Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Invertebrate Communities in the Chai River Based on eDNA Biomonitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
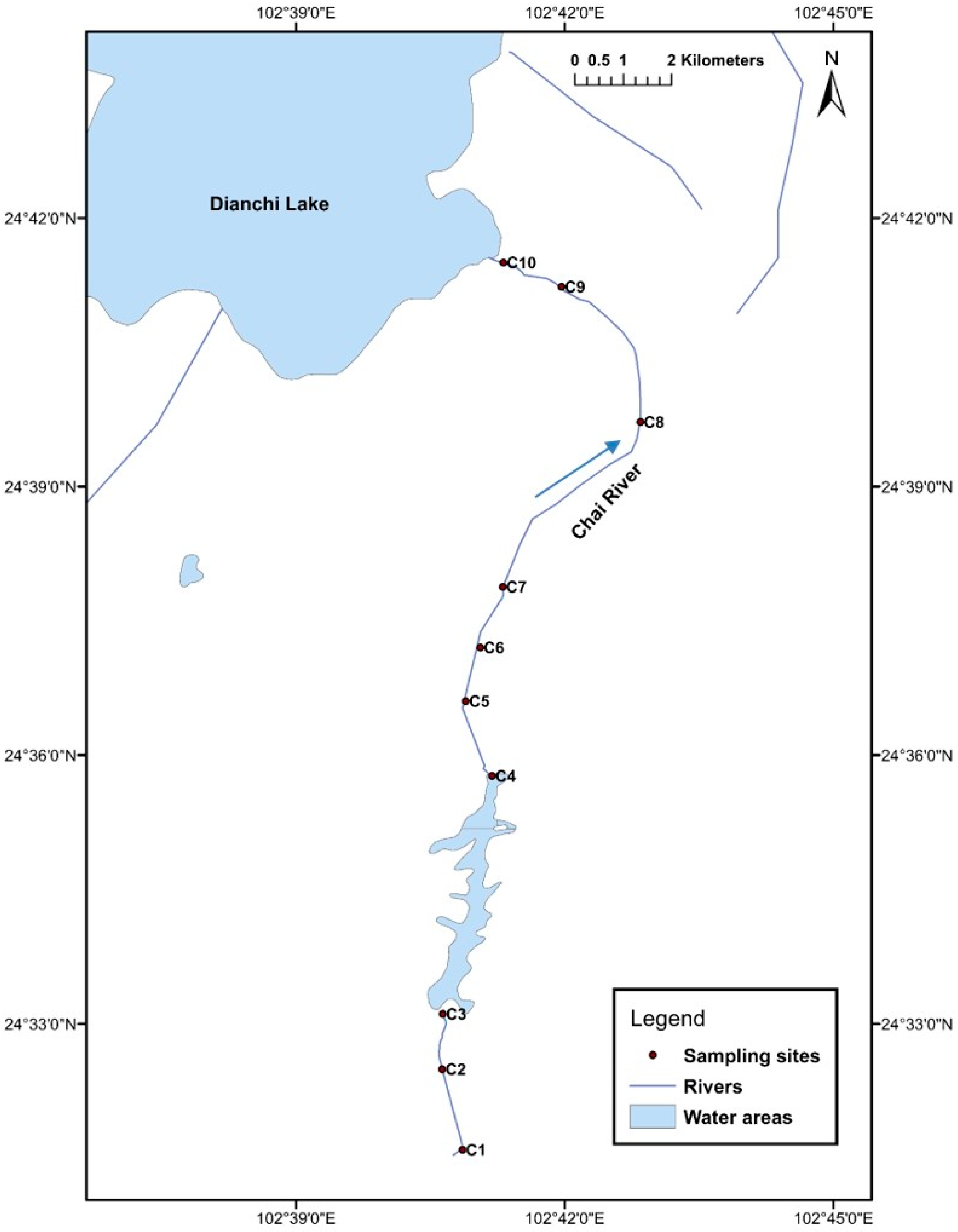
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Environmental Factor Analysis of Water Samples
2.3. eDNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
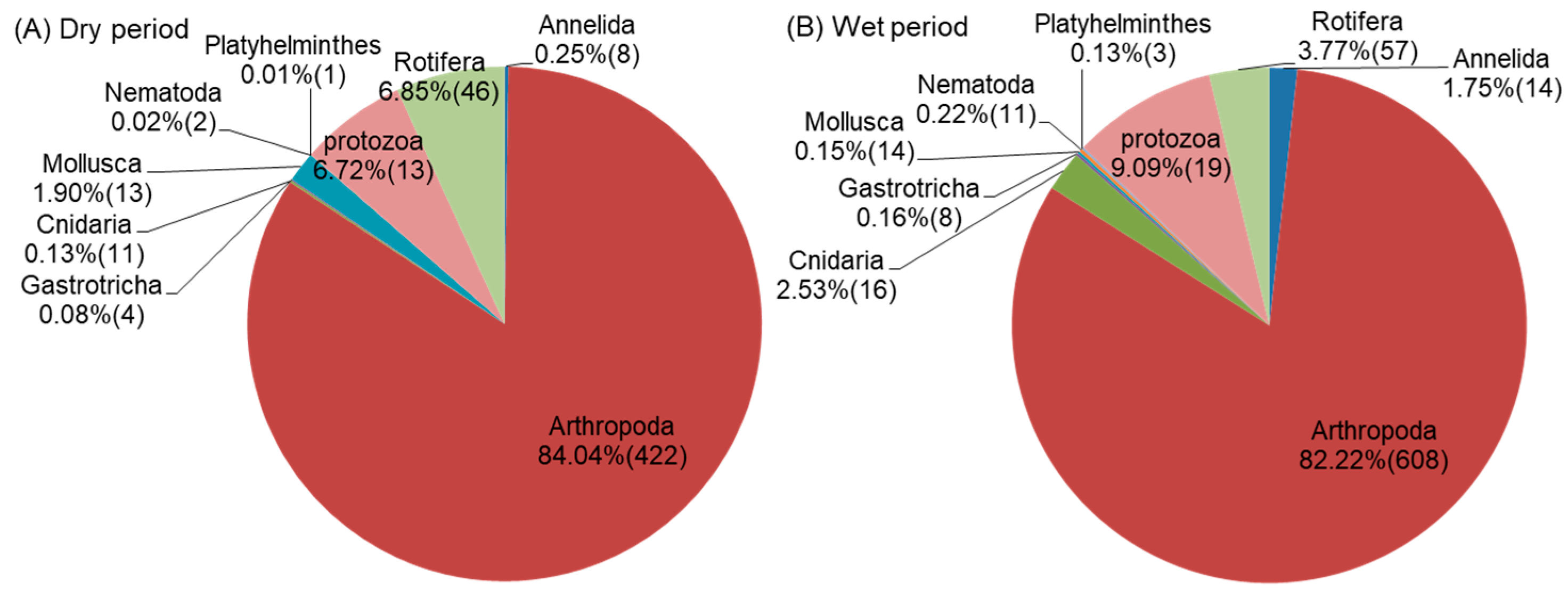
3.1. Overview of Invertebrate Communities
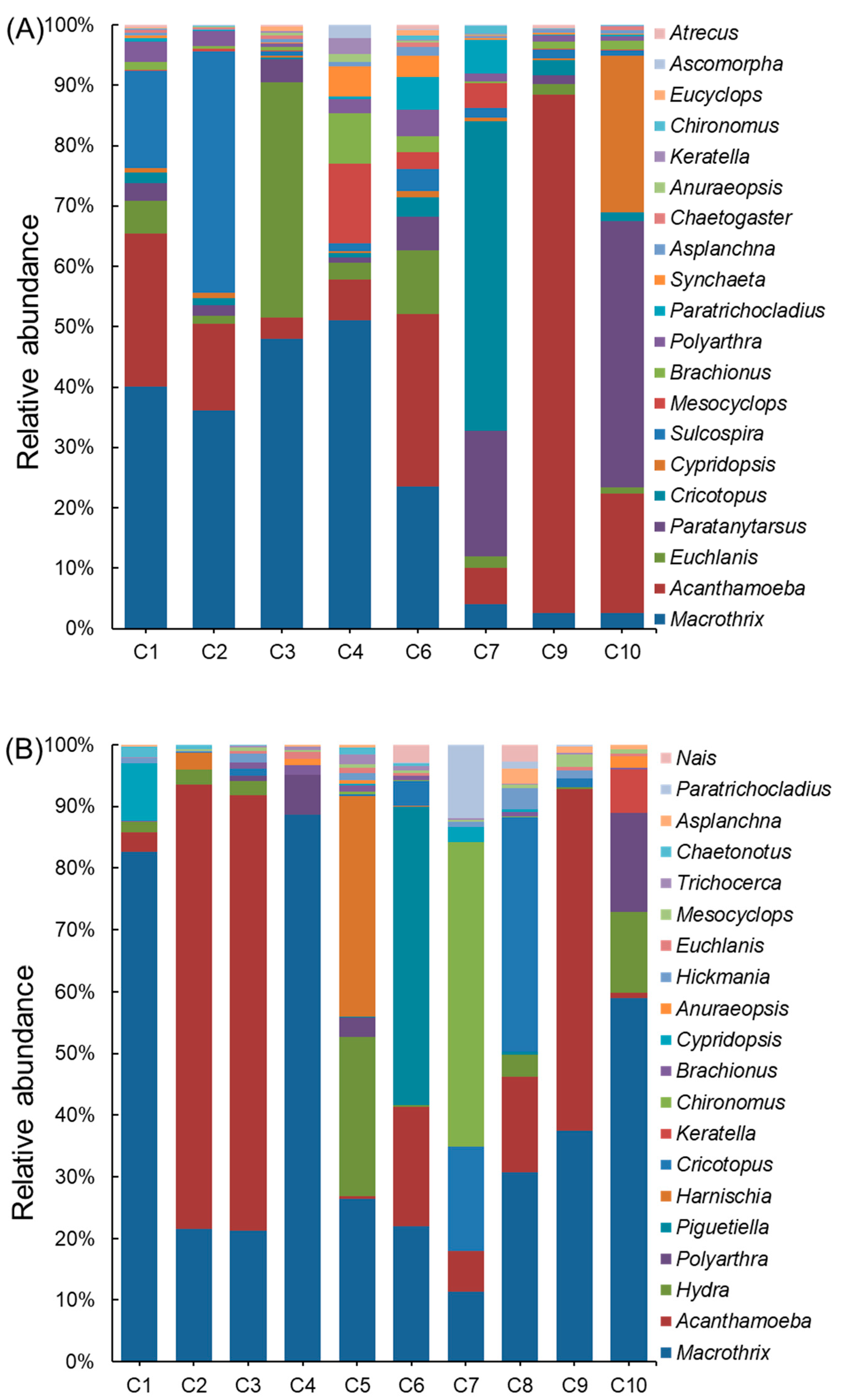
3.2. Spatial and Seasonal Distribution of Invertebrate Communities
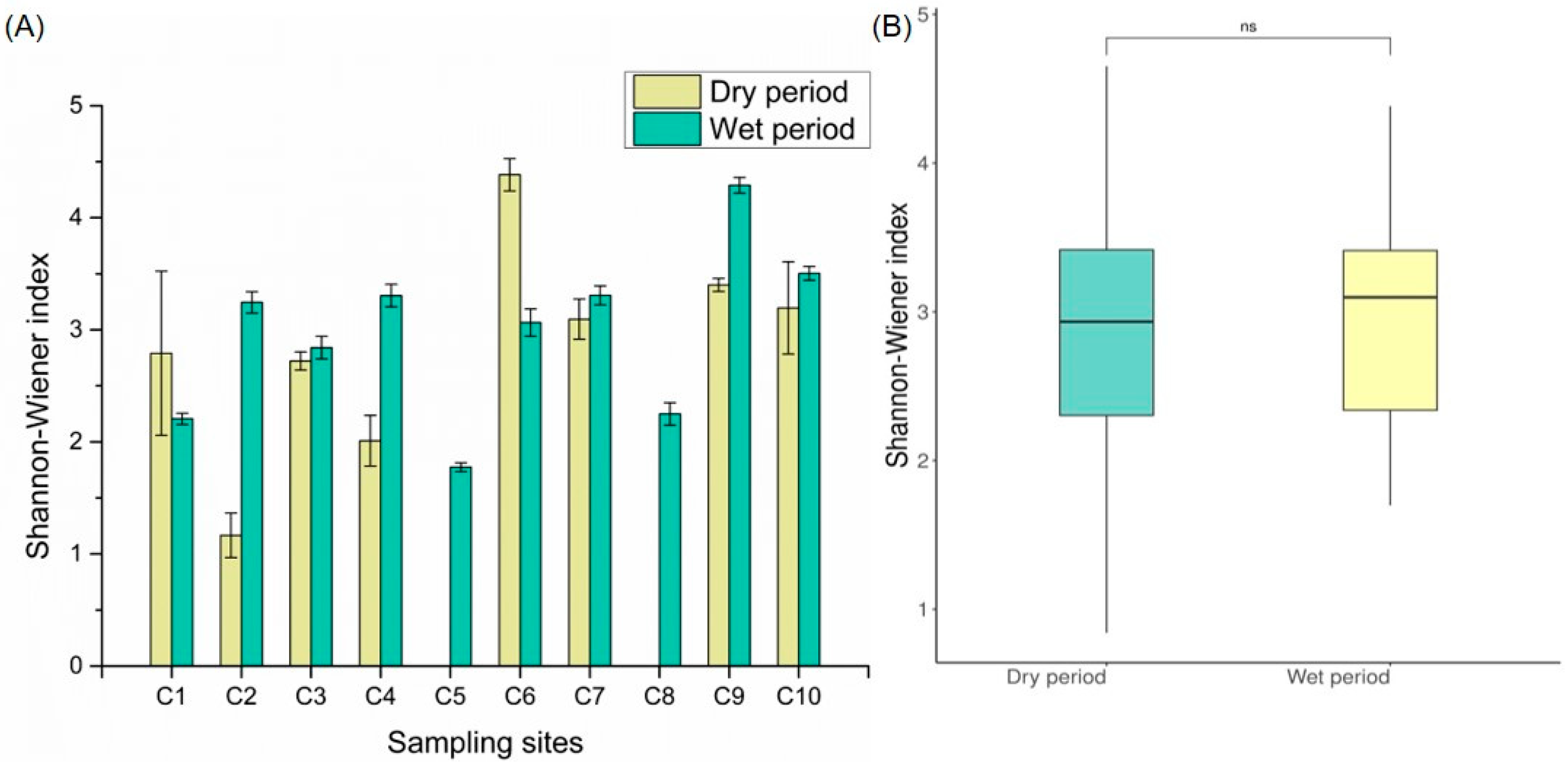
3.3. Invertebrate Diversity Patterns
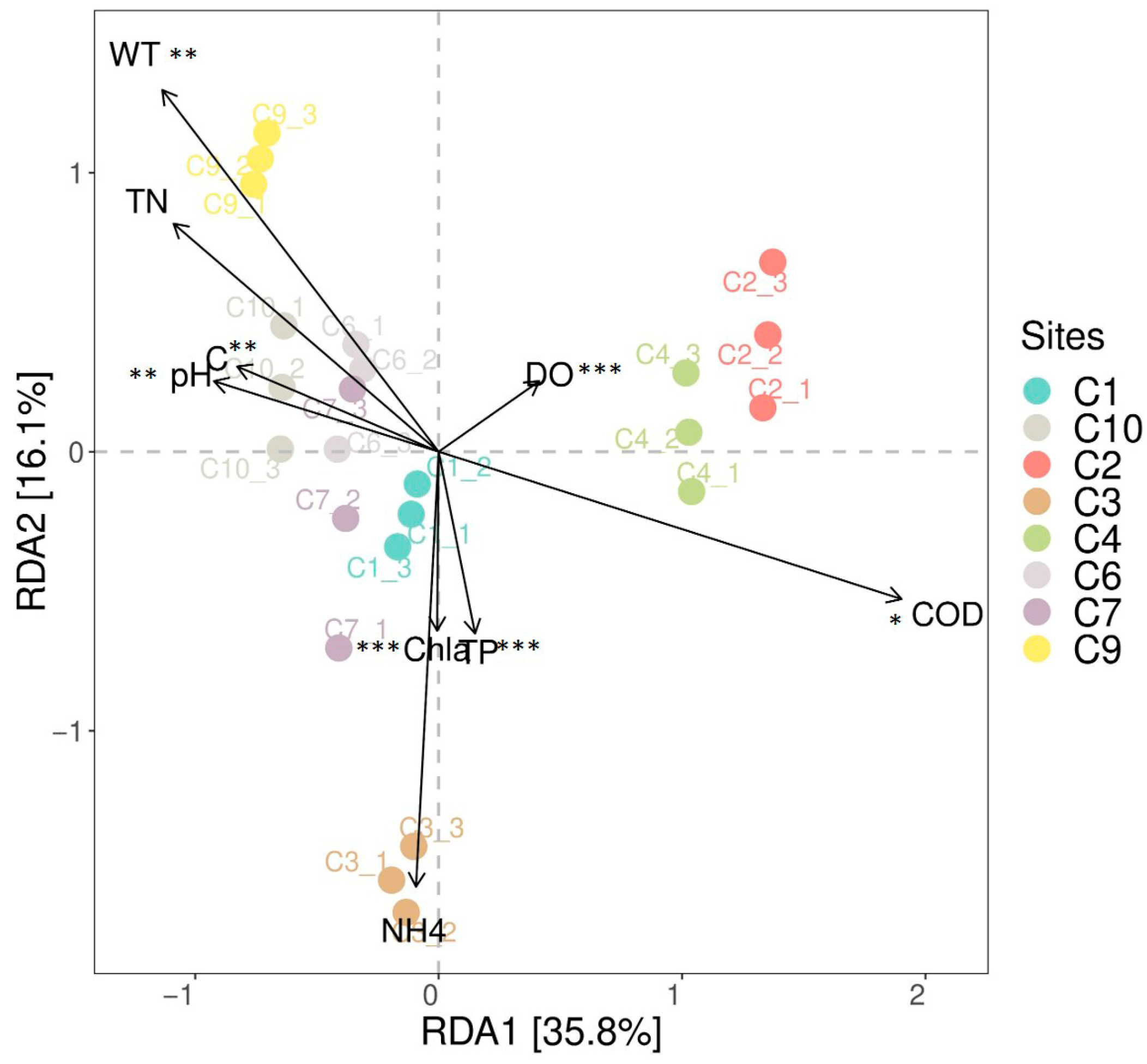
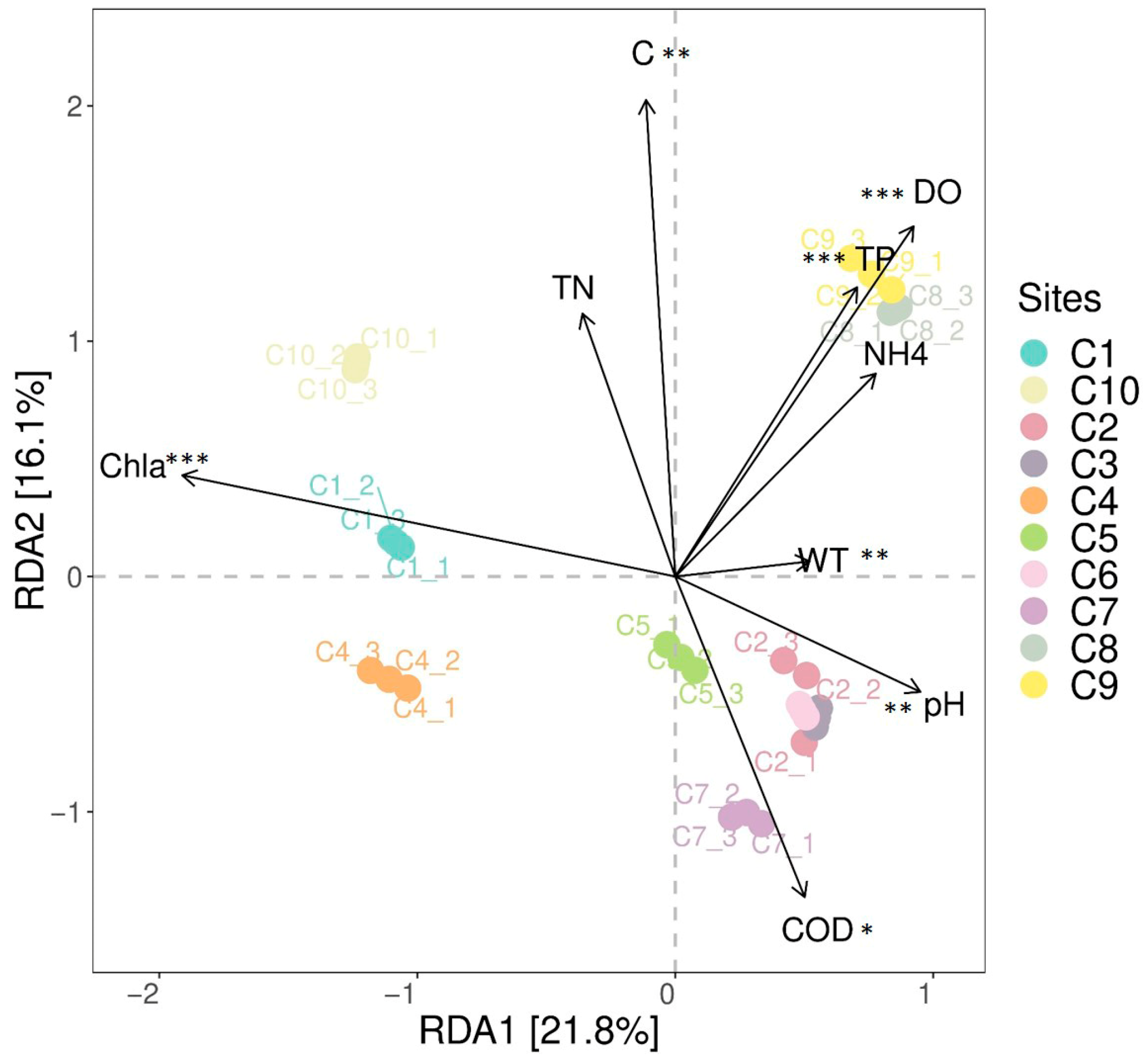
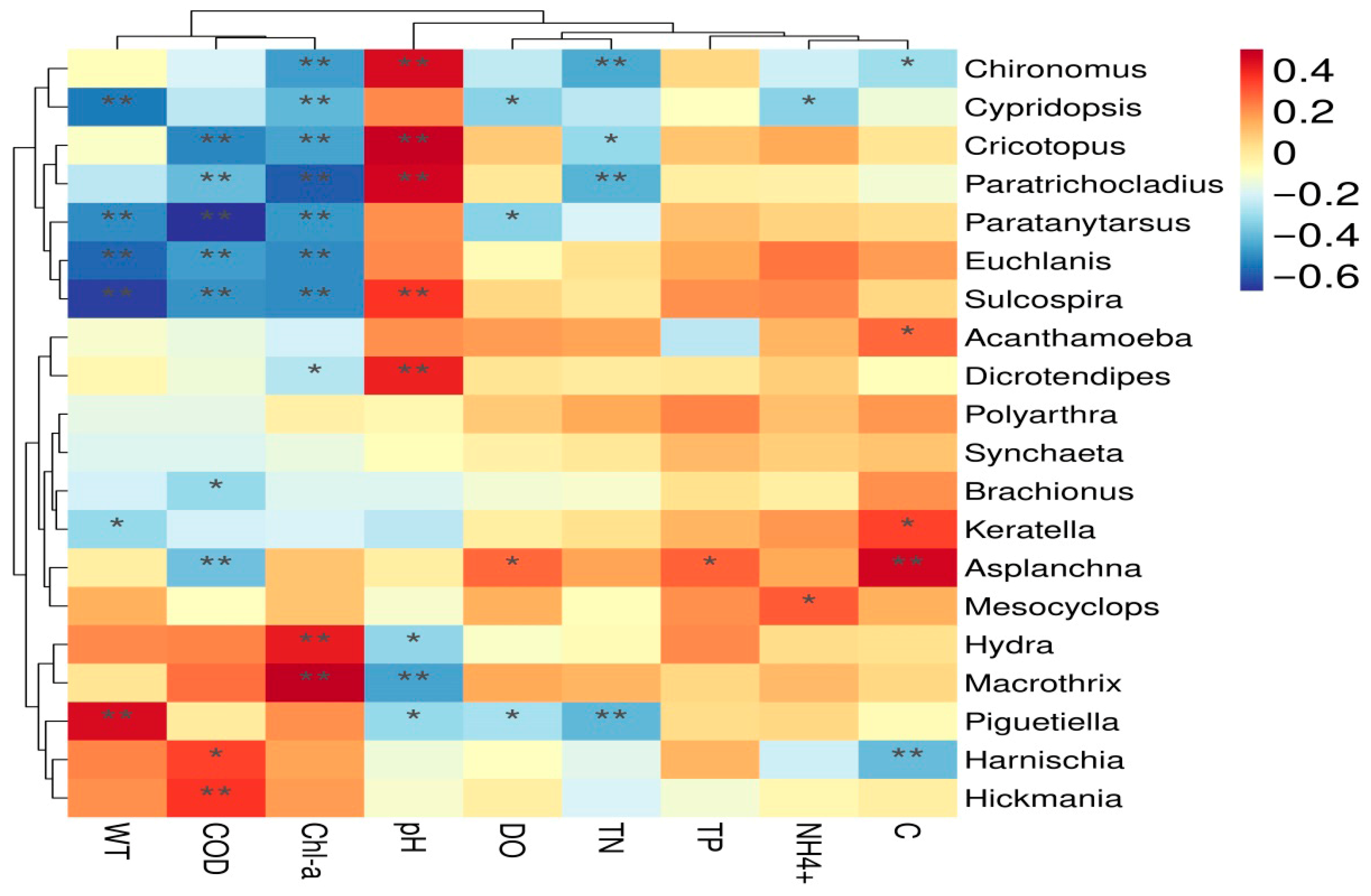
3.4. The Correlation Between the Community Composition of Invertebrate Communities and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. eDNA Metabarcoding Disclosed the Distribution Patterns of Invertebrate Communities in the Chai River
4.2. Invertebrate Diversity Patterns in the Chai River Were Shaped by Environmental Factors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardinale, B.J.; Duffy, J.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Perrings, C.; Venail, P.; Narwani, A.; Mace, G.M.; Tilman, D.; Wardle, D.A.; et al. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature 2012, 486, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, J.Y.; Zhao, F.; Yan, H.M.; Zhang, F.; Wei, X.Q. Impacts of urbanization-induced land-use changes on ecosystem services: A case study of the Pearl River Delta Metropolitan Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWF. Living Planet Report 2020—Bending the Curve of Biodiversity Loss; Almond, R.E.A., Grooten, M., Petersen, T., Eds.; WWF: Gland, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mace, G.M.; Norris, K.; Fitter, A.H. Biodiversity and ecosystem services: A multilayered relationship. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Qin, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals the impact of different land use on multitrophic biodiversity in riverine systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloslavich, P.; Bax, N.J.; Simmons, S.E.; Klein, E.; Appeltans, W.; Aburto-Oropeza, O.; Garcia, M.A.; Batten, S.D.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Checkley, D.M.; et al. Essential ocean variables for global sustained observations of biodiversity and ecosystem changes. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 2416–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulquier, A.; Datry, T.; Corti, R.; von Schiller, D.; Tockner, K.; Stubbington, R.; Gessner, M.O.; Boyer, F.; Ohlmann, M.; Thuiller, W.; et al. Unravelling large-scale patterns and drivers of biodiversity in dry rivers. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macher, T.-H.; Beermann, A.J.; Arle, J.; Foerster, J.; Greyer, M.; Mora, D.; Koschorreck, J.; Rolauffs, P.; Rother, A.; Schüler, S.; et al. Fit for purpose? Evaluating benthic invertebrate DNA metabarcoding for ecological status class assessment in streams under the Water Framework Directive. Water Res. 2025, 272, 122987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y. Biodiversity of aquatic invertebrates based on environmental DNA metabarcoding technology: A case study of Lake Haizhu in Guangzhou. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, K.J.; Probert, P.K.; Jeffries, M. Conservation of aquatic invertebrates: Concerns, challenges and conundrums. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2016, 26, 817–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodkinson, I.D.; Jackson, J.K. Terrestrial and Aquatic Invertebrates as Bioindicators for Environmental Monitoring, with Particular Reference to Mountain Ecosystems. Environ. Manag. 2005, 35, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, C.A.; Mineau, P.; Devries, J.H.; Sanchez-Bayo, F.; Liess, M.; Cavallaro, M.C.; Liber, K. Neonicotinoid contamination of global surface waters and associated risk to aquatic invertebrates: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Xiong, W.; Chen, M.; Xu, J.; Johnson, A.C.; Zhan, A.; Jin, X. Pesticide Pollution Reduces the Functional Diversity of Macroinvertebrates in Urban Aquatic Ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 8568–8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; García Molinos, J.; Heino, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Xu, J. Eutrophication causes invertebrate biodiversity loss and decreases cross-taxon congruence across anthropogenically-disturbed lakes. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, F.; Han, D.; Yan, L.; Yan, S.; Zha, J.; Shen, J. Assessment of benthic invertebrate diversity and river ecological status along an urbanized gradient using environmental DNA metabarcoding and a traditional survey method. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. A Study on Spatiotemporal Pattern of Species and Functional Diversity of Macroinvertebrates in the Mainstream of Yangtze River. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frau, D.; Gutierrez, M.F.; Regaldo, L.; Saigo, M.; Licursi, M. Plankton community responses in Pampean lowland streams linked to intensive agricultural pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Gao, L.; Xu, T. Planktonic algae diversity and its water quality monitoring in Chai River, Baoxiang River and Panlong River, three inflow river of Dianchi Lake. J. Yunnan Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2014, 36, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. The impacts of characteristic pollution sources on the water quality and plankton communities of Inflowing Rivers in Dianchi Lake Basin. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X. eDNA metabarcoding revealed the seasonal and spatial variation of phytoplankton functional groups in the Chai river and their relationship with environmental factors. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2023, 38, 2176374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cao, X.; Fan, H.; Jiang, D.; Huang, Y. Influence of Hydromorphological Factors on Macrozoobenthic Communities in Streams of Lake Dianchi Basin in the Wet Season. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Cai, J.; Su, Y.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Identification of water pollution factors and their spatial distribution with aquatic bioindicators in streams of Lake Dianchi watershed. Acta Entiae Circumstantiae 2011, 31, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, M.; Longo, F.; Lo Valvo, M.; Vizzini, A.; Di Grigoli, A.; Radovic, S.; Arizza, V.; Vecchioni, L.; La Paglia, L.; Queiroz, V.; et al. The Use of Environmental DNA as Preliminary Description of Invertebrate Diversity in Three Sicilian Lakes. Animals 2025, 15, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; He, S.; Hu, B.; Yu, X.; Zhou, S.; He, Y. The settlement and transfer rule of phosphorus in stormwater runoff from phosphorus rich area in Dianchi watershed. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2012, 32, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Environmental Protection Administration; The Water and Wastewater Monitoring Analysis Method Editorial Board. Water and Wastewater Monitoring Analysis Method, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 88–114. [Google Scholar]
- Leray, M.; Yang, J.Y.; Meyer, C.P.; Mills, S.C.; Agudelo, N.; Ranwez, V.; Boehm, J.T.; Machida, R.J. A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: Application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Front. Zool. 2013, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macher, T.-H.; Arle, J.; Beermann, A.J.; Frank, L.; Hupało, K.; Koschorreck, J.; Schütz, R.; Leese, F. Is it worth the extra mile? Comparing environmental DNA and RNA metabarcoding for vertebrate and invertebrate biodiversity surveys in a lowland stream. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Lu, S.; Shao, J.; Dong, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yao, D.; Lin, Y. Assessment of planktonic community diversity and stability in lakes and reservoirs based on eDNA metabarcoding—A case study of Minghu National Wetland Park, China. Environ. Res. 2025, 271, 121025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bao, Y.; Fang, X.; Ruan, Y.; Rong, Y.; Yang, G. A circumpolar study of surface zooplankton biodiversity of the Southern Ocean based on eDNA metabarcoding. Environ. Res. 2024, 255, 119183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aunins, A.A.; Mueller, S.J.; Fike, J.A.; Cornman, R.S. Assessing arthropod diversity metrics derived from stream environmental DNA: Spatiotemporal variation and paired comparisons with manual sampling. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smaoune, G.; Bouchelouche, D.; Taleb, A.; Arab, A. Evaluation of the trophic status in three reservoirs in Algeria (north west) using physicochemical analysis and rotifers structure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 46627–46642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Ren, M.; Wang, H.; Ye, S.; Tang, X.; He, D.; Hu, E.; Li, M.; Pan, B. Riverine network size determined major driving factors of the composition and diversity of aquatic invertebrate communities in a multi-tributary mountain river basin. Water Res. 2025, 276, 123257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, X.; Xie, Z. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of macroinvertebrates in the water source area of the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, W.B.; Seymour, M.; Orsini, L.; Jâms, I.B.; Milner, N.; Edwards, F.; Harvey, R.; de Bruyn, M.; Bista, I.; Walsh, K.; et al. An integrated spatio-temporal view of riverine biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, Y.A.; Manasypov, R.M.; Ermolaeva, N.I.; Antonets, D.V.; Shirokova, L.S.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Environmental factors controlling seasonal and spatial variability of zooplankton in thermokarst lakes along a permafrost gradient of Western Siberia. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Mao, Y.; Huang, Y. DNA metabarcoding of zooplankton communities: Species diversity and seasonal variation revealed by 18S rRNA and COI. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinol, J.; Mir, G.; Gomez-Polo, P.; Agusti, N. Universal and blocking primer mismatches limit the use of high-throughput DNA sequencing for the quantitative metabarcoding of arthropods. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhong, W.; Yang, J.; Altermatt, F.; Zhang, X. Evaluating eDNA and eRNA metabarcoding for aquatic biodiversity assessment: From bacteria to vertebrates. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 21, 100441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Ni, P.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shan, B.; Zhan, A. Zooplankton community structure along a pollution gradient at fine geographical scales in river ecosystems: The importance of species sorting over dispersal. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 4351–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, K.; Yoshizawa, K.; Yoshida, N.; Kazama, F. Progress of eutrophication and change of chironomid fauna in Lake Yamanakako, Japan. Limnology 2004, 5, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Peng, M.; Li, L.; He, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xi, Y.; Tan, F.; Gao, L.; Chai, Y. Community structure characteristics of zooplankton and comprehensive evaluation of water quality in Xiaowan Reservoir area of Lancang River. Freshw. Fish. 2022, 52, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Chicote, J.; Armengol, X.; Rojo, C. Zooplankton species as indicators of trophic state in reservoirs from Mediterranean river basins. Inland Waters 2019, 9, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, D.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Pan, M. Patterns and the determinants of zooplankton community stability in different regions of Lake Dianchi, Yunnan Province, China. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 1752–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, L.; Qi, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R. Community structure of Chironomid larvae and their indicative significance for water quality in streams of Xianju National Park, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 3857–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhu, L.; Lei, K. Analysis of the Comprehensive Management Effects of the Yunnan Lake Inflow Rivers during the 11th Five-Year Plan Period. Environ. Pollut. Prev. 2012, 34, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-X.; Li, M.-R.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.-P.; Yan, Z.-G. A review of the toxic effects of ammonia on invertebrates in aquatic environments. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 122374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurczak, T.; Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A.; Frankiewicz, P.; Kaczkowski, Z.; Oleksińska, Z.; Bednarek, A.; Zalewski, M. Comprehensive approach to restoring urban recreational reservoirs. Part 2—Use of zooplankton as indicators for the ecological quality assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoy, Z.; Abril, M.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Espinosa, C.; Vendrell-Puigmitja, L.; Proia, L. Experimental assessment of salinization effects on freshwater zooplankton communities and their trophic interactions under eutrophic conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Frost, P.C.; Hansson, L.-A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E.; Lürling, M. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ci, F.; Xu, A.; Zhang, X.; Ding, N.; Wan, N.; Lv, Y.; Song, Z. Seasonal Dynamics of Eukaryotic Microbial Communities in the Water-Receiving Reservoir of the Long-Distance Water Diversion Project, China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Behera, P.K. Abundance & distribution of aquatic benthic macro-invertebrate families of river Ganga and correlation with environmental parameters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galic, N.; Hawkins, T.; Forbes, V.E. Adverse impacts of hypoxia on aquatic invertebrates: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z. Relationship between Community Structure of Four Aquatic Organisms and Environmental Factors in Xishui National Nature Reserve, Guizhou Province. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, F.; Xu, S.; Yin, G.; Dong, M. Metabarcoding of zooplankton communities of Dianchi Lake based on the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 gene. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1291632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. The State Environmental Protection Administration, & The State Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, S.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, X.; Zhao, R.; Meng, W. Exploring the feasibility of establishing conductivity criteria for macroinvertebrate based on the field investigations 2015. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2015, 10, 204–214. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Liu, X.; Lu, Q.; Chen, J.; Liang, T.; Wang, W.; Ouyang, S.; Zhou, C.; Wu, X. Seasonal and spatial variability of zooplankton diversity in the Poyang Lake Basin using DNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Groups | SumsOfSqs | MeanSqs | F.Model | R2 | p Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet period_vs._Dry period | 3.066494 | 3.066494 | 8.727725 | 0.143719 | 0.001 | *** |
| (Dry period) up_vs._middle | 0.95746 | 0.95746 | 3.924441 | 0.196966 | 0.002 | ** |
| (Dry period) up_vs._down | 1.380741 | 1.380741 | 4.774432 | 0.200822 | 0.001 | *** |
| (Dry period) middle_vs._down | 0.835896 | 0.835896 | 3.349211 | 0.204855 | 0.01 | ** |
| (Wet period) up_vs._middle | 1.351498 | 1.351498 | 4.407522 | 0.215975 | 0.001 | *** |
| (Wet period) up_vs._down | 1.55737 | 1.55737 | 5.640774 | 0.260655 | 0.001 | *** |
| (Wet period) middle_vs._down | 1.444799 | 1.444799 | 4.424117 | 0.216612 | 0.001 | *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Chang, X.; Xu, S.; Shen, L.; Zhao, Z. Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Invertebrate Communities in the Chai River Based on eDNA Biomonitoring. Diversity 2025, 17, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090660
Lin Y, Xu J, Chang X, Xu S, Shen L, Zhao Z. Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Invertebrate Communities in the Chai River Based on eDNA Biomonitoring. Diversity. 2025; 17(9):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090660
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yuanyuan, Jingge Xu, Xuexiu Chang, Shan Xu, Liang Shen, and Zheng Zhao. 2025. "Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Invertebrate Communities in the Chai River Based on eDNA Biomonitoring" Diversity 17, no. 9: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090660
APA StyleLin, Y., Xu, J., Chang, X., Xu, S., Shen, L., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Spatial and Seasonal Variations in Invertebrate Communities in the Chai River Based on eDNA Biomonitoring. Diversity, 17(9), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090660





