Changes in Biomass Production, Plant Diversity, and Their Relationship During the Early Establishment of Artificial Alpine Grasslands with Different Species Combinations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Experimental Design
2.2. Sampling and Aboveground Biomass Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
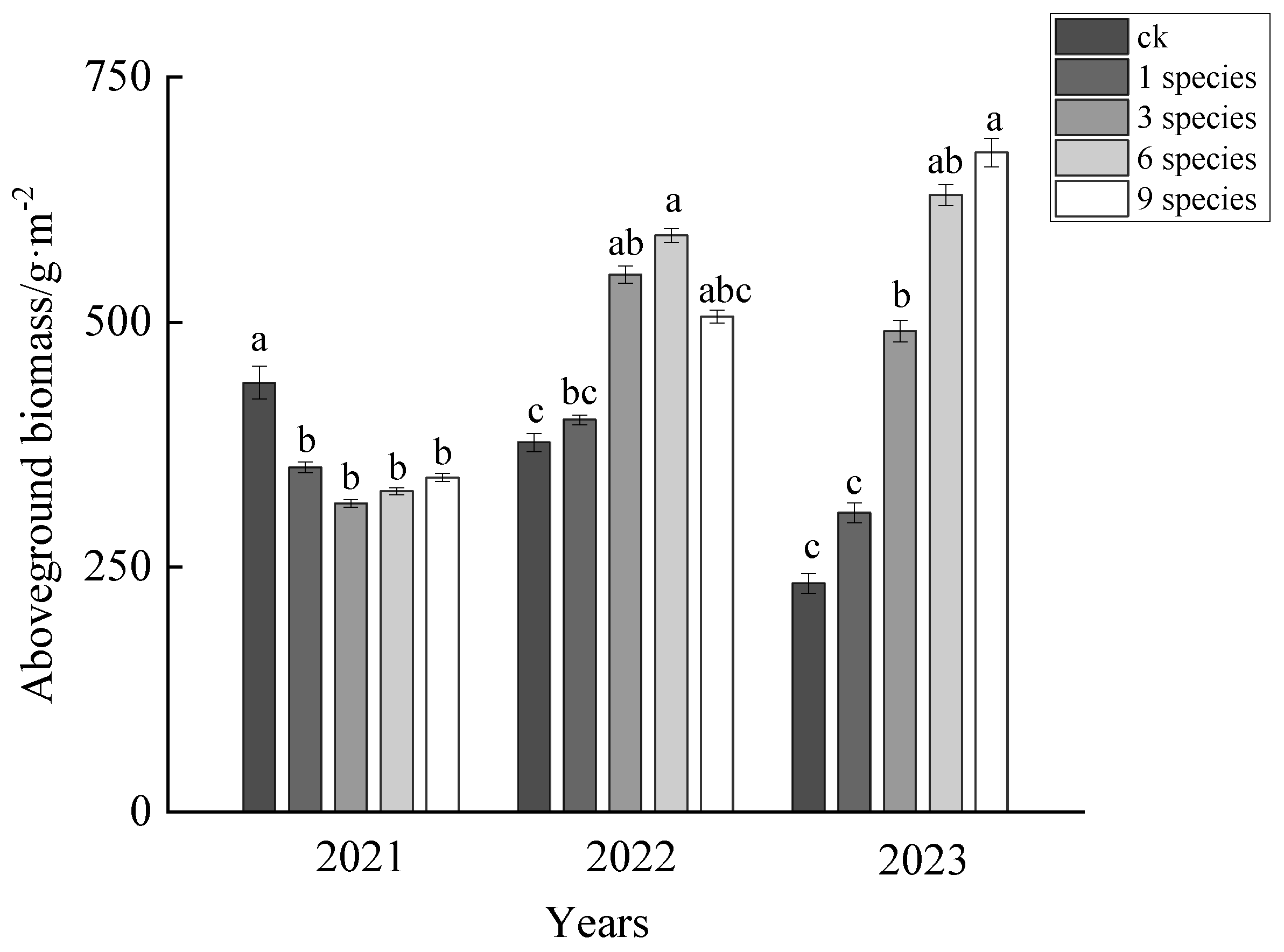
3.1. The Effects of Different Species Combinations on Aboveground Biomass
3.2. The Effects of Different Species Combinations on Plant Diversity
3.3. The Relationship Between Plant Diversity and Biomass Productivity
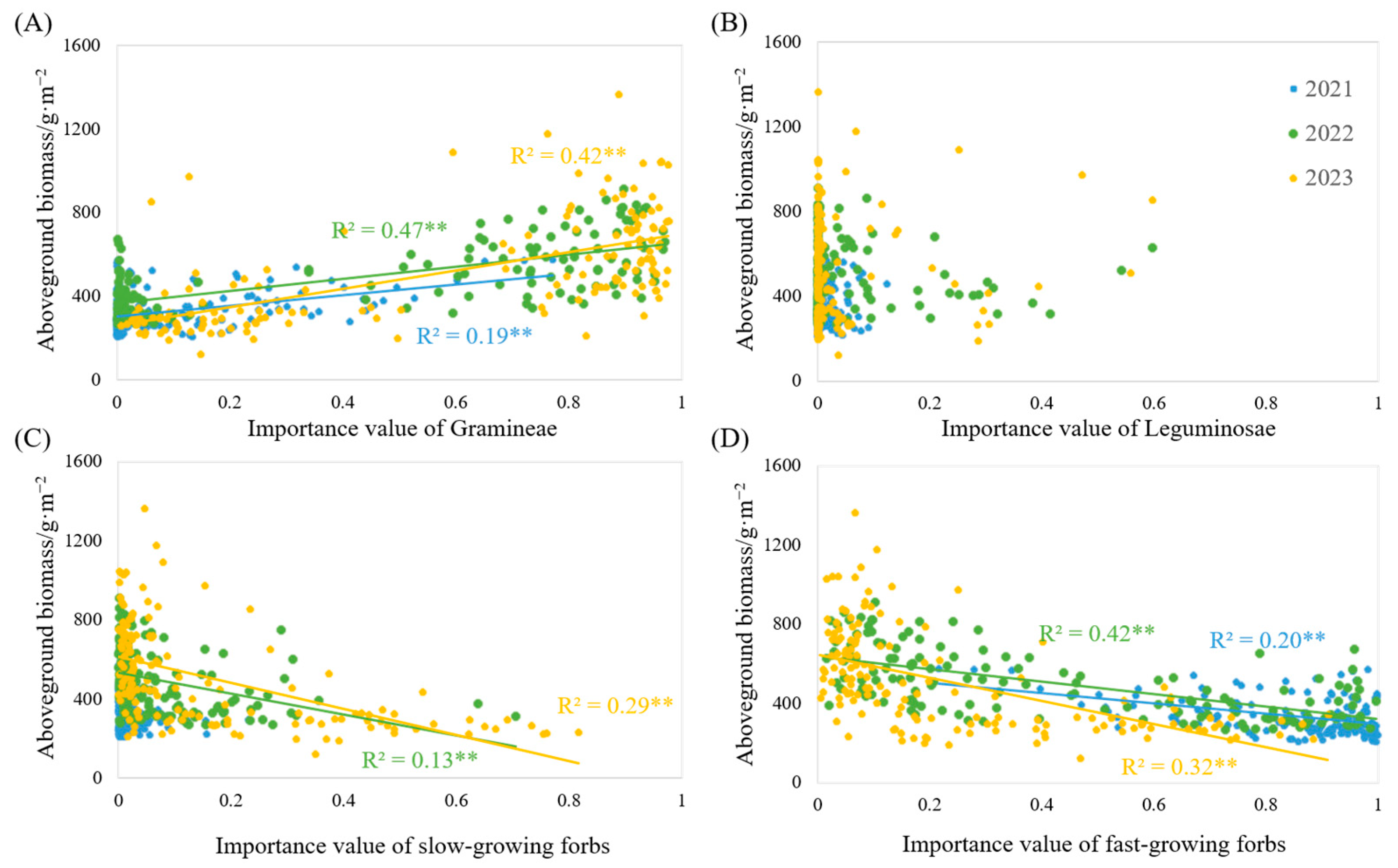
3.4. The Effect of the Importance Value of Each Functional Group on Biomass
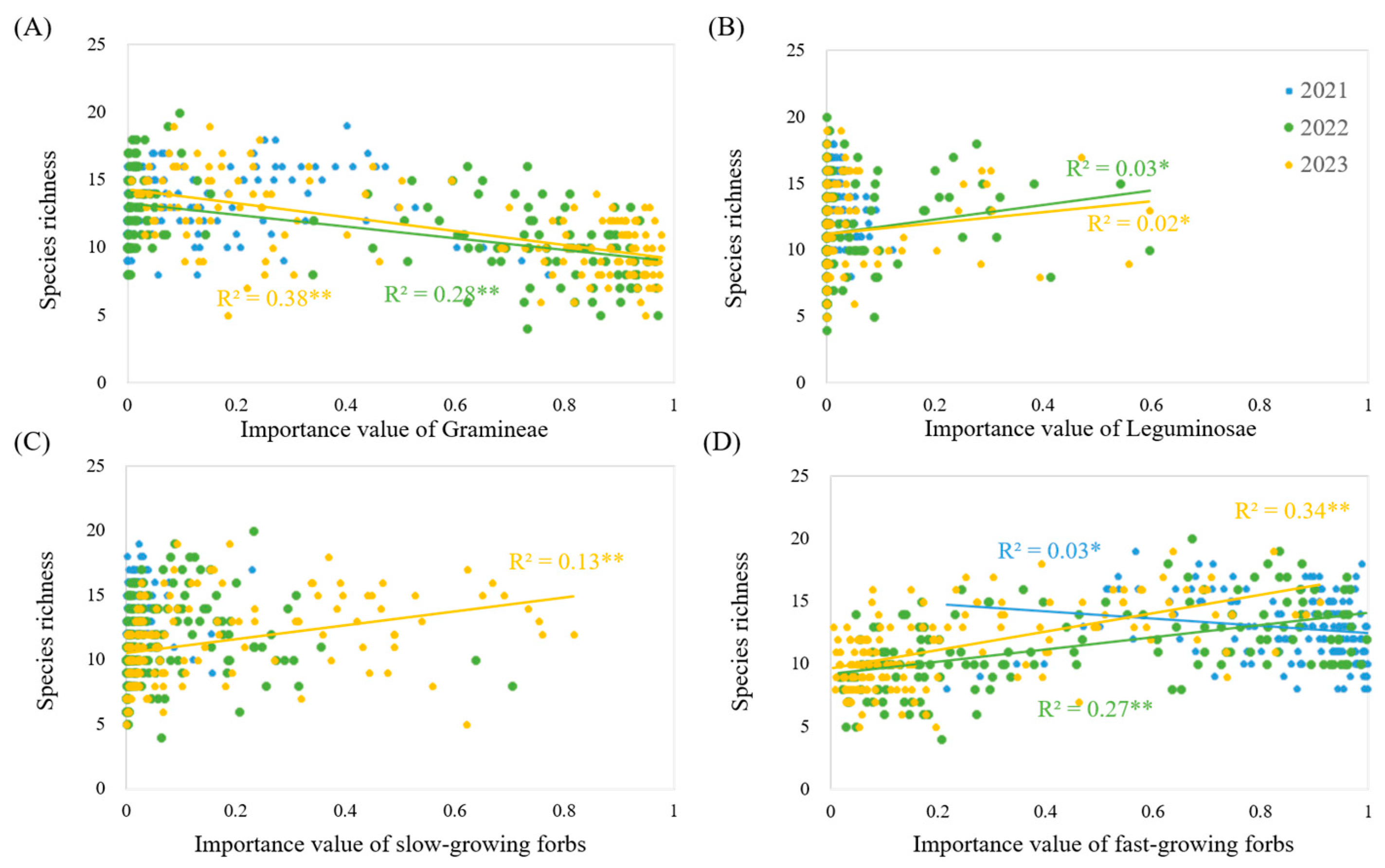
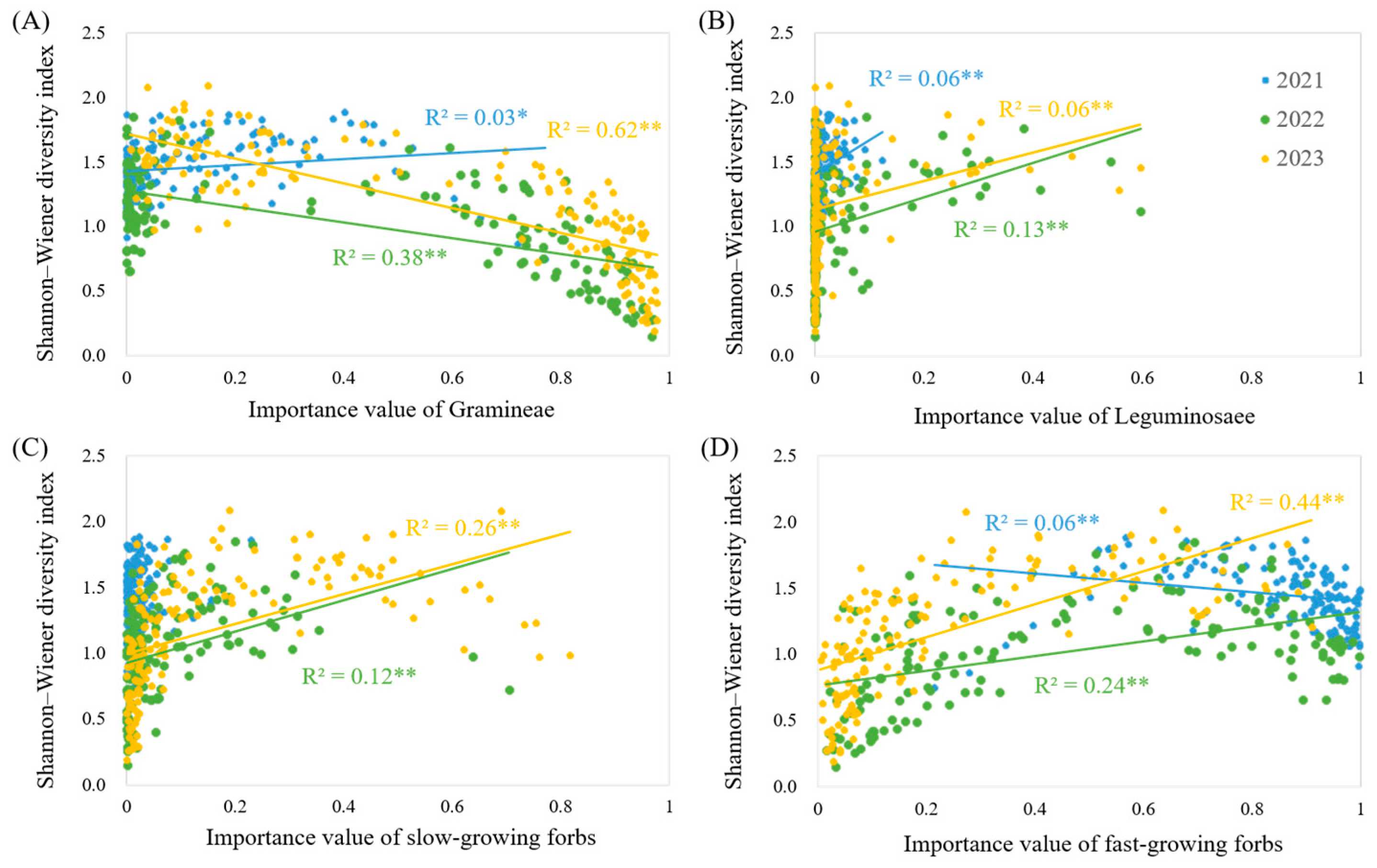
3.5. The Influence of the Importance Value of Each Functional Group on Diversity
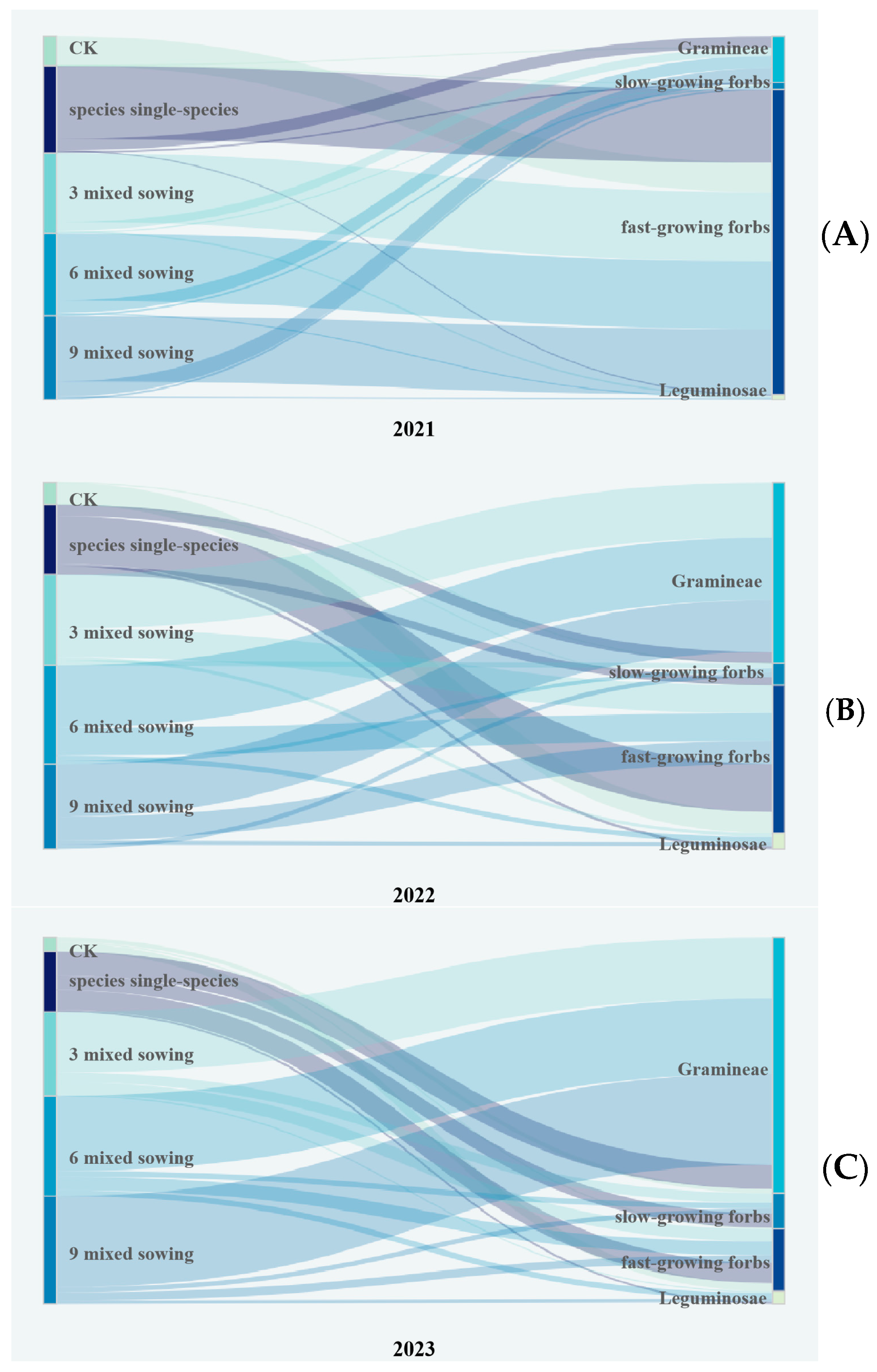
3.6. Community Change of Artificial Grassland
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, S.; Wen, L.; Zhu, L.; Li, X. Implication of coupled natural and human systems in sustainable rangeland ecosystem management in HKH region. Front. Earth Sci. China 2010, 4, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wu, S.; Zhao, D. Variations in alpine grassland cover and its correlation with climate variables on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in 1982–2013. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2017, 37, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.A.; Harte, J.; Zhao, X. Experimental warming causes large and rapid species loss, dampened by simulated grazing, on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Shang, Z.; Gao, J.; Boone, R.B. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 287, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. Belowground biomass and its relationship to environmental factors of natural grassland on the northern slopes of the Qilian Mountains. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2011, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Hou, G.; Shi, P.; Zong, N.; Peng, J. Nitrogen rather than phosphorous addition alters the asymmetric responses of primary productivity to precipitation variability across a precipitation gradient on the Northern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, T.M.; Chen, J.M. Effects of artificial grassland establishment on soil nutrients and carbon properties in a black-soil-type degraded grassland. Plant Soil 2010, 333, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H. Effects of soil characteristics on grassland productivity in long-term artificial grassland establishment. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 54, e03136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.J.; Cardinale, B.J.; Forshay, K.J.; Ives, A.R. Effects of species diversity on community biomass production change over the course of succession. Ecology 2007, 88, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yin, Y.; Song, J.; Li, S. Mixed sowing improves plant and soil bacterial community restoration in the degraded alpine meadow. Plant Soil 2024, 499, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.P.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, H.L.; Liang, D.F.; Wu, X.X.; Li, X.L. The effects of different functional groups and pioneer species on the early establishment of alpine artificial grassland. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2021, 29, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Yu, Z.; Yang, Q.C.; Wan, H.W.; Huang, J.H.; Ji, B.M.; Li, A. Mechanisms regulating the productivity and stability of artificial grasslands in China: Issues, progress, and prospects. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H. The importance of plant functional groups under different fertilization and mowing regimes: Implications for sustainable meadows. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 224, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, S.; Liu, S.; Su, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Tang, L. Relationships between plant diversity and biomass production of alpine grasslands are dependent on the spatial scale and the dimension of biodiversity. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, D.; Klaus, V.H.; Kleinebecker, T.; Boeddinghaus, R.S.; Hinderling, J.; Kandeler, E.; Marhan, S.; Nowak, S.; Sonnemann, I.; Wurst, S.; et al. Recovery of ecosystem functions after experimental disturbance in 73 grasslands differing in land-use intensity, plant species richness and community composition. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 2635–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.B.; Anderson, T.M.; Seabloom, E.W.; Borer, E.T.; Adler, P.B.; Harpole, W.S.; Hautier, Y.; Hillebrand, H.; Lind, E.M.; Pärtel, M.; et al. Integrative modelling reveals mechanisms linking productivity and plant species richness. Nature 2016, 529, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E.; Godwin, C.M.; Cardinale, B.J. Biodiversity effects in the wild are common and as strong as key drivers of productivity. Nature 2017, 549, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Wright, J.P.; Cadotte, M.W.; Carroll, I.T.; Hector, A.; Srivastava, D.S.; Loreau, M.; Weis, J.J. Impacts of plant diversity on biomass production increase through time because of species complementarity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18123–18128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, P.B.; Seabloom, E.W.; Borer, E.T.; Hillebrand, H.; Hautier, Y.; Hector, A.; Harpole, W.S.; O’Halloran, L.R.; Grace, J.B.; Anderson, T.M.; et al. Productivity is a poor predictor of plant species richness. Science 2011, 333, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Niu, J.; Buyantuyev, A.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Dong, J. Productivity–species richness relationship changes from unimodal to positive linear with increasing spatial scale in the Inner Mongolia steppe. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Connolly, J.; Liang, M.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S. Mechanistic links between biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and stability in a multi-site grassland experiment. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 3370–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhu, J.Z. Effects of different mixed sowing patterns on production performance of legume-grass mixture. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2011, 33, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; He, L.F. Primary productivity and community dynamics of mixed perennial grass pasture. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2004, 13, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.J.; Ma, Y.S.; Dong, Q.M.; Shao, X.Q.; Wu, G.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.P.; Wang, X.L. Effects of artificial regulation on production performance of perennial grass mixtures in the region of three rivers sources. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2018, 26, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Li, X.L.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, J. Effects of species combination on community diversity and productivity of alpine artificial grassland. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2020, 28, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar]
- She, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, R.; Chang, T.; Su, H.; Wei, J.; Li, H.; Ma, L. Plant community characteristics, soil nutrients and their interactions in artificial grassland with different establishment years in the Three Rivers Headwater Region. Grassl. Sci. 2023, 69, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Zhang, Q.Q. Plant biomass dynamic of mix-sowed artificial grassland of Baerluke Mountains. Grassl. Turf 2011, 31, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelbach, G.G.; Steiner, C.F.; Scheiner, S.M.; Gross, K.L.; Reynolds, H.L.; Waide, R.B.; Willig, M.R.; Dodson, S.I.; Gough, L. What is the observed relationship between species richness and productivity? Ecology 2001, 82, 2381–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.-F.; van Ruijven, J.; Mommer, L.; De Deyn, G.B.; Berendse, F.; Hoffland, E. Plant species richness promotes soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in grasslands without legumes. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.D.; Ma, T.; Zhou, H.K.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ma, L.; Qin, R.M.; Su, H.Y.; Chang, T.; Wei, J.J.; et al. Characterization of the plant—Soil feedback index in alpine meadow degradation and recovery: A field experiment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.H.; Li, M.H.; Tan, H.H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, W. The relationship between species diversity and aboveground productivity at temporal scale in Yunwushan typical grassland of Ningxia. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 30, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Isbell, F.; Cowles, J.M. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2014, 45, 471–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Reich, P.B.; Knops, J.; Wedin, D.; Mielke, T.; Lehman, C. Diversity and productivity in a long-term grassland experiment. Science 2001, 294, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ruijven, J.; Berendse, F. Diversity–productivity relationships: Initial effects, long-term patterns, and underlying mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grime, J.P. Competitive exclusion in herbaceous vegetation. Nature 1973, 242, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.T.; Zhou, G.Y.; Xiao, Y.M.; Jin, Y.T.; Li, C.B. Effects of long-term precipitation changes and nitrogen addition on species diversity and productivity of alpine grasslands in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2024, 32, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, J.; Jia, L.X.; Zhao, T.Q.; Zhao, M.L. Effects of utilization ways on species diversity, functional traits and aboveground biomass in Stipa grandis steppe. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2019, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, L.X.; Zhang, M.Y.; Li, X.J.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.S. Response of plant community structure and soil water conservation function to forbidden grazing and enclosure in alpine steppe of the Qinghai Lake. Acta Bot. Boreal.-Occident. Sin. 2024, 44, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Liu, H.; Meng, S.; Du, J.Y.; Ren, X.Y.; Liu, G.H. Study on the productivity and weed community dynamics of mixed artificial grasslands in agro-pastoral area. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2023, 31, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Yu, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Yan, R. Response of temperate Leymus chinensis meadow steppe plant community composition, biomass allocation, and species diversity to nitrogen and phosphorus addition. Agronomy 2023, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorny, M.L.; Sheley, R.L.; Svejcar, T.J.; Engel, R.E. Plant species diversity in a grassland plant community: Evidence for forbs as a critical management consideration. West. N. Am. Nat. 2004, 64, 219–230. [Google Scholar]


| Species | Family | Functional Group |
|---|---|---|
| Elymus nutans Griseb. | Gramineae | Gramineae |
| Poa pratensis L. | Gramineae | Gramineae |
| Lolium perenne L. | Gramineae | Gramineae |
| Medicago sativa L. | Leguminosae | Leguminosae |
| Onobrychis viciifolia Scop. | Leguminosae | Leguminosae |
| Melilotus officinalis (L.) Pall. | Leguminosae | Leguminosae |
| Saussurea nigrescens Maxim. | Asteraceae | Slow-growing forbs |
| Gentiana lawrencei Burkill | Gentianaceae | Slow-growing forbs |
| Morina chinensi Diels ex Grüning, Pax & K. Hoffm. | Dipsacaceae | Slow-growing forbs |
| Descurainia sophi (L.) Webb ex Prantl | Brassicaceae | Fast-growing forbs |
| Elsholtzia densa Benth. | Lamiaceae | Fast-growing forbs |
| Thlaspi arvense L. | Brassicaceae | Fast-growing forbs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Feng, R.; Ma, J.; Wang, N.; Ji, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, F.; Li, H.; Liang, D.; et al. Changes in Biomass Production, Plant Diversity, and Their Relationship During the Early Establishment of Artificial Alpine Grasslands with Different Species Combinations. Diversity 2025, 17, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050341
Wang S, Feng R, Ma J, Wang N, Ji L, Zhao X, Wang X, Ren F, Li H, Liang D, et al. Changes in Biomass Production, Plant Diversity, and Their Relationship During the Early Establishment of Artificial Alpine Grasslands with Different Species Combinations. Diversity. 2025; 17(5):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050341
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shu, Runfang Feng, Jikui Ma, Nannan Wang, Linfeng Ji, Xiufen Zhao, Xiaoli Wang, Fei Ren, Honglin Li, Defei Liang, and et al. 2025. "Changes in Biomass Production, Plant Diversity, and Their Relationship During the Early Establishment of Artificial Alpine Grasslands with Different Species Combinations" Diversity 17, no. 5: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050341
APA StyleWang, S., Feng, R., Ma, J., Wang, N., Ji, L., Zhao, X., Wang, X., Ren, F., Li, H., Liang, D., Hu, J., Li, X., & Li, L. (2025). Changes in Biomass Production, Plant Diversity, and Their Relationship During the Early Establishment of Artificial Alpine Grasslands with Different Species Combinations. Diversity, 17(5), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050341





