Biogeography of Timor and Surrounding Wallacean Islands: Endemism in Ants of the Genus Polyrhachis Fr. Smith
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
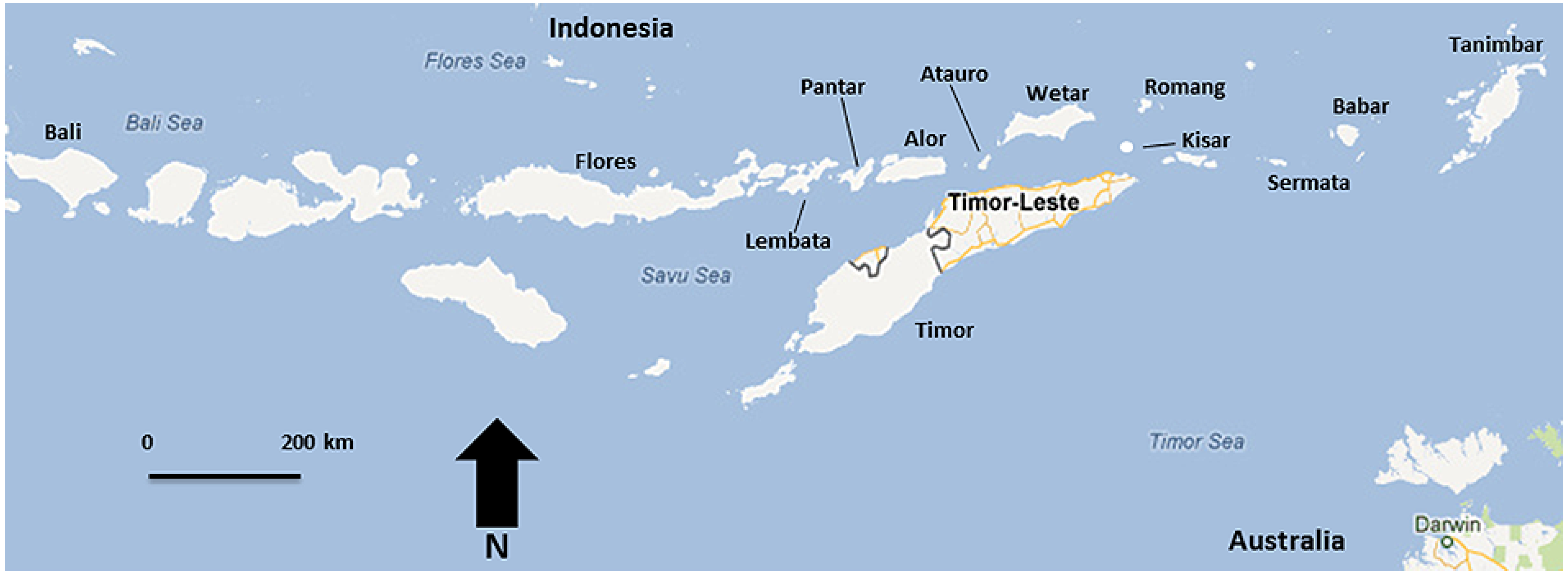
| Island | Survey dates | Survey effort (h) | Habitats sampled (elevation) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flores | June/July 2011 | 6 | Montane forest, secondary forest (625–1,625m) |
| Lembata | November 2011 | 8 | Evergreen swamp forest (0–20 m) |
| Wetar | September–October 2010 | 30 | Evergreen forest, Eucalyptus woodland (0–100 m) |
| Kisar | October 2010 | 20 | Eucalyptus woodland, mangrove (0–150 m) |
| Romang | October 2010 | 30 | Evergreen forest, Eucalyptus woodland (0–600 m) |
| Sermata | November 2010 | 20 | Evergreen forest, mangrove (0–200 m) |
| Babar | August 2011 | 30 | Evergreen forest, Eucalyptus woodland (0–600 m) |
| Tanimbar | August 2011 | 6 | Evergreen forest (0–150 m) |
3. Results and Discussion
| FLORES GROUP | TIMOR GROUP | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flores | Lembata | Pantar | Alor | Timor | Atauro | Wetar | Kisar | Romang | Sermata | Babar | Tanimbar | |
| Campomyrma | ||||||||||||
| Polyrhachis sp. nr. insularis Emery | * | * | ||||||||||
| Chariomyrma | ||||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. arcuata acutinota Forel | * | * | ||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. contemta Mayr | * | |||||||||||
| Polyrhachis costulata Emery | * | * | ||||||||||
| P. constricta Emery | ||||||||||||
| P. gab Forel | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||
| P. sokolova Forel | * | |||||||||||
| Cyrtomyrma | ||||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. gibba Emery | * | * | * | |||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. rastellata (Latreille) | * | |||||||||||
| Hagiomyrma | ||||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. penelope Forel | * | * | ||||||||||
| Hedomyrma | ||||||||||||
| Polyrhachis hera Forel | * | |||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. machaon Santschi | * | |||||||||||
| Polyrhachis sp. A (cf. cupreata Emery) | * | * | * | |||||||||
| Polyrhachis sp. B (cf. cupreata Emery) | * | |||||||||||
| Myrma | ||||||||||||
| Polyrhachis illaudata Walker | * | * | ||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. murina Emery | * | |||||||||||
| P. rixosa Fr. Smith | * | * | ||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. rixosa Fr. Smith | * | * | ||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. villipes Fr. Smith | * | * | ||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. zopyra Fr. Smith | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||||
| Myrmhopla | ||||||||||||
| Polyrhachis acantha chrysophanes Emery | * | * | ||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. acantha chrysophanes Emery | * | |||||||||||
| Polyrhachis(mucronata-gr.) sp | * | |||||||||||
| P. bicolor Fr. Smith | * | |||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. bicolor Fr. Smith | * | |||||||||||
| P. cryptoceroides Emery | * | |||||||||||
| P. dives Fr. Smith | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||
| P. longipes Fr. Smith | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. moesta Emery | * | * | ||||||||||
| Polyhrachis cf. mucronata Fr. Smith | * | * | * | |||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. saevissima Fr. Smith | * | |||||||||||
| Polyrhachis saevissima Fr. Smith | * | |||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. tibialis Fr. Smith | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||
| Myrmothrinax | ||||||||||||
| Polyrhachis cf. thrinax Roger | * | |||||||||||
| Polyrhachis | ||||||||||||
| Polyrhachis olybria Forel | * | |||||||||||
| Species | Distribution |
|---|---|
| P. (Chariomyrma) constricta | Australia, New Guinea |
| P. (Chariomyrma) gab | Australia |
| P. (Chariomyrma) sokolova | Australia, New Guinea, Aru, New Caledonia |
| P. (Chariomyrma) costulata | New Guinea |
| Polyrhachis (Hedomyrma) hera | Seram, Halmahera |
| Polyrhachis (Hedomyrma) illaudata | Sri Lanka, India, Thailand, Malaysia, Borneo, Sumatra, Java, Bali, Sumbawa, Philippines |
| P. (Myrma) rixosa | Sulawesi, Borneo |
| P. (Myrmhopla) acantha chrysophanes | Tanimbar, Flores |
| P. (Myrmhopla) bicolor | Throughout IndoMalaya, New Guinea, Australia |
| P. (Myrmhopla) cryptoceroides | Thailand, Malaysia, Borneo, Sulawesi, Java, Philippines |
| P. (Myrmhopla) dives | Throughout IndoMalaya, New Guinea, Australia |
| P. (Myrmhopla) longipes | Aru, New Guinea |
| P. (Myrmhopla) saevissima | Sulawesi, Sumatra, Seram |
| P. (Polyrhachis) olybria | Thailand, Malaysia, Borneo, Sumatra, Philippines |
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
Appendix
| Identification in Trainor and Andersen (2010) | Revised identification |
|---|---|
| Polyrhachis (Campomyrma) sp. A | Polyrhachis cf. insularis Emery |
| Polyrhachis (Chariomyrma) sp. F (arcuata gp.) | Polyrhachis cf. arcuata acutinota Forel |
| Polyrhachis (Cyrtomyrma) sp. P | Polyrhachis cf. gibba Emery |
| Polyrhachis (Hedomyrma) sp. O (euterpe gp.) | Polyrhachis cf. machaon Santschi |
| Polyrhachis (Myrma) mayri | P. illaudata Walker |
| Polyrhachis (Myrma) sp. nr. villipes | Polyrhachis cf. villipes Fr. Smith |
| Polyrhachis (Myrmhopla) acantha | Polyrhachis acantha chrysophanes Emery |
| Polyrhachis (Myrmhopla) argentea | Polyrhachis cf. tibialis Fr. Smith |
| Polyrhachis sp. nr. bicolor | Polyrhachis cf. bicolor Fr. Smith |
| Polyrhachis (Myrmhopla) bicolor | P. bicolor Fr. Smith |
| Polyrhachis (Myrmhopla) concolor | P. longipes Fr. Smith |
| Polyrhachis (Myrmhopla) cryptoceroides | P. cryptoceroides Emery |
| Polyrhachis (Myrmhopla) dives | P. dives Fr. Smith |
| Polyrhachis gab | P. gab Forel |
| Polyrhachis sp.nr. inconspicua | Polyrhachis cf. insularis Emery |
| Polyrhachis mucronata | Polyhrachis cf. mucronata Fr. Smith |
| Polyrhachis sp. nr. mucronata | Polyrhachis (mucronata-group) sp. |
| Polyrhachis sp. B (bellicosa gp.) | P. olybria Forel |
| Polyrhachis sp. J (cupreata gp.) | Polyrhachis (Hedomyrma) sp. A (cf. cupreata Emery) |
| Polyrhachis sp. K (zopyra gp.) | Polyrhachis cf. murina Emery |
| Polyrhachis sp. L (tibialis gp.) | Polyrhachis cf. moesta Emery |
| Polyrhachis sp. L (zopyra gp.) | Polyrhachis cf. zopyra Fr. Smith |
| Polyrhachis sp. nr. obtusa | Polyrhachis costulata Emery |
| Polyrhachis rixosa | P. rixosa Fr. Smith |
References
- Wallace, A.R. The Malay Archipelago; Tynron Press: Stenhouse, Scotland, 1869. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oosterzee, P. Where Worlds Collide: The Wallace Line; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lohman, D.J.; de Bruyn, M.; Page, T.; von Rintelen, K.; Hall, R.; Ng, P.K.L.; Shih, H.-T.; Carvalho, G.R.; von Rintelen, T. Biogeography of the Indo-Australian Archipelago. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2011, 42, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, J.D.; Jardine, N. Two approaches to zoogeography: A study based on the distributions of butterflies, birds and bats in the Indo-Australian area. Proc. Lin. Soc. Lond. 1968, 179, 153–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, R.A.; Kitchener, D.J. Biogeography of Indonesian snakes. J. Biogeogr. 1997, 24, 725–735. [Google Scholar]
- Clode, D.; O’Brien, R. Why Wallace Drew the Line: A Reanalysis of Wallace’s Bird Collections in the Malay Archipelago and the Origins of Biogeography. In Faunal and Floral Migrations and Evolution in SE Asia–Australasia; Metcalfe, I., Smith, J.M.B., Morwood, M., Davidson, I., Eds.; AA Balkema Publishers: Tokyo, Japan, 2001; pp. 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Inger, R.F.; Voris, H.K. The biogeographical relations of the frogs and snakes of Sundaland. J. Biogeogr. 2001, 28, 863–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, R.A.; Schmitt, L.H.; Suyanto, A. Geographical variation in the morphology of four snake species from the Lesser Sunda Islands, eastern Indonesia. Biol. J. Lin. Soc. 1996, 59, 439–456. [Google Scholar]
- Jønsson, K.A.; Irestedt, M.; Fuchs, J.; Ericson, P.G.P.; Christidis, L.; Bowie, R.C.K.; Norman, J.A.; Pasquet, E.; Fjeldså, J. Explosive avian radiations and multi-directional dispersal across Wallacea: Evidence from the Campephagidae and other crown Corvida (Aves). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2008, 47, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outlaw, D.C.; Voelker, G. Pliocene climatic change in insular southeast Asia as an engine of diversification in Ficedula flycatchers. J. Biogeogr. 2008, 35, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voris, H.K. Maps of Pleistocene sea levels in Southeast Asia: Shorelines, river systems and time durations. J. Biogeogr. 2000, 27, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainor, C.R.; Andersen, A.N. The ant fauna of Timor and neighbouring islands: Potential bridges between the disjunct faunas of South East Asia and Australia. Aust. J. Zool. 2010, 58, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohout, R.J. Three new Polyrhachis sexspinosa-group species from the Philippines (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae). Mem. Qld. Mus. 1987, 25, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kohout, R.J. Nomenclatural changes and new Australian records in the ant genus Polyrhachis Fr. Smith (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae). Mem. Qld. Mus. 1987, 25, 429–438. [Google Scholar]
- Kohout, R.J. A review of the Polyrhachis viehmeyeri species-group (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae). Mem. Qld. Mus. 1990, 28, 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Kohout, R.J. Review of Polyrhachis (Cyrtomyrma) Forel (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae) of Australia, Borneo, New Guinea and the Solomon Islands with descriptions of new species. Mem. Qld. Mus. 2006, 52, 87–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kohout, R.J. A review of the Polyrhachis ants of Sulawesi with keys and descriptions of new species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae). Mem. Qld. Mus. 2008, 52, 255–317. [Google Scholar]
- Kohout, R.J. A review of the Australian Polyrhachis ants of the subgenera Myrmhopla Forel and Hirtomyrma subgen. nov. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae). Mem. Qld. Mus. 2010, 55, 167–204. [Google Scholar]
- Kohout, R.J. A review of the Australian Polyrhachis ants of the subgenera Myrma Billberg, Myrmatopa Forel, Myrmothrinax Forel and Polyrhachis Fr. Smith (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae). Mem. Qld. Mus. Nat. 2012, 56, 25–59. [Google Scholar]
- Dorow, W.H.O. Revision of the ant genus Polyrhachis Smith, 1857 (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae) on subgenus level with keys, checklist of species and bibliography. Cour. Forsch.–Inst. Senckenberg 1995, 185, 1–113. [Google Scholar]
- Robson, S.K.A.; Kohout, R.J. Evolution of nest-weaving behaviour in arboreal nesting ants of the genus Polyrhachis Fr. Smith (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Aust. J. Ent. 2005, 44, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, S.K.A.; Kohout, R.J. A review of the nesting habits and socioecology of the ant genus Polyrhachis Fr. Smith. Asian Myrmecol. 2007, 1, 81–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kohout, R.J. Revision of the subgenus Hedomyrma Forel of the genus Polyrhachis Fr. Smith (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae). 2013, unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Churchill, S. Australian Bats, 2nd ed; Allen and Unwin: Crows Nest, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gjershaug, J.O.; Kvaløy, K.; Røv, N.; Prawiradilaga, D.M.; Suparman, U.; Rahman, Z. The taxonomic status of the Flores Hawk Eagle Spizaetus floris. Forktail 2004, 20, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pianka, E.R.; King, D.; King, R.A. Varanoid Lizards of the World; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sangster, G.; Rozendaal, F.G. Systematic notes on Asian birds. 41. Territorial songs and species-level taxonomy of nightjars of the Caprimulgus macrurus complex, with the description of a new species. Zool. Verh. Leiden 2004, 350, 7–45. [Google Scholar]
- Trainor, C.R.; Verbelen, P.; Johnstone, R.E.J. The avifauna of Alor and Pantar, Lesser Sundas, Indonesia. Forktail 2012, 28, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Schodde, R.; Mason, I.J. Aves (Columbidae to Coraciidae). In Zoological Catalogue of Australia, Volume 37.2: Aves (Columbidae to Coraciidae); Houston, W.W.K., Wells, A., Eds.; Australian Government Publishing Service: Canberra, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Roos, M.C.; Kessler, P.J.A.; Gradstein, R.S.; Baas, P. Species diversity and endemism of five major Malesian islands: Diversity-area relationships. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stattersfield, A.J.; Crosby, M.J.; Long, A.J.; Wege, D.C. Endemic Bird Areas of the World: Priorities for Biodiversity Conservation; BirdLife International: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Aplin, K.; Helgen, K.M. Quaternary murid rodents of Timor Part I: New material of Coryphomys buehleri Schaub, 1937, and description of a second species of the Genus. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2010, 341, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.; Carvalho, V.L.; Ceballos, J.; Freed, P.; Heacox, S.; Lester, B.; Richards, S.J.; Trainor, C.R.; Sanchez, C.; O’Shea, M. The herpetofauna of Timor-Leste: A first report. ZooKeys 2011, 109, 19–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Andersen, A.N.; Kohout, R.J.; Trainor, C.R. Biogeography of Timor and Surrounding Wallacean Islands: Endemism in Ants of the Genus Polyrhachis Fr. Smith. Diversity 2013, 5, 139-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/d5010139
Andersen AN, Kohout RJ, Trainor CR. Biogeography of Timor and Surrounding Wallacean Islands: Endemism in Ants of the Genus Polyrhachis Fr. Smith. Diversity. 2013; 5(1):139-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/d5010139
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndersen, Alan N., Rudolf J. Kohout, and Colin R. Trainor. 2013. "Biogeography of Timor and Surrounding Wallacean Islands: Endemism in Ants of the Genus Polyrhachis Fr. Smith" Diversity 5, no. 1: 139-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/d5010139
APA StyleAndersen, A. N., Kohout, R. J., & Trainor, C. R. (2013). Biogeography of Timor and Surrounding Wallacean Islands: Endemism in Ants of the Genus Polyrhachis Fr. Smith. Diversity, 5(1), 139-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/d5010139




