Response of the Invasive Cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii to Iron and Phosphorus Concentrations in the Habitat: Effects on Growth and Cellular Phosphorus Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. R. raciborskii Cultures and Pretreatment
2.2. R. raciborskii Growth Response to Fe3+ Concentration
2.3. Effect of Fe3+ on Algal Growth and P Distribution with Different P Sources
2.4. Effect of Fe3+ on Algal Growth and P Distribution with Low P Concentration
2.5. Determination of R. raciborskii Growth Parameters
2.6. Extraction of P Distribution Fractions and Determination of P Parameters
2.7. Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity (APA)
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
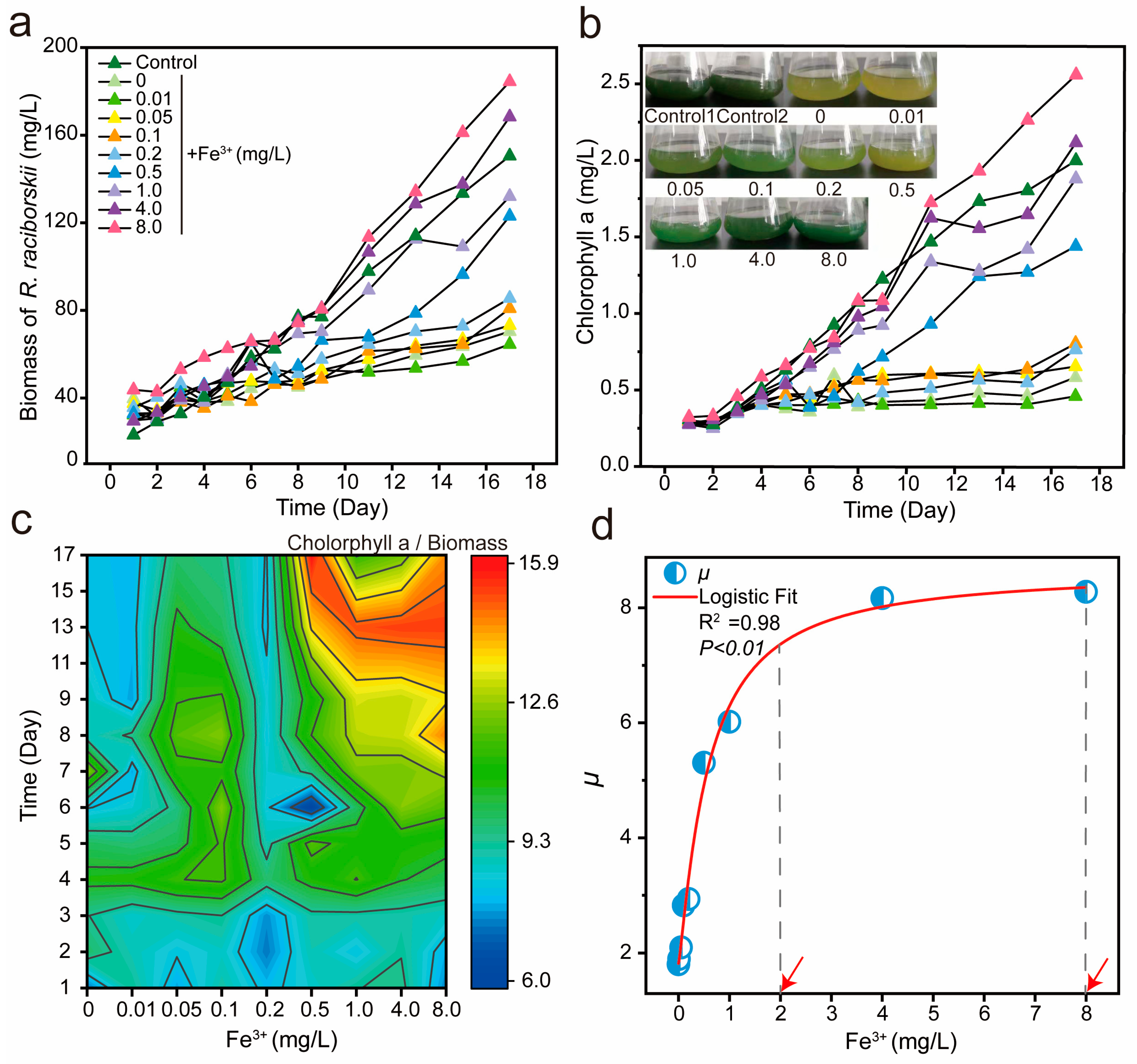
3.1. Correlation Between Growth of R. raciborskii and Fe3+ Concentration
3.2. Fe3+ Promotes IP Uptake Efficiency in R. raciborskii
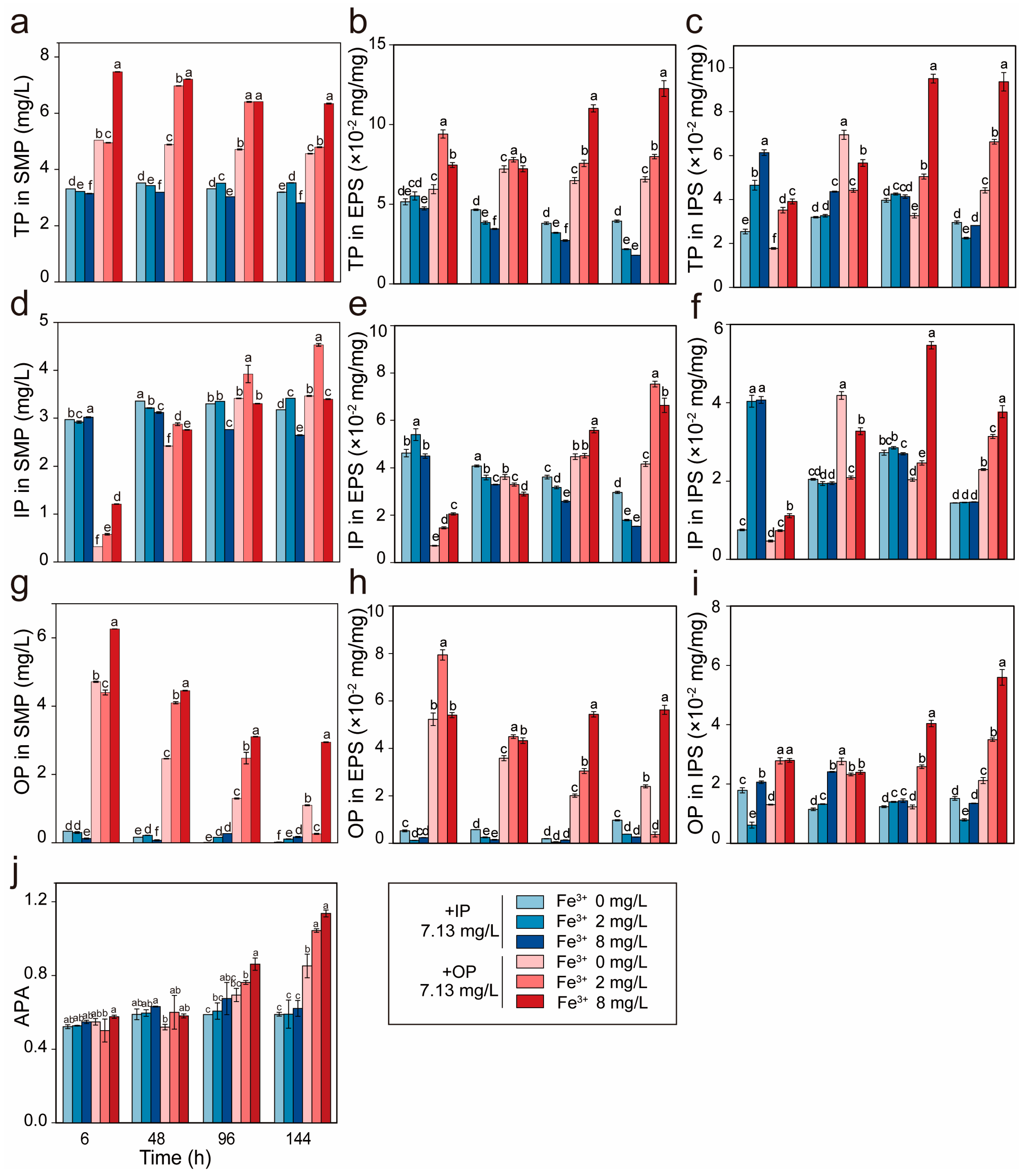
3.3. Fe3+ Enhances IP Translocation and OP Storage in R. raciborskii
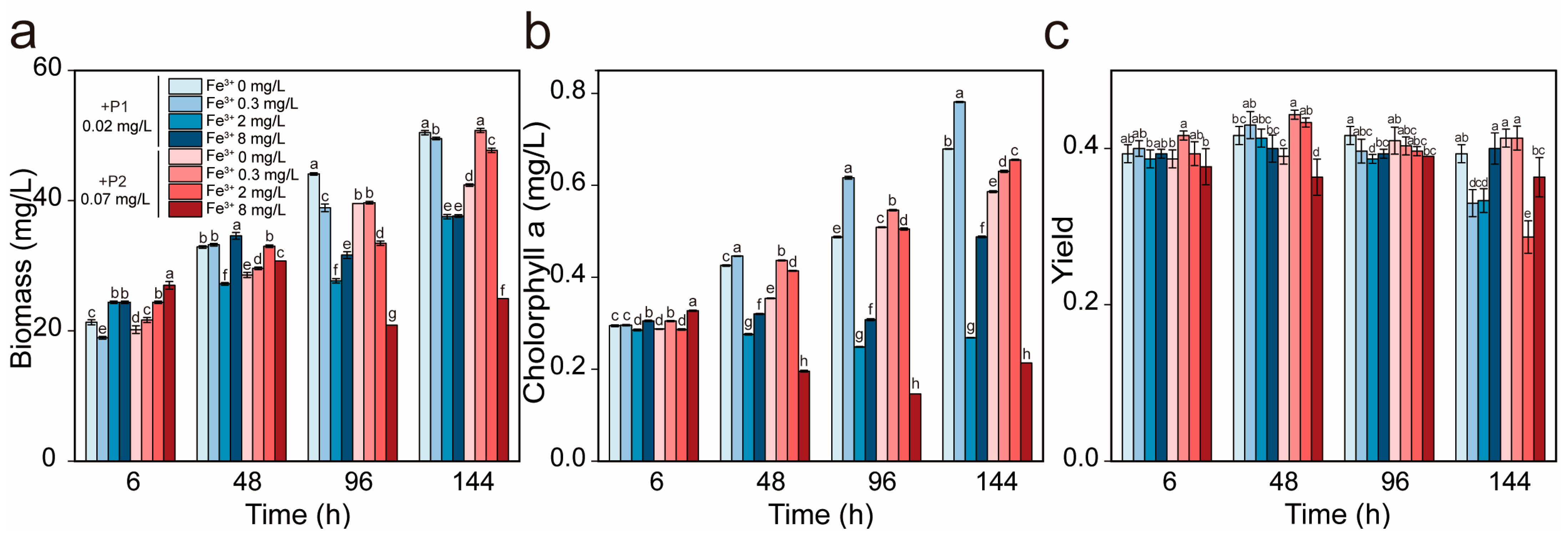
3.4. IP Levels Modulate Fe3+ Inhibition Threshold in R. raciborskii
3.5. Fe3+ Regulates OP-IP Metabolic Conversion in R. raciborskii
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antunes, J.T.; Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: Review of the distribution, phylogeography, and ecophysiology of a global invasive species. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briand, J.; Leboulanger, C.; Humbert, J.; Bernard, C.; Dufour, P. Cylindrospermopsis Raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) Invasion At Mid-Latitudes: Selection, Wide Physiological Tolerance, Orglobalwarming? J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Pearson, L.A.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Orr, P.T.; Neilan, B.A. Increased incidence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in temperate zones—Is climate change responsible? Water Res. 2012, 46, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, C.; Ba, N.; Gugger, M.; Bouvy, M.; Rusconi, F.; CoutÃ, A.; Troussellier, M.; Bernard, C. Seasonal dynamics and toxicity of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Lake Guiers (Senegal, West Africa). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 57, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanier, R.Y.; Deruelles, J.; Rippka, R.; Herdman, M.; Waterbury, J.B. Generic Assignments, Strain Histories and Properties of Pure Cultures of Cyanobacteria. Microbiology 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla, S.; Aubriot, L.; Soares, M.C.S.; González-Piana, M.; Fabre, A.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Lürling, M.; Antoniades, D.; Padisák, J.; Kruk, C. What drives the distribution of the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, A.; Posselt, A.J.; Burford, M.A. Variations in carbon-to-phosphorus ratios of two Australian strains of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zeng, B.; Li, R.; Song, L. Physiological regulation of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) in response to inorganic phosphorus limitation. Harmful Algae 2012, 15, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Hamilton, D.P.; Chuang, A.; Burford, M.A. Intra-population strain variation in phosphorus storage strategies of the freshwater cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, P.D.; Moffett, J.W.; Hynes, A.M.; Webb, E.A. Molecular evidence of iron limitation and availability in the global diazotroph Trichodesmium. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.M.; Tulk, S.E.; Jeans, J.A.; Campbell, D.A.; Bibby, T.S.; Cockshutt, A.M. Photophysiological and Photosynthetic Complex Changes during Iron Starvation in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G. Differences in growth, pigment composition and photosynthetic rates of two phenotypes Microcystis aeruginosa strains under high and low iron conditions. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 55, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, A.J.; Hilborn, E.D. Cyanobacterial blooms, iron, and environmental pollutants. Biometals 2024, 37, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranzler, C.; Rudolf, M.; Keren, N.; Schleiff, E. Iron in Cyanobacteria. In Advances in Botanical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 57–105. [Google Scholar]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Halsey, K.H.; Milligan, A.J. Evolved physiological responses of phytoplankton to their integrated growth environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 2687–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, K.S.; Ahern, C.R.; Udy, J.W. In situ field experiment shows Lyngbya majuscula (cyanobacterium) growth stimulated by added iron, phosphorus and nitrogen. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustka, A.; Carpenter, E.J.; Sañudo-Wilhelmy, S.A. Iron and marine nitrogen fixation: Progress and future directions. Res. Microbiol. 2002, 153, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, F.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Tang, D.; Liu, J. Effect of complex iron on the phosphorus absorption by two freshwater algae. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 4125–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spijkerman, E. Phosphorus limitation of algae living in iron-rich, acidic lakes. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 53, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.J.; Lei, L.M.; Peng, L.; Lin, Q.Q.; Naselli-Flores, L. Iron operates as an important factor promoting year-round diazotrophic cyanobacteria blooms in eutrophic reservoirs in the tropics. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmet, A.; Göksel, M.; Fatih, A.; Olcay, Ş. Air Oxidation of Ferrous Iron in Water. J. Int. Environ. Appl. Sci. 2008, 3, 409–414. [Google Scholar]
- Stumm, W.; Lee, G.F. The chemistry of aqueous iron. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 1960, 22, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.W.; Koedooder, C.; Qiu, B.S.; Shaked, Y.; Keren, N. Iron transport in cyanobacteria—From molecules to communities. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, A.; Takeda, S.; Saito, H.; Nishioka, J.; Nojiri, Y.; Kudo, I.; Kiyosawa, H.; Shiomoto, A.; Imai, K.; Ono, T.; et al. A Mesoscale Iron Enrichment in the Western Subarctic Pacific Induces a Large Centric Diatom Bloom. Science 2003, 300, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.C.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, J.F. Evaluation methods and grading criteria for lake eutrophication. China Environ. Monit. 2002, 18, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Nguyen, B.T.; Zhou, C.; Straka, L.; Lai, Y.S.; Xia, S.; Rittmann, B.E. The distribution of phosphorus and its transformations during batch growth of Synechocystis. Water Res. 2017, 122, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, W.; Cai, Q. Survey, Observation and Analysis of Lake Ecology; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L. Method for Monitoring and Analysis Water and Wastewater; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, T. Effect of different kinds of complex iron on the growth of Anabaena flos-aquae. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 2889–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.J.; Xie, J.; Tan, L.; Lei, L.M.; Peng, L.; Wang, Z.; Naselli-Flores, L. Iron enrichment from hypoxic hypolimnion supports the blooming of Raphidiopsis raciborskii in a tropical reservoir. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Hu, R.P.; Zhong, H.J.; Xiao, L.J.; Lei, L.M.; Han, B.P. Effects of iron on the seasonal dynamics and growth of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Staurastrum spp. in Guangdong Dashahe Reservoir. Reserv. Guangdong. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, T.; Imai, A.; Matsushige, K.; Fukushima, T. Effect of iron complexation with dissolved organic matter on the growth of cyanobacteria in a eutrophic lake. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 44, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Huang, W.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Effects of Iron on Growth, Pigment Content, Photosystem II Efficiency, and Siderophores Production of Microcystis aeruginosa and Microcystis wesenbergii. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 55, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.K. Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Cyanobacteria Responding and Adapting to Iron Limitation; Central China Normal University: Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.Y.; Bai, T.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Tian, L.R. Advances in photosynthetic mechanisms of algae in response to iron deficiency stress. Chin. Agron. Bull. 2022, 38, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.J. Synergistic Effects of Iron and Phosphorus on the Growth of Three Typical Freshwater Algae and the Mechanism of Chemosensory Competition; Guangdong University of Technology: Guangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Van Moorlehem, C. Detection of Bioavailable Phosphorus Forms for the Alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata; KU Leuven: Leuven, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; He, S.; Zhao, L.; Ji, L.; Yang, S.; Wu, Z. Physiological and molecular responses of invasive cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii to ambient phosphorus deficiency. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandori, K.; Ohnishi, S.; Fukusumi, M.; Morisada, Y. Effects of anions on the morphology and structure of hematite particles produced from forced hydrolysis of Fe(NO3)3–HNO3. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 331, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.K. Exploration of the decomposition mechanism of organophosphorus pesticide powders—Acid-base catalysed hydrolysis. Pesticides 1984, 4, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, F.; Liu, R.; Yang, Y.; Ran, X.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z. Dissolved organic phosphorus use by the invasive freshwater diazotroph cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabouille, S.; Tournier, L.; Duhamel, S.; Claquin, P.; Crispi, O.; Talec, A.; Landolfi, A.; Oschlies, A. Organic Phosphorus Scavenging Supports Efficient Growth of Diazotrophic Cyanobacteria Under Phosphate Depletion. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 848647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.N.; Li, Z.K.; Wu, K. Effects and interactions of iron-phosphorus on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB1028 in Taihu Lake. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 15178–15182. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Li, D.; Guan, D. Water quality retrieval and algae inhibition from eutrophic freshwaters with iron-rich substrate based ecological floating beds treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 135584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Growth, extracellular alkaline phosphatase activity, and kinetic characteristic responses of the bloom-forming toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to atmospheric particulate matter (PM2.5, PM2.5–10, and PM > 10). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7358–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Balamurugan, S.; Liu, S.F.; Ji, C.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Yang, W.D.; Jiang, L.; Li, H.Y. Hydrolysis of organophosphorus by diatom purple acid phosphatase and sequential regulation of cell metabolism. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 2918–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Antia, N.J.; Harrison, P.J.; Rhee, G.Y. The Utilization of Inorganic and Organic Phosphorous Compounds as Nutrients by Eukaryotic Microalgae: A Multidisciplinary Perspective: Part 2. CRC Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1984, 11, 13–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, R.P.; Songkasiri, W.; Rittmann, B.E.; Reed, D.T. Surface Complexation of Neptunium(V) onto Whole Cells and Cell Components of Shewanella alga: Modeling and Experimental Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4930–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Vannela, R.; Zhou, C.; Rittmann, B.E. Nutrient acquisition and limitation for the photoautotrophic growth of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 as a renewable biomass source. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Burford, M.A.; Wood, S.A.; Aubriot, L.; Ibelings, B.W.; Prentice, M.J.; Galvanese, E.F.; Harris, T.D.; Hamilton, D.P. Schindler’s legacy: From eutrophic lakes to the phosphorus utilization strategies of cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuac029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, W.; Yang, H.; Ding, G.; Li, B.; Gan, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Response of the Invasive Cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii to Iron and Phosphorus Concentrations in the Habitat: Effects on Growth and Cellular Phosphorus Distribution. Diversity 2025, 17, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060386
Shen W, Yang H, Ding G, Li B, Gan X, Yuan Z, Wang L, Zhang W. Response of the Invasive Cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii to Iron and Phosphorus Concentrations in the Habitat: Effects on Growth and Cellular Phosphorus Distribution. Diversity. 2025; 17(6):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060386
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Wenting, Han Yang, Gaibian Ding, Bo Li, Xin Gan, Zijie Yuan, Liqing Wang, and Wei Zhang. 2025. "Response of the Invasive Cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii to Iron and Phosphorus Concentrations in the Habitat: Effects on Growth and Cellular Phosphorus Distribution" Diversity 17, no. 6: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060386
APA StyleShen, W., Yang, H., Ding, G., Li, B., Gan, X., Yuan, Z., Wang, L., & Zhang, W. (2025). Response of the Invasive Cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii to Iron and Phosphorus Concentrations in the Habitat: Effects on Growth and Cellular Phosphorus Distribution. Diversity, 17(6), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060386






