeers, I. A survey of indoor positioning systems for wireless personal networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claver, J.M.; Ezpeleta, S.; Marti, J.; Pérez-Solano, J.J. Analysis of RF-Based Indoor Localization with Multiple Channels and Signal Strengths; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Bahl, P.; Padmanabhan, V. RADAR: An In-Building RF-Based User Location and Tracking System. In Proceedings of the 19th IEEE INFOCOM Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 26–30 March 2000; pp. 775–784.
- Lorincz, K.; Welsh, M. MoteTrack: A Robust, Decentralized Approach to RF-Based Location Tracking; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 63–82. [Google Scholar]
- Alippi, C.; Mottarella, A.; Vanini, G. A RF Map-Based Localization Algorithm for Indoor Environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS 2005, Kobe, Japan, 23–26 May 2005; pp. 652–655.
- Yao, Q.; Wang, F.Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, K.; Zhao, H. Location Estimation in ZigBee Network Based on Fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Vehicular Electronics and Safety, ICVES, Beijing, China, 13–15 December 2007; pp. 1–6.
- Milioris, D.; Tzagkarakis, G.; Papakonstantinou, A.; Papadopouli, M.; Tsakalides, P. Low-dimensional signal-strength fingerprint-based positioning in wireless LANs. Ad Hoc Netw. 2014, 12, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, B.; Chin, K.W. A comparison of deterministic and probabilistic methods for indoor localization. J. Syst. Softw. 2011, 84, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansemer, S.; Pueschel, S.; Frackowiak, R.; Hakobyan, S.; Grossmann, U. Improved RSSI-bases euclidean distance positioning algorithms for large and dynamic WLAN environements. Int. J. Comput. 2010, 9, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Molina-Garcia, M.; Calle-Sanchez, J.; Alonso, J.; Fernandez-Duran, A.; Barba, F.B. Enhanced in-building fingerprint positioning using femtocell networks. Bell Labs Tech. J. 2013, 18, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, J.; Sales, J.; Marin, R.; Jimenez-Ruiz, E. Localization of mobile sensors and actuators for intervention in low-visibility conditions: the ZigBee fingerprinting approach. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozyyev, A.; Hasbullah, H.; Subhan, F. Combined k-nearest neighbors and fuzzy logic indoor localization technique for wireless sensor network. Res. J. Inf. Technol. 2012, 4, 155–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, H.; Cha, H. Wi-Fi Fingerprint-Based Topological Map Building for Indoor User Tracking. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Embedded and Real-Time Computing Systems and Applications, RTCSA’10, Macau, China, 23–25 August 2010; pp. 105–113.
- Yang, J.; Chen, Y. A Theoretical Analysis of Wireless Localization Using RF-Based Fingerprint Matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing, Miami, FL, USA, 14-18 April 2008; pp. 1–6.
- Narzullaev, A.; Park, Y.; Yoo, K.; Yu, J. A fast and accurate calibration algorithm for real-time locating systems based on the received signal strength indication. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2011, 65, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaashini, K.; Dhivya, G.; Pitchiah, R. Zigbee RF Signal Strength for Indoor Location Sensing—Experiments and Results. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, PyeongChang, Korea, 19–22 February 2012; pp. 12–17.
- Oussar, Y.; Ahriz, I.; Denby, B.; Dreyfus, G. Indoor localization based on cellular telephony RSSI fingerprints containing very large numbers of carriers. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2011, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, P.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H. SIB: Noise Reduction in Fingerprint-Based Indoor Localization Using Multiple Transmission Powers. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Multimedia, MUM’14, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 25–28 November 2014; pp. 208–211.
- De Smith, M.J.; Goodchild, M.F.; Longley, P. Geospatial Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Principles, Techniques and Software Tools; Matador: Leicester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Lee, H.; Dempster, A.; Rizos, C. Method for yielding a database of location fingerprints in WLAN. IEE Proc. Commun. 2005, 152, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumm, J.; Platt, J.C. Minimizing Calibration Effort for an Indoor 802.11 Device Location Measurement System; Technical Report for Microsoft Research MSR-TR-2003-82; Microsoft Research Microsoft Corporation One Microsoft Way: Redmond, WA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Azpurua, M.A.; Ramos, K.D. A comparison of spatial interpolation methods for estimation of average electromagnetic field magnitude. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2010, 14, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ezpeleta, S.; Claver, J.M.; Pérez-Solano, J.J.; Martí, J.V. RF-Based Location Using Interpolation Functions to Reduce Fingerprint Mapping. Sensors 2015, 15, 27322-27340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151027322
Ezpeleta S, Claver JM, Pérez-Solano JJ, Martí JV. RF-Based Location Using Interpolation Functions to Reduce Fingerprint Mapping. Sensors. 2015; 15(10):27322-27340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151027322
Chicago/Turabian StyleEzpeleta, Santiago, José M. Claver, Juan J. Pérez-Solano, and José V. Martí. 2015. "RF-Based Location Using Interpolation Functions to Reduce Fingerprint Mapping" Sensors 15, no. 10: 27322-27340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151027322
APA StyleEzpeleta, S., Claver, J. M., Pérez-Solano, J. J., & Martí, J. V. (2015). RF-Based Location Using Interpolation Functions to Reduce Fingerprint Mapping. Sensors, 15(10), 27322-27340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151027322








