New Trends in Biosensors for Organophosphorus Pesticides
Abstract
:Introduction
Biosensors based on the inhibition of acylcholinesterases
1. Principle



2. Compared features of the different transducing systems
Amperometric transducers
Potentiometric transducers
| Insecticides | Potentiometric (pH effect) | Amperometricn (thiocholine oxidation) |
|---|---|---|
| Aldicarb | 1140 ppb | 1.9 ppb |
| Carbaryl | 1000 ppb | 19 ppb |
| Carbofuran | 6 ppb | 0.02 ppb |
| Dichlorvos | 300 ppb | 22 ppb |
| Response time | 30 min |
| Time of analysis | 60 min |
| Lifetime | 2 days |
| Linear regression | y = 1.295x + 2.777 (x=μg/l) |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.9876 |
| Linear range | 2.5 - 40μg/l |
| Detection limit | 1.0μg/l (ppb) |
| Accuracy | <7.1% |
| Response time | <10 min |
| Time of analysis | <12 min |
| Lifetime | 4 days |
| Linear regression | y = 5.011x – 2.875 (x=μg/l) |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.9959 |
| Linear range | 3.3 - 12μg/l |
| Detection limit | 3.3μg/l (ppb) |
| Accuracy | <8.1% |
| Response time | <5 min |
| Time of analysis | <7 min |
| Lifetime | 4 days |
| Linear regression | y = 1.023x – 3.684 (x=μg/l) |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.9927 |
| Linear range | 16.6 - 82μg/l |
| Detection limit | 10μg/l (ppb) |
| Accuracy | <13.2% |
Effect of the immobilisation technique on operational features of ENFETs

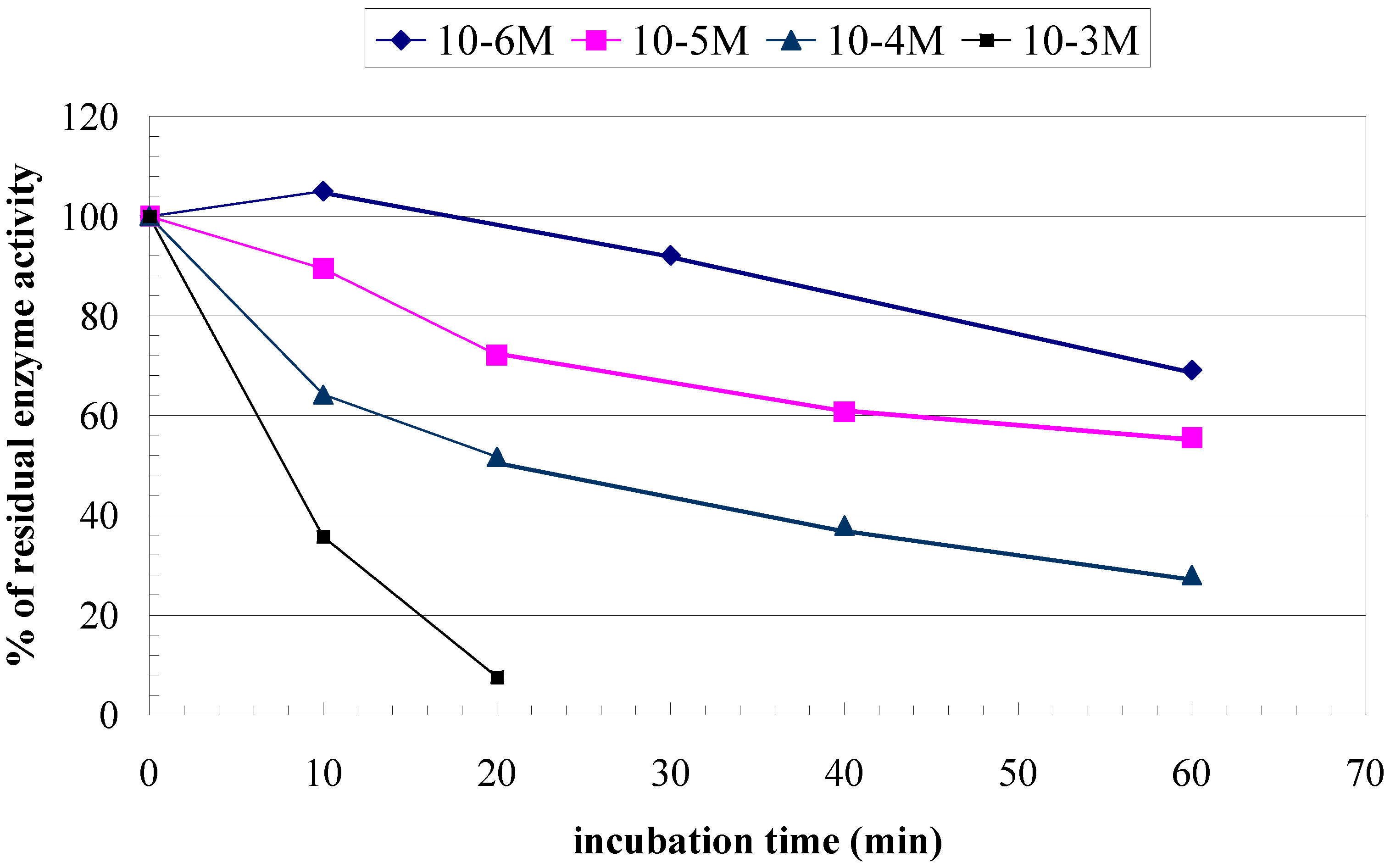
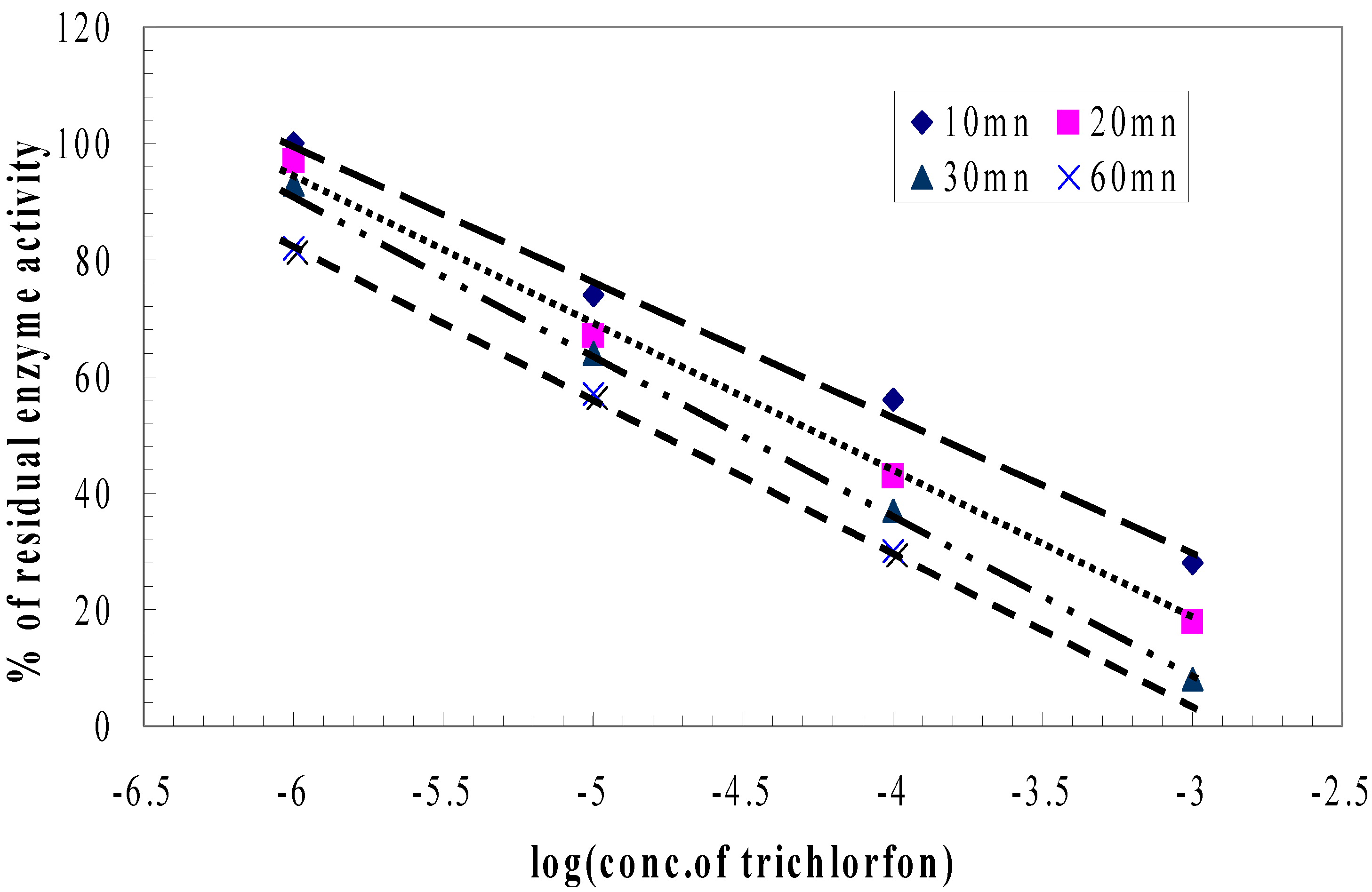
| Membrane | BSA | PVA/SbQ |
|---|---|---|
| Linear dynamic range Stationary mode calibration | 0 – 10 mM 0 – 1 mM | 0 – 10 mM 0 – 1 mM |
| Dynamic range Kinetic mode calibration | 0.2 - 1 mM | 0.2 - 5.8 mM |
| Apparent Km (Michaelis-Menten constant) | 2 mM | 3.8 mM |
| Life-time (dry storage) | 35 days | > 9 months |
| Life-time (storage in buffer) | < 62 days | ~4 months |
| Trichlorfon detection Dynamic range | 10-3M - 10-6M (0.26g.l-1 - 0.26mg.l-1) | 10-3M - 10-6M (0.26g.l-1 - 0.26mg.l-1) |
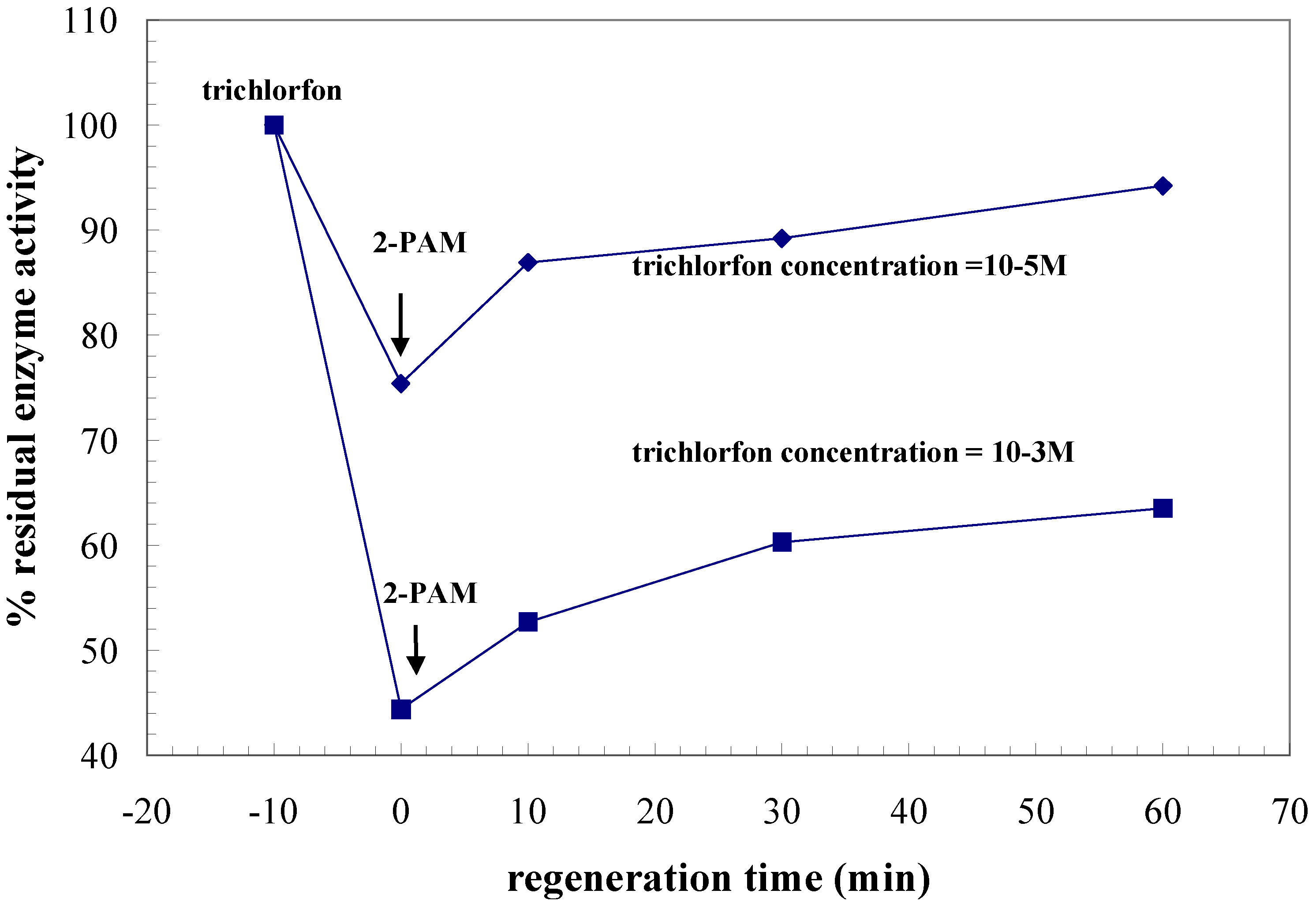
| Trichlorfon detection
Regeneration | PAM-2 Inc. 10-5M, 10 min Reg. 0.1M, 60 min | PAM-2 Inc. 10-5M, 10 min Reg. 0.1M, 60 min |
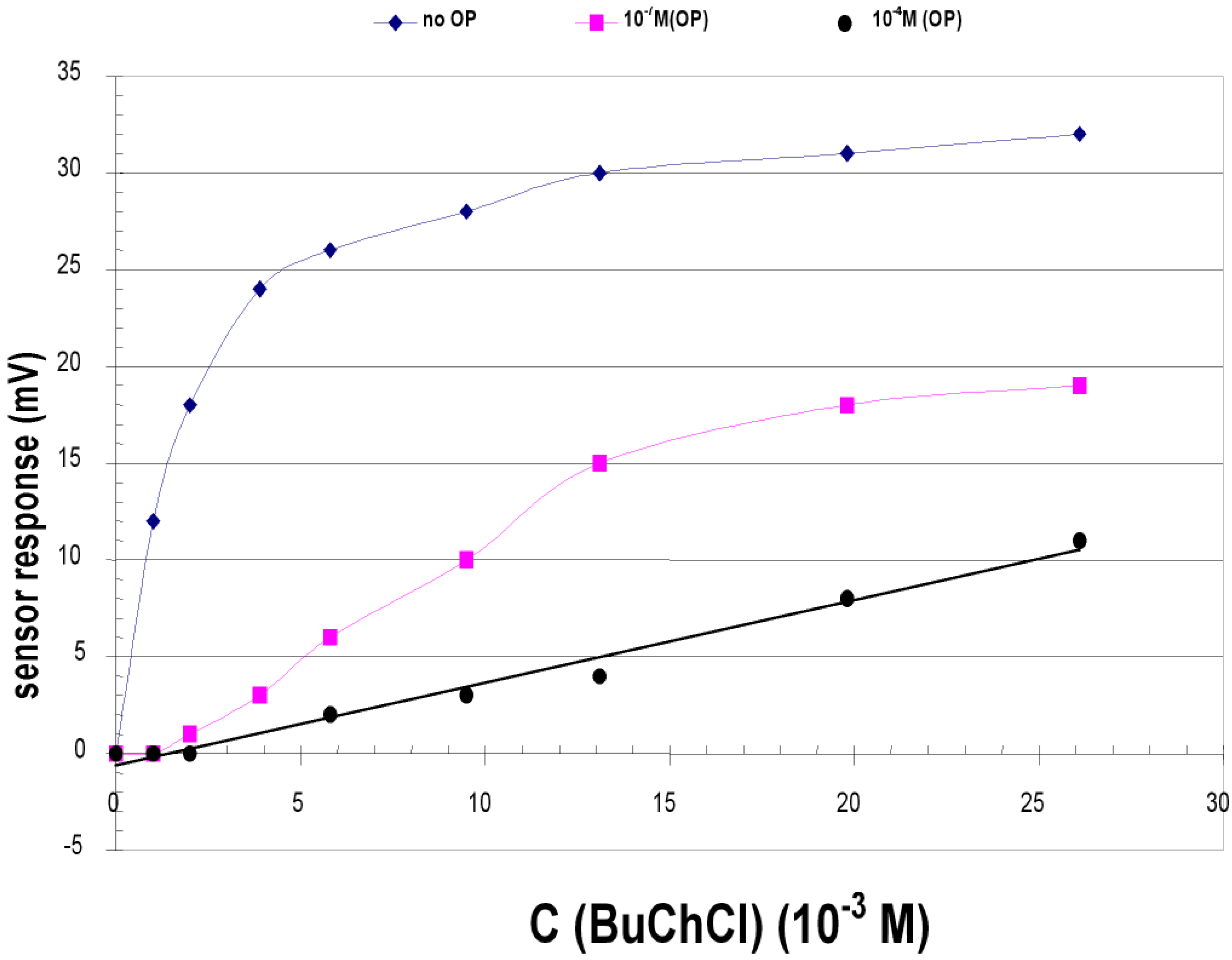
Conductimetric transduction
Optical fibre transduction
3. Conclusion
Biosensors based on inhibition of phosphatases


Biosensors based on organophosphorus hydrolase

- –
- potentiometric pH sensors, detection limits being around 1μM (0.3ppm) for paraoxon
- –
- microelectrodes (detection of p-nitrophenol), detection limit being around 10-7M (27ppb)
- –
- transducers based on optical fibres including pH sensitive dye, detection limit being around 1μM (0.3ppm) [41].
Multisensor system based on enzyme inhibition analysis for determination of different toxic substances
| Urease | BuChE | AcChE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 μM trichlorfon | 0 | 50 | 5 |
| 50 μM trichlorfon | 0 | 70 | 25 |
| 1 mM trichlorfon | 0 | 100 | 85 |
| 100 μM carbofuran | 0 | 100 | 50 |
| 10 μM Ag+ | 0 | 3 | 25 |
| 50 μM Ag+ | 10 | 7 | 70 |
| 10 μM Hg2+ | 15 | 3 | 10 |
| 50 μM Hg2+ | 40 | 7 | 70 |
| Mixture No 1 | 20 | 100 | 30 |
| Mixture No 3 | 95 | 100 | 90 |
| Mixture No 4 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Mixture No 2 | 30 | 100 | 35 |
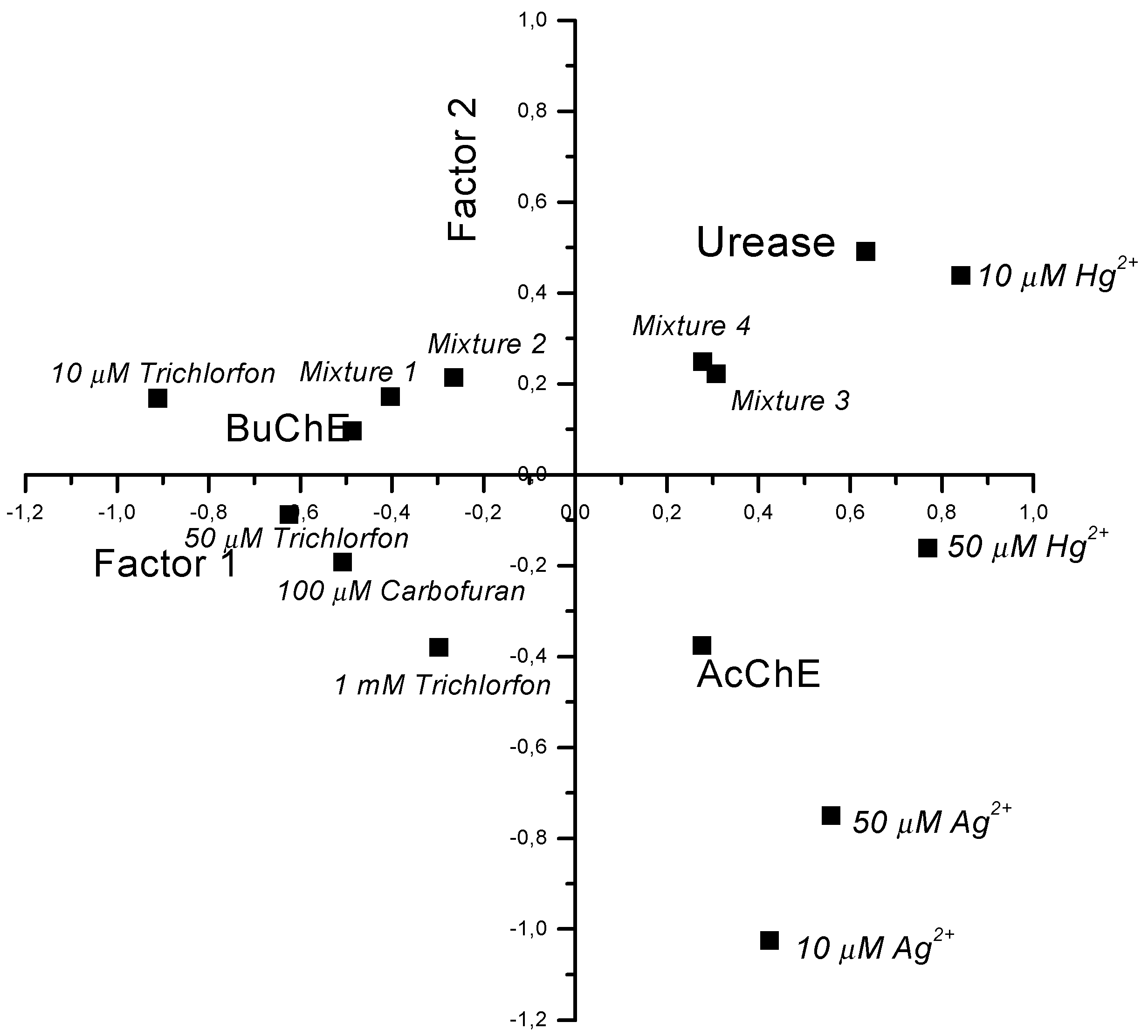
Conclusion
- –
- reversible inhibition of acid and alkaline phosphatases by organophosphorus compounds and carbamates, which avoid reactivation treatment
- –
- selective detection of organophosphorus compounds by organophosphorus hydrolase. This approach presents a lot of advantages concerning selectivity of detection and response time. Nevertheless, detection is done directly in the real sample which could not be convenient for enzymatic reaction and detection limit is much higher than that of inhibition methods.
References
- Budnikov, G. K.; Evtyugin, G. A.; Rizaeva, E. P.; Ivanov, A. N.; Latypova, V. Z. Comparative assessment of electrochemical biosensors for determining inhibitors - Environmental pollutants. J. Anal. Chem. 1999, 54(9), 864–871. [Google Scholar]
- Evtugyn, G. A.; Ivanov, A. N.; Gogol, E. V.; Marty, J. L.; Budnikov, H. C. Amperometric flow-through biosensor for the determination of cholinesterase inhibitors. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 385, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A. L.; Collier, W. A.; Janssen, D. The response of screen-printed enzyme electrodes containing cholinesterases to organo-phosphates in solution and from commercial formulations. Biosens. Bioelec. 1997, 12(7), 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, C.; Pariente, F.; Hernandez, L.; Lorenzo, E. Determination of organophosphorus and carbamic pesticides with an acetylcholinesterase amperometric biosensor using 4-aminophenyl acetate as substrate. Anal. Chim. Acta 1994, 295, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell, D.; Cespedes, F.; Alegret, S.; Martinez-Faregas, E. Amperometric determination of pesticides using biosensor based on polishable graphite-epoxy biocomposite. Anal. Chim. Acta 1994, 290, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell, D.; Cespedes, F.; Martinez-Faregas, E.; Alegret, S. Determination of organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides using a biosensor based on polishable, 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane-modified, graphite-epoxy biocomposite. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 337, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, J.-L.; Sode, K.; Karube, I. Biosensor for detection of organophosphate and carbamate insecticides. Electroanalysis 1992, 4, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mionetto, N.; Marty, J.-L.; Karube, I. Acetylcholinesterase in organic solvents for the detection of pesticides : biosensor application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1994, 9, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchetti, I.; Cagnini, A.; Del Carlo, M.; Coppi, C.; Mascini, M.; Turner, A. P. F. Determination of acetylcholinesterase pesticides in real samples using disposable biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 337, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palleschi, G.; Bernabei, M.; Cremisini, C.; Mascini, M. Determination of organophosphorus insecticides with a choline electrochemical biosensor. Sens. Actuators 1992, B7, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skadal, P. Determination of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides using cobalt phtalocyanine-modified carbon paste electrode and cholinesterase enzyme membrane. Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 252, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skladal, P.; Mascini, M. Sensitive detection of pesticides using amperometric sensors based on cobalt phtalocyanine-modified composite electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1992, 7, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowicz, M.; Hitchman, M. L. Determination of pesticides using electrochemical biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 1996, 15, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, W. R.; Rechnitz, G. A. Enzyme-based electrochemical biosensors for determination of organbophosphorous and carbamate pesticides. Anal. Letters 1999, 32(1), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuna Bastos, V. L. F.; Chuna Bastos, J.; Lima, J. S.; Castro Faria, M. V. Brain aceylcholinesterase as an in vitro detector of organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides in water. Water Res. 1991, 25, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzer, T.; Schwedt, G. Chemometric methods for the development of a biosensor system and the evaluation of inhibition studies with solutions and mixtures of pesticides and heavy metals. Part I. Development of an enzyme electrodes system for pesticides and heavy metal screening using selected chemometric methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 318, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kumaran, S.; Morita, M. Application of a cholinesterase biosensor to screen for organophosphorus pestcides extracted from soil. Talanta 1995, 42, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, S.; Tran-Minh, C. Determination of organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides by flow injection analysis. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 200, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Minh, C.; Pandey, P. C.; Kumaran, S. Studies of acetylcholine sensor and its analytical application based on the inhibition of cholinesterase, Biosens. Bioelectron. 1990, 5, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumschat, C.; Müller Stein, K.; Schwedt, G. Pesticide-sensitive ISFET based on enzyme inhibition, Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 252, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, L.; Colapicchioni, C.; Favero, G.; Sammartino, M. P.; Tomasetti, M. Organophosphorus pesticides (Paraoxon) analysis using solid state sensors, Sens. Actua. 1996, B33, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C.; Cléchet, P.; Nyamsi Hedji, A. M.; Shul'ga, A.; Dzyadevich, S.; Netchiporouk, L. I.; Soldatkin, A. P. Comparison of two transduction modes for design of microbiosensors applicable to detection of pestides. Sensors and Materials 1996, 8(3), 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Nyamsi Hendji, A. M.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C.; Cléchet, P.; Shul'ga, A. A.; Netchiporouk, L. I.; Soldatkin, A. P.; Wlodarski, W. B. Sensitive detection of pesticides using a differential ISFET-based system with immobilized cholinesterases, Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 281, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Chovelon, J. M.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Soldatkin, A. P. Sensitive detection of pesticide using ENFET with enzymes immobilized by cross-linking and entrapment methode. Sens. Actuat. 1999, B 58, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Chovelon, J. M.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Enzyme-octadecylamine Langmuir-Blodgett membranes for ENFET biosensors. Talanta 2000, 52, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K. R.; Foley, M.; Alter, S.; Koga, P.; Eldefrawi, M. E. Light adressable potentiometric biosensor for the detection of anticholinesterases. Anal. Lett. 1991, 24, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, J. L.; Garcia, D.; Rouillon, R. Biosensor: potential in pesticide detection. Trends in Anal. Chem. 1995, 14(7), 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Chovelon, J. M.; Wan, K.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Influence of the surface pressure on the organization of mixed Langmuir-Blodgett films of octadecylamine and butyrylcholinesterase. 1 - Film preparation at the air-water interface. Langmuir 2000, 16(15), 6223–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzyadevich, S. V.; Shul'ga, A. P.; Soldatkin, A. P.; Nyamsi Hendji, A. M.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C. Conductometric biosensors based on cholinesterases for sensitive detection of pesticides. Electroanalysis 1994, 6, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, R. T.; Narayanaswamy, R. Fiber-optic pesticide biosensor based on covalently immobilized acetylcholinesterase and thymol blue. Talanta 1997, 44, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia De Maria, C.; Munoz, T. M.; Townhend, A. Reactivation of an immobilized enzyme reactor for the determination of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Flow injection determination of paraoxon. Anal. Chim. Acta 1994, 295, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobel, W.; Polster, J. Fiber optic biosensor for pesticides based on acetylcholine esterase. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1992, 343, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moris, P.; Alexandre, I.; Roger, M.; Remacle, J. Chemiluminescence assay of organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 302, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K. R.; Cao, C. J.; Valdes, J. J.; Eldefrawi, A. T.; Eldefrawi, M. E. Acetylcholinesterase fiber-optic biosensor for detection of anticholinesterases. Fund. Appl. Toxicol. 1991, 16, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trettnak, W.; Reininger, F.; Zinterl, E.; Wolfeis, O. S. Fiber-optic remote detection of pesticides and related inhibitors of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. Sens. Actuat. 1993, B 11, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, F.; Botrè, F.; Botrè, C. Acid phosphatase/glucose oxidase-based biosensors for the determination of pesticides. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 336, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainina, E. I.; Efremenco, E. N.; Varfolomeyev, S. D.; Simonian, A. L.; Wild, J. R. The development of a new biosensor based on recombinant E. coli for the direct detection of organophosphorus neurotoxins. Biosens. Bioelec. 1996, 11(10), 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchandani, A.; Mulchandani, P.; Chen, W. Enzyme biosensor for determination of organophosphorates. Field Anal. Chem. Technol. 1998, 2(6), 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchandani, P.; Mulchandani, A.; Kaneva, I.; Chen, W. Biosensor for direct determination of organophosphate nerve agents. 1. Potentiometric enzyme electrode. Biosens. Bioelec. 1999, 14, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchandani, A.; Mulchandani, P.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Amperometric thick-film strip electrodes for monitoring organophosphate nerve agents based on immobilized organophosphorus hydrolase. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2246–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R. J.; Pishko, M. V.; Simonian, A. L.; Wild, J. R. Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel-encapsulated fluorophore-enzyme conjugates for direct detection of organophosphorus neurotoxins. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4909–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkhypova, V. N.; Dzyadevych, S. V.; Soldatkin, A. P.; El'skaya, A. V.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Jaffrezic, H.; Martelet, C. Multibiosensor based on enzyme inhibition analysis for determination of different toxic substances. Talanta. (in press). [CrossRef]
- Benzecri, J. P. Correspondence analysis Handbook; Marcel Dekker: Basel, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Greenacre, M. J. Theory and applications of Correspondence Analysis. Academic Press: New York, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2001 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.net). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Jaffrezic-Renault, N. New Trends in Biosensors for Organophosphorus Pesticides. Sensors 2001, 1, 60-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/s10100060
Jaffrezic-Renault N. New Trends in Biosensors for Organophosphorus Pesticides. Sensors. 2001; 1(2):60-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/s10100060
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaffrezic-Renault, Nicole. 2001. "New Trends in Biosensors for Organophosphorus Pesticides" Sensors 1, no. 2: 60-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/s10100060
APA StyleJaffrezic-Renault, N. (2001). New Trends in Biosensors for Organophosphorus Pesticides. Sensors, 1(2), 60-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/s10100060




