Farmland Biodiversity Monitoring Using DNA Metabarcoding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
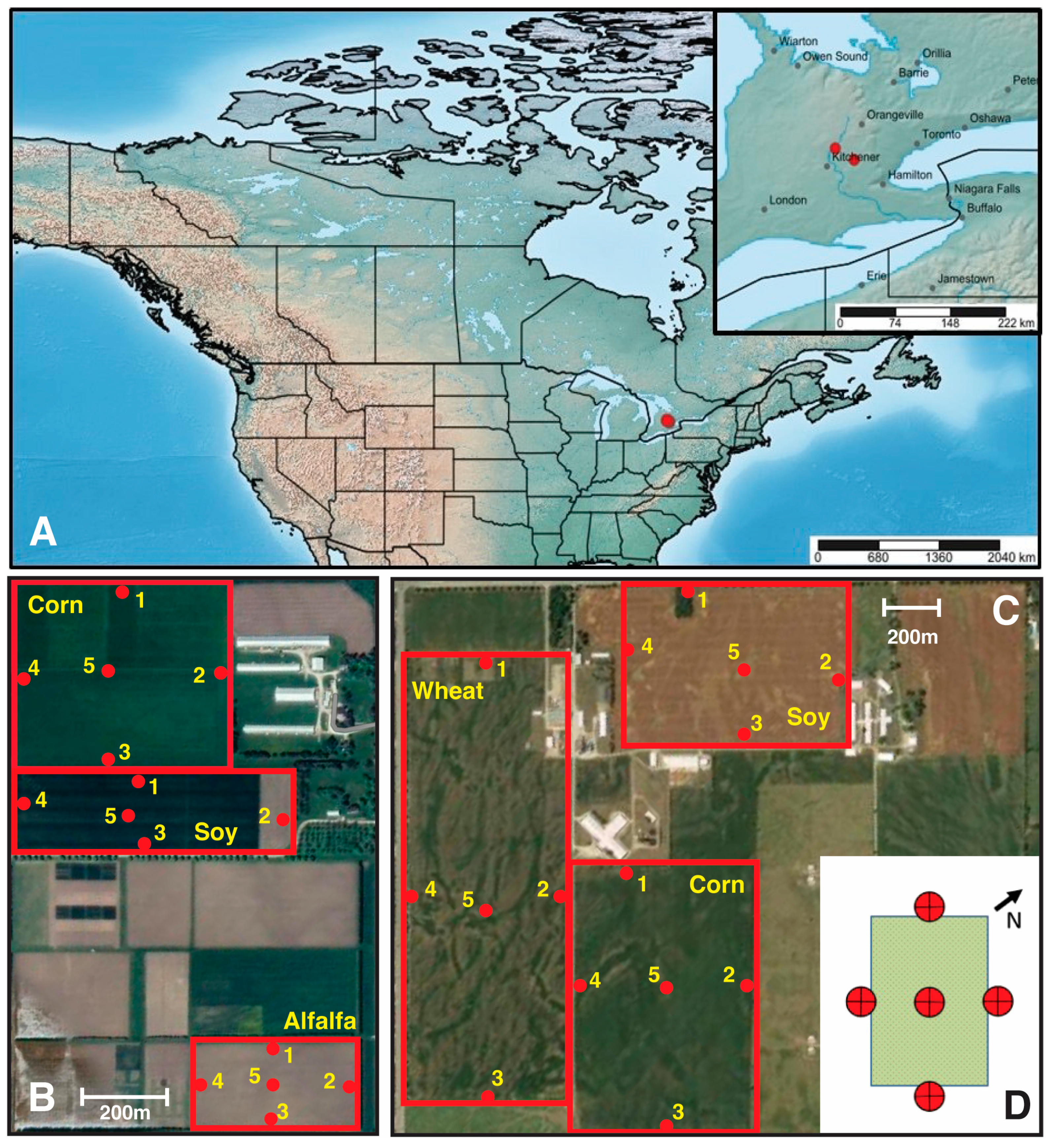
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Reference Library Assembly
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR
2.4. HTS Library Construction
2.5. Data Analysis
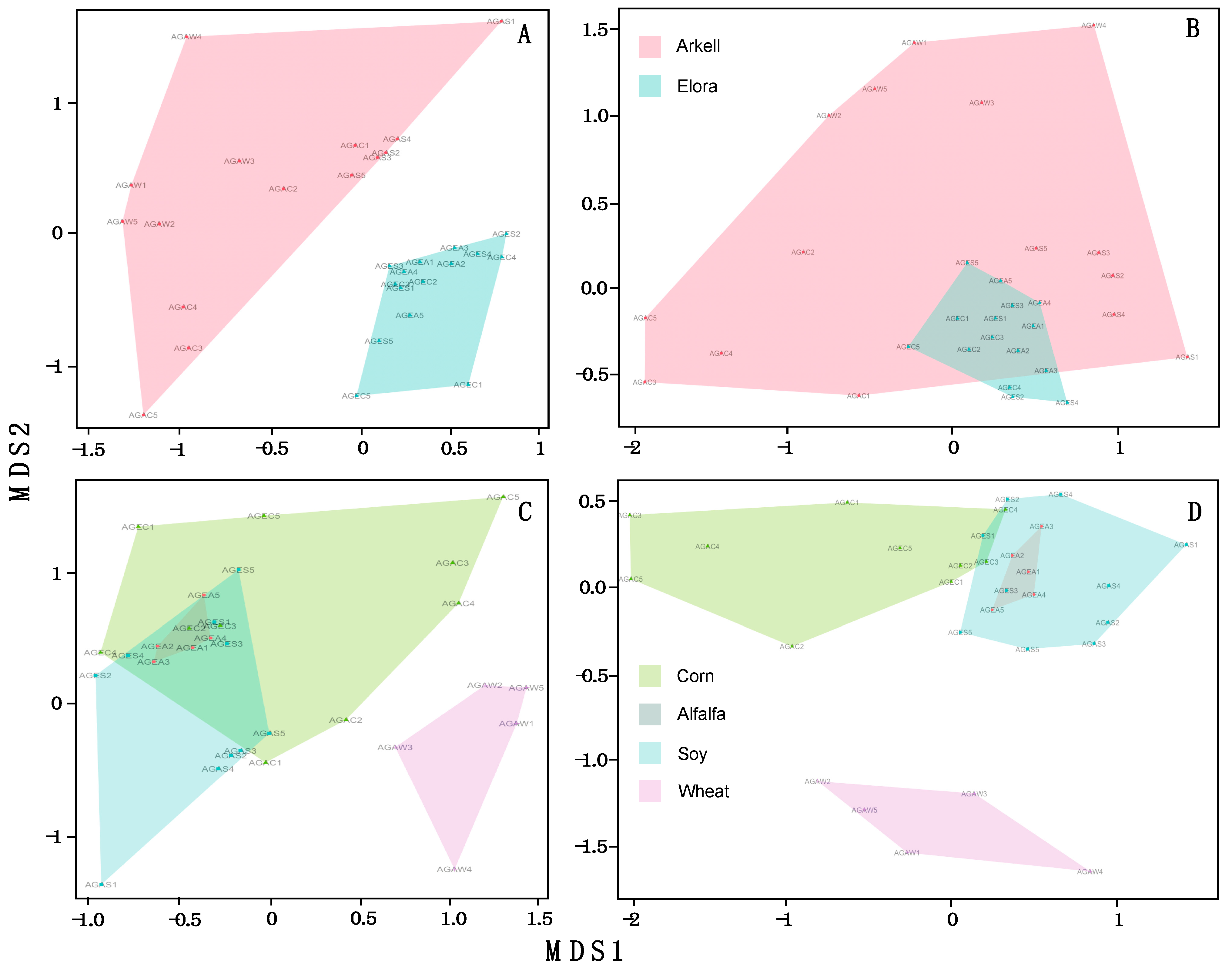
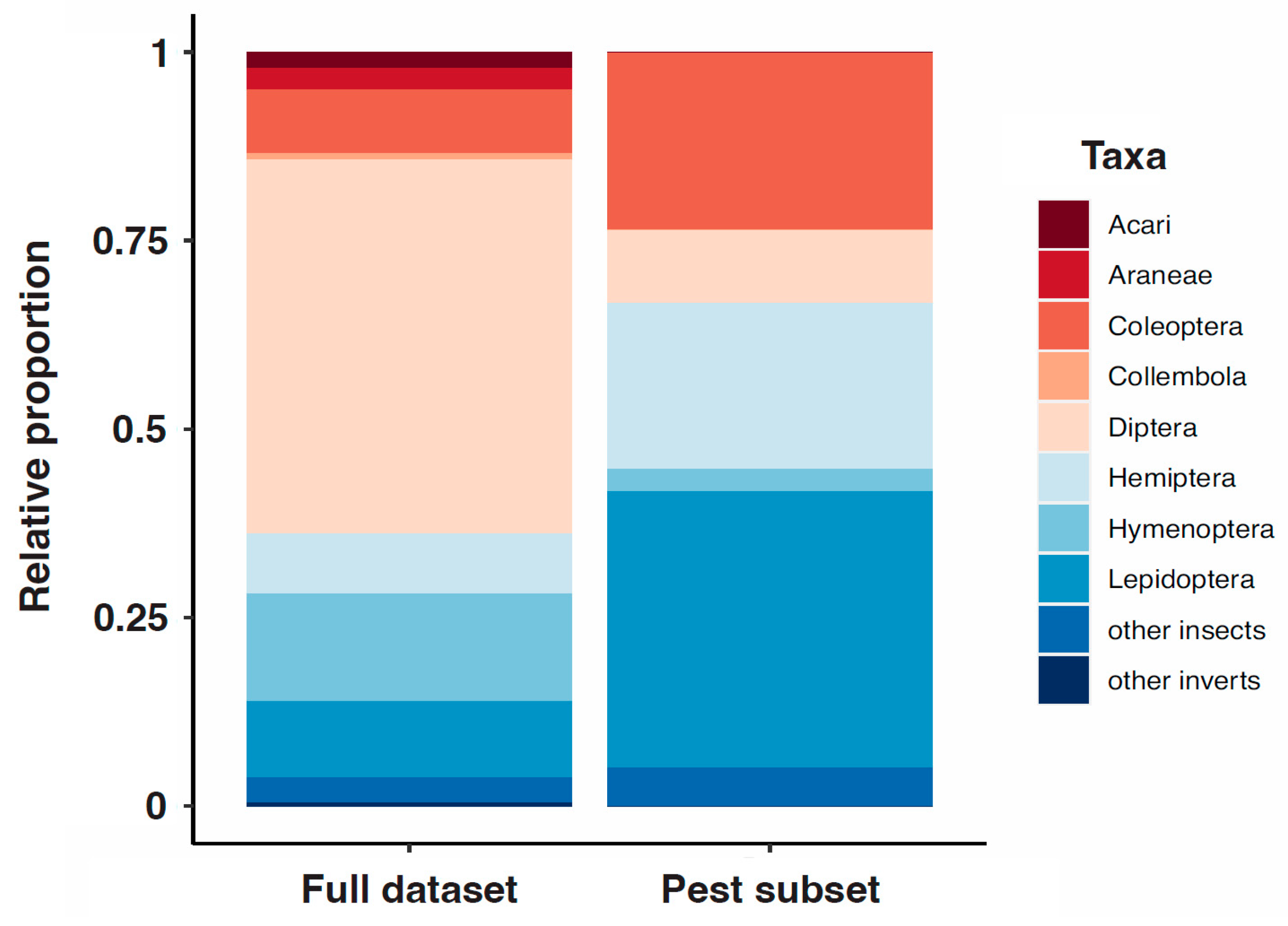
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Losey, J.E.; Vaughan, M. The economic value of ecological services provided by insects. BioScience 2006, 56, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, C.A.; Sorg, M.; Jongejans, E.; Siepel, H.; Hofland, N.; Schwan, H.; Stenmans, W.; Müller, A.; Sumser, H.; Hörren, T.; et al. More than 75 percent decline over 27 years in total flying insect biomass in protected areas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, G. Where have all the insects gone? Science 2017, 356, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, B.C.; Garcia, A. Climate-driven declines in arthropod abundance restructure a rainforest food web. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10397–E10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibold, S.; Gossner, M.M.; Simons, N.K.; Blüthgen, N.; Müller, J.; Ambarli, D.; Ammer, C.; Bauhus, J.; Fischer, M.; Habel, J.C.; et al. Arthropod decline in grasslands and forests is associated with drivers at landscape level. Nature 2019, 574, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G. Worldwide decline of the entomofauna: A review of its drivers. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 232, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, T.G.; Bieg, C.; Harwatt, H.; Pudasaini, R.; Wellesley, L. Food System Impacts on Biodiversity Loss; Energy, Environment and Resources Programme, Chatham House, The Royal Institute of International Affairs: London, UK, 2021.
- Benton, T.G.; Vickery, J.A.; Wilson, J.D. Farmland biodiversity: Is habitat heterogeneity the key? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainese, M.; Isaac, N.J.B.; Powney, G.D.; Bommarco, R.; Öckinger, E.; Kuussaari, M.; Pöyry, J.; Benton, T.G.; Gabriel, D.; Hodgson, J.A.; et al. Landscape simplification weakens the association between terrestrial producer and consumer diversity in Europe. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 23, 3040–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, C.A.; Tewksbury, J.J.; Tigchelaar, M.; Battisti, D.S.; Merrill, S.C.; Huey, R.B.; Naylor, R.L. Increase in crop losses to insect pests in a warming climate. Science 2018, 361, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, S.B.; Yu, Q. Evolution in action: Plants resistant to herbicides. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 317–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.; Denholm, I.; Williamson, M.S.; Nauen, R. The global status of insect resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, J.A.; Hawkins, N.J.; Fraaije, B.A. The evolution of fungicide resistance. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 90, 29–92. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, F.; Franklin, J. State-of-the-art practices in farmland biodiversity monitoring for North America and Europe. Ambio 2016, 45, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, S.C. Nontarget Effects of Agricultural Fungicides; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.; Chng, K.R.; Hui Boey, E.J.; Ng, A.H.Q.; Wilm, A.; Nagarajan, N. INC-Seq: Accurate single molecule reads using nanopore sequencing. Gigascience 2016, 5, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Beng, K.C.; Tomlinson, K.W.; Shen, X.H.; Surget-Groba, Y.; Hughes, A.C.; Corlett, R.T.; Slik, J.W.F. The utility of DNA metabarcoding for studying the response of arthropod diversity and composition to land-use change in the tropics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbrecht, V.; Steinke, D. Scaling up DNA metabarcoding for freshwater macrozoobenthos monitoring. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 64, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braukmann, T.W.A.; Prosser, S.J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Elbrecht, V.; Steinke, D.; Ratnasingham, R.; deWaard, J.R.; Sones, J.E.; Zakharov, E.V.; Hebert, P.D.N. Metabarcoding a diverse arthropod mock community. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, D.; deWaard, S.L.; Sones, J.E.; Ivanova, N.V.; Prosser, S.W.J.; Perez, K.; Braukmann, T.W.A.; Milton, M.; Zakharov, E.V.; deWaard, J.R.; et al. Message in a bottle—Metabarcoding enables biodiversity comparisons across ecoregions. GigaScience 2022, 11, giac040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Sogo, Y.; Doi, H.; Yamanaka, H. Usefulness and limitations of sample pooling for environmental DNA metabarcoding of freshwater fish communities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.L. Applying pollen DNA metabarcoding to the study of plant-pollinator interactions. Appl. Plant Sci. 2017, 5, apps.1600124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasselon, V.; Bouchez, A.; Rimet, F.; Jacquet, S.; Trobajo, R.; Corniquel, M.; Tapolczai, K.; Domaizon, I. Avoiding quantification bias in metabarcoding: Application of a cell biovolume correction factor in diatom molecular biomonitoring. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemain, E.; Davey, M.L.; Kauserud, H.; Epp, L.S.; Boessenkool, S.; Coissac, E.; Geml, J.; Edwards, M.; Willerslev, E.; Gussarova, G.; et al. Fungal palaeodiversity revealed using high-throughput metabarcoding of ancient DNA from arctic permafrost. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aas, A.B.; Davey, M.L.; Kauserud, H. ITS all right mama: Investigating the formation of chimeric sequences in the ITS2 region by DNA metabarcoding analyses of fungal mock communities of different complexities. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 730–741. [Google Scholar]
- Tedersoo, L.; Tooming-Klunderud, A.; Anslan, S. PacBio metabarcoding of Fungi and other eukaryotes: Errors, biases, and perspectives. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1370–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.A.; Trauzzi, G.; Maltby, K.M.; Gibson, T.I.; Ratcliffe, F.C.; Hallam, J.; Rainbird, S.; Maclaine, J.; Henderson, P.A.; Sims, D.W.; et al. Meta-Fish-Lib: A generalized, dynamic DNA reference library pipeline for metabarcoding of fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 99, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- deWaard, J.R.; Ratnasingham, S.; Zakharov, E.V.; Borisenko, A.V.; Steinke, D.; Telfer, A.C.; Perez, K.H.J.; Sones, J.E.; Young, M.R.; Levesque-Beaudin, V.; et al. A reference library for Canadian invertebrates with 1.5 million barcodes, voucher specimens, and DNA samples. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigand, H.; Beermann, A.J.; Ciampor, F.; Costa, F.O.; Csabai, Z.; Duarte, S.; Geiger, M.F.; Grabowski, M.; Rimet, F.; Rulik, B.; et al. DNA barcode reference libraries for the monitoring of aquatic biota in Europe: Gap-analysis and recommendations for future work. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcodes for bio-surveillance: Regulated and economically important arthropod plant pests. Genome 2016, 59, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.R.C.; Anderson, S.J.; Tran-Nguyen, L.T.T.; Sallam, N.; Le Ru, B.P.; Conlong, D.; Powell, K.; Ward, A.; Mitchell, A. Towards a global DNA barcode reference library for quarantine identifications of lepidoptera stemborers, with an emphasis on sugarcane pests. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, M.J.L.; Young, R.G.; Brown, J.W.; Miller, S.E.; Frewin, A.J.; Hanner, R.H. Using DNA barcoding to improve invasive pest identification at U.S. ports-of-entry. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batovska, J.; Piper, A.M.; Valenzula, I.; Cunningham, J.P.; Blacket, M.J. Developing a non-destructive metabarcoding protocol for detection of pest insects in bulk trap catches. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobern, D. BIOSCAN: DNA barcoding to accelerate taxonomy and biogeography for conservation and sustainability. Genome 2021, 64, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.E.; Noack, F. Identifying the landscape drivers of agricultural insecticide use leveraging evidence from 100,000 fields. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5473–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentinsaari, M.; Levesque-Beaudin, V.; Blagoev, G.; deWaard, J.R.; Ho, C.; Steinke, D.; Manjunath, R.; Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. Constructing a Highly Validated DNA Barcode Reference Library for Canadian Animals: Implications for DNA-Based Identifications. Available online: https://id.boldsystems.org (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; Zakharov, E.V.; Telfer, A.C.; Levesque-Beaudin, V.; Milton, M.M.; Pederson, S.; Janetta, P.; deWaard, J.R. Counting animal species with DNA barcodes: Canadian insects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delrieu-Trottin, E.; Williams, J.T.; Pitassy, D.; Driskell, A.; Hubert, N.; Vivani, J.; Cribb, T.H.; Espiau, B.; Galzin, R.; Kulbicki, M.; et al. A DNA barcode reference library of French Polynesian shore fishes. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriniere, J.; Balke, M.; Doczkal, D.; Geiger, M.F.; Hardulak, L.A.; Haszprunar, G.; Hausmann, A.; Hendrich, L.; Regalado, L.; Rulik, B.; et al. A DNA barcode library for 5,200 German flies and midges (Insecta:Diptera) and its implications for metabarcoding-based biomonitoring. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 900–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.L.; Mo, L.; Bu, W.J.; Wang, X.H. The first comprehensive DNA barcode reference library if Chinese Tanytarsus (Diptera: Chironomidae) for environmental DNA metabarcoding. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 27, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M.; Batovska, J.; Cogan, N.O.I.; Weiss, J.; Cunningham, J.P.; Rodoni, B.C.; Blacket, M.J. Prospects and challenges of implementing DNA metabarcoding for high-throughput insect surveillance. GigaScience 2019, 8, giz092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. A DNA-based registry for all animal species: The Barcode Index Number (BIN) System. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.V.; deWaard, J.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. An inexpensive, automation-friendly protocol for recovering high-quality DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2006, 6, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, S.W.J.; deWaard, J.R.; Miller, S.E.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcodes from century-old type specimens using next-generation sequencing. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Penton, E.H.; Burns, J.M.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14812–14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Magurran, A.E. Measuring Biological Diversity; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package; R Package Version 2.5-1. 2018. Available online: https://vegandevs.github.io/vegan/ (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Natural Resources Canada, Canada Centre for Remote Sensing. 2020 Land Cover of Canada. Natural Resources Canada, Federal Geospatial Platform. 2025. Available online: https://osdp-psdo.canada.ca/dp/en/search/metadata/NRCAN-FGP-1-ee1580ab-a23d-4f86-a09b-79763677eb47 (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- QGI.S.org. QGIS Geographic Information System. QGIS Association. 2025. Available online: http://www.qgis.org (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.D.; Martinez, M.C.; Stiles, S.; Miller, P.E.; Zakharov, E.V. Is DNA Barcoding Actually Cheaper and Faster than Traditional Morphological Methods: Results from a Survey of Freshwater Bioassessment Efforts in the United States? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, S.L.; Armstrong, K.F. Rapid, one-step DNA extraction for insect pest identification by using DNA barcodes. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, D.; Braukmann, T.W.A.; Manerus, L.; Woodhouse, A.; Elbrecht, V. Effects of Malaise trap spacing on species richness and composition of terrestrial arthropod bulk samples. Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2021, 5, e59201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestel, J.H.; Field, D.L.; Bateman, P.W.; White, N.E.; Allentoft, M.E.; Hopkins, A.J.M.; Gibberd, M.; Nevill, P. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in agricultural systems: Current uses, limitations and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottrell, D.R.; Bottrell, D.G. Integrated Pest Management; Council on Environmental Quality: Washington, DC, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Deguine, J.P.; Aubertot, J.N.; Flor, R.J.; Lescourret, F.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Ratnadass, A. Integrated pest management: Good intentions, hard realities. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, R.; Lima, J.; deWaard, J.; Humble, L.; Hanner, R. Common goals: Policy implications of DNA barcoding as a protocol for identification of arthropod pests. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 2947–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, Y.L.; Peters, S.M.; Weland, C.; Ivanova, N.V.; Yancy, H.F. Potential use of DNA barcodes in regulatory science: Identification of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s “Dirty 22,” contributors to the spread of foodborne pathogens. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levesque-Beaudin, V.; Miller, M.E.; Dikow, T.; Miller, S.E.; Prosser, S.W.J.; Zakharov, E.V.; McKeown, J.T.A.; Sones, J.E.; Redmond, N.E.; Coddington, J.A.; et al. A workflow for expanding DNA barcode reference libraries through ‘museum harvesting’ of natural history collections. Biodivers. Data J. 2023, 11, e100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, R.; Xie, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, W. A coarse-to-fine network for aphid recognition and detection in the field. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 187, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-H.; Choi, S.H.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Kwon, S.-W.; Kang, Y.J.; Jun, T.-H. Detection of soybean insect pest and a forecasting platform using deep learning with unmanned ground vehicles. Agronomy 2023, 13, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Taylor, G.W.; Kremer, S.C.; Fryxell, J.M. Getting the bugs out of AI: Advancing ecological research on arthropods through computer vision. Ecol. Lett. 2023, 26, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, B.W.; Battle, J.M.; Jackson, J.K.; Dapkey, T. Can DNA barcodes of stream macroinvertebrates improve descriptions of community structure and water quality? J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2011, 30, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscharntke, T.; Klein, A.M.; Kruess, A.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Thies, C. Landscape perspectives on agricultural intensification and biodiversity-ecosystem service management. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.B.; Miller, E.C.; Rhodes, M.K.; Wiens, J.J. Inordinate Fondness Multiplied and Redistributed: The Number of Species on Earth and the New Pie of Life. Q. Rev. Biol. 2017, 92, 229–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haan, N.L.; Zhang, Y.; Landis, D.A. Predicting landscape configuration effects on agricultural pest suppression. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenheim, J.A.; Cluff, E.; Lippey, M.K.; Cass, B.N.; Paredes, D.; Parsa, S.; Karp, D.S.; Chaplin-Kramer, R. Increasing crop field size does not consistently exacerbate insect pest problems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2208813119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.D.; Tooker, J.F. Neonicotinoids pose undocumented threats to food webs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22609–22613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielkopolan, B.; Jakubowska, M.; Obrępalska-Stęplowska, A. Beetles as Plant Pathogen Vectors. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 748093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailleux, A.; Mohl, E.K.; Teixeira Alves, M.; Messelink, G.J.; Desneuz, N. Natural enemy-mediated indirect interactions among prey species: Potential for enhancing biocontrol services in agroecosystems. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukema, J.E.; Leung, B.; Kovacs, K.; Chivers, C.; Britton, K.O.; Englin, J.; Frankel, S.J.; Haight, R.G.; Holmes, T.P.; Liebhold, A.M.; et al. Economic Impacts of Non-Native Forest Insects in the Continental United States. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, R.H. Patterns of species diversity. Biol. Rev. 1965, 4, 510–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgley, C.; Smiley, T.M.; Terry, R.; Davis, E.B.; DeSantis, L.R.; Fox, D.L.; Hopkins, S.S.B.; Jezkova, T.; Matocq, M.D.; Matzke, N.; et al. Biodiversity and topographic complexity: Modern and geohistorical perspectives. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loke, L.H.L.; Chisholm, R.A. Measuring habitat complexity and spatial heterogeneity in ecology. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 15, 2269–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Arkell | Elora | |
|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 35.95% | 85.45% |
| Urban | 27.28% | 7.51% |
| Forest | 31.04% | 6.69% |
| Barren lands | 2.50% | 0.12% |
| Shrubland | 1.26% | 0.10% |
| Grassland | 0.05% | 0% |
| Wetland | 1.04% | 0.10% |
| Water | 0.89% | 0.03% |
| df | Sum of Squares | R2 | F | Pr (>F) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full dataset | ||||||
| Site | 1 | 0.58 | 0.14 | 5.14 | 1.00 × 10−4 | *** |
| Crop type | 3 | 0.70 | 0.17 | 2.08 | 1.00 × 10−4 | *** |
| Residual | 25 | 2.80 | 0.69 | |||
| Total | 29 | 4.07 | 1 | |||
| Pest | ||||||
| Site | 1 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 3.77 | 3.00 × 10−4 | *** |
| Crop type | 3 | 0.85 | 0.30 | 4.15 | 1.00 × 10−4 | *** |
| Residual | 25 | 1.71 | 0.61 | |||
| Total | 29 | 2.83 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steinke, D.; Ashfaq, M.; Ho, C.Y.; Perez, K.H.J.; Sones, J.E.; DeWaard, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R.; Ratnasingham, S.; Zakharov, E.V.; Hebert, P.D.N. Farmland Biodiversity Monitoring Using DNA Metabarcoding. Diversity 2025, 17, 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080585
Steinke D, Ashfaq M, Ho CY, Perez KHJ, Sones JE, DeWaard SL, DeWaard JR, Ratnasingham S, Zakharov EV, Hebert PDN. Farmland Biodiversity Monitoring Using DNA Metabarcoding. Diversity. 2025; 17(8):585. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080585
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteinke, Dirk, Muhammad Ashfaq, Chris Y. Ho, Kate H. J. Perez, Jayme E. Sones, Stephanie L. DeWaard, Jeremy R. DeWaard, Sujeevan Ratnasingham, Evgeny V. Zakharov, and Paul D. N. Hebert. 2025. "Farmland Biodiversity Monitoring Using DNA Metabarcoding" Diversity 17, no. 8: 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080585
APA StyleSteinke, D., Ashfaq, M., Ho, C. Y., Perez, K. H. J., Sones, J. E., DeWaard, S. L., DeWaard, J. R., Ratnasingham, S., Zakharov, E. V., & Hebert, P. D. N. (2025). Farmland Biodiversity Monitoring Using DNA Metabarcoding. Diversity, 17(8), 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080585






