Determining Large Trees and Population Structures of Typical Tree Species in Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Analysis on Large Trees in the Community
2.2.2. Analysis of Large Individuals of Typical Tree Species
2.2.3. Analysis on Population Composition of Typical Tree Species
3. Results
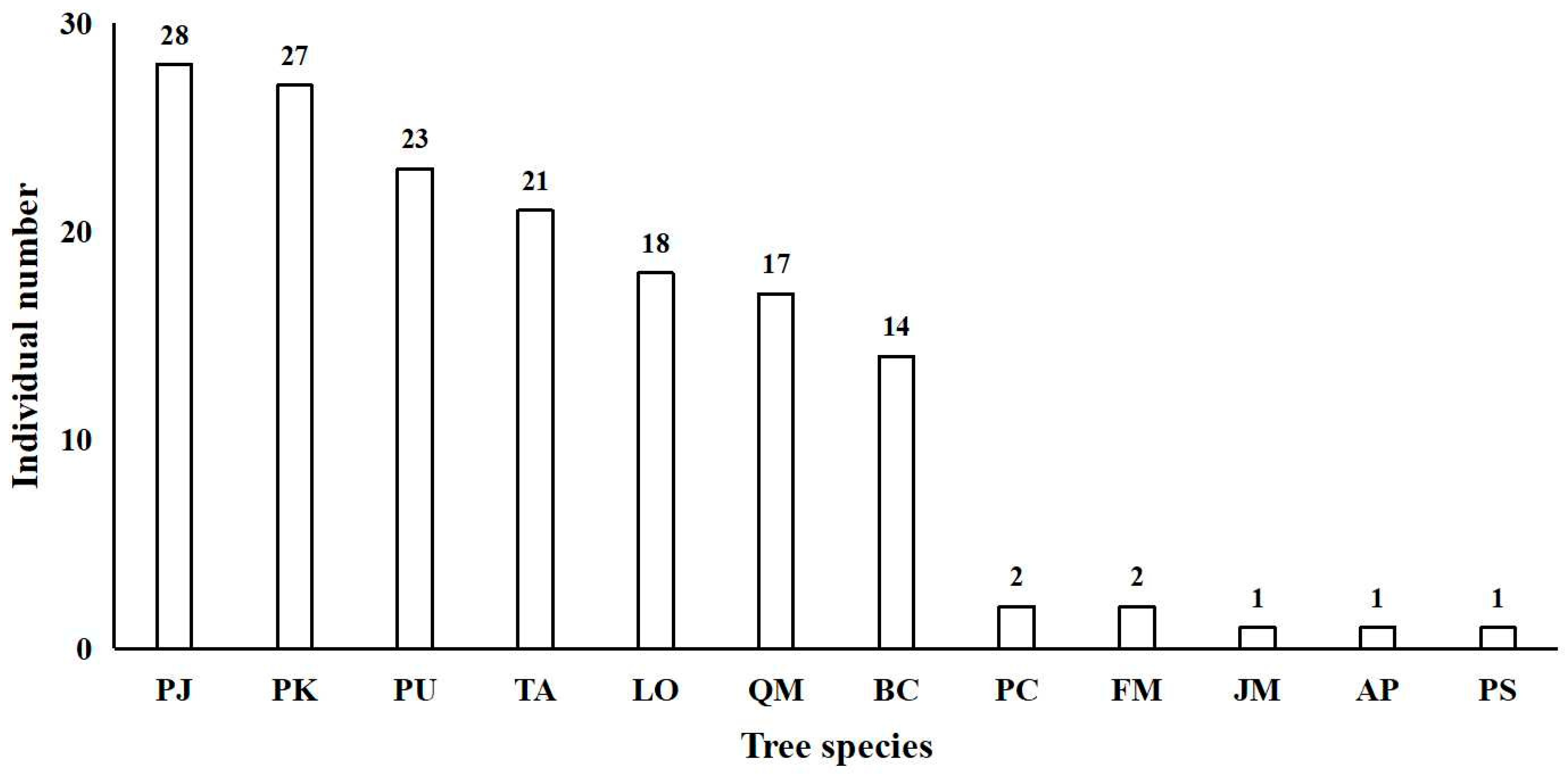
3.1. Species Composition
3.2. Large Tree Number, Species Composition, and Contribution to Basal Area in the Community
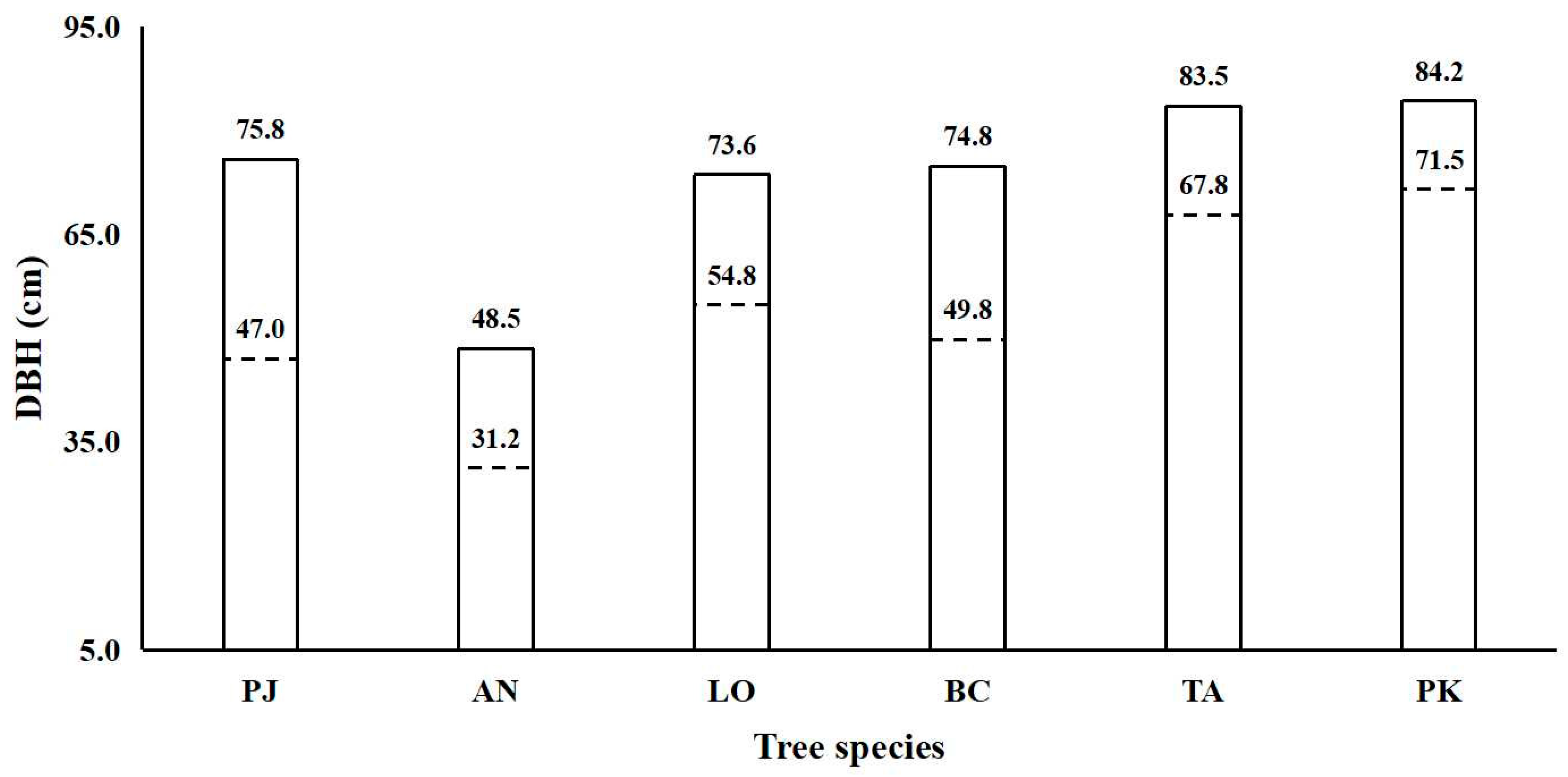
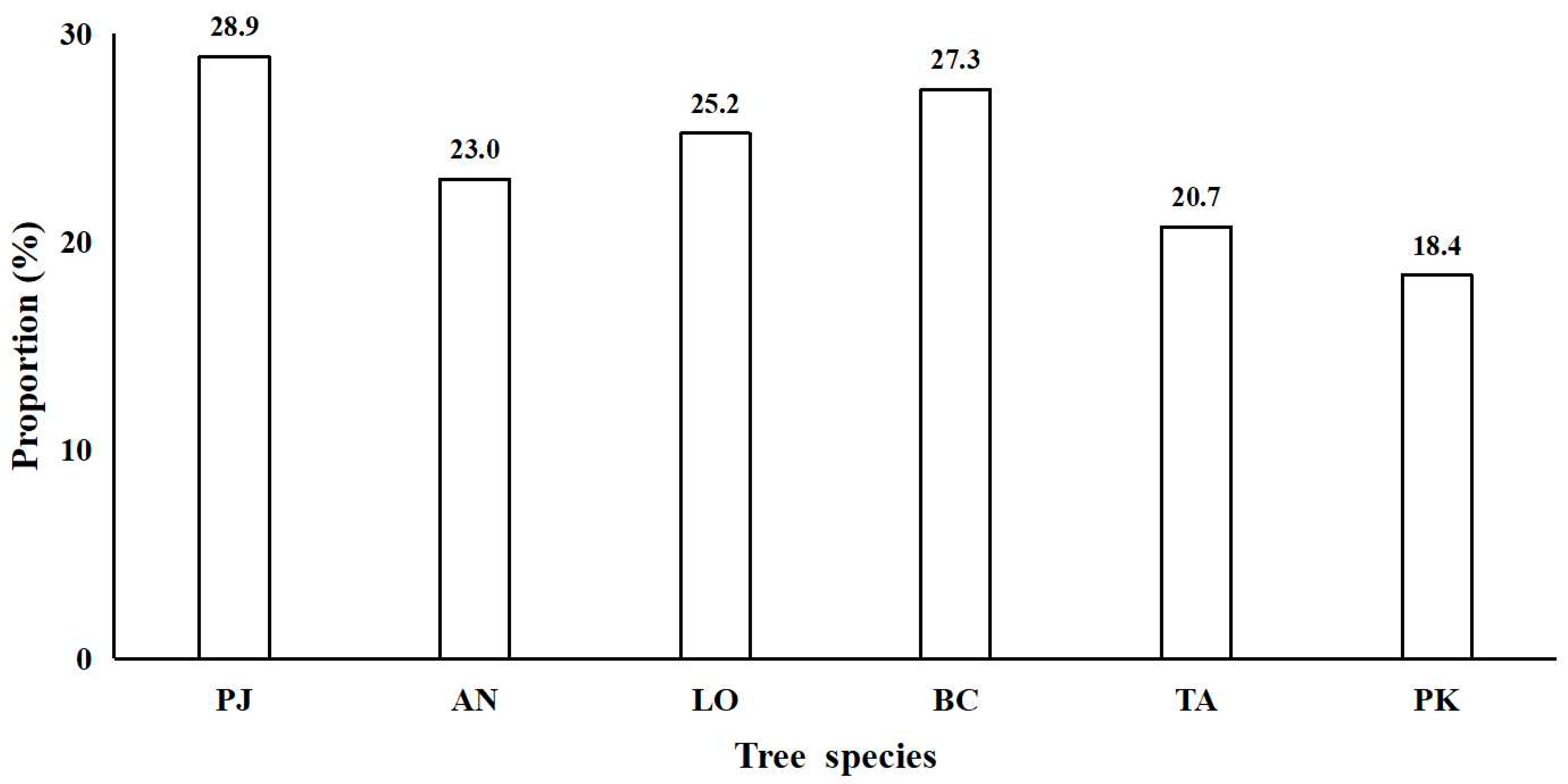
3.3. Large Individual Criteria and Contribution to Basal Area of Typical Tree Species
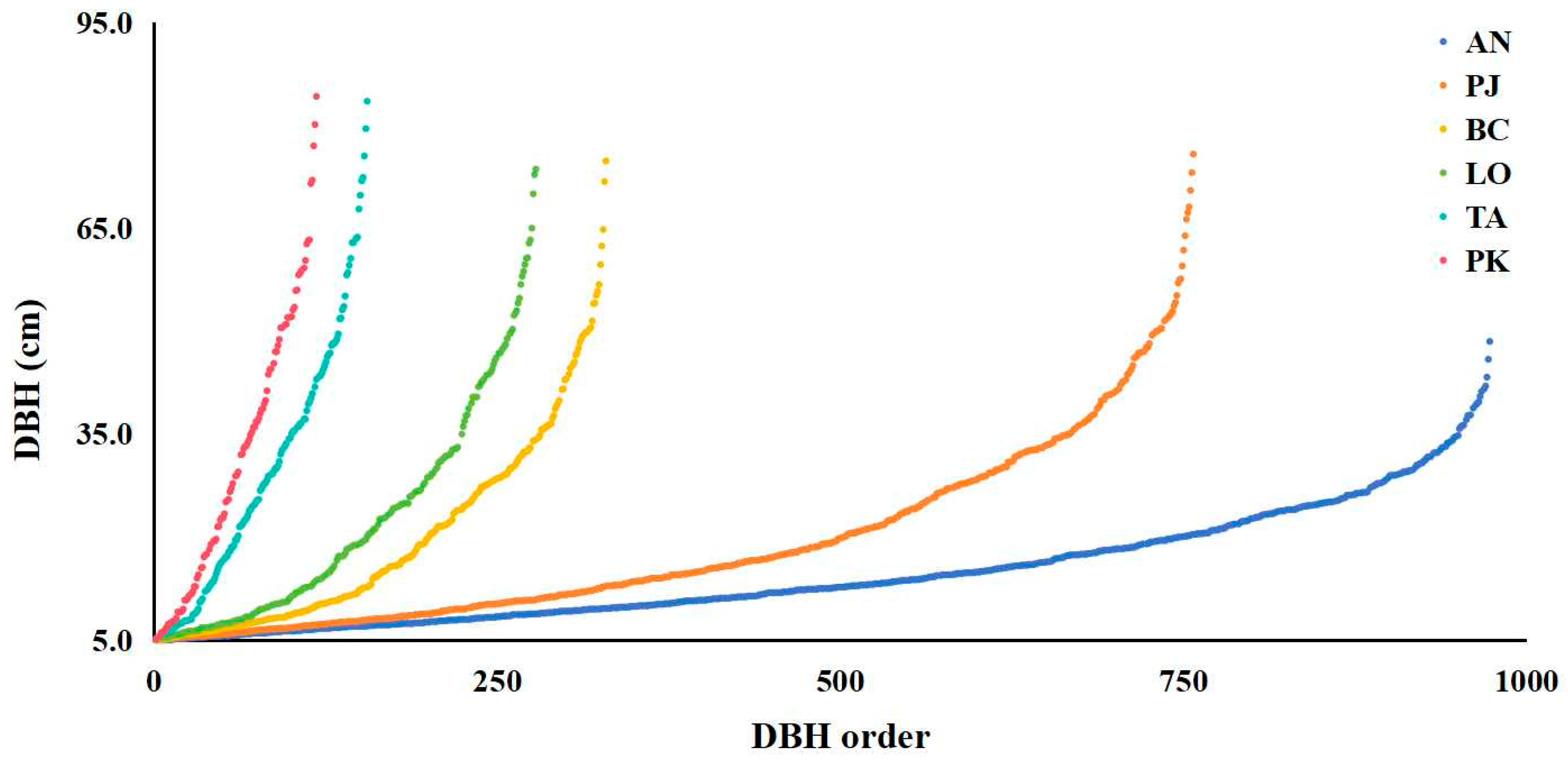
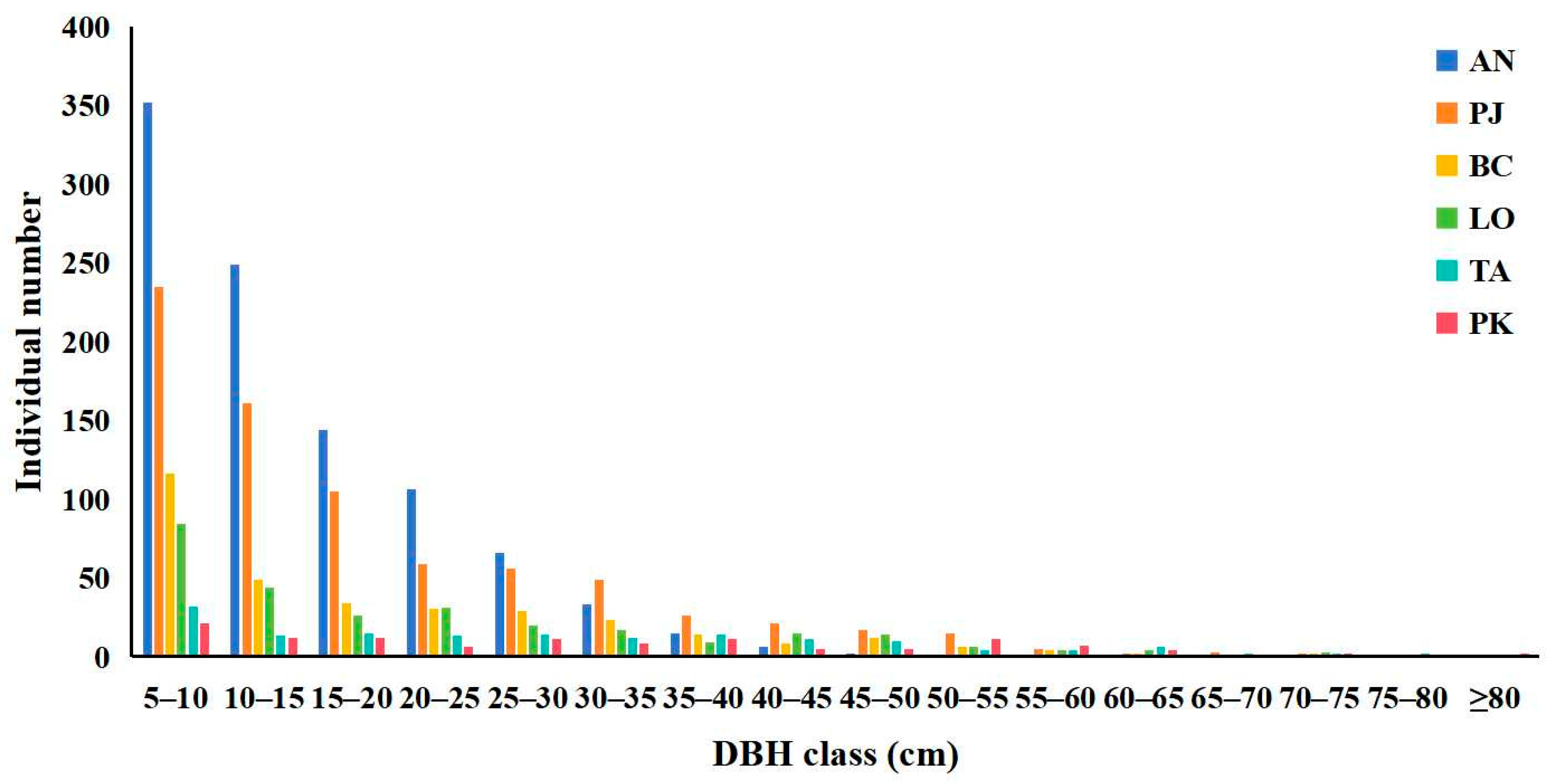
3.4. Diameter Class Structures of Typical Tree Species
4. Discussion
4.1. Large Tree Characteristics and Large Individual Criteria
4.2. Population Structure and Forest Protection
4.3. Limitations and Research Needs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Niu, S.; Liu, Y. Forest Ecology, 3rd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 1–9, 119–153. [Google Scholar]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. 2025. Available online: https://www.forestry.gov.cn/lyj/1/lcdt/20250312/614367.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. China Forestry Resources Report (2014–2018); China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 73–76, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.Z.; Liu, Q.J.; Meng, S.W.; Zhou, G. Long-term monitoring of tree population dynamics of broad-eaved Korean pine forest in Changbai Mountains, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Jia, Z.; Ge, S.; Li, Y.; Kang, D.; Li, J. Dominant species composition, environmental characteristics and dynamics of forests with Picea jezoensis trees in Northeast China. Diversity 2024, 16, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.M.; Yang, H. Competition among dominant tree species in spruce-fir forests of Changbai Mountain. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3089–3097. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, H.; Tong, Y.W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, W.M.; Zhou, L.; Dai, L.M.; Yu, D.P. Competition relationships among key tree species after different intensity selection cutting in broad-leaved Korean pine forests of Changbai Mountain. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Baiketuerhan, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhao, X.H. Relationship between stand structure and productivity of broad-leaved Korean pine forest in Changbai Mountain. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2024, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.Y.; Zhao, X.H. Species diversity patterns and their scale effects in broad-leaved Korean pine forests of Changbai Mountain. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2025, 61, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.B.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhao, X.H. Species diversity and influencing factors of coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest communities in different successional stages of Changbai Mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 7147–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Kou, X.Y.; Fu, X.; Zheng, S.N.; Wu, G.; Lu, Z.H.; Sang, W.G. Coupling key elements and simulating the succession dynamic in the Changbai Mountain temperate forest ecosystem. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 5377–5388. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.T.; Zhang, Q.; Kang, X.G.; Yang, Y.J.; Xu, G.; Zhang, L.X. Community stability for spruce-fir forest at different succession stages in Changbai Mountains, Northeast China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Ge, S.; Li, Y.; Kang, D.; Li, J. Relationship between tree richness and temporary stability of plant communities: A case study of a forest in Northeast China. Forests 2021, 12, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.Q.; Xie, R.; Yang, H. Response of radial growth of three common tree species in spruce-fir and broad-leaved mixed forest of Changbai Mountain to climate change. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2023, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.J.; Wang, L.; Du, Y.J.; Zheng, L.; Zeng, F.S.; Xin, Y. Radial growth response of natural Fraxinus mandshurica to climate in the Changbai Mountains. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 48, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Laurance, W.F. The unique challenges of conserving large old trees. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, J.A.; Struckman, S.; Germain, S.J.; Furniss, T.J. The importance of large-diameter trees to the creation of snag and deadwood biomass. Ecol. Process. 2021, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Wang, L.Q. Big-sized trees and forest functioning: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.Y.; Zhang, H.T.; Tang, Z.Y. Large-sized trees regulating the structural diversity-productivity relationships through shaping different productive processes in a tropical forest. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2025, 292, 20242202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, Z.; Myers, J.A.; Yu, J.; Wang, X. Tree mycorrhizal associations determine how biodiversity, large trees, and environmental factors drive aboveground carbon stock in temperate forests. For. Ecosyst. 2024, 11, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Jiao, J.; Wu, C.; Mu, Y.; Zheng, S.; You, L.; Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Jiang, B. Sparse large trees in secondary and planted forests highlight the need to improve forest conservation and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Tian, L.; Huang, L.; Jin, C.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, E.; Jim, C.Y.; Yang, Y.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; et al. Religious temples are long-term refuges for old trees in human-dominated landscapes in China. Curr. Biol. 2025, 35, 2994–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bölöni, J.; Aszalós, R.; Ódor, P. Lack of large-diameter living trees and low structural diversity characterise managed dry-mesic oak forests in the Hungarian Carpathians. For. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 586, 122706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.R.; Evans, M.J.; Le Roux, D.S.; Cunningham, S.A.; Law, B.; Gibbons, P. Large urban trees are keystone structures for Australian microbats. Biol. Conserv. 2025, 306, 111146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najeeb, N.; Jose, K.; Sreejith, K.A.; Pulla, S.; Suresh, H.S.; Ratnam, J.; Raghavendra, H.V.; Chakravarthy, D.; Chaturvedi, K. Presence of large trees and tree diversity enhances carbon storage in the Western Ghats. Biol. Conserv. 2025, 308, 111250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Q.; Ali, A.; Sanaei, A.; Ruiz-Benito, P.; Jucker, T.; Fang, L.; Bai, E.; Ye, J.; Lin, F.; Fang, S.; et al. Few large trees, rather than plant diversity and composition, drive the above-ground biomass stock and dynamics of temperate forests in northeast China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 481, 118698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestry and Grassland Bureau of Jilin Province. 2024. Available online: http://jllc.jl.gov.cn/zwgk/jllq/slzy/202207/t20220727_2885606.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Antu County Government. 2025. Available online: http://www.antu.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Fusong County Government. 2025. Available online: http://www.fusong.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Changbai County Government. 2025. Available online: http://www.changbai.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. 2021. Available online: https://www.forestry.gov.cn/c/www/gkml/11057.jhtml (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Fang, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, Z.; Tang, Z.; He, J.; Yu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, J.; et al. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory. Biodivers. Sci. 2009, 17, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y. General Ecology, 3rd ed.; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 93–113, 288–312. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.; Lou, A.; Sun, R.; Li, Q. Foundations in Ecology, 4th ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2023; pp. 72–100, 160–188. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, N.; Yang, S.; Wang, T. Medical Statistics, 3rd ed.; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 444–457. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.H.; Shang, T. SPSS Statistical Analysis and Data Mining; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- De Veaux, R.D.; Velleman, P.F.; Bock, D.E. Stats: Data and Models; Geng, X.L., Translator; China Renmin University Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 345–362. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Hao, Z.Q.; Zhou, Y.B.; Yin, R.B. Height niche of some tree species in the Korean pine-broad-leaved forest on Changbai Mountain. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1999, 10, 262–264. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, W.M.; Yu, D.P.; Bao, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Guo, Y.; Dai, L.M. Characteristics of plant species diversity in a windthrow area on Changbai Mountain after 26 years of natural recovery. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Y.Q.; Fan, C.Y.; Zhang, C.Y. Species diversity maintenance mechanism of dark coniferous forests community in Changbai Mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Laurance, W.F.; Franklin, J.F. Global decline in large old trees. Science 2012, 338, 1305–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Laurance, W.F. The ecology, distribution, conservation and management of large old trees. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1434–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.B.; Clark, D.A. Abundance, growth and mortality of very large trees in neotropical lowland rain forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 1996, 80, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Wang, X.; Kang, D.W. Characteristics and roles of large trees in giant panda habitat of Wanglang Nature Reserve. Forests 2023, 14, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, K.; Villa, P.M.; Caldeira, N.; Ribeiro, J.H.C.; Santana, L.D.; Carvalho, F.A. Large-sized trees and altitude drive aboveground carbon stock in Brazilian Atlantic Cloud Forests: An approach based on carbon hyperdominant taxa. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 962, 178448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, P.J.; Gray, A.N. Populations of large-diameter trees are increasing across the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2421780122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagoll, K.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Knight, E.; Fischer, J.; Manning, A.D. Large trees are keystone structures in urban parks. Conserv. Lett. 2012, 5, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, J.A.; Larson, A.J.; Swanson, M.E.; Freund, J.A. Ecological importance of large-diameter trees in a temperate mixed-conifer forest. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slik, J.W.F.; Paoli, G.; McGuire, K.; Amaral, I.; Barroso, J.; Bastian, M.; Blanc, L.; Bongers, F.; Boundja, P.; Clark, C.; et al. Large trees drive forest aboveground biomass variation in moist lowland forests across the tropics. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, J.A.; Furniss, T.J.; Johnson, D.J.; Davies, S.J.; Allen, D.; Alonso, A.; Anderson-Teixeira, K.J.; Andrade, A.; Baltzer, J.; Becker, K.M.L.; et al. Global importance of large-diameter trees. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, K.M.; Esquivel-Muelbert, A.; Bergamin, R.S.; Klipel, J.; Picolotto, R.C.; Frangipani, M.A.; Zanini, K.J.; Cianciaruso, M.V.; Jarenkow, J.A.; Jurinitz, C.F.; et al. Climate and large-sized trees, but not diversity, drive above-ground biomass in subtropical forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 490, 119126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q. Dynamics of Korean pine population in birch forests of the Changbai Mountain. J. Ecol. 1989, 8, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.R.; Wang, S.L. The small-diameter Pinus koraiensis and its role in the stand of natural Korean pine forest. For. Resour. Manag. 1994, 2, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zhao, X.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Hou, J.H. Spatial pattern and canopy structure of Korean pine broadleaved forests in Changbaishan Mountains. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2006, 28 (Suppl. 2), 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Kang, X.G.; Meng, J.H.; Kong, L.; Guo, W.W.; Yue, G. Spatial distribution patterns and associations of dominant tree species in poplar-birch secondary forest stand in Changbai Mountains. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2013, 41, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.L.; Song, X.T.; Fan, C.N.; Liu, D.; Guo, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.X. Analysis of spatial distribution and life structure characteristics of Tilia amurensis natural population. J. Beihua Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 23, 726–732. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.F.; Ge, S.S.; Liang, J.H.; Li, J.Q. Population age structure and dynamics of Pinus koraiensis in a broadleaved Korean pine forest in Changbai Mountain, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 46, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Ge, S.S.; Liang, J.H.; Li, J.Q. Population structure and dynamic characteristics of Tilia amurensis in broad-leaved Korean pine mixed forest in Changbai Mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 5381–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Z. The preliminary study on the structure of Picea jezoensis forest in the southwest slope of Changbai Mountain. Plant Ecol. Geobot. Ser. 1963, 1, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, D.T. Discussion on the utilization of Betula costata forest harvesting. J. Jilin For. Sci. Technol. 1985, 2, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, F.C.; He, H.J.; Liu, B.D.; Wang, G.R.; Li, L. Community structure features of the larch-birch secondary forest on the northeastern slope of Changbai Mountain, Northeast China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2016, 38, 28–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wu, C.L.; Hong, T.; Lin, Z.; Hong, W. Age structure and population dynamics of dominant species in a Betula platyphylla-Larix olgensis forest on swamp ecotone. Guihaia 2017, 37, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.Y.; Zhang, H.R.; Zhang, B.; He, Y.J. Population structure and dynamic characteristics of typical constructive species in natural secondary forest on the northern slope of Changbai Mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 5142–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Kang, X.G.; Yang, Y.J.; Wang, Q.J. Population structures and dynamics of Abies nephrolepis in Changbai Mountain. J. Central South Univ. For. Technol. 2017, 37, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.L. Analysis of the significance of height growth differences in young Pinus koraiensis-Tilia amurensis forests under different transformation methods. For. Sci. Technol. 1985, 5, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Q. The pattern and dynamics of Pinus koraiensis population. J. Northeast For. Univ. 1986, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.L. Optimal harvesting diameter of Abies nephrolepis. Jilin For. Sci. Technol. 1986, 3, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. A study on division of Larix olgensis. J. Northeast For. Univ. 1990, 18, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Q.; Zhu, N. Population structure of Korean pine and its dynamics. J. Ecol. 1990, 9, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.L. Study on diameter structure of secondary forest of Adiessibirica Ledeb in the Northeast Forest Area. For. Resour. Manag. 2014, 2, 83–86,114. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Y.; Lindenmayer, D.; Zheng, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. Size-focused conservation may fail to protect the world’s oldest trees. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 4641–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.R. Forest Mensuration, 4th ed.; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Liang, Y.; Ma, T.X.; Liu, B.; Wu, M.M. The migration of main tree species lags behind climate change in Changbai Mountains. Chin. J. Ecol. 2022, 41, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.S.; Yao, X.Y.; Liu, Y.H. The functional traits of forests at different succession stages and their relationship to terrain factors in Changbai Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 5915–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.S.; Liu, Q.J. Effects of environmental factors on forest community distribution in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve of northeastern China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2023, 45, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
| Tree Species | PJ | BC | LO | TA | PK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AN | −4.0 (0.000) | −4.8 (0.000) | −7.3 (0.000) | −14.5 (0.000) | −16.6 (0.000) |
| PJ | −0.8 (0.951) | −3.3 (0.027) | −10.4 (0.000) | −12.6 (0.000) | |
| BC | −2.5 (0.348) | −9.6 (0.000) | −11.8 (0.000) | ||
| LO | −7.2 (0.001) | −9.3 (0.000) | |||
| TA | −2.1 (0.947) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Ge, S.; Li, Y.; Kang, D.; Li, J. Determining Large Trees and Population Structures of Typical Tree Species in Northeast China. Diversity 2025, 17, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17070491
Yang Y, Jia Z, Ge S, Li Y, Kang D, Li J. Determining Large Trees and Population Structures of Typical Tree Species in Northeast China. Diversity. 2025; 17(7):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17070491
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yutong, Zhiyuan Jia, Shusen Ge, Yutang Li, Dongwei Kang, and Junqing Li. 2025. "Determining Large Trees and Population Structures of Typical Tree Species in Northeast China" Diversity 17, no. 7: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17070491
APA StyleYang, Y., Jia, Z., Ge, S., Li, Y., Kang, D., & Li, J. (2025). Determining Large Trees and Population Structures of Typical Tree Species in Northeast China. Diversity, 17(7), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17070491





