Diversity Patterns and Environmental Drivers of Bivalve Communities in the Caizi Lake Group and Its Major Tributaries During the Initial Post-Fishing Ban Period
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
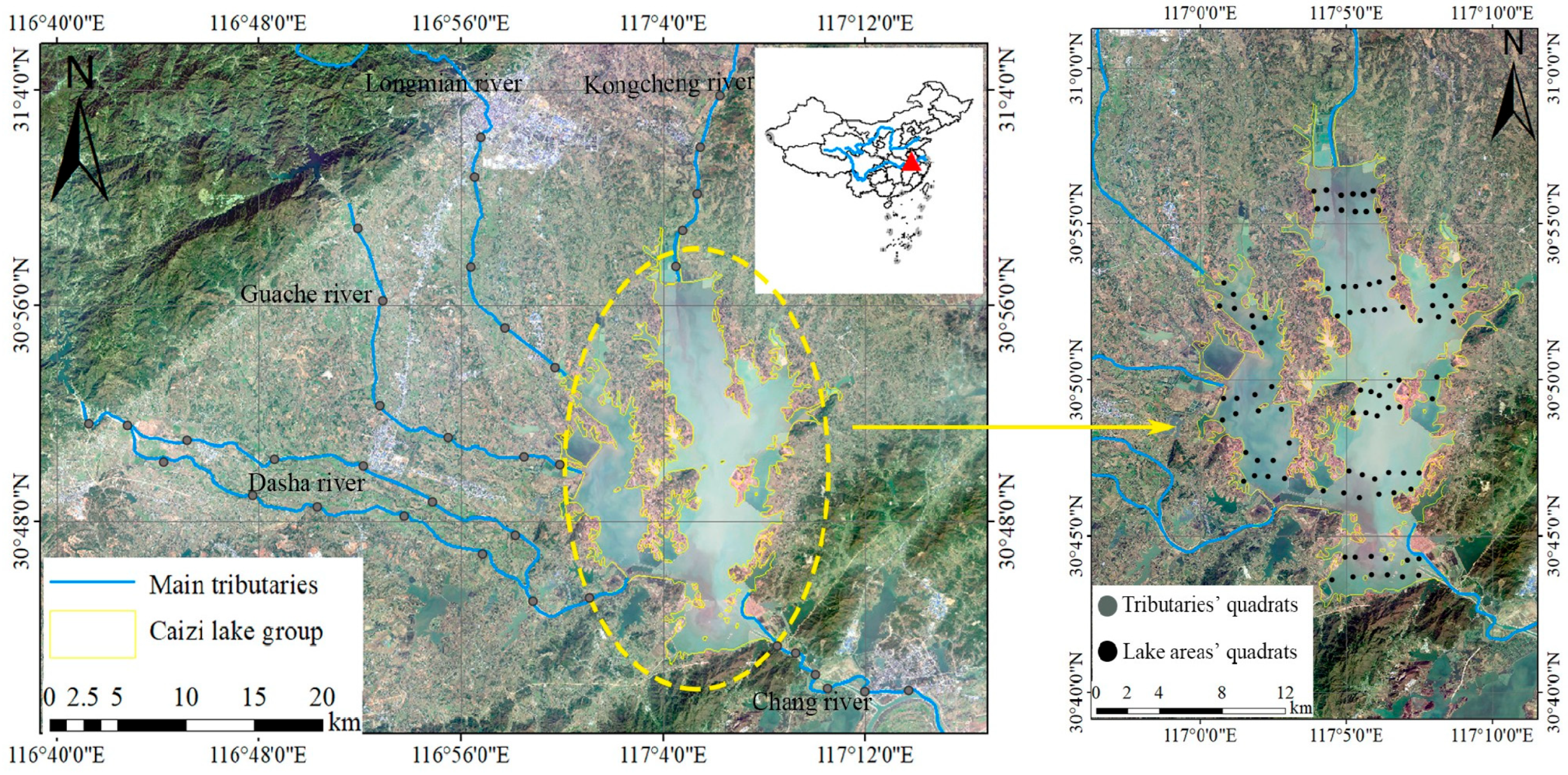
2.1. Collection of Bivalve
2.2. Measurement of Environmental Parameters
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Advantage Status
2.3.2. Diversity Index Analysis
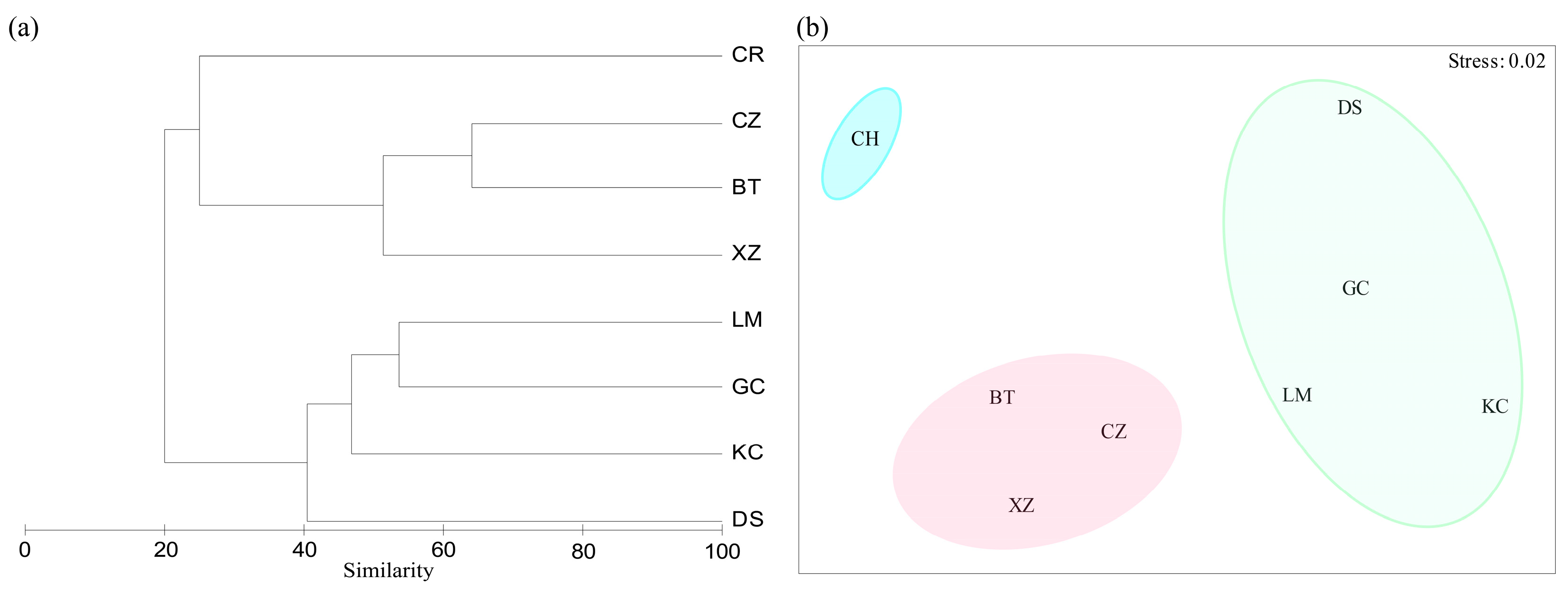
2.3.3. Cluster Analysis and NMDS Analysis
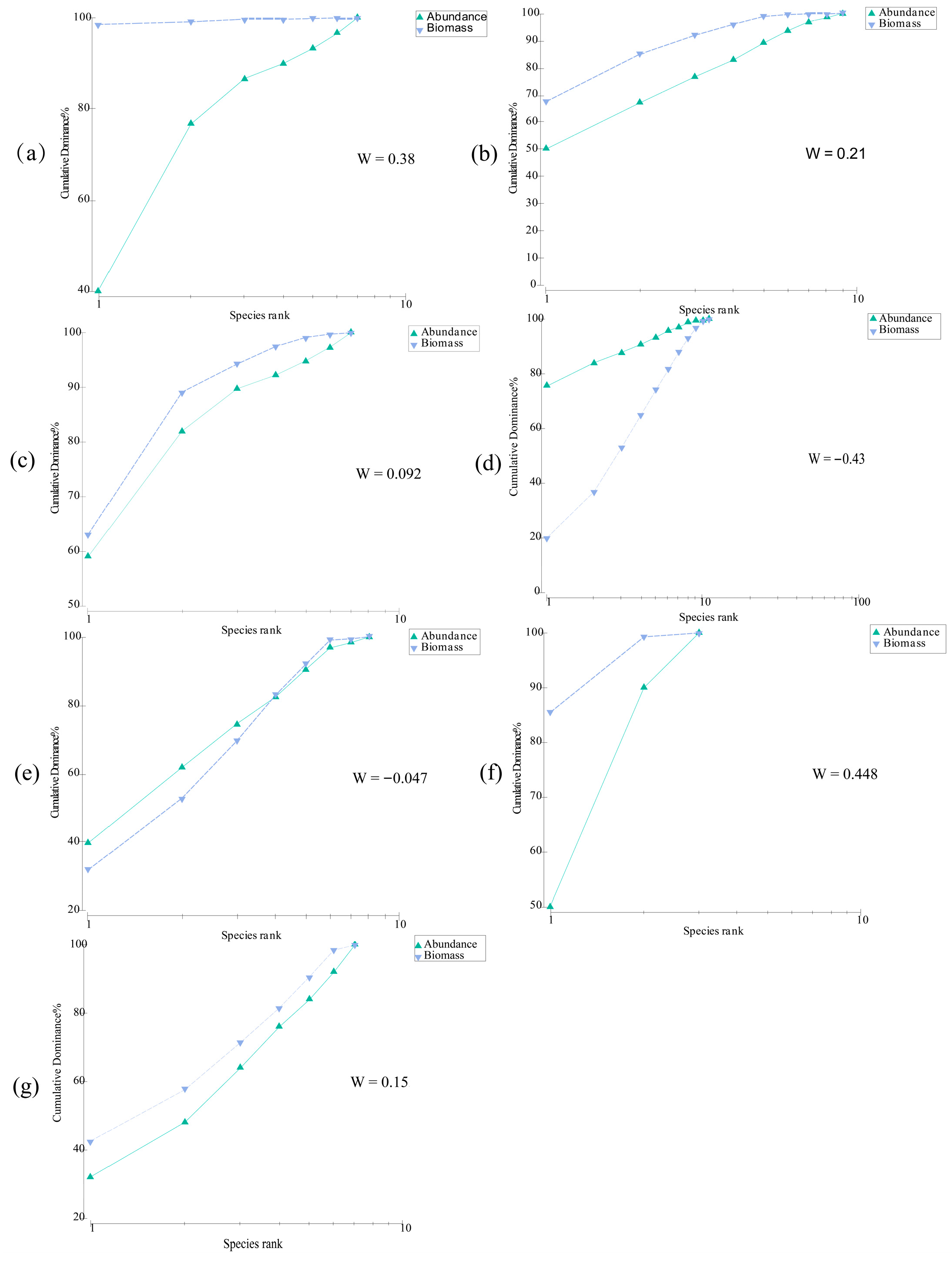
2.3.4. ABC Curve
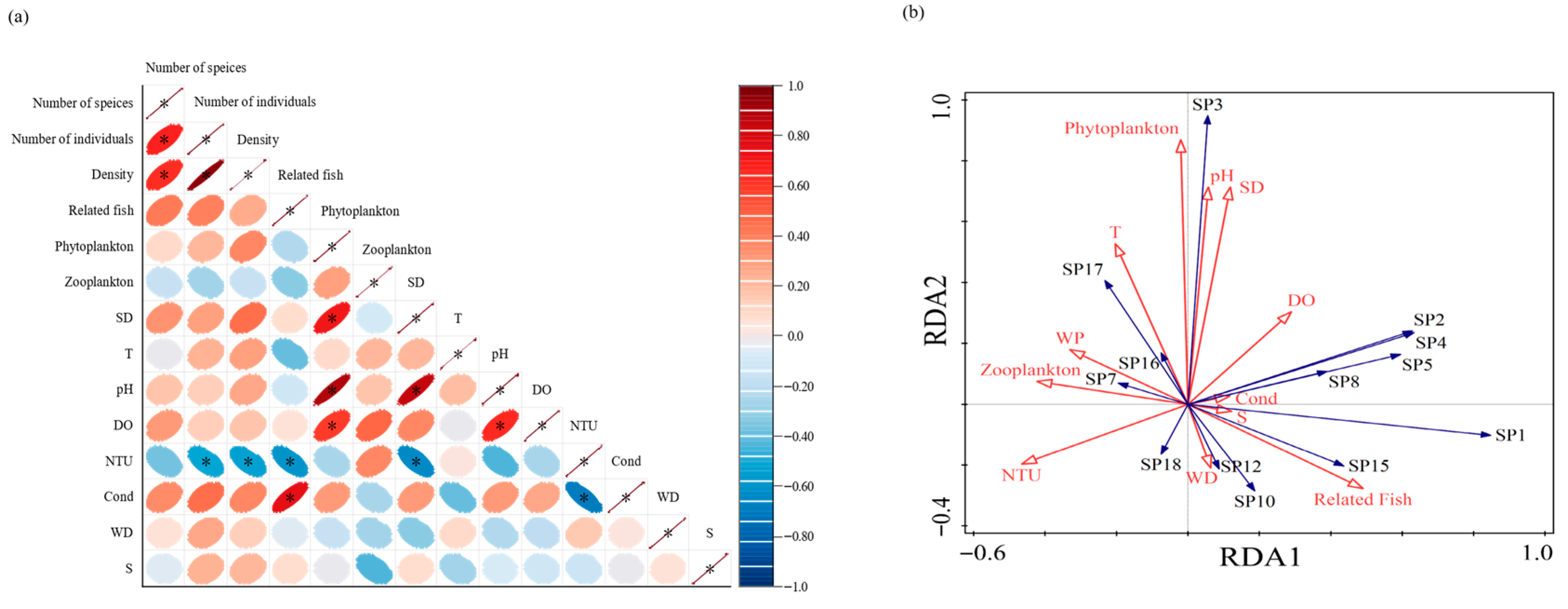
2.3.5. Correlation Analysis of Environmental Factors
3. Results
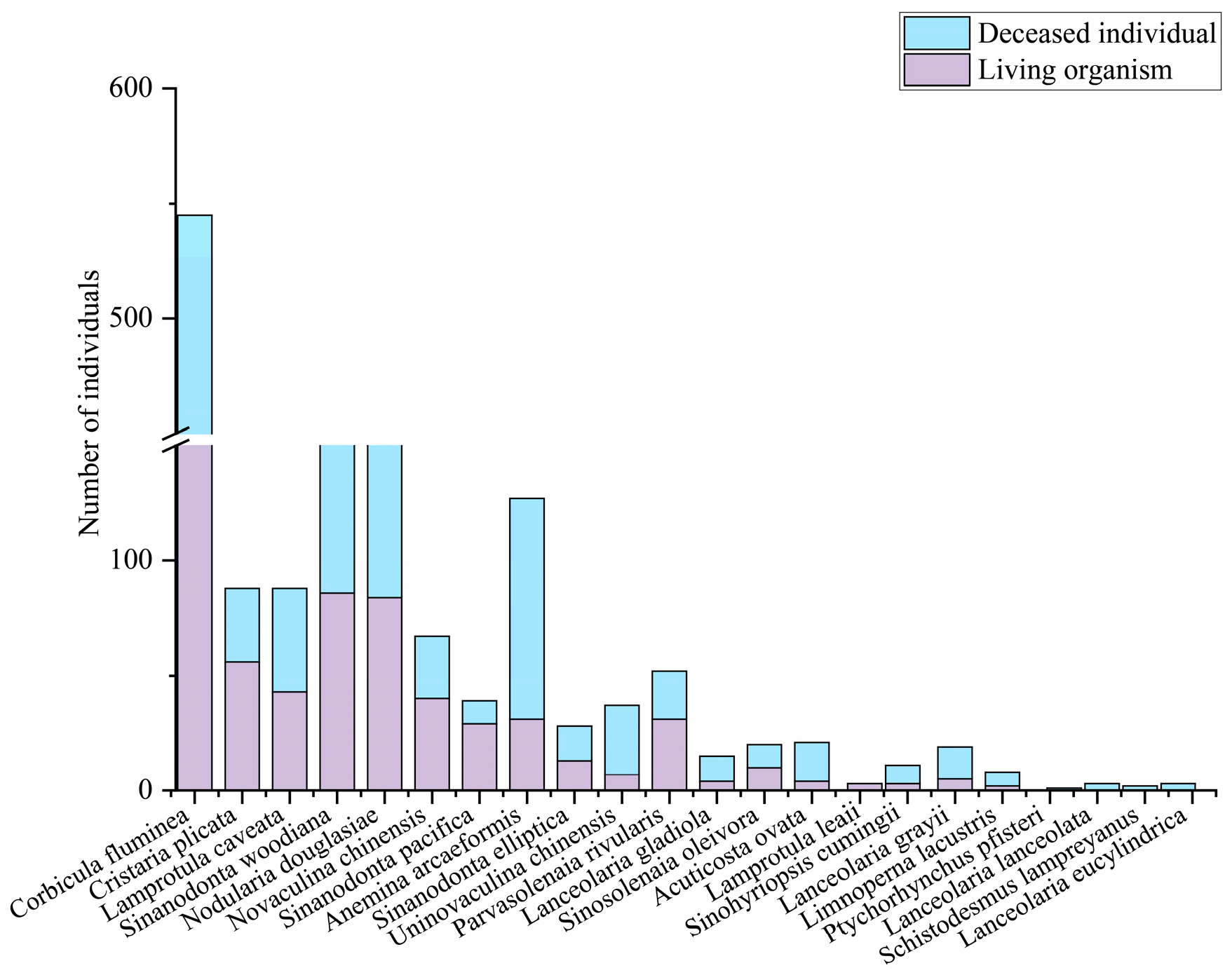
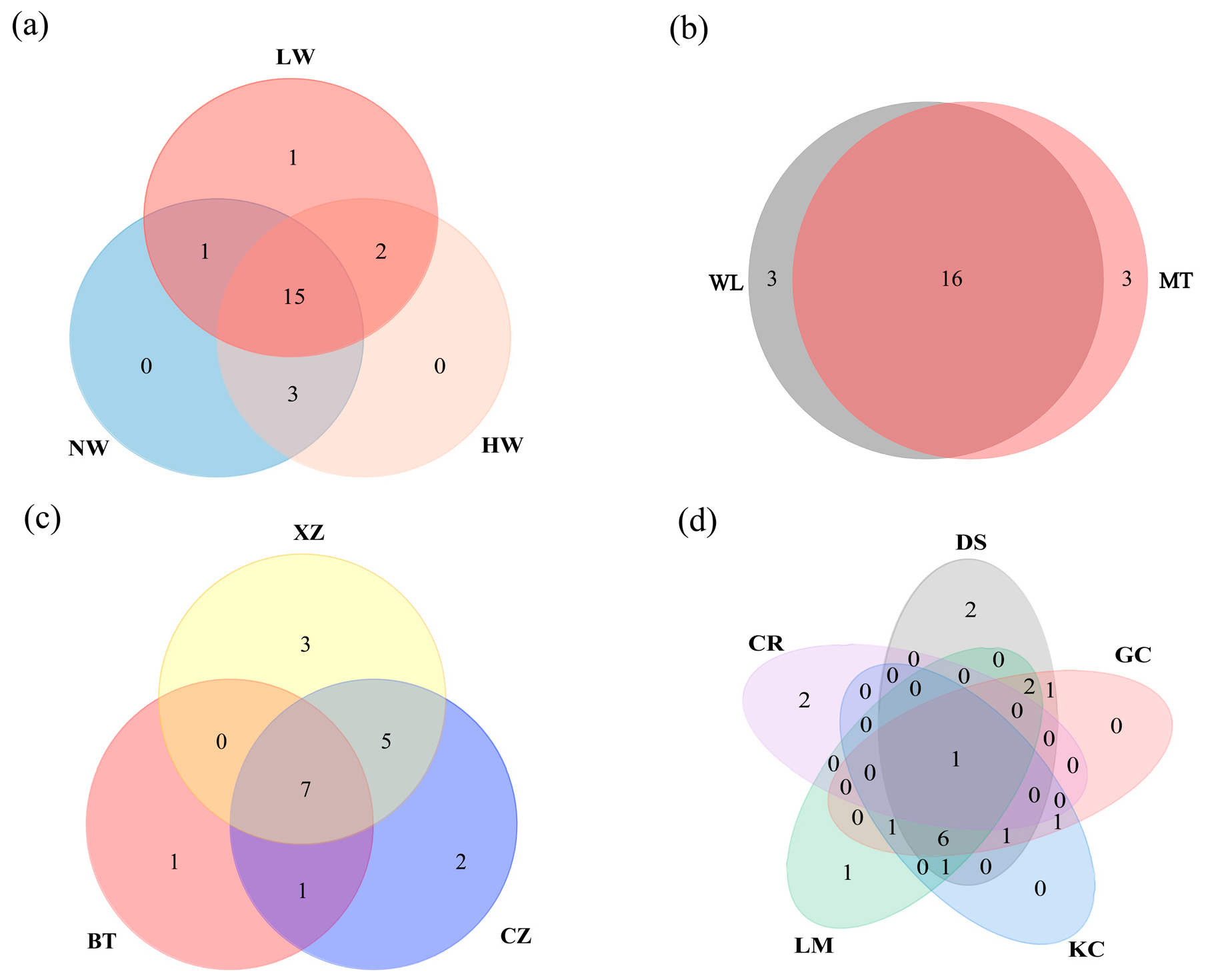
3.1. Species Composition and Spatiotemporal Pattern
3.2. Standing Crop and Spatiotemporal Pattern
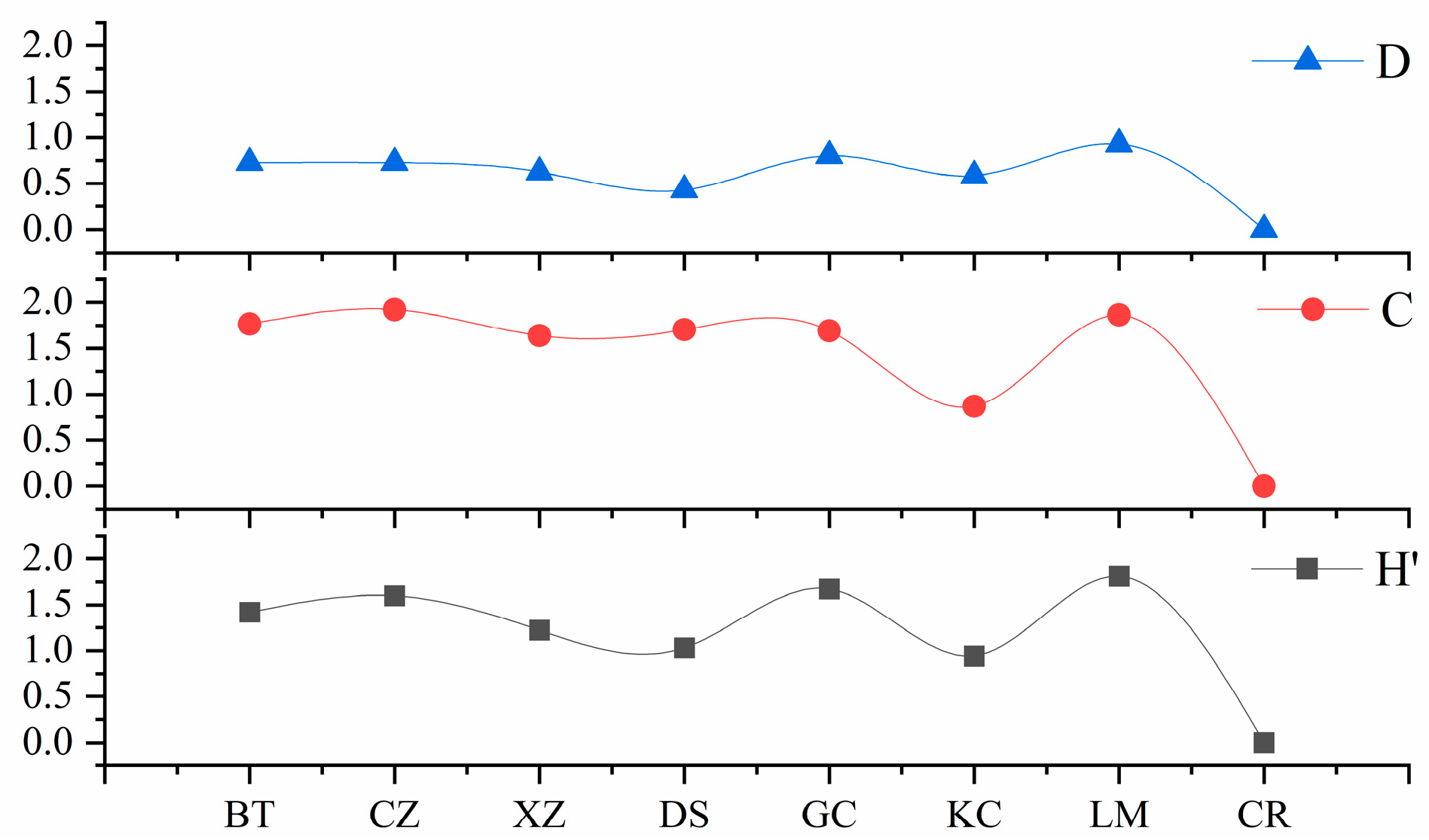
3.3. Community Diversity
3.4. Community Stability
3.5. Correlation Between Community Structure and Environmental Drivers
4. Discussion
4.1. Current Situation of Bivalve Community and Its Diversity
4.2. Spatial Heterogeneity of Bivalves in the Caizi Lake Water System
4.3. The Environmental Drivers of Bivalve Species Diversity in the Caizi Lake Water System
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaughn, C.C.; Hakenkamp, C.C. The functional role of burrowing bivalves in freshwater ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.G.S.; Fujikawa, A.; Abessa, D.M.D.S.; Hortellani, M.A.; Sarkis, J.E.S.; Sígolo, J.B. Uso do bivalve límnico Anodontites tenebricosus (LEA, 1834) no biomonitoramento de metais do Rio Ribeira de Iguape. Quim. Nova 2012, 35, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.B.; Jiang, T. Freshwater Mussel Watch: An innovative approach for interpretations of aquatic pollution and toxicology? J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géba, E.; Rioult, D.; Palluel, O.; Dedourge-Geffard, O.; Betoulle, S.; Aubert, D.; Bigot-Clivot, A. Resilience of Dreissena polymorpha in wastewater effluent: Use as a bioremediation tool? J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C.C.; Hoellein, T.J. Bivalve impacts in freshwater and marine ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 49, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douda, K. Host-dependent vitality of juvenile freshwater mussels: Implications for breeding programs and host evaluation. Aquaculture 2015, 445, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vdovina, O.N.; Tropina, E.F.; Makarycheva, A.Y.; Yerunova, M.G. Patterns of macroinvertebrate distribution in watercourses of the Krasnoyarsk Stolby National Park (East Siberia). Nat. Conserv. Res. 2025, 10, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonina, E.; Tashlykova, N. Diversity of aquatic organisms in the lowland watercourses: A case study in transboundary rivers, Transbaikalia, Russia. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2025, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarev, I.P. Cyclicity in ontogeny and age determination of Flexopecten glaber (Bivalvia, Pectinidae) in the Black Sea. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2024, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydeard, C.; Cowie, R.H.; Ponder, W.F.; Bogan, A.E.; Bouchet, P.; Clark, S.A.; Cummings, K.S.; Frest, T.J.; Gargominy, O.; Herbert, D.G.; et al. The global decline of nonmarine mollusks. Bioscience 2004, 54, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieritz, A.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Bogan, A.E.; Sousa, R.; Walton, S.; Rahim, K.A.A.; Wilson, J.J.; Ng, P.Y.; Froufe, E.; McGowan, S. Factors driving changes in freshwater mussel (Bivalvia, Unionida) diversity and distribution in Peninsular Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Lima, M.; Burlakova, L.E.; Karatayev, A.Y.; Mehler, K.; Seddon, M.; Sousa, R. Conservation of freshwater bivalves at the global scale: Diversity, threats and research needs. Hydrobiologia 2018, 810, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, R.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Xue, T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, K.; Xu, Y.; Qin, J.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Changes and drivers of freshwater mussel diversity patterns in the middle and lower Yangtze River Basin, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2024-2. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Sayer, C.A.; Fernando, E.; Jimenez, R.R.; Macfarlane, N.B.; Rapacciuolo, G.; Böhm, M.; Brooks, T.M.; Contreras-Macbeath, T.; Cox, N.A.; Harrison, I.; et al. One-quarter of freshwater fauna threatened with extinction. Nature 2025, 638, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, R.; Zanatta, D.T.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Gonçalves, D.V.; Bogan, A.E.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Systematics, distribution, biology, and conservation of freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionida) in China. Aquat. Conserv. 2022, 32, 859–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Zanatta, D.T.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Bogan, A.E.; Zieritz, A.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Conservation status assessment and a new method for establishing conservation priorities for freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionida) in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River drainage. Aquat. Conserv. 2020, 30, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ferreira-Rodriguez, N.; Wu, R.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Sixty years of species diversity and population density decline of freshwater mussels in a global biodiversity hotspot. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 46, e02573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Freshwater biodiversity conservation in China: Progress in the Yangtze River basin. Aquat. Conserv. 2022, 32, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, F.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Pan, B.Z.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, H.Z. Assessment of species status of mollusca in the mid-lower Yangtze lakes. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2009, 33, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.G.; Xiong, Y.; Li, D.W.; Bao, Q.L.; Lin, G.Y.; Chu, T. River-lake connectivity and biological corridors restoration at Changjiang River Anhui reach. Yangtze River 2024, 55, 69–74, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, B.; Chen, L.W.; Cao, L. Waterbird Suevey of the Middle and Lower Yangtze River Floodplain in February 2005; China Forestry Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Administrative Division Office of the Aquatic Products Bureau of the People’s Government of Anhui Province. Compilation of Investigation Reports on Fishery Resources in Key Waters of the Huai River System in Anhui Province; Administrative Division Office of the Aquatic Products Bureau of the People’s Government of Anhui Province: Anhui, China, 1982.
- Wang, S.M.; Dou, H.S. Lakes in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 241–242. [Google Scholar]
- Anqing Forestry Administration. Anqing Wetland Nature Reserve Along the Yangtze River Comprehensive Investigation Report; Anqing Forestry Administration: Anqing, China, 2021; pp. 3–30.
- Xu, X.Y.; Zhou, L.Z.; Zhu, W.Z.; Xu, R.X.; Cao, L.L.; Chen, J.Y.; Wang, X. Community structure of macrozoobenthos in Caizi Lake, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.Q.; Sun, Q.Y. The species diversity and distribution of freshwater bivalves in the Anhui section of the Yangtze River Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M. Study on River-Lake Ecosystem Health Assessment Based on Benthic Animal Integrity Index. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Architecture, Zhangjiakou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Y. Economic Fauna of China (Freshwater Mollusk); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979; pp. 7–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; An, J.; Chen, R.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Taxonomy, phylogeny and evolution of freshwater mussels (Unionoida: Unionoidea) in China revealed by multilocus phylogenetic analyses and mitochondrial phylogenomics. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1788–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L. Unionoida; The Straits Publishing & Distributing Group: Fuzhou, China, 2022; pp. 34–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Huang, X.F. Methods for Freshwater Plankton Research; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991; pp. 232, 256–258. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Z. Monograph of Chinese Freshwater Rotifers; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1961; pp. 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.Z.; Du, N.S. Fauna Sinica: Arthropoda: Crustacea: Freshwater Cladocera; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.R. Fauna Sinica: Arthropoda: Crustacea: Freshwater Copepoda; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.F. Protozoology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.J.; Wei, Y.X. Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.S.; Song, Y.F. Atlas of Chinese Freshwater Organisms; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkas, L.; Oliphant, M.S.; Iverson, I.L.K. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. Fish Bull. 1970, 152, 3–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhm, J.L. Use of biomass units in Shannon’s formula. Ecology 1968, 49, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Information theory in ecology. Gen. Syst. 1958, 3, 36–71. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. Ecological Diversity; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 326–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, J.B. Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Psychometrika 1964, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, R. A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities. Mar. Biol. 1986, 92, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd ed.; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, K.; Wang, Y.P.; Xu, S.Y.; Shen, Y.D.; Cao, L.L.; Liu, L. Research ststus of early fish resources in Shijiu Lake during the ban of fishing and their relationship with environmental factors. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2025, 49, 082514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresty and Grassland Administration of China, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China. List of Endangered and Protected Species of China; Law Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Haag, W.R. North American Freshwater Mussels: Natural History, Ecology, and Conservation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.L.; Song, X.L.; Liu, X.J.; Huang, X.C.; Zhou, C.H.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X.P. Taxonomic status and species validities of anodontines based on shell morphology and molecular characteristics. In Proceedings of the Re-election Conference of the Shellfish Branch of the Zoological Society of China and the Chinese Society of Oceanology and Limnology and the 19th Academic Symposium, Nanning, China, 19 October 2019; Zoological Society of China: Beijing, China, 2019; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Strayer, D.L. Freshwater Mussel Ecology: A Multifactor Approach to Distribution and Abundance; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, R.; Antunes, C.; Guilhermino, L. Ecology of the invasive Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774) in aquatic ecosystems: An overview. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 2008, 44, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Rodríguez, N.; Sousa, R.; Pardo, I. Negative effects of Corbicula fluminea over native freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 2018, 810, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Zhou, L.Z. Analysis of wetland landscape pattern variation and its driving factors of Caizi Lake group based on geodetector. Water Resour. Prot. 2021, 37, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangloff, M.; Feminella, J. Stream channel geomorphology influences mussel abundance in southern Appalachian streams, USA. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogan, A.E. Global diversity of freshwater mussels (Mollusca, Bivalvia) in freshwater. In Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment; Kalkman, V.J., Clausnitzer, V., Dijkstra, K.D.B., Orr, A.G., Paulson, D.R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.N.; Gao, W.J.; Zhang, T.Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wu, X.H.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.Z.; Cui, Y.D. Distribution patterns of macrozoobenthos in the mid-lower mainstem of the Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.H.; Zou, W.; Zhang, Q.J.; Li, Y.; Gong, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Lu, S.B.; Cai, Y.J. Characteristics and driving factors of spatiotemporal succession of macrozoobenthos in Poyang Lake. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.F.; Tong, C.F. Community composition and spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of benthic macroinvertebrates in Taipu River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 4619–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, D.C.; Ollard, I.S.; Bespalaya, Y.V.; Bolotov, I.N.; Douda, K.; Geist, J.; Haag, W.R.; Klunzinger, M.W.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Mlambo, M.C.; et al. Freshwater mussel conservation: A global horizon scan of emerging threats and opportunities. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yin, H.B.; Gao, J.F.; Zhang, Z.M.; Cai, Y.J. Benthic macroinvertebrate community structure and environmental determinants in river systems of Chaohu Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C.C. Life history traits and abundance can predict local colonisation and extinction rates of freshwater mussels. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.J.; Su, X.M.; Xie, L.Q. Advances on cyanotoxin toxicology of zoobenthos. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 4570–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Q.; Qiu, J.B.; Li, P.R.; Li, A.F. Multiple toxicological effects of paralytic shellfish toxins and their producing microalgae on diverse aquatic organisms. Water Biol. Secur. 2025, 5, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, M.L.; Findlay, S.E.; Fischer, D. Effects of an invasive bivalve on the zooplankton community of the Hudson River. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 39, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomati, F.; Shurin, J.B.; Andersen, K.H.; Tellenbach, C.; Barton, A.D. Interacting temperature, nutrients and zooplankton grazing control phytoplankton size-abundance relationships in eight Swiss lakes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, L.I.; Moldoveanu, M.M.; Catană, R.D.; Păceșilă, I.; Dumitrache, A.; Gavrilidis, A.A.; Iojă, C.I. Assessing the effects of phytoplankton structure on zooplankton communities in different types of urban lakes. Diversity 2022, 14, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, D.W.; Payne, B.S.; Miller, A.C. The effects of intermittent exposure to suspended solids and turbulence on three species of freshwater mussels. Environ. Pollut. 1987, 45, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, J.B.; Mossa, J. Sediment, land use, and freshwater mussels: Prospects and problems. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1999, 18, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, I.; Garcia Molinos, J. Impacts of increased sediment loads on the ecology of lakes. Biol. Rev. 2009, 84, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | IRI | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Caizi Lake Water System | Lake Areas | Main Tributaries | |
| Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774) | 2045.67 | 1160.43 | 28,677.74 |
| Cristaria plicata (Leach, 1815) | 957.90 | 2206.91 | - |
| Lamprotula caveata (Heude, 1877) | 473.19 | 908.90 | 91.57 |
| Sinanodonta woodiana (Lea, 1834) | 175.86 | 43.21 | 853.48 |
| Nodularia douglasiae (Griffith & Pidgeon, 1833) | 151.62 | 11.25 | 950.26 |
| Acuticosta chinensis (Lea, 1868) | 51.59 | - | 438.38 |
| Sinanodonta pacifica (Heude, 1878) | 6.74 | 3.86 | 25.46 |
| Anemina arcaeformis (Heude, 1877) | 16.70 | 2.17 | 117.56 |
| Sinanodonta elliptica (Heude, 1877) | 9.66 | - | 114.68 |
| Uninovaculina chinensis (Liu & Zhang, 1979) | 5.70 | 34.64 | - |
| Parvasolenaia rivularis (Heude, 1877) | 4.94 | - | 31.45 |
| Lanceolaria gladiola (Heude, 1877) | 2.49 | 2.54 | 12.44 |
| Sinosolenaia oleivora (Heude, 1877) | 1.85 | - | 14.11 |
| Acuticosta ovata (Heude, 1877) | 1.83 | - | 16.77 |
| Lamprotula leaii (Gray, 1833) | 1.47 | 2.06 | - |
| Sinohyriopsis cumingii (Lea, 1852) | 1.01 | 2.41 | - |
| Lanceolaria grayii (Lea, 1834) | 0.60 | 1.67 | - |
| Limnoperna fortunei (Dunker, 1857) | 0.27 | 1.64 | - |
| Species | Occurrence | Shu [20] | Liu [13] | IUCN [14] | Protection Class [48] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mytilidae | |||||
| Limnoperna fortunei | 0.01 | LC | NA | NA | |
| Corbiculidae | |||||
| Corbicula fluminea | 0.35 | LC | NA | LC | |
| Solecurtidae | |||||
| Uninovaculina chinensis | 0.05 | DD | NA | NA | II |
| Unionidae | |||||
| Nodularia douglasiae | 0.12 | LC | LC | LC | |
| Parvasolenaia rivularis | 0.01 | NA | EN | NA | |
| Sinosolenaia oleivora | 0.01 | T | VU | NA | |
| Acuticosta chinensis | 0.06 | NT | LC | LC | |
| Acuticosta ovata | 0.02 | NT | LC | LC | |
| Anemina arcaeformis | 0.05 | LC | LC | LC | |
| Sinanodonta woodiana | 0.15 | LC | LC | LC | |
| Sinanodonta elliptica | 0.02 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Sinanodonta pacifica | 0.04 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Cristaria plicata | 0.19 | LC | LC | LC | |
| Sinohyriopsis cumingii | 0.01 | LC | LC | LC | |
| Lamprotula caveata | 0.14 | LC | LC | LC | |
| Lamprotula leaii | 0.01 | T | LC | LC | II |
| Lanceolaria eucylindrica | 0 | T | NA | NA | |
| Lanceolaria gladiola | 0.02 | T | LC | LC | |
| Lanceolaria grayii | 0.01 | NT | LC | LC | |
| Lanceolaria lanceolata | 0 | NT | NT | LC | |
| Schistodesmus lampreyanus | 0 | T | LC | LC | |
| Ptychorhynchus pfisteri | 0 | T | VU | NT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, C.; Jiang, M.; Ren, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Liu, K. Diversity Patterns and Environmental Drivers of Bivalve Communities in the Caizi Lake Group and Its Major Tributaries During the Initial Post-Fishing Ban Period. Diversity 2025, 17, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17110773
Jiang C, Jiang M, Ren C, Zhang X, Li B, Liu K. Diversity Patterns and Environmental Drivers of Bivalve Communities in the Caizi Lake Group and Its Major Tributaries During the Initial Post-Fishing Ban Period. Diversity. 2025; 17(11):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17110773
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Chao, Min Jiang, Chenliang Ren, Xiaoke Zhang, Bowen Li, and Kai Liu. 2025. "Diversity Patterns and Environmental Drivers of Bivalve Communities in the Caizi Lake Group and Its Major Tributaries During the Initial Post-Fishing Ban Period" Diversity 17, no. 11: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17110773
APA StyleJiang, C., Jiang, M., Ren, C., Zhang, X., Li, B., & Liu, K. (2025). Diversity Patterns and Environmental Drivers of Bivalve Communities in the Caizi Lake Group and Its Major Tributaries During the Initial Post-Fishing Ban Period. Diversity, 17(11), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17110773







