Abstract
The genus Sclerodermus Latreille (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) comprises over 80 species of ectoparasitoids of insect pests in forests, agricultural environments, and stored products with a cosmopolitan distribution. Despite its growing significance in biological control, behavioral ecology, and public health, the taxonomy of the genus remains poorly resolved. This is largely due to morphological reduction and simplification among species, outdated or incomplete original descriptions, and limited access to type material. A particularly problematic case is Sclerodermus cereicollis Kieffer, originally described from two geographically disjunct populations: Giglio Island (Italy, Palaearctic) and Annobón Island (Equatorial Guinea, Afrotropical). The syntype series includes morphologically divergent specimens, casting doubt on their conspecificity. In this study, we redescribe S. cereicollis based on both the original syntypes and newly collected material from Italy. A lectotype is designated to stabilize the nomenclature, and we provide the first molecular data for the species to assess genetic cohesion among populations. Comparative morphological and molecular analyses reveal that the Afrotropical syntypes represent a distinct, previously undescribed species. Accordingly, we describe Sclerodermus annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov., designating a holotype. This study refines species boundaries within Sclerodermus and highlights the value of integrative taxonomy, combining historical and contemporary data, in resolving persistent systematic ambiguities in morphologically conservative taxa.
1. Introduction
The genus Sclerodermus Latreille, 1809, encompasses more than 80 species of bethylid wasps with a cosmopolitan distribution [1]. These wasps are ectoparasitoids of immature stages of insects belonging to the orders Coleoptera, Lepidoptera, and Isoptera [2,3,4,5]. Their hosts are common insect pests in forests, agricultural environments, and stored products [1]. In recent years, Sclerodermus has gained increasing importance for several reasons. Firstly, various species of this genus have been valued and effectively used as biological control agents against insect pests [6]. Secondly, among parasitoid insects, Sclerodermus has evolved a remarkably refined level of social behavior, defined as “quasi-social”, involving cooperative behaviors during host paralysis and cooperative brood care, although without a generational overlap [7,8,9,10]. Lastly, several Sclerodermus species have been reported, together with the mite Pyemotes sp. [11], as agents of sting dermatitis in humans, highlighting their importance as sanitary pests in indoor environments [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22].
The genus Sclerodermus, including S. cereicollis, has recently been studied for its functional morphology [23], reproductive biology [24,25], aggregation behavior [26], and chemical ecology [27].
Although Sclerodermus is morphologically similar to Nothepyris Evans, 1973 and Discleroderma Kieffer, 1904 by having a globoid head [28], these genera were not retrieved as a clade [29]. Sclerodermus is characterized by marked polymorphism and pronounced sexual dimorphism, resulting in evident differences between females and males. These differences include variations in body size, coloration, and the presence or absence of wings and ocelli [30]. As in several other genera of Scleroderminae, such as Acephalonomia Strejček, 1990, and Cephalonomia Westwood, 1833 [29,31], females of this genus are generally reported as apterous and/or micropterous, although macropterous individuals have also been documented [31]. Males are typically winged, with only rare reports of wingless specimens [32,33,34,35].
Despite this increasing interest in Sclerodermus, the taxonomic knowledge of the genus remains superficial and ambiguous. The taxonomy of this genus is particularly challenging for several reasons. First, Sclerodermus species show significant structural reductions in their external morphology. The pronotum and the metapectal–propodeal disc are not carinate; the macropterous forms generally lack ocelli, notauli, and parapsidal signa. In the apterous and macropterous forms, the mesonotum is not divided into the mesoscutum and the mesoscutellum, and the ocelli and the metanotum are almost entirely absent. Additionally, both the head and the metasoma lack distinctive features. This combination of traits significantly reduces the number of available characters with which to differentiate and recognize the species within the genus Sclerodermus.
Further complicating the situation, most species descriptions are outdated and incomplete, often lacking the diagnostic characters employed in modern taxonomy. Color, which was frequently used as a diagnostic trait in older descriptions, has limited taxonomic value since it can vary significantly within the same species or population due to diet or environmental conditions [1]. Moreover, coloration is often similar across different species, typically ranging between various castaneous shades [36]. This scenario becomes even more challenging because no identification keys exist for the species in most zoogeographic regions, except for the Neotropical region [36]. Furthermore, the type material of numerous species is believed to be either lost or in a state of poor preservation, as many species were described many decades ago. This restricted range of types engenders challenges in the comparison of species, thereby compromising the accuracy of identification. Another complication arises from Sclerodermus’ limited dispersal ability. These wasps have a poor flight capacity, as females of most species are apterous or micropterous, while the macropterous forms have delicate, narrow wings with reduced venation [1]. As a result, finding populations in two distinct zoogeographic regions requires careful evaluation of whether they represent different species. Conversely, some species may be anthropophilic, spreading through human-mediated transport; for example, via stored products, furniture, packaging, pallets, wooden crates, softwood lumber, and other wood packaging materials used in international trade [1].
This intricate taxonomic scenario has historically led to numerous misidentifications and synonymies, a problem that persists in the present day. Some species of Scleroderminae, such as Sclerodermus domesticus Latreille, 1809 and Cephalonomia gallicola (Ashmead, 1887), are among the most well-known representatives of the genera Sclerodermus and Cephalonomia, respectively. As flagship species, their names could be mistakenly utilized to identify other Sclerodermus or Cephalonomia species under investigation in ecological, agricultural, or sanitary studies.
Finally, many scientific studies on the biology and ecology of Sclerodermus are hampered by the difficulty of accurately identifying the species under investigation. To date, the only synopsis of Sclerodermus is available for Neotropical species [36], while all other regions still lack revisionary studies. A proper methodology for accurately analyzing the morphological differences among species within the genus Sclerodermus is essential for improving species descriptions and, consequently, our understanding of the systematics of this genus.
Sclerodermus cereicollis Kieffer, 1904, is a species that exemplifies the taxonomic challenges involved in the study of Sclerodermus species. It was originally described by Kieffer (1904) based on two groups of specimens [37]. To date, this species has been sporadically reported both as an ectoparasitoid of xylophagous beetles [14,38] and as a cause of sting dermatitis in humans [14]. The type series of S. cereicollis is currently housed at Museo Civico di Storia Naturale Giacomo Doria (MCSN) in Genoa, Italy [37,39]. The syntype series comprises seven specimens divided into two groups: the first group includes two micropterous females and one macropterous female from Annobón Island (Afrotropical region), an Atlantic Island belonging to Equatorial Guinea, while the second group consists of four micropterous females collected on Giglio Island (Palaearctic region) in Italy. These locations are ecologically distinct and separated by over 5000 km, with the Atlantic Ocean and the Sahara Desert acting as effective barriers. The contrasting Mediterranean climate of Giglio and the equatorial climate of Annobón further reduces the possibility of gene flow between the two populations. According to the principles of allopatric speciation [40], such physical and ecological separation suggests that the two syntype groups may not belong to the same species.
Given this context, the main objectives of the present study—based on both the original type material and newly collected specimens—are as follows: (1) to redescribe the micropterous female of S. cereicollis; (2) to describe, for the first time, the macropterous female, as well as both macropterous and micropterous males; (3) to investigate sexual and wing polymorphism in S. cereicollis; (4) to clarify the taxonomic identity of S. cereicollis and designate a lectotype from the syntype series; (5) to provide the first molecular data for this species and assess genetic cohesion among populations; (6) to evaluate whether the Afrotropical syntypes represent a distinct taxon and, if so, to describe it as a new species through comparative morphological analysis with other known Afrotropical Sclerodermus species; and (7) to designate a holotype for the newly described species.
2. Materials and Methods
The material examined in this study includes both syntype series S. cereicollis—deposited at Museo Civico di Storia Naturale Giacomo Doria, Genoa, Italy (MCSN)—and freshly collected and reared field material that will be deposited at MCSN, Universidade Federal do Espírito Santo, Vitória, Brazil (UFES), and Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil (UFMG).
The nomenclature of the integument sculpture follows Harris [41], while the general morphological terms follow Azevedo et al. [1] and Lanes et al. [42] (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Measurements and indices (Figure 3) used in this study are defined as follows: BL (body length), measured from the apex of the clypeus to the posterior margin of the last metasomal segment; FWL (forewing length), measured from the tegula to the distal margin; LH (length of head), measured in the anterior view from the vertex crest to the median apical margin of the clypeus; WH (width of head), measured in the anterior view as the maximum width, including the eyes; WF (width of frons), measured in the anterior view as the minimum width, usually at the lower margin of the eyes; EL (eye length), measured in the lateral view across its maximum height (length); OOL (ocello–ocular line), measured in the latero-dorsal view as the shortest distance from the dorsal margin of the eye to the posterior ocellus; VOL (vertex–ocular line), measured in the dorsal view, the maximum distance from the eye margin to the vertex crest; WOT (width of ocellar triangle), measured in the anterior view as the maximum width, including the ocelli, DAO (diameter of anterior ocellus), and DPO (diameter of posterior ocellus).
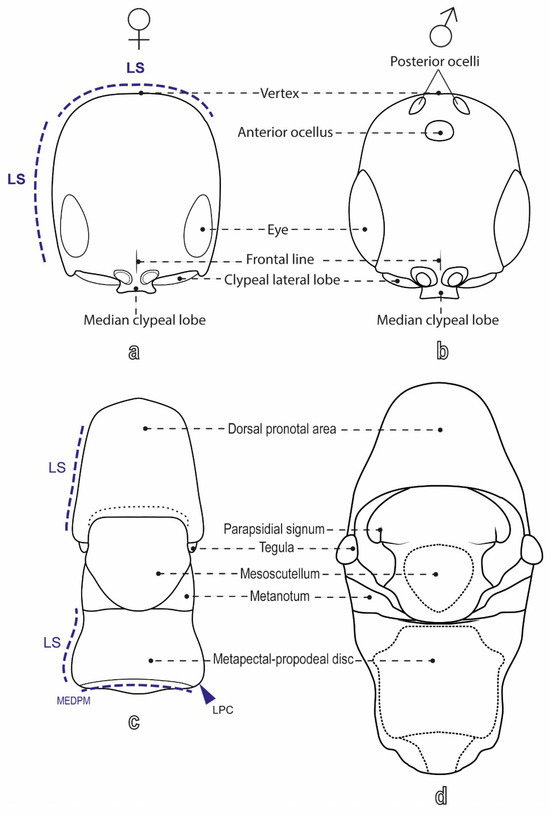
Figure 1.
Labeled diagram of S. cereicollis (reared specimens), dorsal view. (a) Head of female and (b) male; (c) mesosoma of female and (d) male.
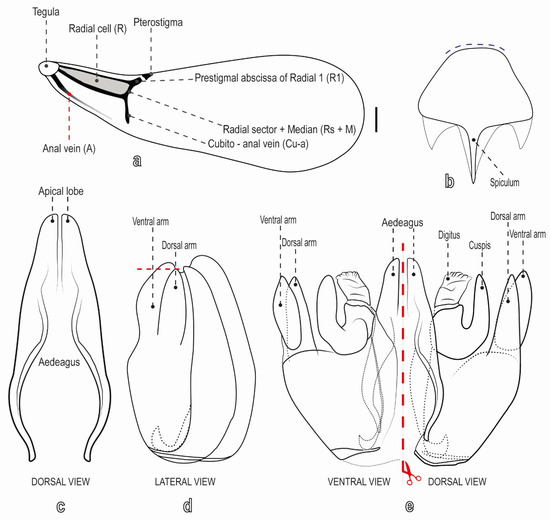
Figure 2.
Labeled diagram of a male of S. cereicollis (reared specimen). (a) Forewing, dorsal view; (b) hypopygium, ventral view (dashed lines indicate the posterior margin; (c) aedeagus; (d) genitalia in lateral and (e) ventral/dorsal views, separated by a red dashed line.
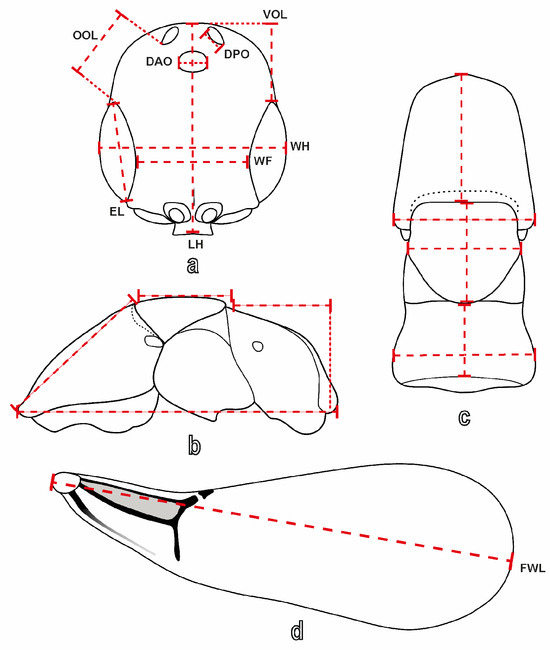
Figure 3.
Morphological measurements in S. cereicollis (field-collected specimen). Dashed lines indicate the measurements. (a) Head of a male, dorsal view; (b) mesosoma of a female in lateral and (c) dorsal view; (d) forewing of a male.
The photographs of adult specimens were taken using a Leica Z16 APO stereomicroscope coupled with a Leica DFC 2 video camera (Leica Microsystems, Heerbrugg, Switzerland), employing a modular dome illumination system, as described by Kawada and Buffington [43]. Images of immature stages were captured using a Wild M420 stereomicroscope coupled to a MikroCam PRO HDMI 5MP camera (Bresser, Rhede, Germany) under fiber-optic illumination (KL 1600 LED, Schott, Stafford, UK). Image stacking and processing were performed using Helicon Focus (HeliconSoft 8.2.2, Kharkiv, Ukraine), and the final composite images were saved at 300 DPI. Line drawings of the head, mesosoma, and forewings were made using a camera lucida attached to a Leica M80 stereomicroscope (Leica Microsystems GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany). Male genitalia and hypopygium were cleaned using Proteinase K, following the protocol proposed by Martinelli et al. [44], and subsequently illustrated using a camera lucida attached to a Leica DM 2500 microscope (Leica Microsystems GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany). The final drawings were vectorized using an image editor and saved at 600 DPI.
To check for apterism, the presence of the tegula was verified. The mesosoma of two micropterous males was dissected and fixed for 3 h in 2.5% glutaraldehyde in a sodium cacodylate buffer (pH 7.2) and then rinsed repeatedly in the same buffer. The samples were dehydrated through a graded ethanol series and subsequently dried in an oven at 40 °C for 24 h. They were then mounted on aluminum stubs using double-sided carbon tape and sputter-coated with a thin (18 nm) layer of gold. The specimens were examined using a field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM LEO 1525, ZEISS, Milan, Italy) with secondary electrons at 5 kV.
2.1. Molecular Protocol
DNA was extracted from the metasoma and mesosoma of eleven specimens (7♀/5♂) using the NucleoSpin Tissue Kit, following the manufacturer’s protocol. The mitochondrial gene cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) was amplified using standard PCR procedures and the primers LCO1490/HCO2198 proposed by Folmer et al. [45]. The thermal cycling profile consisted of an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 1 min, followed by 43 cycles of denaturation (45 s at 95 °C), annealing (45 s at 47 °C), and extension (45 s at 47 °C), with a final extension at 72 °C for 3 min. Amplification products were visualized on 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis (AGE) and purified using the ExoSAP-IT kit (USB Corporation, Cleveland, OH, USA), with incubation at 37 °C for 15 min, followed by inactivation at 80 °C for 15 min.
Purified products were sequenced using a T3500 Genetic Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) at the Núcleo de Biodiversidade Genética Luiz Paulo de Souza Pinto (NuBiGen), Universidade Federal do Espírito Santo (UFES), Brazil. Forward and reverse chromatograms were examined and trimmed using Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software, version 7 [46]. Sequence identity was confirmed through BLAST 2.16.0 (National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda, MD, USA) searches against the GenBank nucleotide database [47]. Potential contamination or pseudogene amplifications were checked by using TBLASTN 2.16.0, (National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda, MD, USA) searches [48].
Sequence alignment was performed using MAFFT version 7 [49], resulting in an average aligned sequence length of ~566 bp.
Molecular analyses were performed on a dataset comprising 14 terminal taxa, including seven sequences retrieved from GenBank: Plastanoxus chittendenii Ashmead, 1893 (GenBank MZ629055), and Prorops nasuta Waterston, 1923 (GenBank MG760784), were used as outgroups. Five species of Sclerodermus, namely S. domesticus Klug, 1809 (GenBank KX827609), S. guani Xiao & Wu, 1983 (GenBank KM649927), S. harmandi (Buysson, 1903) (GenBank AB795306), S. pupariae Yang & Yao, 2012 (GenBank KM649943), and S. sichuanensis Xiao, 1995 (GenBank KM649967), were used for interspecific genetic comparisons. The remaining seven terminals correspond to the specimens analyzed in this study, representing the two S. cereicollis populations, as described in the Material Examined Section.
2.2. Species Delimitation Methods
The nucleotide alignment was used to reconstruct a maximum likelihood (ML) phylogeny and to assess genetic variability within S. cereicollis. The substitution model TIM2+F+I was selected using ModelFinder in IQ-TREE version 2.1.1 [50] under the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC). The ML tree was then generated with ultrafast bootstrap [51] and SH-aLRT support values [52], both calculated using 10,000 resampling replicates. The resulting ML topology was visualized using FigTree version 1.4.3 [53]. The tree was rooted using P. chittendenii (Bethylidae, Scleroderminae).
Pairwise genetic distances were calculated using the Kimura two-parameter model (K2P) of nucleotide substitution [54], implemented in MEGA version 7. The analysis was performed with a Gamma distribution model (G = 1.00) to account for rate variation among sites. Variance estimation was conducted using the bootstrap method with 1000 replicates. Gaps and missing data were treated by pairwise deletion, and all codon positions (1st, 2nd, 3rd), as well as noncoding sites, were included in the analysis. This model was selected to allow a direct comparison between our results and previous studies on Bethylidae, which also used K2P as the substitution model [55,56,57,58].
3. Results
3.1. Sclerodermus cereicollis Kieffer, 1904
Material examined. Type material. Lectotype (here designated), micropterous female, labelled: ITALY, Giglio Island, February 1902, G. Doria (MCSN). Paralectotypes (here designated): three micropterous females, same data as lectotype (MCSN). New material (reared): 10 macropterous males, 13 macropterous females and 13 micropterous females, labelled: ITALY, Como, Ponte Lambro, ex. Psacothea hilaris hilaris (Pascoe) in Ficus carica L. 19.IX.2013, D. Lupi col. (MCSN, UFES, UFMG). 47 macropterous males, 7 micropterous males, 9 macropterous females and 243 micropterous females, labelled: ITALY, rearing lab. In Perugia, September 2011, original population from ITALY, Como, Ponte Lambro, 45°49′40.00″ N 9°13′07.00″ E, Psacothea hilaris hilaris (Pascoe) (MCSN, UFES, UFMG). New material (Field-collected): 2 macropterous males and 1 micropterous females, labelled: ITALY, Monza, Milan, 45.585174/9.268928, July 2023, ex. Xylotrechus stebbingi (Gahan) on dead wood of Celtis australis (L.) [Obs. Molecular A-289 (GenBank: 28S PV843594—COI PV849453), A-294, A-297(GenBank: 28S PV843596—COI PV849455)]; 2 macropterous males and 4 micropterous females, labelled: ITALY, Como, Ponte Lambro, 45.827778/9.218611 ex. Psacothea hilaris hilaris in Ficus carica, 19.IX.2013, D. Lupi col. (MCSN, UFES, UFMG) [Obs. Molecular A-279 (GenBank: 28S PV843590—COI PV849449), A-280 (GenBank: 28S PV843591—COI PV849450), A-296 (GenBank: 28S PV843595—COI PV849454), A-309, A-281 (GenBank: 28S PV843592—COI PV849451), A-282 (GenBank: 28S PV843593—COI PV849452)].
Diagnosis. This species differs from other species of the genus by having the head subrectangular with sides slightly converging anterad, eye elliptical and flagellomeres wider than long, except for the last one, dorsal pronotal area subrectangular with sides slightly incurved only posteriorly, mesonotum as wide as long, isosceles triangle-shaped, with sides almost slightly outcurved and posterior margin rounded.
Redescription, micropterous female (Figure 4a–e and Figure 5a–i). Measurements (mm). Body 1.89–3.12, LH 0.36–0.53, WH 0.3–0.46, WF 0.16–0.24, EL 0.1–0.13, VOL 0.19–0.30, mesosoma 0.53–0.71, metasoma 1.11–1.5. Color. Head castaneous, antenna, mesosoma and legs light castaneous, and metasoma castaneous. Setation. Head with scarce and scattered setae, on gena few setae shorter than EL; flagellum with short and dense suberected setae; mesosoma and metasoma with scarce and scattered setation.
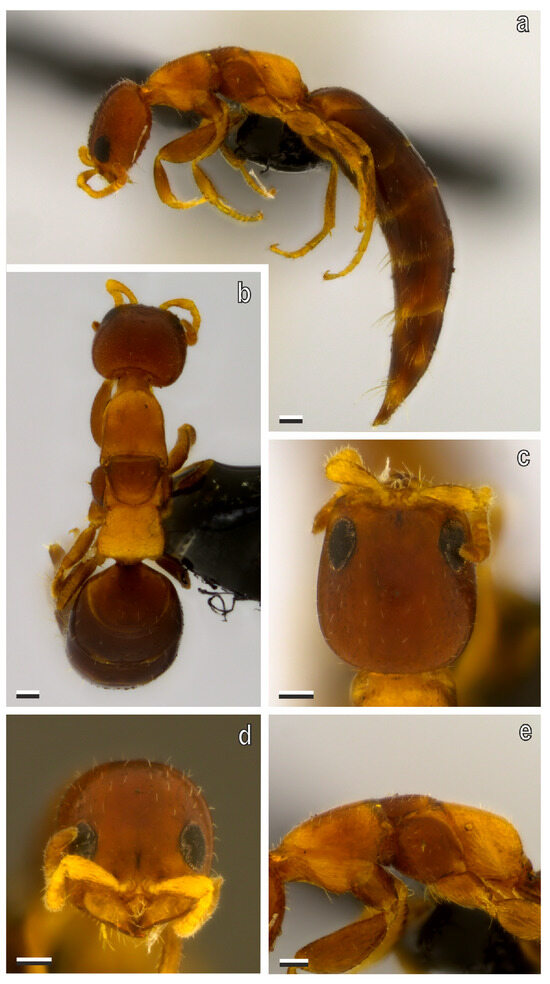

Figure 4.
S. cereicollis, micropterous female (lectotype). (a) Habitus, lateral view; (b) habitus, dorsal view; (c) head in dorsal and (d) anterior view; (e) mesosoma, lateral view. Scale bars = 100 μm.
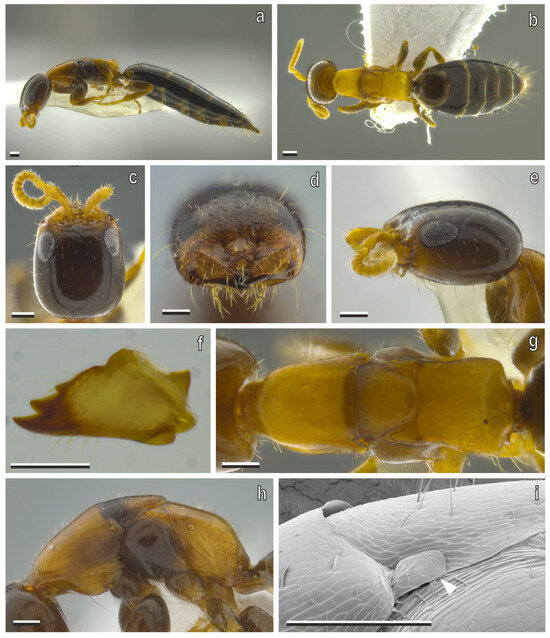

Figure 5.
S. cereicollis, micropterous female (reared specimen). (a) Habitus, lateral view; (b) habitus, dorsal view; (c) head in dorsal, (d) anterior, and (e) lateral views; (f) right mandible, anterior view; (g) mesosoma, dorsal view; (h) mesosoma, lateral view; (i) scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of mesosoma; white arrowhead indicating tegula, typical of micropterous forms. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Head (Figure 4c,d and Figure 5c–e). Head rectangular, 1.15× as long as wide, in dorsal view; globoid in lateral view, sides slightly outcurved and moderately converging anterad, posterior margin of vertex slightly outcurved in dorsal view; frons, vertex and gena imbricate, with few punctures; frontal line sulcate, well-defined and short; mandible robust with three apical teeth, dorsalmost one small, two ventral large and sharp; median clypeal lobe as long as lateral lobes, surface elevated medially; eye subtriangular, flat, located dorso-laterally with gena visible dorsally, next to mandibular base, longer than half VOL, distance from torulus to eye 2.40× torulus width; LH 3.47× EL, WF 1.63× EL; scape slightly curved, wider apically, longer than EL, pedicel longer than flagellum, flagellomeres wider than long, except for distal one, which is elliptical with acute apex; ocelli absent.
Mesosoma (Figure 4e and Figure 5g,h). Surface imbricate; dorsal pronotal area bell-shaped, longer than wide, sides slightly incurved only posteriorly, posterior margin nearly straight; mesonotum isosceles triangle-shaped, sides almost slightly outcurved, posterior margin rounded, as wide as long, with its posterior margin touching anterior margin of metapectal–propodeal disc; metanotum without metanotal trough and metanotal fovea; metapectal–propodeal disc trapezoidal, anterior margin nearly outcurved, sides slightly incurved anteriorly and slightly outcurved posteriorly, and tending to strongly diverging posterad in dorsal view, anterior width rate 0.75× posterior width. Marginal edge between disc and lateral surface of metapectal–propodeal complex bluntly right-angled (90–180°), in posterior view, posterior margins rounded, forming single convexity in lateral view, metapectal–propodeal disc 0.74× as long as wide, shorter than mesonotum, latero-posterior corners rounded, smoothly curved, without distinct angle or point, in postero-dorsal view; lateral marginal, metapostnotal median and posterior transverse carinae absent.
Metasoma. Stout; posterior margin of sternite IV–V with pair of longitudinal fissures.
Description, macropterous female (Figure 6a–g). Measurements (mm). Body 2.94–4.25, LH 0.55–0.59, WH 0.43–0.52, WF 0.25–0.29, EL 0.17–0.25, FWL 1.61, OOL 0.27, WOT 0.11–0.15, DAO 0.04, DPO 0.053, VOL 0.33, mesosoma 1.32–1.36, metasoma 2.32–2.4. Color. Head and metasoma dark castaneous, antenna light castaneous, mesosoma and legs castaneous; wings hyaline. Setation. Head with scarce and scattered setae, on gena few setae shorter than EL; flagellum with short and dense suberected setae; mesosoma and metasoma with scarce and scattered setation; forewing setation dense.
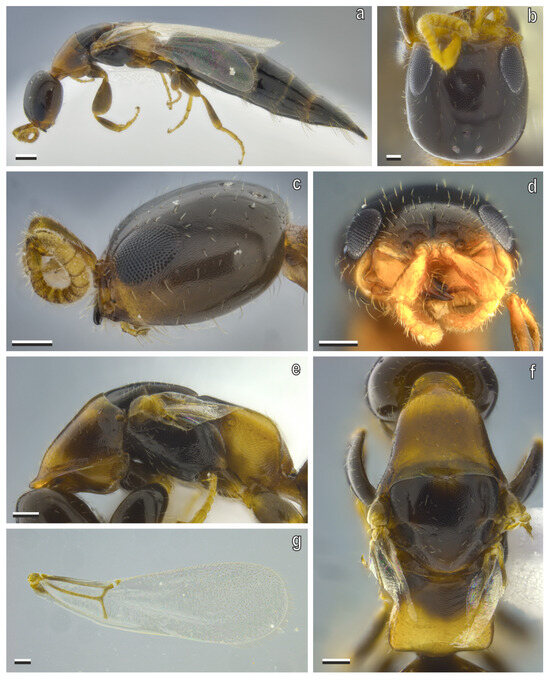

Figure 6.
S. cereicollis, macropterous female (reared specimen). (a) Habitus, lateral view; (b) head in dorsal, (c) lateral, and (d) anterior views; (e) mesosoma in lateral and (f) dorsal views; (g) forewing, dorsal view. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Head (Figure 6b–d). Head rectangular, 1.13–1.27× as long as wide, in dorsal view, globoid in lateral view, sides slightly outcurved, and moderately converging anterad, posterior margin of vertex straight or nearly so in dorsal view; frons, vertex and gena imbricate, with few punctures; frontal line well-defined and short; mandible robust with three apical teeth, dorsalmost one small, two ventral large and sharp; median clypeal lobe as long as lateral lobes, surface elevated medially; eye subtriangular, flat, located dorso-laterally with gena visible dorsally, next to mandibular base, longer than half VOL; LH 2.4–3.3× EL, WF 2.0–2.2× EL; ocelli present, forming equilateral triangle, anterior ocellus posterior to supra-ocular line, posterior ocelli far from vertex by distance longer than DPO; scape slightly curved, wider apically, longer than EL, pedicel longer than flagellum, flagellomeres wider than long, except for distal one, which is elliptical with acute apex.
Mesosoma (Figure 6e,f). Surface imbricate; dorsal pronotal area bell-shaped, wider than long, sides slightly incurved only posteriorly, posterior margin nearly straight; mesoscutum wider than long, notaulus fully absent; parapsidal signum weak but complete; mesoscutellum trapezoidal, as wide as long, sides almost straight, posterior margin rounded, not touching anterior margin of metapectal–propodeal disc; mesoscutum–scutellar suture absent; metanotum with metanotal trough weakly developed and metanotal fovea absent; metapectal–propodeal disc trapezoidal, anterior margin nearly outcurved, sides slightly incurved only anteriorly, and tending to strongly diverging posterad in dorsal view, anterior width 0.74× posterior width; marginal edge between disc and lateral surface of metapectal–propodeal complex bluntly right-angled (90–180°), in posterior view, marginal edge between disc and posterior margins of metapectal–propodeal complex rounded, forming single convexity, in lateral view, metapectal–propodeal disc wider than long, 0.97× as long as wide, longer than mesoscutellum, latero-posterior corners rounded, smoothly curved without distinct angle or point, in postero-dorsal view; lateral marginal, metapostnotal median and posterior transverse carinae absent.
Wings (Figure 6g). Costal vein (C) absent, median + cubital vein (M + Cu) present, nebulous basally; anal vein (A) present, nebulous in aspect for almost its entire extent, not joining end of cubito-anal vein (cu-a), cu-a present, long 2× Rs + M vein; costal cell (C) opened, by absence of costal vein, radial cell (R) closed, first cubital cell (1Cu) opened at posterodistal corner, pterostigma slender, prestigmal abscissa of radial 1 (R1) present; following cells absent: second radial cross & radial sector (2r-rs&Rs), poststigmal abscissa of radial 1 (R1), radial sector (Rs), second radial 1 cell (2R1) and first radial 1 cell (1R1); hind wing with three distal hamuli irregularly spaced.
Metasoma. Stout; posterior margin of sternite IV–V with pair of longitudinal fissures.
Description, micropterous male (Figure 7a–g). Measurements (mm). Body 3.09–3.44, LH 0.59–0.62, WH 0.6–0.74, WF 0.34–0.38, EL 0.29–0.32, OOL 0.23–0.27, WOT 0.21–0.25, DAO 0.08–0.09, DPO 0.07–0.08, VOL 0.17–0.23, mesosoma 1–1.1, metasoma 1.5–1.72. Color. Head, mesosoma and metasoma dark castaneous; antenna and legs castaneous. Setation. Head with scarce and scattered setae, on gena few setae shorter than EL; flagellum with short and dense suberected setae; mesosoma and metasoma with scarce and scattered setation.
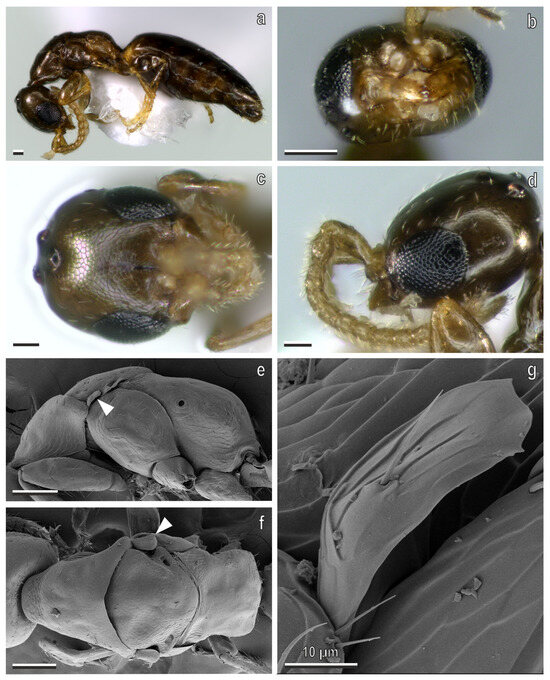
Figure 7.
S. cereicollis, micropterous male (reared specimen). (a) Habitus, lateral view; (b) head in anterior, (c) dorsal, and (d) lateral views; (e,f) scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of metasoma in (e) lateral and (f) dorsal views, showing the tegula (white arrowhead); (g) detail of the tegula. Scale bars: (a–f) 100 μm; (g) 10 μm.
Head (Figure 7b–d). Head quadrate, as long as wide, in dorsal view; globoid in lateral view, sides strongly outcurved, and parallel, not converging anterad or posterad; vertex moderately outcurved, in dorsal view; frons, vertex and gena imbricate, with few punctures; frontal line well-defined and short; mandible robust, with three apical teeth, dorsalmost one small, two ventral large and sharp; median clypeal lobe as long as lateral lobes, surface elevated medially; eye suboval, bulging, located laterally with gena not visible dorsally, next to mandibular base, and longer than half VOL; distance between torulus and eye 0.75× torulus width; LH 1.94–2.03× EL, WF 1.17–1.19× EL; ocelli present, forming equilateral triangle, anterior ocellus posterior to supra-ocular line, posterior ocelli close to vertex crest; scape slightly curved, wider apically, longer than EL, pedicel longer than flagellum, first two flagellomeres as long as wide, other flagellomeres longer than wide, distal one elliptical with acute apex.
Mesosoma (Figure 7e,f). Surface imbricate; dorsal pronotal area bell-shaped, wider than long, sides slightly incurved only posteriorly, posterior margin slightly incurved in dorsal view; mesoscutum wider than long, notaulus fully absent; parapsidal signum absent; mesoscutum totally fused with mesoscutellum, equilateral triangle-shaped, longer than wide, sides almost straight, posterior margin broadly rounded, and touching anterior margin of metapectal–propodeal disc; mesoscutum–scutellar suture absent; metanotum with metanotal trough and metanotal fovea strongly reduced; metapectal–propodeal disc trapezoidal, anterior margin slightly incurved, sides strongly incurved anteriorly and slightly outcurved posteriorly, tending to be parallel posterad in dorsal view; marginal edge between disc and lateral surface of metapectal–propodeal complex nearly perpendicular (∼90°) in posterior view, marginal edge between disc and posterior margins of metapectal–propodeal complex bluntly angled (90–180°), with outcurved dorsal margin, in lateral view, metapectal–propodeal disc wider than long, 0.65× as long as wide, shorter than mesoscutellum, latero-posterior corners rounded, smoothly curved, without distinct angle or point in postero-dorsal view; lateral marginal, metapostnotal median and posterior transverse carinae absent.
Metasoma. Stout; posterior margin of sternite IV–V with pair of longitudinal fissures.
Description, macropterous male (Figure 8a–j). Measurements (mm). Body 1.95–2.63, LH 0.40–0.49, WH 0.36–0.45, WF 0.21–0.27, EL 0.17–0.21, FWL 1.28, OOL 0.16–0.19, WOT 0.13–0.16, DAO 0.045, DPO 0.039 mm, VOL 0.153, mesosoma 0.68–1.01, metasoma 0.87–1.13. Color. Head, mesosoma, legs and metasoma dark castaneous, and antenna light castaneous; wings hyaline. Setation. Head with scarce and scattered setae, on gena few setae shorter than EL; flagellum with short and dense suberected setae; mesosoma and metasoma with scarce and scattered setation; forewing setation dense.
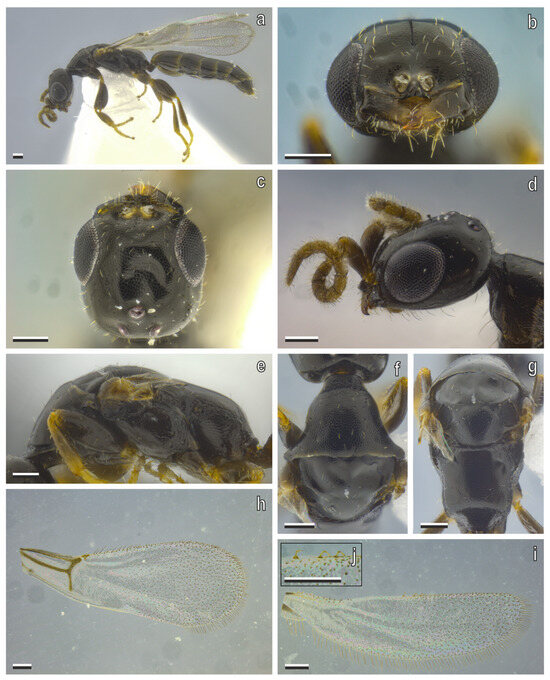

Figure 8.
S. cereicollis macropterous male (reared specimen). (a) Habitus, lateral view; (b) head in anterior, (c) dorsal, and (d) lateral views; (e) metasoma, lateral view; (f) pronotum, dorsal view; (g) mesonotum and metapectal–propodeal disc, dorsal view; (h) forewing, dorsal view; (i) hind wing, dorsal view; (j) hamuli. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Head (Figure 8b–d). Head rectangular or subrectangular, 1.1× as long as wide in dorsal view, globoid in lateral view, sides strongly outcurved, and parallel, not converging anterad or posterad; vertex moderately outcurved, in dorsal view; frons, vertex and gena imbricate, with few punctures; frontal line well-defined and short; mandible robust, with three apical teeth, dorsalmost one small, two ventral large and sharp; median clypeal lobe as long as lateral lobes, surface elevated medially; eye suboval, bulging, located laterally with gena not visible dorsally, next to mandibular base, and longer than half VOL; distance between torulus and eye 2.96× torulus width; LH 2.3× EL, WF 1.8–1.9× EL; ocelli present, forming equilateral triangle, anterior ocellus posterior to supra-ocular line, posterior ocelli close to vertex crest; scape slightly curved, wider apically, longer than EL, pedicel longer than flagellum, flagellomeres longer than wide, distal one elliptical with acute apex.
Mesosoma (Figure 8e–g). Surface imbricate; dorsal pronotal area bell-shaped, wider than long, sides slightly incurved only posteriorly, posterior margin nearly straight in dorsal view; mesoscutum wider than long, notaulus fully absent; parapsidal signum weak but complete; mesoscutellum equilateral triangle-shaped, longer than wide, sides almost straight, posterior margin broadly straight, and not touching anterior margin of metapectal–propodeal disc; mesoscutum–scutellar suture sulcate, evenly arched, ends not dilated; metanotum with metanotal trough and metanotal fovea strongly reduced; metapectal–propodeal disc trapezoidal, anterior margin nearly straight, sides slightly incurved anteriorly and slightly outcurved posteriorly, tending to slightly diverging posterad in dorsal view, anterior width 0.97× posterior width; marginal edge between disc and lateral surface of metapectal–propodeal complex nearly perpendicular (∼90°) in posterior view, marginal edge between disc and posterior margins of metapectal–propodeal complex bluntly angled (90–180°), with outcurved dorsal margin, in lateral view, metapectal–propodeal disc wider than long, 0.84× as long as wide, longer than mesoscutellum, latero-posterior corners rounded, smoothly curved, without distinct angle or point in postero-dorsal view; lateral marginal, metapostnotal median and posterior transverse carinae absent.
Wings (Figure 2a and Figure 8h–j). Costal vein (C) absent; median + cubital vein (M + Cu) present, nebulous basally; anal vein (A) present, nebulous in aspect for almost its entire extent, not joining end of cubito-anal vein (cu-a), cu-a present, long 2× Rs + M vein; costal cell (C) opened, by absence of costal vein; radial cell (R) closed, first cubital cell (1Cu) opened at posterodistal corner; pterostigma slender, prestigmal abscissa of radial 1 (R1) present, poststigmal abscissa of radial 1 (R1) absent; following cells absent: second radial cross & radial sector (2r-rs&Rs), radial sector (Rs), second radial 1 cell (2R1), first radial 1 cell (1R1); hind wing with three distal hamuli irregularly spaced.
Metasoma. Stout; posterior margin of sternite IV–V with pair of longitudinal fissures; hypopygeal posterior margin straight, or nearly so (Figure 2b). Genitalia (Figure 2c–e): harpe divided in two arms, with dorsal arm narrower and longer than ventral arm, in lateral view, dorsal arm apex posterior to ventral arm apex, in lateral view; cuspis wide, with apical margin outcurved; aedeagus with pair of pointed apical lobes; aedeagal apodeme narrow and elongated.
Variations among micropterous females. Type series: The head shape is subrectangular or rectangular among the type specimens. The metapectal–propodeal disc is variable in width, with lateral margins from lightly to moderately widening. Reared specimens: The body size is variable, with some specimens being extremely small (less than 2 mm). The head is highly variable in shape, ranging from subrectangular to rectangular (Figure 9a–d). The sides can be almost straight or slightly to strongly outcurved. They can also be parallel or slightly to strongly converging anterad. The metapectal–propodeal disc varies in shape among specimens, with the sides being slightly to strongly diverging posterad (Figure 9e–g).

Figure 9.
Morphological variations in micropterous females of reared specimens and the type series. Micropterous females of S. cereicollis reared in the university lab: (a–d) head and (e–g) mesosoma; (d) posterior ocelli (white arrowheads) in a micropterous female of S. cereicollis reared in the university lab; (h) forewings (white arrowhead) and undeveloped hind wing (black arrowhead) in a micropterous female of S. cereicollis (reared specimen), dorsal view. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Variations among macropterous females. The macropterous females of the field-collected specimens show the head subrectangular or rectangular with the posterior margin from straight to slightly outcurved. The metapectal–propodeal disc is tendentially homogenous in shape, with sides strongly outcurved posterad.
Variations among macropterous males. The population of S. cereicollis reared in the university laboratory also encompasses six specimens of micropterous males (Figure 7a–g).
Ecology and hosts. Sclerodermus cereicollis was discovered in Italy in natural association with the pupa of the buprestid beetle Capnodis tenebrionis (Linnaeus, 1761), commonly known as the Peach Flatheaded Rootborer [38]. It was also found on fig trees (Ficus carica Linnaeus) in association with the Yellow Longhorn Beetle, Psacothea hilaris hilaris (Pascoe, 1857) [59]. The stock laboratory culture of this species was reared on the following potential natural hosts: Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky, 1853), Anoplophora chinensis (Forster, 1771), Psacothea hilaris hilaris [24,59], Trichoferus holosericeus (Rossi, 1790) and Hylotrupes bajulus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) [23,27] and on a factitious host Corcyra cephalonica (Stainton, 1866) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) [23,26,27]. We also found this species in natural association with the longhorn beetle Xylotrechus stebbingi (Gahan, 1906) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae).
Distribution. The syntype series was collected in Giglio Island (Italy) [37]. The field specimens and the reared specimens were collected in North Italy around Milan [59]. This species was already reported for Italy [38].
Remarks. This species was identified as S. brevicornis in various scientific works [7,8,9,24,25,26,35,60].
3.2. Sclerodermus annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov.
Material examined. Type material. Holotype (here designated), micropterous female, labelled: EQUATORIAL GUINEA, Annobón Islands, April–May 1902, L. Fea col. (MCSN). Paratypes (here designated): 1 micropterous female and 1 macropterous female, same data as holotype.
Diagnosis. This new species is similar to Sclerodermus cadavericus. The main distinguishing characters from S. cadavericus are as follows: in the micropterous females of S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov. the sides of the head are parallel to slightly converging anterad and the posterior margin of the vertex is slightly outcurved; the dorsal pronotal area is longer than wide (Figure 10b,g).
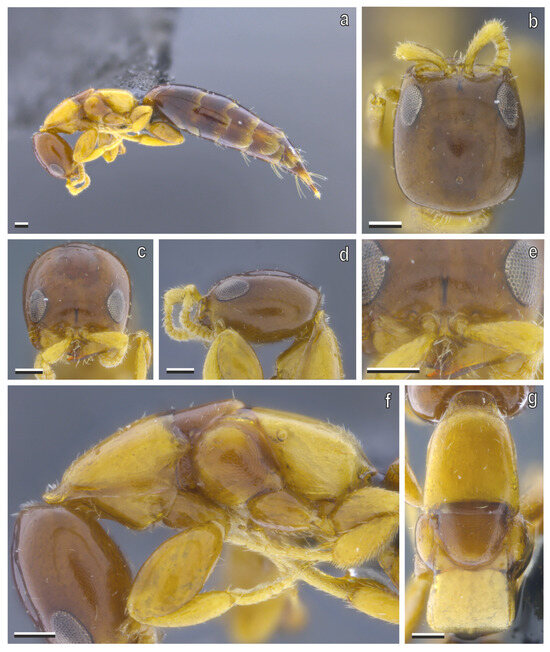
Figure 10.
S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov. micropterous female (holotype). (a) Habitus, lateral view; (b) head in dorsal, (c) anterior, and (d) lateral views; (e) detail of clypeus, anterior view; (f) mesosoma in lateral and (g) dorsal views. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Description, micropterous female (holotype). (Figure 10a–g) Measurements (mm). Body 3.13, LH 0.53, WH 0.5, WF 0.28, EL 0.16, VOL 0.31, mesosoma 1.0, metasoma 1.6. Color. Head, antenna, mesosoma, and legs light castaneous, metasoma castaneous. Setation. Head with scarce and scattered setae, on gena few setae shorter than EL; flagellum with short and dense suberected setae; mesosoma and metasoma with scarce and scattered setation.
Head (Figure 10b–e). Head rectangular, 1.13× as long as wide, in dorsal view; globoid in lateral view, sides slightly outcurved, and slightly converging anterad; posterior margin of vertex slightly outcurved in dorsal view; frons, vertex and gena imbricate, with few punctures; frontal line well-defined and short; mandible robust with three apical teeth, dorsalmost one small, two ventral large and sharp; median clypeal lobe as long as lateral lobes, surface elevated medially; eye subtriangular, flat, located dorso-laterally with gena visible dorsally, next to mandibular base, shorter than half VOL; distance between torulus and eye 2.2× torulus width; LH 3.59 EL, WF 1.8 EL scape slightly curved, wider apically, longer than EL, pedicel longer than flagellum, flagellomeres wider than long, except for distal one, which is elliptical with acute apex.
Mesosoma. (Figure 10f,g) Surface imbricate; dorsal pronotal area bell-shaped, longer than wide, sides straight or nearly so, posterior margin nearly straight; mesonotum isosceles triangle-shaped, sides almost straight, posterior margin rounded, wider than long, with its posterior margin touching anterior margin of metapectal–propodeal disc; metanotum without metanotal trough and metanotal fovea; metapectal–propodeal disc trapezoidal, anterior margin nearly outcurved, sides straight or nearly so, and tending to slightly diverging posterad, in dorsal view, anterior width rate 0.81× posterior width; marginal edge between disc and lateral surface of metapectal–propodeal complex bluntly right-angled (90–180°), in posterior view, marginal edge between disc and posterior margins rounded, forming single convexity, in lateral view, metapectal–propodeal disc 0.72× as long as width, shorter than mesonotum, latero-posterior corners rounded, smoothly curved, without distinct angle or point, in postero-dorsal view; lateral marginal, metapostnotal median and posterior transverse carinae absent.
Metasoma. Metasoma stout, posterior margin of sternite IV–V with pair of longitudinal fissures.
Description, macropterous female (paratype). (Figure 11a–f) Measurements (mm). Body 3.12, LH 0.52, WH 0.42, WF 0.23, EL 0.16, OOL 0.23, WOT 0.09, DAO 0.02, DPO 0.02, mesosoma 1.03, metasoma 1.6. Color. Head, mesosoma and metasoma castaneous, legs and antennae light castaneous, wings hyaline. Setation. Head with scarce and scattered setae, on gena few setae shorter than EL; flagellum with short and dense suberected setae; mesosoma and metasoma with scarce and scattered setation; forewing setation dense.
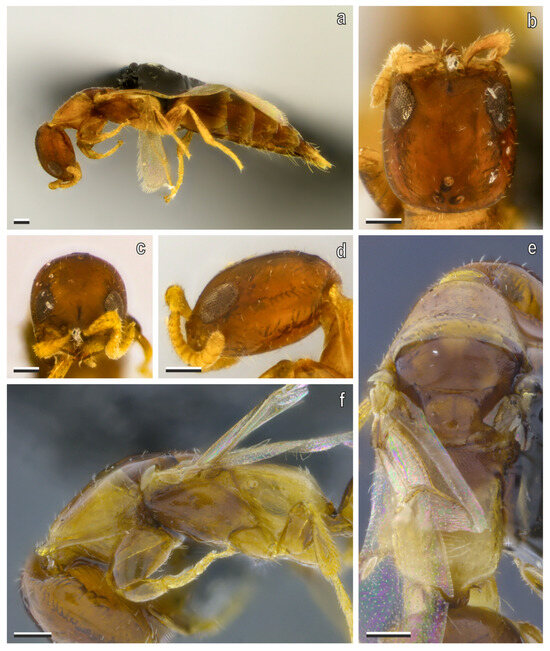

Figure 11.
S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov. macropterous female (paratype). (a) Habitus, lateral view; (b) head in dorsal, (c) anterior and (d) lateral views; (e) mesosoma in dorsal and (f) lateral views. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Head. (Figure 11b–d) Head rectangular, 1.16× as long as wide, in dorsal view, globoid in lateral view, sides slightly outcurved and moderately converging anterad; posterior margin of vertex slightly outcurved in dorsal view; frons, vertex and gena imbricate, with few punctures; frontal line well-defined and short; mandible robust with three apical teeth, dorsalmost one small, two ventral large and sharp; median clypeal lobe as long as lateral lobes, surface elevated medially; eye subtriangular, flat, dorso-laterally with gena visible dorsally, next to mandibular base, longer than half VOL; LH 2.73× EL, WF 1.6× EL; ocelli present, forming equilateral triangle, anterior ocellus posterior to supra-ocular line, lateral ocelli far from vertex by a length longer than DPO; scape slightly curved, wider apically, longer than EL, pedicel longer than flagellum, flagellomeres tendentially wider than long, except for the distal one, which is elliptical with acute apex.
Mesosoma. (Figure 11e,f) Surface imbricate; dorsal pronotal area bell-shaped, wider than long, sides slightly incurved only posteriorly, posterior margin nearly straight, mesoscutum wider than long, notaulus fully absent, parapsidal signum weak but complete; mesoscutellum isosceles triangle-shaped, longer than wide, sides almost straight, posterior margin rounded, not touching anterior margin of metapectal–propodeal disc; mesoscutum-mesoscutellar suture as thin line, and evenly arched, ends not dilated; metanotum with metanotal trough weakly developed and metanotal fovea absent; metapectal–propodeal disc trapezoidal, anterior margin nearly straight, sides straight or nearly so, and tending to slightly converging posterad in dorsal view, anterior width 1.13× posterior width; marginal edge between disc and lateral surface of metapectal–propodeal complex bluntly right-angled (90–180°), in posterior view, marginal edge between disc and posterior margins rounded, forming single convexity, in lateral view, metapectal–propodeal disc longer than wide, 1.3× as long as wide, longer than mesoscutellum, latero-posterior corners rounded, smoothly curved without distinct angle or point, in postero-dorsal view; lateral marginal; metapostnotal median and posterior transverse carinae absent.
Wings. Costal vein (C) absent, median + cubital vein (M + Cu) present, nebulous at the base; anal vein (A) present, nebulous in aspect for almost its entire extent, not joining end of cubito-anal vein (cu-a), cu-a present, long 2× the Rs + M vein; costal cell (C) opened, by absence of costal vein; radial cell (R) closed; first cubital cell (1Cu) opened at posterodistal corner; pterostigma slender, prestigmal abscissa of radial 1 (R1) present, poststigmal abscissa of radial 1 (R1) absent, following cells absent: second radial cross & radial sector (2r-rs&Rs), radial sector (Rs), second radial 1 cell (2R1) and first radial 1 cell (1R1); hind wing with three number of distal hamuli three, irregularly spaced.
Metasoma. Stout; posterior margin of sternite IV–V with pair of longitudinal fissures.
Variations among micropterous females. Type series: The Afrotropical holotype has only the anterior ocellus on the head (Figure 10b). The head shape is subrectangular or rectangular among the type specimens (Figure 10b and Figure 12d). The lateral margins of the head are from tendentially parallel to slightly converging anterad. The metapectal–propodeal disc is variable in width, with lateral margins from lightly to moderately widening posterad (Figure 10g and Figure 12e).

Figure 12.
S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov. micropterous female (paratype). (a) Habitus, lateral view; (b) mesosoma and head in lateral view; (c) head in anterior and (d) dorsal views; (e) mesosoma in dorsal view. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Variations among macropterous females. The macropterous female has the metapectal–propodeal disc with sides slightly converging posterad (Figure 11e), while S. cereicollis field specimens have the sides tendentially moderately diverging posterad (Figure 6f).
Ecology and host. This species was first reported in Annobón Island, Equatorial Guinea, Africa without an indication of the host, and then in Kinshasa, Dem. Rep. Congo, in this case, in association with unidentified xylophagous beetles infesting furniture [14].
Distribution. Annobón Island, Equatorial Guinea, Africa [37].
Remarks. The available material on S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov. consists of one macropterous female and two micropterous females. These specimens were identified by Kieffer [37] as S. cereicollis.
This species differs from the other Afrotropical species (S. pictiventris, S. wollastonii, and S. cadavericus) primarily in the shape of the head and the metapectal–propodeal disc (see the Identification key below and the Discussion). The holotype, consisting of the female, was designated, and the other specimens, one macropterous female and one macropterous female, as paratypes.
Bequaert (1924) reported specimens identified as S. cereicollis and attributed them as responsible for an outbreak of sting dermatitis in Kinshasa [14]. Our study provides the opportunity to hypothesize that the specimens involved in those dermatitis cases were probably not S. cereicollis, but rather the newly described species, S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov. It was not possible to study the specimens mentioned in this report.
Etymology. The specific epithet annobonensis refers to the type locality, Annobón Island.
3.3. Molecular Analyses
The COI sequences were successfully amplified from seven (6♀/1♂) out of the eleven sampled specimens (~64%).
The intraspecific genetic distance within S. cereicollis ranged from 0% to 3%, confirming genetic cohesion between the two field-collected populations, including both males and females, supporting their conspecific status (Table 1). The interspecific genetic distances between S. cereicollis and the other Sclerodermus species ranged from 3% to 20%. The smallest distance (3%) was observed between S. cereicollis and S. sichuanensis, S. guani, and S. pupariae, indicating their close evolutionary relationship. In contrast, the largest interspecific distance (20%) was detected between S. cereicollis and S. domesticus, demonstrating greater divergence, and the genetic distances between Sclerodermus and species from other genera (Plastanoxus and Prorops) ranged from 20% to 32%, reinforcing the clear genetic separation at the genus level (Table 1).

Table 1.
Pairwise genetic distances (K2P) between S. cereicollis and related species.
The ML tree (Figure 13) clustered all Sclerodermus species into a clade with high statistical support (bootstrap = 95.5%). Within this clade, the two newly sampled populations of S. cereicollis formed a single cluster, confirming that they belong to the same species. This clade, which also supported the male–female association, received strong bootstrap support (bootstrap = 92.4%), reinforcing the taxonomic identification.
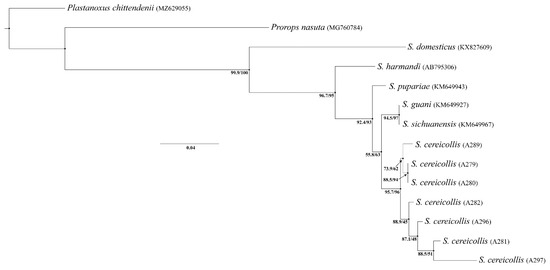
Figure 13.
A maximum likelihood tree based on the cytochrome c oxidase I (COI) sequence dataset. Ultrafast bootstrap values are given below the nodes. The tips are labeled with the specimen ID or GenBank accession number.
4. Discussion
The morphological analysis of the European and Afrotropical syntypes’ type series did not include genitalia or hypopygia, both of which are critical structures for reliable species identification in Bethylidae [1]. Notably, all the Afrotropical syntypes were female, and the male remains unknown. In addition, molecular analyses could not be performed on the syntype material due to preservation constraints. Morphological examination of the females revealed considerable variability in head shape (Figure 4c, Figure 10b and Figure 12d) and in the structure of the metapectal–propodeal disc (Figure 4b, Figure 10g and Figure 12e). This variation is also evident in the head (Figure 9a–d) and metapectal–propodeal disc (Figure 9e–g) of the field-collected specimens, which complicates the assessment of species boundaries based solely on these characters.
Despite this, distinct and consistent differences were observed between macropterous forms of the two syntype groups. The Afrotropical type specimens exhibit a slightly outcurved posterior head margin (Figure 11b), a trapezoidal mesonotum that is longer than wide with a broadly straight posterior margin, and a narrow mesoscuto–scutellar suture (Figure 11e). The metapectal–propodeal disc is 1.3× longer than it is wide, with nearly straight anterior and lateral margins that slightly converge posteriorly (Figure 11e). Its anterior width is 1.13× the posterior width. In contrast, the European field-collected specimens identified as S. cereicollis display a nearly straight vertex (Figure 6b), an equilateral-triangle-shaped mesonotum as long as it is wide, with a rounded posterior margin, and no visible mesoscuto–scutellar suture (Figure 6f). The metapectal–propodeal disc is 0.74× as long as it is wide, with an outwardly curved anterior margin and slightly incurved sides that diverge posteriorly (Figure 6f). The anterior width is only 0.74× the posterior width.
These consistent morphological distinctions, particularly in macropterous forms, support the hypothesis that the Afrotropical and the European syntype series represent distinct taxonomic entities.
Assigning both syntype groups to a single species would obscure true biological diversity and contradict both the biological and phylogenetic species concepts, which emphasize reproductive or evolutionary cohesion [40,61]. Recognizing the European syntypes as Sclerodermus cereicollis in a strict sense and describing the Afrotropical syntypes as a distinct species ensures taxonomic clarity and better reflects the observed morphological differences and biogeographic separation.
4.1. Taxonomic Identity of Sclerodermus cereicollis
The eastern Palaearctic region includes 24 species of Sclerodermus [39]. Examination of the European syntypes from Giglio Island confirmed that the field-collected specimens are conspecific with S. cereicollis, based on a set of diagnostic characters. These include a subrectangular head, with slightly outcurved sides that moderately converge anterad, and a slightly outcurved posterior margin of the vertex in dorsal view. Additional shared traits are the flagellomeres being wider than they are long (except for the last distal one) and a trapezoidal metapectal–propodeal disc that can strongly diverge posterad in the dorsal view (Figure 5g). In the field-collected specimens, the anterior width of the disc is 0.79× its posterior width, closely matching the lectotype, which shows a ratio of 0.75×.
Among the eastern Palaearctic species, S. cereicollis is most similar to S. ephippius Saunders, 1881. However, S. ephippius differs in several key morphological traits. It has a barrel-shaped head, as long as it is wide, with parallel sides, and subrounded eyes (Figure 14a). The dorsal pronotal area has nearly straight sides, and the mesonotum narrows more distinctly posterad, so that the posterior area is more distinctly narrow than the anterior area, which is wider than it is long, with sides that are almost straight (Figure 14d). In contrast, S. cereicollis possesses a subrectangular head, slightly longer than it is wide, with sides gently converging anterad, and elliptical eyes (Figure 14c). The sides of the dorsal pronotal area are incurved only posteriorly. The mesonotum shows minimal narrowing posterad, so that the posterior area is not significantly narrower than the anterior area. It is approximately as wide as it is long, with slightly outcurved sides and a broadly rounded posterior margin (Figure 14f).
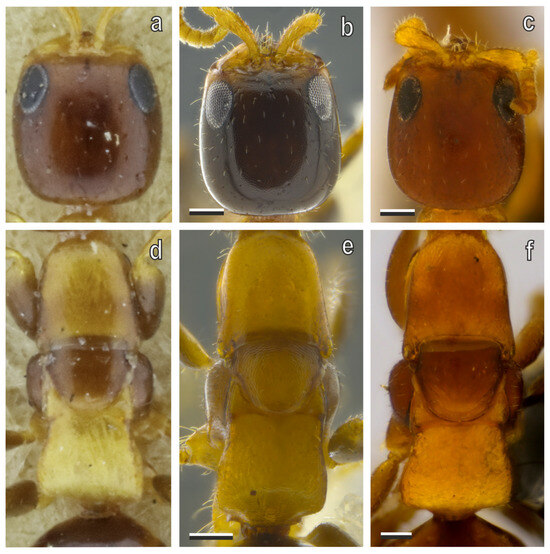

Figure 14.
(a–c) Head and (d–f) mesosoma in micropterous females of (a,d) S. ephippius, (b,e) S. cereicollis (reared specimens), and (c,f) S. cereicollis (lectotype), in dorsal view. Scale bars = 100 μm.
4.2. Genetic Evidence for Conspecificity of European Syntypes and Field Specimens
Molecular data derived from both males and female specimens of S. cereicollis, encompassing individuals from reared populations and field-collected material, support the conspecific status of these two groups. Intraspecific genetic distances ranged from 0% to 3% (Table 1), which is within the typical range reported for intraspecific variation in bethylid wasps [56,58]. This genetic cohesion is further corroborated by the ML phylogeny (Figure 9), where all individuals from both populations form a single, well-supported clade (Bootstrap = 92.4%), confirming their assignment to the same species.
Notably, one male (specimen A297) from field-collected material showed a genetic distance of exactly 3% when compared to some other conspecific specimens. This higher divergence may reflect natural intraspecific diversity, potentially accentuated by the species’ reproductive mode. Sclerodermus spp. reproduce via arrhenotokous parthenogenesis, whereby males develop from unfertilized eggs and may exhibit increased genetic variability relative to females [62].
Despite this minor divergence, the molecular evidence consistently indicates the absence of cryptic species or hidden genetic lineages between the two sampled populations. This molecular confirmation strengthens the morphological identification and validates the male–female association within S. cereicollis. Future analyses, incorporating a larger sample of males from different populations, could help assess whether this slight male-biased divergence is a recurrent pattern or an isolated observation.
4.3. Taxonomic Identity of Sclerodermus annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov.
Given that the Afrotropical group originates from Annobón Island, Equatorial Guinea, a comparative analysis was carried out with all currently described Afrotropical species of Sclerodermus. The Afrotropical fauna of this genus remains poorly studied, with only four species recorded from the region: S. pictiventris Kieffer, 1921 [63] (Sudan; Figure 15a–d), S. wollastonii Westwood, 1881 [22] (Saint Helena and Sierra Leone; Figure 15b–e), and S. cadavericus Benoit, 1957 [2] (Kenya, Uganda, and D.R. Congo; Figure 15c–f).
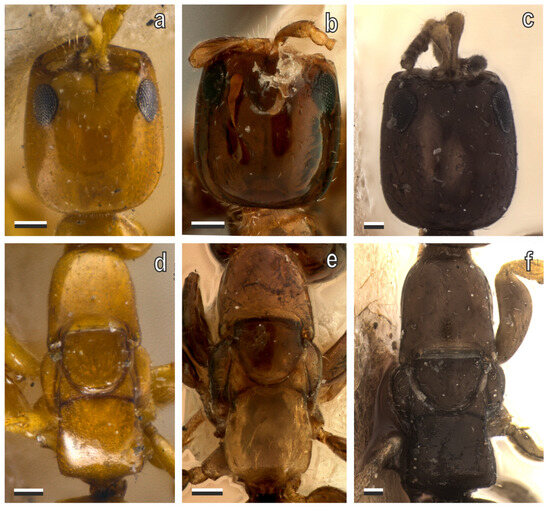

Figure 15.
(a–c) Head and (d–f) mesosoma in micropterous females of Afrotropical species of Sclerodermus (type specimens): (a,d) S. pictiventris (syntype); (b,e) S. wollastonii (syntype), and (c,f) S. cadavericus (holotype), in dorsal view. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Among these, the micropterous forms of the Afrotropical syntype series are most similar to S. cadavericus, particularly in the anterad converging head, the subrectangular dorsal pronotal area, and the trapezoidal shape of the metapectal–propodeal disc. However, several distinguishing characters are evident. The Afrotropical syntypes are notably smaller in size (1.89–3.12 mm) compared to S. cadavericus (up to 4 mm). In addition, the head of the former is slightly shorter with more outcurved sides; the eye is subtriangular and rounded, whereas in S. cadavericus, it is elongated and elliptical. The mesonotum of S. cereicollis is conspicuously wider posteriorly, in contrast to the narrowing observed in S. cadavericus. Furthermore, the metapectal–propodeal disc is shorter and less expanded posteriorly in S. cereicollis.
It is important to note that the type series of S. cadavericus includes only allotypes—genitalia and wings—but lacks macropterous specimens. Consequently, comparative analysis of macropterous forms for this species was not feasible.
Based on the above morphological comparisons, the Afrotropical syntype’s specimens do not correspond to any currently described Afrotropical species. Accordingly, a new species—Sclerodermus annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov.—is here described, and a holotype is designated from the original series.
The micropterous females of the Afrotropical species of Sclerodermus can be easily identified by the following key:
- 1.
- Head and metapectal–propodeal disc barrel-shaped (Figure 15b) … S. wollastonii Westwood, 1881
Head subrectangular or rectangular (Figure 10b); metapectal–propodeal disc trapezoidal (Figure 10g)… 2
- 2.
- Metapectal–propodeal disc with sides slightly divergent posterad (Figure 10g) … 3
Metapectal–propodeal disc with sides strongly divergent posterad (Figure 15f)… S. cadavericus Benoit, 1957
- 3.
- Head with sides nearly straight and strongly convergent anterad (Figure 15a) … S. pictiventris Kieffer, 1921
Head with sides slightly outcurved and slightly convergent anterad (Figure 10b) … S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov.
4.4. Comparative Morphology of Afrotropical Sclerodermus Species
4.4.1. Micropterous Forms
Size. Afrotropical species are generally similar in size, except for S. cadavericus, which is noticeably larger (about 4 mm).
Color. Although body color is highly variable at the intraspecific level [1], the syntypes of S. pictiventris are distinctly paler than those of other species and exhibit prominent dark spots on the metasoma. S. cadavericus also differs by having an overall darker body (Figure 15c,f), though only the holotype is currently available for this species.
Head. In Afrotropical species, the head is typically rectangular or nearly so, with sides that may be slightly outcurved. Exceptions include S. pictiventris (Figure 15a) and S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov. (Figure 10b), in which the sides are nearly parallel or slightly converging anterad. The posterior margin of the vertex is usually straight in S. pictiventris (Figure 15a) and S. wollastonii (Figure 15b), or slightly outcurved in S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov. (Figure 10b) and S. cadavericus (Figure 15c). In S. cereicollis, head shape shows greater intraspecific variability (Figure 4c and Figure 9a–d).
Mesosoma. The mesosoma is a key region for distinguishing species within the genus Sclerodermus, despite the general reduction of diagnostic characters typical of the subfamily Scleroderminae. Crucial areas include the mesosoma, which remains essential for recognizing species differences. Key areas include the dorsal pronotal area, the mesoscutum, and the metapectal–propodeal disc. These structures show significant variation in shape and direction of the anterior, lateral, and posterior sides.
The mesoscutum is usually equilateral-triangular, with rounded or slightly straight margins. In S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov. (Figure 10g), S. pictiventris (Figure 15d), and S. wollastonii (Figure 15e), the mesoscutum is more elongate, with rounded lateral and posterior margins, and is as long as it is wide. In S. wollastonii, it is typically longer than it is wide.
The sides of the metapectal–propodeal disc range from slightly to strongly divergent posterad, giving the disc a trapezoidal appearance. In S. cereicollis (a European species), these sides are variable from slightly to strongly divergent, whereas in most Afrotropical species (e.g., S. cadavericus, S. pictiventris, and S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov.), they are only slightly divergent. In S. wollastonii, the metapectal–propodeal disc is typically barrel-shaped, with fully outcurved sides (Figure 15e).
The posterior margin of the metapectal–propodeal complex is rounded in most Afrotropical species (e.g., S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov., S. pictiventris, S. wollastonii), forming a single convexity. In contrast, it appears bluntly angled in S. cadavericus when viewed laterally (Figure 15f). This character is particularly useful for distinguishing species. In many European species (e.g., S. brevicornis, S. domesticus, S. fasciatus Westwood, 1939, and S. cylindricus Westwood, 1839), the posterior margin is more or less angled. In some species, such as S. fasciatus and S. domesticus, the latero-posterior corners are pointed, forming distinct tips in the postero-dorsal view.
4.4.2. Macropterous Forms
Size and color. These are generally consistent with those observed in micropterous forms. However, macropterous individuals exhibit a different mesosoma architecture due to the presence of fully developed wings and the corresponding musculature. Macroptery occurs in both sexes. In Sclerodermus, males are typically macropterous and only rarely micropterous; females are predominantly micropterous, with macropterous individuals being rare. Macropterous forms have been observed in Afrotropical species types S. annobonensis sp. nov., S. pictiventris, and S. wollastonii. In S. cadavericus, only male allotypes are present.
Head. In macropterous forms, the head bears ocelli, typically located posterior to the supra-ocular line and situated close to the vertex in the Afrotropical species. The head shape is typically distinctive in S. wollastonii, where the sides are slightly outcurved and converge anteriorly, and the posterior margin of the vertex is moderately outcurved. In macropterous S. cadavericus, the mandible bears two apical teeth, whereas three are present in the other species [2].
Mesosoma. Mesosoma morphology varies between Afrotropical species. In the female of S. pictiventris, the pronotal dorsal area is notably distinct: the sides are strongly incurved posteriorly, and the posterior margin is also incurved.
In macropterous forms, the mesonotum is divided into the mesoscutum and the mesoscutellum. These structures differ across species in both shape and the development of the parapsidal signum. The notaulus is always absent. The parapsidal signum is generally weekly developed, except in S. pictiventris, where it is well-impressed on the tegument.
The mesoscutellum is trapezoidal in S. annobonensis sp. nov. and S. pictiventris—longer than wide in the former, and wider than long in the latter. In S. wollastonii, the mesoscutellum is more rounded and also wider than it is long.
The metapectal–propodeal complex also shows marked interspecific variation. In the dorsal view, it appears trapezoidal in S. annobonensis sp. nov. and S. wollastonii and more rectangular in S. pictiventris. The ratio between the anterior and the maximum posterior widths is 1.13 in S. annobonensis sp. nov., 1.10 in S. wollastonii, and 1.02 in S. pictiventris, consistent with its more rectangular shape.
Wings. Wing morphology is largely similar among Afrotropical species. In S. pictiventris, the anal vein is tubular along most of its length, whereas in other species, it becomes more nebulous distad. The hind wing bears three hamuli, with their spacing varying across species. In S. wollastonii, the hamuli are evenly spaced.
4.5. Morphological Variability, Wing Polymorphism, and Taxonomic Implications in Sclerodermus
In the present study, we observed a certain degree of variability concerning the presence or absence of wings and ocelli. Some micropterous specimens exhibited posterior ocelli along with a weakly developed anterior ocellus (Figure 9d), whereas the micropterous holotype of S. annobonensis sp. nov. possessed only the anterior ocellus (Figure 10b). This variability also extends to wing development. However, among the specimens examined for this study, only micropterous and macropterous individuals of both sexes were observed: no apterous specimens were recorded. In the smallest specimens, the tegulae could be discerned only by means of scanning electron microscopy (Figure 5i and Figure 7e–g). This raises doubt about the actual occurrence of apterous forms in other species of the genus Sclerodermus. Further studies are needed to clarify this issue and assess the extent of this morphological trait across the genus.
Significant morphological variability was also observed in the head and mesosoma, both in the type series and in the reared specimens (Figure 9a–g). This variation may be attributed to inbreeding. This phenomenon, together with arrhenotokous parthenogenesis, is an ecological strategy typical of the genus Sclerodermus [9,64] and many other parasitoid wasps, promoting reproductive success in environments where mates are scarce or populations are isolated [65]. However, this strategy also results in several morphological consequences: fluctuating asymmetry, malformations, alterations in secondary sexual traits, and color variations [66]. These pronounced morphological effects, particularly evident in reared specimens, could be a recurrent pattern in the Sclerodermus genus, characterized by inbreeding reproduction. A variability in specimen size was also observed in the reared population. According to Malabusini et al. (2024) [67], this variation does not appear to result from inbreeding, but rather from differences in host size.
Finally, such variability complicates species delimitation in the absence of comparative analyses of male genitalia and molecular investigations, which are often unfeasible when dealing with type series preserved in museum collections.
5. Conclusions
The integrative analysis of biogeographic, morphological, and—where available—molecular data supports the hypothesis that the original syntype series of Sclerodermus cereicollis comprises two distinct species. The European and Afrotropical syntypes are separated by substantial geographic and ecological barriers, exhibit consistent morphological divergence—particularly in macropterous forms—and, in the case of the European population, demonstrate clear genetic cohesion between historical types and recently collected field material. A lectotype has been designated, and the corresponding DNA sequence has been deposited in GenBank.
The formal description of the Afrotropical taxon as S. annobonensis Masini, Colombo & Azevedo sp. nov., with the designation of a new holotype, ensures taxonomic clarity and provides a more accurate representation of species diversity within the genus. Concurrently, the confirmation of conspecificity between the European syntypes and extant populations reaffirms the identity of S. cereicollis in a strict sense.
Collectively, these findings highlight the value of re-examining historical type material using modern integrative approaches to resolve cryptic diversity and uphold nomenclatural stability within the Bethylidae.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.M., W.D.C. and C.O.A.; methodology, W.D.C. and C.O.A.; formal analysis, P.M. and C.O.A.; investigation, P.M., G.S., M.R. and D.L.; data curation, C.O.A.; writing—original draft preparation, P.M. and C.O.A.; writing—review and editing, P.M., G.S., M.R., D.L., W.D.C. and C.O.A.; supervision, W.D.C. and C.O.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the editorial board and the anonymous reviewers who helped us improve the quality of this contribution. This contribution was supported by FAPES PRONEX #980/2022. WDC is grateful to the FAPES/CNPq PROTAX grant for providing undergraduate and post-doctoral fellowship bursaries. COA is grateful for a research fellowship provided by CNPq (grant #302613/2022-6). The PhD position of PM was partially funded by Ecotrade Solution Srl. We are grateful to Chirlei D. de Brito and Manuela Silva de Amorim, as well as to Bruno Bastos Won Rondon de Souza, Wilson José Marques Junior, João Lorenzo Mendes Nunes, and Leonardo Rezeda Pereira, and to Pedro Paulo Araújo Barbosa and Alexsander Prate Croci, for their valuable support during the morphological analysis of the specimens. We also thank Sharon Bianchi, Lucia Boccalini, Laura Brasher, Giulia Calzuola, Ludovica D’Andrea, Rosa Fittipaldi, Erica Holzer, Bita Hosseini, Riccardo Mannaioli, Francesco Pallini, Viola Prussiani, Giorgia Carboni Marri, Valerio Saitta, and Serena Malabusini for their significant contributions to the rearing of insect specimens. We express our sincere appreciation to the Universidade Federal do Espírito Santo (Brazil) for generously sharing their expertise on the taxonomy and phylogeny of bethylid wasps and for hosting Paolo Masini and providing all the necessary support during his research stay in Brazil. Finally, we gratefully acknowledge the support of the Erasmus + Program of the European Union, which partially funded PM’s international mobility and research activities during his stay in Brazil. Finally, we would like to express our sincere gratitude to the Natural History Museum “Giacomo Doria” in Genoa, and in particular to the Maria Tavano and Roberto Poggi, for kindly providing access to the type specimens studied. Their support and assistance have been invaluable for the completion of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BL | body length |
| COI | cytochrome c oxidase I |
| DAO | diameter of anterior ocellus |
| DPO | diameter of posterior ocellus |
| EL | eye length |
| FWL | forewing length |
| LH | length of head |
| MCSN | Museo Civico di Storia Naturale Giacomo Doria, Genoa, Italy |
| OOL | ocello–ocular line |
| UFES | Universidade Federal do Espírito Santo, Vitória, Brazil |
| UFMG | Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil |
| VOL | vertex–ocular line |
| WH | width of head |
| WOT | width of ocellar triangle |
References
- Azevedo, C.O.; Alencar, I.D.; Ramos, M.S.; Barbosa, D.N.; Colombo, W.D.; Vargas, J.M.; Lim, J. Global guide of the flat wasps (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae). Zootaxa 2018, 4489, 1–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, P.L.G. Un nouveau Sclerodermus vulnérant pur l’homme en Afrique Centrale (Hymenoptera-Bethylidae). Bull. Ann. Soc. R. Entomol. Belg. 1957, 93, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bridwell, J.C. Some Notes on Hawaiian and other Bethylidae (Hymenoptera) with the Description of a New Genus and Species. 2nd Paper. Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 1920, 4, 291–314. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, M.L.; Yang, Z.Q.; Zeng, F.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Bai, L.; Liu, S.J.; Sun, J. Biology and mass rearing of Sclerodermus pupariae Yang et Yao (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae), an important ectoparasitoid of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in China. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2008, 51, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Yao, Y.X.; Gould, J.R.; Cao, L.M. A new species of Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) parasitizing Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) from China, with a key to Chinese species in the genus. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2012, 105, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Sun, J. Recent advances in biological control of important native and invasive forest pests in China. Biol. Control China 2014, 68, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.K.; Lupi, D.; Jucker, C.; Hardy, I.C. Kinship effects in quasi-social parasitoids I: Co-foundress number and relatedness affect suppression of dangerous hosts. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 130, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.K.; Hardy, I.C.; Jucker, C.; Lupi, D. Kinship effects in quasi-social parasitoids II: Co-foundress relatedness and host dangerousness interactively affect host exploitation. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 130, 642–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabusini, S.; Lupi, D. Exploring the Biology of Quasi-Social Idiobiont Parasitoids in the Genus Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Insects 2024, 15, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Meng, L.; Kapranas, A.; Xu, F.; Hardy, I.C.W.; Li, B. Mutually beneficial host exploitation and ultra-biased sex ratios in quasisocial parasitoids. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stingeni, L.; Hansel, K.; Casciola, G.; Bianchi, L.; Tramontana, M.; Marietti, R.; Zampetti, S.; Napoli, F.; Miñón Llera, G.; Biancolini, F.; et al. Human ectoparasitosis by mites of the genus Pyemotes Amerling 1861 (Acarina: Pyemotidae). Ital. J. Dermatol. Venerol. 2023, 158, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahina, S. On a remarkable case of the biting of a parasitic wasp, Sclerodermus nipponensis Yuasa in Tokyo (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae). Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1953, 6, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, L. On an unusual parasitic dermatosis due to Sclerodermus brevicornis. Minerva Dermatol. 1967, 42, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bequaert, J. Un Hyménoptère Béthylide qui pique l’homme au Congo. Ann. Soc. Belg. Méd. Trop. 1924, 4, 163–165. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, F.; Jacquemin, P. Effets des piqures de Scleroderma (Hyménoptères Bethylidae) et revision des espèces nord-africaines. Bull. Soc. Hist. Nat. Afr. Nord. 1948, 39, 160–167. [Google Scholar]
- Marhic, E. Liste preliminaire des Bethylidae de France (Hymenoptera: Chrysidoidea). Osmia 2022, 10, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, P.; Stingeni, L.; Salerno, G.; Saitta, V.; Azevedo, C.O.; Rebora, M.; Ornielli, M.; Hansel, K.; Bianchi, L.; Casciola, G. Human ectoparasitoses by flat wasps of the genera Sclerodermus and Cephalonomia (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2025, 50, 1508–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, G.; Inghilesi, A.F.; Materassi, V.; Mazza, U.; Milanesi, N.; Cervo, R. Infestazioni da Sclerodermus domesticus Klug, 1809 e problematiche associate (Hymenopera: Behtylidae). Onychium 2014, 10, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, W.S. Insects, Ticks, Mites and Venomous Animals of Medical and Veterinary Importance. Part II. Public Health. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1931, 21, 701. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, G.A. A minute bethylid wasp of medical interest. Proc. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. Ser. A General Entomol. 1948, 23, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.O. XXXII. Monograph upon the Hymenopterous Genus Scleroderma. Trans. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1839, 2, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.O. VIII. Observations on the Hymenopterous genus Scleroderma, Klug, and some allied groups. Trans. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1881, 29, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, P.; Piersanti, S.; Lupi, D.; Salerno, G.; Rebora, M. Antennal chemoreceptors in the European ectoparasitoid Sclerodermus cereicollis (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2024, 87, 2275–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, D.; Favaro, R.; Jucker, C.; Azevedo, C.O.; Hardy, I.C.; Faccoli, M. Reproductive biology of Sclerodermus brevicornis, a European parasitoid developing on three species of invasive longhorn beetles. Biol. Control 2017, 105, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabusini, S.; Hardy, I.C.; Jucker, C.; Savoldelli, S.; Lupi, D. How many cooperators are too many? Foundress number, reproduction and sex ratio in a quasi-social parasitoid. Ecol. Entomol. 2022, 47, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabusini, S.; Hardy, C.V.; Jucker, C.; Guanzani, G.; Savoldelli, S.; Lupi, D. Reproductive performance effects of rearing the quasi-social parasitoid, Sclerodermus brevicornis (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae), on a factitious host. J. Insect Sci. 2023, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, P.; Austeri, L.; Rebora, M.; Piersanti, S.; de Francesco, F.; Salerno, G. Olfactory cues in the host-location of the European ecto-parasitoids Sclerodermus cereicollis and Sclerodermus domesticus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2024, 109, 102441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, C.O.; Vargas, J.M.; Colombo, W.D. Synopsis of world Discleroderma Kieffer (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae). Zootaxa 2020, 4742, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas R., J.M.; Colombo, W.D.; Azevedo, C.O. Revisited phylogeny of Scleroderminae (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) reveals a plastic evolutionary history. Arthropod Syst. Phylogeny 2020, 78, 217–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanes, G.; Azevedo, C.O. Phylogeny and Taxonomy of Sclerodermini (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae, Epyrinae). Insect Syst. Evol. 2008, 39, 55–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, W.D.; Azevedo, C.O. Revalidation of the polymorphic genus Acephalonomia (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) and description of a new species from Micronesia. Eur. J. Entomol. 2020, 117, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, K.; Yang, Z.; Jennings, D.E.; Duan, J.J. Effects of biotic and abiotic factors on phenotypic partitioning of wing morphology and development in Sclerodermus pupariae (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvarla, M.J. A review of Sclerodermus Latreille, 1809 (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) infestations and report of the first case in North America North of Mexico. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.K.; Lupi, D.; Hardy, I.C. Co-foundress confinement elicits kinship effects in a naturally sub-social parasitoid. J. Evol. Biol. 2020, 33, 1068–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, C.; Hardy, C.V.; Malabusini, S.; de Milato, S.; Zen, G.; Savoldelli, S.; Lupi, D. Factors affecting the reproduction and mass-rearing of Sclerodermus brevicornis (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae), a natural enemy of exotic flat-faced longhorn beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae: Lamiinae). Insects 2020, 11, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, C.O.; Colombo, W.D. Synopsis of the Neotropical Sclerodermus Latreille (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae) with description of a new species attacking human beings. Zootaxa 2022, 5124, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, J.J. Description de un nouveaux Dryniinae et Bethylinae du musée civic de génes. Ann. Mus. Civ. Storia Nat. Genova 1904, 1, 351–412. [Google Scholar]
- Marannino, P.; de Lillo, E. The peach flatheaded rootborer, Capnodis tenebrionis (L.), and its enemies. IOBC WPRS Bull. 2007, 30, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Gordh, G.; Moczar, L. A catalog of the world Bethylidae (Hymenoptera: Aculeata). Mem. Am. Entomol. Inst. 1990, 46, 1–364. [Google Scholar]
- Coyne, J.A.; Orr, H.A. Speciation; Sinauer Association: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.A. A glossary of surface sculpturing. Occas. Pap. Bur. Entomol. Calif. Dep. Agric. 1979, 28, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lanes, G.O.; Kawada, R.; Azevedo, C.O.; Brothers, D.J. Revisited morphology applied for systematics of flat wasps (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae). Zootaxa 2020, 4752, 1–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, R.; Buffington, M.L. A scalable and modular dome illumination system for scientific microphotography on a budget. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, A.B.; Waichert, C.; Barbosa, D.N.; Fagundes, V.; Azevedo, C.O. The use of proteinase K to access genitalia morphology, vouchering and DNA extraction in minute wasps. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2017, 89, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSIBLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Haeseler, A.V.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Haeseler, A.V. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. Figtree v1.4.3 [Computer Software]. Available online: https://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotides sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y. Molecular identification of sibling species of Sclerodermus (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) that parasitize buprestid and cerambycid beetles by using partial sequences of mitochondrial DNA cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 and 28S ribosomal RNA gene. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, W.D.; Waichert, C.; Azevedo, C.O. Molecular and Morphological Species Delimitation of Epyrinae (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae) from Papua New Guinea. In Insects of Mount Wilhelm, Papua New Guinea, 2nd ed.; Robillard, T., Legendre, F., Villemant, C., Leponce, M., Eds.; Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle: Paris, France, 2020; pp. 209–319. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.; Terayama, M.; Eguchi, K. Revision of Taiwanese and Ryukyuan species of Eleganesia Alencar & Azevedo, 2018 (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae). Zool. Anz. 2021, 294, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, W.J., Jr.; Colombo, W.D.; Azevedo, C.O. Insights into the systematics of Afrotropical Laelius (Hymenoptera, Bethylidae): Combining molecular and morphological data to associate dimorphic species. Zool. Anz. 2023, 306, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, D.; Bernardo, U.; Bonsignore, C.P.; Colombo, M.; Dindo, M.L.; Faccoli, M.; Ferracini, C.; Gualtieri, L.; Marullo, R.; Mazzon, L.; et al. Insects and globalization: Sustainable control of exotic species in Italian agro-forestry ecosystems. Landscape management for functional biodiversity. IOBC WPRS Bull. 2014, 100, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, M.K.; Jucker, C.; De Marchi, B.; Hardy, I.C.; Lupi, D. Performance of Sclerodermus brevicornis, a parasitoid of invasive longhorn beetles, when reared on rice moth larvae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2021, 169, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz, K. Species concepts and species delimitation. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannebakker, B.A.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Van Alphen, J.J.; Brakefield, P.M.; Zwaan, B.J. The genetic basis of male fertility in relation to haplodiploid reproduction in Leptopilina clavipes (Hymenoptera: Figitidae). Genetics 2004, 168, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieffer, J.J. Nouveaux Bethylides du Soudan Égyptien. Ann. Soc. Sci. Bruxelles. 1921, 40, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Maternal care in the parasitoid Sclerodermus harmandi (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Zwaan, B.J. Inbreeding and outbreeding depression in wild and captive insect populations. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2025, 70, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vayssade, C.; De Fazio, C.; Quaglietti, B.; Auguste, A.; Ris, N.; Fauvergue, X. Inbreeding depression in a parasitoid wasp with single-locus complementary sex determination. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malabusini, S.; Hardy, I.C.W.; Jucker, C.; Savoldelli, S.; Lupi, D. Multiple foundresses and multiple hosts: The influences of kinship and host quality on group reproduction in a quasi-social parasitoid. Ecol. Entomol. 2024, 49, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).