Regulatory Effects of Green Manure Combined with Nitrogen Reduction on Carbon-Cycling Functional Genes and Microbial Communities in Paddy Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample Collection
2.4. Determination of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.5. DNA Extraction and Metagenomic Sequencing
2.6. Metagenomic Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Combined Application of Green Manure and Reduced N Fertilizer on the Physicochemical Properties of Rice Soil
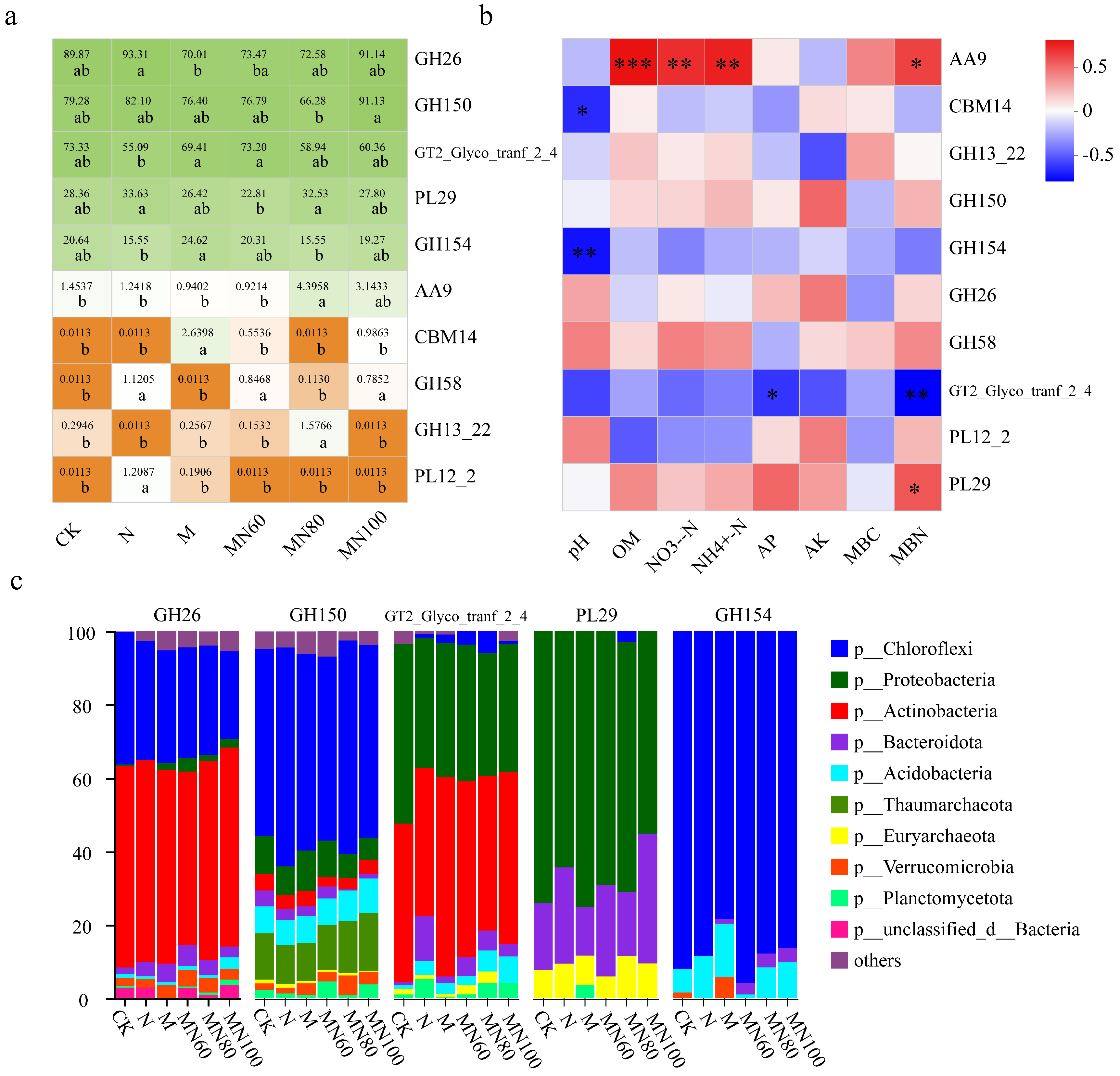
3.2. Effects of Combined Application of Green Manure and Reduced N Fertilizer on Rice Soil CAZy Database Carbohydrate-Active Enzyme Functional Genes
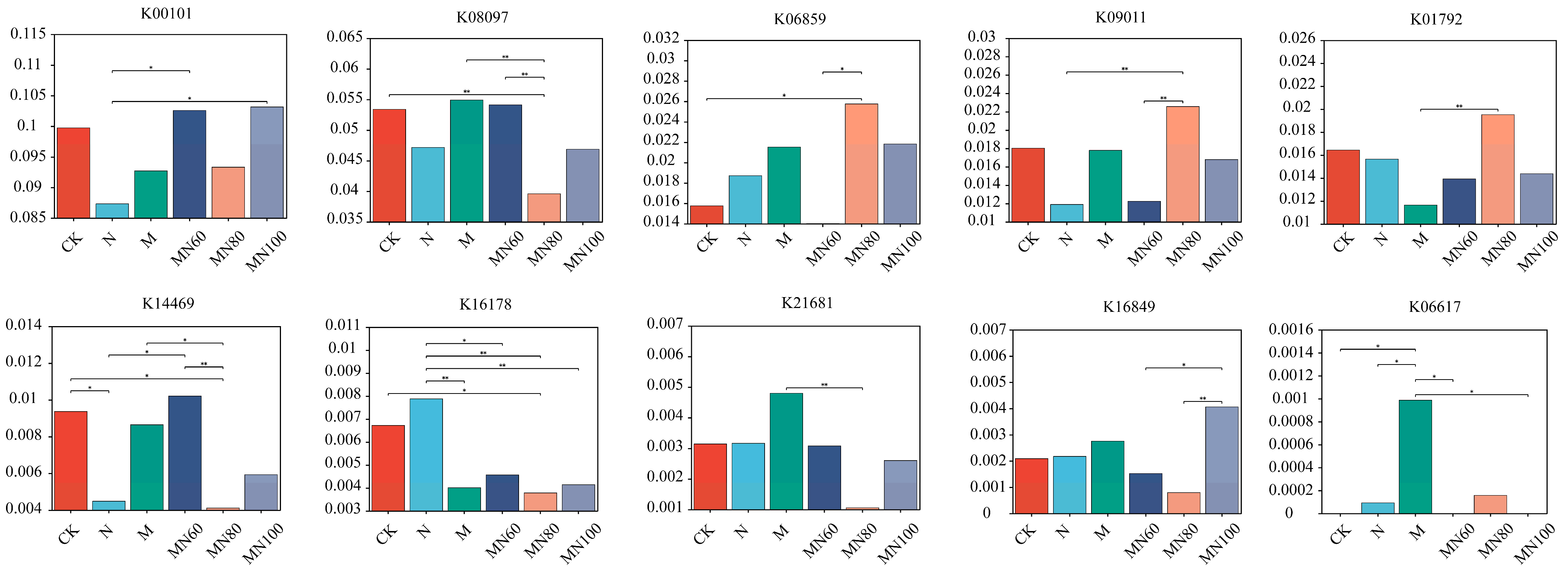
3.3. Effects of Combined Application of Green Manure and Reduced N Fertilizer on Rice Soil KEGG Database Functional Genes
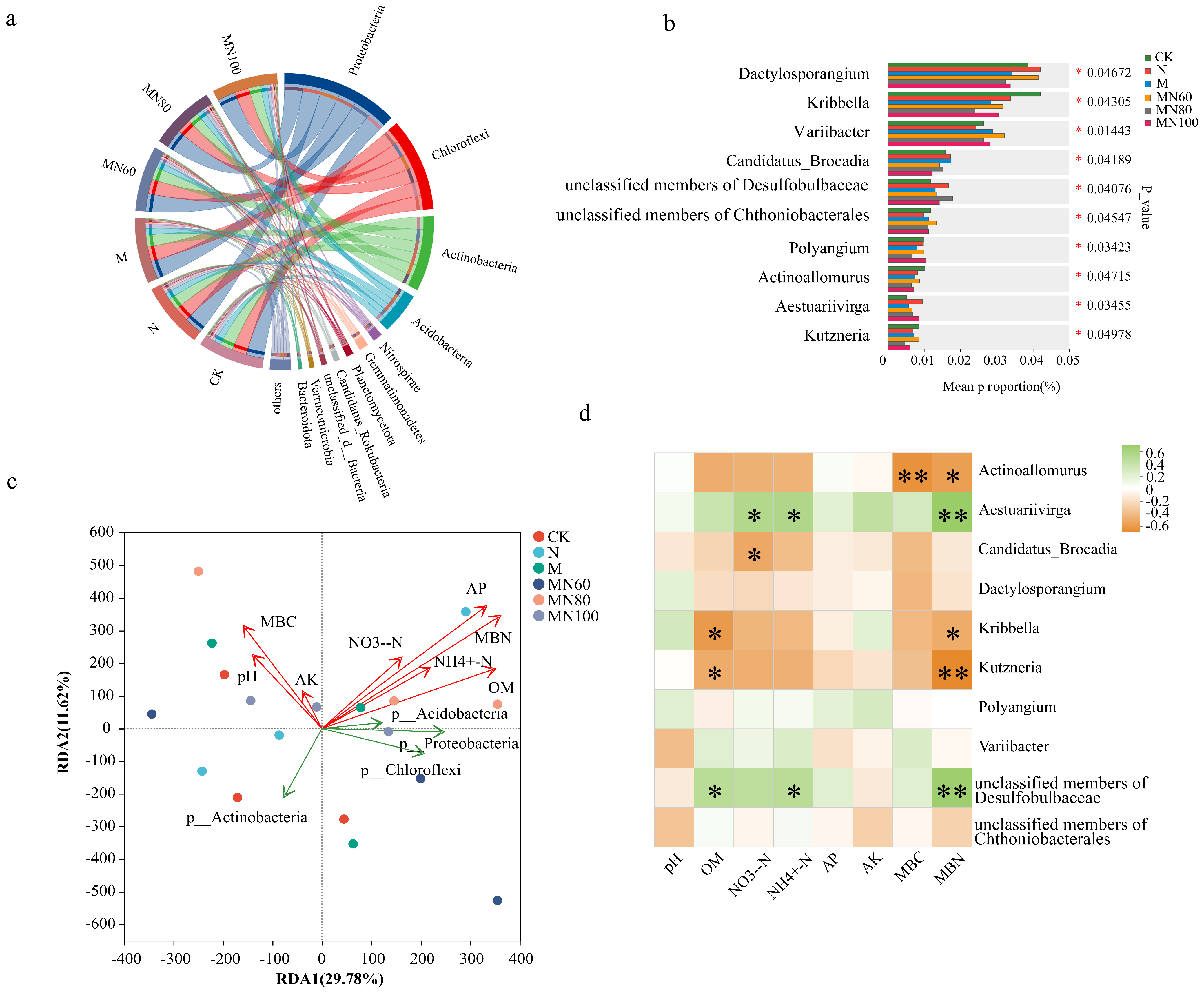
3.4. Effects of Combined Application of Green Manure and Reduced N Fertilizer on Microbial Communities Carrying Carbon Cycle Functional Genes in Rice Soil
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamamoto, N.; Oishi, R.; Suyama, Y.; Tada, C.; Nakai, Y. Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria Rather than Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea were Widely Distributed in Animal Manure Composts from Field-Scale Facilities. Microbes Environ. 2012, 27, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, G.; Su, S.; Lu, J.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, S.; Li, X. Effects of optimized nitrogen fertilizer management on the yield, nitrogen uptake, and ammonia volatilization of direct-seeded rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 4553–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.W.; Sutton, M.A.; Galloway, J.; Klimont, Z.; Winiwarter, W. How a century of ammonia synthesis changed the world. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yin, W.; Chai, Q.; Fan, Z.; Hu, F.; Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Yu, A.; Coulter, J.A. No tillage with previous plastic covering increases water harvesting and decreases soil CO2 emissions of wheat in dry regions. Soil. Till Res. 2021, 208, 104883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, L.; Zhai, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Jiao, C.; Shen, Z. National assessment of nitrogen fertilizers fate and related environmental impacts of multiple pathways in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Dai, J.; Hu, W.; Li, X.; Brooks, M.; Xie, L.; et al. Green Manure Amendment Can Reduce Nitrogen Fertilizer Application Rates for Oilseed Rape in Maize–Oilseed Rape Rotation. Plants 2021, 10, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, P.; Ma, C.; Yi, K.; Jia, X. Revealing the underlying molecular basis of phosphorus recycling in the green manure crop Astragalus sinicus. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, S.; Sharma, V.; Mohammed, A.T.; Djaman, K. Impacts of Cover Crops on Soil Physical Properties: Field Capacity, Permanent Wilting Point, Soil-Water Holding Capacity, Bulk Density, Hydraulic Conductivity, and Infiltration. Trans. ASABE 2018, 61, 1307–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S. Winter legume-rice rotations can reduce nitrogen pollution and carbon footprint while maintaining net ecosystem economic benefits. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Ma, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Mu, Y. Weed suppression and antioxidant activity of Astragalus sinicus L. decomposition leachates. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1013443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, M.; Uchida, Y. Long-term use of green manure legume and chemical fertiliser affect soil bacterial community structures but not the rate of soil nitrate decrease when excess carbon and nitrogen are applied. Soil. Res. 2017, 55, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Fan, F.; Ma, X.; Yin, H.; Zhang, C.; Feng, K.; Deng, Y. Thirty-one years of rice-rice-green manure rotations shape the rhizosphere microbial community and enrich beneficial bacteria. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Xie, J.; Du, J.; Ge, H.; Wei, C.; Qian, H.; Liang, H.; Nie, J.; Hu, F.; Gao, S.; et al. Rice straw nitrogen can be utilized by rice more efficiently when co-incorporating with milk vetch. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Nie, J.; Liang, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, J.; Liao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Gao, S.; Cao, W. Paddy fields can gain high productivity with low net global warming potential by utilizing green manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Song, Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, R.; Cai, C.; Lv, S.; Liao, Y.; Nie, J.; Duan, T.; Cao, W. Planting Chinese milk vetch with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation enhances phosphorus turnover by altering the structure of the phoD-harboring bacteria community. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2024, 123, 103678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Xie, J.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Hu, F.; Gao, S.; Cao, W. Application of milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) with reduced chemical fertilizer improves rice yield and nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium use efficiency in southern China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 144, 126762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cui, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hao, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Qin, Y. Effects of rice stalks mulching combined with green manure (Astragalus smicus L.) incorporated into soil and reducing nitrogen fertilizer rate on rice yield and soil fertility. Acta Agron. Sin. 2022, 48, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-J.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.-L.; Li, X.-L. Teaching reform and exploration of the “Soil Agrochemical Analysis” course based on professional accreditation thinking. Ind. Sci. Technol. Forum 2024, 23, 174–176. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.Y.; Zhang, C.X. Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect. Sci. 2013, 20, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, A.; Fagnano, M.; Fierro, A. Potential role of compost and green manure amendment to mitigate soil GHGs emissions in Mediterranean drip irrigated maize production systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Chen, Y.; Hao, Y. Effects of green-manure and tillage management on soil microbial community composition, nutrients and tree growth in a walnut orchard. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Guan, C.; Guan, M. Decomposition of Rapeseed Green Manure and Its Effect on Soil under Two Residue Return Levels. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Ladha, J.K.; Ali, M. Green manure technology: Potential, usage, and limitations. A case study for lowland rice. In Management of Biological Nitrogen Fixation for the Development of More Productive and Sustainable Agricultural Systems: Extended Versions of Papers Presented at the Symposium on Biological Nitrogen Fixation for Sustainable Agriculture; Ladha, J.K., Peoples, M.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Nie, J.; Cao, W.; Gao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Y. Long-term green manuring to substitute partial chemical fertilizer simultaneously improving crop productivity and soil quality in a double-rice cropping system. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 142, 126641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Lv, W.; Liao, X.; Brooks, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Hu, W.; Dai, J.; et al. Green Manure Amendment Increases Soil Phosphorus Bioavailability and Peanut Absorption of Phosphorus in Red Soil of South China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X. The Application of Orychophragmus violaceus as a Green Manure Relieves Continuous Cropping Obstacles in Peanut Cultivation by Altering the Soil Microbial Community and Functio nal Gene Abundance. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nut. 2024, 24, 4727–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Fan, K.; Gao, S.; Chang, D.; Li, G.; Liang, T.; Liang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Che, Z.; et al. Green manuring relocates microbiomes in driving the soil functionality of nitrogen cycling to obtain preferable grain yields in thirty years. Sci. China Life Sci. 2024, 67, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Nepstad, D.C.; Ishida, F.Y.; Brando, P.M. Effects of an experimental drought and recovery on soil emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and nitric oxide in a moist tropical forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2582–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.F.; Mello, B.; Schrago, C.G. Performance of Hidden Markov Models in Recovering the Standard Classification of Glycoside Hydrolases. Evol. Bioinform. 2017, 13, 1609449705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, G.; Kumar, J.; Sangwan, R.S.; Singh, S.P. Metagenomic analysis of geothermal water reservoir sites exploring carbohydrate-related thermozymes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimel, J.; Gulledge, J. Microbial Community Structure and Global Trace Gases. Glob. Change Biol. 1998, 4, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aon, M.A.; Colaneri, A.C., II. Temporal and spatial evolution of enzymatic activities and physico-chemical properties in an agricultural soil. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2001, 18, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ni, H.; Jiao, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, B.; Liang, Y. Coexistence patterns of soil methanogens are closely tied to methane generation and community assembly in rice paddies. Microbiome 2021, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Yao, L.; Zhu, M.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Dijkstra, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, B. Replacing urea-N with Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) mitigates CH4 and N2O emissions in rice paddy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 336, 108033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.; Wang, T.; Huang, J.; Danso, F.; Bankole, O.O.; Deng, A.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Leguminous green manure mitigates methane emissions in paddy field by regulating acetoclastic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2022, 108, 103380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, T.; Lei, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, L.; Zou, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, X.; Fang, W. Leguminous green manure intercropping changes the soil microbial community and increases soil nutrients and key quality components of tea leaves. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Wen, J.; Mo, F.; Liu, Y. Continuous manure application strengthens the associations between soil microbial function and crop production: Evidence from a 7-year multisite field experiment on the Guanzhong Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 338, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Mehmood, I.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Jia, R.; Gui, H.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Xu, X.; Smith, P.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Not all soil carbon is created equal: Labile and stable pools under nitrogen input. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Catherine, C.; Rathnasingh, C.; Somasundar, A.; Park, S. Production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid from glycerol by recombinant Pseudomonas denitrificans. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 3177–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canarini, A.; Fuchslueger, L.; Schnecker, J.; Metze, D.; Nelson, D.B.; Kahmen, A.; Watzka, M.; Pötsch, E.M.; Schaumberger, A.; Bahn, M.; et al. Soil fungi remain active and invest in storage compounds during drought independent of future climate conditions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Ma, S.; Pan, J.; Cui, Q.; Zheng, W.; Ding, L.; Liang, X.; Xu, B.; Guo, X.; Rillig, M.C. Microbial metabolism influences microplastic perturbation of dissolved organic matter in agricultural soils. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrad017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| pH | OM (g/kg) | NO3—-N (mg/kg) | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | MBC (mg/kg) | MBN (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ck | 6.97 ± 0.02 ab | 29.38 ± 0.86 c | 3.74 ± 0.22 f | 2.38 ± 0.29 e | 8.27 ± 0.90 a | 153.30 ± 2.04 b | 536.30 ± 10.90 c | 65.21 ± 5.00 d |
| N | 7.01 ± 0.03 a | 30.98 ± 0.27 bc | 5.30 ± 0.40 d | 3.44 ± 0.28 d | 9.30 ± 1.67 a | 157.37 ± 1.76 ab | 579.99 ± 13.62 bc | 85.47 ± 4.83 ab |
| M | 6.89 ± 0.02 c | 31.60 ± 0.61 b | 4.32 ± 0.38 e | 3.18 ± 0.07 d | 7.53 ± 1.14 a | 154.77 ± 1.37 b | 596.60 ± 14.95 bc | 77.62 ± 2.51 c |
| MN60 | 6.94 ± 0.04 bc | 32.33 ± 1.13 b | 8.67 ± 0.40 c | 4.65 ± 0.36 c | 7.50 ± 1.18 a | 145.47 ± 2.67 c | 626.24 ± 57.75 ab | 78.95 ± 4.15 bc |
| MN80 | 6.93 ± 0.04 bc | 34.18 ± 1.33 a | 10.07 ± 0.15 b | 5.31 ± 0.25 b | 8.24 ± 0.88 a | 148.37 ± 4.50 c | 647.19 ± 38.22 ab | 85.83 ± 2.59 ab |
| MN100 | 6.94 ± 0.03 bc | 34.29 ± 1.24 a | 11.50 ± 0.10 a | 5.96 ± 0.49 a | 8.22 ± 1.37 a | 160.57 ± 2.95 a | 686.79 ± 64.30 a | 86.92 ± 2.07 a |
| AAs | CBMs | CEs | GHs | GTs | PLs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 41,779.3 ± 4480.3 | 17,232.7 ± 1920.8 | 65,954.0 ± 7475.9 | 160,922.0 ± 19,696.6 | 189,020.7 ± 23,519.3 | 16,572.0 ± 1962.4 |
| N | 39,870.0 ± 1828.0 | 16,580.7 ± 306.7 | 63,798.7 ± 1667.0 | 154,962.7 ± 6329.2 | 180,926.0 ± 2659.5 | 15,721.3 ± 561.3 |
| M | 35,777.3 ± 2729.7 | 14,721.3 ± 1672.0 | 56,504.0 ± 4928.7 | 137,442.7 ± 9662.0 | 156,334.0 ± 11,012.5 | 13,950.0 ± 1436.3 |
| MN60 | 38,746.0 ± 3150.5 | 16,295.3 ± 1646.2 | 61,659.3 ± 5405.1 | 151,090.7 ± 13,966.3 | 176,364.0 ± 12,303.5 | 15,110.0 ± 1267.9 |
| MN80 | 39,857.3 ± 3776.6 | 17,253.3 ± 1964.5 | 63,846.7 ± 6646.5 | 157,398.0 ± 14,146.9 | 185,028.7 ± 21,346.6 | 16,014.0 ± 2031.3 |
| MN100 | 37,654.0 ± 1183.7 | 16,347.3 ± 1135.0 | 60,400.7 ± 4193.5 | 148,966.7 ± 10,646.3 | 172,242.0 ± 16,330.5 | 15,270.7 ± 1680.2 |
| RDA1 | RDA2 | r2 | p_Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.905641498962706 | −0.42404419 | 0.116445748560955 | 0.378 |
| OM | −0.515243361 | −0.857043919 | 0.430271496125382 | 0.012 |
| NO3−-N | −0.477703144 | −0.878521318 | 0.412697504543318 | 0.018 |
| NH4+-N | −0.453730894 | −0.891138752 | 0.358462972974902 | 0.039 |
| AP | −0.033952611 | −0.999423444 | 0.0818533371393249 | 0.559 |
| AK | 0.270470566929879 | −0.962728244 | 0.0319713652600724 | 0.782 |
| MBC | −0.194361376 | −0.980929995 | 0.213055185626319 | 0.165 |
| MBM | −0.146509448 | −0.989209271 | 0.322995681607404 | 0.055 |
| RDA1 | RDA2 | r2 | p_Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | −0.504625695 | 0.863338234908506 | 0.0473741743860555 | 0.677 |
| OM | 0.862536916938697 | 0.505994137236676 | 0.209605231201552 | 0.164 |
| NO3−-N | 0.719392375584055 | 0.694603923075251 | 0.0905588181463002 | 0.498 |
| NH4+-N | 0.798342694606955 | 0.60220340580879 | 0.108769382631094 | 0.421 |
| AP | 0.752087542681751 | 0.659063220141229 | 0.327841813510869 | 0.048 |
| AK | −0.112674092 | 0.993631998818453 | 0.00937266629733166 | 0.931 |
| MBC | −0.354079176 | 0.935215449607062 | 0.0855331282118148 | 0.514 |
| MBM | 0.780273607484678 | 0.625438324267747 | 0.331944622132729 | 0.053 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Dong, W.; Wei, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liang, H.; Mo, Y.; Ou, H.; He, T.; et al. Regulatory Effects of Green Manure Combined with Nitrogen Reduction on Carbon-Cycling Functional Genes and Microbial Communities in Paddy Soils. Diversity 2025, 17, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120825
Li Z, Peng X, Dong W, Wei C, Wang Y, Yu Y, Liang H, Mo Y, Ou H, He T, et al. Regulatory Effects of Green Manure Combined with Nitrogen Reduction on Carbon-Cycling Functional Genes and Microbial Communities in Paddy Soils. Diversity. 2025; 17(12):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120825
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhongyi, Xiaohui Peng, Wenbin Dong, Caihui Wei, Yuning Wang, Yuefeng Yu, Hai Liang, Yongcheng Mo, Huiping Ou, Tieguang He, and et al. 2025. "Regulatory Effects of Green Manure Combined with Nitrogen Reduction on Carbon-Cycling Functional Genes and Microbial Communities in Paddy Soils" Diversity 17, no. 12: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120825
APA StyleLi, Z., Peng, X., Dong, W., Wei, C., Wang, Y., Yu, Y., Liang, H., Mo, Y., Ou, H., He, T., Tang, H., & Tang, M. (2025). Regulatory Effects of Green Manure Combined with Nitrogen Reduction on Carbon-Cycling Functional Genes and Microbial Communities in Paddy Soils. Diversity, 17(12), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17120825









