Macrozoobenthic Communities in the Upwelling Area off Chile (36° S) with Special Consideration of the Oxygen Minimum Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Work
2.2. Laboratory Work
2.3. Statistical Analysis
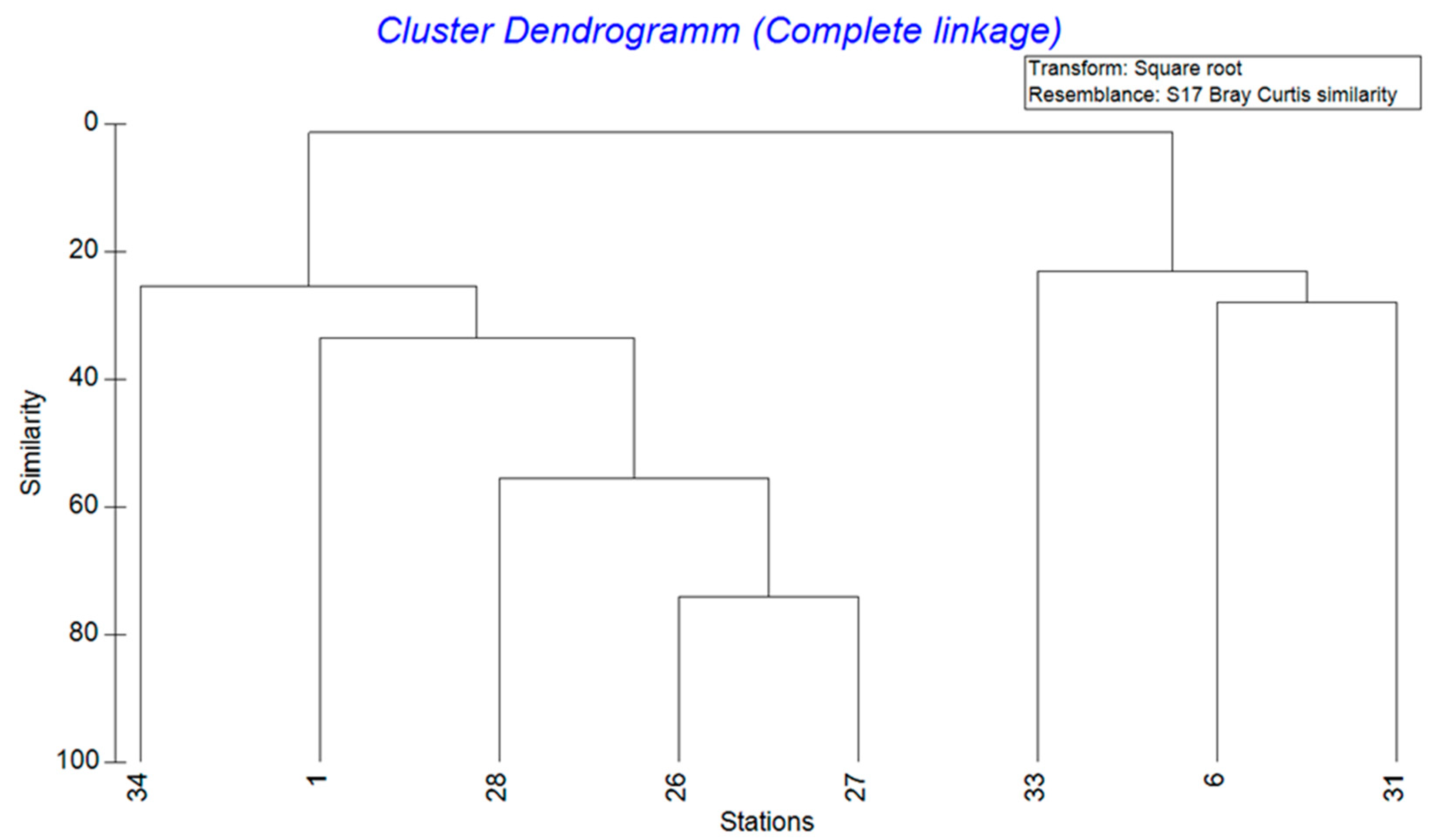
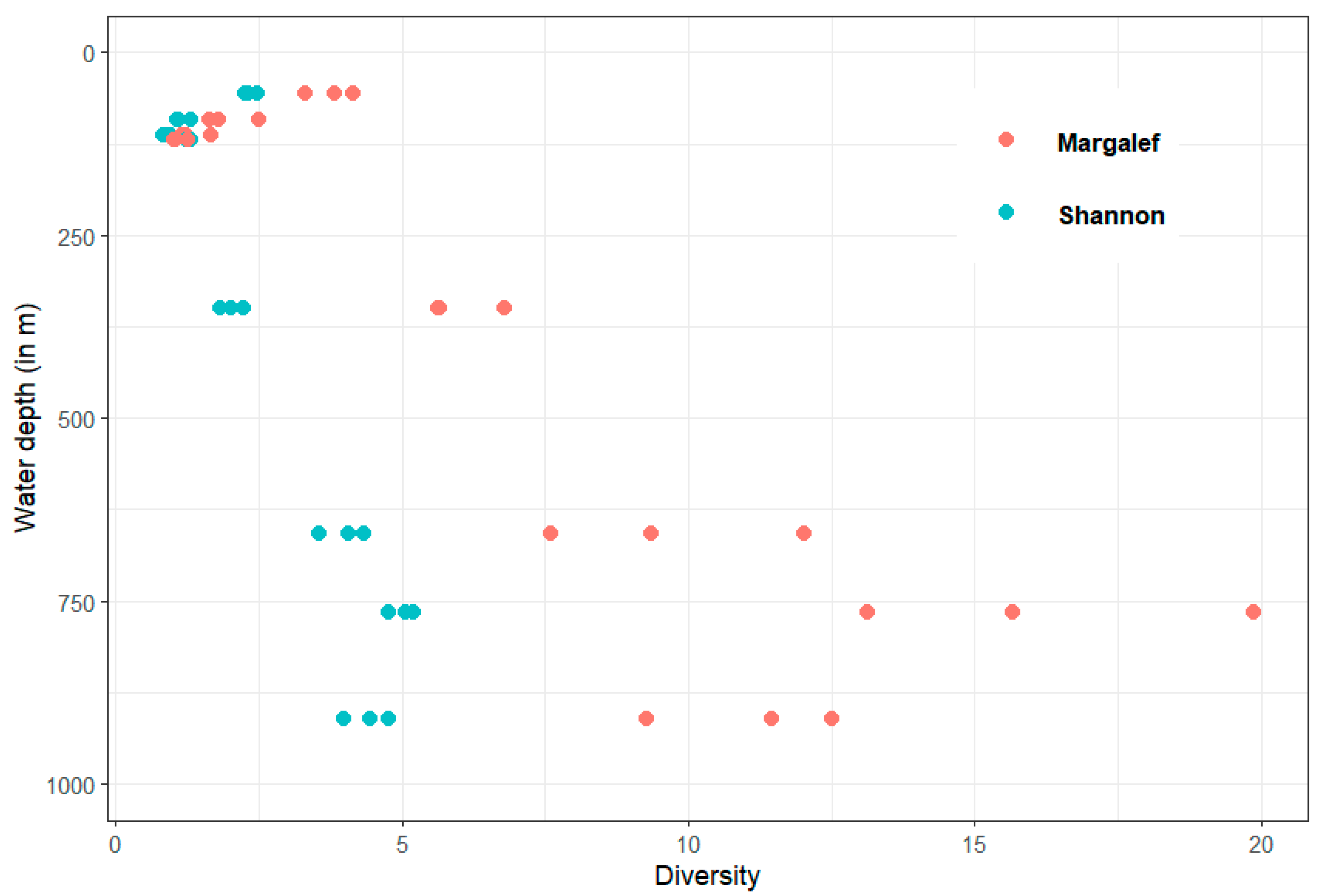
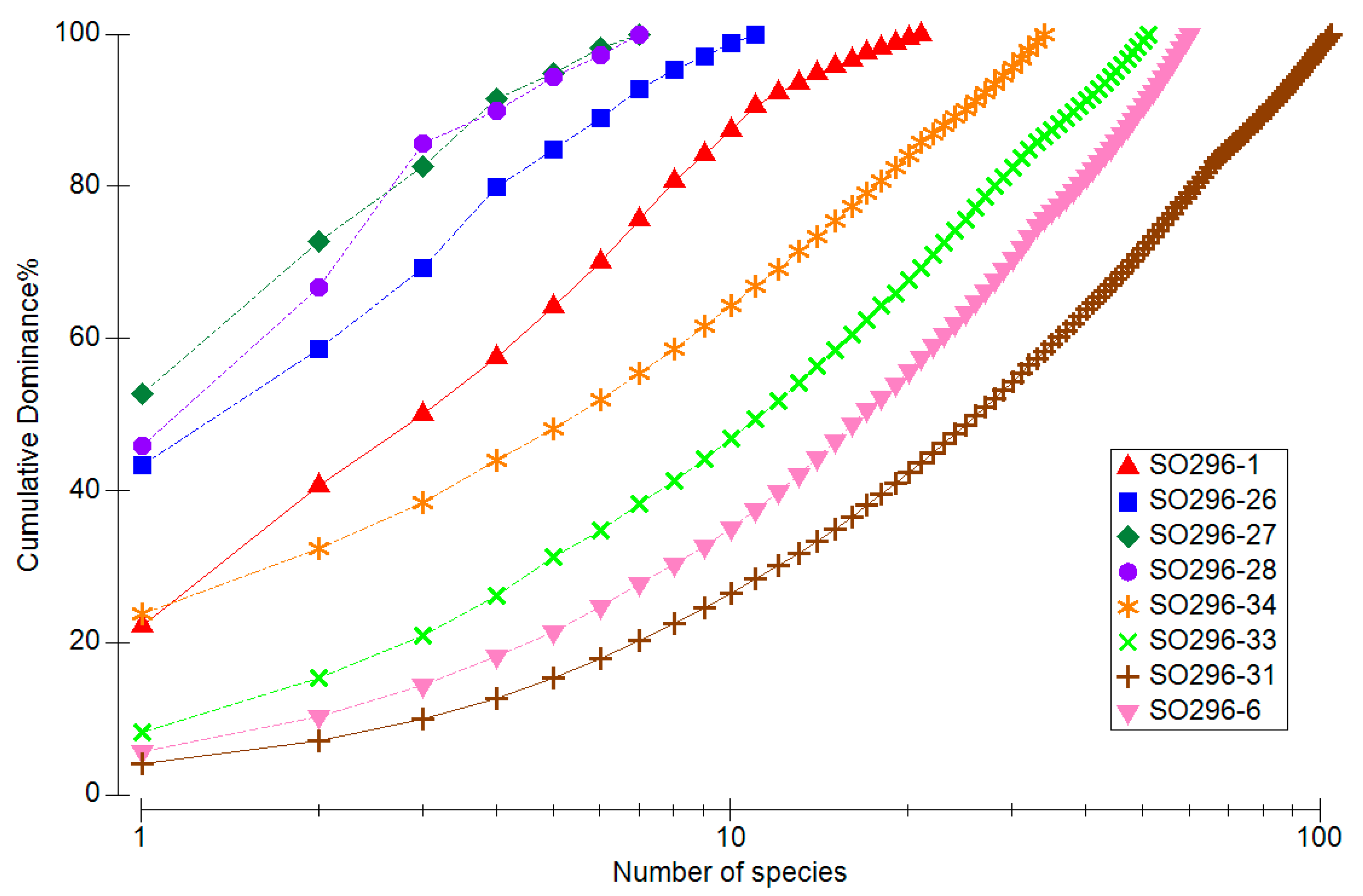
3. Results
3.1. Abundance, Biomass and Diversity
3.2. Species-Specific Differences
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breitburg, D.; Levin, L.A.; Oschlies, A.; Grégoire, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Conley, D.J.; Garçon, V.; Gilbert, D.; Gutiérrez, D.; Isensee, K.; et al. Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 2018, 359, eaam7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, L.A.; Ekau, W.; Gooday, A.J.; Jorissen, F.; Middelburg, J.J.; Naqvi, S.W.A.; Neira, C.; Rabalais, N.N.; Zhan, J. Effects of natural and human-induced hypoxia on coastal benthos. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 2063–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A.; Ekau, W.; Gooday, A.J.; Jorissen, F.; Middelburg, J.J.; Naqvi, W.; Neira, C.; Rabalais, N.N.; Zhang, J. Environmental Influences on Regional Deep-Sea Species Diversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 51–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, O.; Pantoja, S. The oxygen minimum zone of the eastern South Pacific. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2009, 56, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karstensen, J.; Stramma, L.; Visbeck, M. Oxygen minimum zones in the eastern tropical Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Prog. Oceanogr. 2008, 77, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, M.; Macaya, E.; Acuna, E.; Arntz, W.; Bastias, H.; Brokordt, K.; Camus, P.; Castilla, J.; Castro, L.; Cortés, M.; et al. The Humboldt Current System of Northern and Central Chile. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2007, 45, 195–345. [Google Scholar]
- Helly, J.J.; Levin, L.A. Global distribution of naturally occurring marine hypoxia on continental margins. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2004, 51, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, V.A.; Espinoza, C. New communities of large filamentous sulfur bacteria in the eastern South Pacific. Int. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, H.N.; Strotmann, B.; Gallardo, V.A.; Jørgensen, B.B. Population study of the filamentous sulfur bacteria Thioploca spp. off the Bay of Concepción, Chile. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 200, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossing, H.; Gallardo, V.A.; Jørgensen, B.B.; Huttel, M.; Nielsen, L.P.; Schulz, H.; Canfield, D.E.; Forster, S.; Glud, R.N.; Gundersen, J.K.; et al. Concentration and transport of nitrate by the mat-forming sulphur bacterium Thioploca. Nature 1995, 374, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høgslund, S.; Revsbech, N.P.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jørgensen, B.B.; Gallardo, V.A.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Nielsen, J.L.; Holmkvist, L.; Arning, E.T.; Nielsen, L.P. Physiology and behaviour of marine Thioploca. ISME J. 2009, 3, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, V.A.; Fonseca, A.; Musleh, S.; Espinoza, C. Extrapolations of Standing-Stocks of Big Bacteria in Humboldt Eastern Boundary Current Ecosystem (HEBCE). Ocean. Mar. Biol. 2013, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bon, M.; Grall, J.; Gusmao, J.B.; Fajardo, M.; Harrod, C.; Pacheco, A.S. Functional changes in benthic macrofaunal communities along a natural gradient of hypoxia in an upwelling system. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2021, 164, 112056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, E.; Quiñones, R.; Palma, M.; Sellanes, J.; Gallardo, V.A.; Gerdes, D.; Rowe, G. Biomass size-spectra of microbenthic communities in the oxygen minimum zone off Chile. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A. Oxygen minimum zone benthos: Adaptation and community response to hypoxia. Ocean. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 2003, 41, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, E.; Quiñones, R.A.; González, R.R.; Gallardo, V.A.; Jessen, G. Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of Paraprionospio pinnata (Polychaeta: Spionidae) in central Chile. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2007, 87, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.R.; Quiñones, R.A. Pyruvate Oxidoreductases Involved in Glycolytic Anaerobic Metabolism of Polychaetes from the Continental Shelf off Central-South Chile. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, P.A.; Gage, J.D. Morphological responses of macrobenthic polychaetes to low oxygen on the Oman continental slope, NW Arabian Sea. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, K.; Loick-Wilde, N.; Yuen, B.; Osvatic, J.T.; Wäge-Recchioni, J.; Hausmann, B.; Petersen, J.M.; Fabian, J.; Wodarg, D.; Zettler, M.L. Chemoautotrophy, symbiosis and sedimented diatoms support high biomass of benthic molluscs in the Namibian shelf. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellanes, J.; Krylova, E. A new species of Calyptogena (Bivalvia: Vesicomyidae) from a recently discovered methane seepage area off Concepción Bay, Chile (~36°S). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, O.; Sellanes, J. New species of Thyasiridae from a methane seepage area off Concepción, Chile. Zootaxa 2005, 1092, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sellanes, J.; Quiroga, E.; Neira, C.; Gutiérrez, D. Changes of macrobenthos composition under different ENSO cycle conditions on the continental shelf off central Chile. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006; Volume 29, pp. 1060–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Huettel, M.; Forster, S.; Klöser, S.; Fossing, H. Vertical migration in the sediment-dwelling sulfur bacteria Thioploca spp. in overcoming diffusion limitations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, F.; Gallardo, V.A.; Baltazar, M. The structure of the benthic macrofauna collected across a transect at the central chile shelf and relationships with giant sulfur bacteria Thioploca spp. mats. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1999, 40, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zettler, M.L.; Bochert, R.; Pollehne, F. Macrozoobenthos diversity in an oxygen minimum zone off northern Namibia. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A.; Gage, J.D.; Martin, C.; Lamont, P.A. Macrobenthic community structure within and beneath the oxygen minimum zone, NW Arabian Sea. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 189–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, K.; Zettler, M.L. Gradients and instability: Macrozoobenthic communities in the Benguela Upwelling System off Namibia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 291, 108421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, M.; Quiroga, E.; Gallardo, V.A.; Arntz, W.; Gerdes, D.; Schneider, W.; Hebbeln, D. Macrobenthic animal assemblages of the continental margin off Chile (22° to 42° S). J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 2005, 85, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, V.A.; Palma, M.; Carrasco, F.D.; Gutiérrez, D.; Levin, L.A.; Cañete, J.I. Macrobenthic zonation caused by the oxygen minimum zone on the shelf and slope off central Chile. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 2475–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D.; Gallardo, V.A.; Mayor, S.; Neira, C.; Vásquez, C.; Sellanes, J.; Rivas, M.; Soto, A.; Carrasco, F.; Baltazar, M. Bioturbation potential of macrofauna in sublitoral organic-rich sediments off central Chile: Spatial and temporal variation under ‘El Niño’ 1997/98. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 202, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, V.A.; Carrasco, F.D.; Roa, R.; Cañete, J.I. Ecological patterns in the benthic macrobiota across the continental shelf off central Chile. Ophelia 1995, 40, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.S.; González, M.T.; Bremner, J.; Oliva, M.; Heilmayer, O.; Laudien, J.; Riascos, J.M. Functional diversity of marine macrobenthic communities from sublittoral soft-sediment habitats off northern Chile. Helgol. Mari. Res. 2011, 65, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, D.M.; Maybury, C.A.; Ewing, R.M. Feeding behavior and general ecology of several Spionid polychaetes from the Chesapeake Bay. J. Exp. Mar. Ecol. Biol. 1981, 54, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquer-Sunyer, R.; Duarte, C.M. Thresholds of hypoxia for marine biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 107, 15452–15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramma, L.; Schmidtko, S.; Levin, L.A.; Johnson, G.C. Ocean oxygen minima expansions and their biological impacts. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2010, 57, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villnäs, A.; Norkko, J.; Lukkari, K.; Hewitt, J.; Norkko, A. Consequences of increasing hypoxic disturbance on benthic communities and ecosystem functioning. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Marine benthic hypoxia: A review of its ecological effects and the behavioural responses of benthic macrofauna. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 1995, 33, 245–303. [Google Scholar]


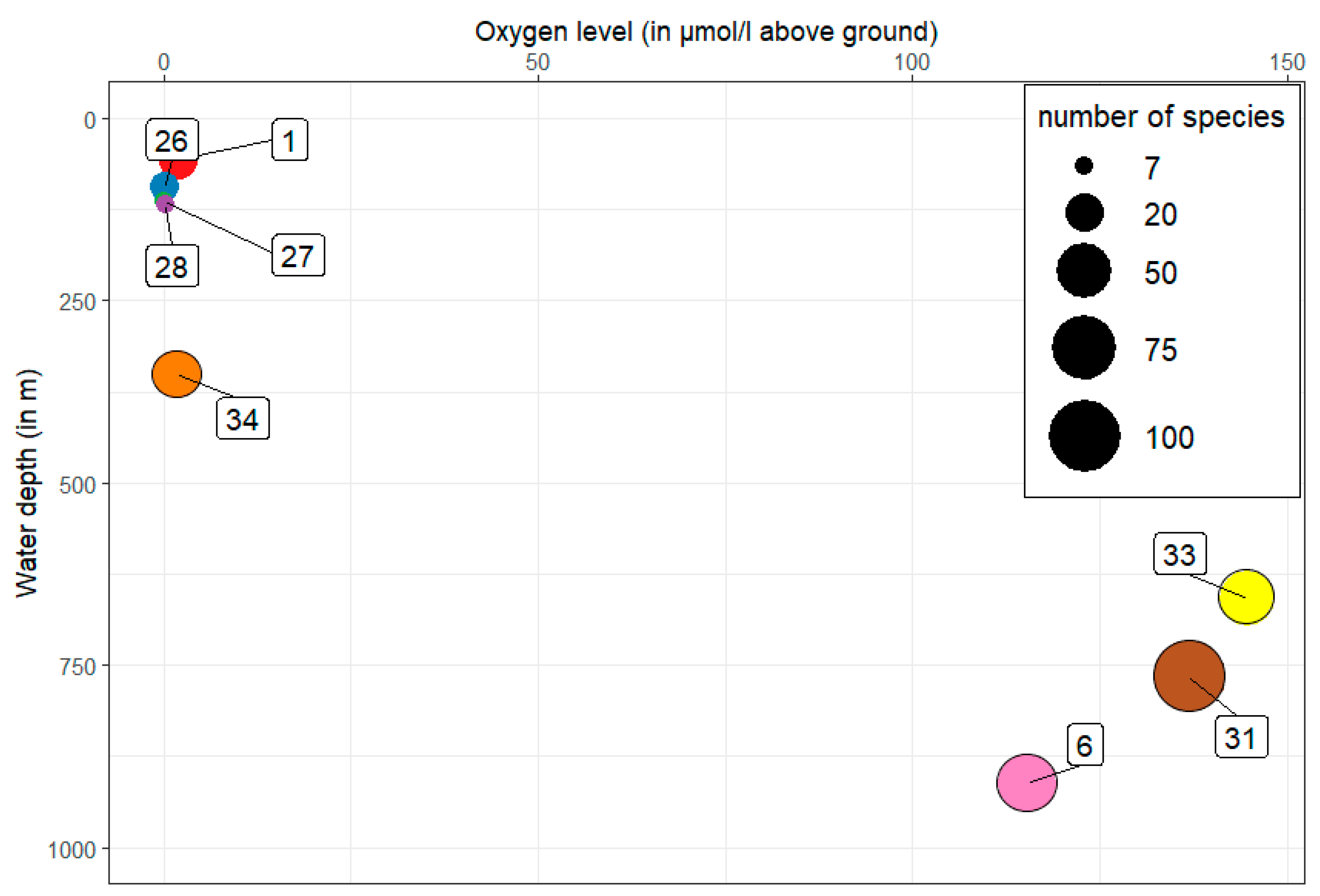


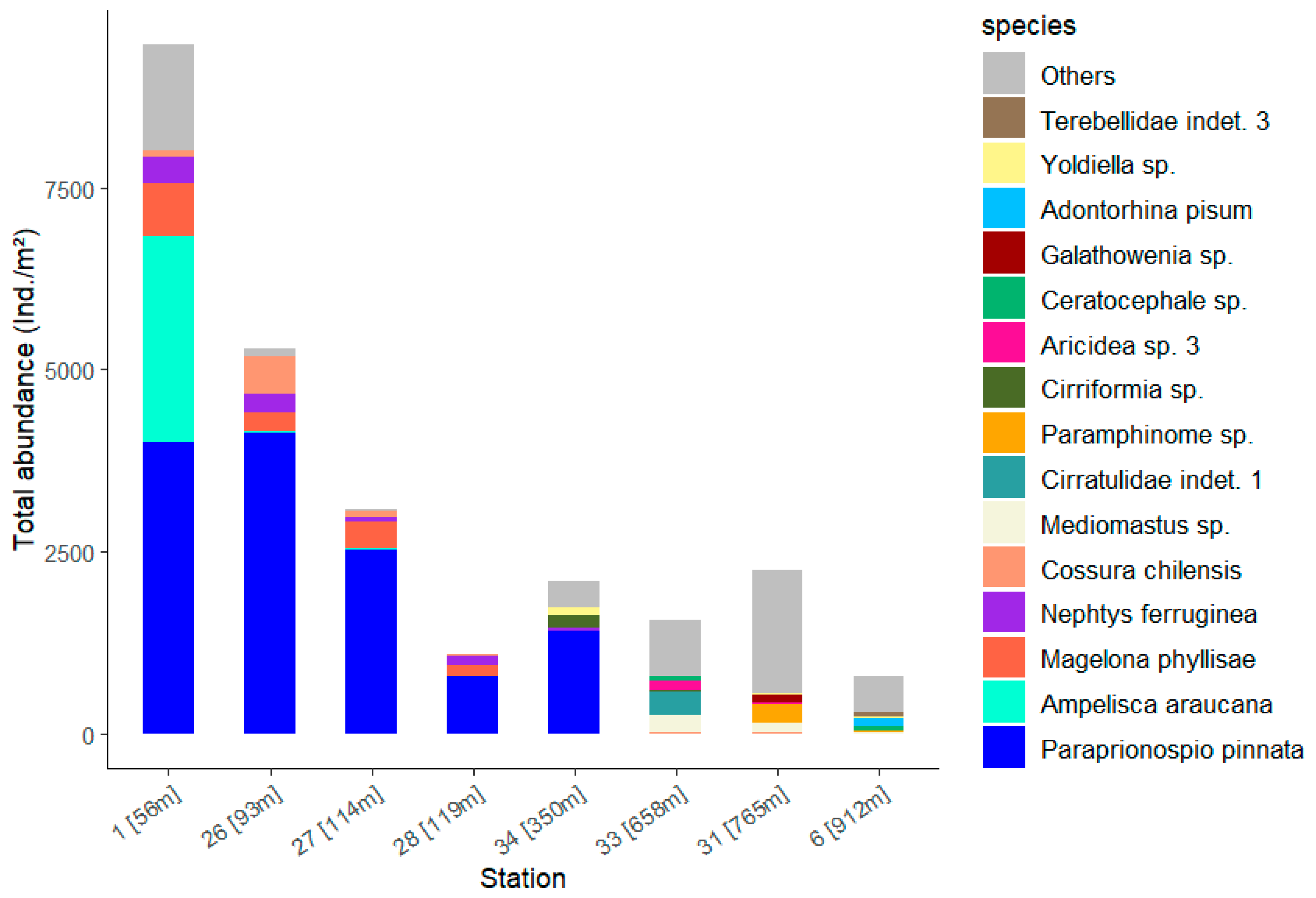
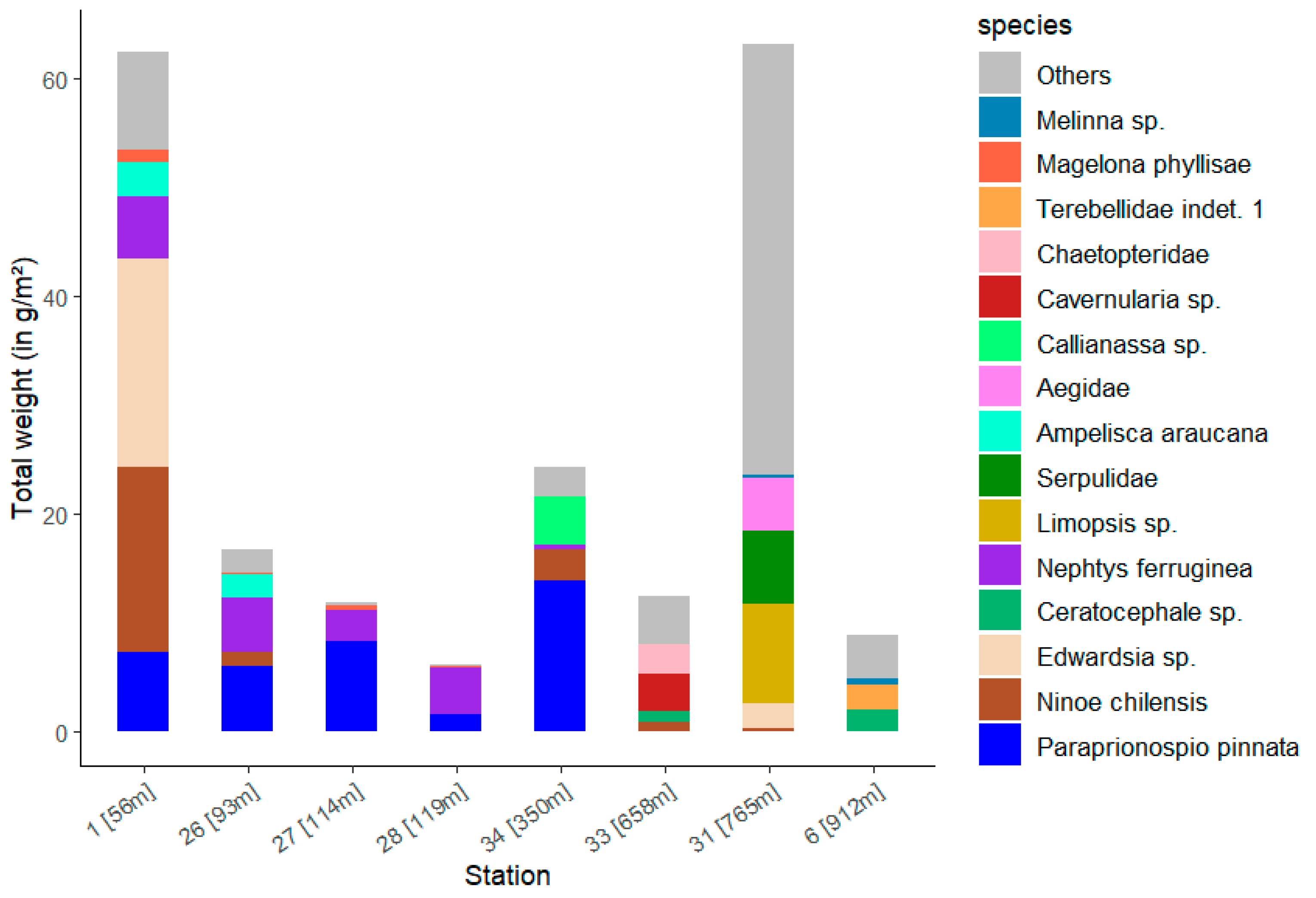

| Station | Water Depth (in m) | Salinity (psu) | Oxygen Level (in µmol/L Above Seabed) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56 | 34.6 | 1.96 |
| 26 | 93 | 34.6 | 0.07 |
| 27 | 114 | 34.4 | 0.00 |
| 28 | 119 | 34.6 | 0.27 |
| 34 | 350 | 34.7 | 1.66 |
| 33 | 658 | 34.6 | 144.64 |
| 31 | 765 | 34.3 | 136.90 |
| 6 | 912 | 34.3 | 115.30 |
| Station | S | N | ES (50) | H’ (log2) | DMg (log) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21 | 9472 | 8.52 | 2.41 | 5.03 |
| 26 | 11 | 5293 | 5.06 | 1.24 | 2.69 |
| 27 | 7 | 3080 | 3.83 | 0.94 | 1.72 |
| 28 | 7 | 1093 | 3.82 | 1.31 | 1.97 |
| 34 | 34 | 2094 | 9.95 | 2.17 | 10.23 |
| 33 | 51 | 1584 | 18.66 | 4.26 | 19.05 |
| 31 | 104 | 2242 | 28.58 | 5.64 | 30.71 |
| 6 | 60 | 784 | 24.97 | 5.02 | 20.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krug, A.S.; Zettler, M.L. Macrozoobenthic Communities in the Upwelling Area off Chile (36° S) with Special Consideration of the Oxygen Minimum Zone. Diversity 2025, 17, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040278
Krug AS, Zettler ML. Macrozoobenthic Communities in the Upwelling Area off Chile (36° S) with Special Consideration of the Oxygen Minimum Zone. Diversity. 2025; 17(4):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040278
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrug, Anna S., and Michael L. Zettler. 2025. "Macrozoobenthic Communities in the Upwelling Area off Chile (36° S) with Special Consideration of the Oxygen Minimum Zone" Diversity 17, no. 4: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040278
APA StyleKrug, A. S., & Zettler, M. L. (2025). Macrozoobenthic Communities in the Upwelling Area off Chile (36° S) with Special Consideration of the Oxygen Minimum Zone. Diversity, 17(4), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040278







