Abstract
The Dongting Lake wetland is an important habitat for rodents. In order to understand the structural characteristics of rodent communities and the effect of groundwater level on them, this study explored the changes in rodent community structure in four different habitats (Carex, Reeds, Carex + Reeds, and Poplar) from 2003 to 2023. Meanwhile, the relationships between groundwater level, nutrient composition of Carex brevicuspis, and structural characteristics of rodent communities were analyzed. The results showed that the advantages of rodent species in the four different habitats are different, and the community structure of rodents has undergone significant changes in recent years. A significant correlation between groundwater level and the nutrient composition of C. brevicuspis was found. Further analysis shows a significant correlation between the nutritional components of C. brevicuspis and the population structure of rodents. Crude protein, total phosphorus, and dry matter were three key plant nutrient indicators that were significantly correlated with both capture rate and the community diversity index (p < 0.05). Total phosphorus and crude protein were significantly negatively correlated with capture rate and Simpson’s index (p < 0.05), but significantly positively correlated with Pielou’s index and Shannon–Wiener’s index (p < 0.05), while the dry matter was completely opposite. The research conclusions suggest that different habitats and groundwater levels affect different characteristics of rodent community structures, and that plant nutrients are likely to be the mediator.
1. Introduction
Rodents are a vital part of the ecosystem and can be used as an important indicator for environmental monitoring [1]. Rodent community structures vary across ecosystems, which is the result of the interaction between internal factors of the species and external environmental factors [2]. In the process of the above interactions, information is transmitted, both at the individual scale and at the population scale. Exploring the mechanisms of rodent community formation is not only important for rodent management but also an important basis for evaluating ecosystem health. As the largest mammalian group, rodents have become an important model for the study of animal community mechanisms [3,4]. Research has shown that the number of rodent species increases with succession, and rodent species richness could be considered as a baseline of diversity indices in a variety of grassland habitats [5]. External biological factors, such as prey, are important factors affecting rodent communities. Temporary prey may bring about temporarily mixed animal groups, but current research is more concerned with the structural characteristics of stable mixed animal communities [6]. Research has emphasized that there might be particular value in heterospecifics of the same trophic level, because these species often require similar resources, need to avoid similar predators, and might impose lower competitive costs at close distances than conspecifics [7]. Plants also play an important role in the formation of rodent communities, providing not only a food source but also a hiding place for rodents. Studies have shown that changing plant species within habitats also results in important changes in rodent composition [8]. In addition to biotic factors, abiotic environmental factors such as temperature and rainfall also have important effects on rodent communities [9]. Temperature and maximum precipitation per day were identified as significant drivers of the rodent and shrew presence, which would also affect the already threatened Pannonic root vole [10].
Wetlands are biodiversity hotspots and important habitats for rodents [11]. Current attention to rodent communities is focused on habitats such as forests, agricultural fields, and grasslands, while attention to rodent communities in wetlands needs to be strengthened urgently [12]. Dongting Lake is located in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and is one of the most important storage lakes of the Yangtze River [13], which is also an important global biodiversity hotspot [14,15]. Mammals in the Dongting Lake area are dominated by rodents and Alexandromys fortis (formerly known as Microtus fortis) [16] and Apodemus agrarius are the most important rodent species in the region [17,18]. Rodents in the Dongting Lake region play a significant role in the local ecosystem. They not only have the potential to transmit diseases but also pose a threat to crops, causing biological disasters [19]. Previous studies have shown that ENSO-driven precipitation [20], vegetation coverage [21], and succession of rodent community structure are closely related. In recent years, research has shown that the structure of rodent communities in the Dongting Lake area has changed dramatically with the changes in environmental conditions, especially following the construction of the Three Gorges Project [22]. Before the construction of the Three Gorges Project, Dongting Lake beaches were dominated by A. fortis, which usually lived on the beaches and were forced to move into the farmland only during the high water season, causing disasters to crops [19]. In contrast to A. fortis, before the construction of the Three Gorges Project, A. agrarius mainly lived in the farmland around Dongting Lake and hardly ever entered the Dongting Lake beaches [17]. After the construction of the Three Gorges Project, the rodent community on the Dongting Lake beach changed significantly, especially characterized by the invasion of A. agrarius and the coexistence with A. fortis [23]. Different rodent species have different characteristics, and exploring the key driving factors of rodent community succession in the Dongting Lake wetland is a prerequisite for achieving rodent management in the region.
Water is a key environmental factor in wetland ecosystems, playing an important role in all ecological elements such as soil, vegetation, and animals [24]. Dramatic water level changes are one of the typical characteristics of Dongting Lake, and water level is one of the key environmental factors affecting the structure of biological communities in the area, including surface water level and groundwater level [25]. With the construction of the Three Gorges Dam, the hydrological characteristics of Dongting Lake have further changed significantly and have further important impacts on the biological communities [26]. The study showed that the typical vegetation area of Dongting Lake wetland clearly changed on the whole lake scale from 1985 to 2020, and the main hydrological variables affected the change of the area of Carex brevicuspis and Phragmites australis in Dongting Lake wetland [27]. Serving as a critical wintering habitat for migratory birds along the East Asian–Australasian Flyway, the analysis showed that water level changed the habitat suitability of migratory birds by changing vegetation distribution at different elevations [28]. Until now, the main focus of research on Dongting Lake has been on the impact of surface water level on vegetation communities, and there are no research reports on the relationship between groundwater level and rodent community characteristics in Dongting Lake. Research shows that the groundwater level has a significant impact on vegetation nutrition [29,30] and C. brevicuspis is also one of the main foods for both A. fortis and A. agrarius [31,32]. Based on the principle of material and information flow in ecosystems, this study hypothesizes that groundwater level is an important factor influencing the succession of rodent community structures in Dongting Lake and acts primarily through plants as a mediator.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Survey of Rodent Communities in Dongting Lake
The research group has long been concerned about the changes in the structure of the rodent community in Dongting Lake, and 18 typical long-term survey sites have been established around Dongting Lake [21], covering all rodent habitats in the area. Research ensures that the survey sites are evenly distributed along the coast of Dongting Lake, while randomly determining the specific locations of the survey points. Since 2003, when the construction of the Three Gorges Project was completed, four typical habitats (Carex, Reeds, Carex + Reeds, and Poplar) have been monitored to evaluate the succession characteristics of rodent communities in Dongting Lake (Figure S1). More details about the survey sites are shown in Table S1. Snap traps were used in the census, and fresh sunflower seeds were used as bait. Each mouse trap is spaced 5 m apart, with 100 traps placed on each sample line. Set up 3 survey lines at each survey site, with a minimum interval of 20 m between each survey line. Place mouse traps in the evening and retrieve them the next morning to count the species and quantities of rodents captured. The survey is conducted every quarter, unless the survey site is flooded or difficult to reach. Each rodent community survey at each survey site lasts for 3 days. More details of the survey process and survey locations are provided in our previous study [17]. During the survey process, the survey points are not absolutely consistent. In order to ensure the stability of the habitat, we will make acceptable adjustments to the survey points. Then, the associated rodent community indices, including the Simpson index, Shannon–Wiener index, and Pielou index, were calculated according to the following equation [33,34]:
- Capture rate
C is the population density (%), A is the number of rodents, and B is the number of effective snap traps.
- Simpson index
S is the number of rodent species comprising the community, Ni is the number of individuals captured of species i, and N is the total number of individuals captured.
- Shannon–Wiener index
- Pielou index
2.2. Data Collection on Groundwater Level in Dongting Lake
Day-by-day long-term monitoring of groundwater level data in Dongting Lake was conducted by Dongting Lake Station for Wetland Ecosystem Research, Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (29°30′ N, 112°48′ E) during 2019–2022. Low, medium, and high groundwater level monitoring points were set up at distances of 100 m, 1000 m, and 2000 m from the bank, respectively. At the same time, the study obtained the daily water level data of Dongting Lake from the website of Hunan Hydrology Public Service “One Map” (http://yzt.hnswkcj.com, accessed on 18 August 2025) from 2002 to 2023. Based on the above data, a linear regression model was established using the relationship between the groundwater level data and water level data of known years, and all groundwater level data of Dongting Lake were finally obtained.
2.3. Determination of Plant Constituents
Carex brevicuspis is the main plant species on the beaches of Dongting Lake and the most important food source for rodents [19,35]. Five 1 m × 1 m C. brevicuspis samples were set up at each groundwater level, with a parallel distance of about 200 m between each sample [35]. The habitat is Carex, and the plant samples were taken every month. The above-ground portion of all C. brevicuspis in the sampling was cut, and the collected C. brevicuspis samples were placed in large plastic bags. The time and place were recorded. Then, the plant samples were dried and ground for the determination of nutrient content. The dry matter [36], crude ash [37], neutral detergent fiber [38], acid detergent fiber [38], crude protein [39], and total phosphorus [40] of C. brevicuspis were determined with reference to standard methods for the determination of plant nutrient content [41].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The ANOVA and LSD were used to test the differences in nutritional components of C. brevicuspis between the different groundwater levels, and the above process was performed using SPSS 23.0 software. Pearson correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between the nutritional components of C. brevicuspis and community diversity index (Pielou, Shannon, and Simpson). The above correlation analysis process was conducted using Origin 2021. Data results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD), with p < 0.05 considered significant and p < 0.01 considered highly significant. The investigation process was authorized by the Dongting Lake Station for Wetland Ecosystem Research, Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and conducted under their supervision.
3. Result and Analysis
3.1. Capture Rate and Rodent Species in Different Habitats of the Dongting Lake Area
Habitat types of the Dongting Lake beach are complex, with a mosaic distribution among different types. Four typical habitats inhabited by rodents in Dongting Lake beach were selected to analyze the characteristics of the rodent community in the study: Carex, Reeds, Carex + Reeds, and Poplar (Figure 1 and Figure S1, Table S1). During the period 2003–2023, a total of 57,921 traps were placed on the beach of Dongting Lake in the study, capturing a total of 5931 rodents. A total of eight species of rodent were captured: A. agrarius, A. fortis, Micromys minutus, Niviventer confucianus, Niviventer fulvescens, Rattus losea, Rattus norvegicus, and Rattus tanezumi. Among them, A. agrarius and M. fortis have high capture rates and are the dominant rodent species on the beach of Dongting Lake. A total of six species of rodent were captured in the Carex habitat: A. agrarius, A. fortis, M. minutus, N. confucianus, R. losea, and R. norvegicus. Of these, the proportion of A. fortis was higher than that of other rodent species in the Carex habitat from 2005–2009, and after 2011, A. fortis, A. agrarius were the dominant rodent species (Figure S1). In the Reed habitat, a total of four species of rodent were captured: A. agrarius, A. fortis, M. minutus, and R. norvegicus. In 2003, only A. agrarius was captured, and A. agrarius and A. fortis together were the dominant species in the Reeds habitat from 2006 onwards. In the Carex + Reeds habitat, A. agrarius, A. fortis, M. minutus, and R. norvegicus were also captured, and A. agrarius and A. fortis were the dominant species. In the Poplar habitat, a total of seven species of rodents were captured: A. agrarius, A. fortis, N. confucianus, N. fulvescens, R. losea, R. norvegicus, and R. tanezumi, with A. fortis being the advantage species in 2007, and then A. agrarius was the advantage species in 2008 and beyond (Figure S1).
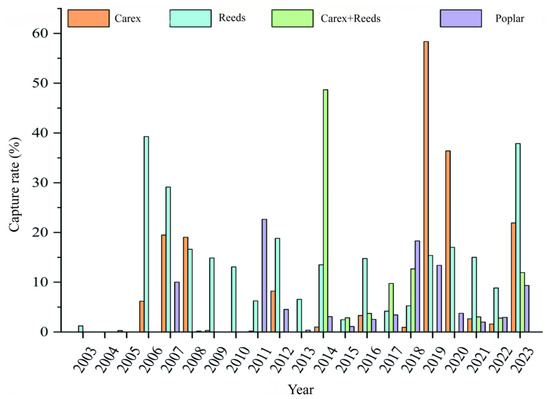
Figure 1.
Interannual variation of rodent capture rate in different habitats. Note: Carex, Reeds, Carex + Reeds, and Poplar specifically refer to the four typical habitats selected in the study.
3.2. Diversity Index of Rodent Communities in Different Habitats
Among the four typical habitats of the Dongting Lake beach, the poplar forest (Poplar habitat) was the most species-rich with seven species of rodents, while Reeds and Carex + Reeds had the fewest species (Table 1). In the Carex habitat, Shannon–Wiener index (0.3414) and Pielou index (0.1905) were the lowest, and Simpson index (0.8338) was high. The Reeds habitat was the complete opposite of the Carex habitat, possessing the highest Shannon–Wiener index (0.8315) and Pielou index (0.5998) and the lowest Simpson index (0.4669). Analyzing the diversity index relationship between different habitats (Table S2), the results showed that there was a highly significant correlation between different habitats (p < 0.05), except for the non-significant correlation between Carex + Reeds and Poplar habitats. Regression analysis of the three community diversity indices in different habitats showed significant negative correlation between the Simpson index and both the Shannon–Wiener index and the Pielou index (Figure S3, p < 0.05). The correlation between Pielou index and Shannon–Wiener index was positive but not significant (p > 0.05).

Table 1.
Diversity characteristics of rodent communities in different habitats.
3.3. Relationship Between the Groundwater Level and the Nutrient Composition of Plants
The effect of annual average groundwater level on the various nutrient compositions of C. brevicuspis was analyzed, and the results showed that groundwater level had different effects on different nutrients (Figure 2). The content of dry matter, crude ash, neutral detergent fiber, and acid detergent fiber all decreased and then increased with the increase in groundwater level, but the differences were not significant under different groundwater levels (p > 0.05). The crude protein content increased with increasing groundwater level, but the difference was not significant either (p > 0.05). Total phosphorus content decreased (p > 0.05) and then increased significantly (p < 0.05) with the increasing groundwater level. Pearson’s correlation analysis between annual groundwater level and nutrient composition of C. brevicuspis showed that crude protein and total phosphorus were highly significantly positively correlated with annual groundwater level (p < 0.01), while dry matter, crude ash, neutral detergent fiber, and acid detergent fiber were all negatively correlated with annual groundwater level (p < 0.01, Figure S4).
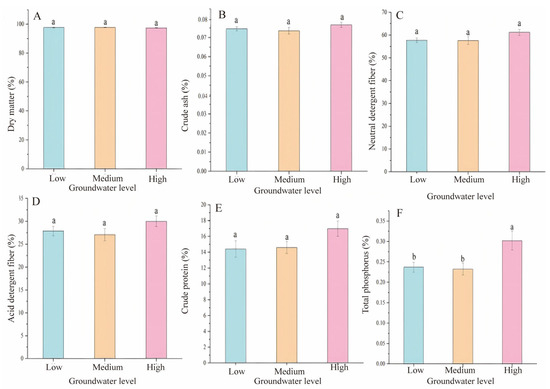
Figure 2.
Effects of different annual groundwater levels (low, medium, and high) on nutrient composition of C. brevicuspis. (A): dry matter; (B): crude ash; (C): neutral detergent fibers; (D): acidic detergent fibers; (E): crude protein; (F): total phosphorus. Note: The letters represent the results of one-way ANOVA, and completely different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.4. Relationship Between the Nutrient Composition of Plant and Rodent Communities
Correlation analysis of the nutrient composition of C. brevicuspis with community structure indicators of rodents in different habitats showed that the crude ash was not significantly related to either capture rate or the rodent community diversity index (p > 0.05), but other plant nutrients were significantly related to at least one diversity index (Figure 3). Acid detergent fiber and neutral detergent fiber were significantly and positively correlated with rodent capture rate (p < 0.05), with correlation coefficients of 0.51 and 0.42, respectively, but there was no significant relationship with community diversity indices (p > 0.05). Crude protein, total phosphorus, and dry matter were three key plant nutrient indicators that were significantly correlated with both capture rate and community diversity index (p < 0.05). Total phosphorus and crude protein were significantly negatively correlated with capture rate and Simpson’s index (p < 0.0), but significantly positively correlated with Pielou’s index and Shannon–Wiener’s index (p < 0.05), and the correlation coefficients varied little. Dry matter was completely opposite to total phosphorus and crude protein, and was significantly positively correlated with capture rate and Simpson’s index (p < 0.05), and significantly negatively correlated with Pielou’s index and Shannon–Wiener’s index (p < 0.05), but the correlation coefficients were all higher than those of total phosphorus and crude protein.
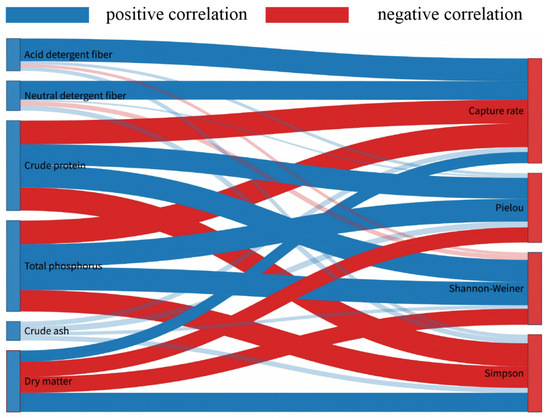
Figure 3.
Correlation between the rodent communities and the nutrient composition of C. brevicuspis in Dongting Lake. Red color indicates negative correlation, blue color indicates positive correlation, high transparency indicates non-significant (p > 0.05), and low transparency indicates significant correlation (p < 0.05).
3.5. The Relationship Between Groundwater Level and Rodent Communities
The correlation analysis between groundwater level and rodent community characteristics showed that there was no significant relationship between groundwater level and species number, capture rate, and community diversity index (p > 0.05, Figure S5). Further analysis of the impact of different groundwater levels in different habitats on the characteristics of rodent communities revealed that the effects vary across different habitats (Table 2). In the Poplar habitat, the capture rate, richness, and Shannon–Wiener index of the high groundwater level are the highest, but the Simpson index is the lowest. The capture rate, species number, and Simpson index of high groundwater level are relatively high in both the Carex and Reed habitats, but the Shannon–Wiener index and Pielou index are the smallest. In the Carex + Reeds habitat, the capture rate and Simpson index of high groundwater level are the highest, but the Shannon–Wiener index and Pielou index are the lowest.

Table 2.
Diversity characteristics of rodent communities by habitat groundwater level (low, medium, high).
4. Discussion
During the research period, significant changes occurred in the rodent communities in different habitats of the Dongting Lake beach. In the Carex habitat, from 2005 to 2009, A. fortis was the dominant species. After 2011, A. agrarius flooded into the lake beach and became the dominant species of the Carex habitat with A. fortis. In 2003, there was only A. agrarius in the Reeds habitat, but after 2006, both A. agrarius and A. fortis became dominant species in the Reeds habitat. In the Carex + Reeds habitat, A. fortis was the dominant species only in 2014 and 2021, while A. agrarius was the dominant species in other years. In the Poplar habitat, A. fortis was the dominant species in 2007, and A. agrarius was the absolute dominant species in 2008 and beyond. The changes in the community structure of rodents in different habitats mentioned above are closely related to the Three Gorges Project, which was constructed in 1994 and began storing water in 2003 [42]. The research results are consistent with Zheng Puyang et al. (2020), which suggest that the operation of the Three Gorges Project has changed the hydrological pattern of Dongting Lake. The changes in hydrological characteristics have led to changes in vegetation succession, further causing changes in the dynamics of the rodent communities in Dongting Lake [43]. In the study, the Shannon–Wiener indices of Reeds, Carex + Reeds, and Poplar were higher than those of the Carex habitat, which may be due to higher human interference in the above three habitats, and appropriate human interference can improve species diversity [44]. The changes in rodent communities should be given sufficient attention in order to achieve effective management of rodents. The harm caused to crops by A. fortis is stronger than that of A. agrarius [19], but the risk of disease transmission by A. agrarius is higher [45]. As A. agrarius expands between various habitats on the beach, more attention must be paid to the community succession to ensure human health. At the same time, previous studies have shown that due to factors such as environment and food, the reproductive characteristics of A. agrarius and A. fortis on the Dongting Lake beach are different [23]. Therefore, management measures for these two types of rodents are also different.
Carex spp., especially C. brevicuspis, is one of the important plant populations in the wetland ecosystem of Dongting Lake [19]. Carex spp. communities are of great significance for water balance and climate environment regulation in the region, and also provide food raw materials and habitats for rare birds, rodents, and fish [46]. In Dongting Lake, the Carex spp., which has the characteristics of high biomass and high nutritional value, sprouts and grows rapidly after the water recedes in November each year, and stops growing in May of the following year [47]. In wetland ecosystems, water level is often a key factor restricting vegetation growth and reproductive dynamics, which in turn has a decisive impact on vegetation succession, species richness, distribution patterns, and vegetation composition [48]. Previous studies have shown that the distribution of C. brevicuspis in Dongting Lake is closely related to water level, and changes in water level have a significant impact on the growth and clonal reproduction characteristics of C. brevicuspis at different elevations [48], but there has been less attention paid to groundwater level. During the dry season, the Carex spp. in the Dongting Lake area mainly relies on the supply of groundwater. Therefore, the groundwater level is an important environmental factor that determines the nutritional composition and distribution of Carex spp. In this study, the nutritional composition of C. brevicuspis varies at different groundwater levels, which can further affect rodents’ choices of food and habitat. Different nutrients in plants can have different effects on rodents. Protein is an essential nutrient for rodents to maintain their life, growth, development, and reproduction, and moderate protein in plants can improve the palatability, thereby benefiting population growth [49]. In this study, crude protein, total phosphorus, and the diversity index of rodent communities were significantly positively correlated, indicating that the above elements are beneficial for the maintenance of rodent communities. The research results further suggest that in the process and control of rodents, the community structure and species composition of plants in the ecosystem can be regulated to break the nutritional balance in rodents, ultimately achieving effective regulation of rodent populations [50]. Research suggests that planting crops with low sugar content makes it difficult to meet the nutritional needs of rodents and can reduce the population density of Lasiopodomys brandtii [51]. Based on the relationship between plants and rodents, the construction of sustainable agricultural and forestry ecosystems and the control of rodent hazards are increasingly being emphasized [52]. Previous studies have shown that the content of protein, fiber, and tannic acid has significant effects on the feeding behavior and reproduction of A. fortis [53]. However, these studies are limited to the laboratory and lack attention to how plant nutrition is transmitted to rodent communities in the wild. In recent years, C. brevicuspis in Dongting Lake has been mown in large quantities in winter, further altering the nutritional composition of the plant [54]. Long-term monitoring of changes in the nutrient composition of moss and rodent community structure in Dongting Lake is of great significance. On the other hand, there is also a drawback worth noting, which is that plant samples are not completely synchronized with rodent communities. It is necessary to provide fully synchronized data in subsequent research to obtain more reliable results.
Most rodents have a digging habit, so there is a close relationship between soil and rodents [55,56]. Groundwater can have a series of impacts on the structure of rodent communities through various media, such as soil and plants. This study demonstrates the possible pathways by which groundwater levels ultimately affect rodent communities by altering plant nutrient composition. The groundwater level can also affect the habitat preference of rodents by influencing soil physical and chemical properties. In the study, experiments were designed to explore habitat spaces, selecting for rodents under different water level conditions (Figure S6). Set three groundwater levels, high (−20 cm), medium (−40 cm), and low (−60 cm), respectively, and calculate the proportion of activity duration of A. fortis and A. agrarius in soil environments with different groundwater levels. The research results show that the activity duration of A. fortis and A. agrarius in the high groundwater level layer is significantly higher than that in the low groundwater level layer and the medium groundwater level layer (Figure 4, p < 0.01). Therefore, the differences in soil selection preferences between A. fortis and A. agrarius are smaller than the influence of vegetation on the above two mouse species through the groundwater level. It is necessary to pay more attention to the mechanism of groundwater level driving the succession of rodent communities.
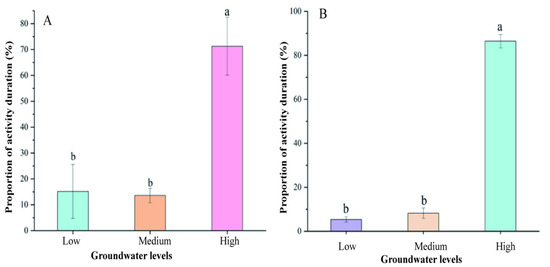
Figure 4.
The proportion of activity duration of A. fortis and A. agrarius in different groundwater levels. (A): A. fortis; (B): A. agrarius. Note: The letters represent the results of one-way ANOVA, and completely different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
The rodent community structure is a composite of the number of species, population size, and population distribution [3]. The community diversity index is an important aspect of measuring community structure, but there is currently no diversity index that can independently evaluate community structure, so many diversity indices are calculated [57]. Choosing different diversity indices may yield different results. For example, the Reciprocal Simpson Index is also an important diversity index [58]. If this index is chosen in this study, the relationship between plant nutrients and rodents is opposite to the Simpson index. Therefore, the above research results remind us that it is difficult to generalize the relationship between environmental factors and rodent community structures, and research should focus on specific diversity indices. There are still other challenges to conducting research on the structure of rodent communities, especially in terms of the long-term succession of rodent community structure. These challenges pose difficulties for the effective management of rodents. Rodents are different from plants, and their vigilance makes it possible for any environmental disturbance to affect monitoring results. For example, the temperature during the investigation period can affect the capture rate of rodents.
5. Conclusions
The Dongting Lake wetland is a typical freshwater lake wetland ecosystem in China. In recent years, there have been many outbreaks of rodent damage in the area, which have brought huge economic losses. Carex brevicuspis is an important food source for rodents inhabiting the lake beach, and groundwater indirectly affects the growth of C. brevicuspis by directly regulating soil. Through long-term monitoring of rodent communities in four typical habitats on the Dongting Lake beach, it has been confirmed that rodent communities vary in different habitats. With the impact of the Three Gorges Project on the hydrological pattern of Dongting Lake, significant changes have occurred in the composition of rodents in all four habitats. Further analysis of the impact of groundwater on the nutritional composition of C. brevicuspis revealed that crude protein and total phosphorus showed highly significant positive correlations with annual groundwater levels. Research has shown a significant correlation between plant nutritional components and rodent community structure, particularly in terms of crude protein and total phosphorus content. Different habitats and groundwater levels have different characteristics of rodent community structure, and plant nutrients are likely to be the link between groundwater levels and rodent communities in the Dongting Lake area. The research results further suggest that in the process and control of rodents, the community structure and species composition of plants in the ecosystem can be regulated to break the nutritional balance in rodents, ultimately achieving effective regulation of rodent populations. Exploring the drivers of changes in rodent community structure in Dongting Lake is the theoretical basis for effective management of rodent populations in the region.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d17080587/s1, Figure S1. Typical habitat of Dongting Lake beach; Figure S2. The interannual variation of the proportion of rodent species in different habitats; Figure S3. Regression analysis between two indices (A) relationship between Pielou index and Shannon-Wiener index, (B) relationship between Simpson index and Shannon-Wiener index, (C) relationship between Simpson index and Pielou index; Figure S4. Correlation between mean annual groundwater level change and C. brevicuspis nutrient composition; Figure S5. Correlation between annual groundwater levels and the community structure of lake beach rodents in Dongting Lake; Figure S6. Experimental design of selection bias of A. fortis and A. agrarius on soils with different groundwater level; Table S1. The details about the survey sites in the study; Table S2. Comparison of diversity index of rodent communities in different habitats (t-test).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z., X.N. and Z.X.; methodology, Y.H., C.Z., and M.Z.; software, Y.H.; formal analysis, Y.H.; investigation, Y.H., C.Z. and M.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, T.H., Y.H., and T.Y.; writing—review and editing, T.H., J.L. and Z.X.; supervision, Y.Z., Z.H. and Z.X.; project administration, Z.H. and Z.X.; funding acquisition, T.H., X.N., M.Z. and Z.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, grant number 2022YFD1400400; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number U20A20118; the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, grant number 2024JJ5064; the College Students’ Innovative Entrepreneurial Training Plan Program of Shaanxi Province, grant number XN2025006031; and the Open Fund of the Hunan Engineering Research Center of Ecological Environment Intelligent Monitoring and Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Technology in Dongting Lake, grant number 2022-DTH-01. The APC was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences (protocol code U20A20118, 1 January 2020).
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Douglass, R.J. Assessment of the use of selected rodents in ecological monitoring. Environ. Manag. 1989, 13, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchella, D.J.; Scott, M.E. Parasitism: A cryptic determinant of animal community structure. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1991, 6, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.S. Desert Rodent Community Structure: A Test of Four Mechanisms of Coexistence. Ecol. Monogr. 1989, 59, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, L.; Henttonen, H. Rodent dynamics as community processes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1988, 3, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenant, N.L.; Cavallini, P. Correlating rodent community structure with ecological integrity, Tussen-die-Riviere Nature Reserve, Free State province, South Africa. Integr. Zool. 2007, 2, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodale, E.; Sridhar, H.; Sieving, K.E.; Bangal, P.; Colorado, Z.G.J.; Farine, D.R.; Heymann, E.W.; Jones, H.H.; Krams, I.; Martínez, A.E.; et al. Mixed company: A framework for understanding the composition and organization of mixed-species animal groups. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 889–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodale, E.; Beauchamp, G.; Magrath, R.D.; Nieh, J.C.; Ruxton, G.D. Interspecific information transfer influences animal community structure. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.L.; Homyack, J.A.; Wigley, T.B.; Miller, D.A.; Kalcounis-Rueppell, M.C. Effects of habitat modification on cotton rat population dynamics and rodent community structure. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 376, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura-Rojas, P.D.; González-Romero, A.; Moreno, C.E.; Sosa, V.J. Effect of rainfall, temperature and climate change on the ecology of the rodents of arid zones: A review. Mammal Rev. 2025, 55, e12372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefke, K.; Landler, L. Long-term monitoring of rodent and shrew communities in a biodiversity hot-spot in Austria using barn owl (Tyto alba) pellets. Acta Oecologica 2020, 109, 103660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, K.L.; Rota, C.T.; Frantz, M.W.; Anderson, J.T. Restored Wetland Size and Age Influence Small Mammal Communities in West Virginia, USA. Wetlands 2024, 44, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliwicz, J. Competitive Interactions within a Forest Rodent Community in Central Poland. Oikos 1981, 37, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Fang, H.; Zhang, L.; Su, X.; Fu, X.; Huang, H.Q.; Parker, G.; Hassan, M.A.; Meghani, N.A.; Anders, A.M.; et al. Poyang and Dongting Lakes, Yangtze River: Tributary lakes blocked by main-stem aggradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2101384119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, D.; Jin, X.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Pellissier, L.; Johnson, A.C.; Wu, F.; Zhang, X. Long-term wetland biomonitoring highlights the differential impact of land use on macroinvertebrate diversity in Dongting Lake in China. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Jin, X.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, J.; Yi, P. The relationship between landscape pattern and plant species diversity in east Dongting lake wetland based on different Eco-environment. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 355, 124187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissovsky, A.A.; Petrova, T.V.; Yatsentyuk, S.P.; Golenishchev, F.N.; Putincev, N.I.; Kartavtseva, I.V.; Sheremetyeva, I.N.; Abramson, N.I. Multilocus phylogeny and taxonomy of East Asian voles Alexandromys (Rodentia, Arvicolinae). Zool. Scr. 2018, 47, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z. Synergistic succession of the small mammal community and herbaceous vegetation after reconverting farmland to seasonally flooded wetlands in the Dongting Lake Region, China. Mammal Study 2018, 43, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.; Mei-Wen, Z.; Bo, L.I.; Kai-Rong, W. Rodent community structure and succession in different ecotypic areas in Dongting Lake region. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2003, 19, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; Shen, G.; Wang, Y. Habitat evaluation for outbreak of Yangtze voles (Microtus fortis) and management implications. Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Effect of ENSO-driven precipitation on population irruptions of the Yangtze vole Microtus fortis calamorum in the Dongting Lake region of China. Integr. Zool. 2010, 5, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Nan, X.; Hu, Z.; Xu, Z. Effects of Vegetation Cover on Community Structure of Rodents Based on Long Time Series from Dongting Lake, China. Biology 2025, 14, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Guo, C.; Huang, G.; Shen, G.; Zhou, X. Small mammal community succession on the beach of Dongting Lake, China after the Three Gorges Project. Integr. Zool. 2014, 9, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, G.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, X.; Huang, H. The reproductive status of Apodemus agrarius populations inhabiting the lake beach in Lake Dongting area after Three Gorges Project. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar]
- Jolly, I.D.; McEwan, K.L.; Holland, K.L. A review of groundwater–surface water interactions in arid/semi-arid wetlands and the consequences of salinity for wetland ecology. Ecohydrology 2008, 1, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zhang, S.; Huang, G.; Zhang, R. Analysis of Long-Term Water Level Variation in Dongting Lake, China. Water 2016, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Chen, H.; Hou, Y.; Finlayson, B.; Li, M.; Chen, J. Lowering water level of Dongting lake of the Mid-Yangtze River in response to large-scale dam construction: A 60-year analysis. Geomorphology 2021, 391, 107894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, D.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Luan, Z. Typical vegetation dynamics and hydrological changes of Dongting Lake wetland from 1985 to 2020. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2024, 24, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, W. The impacts of water level fluctuations of East Dongting Lake on habitat suitability of migratory birds. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatert, N.; Sanchez-Pérez, J.M.; Trémolières, M. Spatial and temporal variations of nutrient concentration in the groundwater of a floodplain: Effect of hydrology, vegetation and substrate. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1511–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Li, G.; Li, J. Dominant roles but distinct effects of groundwater depth on regulating leaf and fine-root N, P and N:P ratios of plant communities. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 14, 1158–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.Y.; Zhang, M.W.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Li, J.X.; Yang, Y.C.; Xu, Z.G. Dietary Habit of Apodemus agrarius in Dongting Lake Area. Chin. J. Zool. 2012, 47, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, F.; Yunlin, Z.; Meiwen, Z.; Yong, W.; Zhenggang, X.; Jiao, P. Research on feeding of laboratory-bred adult Microtus fortis calamorum on carex. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2016, 27, 546–548. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell. Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellerberg, I.F.; Fedor, P.J. A tribute to Claude Shannon (1916–2001) and a plea for more rigorous use of species richness, species diversity and the ‘Shannon–Wiener’ Index. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, 12, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, X.-S.; Zou, Y.-A.; Zhang, P.-Y.; Li, F.; Hou, Z.-Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, J.; Deng, Z.-M.; Zhong, J.-R.; et al. Exploring the relative contribution of flood regimes and climatic factors to Carex phenology in a Yangtze River-connected floodplain wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiex, N.J.; Erem, T.V. Determination of Water (Moisture) and Dry Matter in Animal Feed, Grain, and Forage (Plant Tissue) by Karl Fischer Titration: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 85, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, H.J.; Tilden, D. Report on Ash in Fruit Products. J. Assoc. Off. Agric. Chem. 2020, 10, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman, M.M.; Lane, S.A. Comparison of Dietary Fiber Methods for Foods. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 2020, 64, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiex, N. Evaluation of Analytical Methods for the Determination of Moisture, Crude Protein, Crude Fat, and Crude Fiber in Distillers Dried Grains with Solubles. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 92, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, K.D.; Hoffman, W.M. Report on Phosphorus in Fertilizers: I. Preparation of Solution of Sample for Total Phosphorus Determination. J. Assoc. Off. Agric. Chem. 2020, 40, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Dai, E.; Luobu, D.; Fu, G. Effects of Climate Change and Fencing on Forage Nutrition Quality of Alpine Grasslands in the Northern Tibet. Plants 2023, 12, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.-Y.; Xie, Y.-H.; Tang, Y.; Li, F.; Zou, Y.-A. Changes of Vegetation Distribution in the East Dongting Lake After the Operation of the Three Gorges Dam, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J. The Situation of Small Mammal Community in Beach of Dongting Lake after the Official Operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Chin. J. Zool. 2020, 55, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Gu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Teng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. High seed diversity and availability increase rodent community stability under human disturbance and climate variation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Jiao, S.; Li, Z.; Yi, B.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Hu, F.; et al. Apodemus agrarius is a potential natural host of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS)—Causing novel bunyavirus. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 71, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Z.; He, R.; Wang, S.; Guo, Z. Analysis on Nutritional Content in Different Part of Carex brevicuspis in Dongting Lake. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2016, 305–307. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.-S.; Xie, Y.-H.; Deng, Z.-M.; Li, F.; Hou, Z.-Y. A change from phalanx to guerrilla growth form is an effective strategy to acclimate to sedimentation in a wetland sedge species Carex brevicuspis (Cyperaceae). Flora-Morphol. Distrib. Funct. Ecol. Plants 2011, 206, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xiang, W.; Xie, Y. Effects of water levels on the growth and reproductive characteristics of Carex brevicuspis growing on sites with different elevations. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Chen, J. Effects of Fat and Protein Levels on Foraging Preferences of Tannin in Scatter-Hoarding Rodents. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, E.M.; Neby, M. Small rodent population cycles and plants—After 70 years, where do we go? Biol. Rev. 2024, 99, 265–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, D.H. Thermogenesis, food intake and serum leptin in cold-exposed lactating Brandt’s voles Lasiopodomys brandtii. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurišić, A.; Ćupina, A.I.; Kavran, M.; Potkonjak, A.; Ivanović, I.; Bjelić-Čabrilo, O.; Meseldžija, M.; Dudić, M.; Poljaković-Pajnik, L.; Vasić, V. Surveillance Strategies of Rodents in Agroecosystems, Forestry and Urban Environments. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Wang, Y.; Deng, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Effects of protein, fiber, and tannic acid on food intake of Microtus fortis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 941–948. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Xia, L.; Pan, B.; Zou, Y.; Li, F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Mowing of Carex brevicuspis (Cyperaceae) improves food quality for herbivorous geese in Dongting Lake: The potential mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1566808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, C.; Dodaro, G.; Di Bagno, E.; Amori, G. Reviewing an eco-biogeographic question at regional scale: The unexpected absence of a ubiquitous mammal species (Microtus savii, Rodentia) in coastal Southern Tuscany (central Italy). Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. E Nat. 2019, 30, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, C.; Dodaro, G.; Di Bagno, E.; Amori, G. Small mammal assemblages in land-reclaimed areas: Do historical soil use changes and recent anthropisation affect their dominance structure? Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 32, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.D.; Tello, J.S. Diversity begets diversity: Relative roles of structural and resource heterogeneity in determining rodent community structure. J. Mammal. 2011, 92, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, R. Combining richness and abundance into a single diversity index using matrix analogues of Shannon’s and Simpson’s indices. Ecography 2006, 29, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).