Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Assemblages Driven by Environmental Factors Along Trophic Gradients in Thai Lentic Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
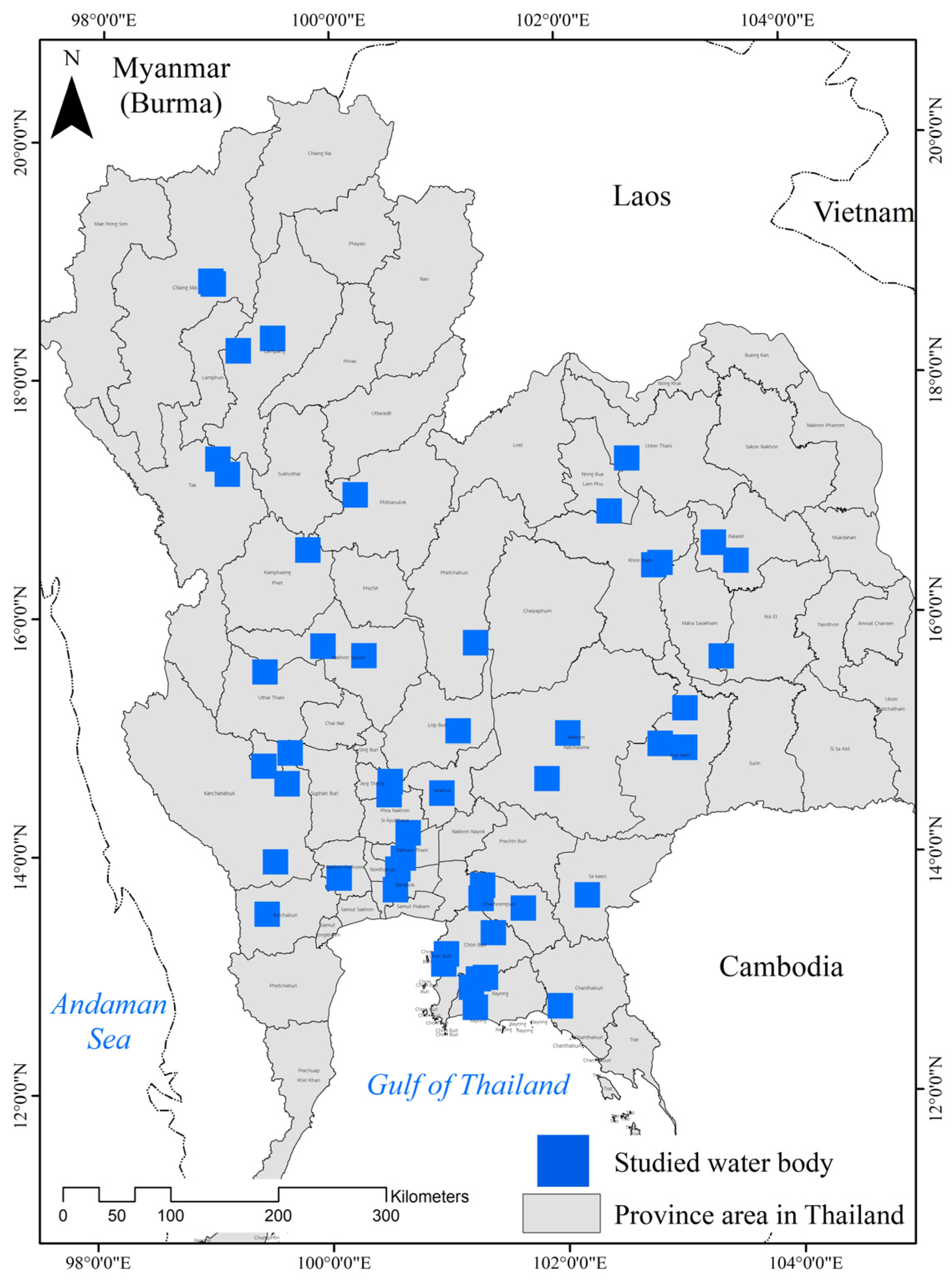
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Field Sampling and Water Quality Analysis
2.2.1. In Situ Water Quality Measurement and Phytoplankton–Zooplankton Sampling
2.2.2. Water Quality Analysis and Plankton Study in the Laboratory
2.3. Data and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
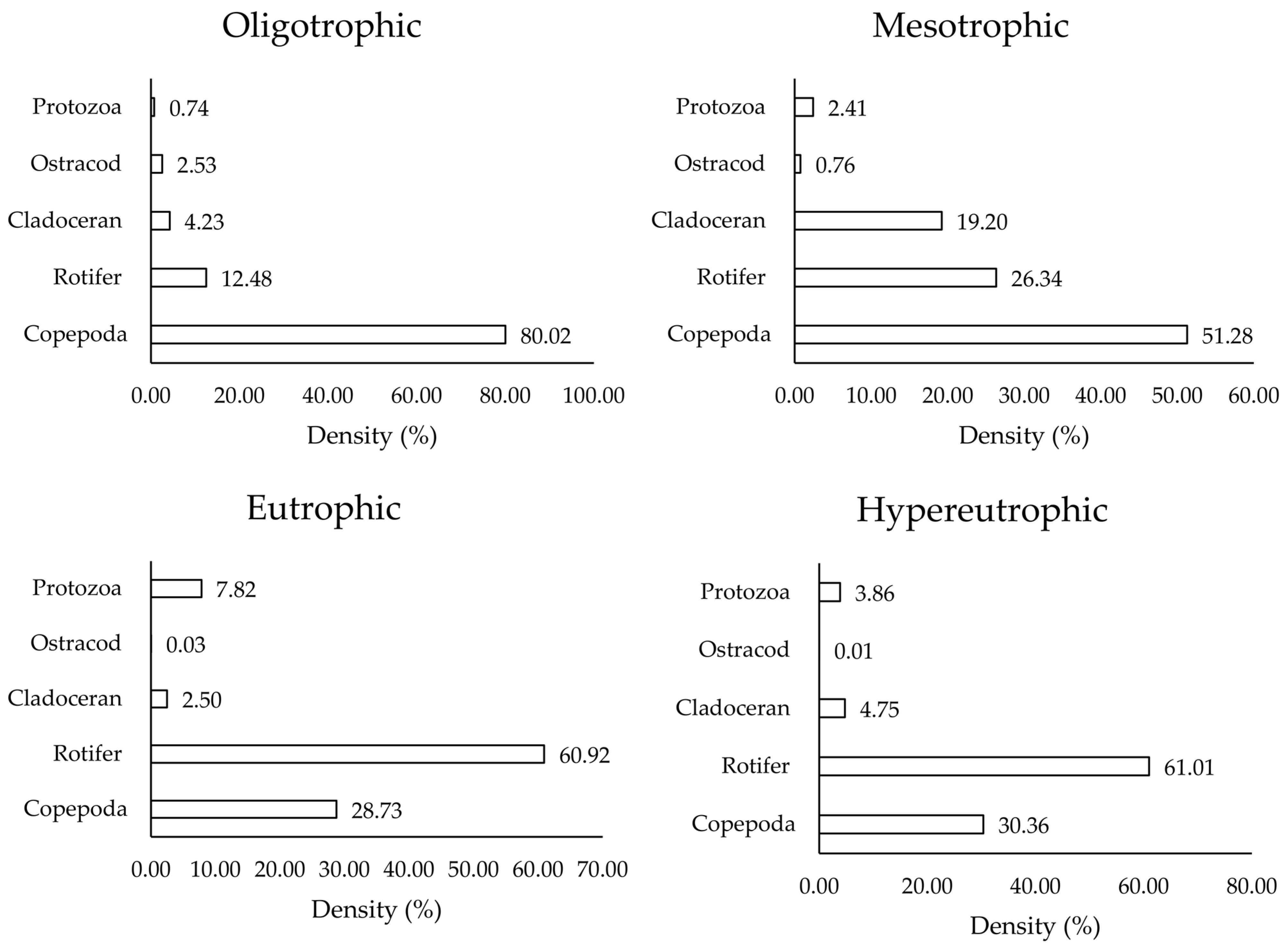
3.1. Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Distribution Across Different Trophic States
3.2. Dominant Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Species
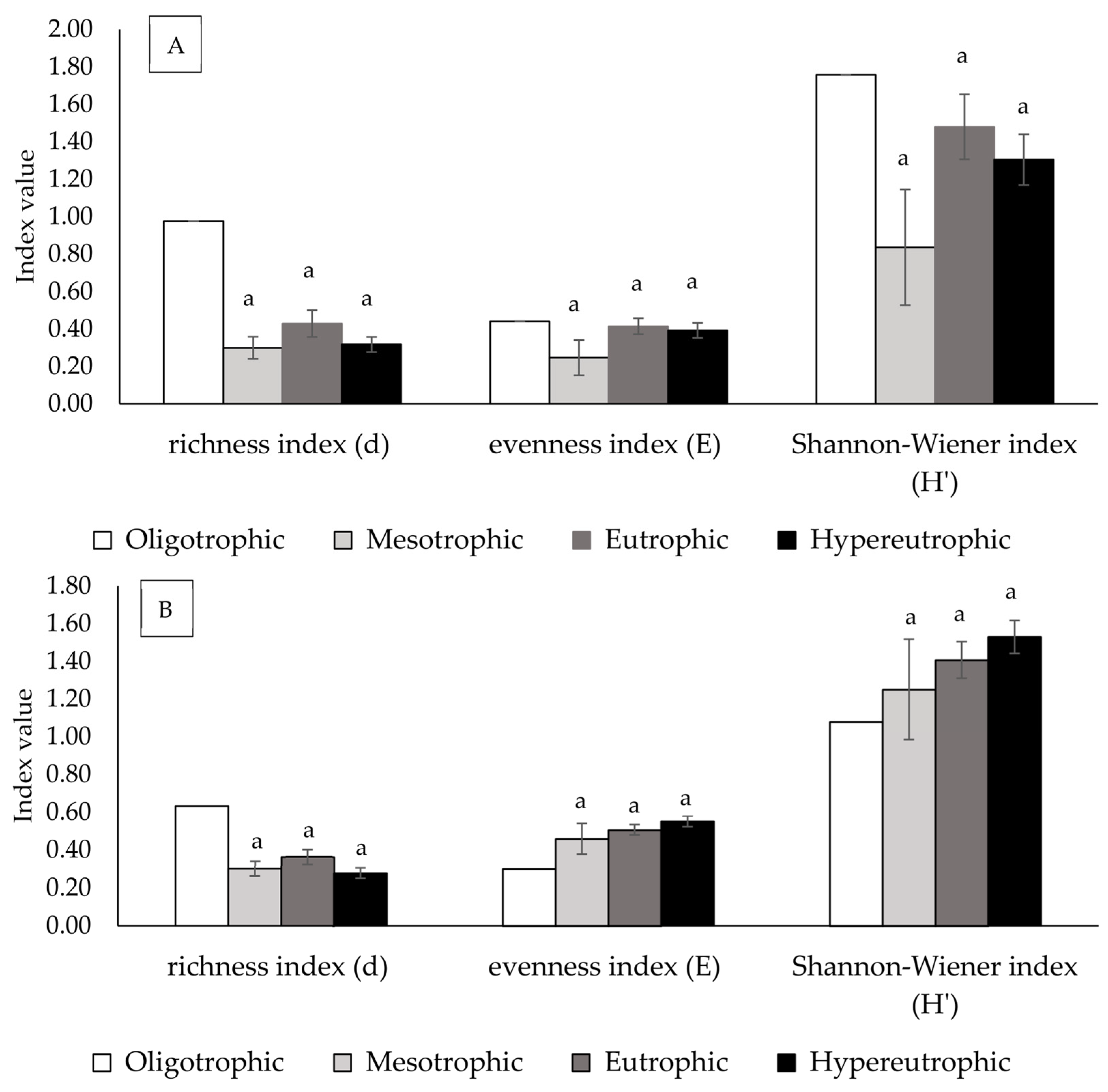
3.3. Effects of Trophic Status on Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Richness, Evenness, and Shannon-Wiener Indices
3.4. Assessing the Relationship Between Water Quality, Phytoplankton, and Zooplankton Using Correlation Analysis
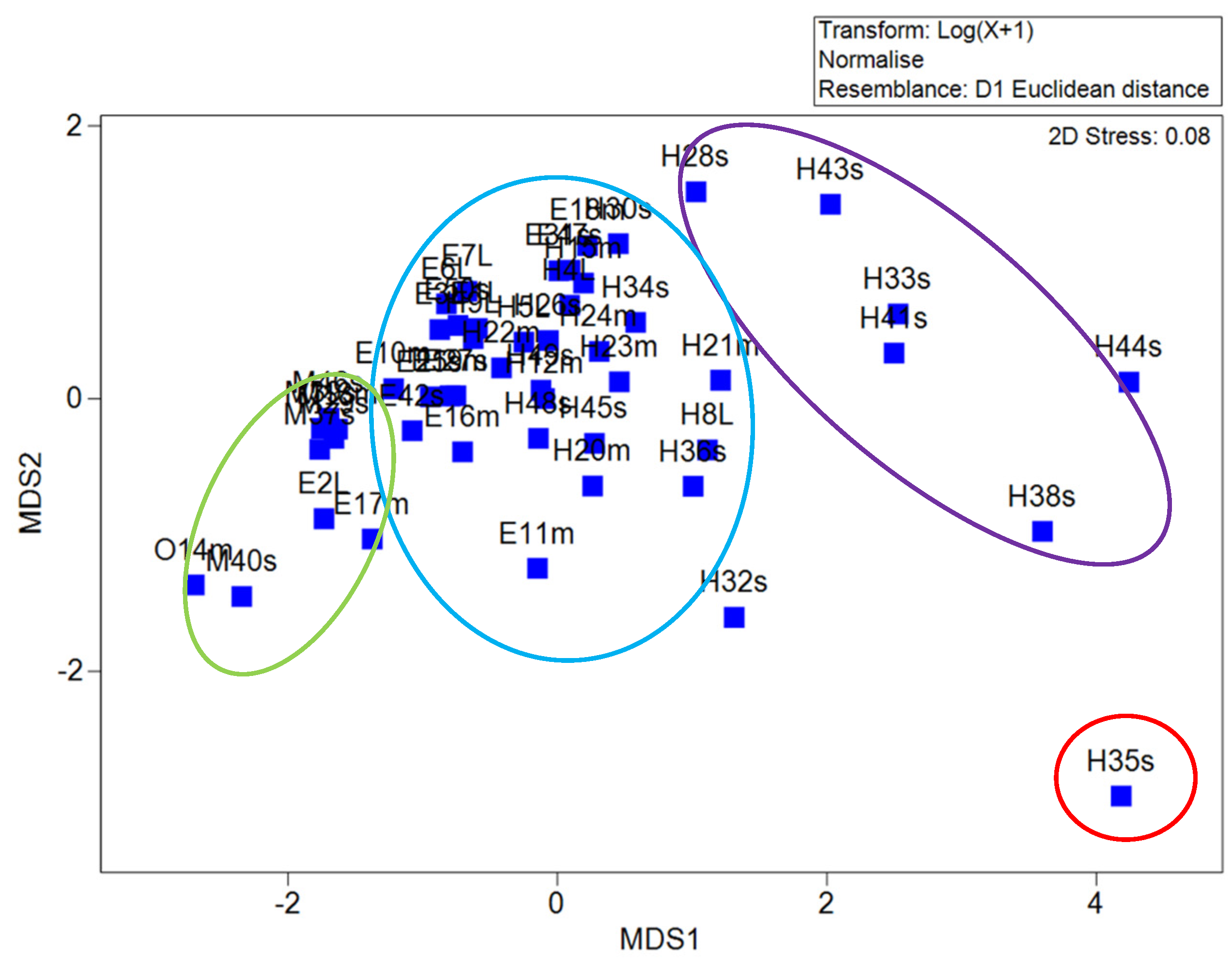
3.5. Multidimensional Scaling Analysis
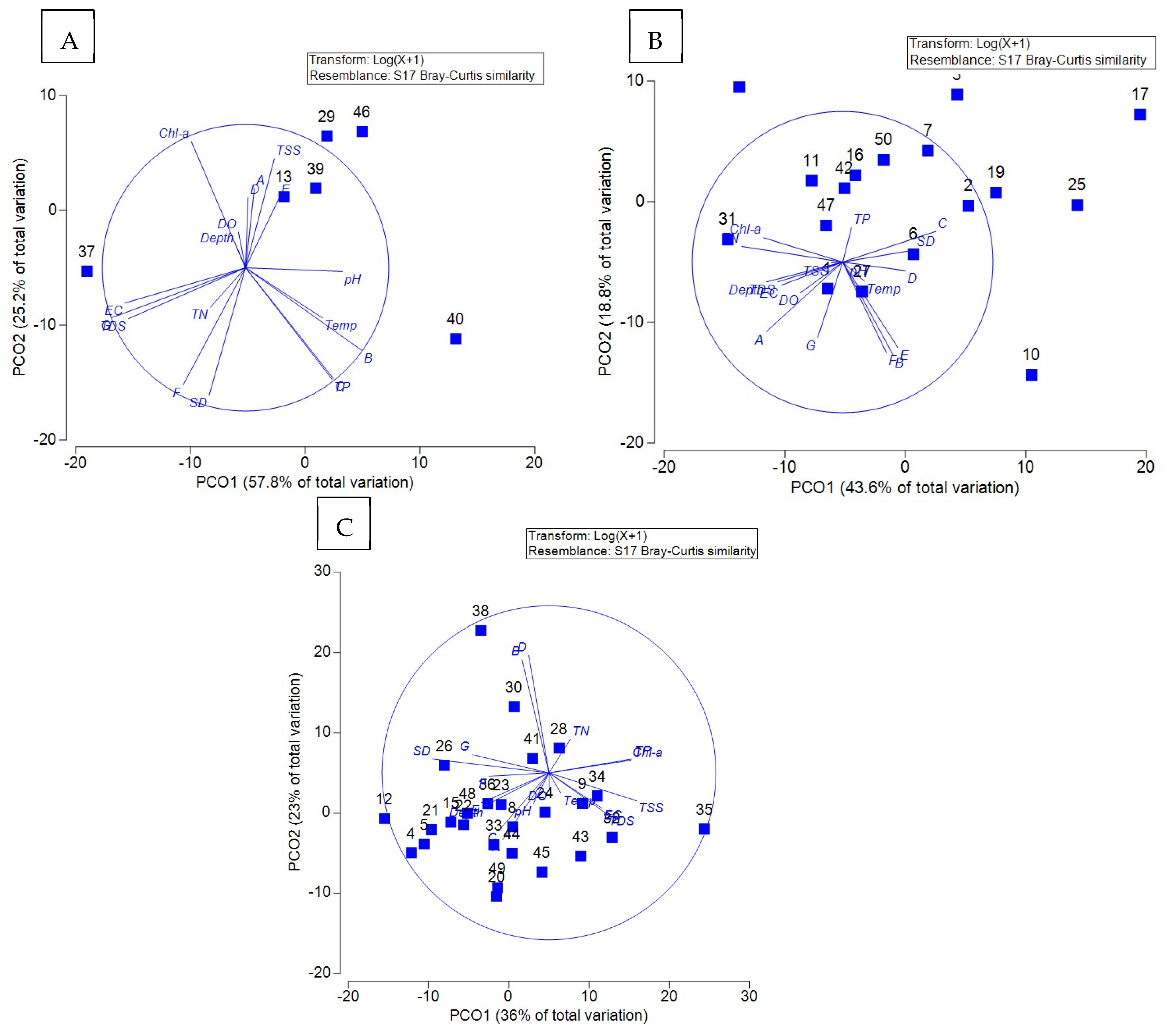
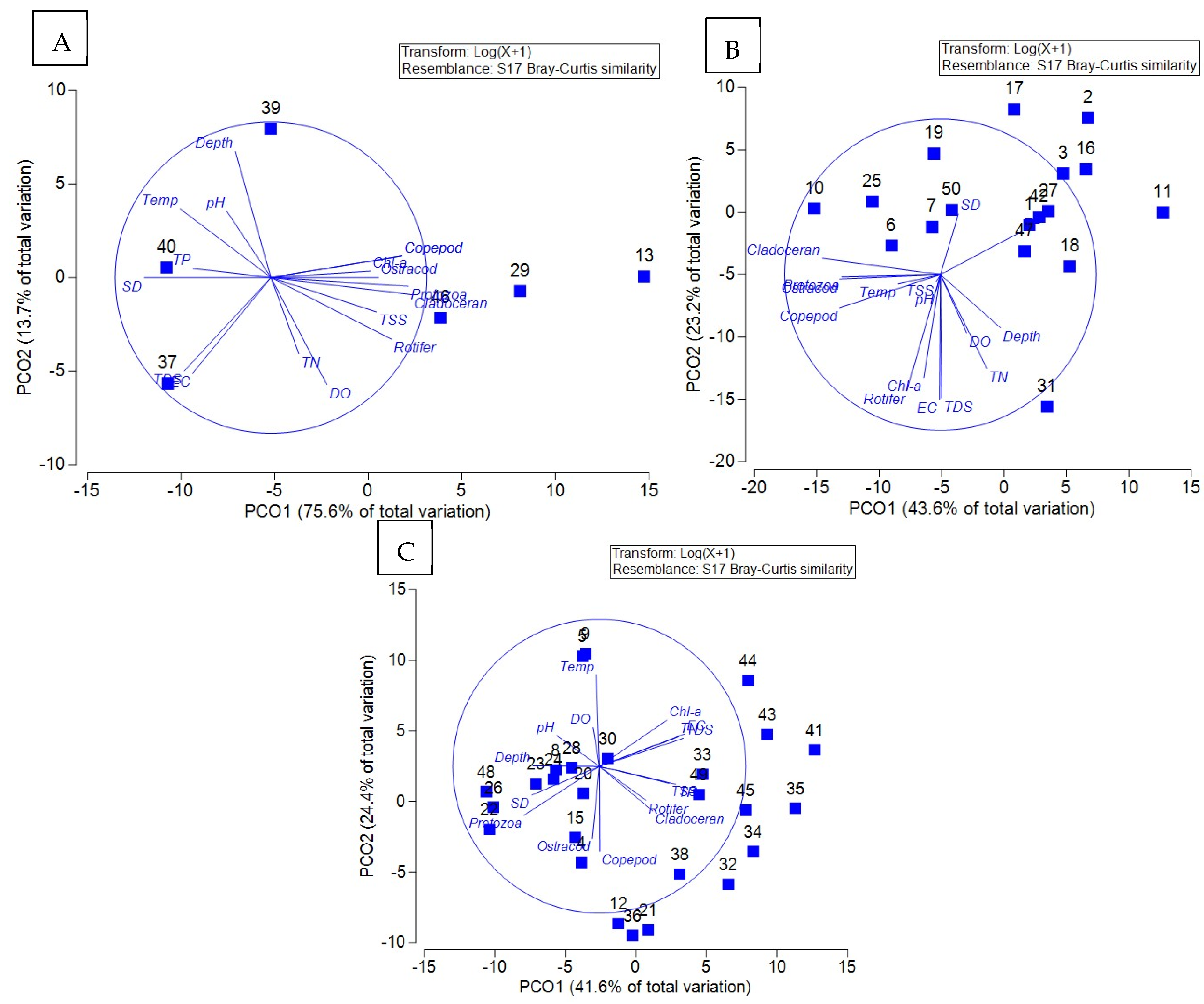
3.6. Principal Coordinate Analysis of the Relationship Between Water Quality and Plankton Communities in Trophic Water Bodies
4. Discussion
4.1. Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Distribution Across Different Trophic States
4.2. Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Richness, Evenness, and Shannon–Wiener Indices Among Water Bodies Across Different Trophic States
4.3. The Relationship Between Water Quality, Phytoplankton, and Zooplankton
4.4. Analysis of Multidimensional Scaling and Principal Coordinate Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonati, M.; Poikane, S.; Pringle, C.; Stevens, L.; Turak, E.; Heino, J.; Richardson, J.; Bolpagni, R.; Borrini, A.; Cid, N.; et al. Characteristics, main impacts, and stewardship of natural and artificial freshwater environments: Consequences for biodiversity conservation. Water 2020, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobacina, L.; Fasano, F.; Mezzanotte, V.; Fornaroli, R. Effects of water temperature on freshwater macroinvertebrates: A systematic review. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2023, 98, 191–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijewardene, L.; Wu, N.; Qu, Y.; Guo, K.; Messyasz, B.; Lorenz, S.; Riis, T.; Ulrich, U.; Fohrer, N. Influences of pesticides, nutrient, and local environmental variables on phytoplankton communities in lentic small water bodies in German lowland agricultural area. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, M.W.; Sengupta, D.; Chowdhury, A. Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: Their benefits and hazards. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, J.; Luoto, M. Is catchment productivity a useful predictor of taxa richness in lake plankton communities? Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, L.I.; Moldoveanu, M.M.; Catana, R.D.; Pacesila, I.; Dumitrache, A.; Gavrilidis, A.A.; Ioja, C.I. Assessing the effects of phytoplankton structure on zooplankton communities in different types of urban lakes. Diversity 2022, 14, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochocka, A.; Pasztaleniec, A. Sensitivity of plankton indices to lake trophic conditions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamou, G.; Katsiapi, M.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Michaloudi, E. Trophic state assessment based on zooplankton communities in Mediterranean lakes. Hydrobiologi 2019, 844, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, K.E.; Reavie, E.D.; Figary, S.; Rudstam, L.G.; Watkins, J.M.; Scofield, A.; Filstrup, C.T. Zooplankton-phytoplankton biomass and diversity relationship in the Great Lakes. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Smith, V.H. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in streams. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elser, J.J.; Goldman, C.R. Zooplankton effects on phytoplankton in lakes of contrasting trophic status. Am. Soc. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekvall, M.K.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Hansson, L. Linking cascading effects of fish predation and zooplankton grazing to reduced Cyanobacterial biomass and toxin levels following biomanipulation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuttarunggoon, N.; Anurakpongsatorn, P.; Tantanasarit, S.; Mahujchariyawong, J. Characterization of water quality in Bunboraped wetland, Thailand using self organizing map for water quality management. EnvironmentAsia 2020, 13, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Singkran, N. Determining overall water quality related to anthropogenic influences across freshwater systems of Thailand. Water Resour. Dev. 2017, 33, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertphon, R.; Jitchum, P.; Chaichana, R. Water chemistry, phytoplankton diversity and severe eutrophication with detection of Microcystin contents in Thai tropical urban ponds. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 5939–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descy, J.-P.; Leprieur, F.; Pirlot, S.; Leporcq, B.; Van Wichelen, L.; Peretyatko, A.; Teissier, S.; Codd, G.A.; Triest, L.; Vyverman, W.; et al. Identifying the factor determining blooms of cyanobacteria in a set of shallow lakes. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 34, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulic, M.; Hand, J.; Lord, L. Water-Quality Assessment for the State of Florida Section 305(B) Main Report; Bureau of Water Resources Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1996; p. 317. [Google Scholar]
- Talling, J.F.; Driver, D. Some problems in the estimation of chlorophyll-a in phytoplankton. In Proceedings of the Conference of Primary Productivity Measurement, Marine and Freshwater, Honolulu, HA, USA, 21 August–6 September 1961; Atomic Energy Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 1963; pp. 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wongrat, L.; Wongrat, P.; Ruangsomboon, S. Plankton; Faculty of Fisheries, Kasetsart University: Bangkok, Thailand, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, C.E. The measurement of biodiversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menhinick, E.F. A comparison of some species-individuals diversity indices applied to samples of field insects. Ecology 1964, 45, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPSS About SPSS Inc. Available online: http://www.spss.com.hk/corpinfo/history.htm (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v7: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Devon, UK, 2015; 296p. [Google Scholar]
- Nasution, A.K.; Takarina, N.D.; Thoha, H. The presence and abundance of harmful dinoflagellate alae related to water quality in Jakarta Bay, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 2021, 22, 2909–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesukko, C.; GaJaswni, N.; Peerapornpisal, Y.; Voinov, A. Relationships between seasonal variation and phytoplankton dynamics in Kaeng Krachan reservoir, Phetchaburi province, Thailand. Nat. Hist. J. Chulalongkorn Univ. 2007, 7, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertsin, T.; Yavichai, S.; Pingmano, C. Diversity of phytoplankton and water quality in Mae Suai reservoir during the rainy season. Prog. Appl. Sci. Tech. 2025, 8, 184–199. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, R.M.; Greco, A.; Nanda, A.; Rios-Ruiz, C.; Wang, Y.; Yoon, P.; Restaina, D.J.; Gaynor, J.J.; Bologna, P.A.X.; Chu, T. Detection and characterization of the Cyanobacteria and Cyanophages of Barnegat Bay, New Jersey. J. Environ. Prot. 2019, 10, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, Z.; Lv, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, S.; Feng, J. Cyanobacteria as dominant mediator of altitudinal gradient effects on phytoplankton community diversity in freshwater ecosystems: Evidences from the freshwater Lakes along the Hu Line. Water Res. X 2025, 26, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Luque, E.; Bhaya, D.; Grossman, A.R. Polyphosphate: A multifunctional metabolite in Cyanobacteria and algae. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 938. [Google Scholar]
- Hessen, D.O.; Faafeng, B.A.; Brettum, P.; Andersen, T. Nutrient enrichment and planktonic biomass ratios in lakes. Ecosystems 2006, 9, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisse, T.; Gröschl, B.; Bergkemper, V. Phytoplankton response to short-term temperature and nutrient changes. Limnologica 2016, 59, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, E.A.; El-Mallah, A.M.; Abdel-Baki, A.-A.S.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Reyad, A.; Abdel-Tawab, H. Effect of environmental variables on zooplankton in various habitats of the Nile River. Water 2024, 16, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansano, A.S.; Hisatugo, K.F.; Leite, M.A.; Regali-Seleghim, M.H. Seasonal variation of the protozooplanktonic community in a tropical oligotrophic environment (Ilha Solteira reservoir, Brazil). Braz. J. Biol. 2013, 73, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Külköylüoglu, O.; Sari, N.; Dügel, M.; Dere, S.; Dalkiran, N.; Aygen, C.; Dincer, C. Effects of limnoecological changes on the Ostracoda (Crustacea)community in a shallow lake (Lake Çubuk, Turkey). Limnologica 2014, 46, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarova, N.; Napiórkowski, P. Are rotifer indices suitable for assessing the trophic status in slow-flowing waters of canals. Hydrobiologia 2024, 851, 3013–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pransertphon, R.; Chaichana, R.; Jitchum, P. Seasonal variation of zooplankton assemblages and their response to water chemistry and microcystin content in shollow lakes in Thaland. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2023, 75, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturej, E.; Kowalska, E. Rotifers trophic state indices as ecosystem indicators in Brackish coastal waters. Oceanologia 2013, 55, 887–889. [Google Scholar]
- Umi, W.A.D.; Yusoff, F.M.; Yusof, Z.N.B.; Ramli, N.M.; Sinev, A.Y.; Toda, T. Composition, distribution, and biodiversity of zooplanktons in tropical lentic ecosystems with different environmental conditions. Arthropoda 2024, 2, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogfors, H.; Motwani, N.H.; Haidu, S.; El-Shehawy, R.; Holmborn, T.; Vehmaa, A.; Engström-öst, J.; Bretemark, A.; Gorokhova, E. Bloo-forming cyanobacteria support copepoda reproduction and development in the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, C.R.; Diniz, L.P.; da Silva, A.J.; Fonseca, G.; Carneiro, L.S.; de Melo Junior, M.; Caliman, A. Zooplankton species distribution, richness and composition across tropical shallow lakes: A large scale assessment by biome, lake origin, and lake habitat. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2020, 56, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nes, E.H.V.; Scheffer, M.; Berg, M.S.V.D.; Coops, H. Dominance of charophytes in eutrophic shallow lakes-When should we expect it to be an alternative stable state? Aquat. Bot. 2002, 72, 275–296. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, E.; Lazzari, P.; Cossarini, G. Phytoplankton diversity emerging from chromatic adaptation and competition for light. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 204, 102789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, S.; Tamminen, T.; Ptacnik, R.; Andersen, T. Phytoplankton species richness, evenness, and production in relation to nutrient availability and imbalance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1393–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardinaal, W.E.A.; Tonk, L.; Janse, I.; Hol, S.; Slot, P.; Huisman, J.; Visser, P.M. Competition for light between toxic and nontoxic strains of the harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perbiche-Neves, G.; Saito, V.S.; Previattelli, D.; Rocha, C.E.F. Cyclopoid copepoda as bioindicators of eutrophication in reservoirs: Do patterns hold for large spatial extents. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyn’ska-Kippen, N.; Joniak, T. Zooplankton diversity and macrophyte biometry in shallow water bodies of various trophic state. Hydrobiologia 2016, 774, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska, K.; Napiórkowska-Krzebietke, A.; Bogacka-Kapusta, E.; Stawecki, K.; Traczuk, P.; Ulikowski, D. Algae-zooplankton relationships during the year-round cyanobacterial blooms in a shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 2023, 10, 10–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Teurlincx, S.; Janse, J.H.; Paerl, H.W.; Mooij, W.M.; Janssen, A.B.G. Exploring how cyanobacterial traits affect nutrient loading thresholds in shallow lakes: A modelling approach. Water 2020, 12, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Zhou, J. Phytoplankton community structure and water quality assessment in Xuanwu Lake, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 11, 1303851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesh, I.; Schubert, H.; Skarlato, S. Abiotic stability promotes dinoflagellate blooms in marine coastal ecosystems. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 251, 107239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Prabha, D. Evalution of trophic state conditions in the three urban perennial lakes of the Coimbatore district, Tamil Nadu: Based on water quality parameters and rotifer composition. HydroResearch 2024, 7, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, E.; Canfield, J.; Curtis, E.; Watkins, I. Relationships between zooplankton abundance and chlorophyll a con-centrations in Florida Lakes. J. Freshw. Ecol. 1984, 2, 335–344. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, A.; Liu, J.; Xing, C.; Huang, S.; Huo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, W. Turnover of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities driven by human-induced disturbances and climate changes in a small urban coastal wetland. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Colmenares, M.E.; Sendra, M.D.; Sòria-Perpinyà, X.; Soria, J.M.; Vicente, E. The Use of Zooplankton Metrics to Determine the Trophic Status and Ecological Potential: An Approach in a Large Mediterranean Watershed. Water 2021, 13, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, I.C.; Green, J.D.; Thomasson, K. Do rotifer have potential as bioindicators of lake trophic state? SIL Proc. 2001, 27, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Division | Water Parameters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHYTOPLANKTON | Chl-a (µg/L) | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | Temp (C) | pH | DO (mg/L) | TDS (mg/L) | TSS (mg/L) | EC (µs/cm) | SD (m) |
| Cyanophyta | 0.067 | 0.101 | −0.082 | −0.051 | 0.331 * | 0.287 * | 0.383 ** | −0.132 | 0.403 ** | −0.117 |
| Chlorophyta | 0.023 | 0.456 ** | 0.317 * | −0.284* | −0.158 | −0.358 * | −0.024 | −0.052 | 0.007 | −0.010 |
| Charophyta | −0.165 | −0.098 | −0.057 | 0.198 | 0.078 | 0.002 | −0.086 | −0.105 | −0.099 | 0.349 * |
| Euglenozoa | −0.006 | 0.334 * | 0.238 | −0.061 | −0.206 | −0.221 | −0.058 | 0.035 | −0.043 | −0.023 |
| Heterkontophyta | −0.173 | −0.112 | −0.141 | −0.070 | −0.155 | −0.076 | −0.121 | −0.113 | −0.095 | 0.067 |
| Ochrophyta | −0.099 | −0.071 | −0.098 | −0.027 | −0.200 | −0.013 | −0.036 | −0.052 | −0.017 | −0.009 |
| Dinophyta | −0.202 | −0.161 | −0.211 | 0.054 | −0.040 | 0.319 * | −0.053 | −0.153 | −0.039 | 0.317 * |
| ZOOPLANKTON | ||||||||||
| Copepoda | 0.033 | −0.119 | 0.098 | −0.219 | −0.039 | 0.061 | −0.134 | 0.035 | −0.117 | −0.035 |
| Rotifer | 0.278 | 0.127 | 0.358 * | 0.010 | 0.147 | 0.157 | 0.387** | 0.031 | 0.422 ** | −0.156 |
| Cladoceran | −0.101 | −0.097 | 0.022 | −0.091 | −0.242 | 0.006 | −0.089 | −0.021 | −0.082 | 0.013 |
| Ostracod | −0.169 | −0.120 | −0.138 | −0.162 | −0.196 | −0.106 | −0.154 | −0.116 | −0.152 | 0.496 ** |
| Protozoa | −0.132 | −0.131 | −0.141 | −0.135 | −0.075 | −0.095 | −0.064 | −0.117 | −0.095 | −0.034 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phonmat, P.; Chaichana, R.; Rakasachat, C.; Klongvessa, P.; Chanthorn, W.; Moukomla, S. Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Assemblages Driven by Environmental Factors Along Trophic Gradients in Thai Lentic Ecosystems. Diversity 2025, 17, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060372
Phonmat P, Chaichana R, Rakasachat C, Klongvessa P, Chanthorn W, Moukomla S. Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Assemblages Driven by Environmental Factors Along Trophic Gradients in Thai Lentic Ecosystems. Diversity. 2025; 17(6):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060372
Chicago/Turabian StylePhonmat, Peangtawan, Ratcha Chaichana, Chuti Rakasachat, Pawee Klongvessa, Wirong Chanthorn, and Sitthisak Moukomla. 2025. "Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Assemblages Driven by Environmental Factors Along Trophic Gradients in Thai Lentic Ecosystems" Diversity 17, no. 6: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060372
APA StylePhonmat, P., Chaichana, R., Rakasachat, C., Klongvessa, P., Chanthorn, W., & Moukomla, S. (2025). Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Assemblages Driven by Environmental Factors Along Trophic Gradients in Thai Lentic Ecosystems. Diversity, 17(6), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17060372






