Leaf Stoichiometric Characteristics of Three Dominant Plant Species in the Water–Land Ecotone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Plot Establishment and Sampling
2.3. Element Measurements
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; Interlandi, S.; Kilham, S.S.; McCauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Janssens, I.A.; Ciais, P.; Obersteiner, M.; Peñuelas, J. Recent advances and future research in ecological stoichiometry. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2021, 50, 125611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Peñuelas, J. The C: N: P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 14, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S. N: P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, D.T.; Hanson, J.B. The mineral nutrition of higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1980, 31, 239–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Poorter, H.J.P.C. Photosynthetic acclimation of plants to growth irradiance: The relative importance of specific leaf area and nitrogen partitioning in maximizing carbon gain. Plant Cell Environ. 2001, 24, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Fang, J.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sepulcre, A.; Amaral, J.R.; Gautam, N.; Mohamed, A.; Naik, S. The eco-evolutionary dynamics of stoichiometric homeostasis. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2024, 39, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Reviews and syntheses: Ecological stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in shrubs and shrublands. EGUsphere 2025, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatla, S.C.; Lal, M.A. Plant Physiology, Development and Metabolism; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, B.; Heald, R.; Johnson, A.; Morgan, D.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular Biology of the Cell: Seventh International Student Edition with Registration Card; W.W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marschner, H. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ågren, G.I. Stoichiometry and nutrition of plant growth in natural communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhoff, A.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Elser, J.J.; Enquist, B.J. Phylogenetic and growth form variation in the scaling of nitrogen and phosphorus in the seed plants. Am. Nat. 2006, 168, E103–E122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minden, V.; Kleyer, M. Internal and external regulation of plant organ stoichiometry. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A.F.M. The vegetation N:P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Gosselink, J.G. Wetlands; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bastviken, D.; Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Crill, P.M.; Enrich-Prast, A. Freshwater methane emissions offset the continental carbon sink. Science 2011, 331, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, N.C. How much wetland has the world lost? Long-term and recent trends in global wetland area. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2014, 65, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenasso, M.L.; Pickett, S.T.; Weathers, K.C.; Jones, C.G. A framework for a theory of ecological boundaries. BioScience 2003, 53, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Decamps, H. The ecology of interfaces: Riparian zones. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1997, 28, 621–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayranli, B.; Scholz, M.; Mustafa, A.; Hedmark, Å. Carbon storage and fluxes within freshwater wetlands: A critical review. Wetlands 2010, 30, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Stocker, B.D.; Zhang, Z.; Malhotra, A.; Melton, J.R.; Poulter, B.; Kaplan, J.O.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Siebert, S.; Minayeva, T.; et al. Extensive global wetland loss over the past three centuries. Nature 2023, 614, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Zhao, Q. Characteristics of climate change in typical karst plateau lake: A case study of Caohai in Guizhou. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull 2020, 36, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; An, Y.; Wang, P.; Ma, L. Study on biodiversity conservation hotspots in Guizhou. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 21, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yao, S. Ecological safety evaluation of Caohai Lake wetland in Weining. J. Hydroecology 2018, 39, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Fu, P.; Yang, R. Assessment of wetland ecosystem health in the Caohai lake of Guizhou province. Earth Environ. 2014, 42, 68–81. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, R.; Du, M. Temporal and influencing factors of Caohai water quality from 2013 to 2022. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2024, 50, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, M. Study on the Synergistic Evolutionary Pattern of Plant-Soil System in the Aquatic–Terrestrial Ecotones of Lake Caohai. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou Minzu University, Guiyang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, G.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Z. Characteristics and driving mechanism of wetland landscape pattern change in karst region of southwest China over past 35 years: A case study of Caohai wetland in Guizhou. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Xia, P.; Song, X.; Lin, T.; Cao, H. Community structure and functional diversity of epiphytic bacteria and planktonic bacteria on submerged macrophytes in Caohai Lake, southwest of China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; He, Z.; Wang, K. RS−based vegetation classification of Caohai Wetland in Weining, Guizhou. Guizhou Sci. 2021, 39, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, M.; Ran, J.; Wu, C. Study on the growth laws of Phragmites australis in Caohai, Weining, Guizhou. Guizhou For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- McGroddy, M.E.; Daufresne, T.; Hedin, L.O. Scaling of C:N:P stoichiometry in forests worldwide: Implications of terrestrial redfield-type ratios. Ecology 2004, 85, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, D.A.; Williams, M.; Rastetter, E.B. A model analysis of N and P limitation on carbon accumulation in Amazonian secondary forest after alternate land-use abandonment. Biogeochemistry 2003, 65, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Walters, M.B.; Ellsworth, D.S. From tropics to tundra: Global convergence in plant functioning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13730–13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Kerkhoff, A.J.; Swenson, N.G.; Enquist, B.J. Biological stoichiometry of plant production: Metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Reich, P.B.; Ian Woodward, F.; Wang, Z. Biogeography and variability of eleven mineral elements in plant leaves across gradients of climate, soil and plant functional type in China. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Penuelas, J. The elemental stoichiometry of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems and its relationships with organismic lifestyle and ecosystem structure and function: A review and perspectives. Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Cassman, K.E.N.; Cleveland, C.; Crews, T.; Field, C.B.; Grimm, N.B.; Howarth, R.W.; Marino, R.; Martinelli, L.; Rastetter, E.B.; et al. Towards an ecological understanding of biological nitrogen fixation. Biogeochemistry 2002, 57, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Q.; Bai, J.; Gao, H.; Huang, L.; Xiao, R. Decomposition and return of C and N of plant litters of Phragmites australis and Suaeda salsa in typical wetlands of the Yellow River Delta, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ågren, G.I. The C: N: P stoichiometry of autotrophs–theory and observations. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Meng, B.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Tu, S. Effect of reed expansion on habitat adaptation and behavioral activity characteristics of Grus nigricollis in Guizhou Caohai National Nature Reserve. Chin. J. Wildlife 2025, 46, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- White, P.J.; Broadley, M.R. Calcium in plants. Ann. Bot. 2003, 92, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.R.; DeLaune, R.D.; Inglett, P.W. Biogeochemistry of Wetlands: Science and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.X.; Wu, P.; Yang, S.D.; Liu, S.; Liao, J.H. Hydrochemistry characteristics and estimation of the dissolved inorganic carbon flux in the Caohai lake wetland catchment of Guizhou Province. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2021, 42, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J.; Wright, I.J.; Niklas, K.J.; Hedin, L.; Elser, J.J. Evidence of a general 2/3-power law of scaling leaf nitrogen to phosphorus among major plant groups and biomes. Proc. R. Soc. Ser. B 2010, 277, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, R.A.; Wyn Jones, R.G. A hypothesis relating critical potassium concentrations for growth to the distribution and functions of this ion in the plant cell. New Phytol. 1984, 97, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.; Pottosin, I. Regulation of potassium transport in plants under hostile conditions: Implications for abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 151, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
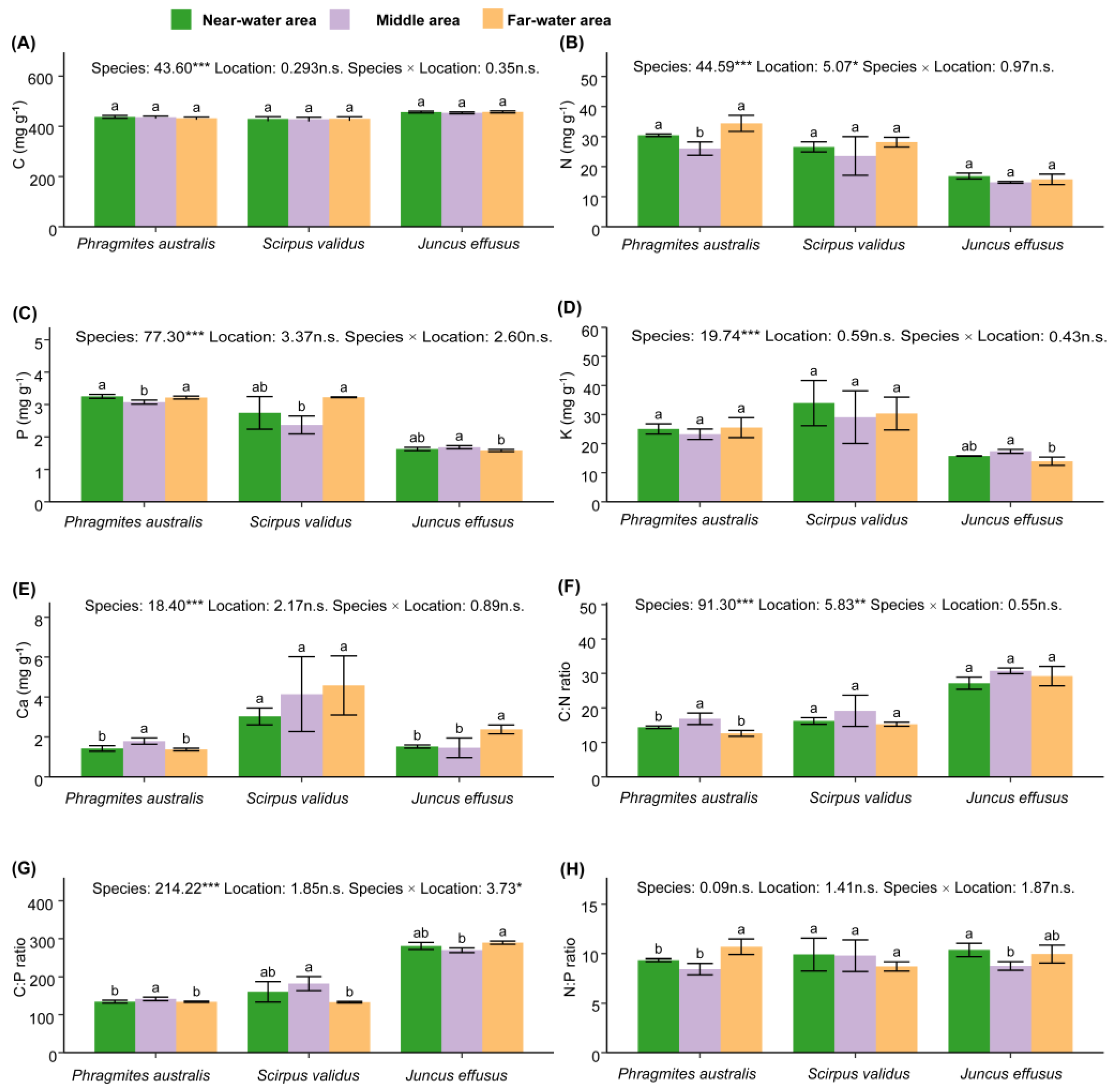

| Species | Nutrients | Near-Water Area (mg g−1) | Middle-Area (mg g−1) | Far-Water Area (mg g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phragmites australis | C | 437.77 ± 5.67 | 435.74 ± 5.15 | 431.66 ± 5.48 |
| N | 30.44 ± 0.42 | 26.00 ± 2.21 | 34.4 ± 2.66 | |
| P | 3.25 ± 0.06 | 3.08 ± 0.06 | 3.22 ± 0.04 | |
| K | 25.06 ± 1.76 | 23.24 ± 1.8 | 25.52 ± 3.43 | |
| Ca | 1.42 ± 0.14 | 1.79 ± 0.16 | 1.37 ± 0.06 | |
| Scirpus validus | C | 429.22 ± 8.99 | 427.69 ± 8.45 | 429.84 ± 8.06 |
| N | 26.56 ± 1.68 | 23.55 ± 6.44 | 28.16 ± 1.61 | |
| P | 2.74 ± 0.50 | 2.37 ± 0.28 | 3.23 ± 0.01 | |
| K | 33.96 ± 7.79 | 29.1 ± 9.08 | 30.37 ± 5.65 | |
| Ca | 3.03 ± 0.42 | 4.14 ± 1.87 | 4.58 ± 1.48 | |
| Juncus effusus | C | 456.63 ± 3.84 | 453.44 ± 3.64 | 457.23 ± 4.07 |
| N | 16.86 ± 0.98 | 14.75 ± 0.30 | 15.75 ± 1.73 | |
| P | 1.63 ± 0.05 | 1.68 ± 0.05 | 1.58 ± 0.04 | |
| K | 15.73 ± 0.10 | 17.32 ± 0.67 | 13.93 ± 1.43 | |
| Ca | 1.51 ± 0.08 | 1.46 ± 0.49 | 2.38 ± 0.23 |
| Species | Stoichiometric Ratio | Near-Water Area | Middle-Area | Far-Water Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phragmites australis | C:N | 14.39 ± 0.38 | 16.85 ± 1.66 | 12.59 ± 0.86 |
| C:P | 134.54 ± 3.73 | 141.73 ± 4.63 | 134.19 ± 1.53 | |
| N:P | 9.35 ± 0.15 | 8.45 ± 0.58 | 10.69 ± 0.79 | |
| Scirpus validus | C:N | 16.21 ± 0.95 | 19.18 ± 4.52 | 15.28 ± 0.59 |
| C:P | 160.49 ± 26.85 | 182.14 ± 18.59 | 133.2 ± 2.01 | |
| N:P | 9.91 ± 1.65 | 9.8 ± 1.59 | 8.72 ± 0.47 | |
| Juncus effusus | C:N | 27.16 ± 1.78 | 30.74 ± 0.83 | 29.24 ± 2.82 |
| C:P | 280.68 ± 9.38 | 269.34 ± 6.27 | 289.48 ± 4.22 | |
| N:P | 10.36 ± 0.68 | 8.77 ± 0.43 | 9.96 ± 0.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, X.; Li, W.; Zou, S.; He, B.; Xue, X. Leaf Stoichiometric Characteristics of Three Dominant Plant Species in the Water–Land Ecotone. Diversity 2025, 17, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100697
Bai X, Li W, Zou S, He B, Xue X. Leaf Stoichiometric Characteristics of Three Dominant Plant Species in the Water–Land Ecotone. Diversity. 2025; 17(10):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100697
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Xiaolong, Wangjun Li, Shun Zou, Bin He, and Xiaohui Xue. 2025. "Leaf Stoichiometric Characteristics of Three Dominant Plant Species in the Water–Land Ecotone" Diversity 17, no. 10: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100697
APA StyleBai, X., Li, W., Zou, S., He, B., & Xue, X. (2025). Leaf Stoichiometric Characteristics of Three Dominant Plant Species in the Water–Land Ecotone. Diversity, 17(10), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100697






