Fish Distribution in Far Western Queensland, Australia: The Importance of Habitat, Connectivity and Natural Flows
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
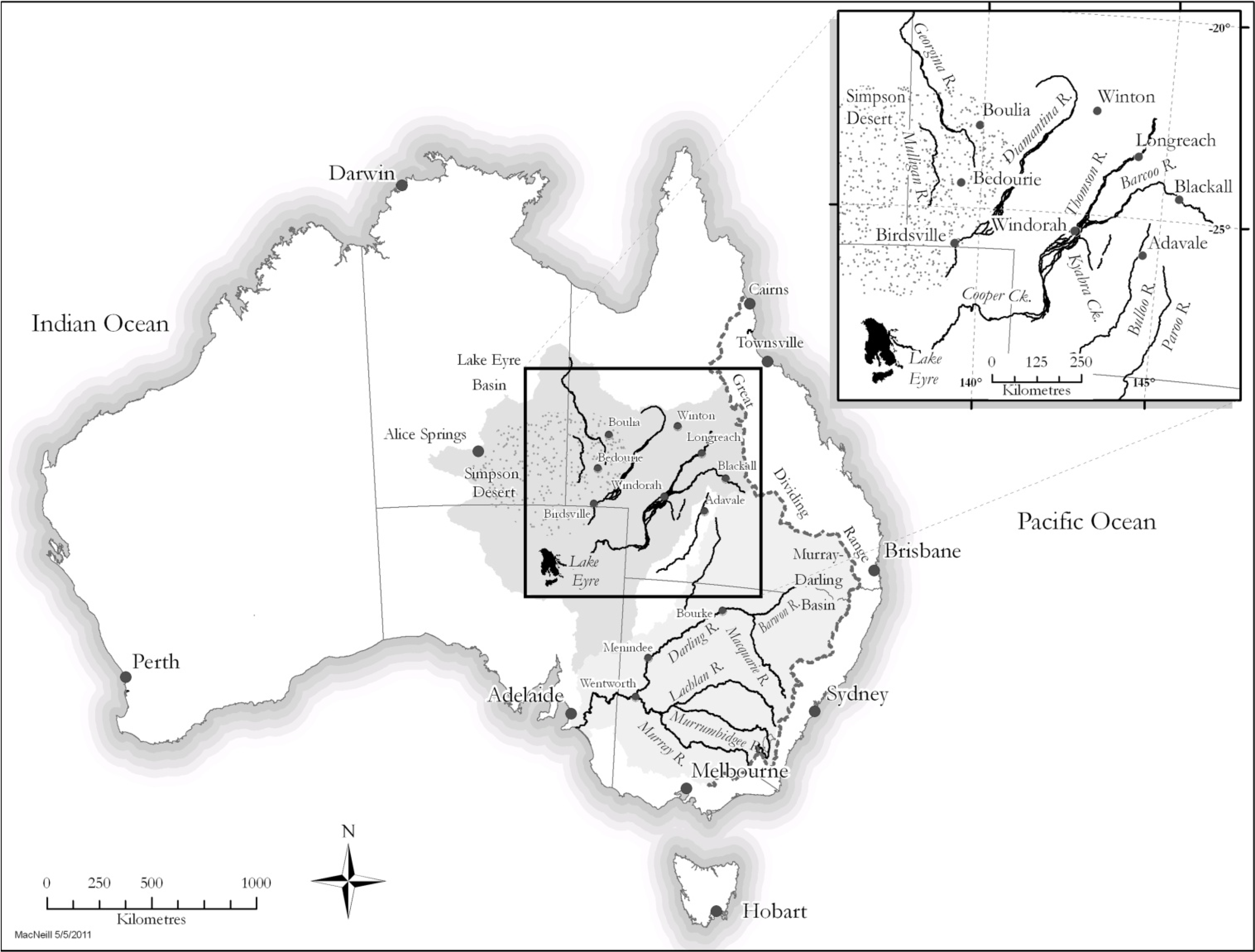
2.1. Field Methods
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fish Species Presence/Absence Results
| Species | Catchment (Total Number of Sites Sampled 2006–2008) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mulligan (6) | Georgina (12) | Diamantina (14) | Thomson (27) | Barcoo (19) | Cooper (21) | Kyabra (24) | Bulloo (12) | |
| Nematolosa erebi (Bony bream) | 83.3 | 83.3 | 78.6 | 100 | 89.5 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Neosiluroides cooperensis (Cooper Creek catfish) | 44.4 | 26.3 | 33.3 | |||||
| Neosiluris hyrtlii (Hyrtl’s tandan) | 75 | 42.9 | 62.9 | 47.4 | 80.9 | 58.3 | 66.6 | |
| Porochilus argenteus (Silver tandan) | 83.3 | 50 | 71.4 | 74 | 57.9 | 85.7 | 91.6 | 91.6 |
| Retropinna semoni (Australian smelt) | 70.8 | 33.3 | 26.3 | 33.3 | ||||
| Melanotaenia splendida tatei (Desert rainbowfish) | 50 | 91.6 | 35.7 | 51.9 | 42.1 | 23.8 | 75 | 58.3 |
| Ambassis sp. (Northwest Ambassis or Glassfish) | 83.3 | 100 | 22.2 | 36.8 | 9.5 | 37.5 | 83.3 | |
| Macquaria sp. (Yellowbelly) | 41.6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 95.2 | 95.8 | 75 | |
| Amniataba percoides (Banded grunter) | 16.6 | 83.3 | ||||||
| Bidyanus welchi (Welch’s grunter) | 8.3 | 7.1 | 22.2 | 10.5 | 28.6 | 25 | ||
| Leiopotherapon unicolour (Spangled perch) | 100 | 50 | 42.9 | 77.8 | 42.1 | 42.9 | 87.5 | 100 |
| Scortum barcoo (Barcoo grunter) | 33.3 | 16.6 | 21.4 | 29.6 | 26.3 | 47.6 | 8.3 | |
| Glossogobius aureus (Golden goby) | 75 | 7.1 | ||||||
| Hypseleotris sp. (Carp gudgeon) | 59.3 | 47.4 | 19 | 83.3 | 58.3 | |||
| Oxyeleotris lineolatus (Sleepy cod) | 3.7 | |||||||
| Carassius auratus (Goldfish) | 7.4 | 10.5 | ||||||
| Gambusia holbrooki (Gambusia) | 14.3 | |||||||
| Total Number Of Species | 7 | 11 | 9 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 11 | 8 |
| Factor | Global R | p | Significant Pairwise Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catchment | 0.314 | 0.001 | Bulloo River vs. Kyabra Creek (0.029) Bulloo River vs. Cooper Creek (0.001) Bulloo River vs. Thomson River (0.004) Bulloo River vs. Barcoo River (0.005) Bulloo River vs. Mulligan River (0.001) Bulloo River vs. Georgina River (0.001) Bulloo River vs. Diamantina River (0.002) Kyabra Creek vs. Cooper Creek (0.001) Kyabra Creek vs. Barcoo River (0.011) Kyabra Creek vs. Mulligan River (0.001) Kyabra Creek vs. Georgina River (0.001) Kyabra Creek vs. Diamantina River (0.001) Cooper Creek vs. Barcoo River (0.032) Cooper Creek vs. Mulligan River (0.001) Cooper Creek vs. Georgina River (0.001) Cooper Creek vs. Diamantina River (0.001) Thomson River vs. Mulligan River (0.001) Thomson River vs. Georgina River (0.001) Thomson River vs. Diamantina River (0.002) Barcoo River vs. Georgina River (0.001) Barcoo River vs. Diamantina River (0.024) Mulligan River vs. Diamantina River (0.008) Georgina River vs. Diamantina River (0.001) |
| Season | 0.064 | 0.035 | Late summer vs. winter (0.038) |
| Antecedent flow | 0.096 | 0.001 | Within-channel flow vs. major flood (0.004) Within-channel flow vs. no flow (0.001) Major flood vs. minor/moderate flood (0.001) |
| Waterhole type | 0.136 | 0.009 | Permanent channel vs. ephemeral lake (0.003) Ephemeral channel vs. ephemeral lake (0.047) |
| Species | Average abundance per sample | Percent contribution to observed differences (>5%). | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early summer | Late summer | Winter | Late summer vs. winter | |
| 100.74 | 76.81 | 13.08 | 5.14 | |
| Hyrtl’s tandan | 29.57 | 91.45 | - | 11.54 |
| Silver tandan | 10.70 | 39.30 | 7.46 | 9.48 |
| Australian smelt | 11.48 | - | - | 6.62 |
| Desert rainbowfish | - | 47.60 | 20.58 | 10.43 |
| Glassfish | 17.13 | 25.91 | - | 9.42 |
| Yellowbelly | 14.52 | 17.64 | 9.92 | 6.07 |
| Spangled perch | 9.57 | 30.51 | 5.65 | 9.96 |
| Carp gudgeon | 1.7 | - | 2.54 | 8.89 |
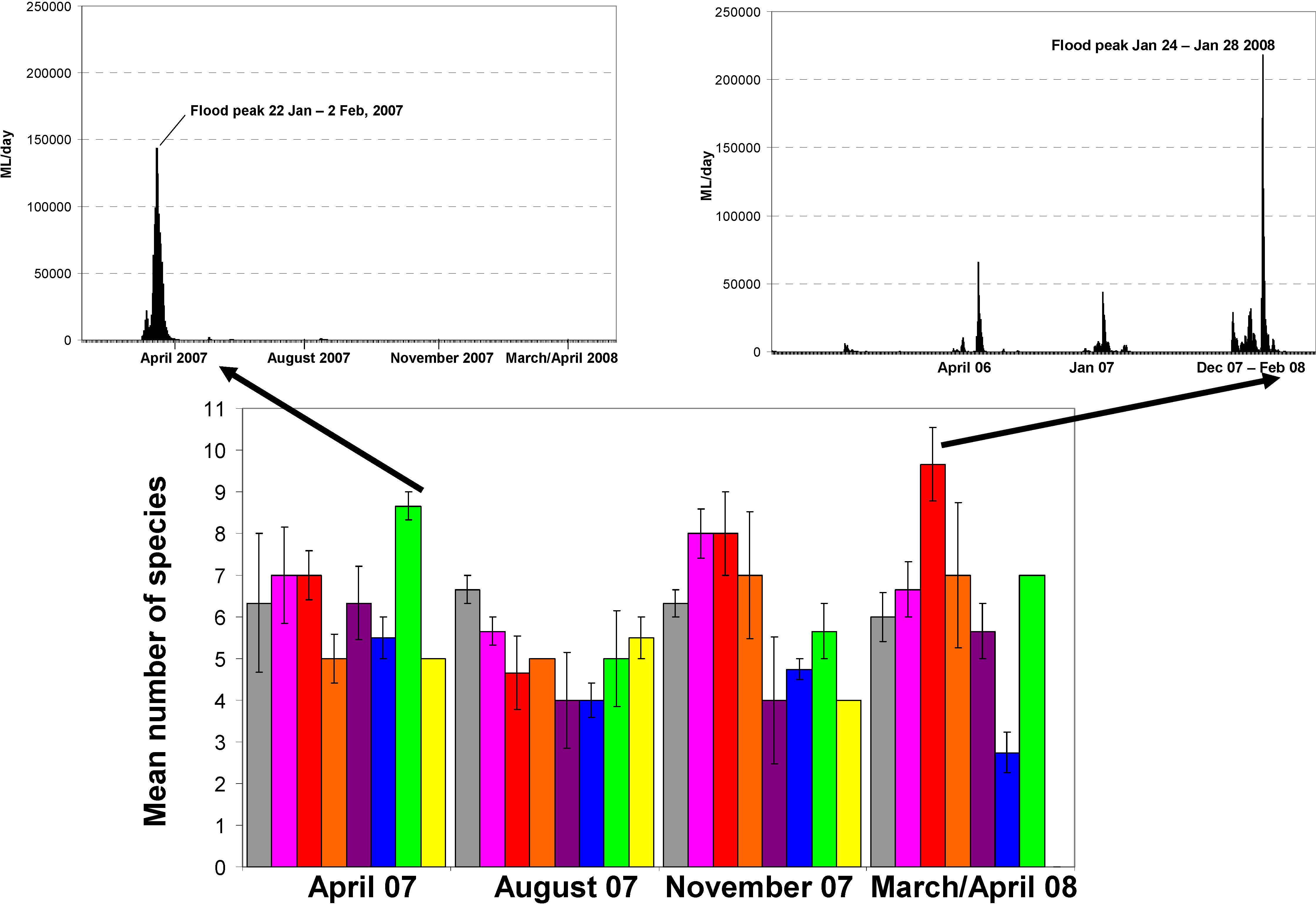
| Species | Average Abundance Per Sample | Percent Contribution to Observed Differences (>5%). | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent within-channel | Ephemeral within-channel | Ephemeral lakes | Permanent within-channel vs. ephemeral lakes | Ephemeral within-channel vs. ephemeral lakes | |
| Bony bream | 43.28 | 83.21 | 127.88 | 24.21 | 23.64 |
| Hyrtl’s tandan | 34.11 | - | - | 10.24 | 7.85 |
| Silver tandan | 7.64 | 58.89 | 43.88 | 14.73 | 15.16 |
| Desert rainbowfish | - | 38.79 | - | 9.86 | 12.9 |
| Glassfish | - | - | 80.88 | 12.52 | 11.03 |
| Yellowbelly | 14.67 | 18.74 | 10.63 | 11.45 | 9.79 |
| Spangled perch | 11.05 | 37.47 | 25.94 | 7.71 | 9.68 |
3.2. Discussion
3.2.1. Unique Species
3.2.2. Translocated and Alien Species
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Nanson, G.C.; Price, D.M.; Jones, B.G.; Maroulis, J.C.; Coleman, M.; Bowman, H.; Cohen, T.J.; Pietsch, T.J.; Larsen, J.R. Alluvial evidence for major climate and flow regime changes during the middle and late Quaternary in eastern central Australia. Geomorphology 2008, 101, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, R. The Distribution of Two Endangered Fish in Queensland. Endangered Species Unit Project Number 276; Final Report Part B: The Distribution and Status of the Red-Finned Blue-Eye, Australian Nature Conservation Agency: Canberra, Australia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Fairfax, R.; Fensham, R.; Wager, R.; Brooks, S.; Webb, A.; Unmack, P. Recovery of the red-finned blue-eye: An endangered fish from springs of the Great Artesian Basin. Wildl. Res. 2007, 34, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, U.S.; Welcomme, R.L. An analysis of fish species richness in natural lakes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2002, 65, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.I.; Knowler, D.J.; Leveque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prier-Richard, A.H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater Diversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, F.B.; Moss, R.E. Historic changes in fish communities and aquatic habitats in plains streams of Kansas. In Community and Evolutionary Ecology of North American Stream Fishes; Matthews, W.J., Heins, C.C., Eds.; University of Oklahoma Press: Norman, OK, USA, 1987; pp. 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, C.J.M.; Sim, T.C. A survey of central Australian ichthyology. Aust. J. Zool. 1978, 15, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, C.J.M. Studies on central Australian fishes: Further observations and records, Part I. S. Aust. Nat. 1979, 53, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, C.J.M. Adaptations of fishes in arid Australia. In Evolution of the Flora and Fauna of Arid Australia; Barker, W.R., Greenslade, P.J.M., Eds.; Peacock Publications: South Australia, Australia, 1982; pp. 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn, L.C. The Distribution of Fish in New South Wales; No. 7; Australian Society for Limnology Special Publication: Sydney, Australia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.H.; Gehrke, P.C. Fish and Rivers in Stress—The NSW Rivers Survey; NSW Fisheries Office of Conservation and the Cooperative Research Centre for Freshwater Ecology: Cronulla/Canberra, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wager, R.; Unmack, P.J. Fishes of the Lake Eyre Catchment in Central Australia; Queensland Department of Primary Industries: Brisbane, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, G.R.; Midgley, S.H.; Allen, M. Field Guide to the Freshwater Fishes of Australia; Western Australian Museum: Perth, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pusey, B.; Kennard, M.; Arthington, A. Freshwater Fishes of North-Eastern Australia; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Unmack, P.J. Biogeography. In Ecology of Australian Freshwater Fishes; Humphries, P., Walker, K., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Humphries, P.; Walker, K.F. The ecology of Australian freshwater fishes: An introduction. In Ecology of Australian Freshwater Fishes; Humphries, P., Walker, K., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Puckridge, J.T.; Sheldon, F.; Walker, K.F.; Boulton, A.J. Flow variability and the ecology of large rivers. Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1998, 49, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerezsy, A. Desert Fishing Lessons: Adventures in Australia’s Rivers; University of Western Australia Press: Perth, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Arthington, A.H.; Balcombe, S.R. Extreme hydrologic variability and the boom and bust ecology of fish in arid-zone floodplain rivers: A case study with implications for environmental flows, conservation and management. Ecohydrology 2011, 4, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, G.; Pavey, C.; Dickman, C. Greening of arid Australia: New insights from extreme years. Austral Ecol. 2013, 38, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenville, A.; Wardle, G.; Dickman, C. Extreme rainfall events predict irruptions of rat plagues in central Australia. Austral Ecol. 2013, 38, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, S.H.; Midgley, M.; Rowland, S.J. Fishes of the Bulloo-Bancannia drainage division. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1991, 30, 505–508. [Google Scholar]
- Long, P.E.; Humphery, V.E. Fisheries Study Lake Eyre Catchment—Thomson and Diamantina. Drainages December 1995; Department of Primary Industries: Brisbane, Australia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Puckridge, J.T. The Role of Hydrology in the Ecology of Cooper Creek, Central Australia: Implications for the Flood Pulse Concept. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, V.; Long, P. Wetland, Fish and Habitat Survey in the Lake Eyre Basin, Queensland: Final Report; Queensland Department of Natural Resources and Mines: Brisbane, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Costelloe, J.F.; Hudson, P.J.; Pritchard, J.C.; Puckridge, J.T.; Reid, J.R.W. ARIDFLOW Scientific Report: Environmental Flow Requirements of Arid Zone Rivers with Particular Reference to the Lake Eyre Drainage Basin; Final Report to South Australian Department of Water, Land and Biodiversity Conservation and Commonwealth Department of Environment and Heritage School of Earth and Environmental Sciences; University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Arthington, A.H.; Balcombe, S.R.; Wilson, G.A.; Thoms, M.C.; Marshall, J. Spatial and temporal variation in fish assemblage structure in isolated waterholes during the 2001 dry season ofan arid-zone river, Cooper Creek, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2005, 56, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcombe, S.R.; Bunn, S.E.; Arthington, A.H.; Fawcett, J.H.; McKenzie-Smith, F.J.; Wright, A. Fish larvae, growth and biomass relationships in an Australian arid zone river: Links between floodplains and waterholes. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 2385–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerezsy, A. The Distribution, Recruitment and Movement of Fish in Far Western Queensland. Ph.D. Thesis, Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kerezsy, A.; Balcombe, S.R.; Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E. Continuous recruitment underpins fish persistence in the arid rivers of far western Queensland, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerezsy, A.; Balcombe, S.R.; Tischler, M.; Arthington, A.H. Fish movement strategies in an ephemeral river in the Simpson Desert, Australia. Aust. Ecol. 2013, 38, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensham, R.; Silcock, J.; Kerezsy, A.; Ponder, W. Four desert waters: Setting arid zone wetland conservation priorities through understanding patterns of endemism. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 2459–2467. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.; Ponniah, M.; Hurwood, D.; Chenoweth, S.; Arthington, A. Strong genetic structuring in a habitat specialist, the Oxleyan pygmy perch, Nannoperca oxleyana. Heredity 1999, 83, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, W.F.; Unmack, P.J.; Burgess, C.; Minckley, W.L. Rarity, fragmentation, and extinction risk in desert fishes. Ecology 2002, 83, 3250–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerezsy, A.; Fensham, R. Conservation of the endangered red-finned blue-eye, Scaturiginichthys. vermeilipinnis, and control of alien eastern gambusia, Gambusia. holbrooki, in a spring wetland complex. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2013, 64, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Changes in Marine Communities: An. Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation; Natural Environment Research Council, Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Balcombe, S.R.; Arthington, A.H.; Foster, N.D.; Thoms, M.C.; Wilson, G.G.; Bunn, S.E. Fish assemblages of an Australian dryland river: Abundance, assemblage structure and recruitment patterns in the Warrego River, Murray-Darling Basin. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2006, 57, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcombe, S.R.; Arthington, A.H.; Thoms, M.C.; Wilson, G.G. Fish assemblages patterns across a gradient of flow regulation in an Australian dryland river system. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.M.; Hillyer, M.J. Patterns of connectivity among populations of Cherax destructor (Decapoda: Parastacidae) in western Queensland, Australia. Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 54, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Baker, A.M.; Bartlett, C.; Bunn, S.; Goudkamp, K.; Somerville, J. Past and present patterns of connectivity among populations of four cryptic species of freshwater mussels Velesunio. spp. (Hyriidae) in central Australia. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 3197–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, J.A.; Hughes, J.M.; Baker, A.M. Patterns of gene flow in two species of eel-tailed catfish, Neosiluris. hyrtlii and Porochilus. argenteus (Siluriformes: Plotosidae), in western Queensland’s dryland rivers. Biol. J. Linnean Soc. 2006, 87, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, J.A.; Fausch, K.D. Multiscale processes regulate brassy minnow persistence in a Great Plains river. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 840–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, W.F.; Kennedy, C.M.; Unmack, P.J. Quantifying rarity, losses, and risks for native fishes of the lower Colorado River Basin: Implications for Conservation Listing. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, W.J.; Marsh-Matthews, E. Effects of drought on fish across axes of space, time and ecological complexity. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 1232–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrongiello, J.; Beatty, S.; Bennet, J.; Crook, D.; Ikedife, D.; Kennard, M.; Kerezsy, A.; Lintermans, M.; McNeil, D.; Pusey, D.; et al. Climate change and its implications for Australia’s freshwater fish. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcombe, S.R.; Arthington, A.H. Temporal changes in fish abundance in response to hydrological variability in a dryland floodplain river. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerezsy, A. Unpublished work. 2009–2014.
- Sambell, B.; Ausyfish owner/director. Personal communication, 2010.
- Hutchison, M.; Queensland Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries. Personal communication, 2011.
- Cockayne, B.; Queensland Department of Natural Resources and Mines. Personal communication, 2013.
- Kerezsy, A. Unpublished work. 2013.
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kerezsy, A.; Arthington, A.H.; Balcombe, S.R. Fish Distribution in Far Western Queensland, Australia: The Importance of Habitat, Connectivity and Natural Flows. Diversity 2014, 6, 380-395. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6020380
Kerezsy A, Arthington AH, Balcombe SR. Fish Distribution in Far Western Queensland, Australia: The Importance of Habitat, Connectivity and Natural Flows. Diversity. 2014; 6(2):380-395. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6020380
Chicago/Turabian StyleKerezsy, Adam, Angela H. Arthington, and Stephen R. Balcombe. 2014. "Fish Distribution in Far Western Queensland, Australia: The Importance of Habitat, Connectivity and Natural Flows" Diversity 6, no. 2: 380-395. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6020380
APA StyleKerezsy, A., Arthington, A. H., & Balcombe, S. R. (2014). Fish Distribution in Far Western Queensland, Australia: The Importance of Habitat, Connectivity and Natural Flows. Diversity, 6(2), 380-395. https://doi.org/10.3390/d6020380




