The Yellow Sea Green Tides: Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Long-Distance Transport and Influencing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diversified Macroalgae Monitoring Realized by Remote Satellites
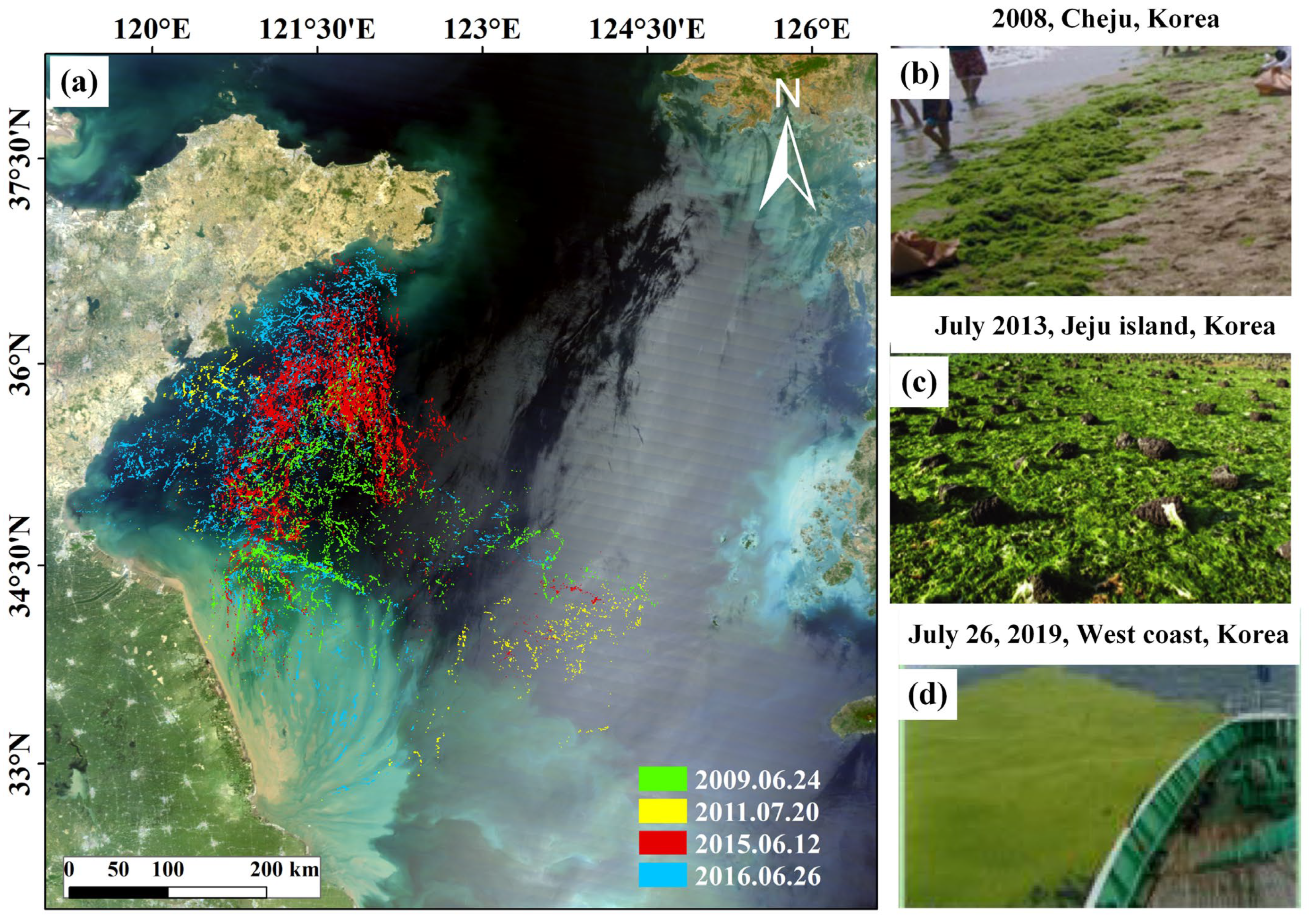
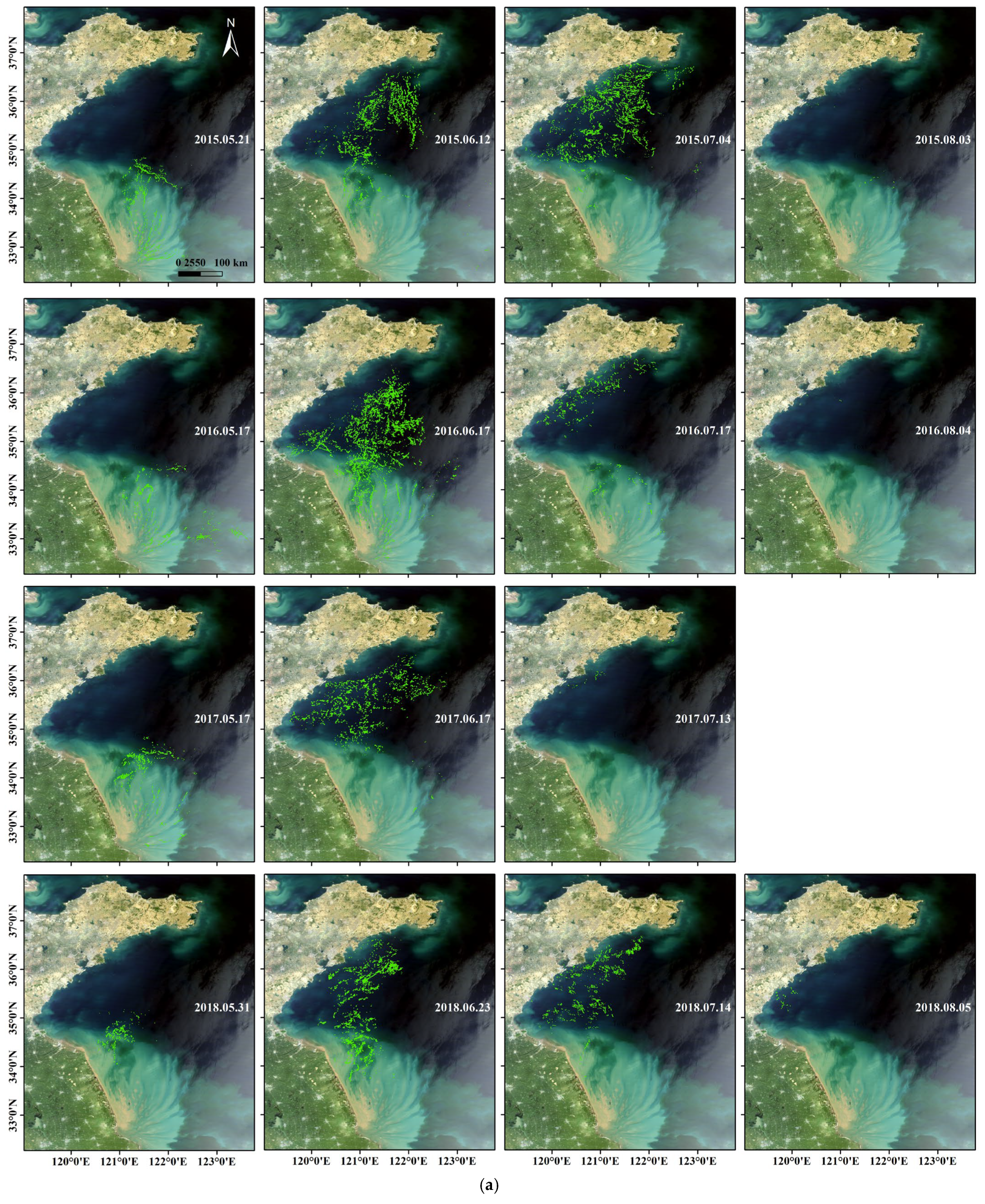
3. Spatiotemporal Variation in the Long-Distance Transport of Green Tides
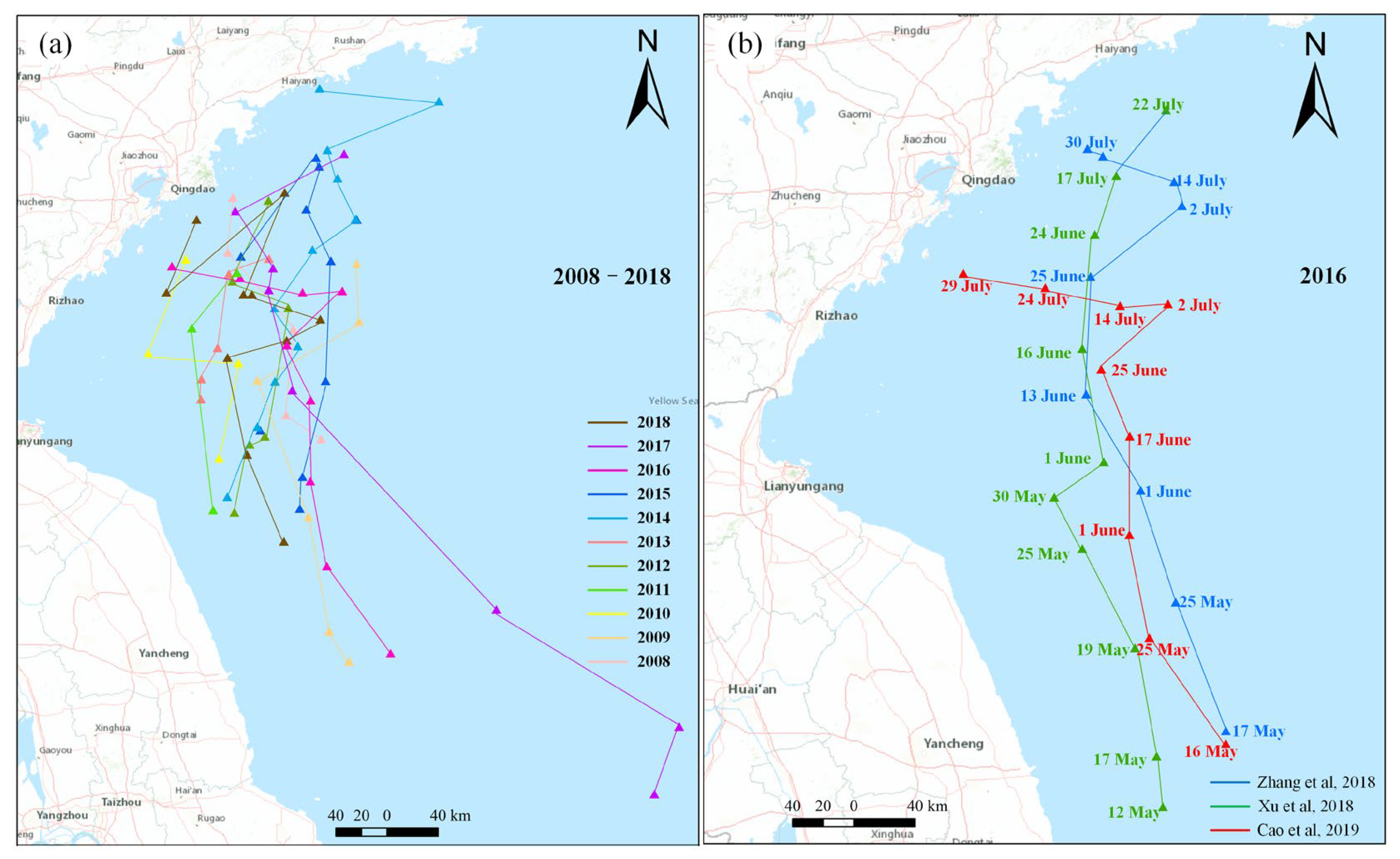
3.1. Long-Distance Drifting
3.1.1. Northward Drifting
3.1.2. Eastward Drifting
3.2. Final Landing and Decomposing Process
4. Interannual Variability in the Size of Green Tide Bloom
4.1. Macroalgae Coverage
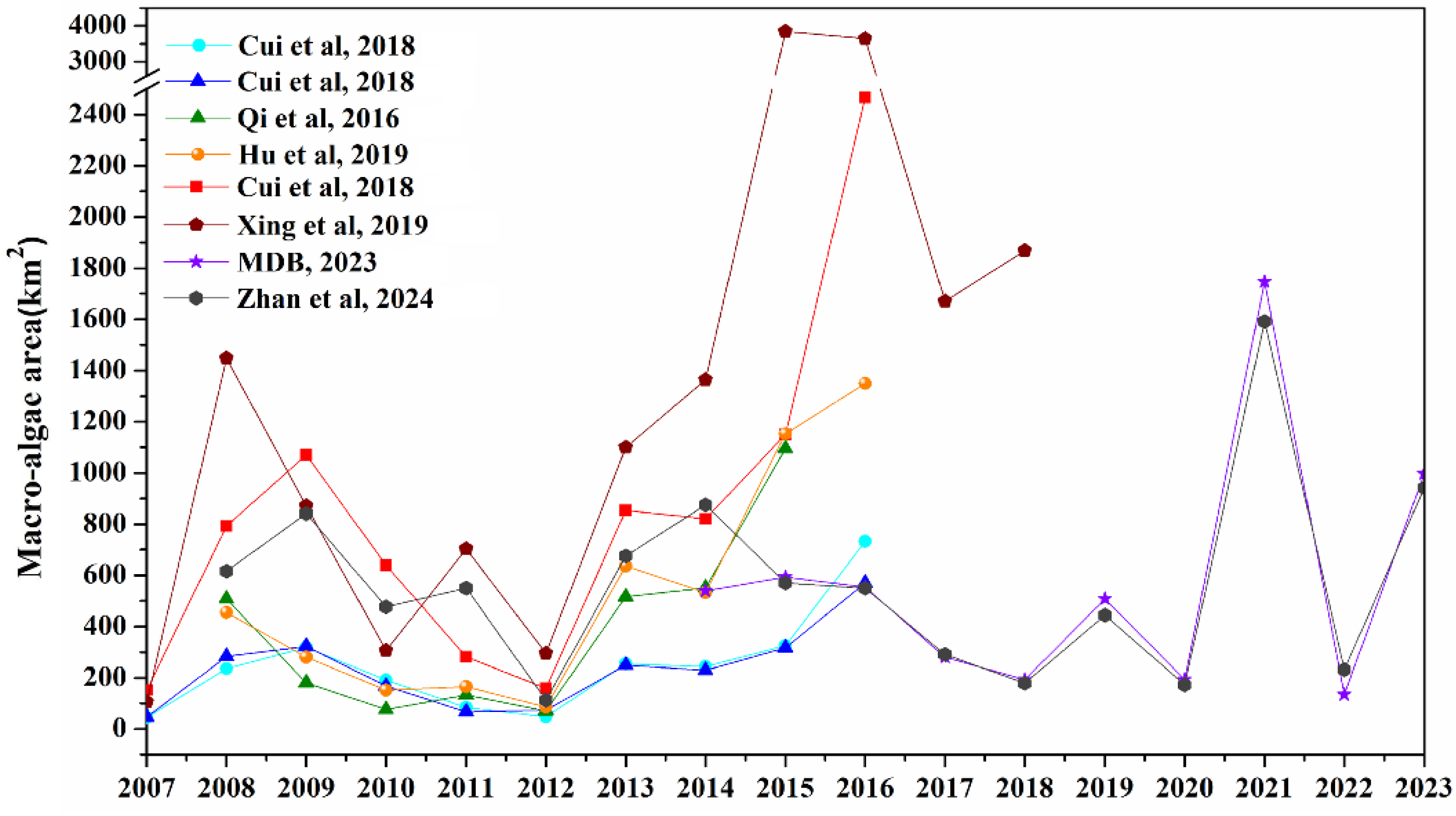
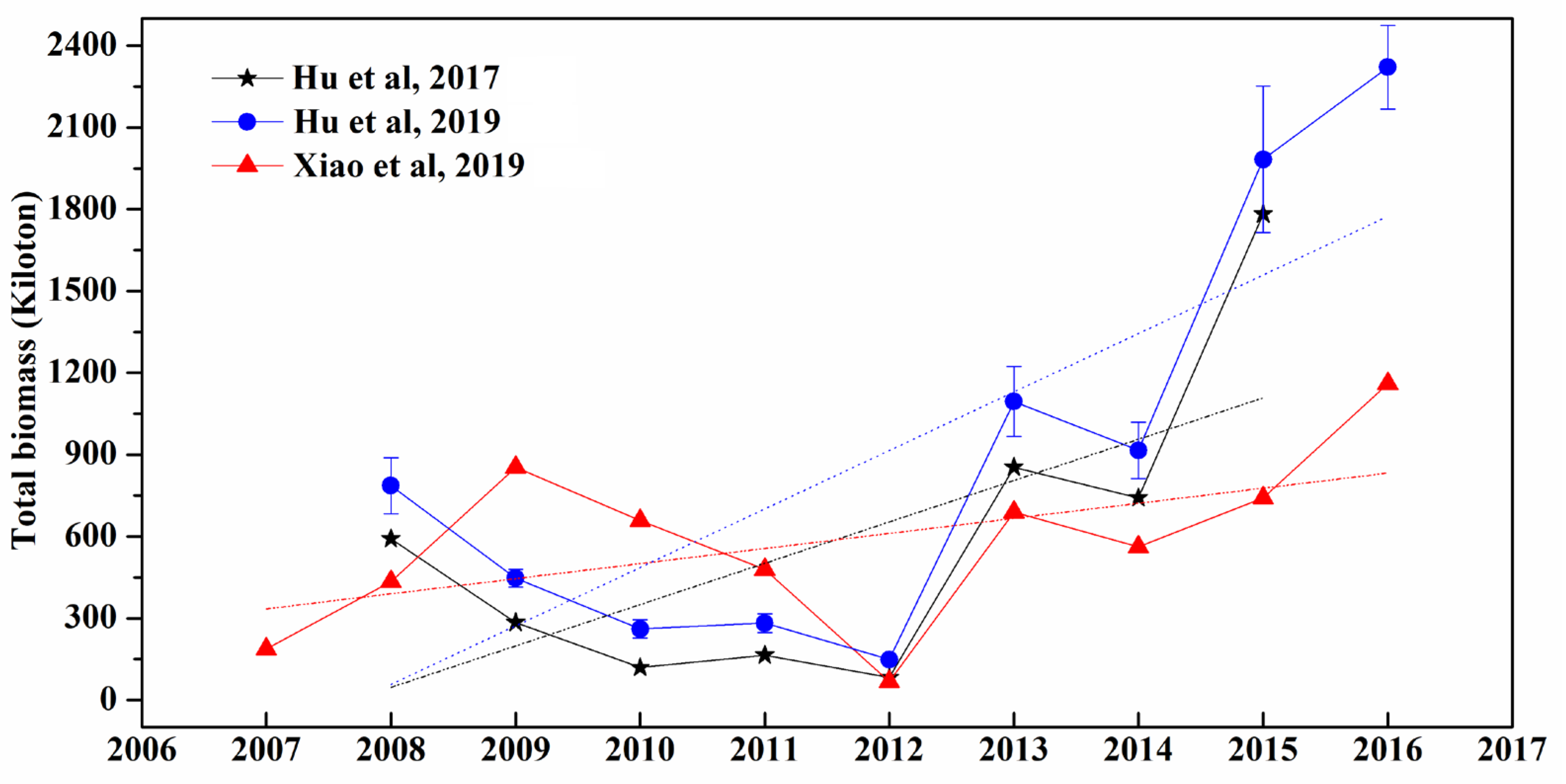
4.2. Macroalgae Biomass
5. Factors Leading to the Variations
5.1. Abiotic Factors
5.2. The Rapid Expansion and Cultivation of Porphyra Mariculture in Jiangsu Province
5.3. Monsoons and Ocean Currents
6. Concluding Remarks and Research Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Y.; Liang, C.; Xu, D.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Q. ‘Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: Taking the world’s largest example. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, P.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Shi, X.; Su, R.; et al. Ulva prolifera green-tide outbreaks and their environmental impact in the Yellow Sea, China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Sun, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X. Temporal variability in zooplankton community in the western Yellow Sea and its possible links to green tides. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H. The response of the carbonate system to a green algal bloom during the post-bloom period in the southern Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 94, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, D.; Keesing, J.; Gong, J. Macroalgal blooms favor heterotrophic diazotrophic bacteria in nitrogen-rich and phosphorus-limited coastal surface waters in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Wu, L.; Tian, L.; Cui, T.; Li, L.; Kong, F.; Gao, X.; Wu, M. Remote sensing of early-stage green tide in the Yellow Sea for floating-macroalgae collecting campaign. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.; Xing, Q.; Shi, P. World’s largest macroalgal bloom caused by expansion of seaweed aquaculture in China. Marine Pollution Bulletin. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; He, M. Origin and Offshore Extent of Floating Algae in Olympic Sailing Area. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union. 2008, 89, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, D. Who made the world’s largest green tide in China?—An integrated study on the initiation and early development of the green tide in Yellow Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Pang, I.; Moon, I.; Ryu, J. On physical factors that controlled the massive green tide occurrence along the southern coast of the Shandong Peninsula in 2008: A numerical study using a particle-tracking experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, C12036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Dai, D.; Simpson, J.; Svendsen, H. Banded structure of drifting macroalgae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; An, D.; Zheng, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Tian, L.; Chen, J. Monitoring seaweed aquaculture in the Yellow Sea with multiple sensors for managing the disaster of macroalgal blooms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Wei, X.; Li, H.; Han, Z. A study of the environmental factors influencing the growth phases of Ulva prolifera in the southern Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, D.; Anderson, D.; Valiela, I. Introduction to the Special Issue on green tides in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; He, P.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Shin, J.; Kim, K.Y.; Ryu, J. Long-Term Trend of Green and Golden Tides in the Eastern Yellow Sea. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 90, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T.; Gong, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Liang, X. Remote sensing estimation of the biomass of floating Ulva prolifera and analysis of the main factors driving the interannual variability of the biomass in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, C.; Ming-Xia, H.E. Remote estimation of biomass of Ulva prolifera macroalgae in the Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Xing, Q.; Shang, S. Long-term trend of Ulva prolifera blooms in the western Yellow Sea. Harmful Algae 2016, 58, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Hu, C.; Tang, D.; Tian, L.; Tang, S.; Wang, X.; Lou, M.; Gao, X. World’s Largest Macroalgal Blooms Altered Phytoplankton Biomass in Summer in the Yellow Sea: Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12297–12313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Geng, H.; Hong, X.; Kong, F.; Yu, R. Strong interannual variation of green tides in the southern Yellow Sea: Crucial factors and implications on management strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 216, 117989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Li, F.; Wei, Y.; Yang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J. Super-resolution optical mapping of floating macroalgae from geostationary orbit. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, C70–C77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, K.; Gong, N.; Shen, L.; Han, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, K.; Kong, D.; Pan, X.; Cong, P. Why did the world’s largest green tides occur exclusively in the southern Yellow Sea? Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 200, 106671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, C.; Miao, X.; Fan, S.; Fu, M.; Xia, T.; Zhang, X. The drifting and spreading mechanism of floating Ulva mass in the waterways of Subei shoal, the Yellow Sea of China–Application for abating the world’s largest green tides. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Han, H.; Hua, L.; Wei, Z.; Yu, K.; Shi, H.; Kim, J.K.; Yarish, C.; He, P. Tracing the origin of green macroalgal blooms based on the large scale spatio-temporal distribution of Ulva microscopic propagules and settled mature Ulva vegetative thalli in coastal regions of the Yellow Sea, China. Harmful Algae 2016, 59, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Han, H.; Shi, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, K.; Xu, R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; et al. Changes to the biomass and species composition of Ulva sp. on Porphyra aquaculture rafts, along the coastal radial sandbank of the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 93, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.; Liang, X.; Gong, J.; Tong, C.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Assessing and refining the satellite-derived massive green macro-algal coverage in the Yellow Sea with high resolution images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2018, 144, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Hu, C. Mapping macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea using HJ-1 and Landsat data: Application of a virtual baseline reflectance height technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.; Meng, J. Satellite monitoring of massive green macroalgae bloom (GMB): Imaging ability comparison of multi-source data and drifting velocity estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zeng, K.; Hu, C.; He, M.-X. On the remote estimation of Ulva prolifera areal coverage and biomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xing, Q.; Li, X.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Zou, J. Assessment of the Impacts From the World’s Largest Floating Macroalgae Blooms on the Water Clarity at the West Yellow Sea Using MODIS Data (2002–2016). IEEE J. STARS 2018, 11, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.; Min, J.; Ryu, J. Detecting massive green algae (Ulva prolifera) blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) data. Ocean Sci. J. 2012, 47, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Green macroalgae blooms in the Yellow Sea during the spring and summer of 2008. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, C12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Fearns, P.; Keesing, J.; Liu, D. Quantification of floating macroalgae blooms using the scaled algae index. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.; Choi, B.; Kim, Y.; Park, Y. Tracing floating green algae blooms in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea using GOCI satellite data and Lagrangian transport simulations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesing, J.; Liu, D.; Fearns, P.; Garcia, R. Inter- and intra-annual patterns of Ulva prolifera green tides in the Yellow Sea during 2007–2009, their origin and relationship to the expansion of coastal seaweed aquaculture in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Hou, Y.; Meng, M.; Liu, C. A Novel Approach of Monitoring Ulva pertusa Green Tide on the Basis of UAV and Deep Learning. Water 2023, 15, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Barnes, B.B.; Lapointe, B.E.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, M. Climate and Anthropogenic Controls of Seaweed Expansions in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.; Fu, J.; Shi, X.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, G.; Sha, Z.; Cui, H.; Wu, J. Dissipation of Ulva prolifera green tides across various spatial and temporal scales and the short-term effects on marine environments. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 207, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, M. Green Tides of the Yellow Sea: Massive Free-Floating Blooms of Ulva prolifera. In Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms; Glibert, P.M., Berdalet, E., Burford, M.A., Pitcher, G.C., Zhou, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. A review of the green tides in the Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 119, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, M.; Guan, W.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Q. Drifting trajectories of green algae in the western Yellow Sea during the spring and summer of 2012. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ju, L.; Chen, M. Interannual variability of Ulva prolifera blooms in the Yellow Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4099–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, L. The seasonal dissipation of Ulva prolifera and its effects on environmental factors: Based on remote sensing images and field monitoring data. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 860–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Cui, X.; Liang, J.; Song, X. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Morphological Characteristics of Ulva prolifera Distribution in the Yellow Sea, China in 2016–2018. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Zhao, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Guan, C.; Hou, C.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y. Ecological effects of Ulva prolifera green tide on bacterial community structure in Qingdao offshore environment. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Oh, H.; Hwang, J.; Suh, Y.; Park, M.; Shin, J.; Kim, W. Tracking the Movement and Distribution of Green Tides on the Yellow Sea in 2015 Based on GOCI and Landsat Images. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2017, 33, 97–109. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Choi, D.; Noh, J.; Ryu, J.; Lee, J.; Jang, P.; Lee, T.; Choi, D. Occurrence of Green Macroalgae (Ulva prolifera) Blooms in the Northern East China Sea in Summer 2008. Ocean Polar Res. 2010, 32, 351–359. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Han, L. Drift path of green tide and the impact of typhoon “Chan-hom” in the Chinese Yellow Sea based on GOCI images in 2015. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 60, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jang, J.; Kim, J.; Byeon, S.; Kim, S.; Choi, S. Species composition, diversity, and distribution of the genus Ulva along the coast of Jeju Island, Korea based on molecular phylogenetic analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e219958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Su, R.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, C.; Shi, X. Extraction and identification of toxic organic substances from decaying green alga Ulva prolifera. Harmful Algae 2020, 93, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, T.; Kong, F.; Zhou, M. Tracing the settlement region of massive floating green algae in the Yellow Sea. J. Ocean. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Xiao, J.; Pang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Miao, J.; Li, Y. Effect of the large-scale green tide on the species succession of green macroalgal micro-propagules in the coastal waters of Qingdao, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 126, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yu, R.; Zhou, M.-J. Effects of the decomposing green macroalga Ulva (Enteromorpha) prolifera on the growth of four red-tide species. Harmful Algae 2012, 16, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.; Luan, S.; Wang, D.; Jiang, W.; Xue, M.; Liu, J.; Cui, Y. Effects of Ulva prolifera dissipation on the offshore environment based on remote sensing images and field monitoring data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D. The Spatiotemporal Variation Research of Ulva Prolifera Blooms Dissipation in the Southern Yellow Sea. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Liu, G.; Huang, S.; Gao, S.; Yuan, C.; Xu, J.; Wu, P.; Huang, R.; et al. Analysis on the causes of massive stranding of Yellow Sea green tide on Lianyungang and Rizhao coasts in 2022. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Song, D. Analysis of environmental factors affecting the large-scale long-term sequence of green tide outbreaks in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 260, 107504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Niu, L.; Wu, M.; Kaufmann, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Kong, Q.; Chen, B. Identification of Green Tide Decomposition Regions in the Yellow Sea, China: Based on Time-Series Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Gao, S.; Huo, Y.; Cui, J.; Shen, H.; Liu, G.; He, P. Annual patterns of macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea during 2007–2017. PLoS ONE. 2019, 14, e0210460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yuen, K.-V.; Gu, X.; Sun, C.; Gao, L. Influences of environmental factors on the dissipation of green tides in the Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 189, 114737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. 2023 Bulletin of China Marine Disaster. 2024. Available online: https://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202404/t20240429_2844013.html (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Zhan, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Qu, S.; Wang, P.; Rong, X. Long-Term Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Ulva prolifera Green Tide and Effects of Environmental Drivers on Its Monitoring by Satellites: A Case Study in the Yellow Sea, China, from 2008 to 2023. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Qi, L.; Hu, L.; Cui, T.; Xing, Q.; He, M.; Wang, N.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, Y.; et al. Mapping Ulva prolifera green tides from space: A revisit on algorithm design and data products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, R.; Heesch, S.; Mac Monagail, M.; O’Donnell, M.; Daly, E.; Wilkes, R.J.; Morrison, L. Spatial and temporal variability of biomass and composition of green tides in Ireland. Harmful Algae 2019, 81, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Dong, M.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Q. Seasonal and interannual variations of nutrients in the Subei Shoal and their implication for the world’s largest green tide. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Q.; Chen, L.; Yu, K.; He, P. Adaptability of free-floating green tide algae in the Yellow Sea to variable temperature and light intensity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Han, X.; Shi, X. Changes in concentrations of oxygen, dissolved nitrogen, phosphate, and silicate in the southern Yellow Sea, 1980–2012: Sources and seaward gradients. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiela, I.; Mcclelland, J.; Hauxwell, J.; Behr, P.J.; Hersh, D.; Foreman, K. Macroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: Controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Peng, K.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Fu, M.; Fan, S.; Zhu, M.; Li, R. Effects of temperature on the germination of green algae micro-propagules in coastal waters of the Subei Shoal, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, P.; Huo, Y.; Yu, K.; He, P. The fast expansion of Pyropia aquaculture in “Sansha” regions should be mainly responsible for the Ulva blooms in Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 189, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yin, Y. An early forecasting method for the drift path of green tides: A case study in the Yellow Sea, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2018, 71, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Tong, Y.; Li, S.; Xia, Z.; Hu, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, P. Advances in the research on micropropagules and their role in green tide outbreaks in the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xia, J.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, K.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.; Tong, Y.; Xia, L.; Qin, Y.; et al. Controlling the source of green tides in the Yellow Sea: NaClO treatment of Ulva attached on Pyropia aquaculture rafts. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Satellite Discovery Time | Maximum Distribution Area Data | Time of Extinction | Bloom Duration (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | Mid-May | 7.12 | Early September | 110 |
| 2009 | Mid-May | 7.02 | Late August | 94 |
| 2010 | Late April | 7.10 | Mid-August | 76 |
| 2011 | Late May | 7.19 | Late August | 82 |
| 2012 | Late March | 6.13 | Mid-August | 106 |
| 2013 | Mid-May | 6.30 | Mid-August | 96 |
| 2014 | Mid-May | 7.14 | Mid-August | 95 |
| 2015 | Mid to late May | 6.19 | Early August | 93 |
| 2016 | Early May | 6.25 | Early August | 85 |
| 2017 | Mid-May | 6.19 | Mid to late July | 68 |
| 2018 | Late May | 6.29 | Mid-August | 91 |
| 2019 | Mid to late May | 6.27 | Early September | 119 |
| 2020 | Late May | 6.15 | Late July | 64 |
| 2021 | Mid-May | 6.26 | Late August | 97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, F.; Sun, B.; Meng, L.; Zou, T. The Yellow Sea Green Tides: Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Long-Distance Transport and Influencing Factors. Diversity 2025, 17, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090614
Qu F, Sun B, Meng L, Zou T. The Yellow Sea Green Tides: Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Long-Distance Transport and Influencing Factors. Diversity. 2025; 17(9):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090614
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Fanzhu, Bowen Sun, Ling Meng, and Tao Zou. 2025. "The Yellow Sea Green Tides: Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Long-Distance Transport and Influencing Factors" Diversity 17, no. 9: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090614
APA StyleQu, F., Sun, B., Meng, L., & Zou, T. (2025). The Yellow Sea Green Tides: Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Long-Distance Transport and Influencing Factors. Diversity, 17(9), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090614