Abstract
Background: Lake Al-Asfar in KSA was used as a sink for wastewater for decades and suffered from pollution. The lake is a habitat to different microbial species that play important ecological roles, some of which are good, and some are bad and even pathogenic. In a previous investigation, algal-bacteria consortia have proven to be beneficial in bioremediating heavy metals and hydrocarbons in Lake Al-Asfar. The identity of algae was revealed to be Chlorella sp. and Geitlernema sp. in the consortia. The identity of the heterotrophic bacterial partners, on the other hand, awaits investigation and is addressed in the present research. On the other hand, investigating the diversity of Protozoa and parasites is also tackled as they represent indicators of pollution. Some pose serious health risks, but some of them also contribute to reducing some of the pollution levels. Methods: Bacteria associated with algae were isolated in pure form. The polyphasic approach was used to identify bacterial samples, including staining procedures, the use of Vitek technology, and scanning electron microscopy. This information was integrated with structure information such as capsule presence, endospore formation, and wall characteristics indicated by Gram stain. With regard to protists including Protozoa and parasites, Light microscopy and taxonomic books of identification were used to reveal their identity. Results: three main bacterial strains belonging to the following genera were identified: Sphingomonas, Rhizobium, and Enterbacter. The last is potentially pathogenic and poses health risks to Lake goers. Rhizobium, on the other hand, is most likely found in the lake from agricultural wastewater and is a nitrogen fixer that increases the fertility of crops. The first bacterium is associated with special lipid metabolism and is hardly pathogenic. Several diverse microscopic forms of protists, mainly Protozoa and parasites, were identified, which included Entamoeba histolytica, Balantidium coli, Ascaris lumbricoides, Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, and Gymnodinium sp. Discussion: The three types of bacteria identified have metabolic activities that are associated with bioremediation. On the other hand, protists, including Protozoa and parasites, are regular members of wastewater communities and help in scavenging solid wastes, but they cause hazards such as secreting toxins, causing disease, and impacting the bioremediation potential by feeding on beneficial bioremediating algae and bacteria. This is part of the wastewater ecosystem dynamics, but efforts must be exerted to minimize, if not completely eliminate, pathogenic parasites in order to maximize the growth of algal consortia. Conclusions: Vitek technology is an emerging less time- and effort-consuming fast technology for identifying bacteria. Bacteria identified have significant ecological bioremediating roles, together with their algal partners, but some pose pathogenic risks. Identifying co-inhabitants like protists and parasites helps to shed light on their impact on one another and pave the way for restoration efforts that minimize the biological hazards and maximize the use of beneficial local microorganisms.
1. Introduction
Environmental pollution, with its different types including biological and chemical pollution, is the most serious threat to ecosystem sustainability in the current century [1]. The increased anthropogenic activities like burning fossil fuels, application of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, and use of complex chemicals, together with dumping of untreated domestic waste that contained dangerous parasites and pathogens, all caused harm to all forms of life [1]. Hence, there is a crucial need to develop some efficient and cost-effective solutions in order to remediate the pollutants, prevent the further deterioration in the ecosystem, and prevent any health hazards. The carcinogenic nature of some of these pollutants further amplifies their deleterious effects [1]. The removal/degradation of these pollutants by the algae and bacterial consortia, i.e., bioremediation, is a promising approach to decontaminate the polluted sites [2]. With regard to microbial bioremediation, [3] reported that bacterial consortia proved to be well-suited for the bioremediation process instead of single-strain bacteria. It was found that bacteria mixtures showed 98.3% remediation efficiency for Pb, 85.4% efficiency for Cd, and 5.6% efficiency for Cu [3]. Indeed, bacterial spp. isolated from rhizosphere are active decontaminators of polluted areas through their enzymatic activities [4]. Most of these enzymes are common among all the biological agents such as algae, bacteria, and cyanobacteria [5], which is a very important fact that supports the use of these organisms as bio-remediators. For instance, the activity of glutathione-S-transferases detoxifies a wide range of pollutants from the bacterial surroundings [5]. Similarly, the presence of enzymes such as cytochrome P450, hydrolases, dehydrogenases, laccases, proteases, dehalogenases, and lipases degrade different classes of pollutants [6]. Most of these enzymes were also reported in cyanobacteria such as Nostoc and Anabaena, which enabled these species to degrade pollutants like lindane and p-chlorobenzoic acid [5]. Bacteria exhibit a unique metabolic activity that allowed the degradation of organic pollutants, including PAHs, even under anaerobic conditions [4]. This is in contrast to aerobic conditions, where bacteria employ deoxygenases and dehyrogenases enzymes to cleave the aromatic ring. Bacteria break the aromatic ring under anaerobic environment by utilizing a reductive reaction and generating final electron acceptors other than oxygen [4]. The enzymes involved in hydrocarbon degradation may act synergistically and are comprised of alcohol dehydrogenase, alkane hydroxylase, lipases, etc. [7]. These enzymes may be recorded on contaminated sites where the bacterial groups of different strains are co-existing [7]. Although different microbial species possess different absorptive capacities, the capacity may be improved by changing the experimental conditions and pretreating microbes [8]. The bacterial species that have been identified as suitable candidates for heavy metal degradation include Bacillus subtilis, Cyanobacteria, Corynebacterium, and Rhodococcus erythropolis [2]. The efficiency of bacterial degradation, however, varies with respect to numerous environmental factors, such as the ambient temperature, soil acidity, bioavailability, and valence state of the metal ions [2]. This application is valid for a variety of contaminants, including heavy metals and hydrocarbons, and appears to be a sustainable and eco-friendly approach, in contrast to conventional physical and chemical methods, for cleaning up the polluted areas [1]. Heavy metals, in particular, are hard to remove and have been shown to be toxic to most microbes [8]. Thus, the development of bioremediating mechanisms, including detoxification of inorganic metals by microbes of unique metabolism and bioremediation capabilities, is much needed [8]. The higher efficacy of algae and some bacterial species in removing environmental contaminants has been shown by various researchers, which is strongly related to metabolic machinery and cellular components of these organisms [9]. Recenty, Altammar et al. (2024 [10]) demonstrated the bioremediating ability of algal–bacterial consortia that allowed the removal of both heavy metals and hydrocarbons from Lake Al-Asfar. But the question remains, if they are able to bioremediate the Lake, what limits their bioremediating potential? Part of the answer is that they are being fed on by grazers, including Protozoa, parasitic worms, and some dinoflagellates. This leads to the next question, which is why these organisms are present in the lake in the middle of the desert. This dictates having a deep understanding of Lake Al-Asfar’s nature and its water resources.
Water drainage from agricultural lands carries enormous amounts of pesticides, fertilizers, which, along with industrial effluents, increase the level of heavy metal contamination in this lake [11]. Also the urban and industrial development in the Al-Ahsa region has increased pollution levels in the lake [11]. A detailed investigation on the level of pollutants in the lake for a year suggested seasonal variation in the accumulation of heavy metals [12]. For instance, the maximum pollution of the lake with heavy metals was recorded during winter and autumn, whereas moderate pollution was noticed during summer and [12]. However, information related to biotic components of the lake with respect to heavy metals pollution is scarce and rather limited [12]. A proper estimation for the chemical and biological pollutants in the lake may be helpful to predict the survival of wildlife in the coming years [12]. Indeed, information regarding pathogenic Protozoa and animal parasites shows that they are associated with pollution and unsanitary conditions in which they multiply and are a potent threat to human health [13]. With regard to other co-inhabitants of the lake, many protists and parasites are present, but their identity was not studied before. It is important to shed light on those organisms, as some of them graze and prey on algal–bacterial communities, thus limiting those beneficial bio-remediatory communities on one hand. Others are parasitic and cause diseases in human and animals when conditions for their multiplication and transmission are created [13]. On the other hand, those animal forms can be beneficial in their part in bioremediation. Protists such as Protozoa and parasites are single-celled organisms that show a high level of flexibility to environmental conditions where they live. They perform diverse functions in the ecosystems that include nutrient cycling and predation, hence, controlling the population of other microorganisms. Amoebas, Ciliates, and flagellates are all considered Protozoa, which consume bacteria, algae, and particles of organic matter besides regulating microbial populations and enhancing cycling of nutrients in the ecosystems. While some of the Protozoa have non-parasitic lifestyles and do not cause harm to their hosts [14], Leishmania, Trypanosoma sp., and Plasmodium sp. are Protozoan parasites. Though their role or involvement in bioremediation has not been confirmed, there are recent suggestions that changes in pollution and the ecosystem could influence their transmission. In reaction to pollution, some changes occur in the host’s immune system, which makes it vulnerable to these pathogens either through a weakening of the immunity or through modification of the host environment that favors vectors. For example, Leishmania transmission is linked with deforestation or perhaps urbanization, which may be related to the level of pollution arising from industries or farming activities [14]. Just like water pollutants that harm the quality of water encourage the unnatural growth of waterborne parasites, such as Cryptosporidium and Giardia, that graph in polluted and eutrophic water systems. Highly pathogenic animals, including Ascaris and Fasciola (flukes) worms that have many microscopic developmental stages, can also be witnessed in wastewater sinks.
With regard to Lake Al-Asfar, [10] addressed the chemical pollution and the use of algal–bacterial consortia to bioremediate that pollution. They characterized the algal identities of these consortia. However, their bacterial partners were not identified. Here in the present study, one of our objectives is to characterize the identities of bacterial strains involved in the bioremediating consortia using a polyphasic description approach and to show their beneficial and harmful aspects. In addition, the identity of the most dominant grazing fauna found in the lake and their possible ecological impact, especially on bioremediating organisms as well as their potential health risks, are also addressed.
The overall goal is to provide a holistic notion of the ecosystem dynamics in that lake and facilitate its restoration into a recreational, hygienic, and economically valuable natural facility.
2. Materials and Methods
The research was conducted at the laboratory of the Biological Sciences Department, College of Science, King Faisal University, located in the AI Ahsa region of the East Governorate, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
As described in [10], the microbial consortia water samples were carefully collected using sterile containers from the banks of Al-Asfar Lake, which is located in the southern part of the Eastern region of Saudi Arabia, specifically in east of Al-Hassa 25″05′ and 25″40′ northern latitude and 49″55′ eastern longitude. The samples were taken from six different near-shore locations where wind is expected to blow the flora/fauna developed in the middle of the lake towards the shore. Also, the near-shore location is usually rich in submerged macrophytes, which will add to the nutrient loading and, consequently, are a suitable habitat for the growth of aquatic fauna/flora [15].
2.1. The Isolation and Purification of Bacterial Strains Associated with Algal Samples from Lake Al-Asfar
The water samples were spun at 6000 rpm. Then, the pellets containing algal–bacterial consortia were spread on solidified growth medium, and the bacterial colonies were picked up and spread on nutrient agar plates (HIMEDIA) and incubated at 30 °C for 24 h [16]. Pure colonies of bacteria samples were inoculated on 70% broth media (HIMEDIA) for preservation. All the pure bacterial species were inoculated into 30% Glycerol (v/v) as well, incubated at 30 °C for 24 h, and then were kept in a fridge at −4 °C to be used in future experiments.
2.2. Staining Investigations
Subsequent staining investigations were carried out to reveal the morphological characteristics of the isolated bacteria. These investigations included Gram staining, which revealed the cell wall composition; spore staining, which revealed whether the bacteria had endospores; and capsule staining, which highlighted the existence of protective extracellular structures. Through using these staining methods, a deeper insight into the features of the isolated bacterial strains in Lake Al-Asfar can be obtained. Together, these methods allowed for a thorough examination of the rich microbiological life in the lake.
2.2.1. Gram Staining
This investigation was carried out using the following steps:
- Crystal Violet: Crystal violet stain is used extensively, enabling cells to take up the dye and stain the bacterial smear.
- Iodine Treatment: Iodine is used as a mordant, combining with the crystal violet to produce a combination that the bacteria are unable to break through.
- Alcohol Decolorization: Differential decolorization occurs after rinsing the slide with alcohol. Gram-negative bacteria are unable to hold the crystal violet–iodine combination, whereas Gram-positive bacteria are able to do so.
- Counterstain with Safranin: Safranin stain is applied to the slide, giving the bleached Gram-negative bacteria a distinct hue.
2.2.2. Spore Stain
This investigation was performed using the following steps:
- Application of Malachite Green: Malachite green, which is used to stain bacteria, seeps deep into the endospores, filling the smear.
- Heat Application: Malachite green is allowed to more easily penetrate the spores by slightly heating the slide.
- Water Rinse: The extra stain on the slide is washed away with water.
- Safranin Counterstain: The vegetative cells are stained a crimson colour when safranin is added to the slide.
2.2.3. Capsule Stain
- Negative Staining: A negative stain, such as India ink, was used with the bacterial smear to stain the background but not the bacterial capsule.
- Slide Air-Drying: The bacterial cells and unstained capsules are set by letting the slide air-dry.
- Crystal Violet Treatment: To better see the germs, a crystal violet dye is used.
2.3. Vitek 2 for Bacterial Samples Characterisation
Working Method of the VITEK 2 Device
The information gained from previous Gram-staining procedures is complemented with the following Vitek analysis for bacterial samples characterization. The bacterial identities were investigated using the VITEK 2® COMPACT (BioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France), College of Medicine, King Faisal University. This analysis is mostly based on their metabolic profiling and integrating this with the structure and morphological information. The metabolic profiling of the organisms is supported by an extensive database to allow comparisons and minimize characterization errors. The protocol used, according to the manufacturer’s instructions, is summarized in the following section.
- Sample Preparation:
An isolated bacterial culture is then obtained from a single colony on an agar using an inoculation loop; an inoculum is prepared using a sterile saline solution. Standardization of bacterial suspension is done thus to allow comparison across the test plates; turbidity is normally adjusted to 0.5 McFarland standard using a densitometer.
- 2.
- Inoculation of the ID Card:
Microbial culture in the form of a bacterial suspension is pipetted into wells in a VITEK 2 identification or ID card that is designed with several wells that are already filled with specific biochemical reagents. Each well thus investigates a specific metabolic attribute or enzymic function of the bacteria.
- 3.
- Automating in the VITEK 2 System:
The indicated ID card is then introduced into the VITEK 2 system. The card is sealed immediately by the system and transported to the incubator.
- 4.
- Incubation and Monitoring:
The ID card is then allowed to incubate in the machine at 35–37 degrees Celsius for several hours. In incubation the target bacterial cells come in contact with the substrates in the wells, and biochemical reactions take place. These reactions lead to changes in color, an increase in turbidity, or any other visible changes in the wells.
- 5.
- Photometric Detection:
During the reaction the device employs a photometer to sense variations in the optical properties of the wells. This may involve colorimetric variations or variations in light transmission occasioned by bacterial growth.
- 6.
- Data Interpretation:
The VITEK 2 software Systems version 0.02.4 automatically tests the pattern of reactions and overlays the profile against the database that contains information on thousands of bacterial species. As a result of the comparison of the current mass spectrum with a database-dependent standard, the system offers a bacterial identification and the level of confidence in this identification.
- 7.
- Output and Reporting:
After the analysis, the VITEK 2 releases the detected bacterial species’ report. If the AST is done, the system also gives a profile of antibiotic resistance or sensitivity for the bacteria tested.
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Bacterial Sample
Bacterial colonies were fixed using 3% glutaraldehyde for 4 h at 25 °C. Then, the cells were washed three successive times using 0.1 M phosphate buffer for 15 min each time. Following that, cells were dehydrated in an ethanol series in the following order: 35%, 50%, 70%, 80%, and 95%, three changes at 100% for 15 min per wash, which was followed by a final wash with acetone for 5 min before drying in carbon dioxide and sputtering with gold. Examination of bacterial cells was performed using a scanning electron microscope (Joel JSM-5510LV, JEOL USA, Inc., Peabody, MA, USA) connected to a computer [16].
2.5. Identification of Protozoa and Parasites from Lake Al-Asfar by Light Microscopy
Ten water samples were collected randomly from different localities of Al-Asfar Lake. The collected water samples were directly transferred to the Zoology Laboratory, Biological Sciences Department, King Faisal University. Samples were processed within 24–48 h of the collection. A drop of the precipitate was transferred to a clean slide, covered with a coverslip, and examined using an Ikon light microscope with a Swifit Cam camera (SC1803R-CK). All specimens were investigated.
3. Results
3.1. Gram Staining
One bacterium designated (B1) was found to be Gram-positive bacteria as it appeared purple, because of the entrainment of the crystal violet dye within their thick cell walls. While four other bacterial isolates (A1, A2, C1, C2) were all Gram-negative bacteria, which appear red in color, after the violet color was washed from them because of their thin peptidoglycan walls, the anti-dye enters the wall and colors it (Figure 1).
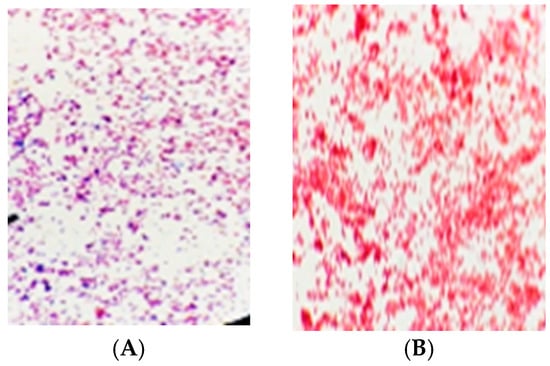
Figure 1.
Light micrographs showing morphological characterization using a light micrograph of Gram-negative (A) strain and Gram-positive strain (B) bacterial strains.
3.1.1. Spore Stain
All the bacteria appeared in the form of vegetative cells. None of the cells were endospore forming that had pinkish (A) to brownish red colour (B) (Figure 2).
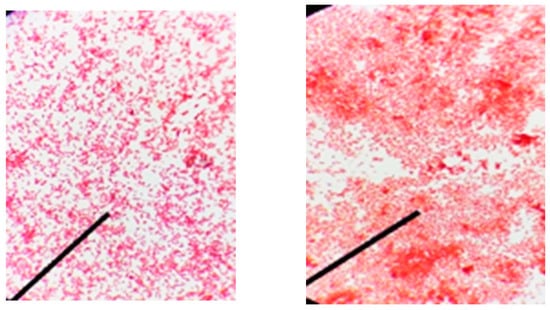
Figure 2.
Light micrographs showing vegetative cells with no endospores after spore staining.
3.1.2. Capsule Stain
All bacteria cells appeared with a dark violet color and a colorless background, indicating the presence of a capsule. The bacterial capsule acts as a protective layer and sometimes as a virulence factor and gives pathogenicity to the bacterial cells (Figure 3) whether A-Gram positive or B-Gram negative bacteria.
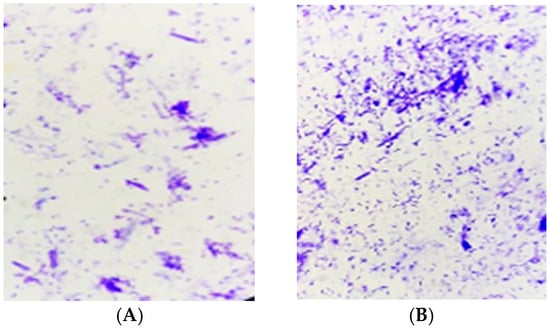
Figure 3.
Morphological characterization and light micrograph of capsule stain for bacterial strains. (A) Gram-positive bacteria after capsule staining, (B) Gram-negative bacteria after capsule staining.
3.2. Investigating Bacterial Identity Using VITEK Technology
The VITEK investigation on bacterial identities of the bacterial isolates revealed only three with an excellent percentage of similarity/discrimination as compared to the database of the device. The three isolated are listed in Table 1 together with their characteristics. Two belonged to Alphaproteobacteria, and one belonged to Firmicutes (Table 1).

Table 1.
The identification of bacterial isolates that are found in association with algal partners in the bioremediatory communities using VITEK technology.
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
The scanning electromicrographs emphasised the VITEK outcome where the rod-shaped morphology and size were confirmed for both Sphingomas paucimobilis (Figure 4A) and Rhizobium radiobacter (Figure 4C), whereas the coccoid morphology was confirmed for Enterococcus faecalis (Figure 4B).
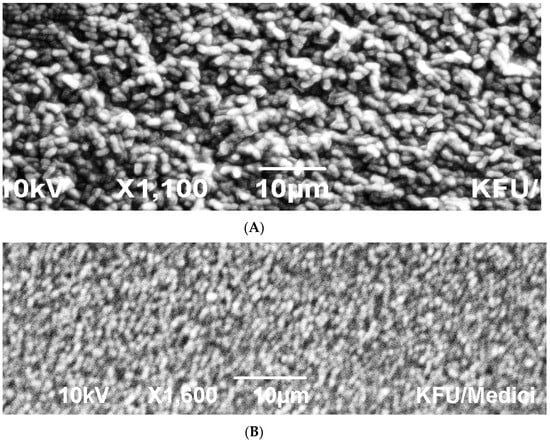
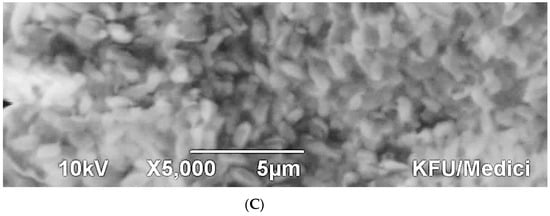
Figure 4.
SEM micrographs showing the three (A–C) different bacterial isolates. (A) Scanning electromicrographs showing cells of Sphingomas paucimobilis (scale bar 10 μm); (B) Scanning electromicrographs showing cells of Enterococcus faecalis (scale bar 10 μm); (C) Scanning electromicrographs showing cells of Rhizobium radiobacter Scale bar 5 μm).
3.4. Protozoa and Parasites Identified by Light Microscopy
Several protists including Protozoa and parasites were identified using light microscopy. The most common types encountered are listed in Table 2. Entamoeba histolytica and Ascaris lumbricoides frequently occurred in all samples (Figure 5).

Table 2.
The most common protists and parasites in Lake Al-Asfar, their classification, and their characteristics.
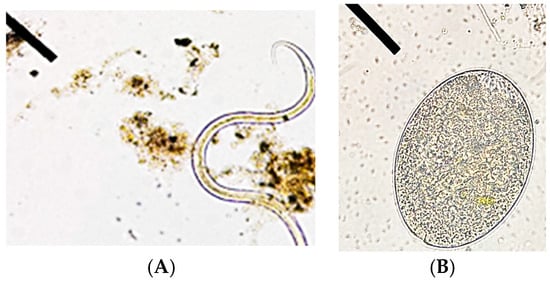
Figure 5.
Microscopic images of parasites mainly (A) Ascaris lumbricoides and (B) Entamoeba histolytica.
4. Discussion
Microorganisms eradicate some heavy metals by utilizing the metal ions for their own growth and development while producing other common compounds like carbon dioxide, methane, and water [1]. This conversion, however, occurs with the help of enzyme-catalyzed reactions [1]. The most frequently used microorganism, i.e., bacteria, have the potential to decontaminate polluted sites rapidly and in an eco-friendly manner [1]. Interestingly, bacteria can perform degradation reactions in all types of habitats such as soil, sludge, water, superficial linings, and subsurface materials [2]. Secretions due to bacterial metabolism are capable of dissolving heavy metals [2]. The main approaches involved in decontamination of heavy metals-polluted sites are biosorption, precipitation, and enzymatic reactions [2]. Generally, several methods function together and involve electrostatic interactions, surface complex formation, and ion exchange [8]. Metal ions are either degraded or transformed into relatively less toxic or inert [2]. Here, we identified three types of bacteria that are partners in the algae–bacteria bioremediatory consortia. The algal types were identified previously [10], but the bacterial members of the consortia were unknown. We used a polyphasic approach that integrates the morphological, metabolic, and structure to investigate their identity. The present study revealed their identity to be Sphingomas paucimobilis, Rhizobium radiobacter, and Enterococcus faecalis. The diversity of bacterial genera involved in bioremediation shows both metabolic versatility of these genera. Indeed, [2] showed that Bacillus subtilis, Cyanobacteria, Corynebacterium, and Rhodococcus erythropolis are good bio-remediators of heavy metals because they interact on the surface with the metal followed by the intracellular sequestration of these metals. These bacteria use extracellular biosorption strategy to attract metal ions. Also, enzymes similar to glutathione S transferase are involved in degradation; these enzyme act as catalysts to transform these metals into forms that are less toxic such as nanoforms [17]. In the case of hydrocarbons removal, bacteria use deoxygenases and hydrolases, especially under anaerobic conditions where they transfer hydrogen to other places and reduce the hydrocarbon to break it down—for instance, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) as reported previously [4,18]. However, and despite the good impact of these bacteria in ibioremediation, other bad and rather negative aspects are associated with these bacteria. In order to give a holistic idea of these bacteria, their metabolic and pathogenic activities are discussed. With regard to Enterococcus faecalis, it is a well-known pathogen that can cause infection of the both the digestive system and the urinary tract. Their pathogenicity is mainly attributed to their enzymes; for example, they produce gelatinase [19], an enzyme that degenerates gelatin and other proteins, which assist in tissue invasion and infection. Another is superoxide dismutase, which enables the bacterium to scavenge reactive oxygen species, thereby promoting tolerance to oxidative stress. These enzymes, together with the metabolic versatility, enable E. faecalis to form infections. Its presence in Lake Al-Asfar certainly holds health risks. Although Enterococcus faecalis is a pathogen, new studies have considered it as a possible bioremediation agent, especially effective in remediating heavy metal contamination. Some subtypes of E. faecalis have proven to withstand and absorb poisonous ions such as cadmium, lead, and mercury. By producing biofilm layers and secreting metal-binding proteins, it can decrease the toxicity of the metal ions-contaminated environment. It also assists in the stabilization of basin metals to lessen their toxicity and their ability to move, which is important in decontaminating polluted environments. With regard to their effects on hydrocarbons, it could be noted that Enterococcus faecalis was active in removing azo dyes resulting from the textile industry [20].
With regard to Rhizobium radiobacter, a nitrogen fixer commonly associated with plant roots, it possesses several enzymes instrumental in plant host recognition and interaction as well as survival in the environment. With regard to bioremediation, Rhizobium radiobacter was identified to possess the ability to remove contaminants from the environment, especially the heavy metals. Its ability to form biofilm and establish binding with metals thereby allows the bacterium to stabilize potentially hazardous elements such as cadmium or arsenic in the soil. While it is not as well investigated for its part in hydrocarbon degradation, its association with soil and its metabolic versatility points to it as a candidate to metabolize organic pollutants. Even though Rhizobium radiobacter is not an inherent hydrocarbon degrader, the ubiquity of this bacterium together with its physiological adaptability indicates a likely contribution towards the process of hydrocarbon bioremediation. Nitrogen is a key nutrient required by the degrading bacteria, and being a nitrogen fixer together with its associations with plants it can also improve rooting phytoremediation of hydrocarbons mainly in farmland soils that have been polluted by hydrocarbons [21]. Being found in the water of Lake Al-Asfar is no surprise, as the lake is a major sink for wastewater.
With regard to Sphingomonas paucimobilis, this bacterium is a Gram-negative rod that can infect immunosuppressed or immunocompetent individuals in the community or hospital [22]. Nonetheless, it possesses some of the highly active enzymes in the degradation of organic compounds. The enzyme dioxygenase is a very important enzyme for the breakdown of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which are complex substances that are challenging to metabolize. Other enzymes such as oxidases and hydrolases also contribute to its ability to metabolize a great number of substances. These enzymes allow S. paucimobilis to adapt to contaminated environments where it can utilize contaminants as the source of carbon and energy for the bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which are often present in contaminated soils and water or as a result of industrial waste discharge and fossil fuel burning. These enzymes, such as dioxygenases, oxidize these toxic compounds into less toxic products, allowing S. paucimobilis to play a significant role in the bioremediate of hydrocarbon-contaminated environments. Sphingomonas paucimobilis is known to associate with environments that contain depolluted oil and other industrial products and waste materials, including PAHs. It also has the capability to fix and immobilize heavy metals, so that these metals will be non-mobile and non-toxic. S. pacuimobilis is particularly effective due to its stability in extreme conditions such as polluted areas. Its ability to break down both hydrocarbons and heavy metals makes the bacterium a potential candidate for bioremediation. With regard to protists in wastewater, some parasites such as Cryptosporidium and Giardia are widely distributed Protozoan parasites that contaminate drinking water that has been affected by raw or treated sewage or animal wastes. They transmit diseases like a stomach flu among people. These waterborne Protozoans can withstand unfavorable conditions, and they are difficult to eliminate once they have entered water systems. Nonetheless, the role of Protozoa in the bioremediation process is gaining much attention nowadays. Though they are not involved in the direct degradation of pollutants, Protozoa are central to bioremediation processes. Protozoa exert predation on bacterial populations [23], which facilitates the growth of pollutant-degrading bacteria such as those related to heavy metals or hydrocarbons. In this way, this bacterial grazing effect sustains a population of microbes that unceasingly degrade pollutants from environments that are polluted. Moreover, with regard to the use of VITEK technology as a tool in bacterial identification, Al mousa et al. (2024) [24] successfully detected the presence of bacterial communities through metabolic profiling using VITEK technology and even revealed that they are capable of xenobiotic removal.
Indeed, there is a huge lack of studies on the direct role of Protozoa and parasites in heavy metal detoxification, or the fact that they can affect the transport and solubility of metals only. Some protection from metals is seen where the Protozoa alter their cell membranes or produce compounds that bind with the metals. This resistance can alter the microbial population in a way that only metal-tolerant bacteria would survive this, and these bacteria are usually able to demetallize metals. Furthermore, parasites are found to be more frequent in polluted environments, and some heavy metals in water-polluted environments have been deciphered to be related to greater frequency rates of parasitic diseases in fishes and amphibians. Conversely, it is postulated that environmental pollution avails conditions that enhance parasitic diseases by probably lowering the susceptibility of host organisms or by the promotion of conditions in the vectors or intermediate host [25]. Mostafa et al. (2023) [26] reported that Protozoa seem to be an excellent indicator to assess both toxicity and pollution of wastewater in both freshwater and marine habitats. Pouline and Valtonin (2002) [27] reported that there are numerous factors that affect parasitic community structure and that the local conditions at a given time can determine whether the parasite is found or not, i.e., no definite repeated succession pattern can be identified for parasites as their presence is related to the nature of pollution and water quality in that locality at a specific time. Therefore, the predictability of helminth community structure in many cases is not feasible. Although the conditions of our lake are hardly found anywhere but some similarities in the Protozoa composition was found in two water bodies found in [28], where they found Balantidium coli, Cryptosporidium sp., Entamoeba spp., amoebas, Microsporidium sp., and Ascaris lumbricoides, among others in those water bodies. They reported that parasitic contamination remained persistent throughout the year and was found to be independent of physicochemical parameters such as temperature, pH, etc., and bacterial concentration of water. We speculate that in both cases of those lakes and Lake Al-Asfar, this similarity in parasite community composition is mostly related to water pollution. In agreement with this [29], the Protozoa community structure in the eutrophic Lake Donghu, which is a large shallow lake in Wuhan City, China, was studied. They sampled Protozoa communities on regular intervals and found that community structure is changed gradually, and these changes are linked to water quality rather than seasons, thereby indicating that Protozoal community structure is linked to water pollution. According to [30], parasites can be good bioremediating agents for toxic metals and even for organic pollutants [31].
With regard to Protozoa and parasites from Lake Al-Asfar, the analysis of Lake Al-Asfar samples revealed a variety of Protozoa and parasites, each with significant ecological and pathogenic implications. Among these, Entamoeba histolytica was identified, indicating a potential for fecal contamination. This Protozoan is notorious for causing amoebic dysentery, leading to severe gastrointestinal symptoms in infected individuals. Its cysts are resilient and can survive in freshwater environments, posing a risk to those who rely on the lake for drinking water or recreational activities [32]. Additionally, Balantidium coli suggests zoonotic transmission risks, particularly from areas with livestock. This ciliated Protozoan can cause balantidiasis, characterized by diarrhea and abdominal pain [33]. Its detection highlights the need for improved sanitation and waste management practices in surrounding agricultural regions [34]. Fertilized eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides were also found, indicating possible contamination from human waste. This soil-transmitted helminth can lead to ascariasis, resulting in malnutrition and other health issues. The presence of A. lumbricoides in the lake suggests ongoing sanitation challenges in the region [32]. Among other Protozoa, Amoeba, Paramecium, and Euglena were observed. Amoeba are known for their adaptability and ability to thrive in various freshwater conditions, playing a role in nutrient cycling [35]. Paramecium, with their cilia, contribute to the microbial balance and help in the decomposition process [36]. Euglena sp., the protist with shared animal and algal features is characterized by r unique flagellum, lack of cell walllongitudinal cell fission and its photosynthetic activity in aquatic environments in addition to its mixotrophic mode and can indicate water quality changes [37]. The relationships between these parasites and pollution are complex. Increased nutrient levels from agricultural runoff can support harmful algal blooms, which may create environments conducive to the survival and spread of Protozoa and parasites [38]. Additionally, certain Protozoa and nematodes can accumulate heavy metals, which could enhance their pathogenic effects [39]. Furthermore, the presence of dinoflagellates, which are diverse have shared characteristics between animals and algae and most of them are toxin producers, adds further complexity to the ecosystem biotic structure and the health risks as well. These organisms can influence nutrient dynamics and may serve as indicators of pollution levels [40]. For instance, the detection of Gymnodinium sp. points to changing water quality conditions. Some species are toxin-producers and their proliferation can lead to harmful blooms that affect co-inhabitants and water quality
Monitoring these organisms is critical for understanding their impact on aquatic ecosystems and human health. Efforts in bioremediation targeting heavy metals and hydrocarbons may inadvertently alter these dynamics, making it essential to consider how these organisms interact with pollutants when developing management strategies. The findings from Lake Al-Asfar illustrate the pressing need for comprehensive monitoring and management of both environmental hazards for public safety. Moreover, addressing the underlying pollution sources and improving water quality are crucial steps in mitigating the risks posed by these pathogens.
5. Conclusions
Many microorganisms in Lake Al-Asfar play important ecological roles that impact the ecosystem, especially in wastewater basins. In this study, three bacterial strains, which are members of bioremediating algal bacteria consortia, were identified using polyphasic approaches, including advanced VITEK technology. Although reported as active bio-remediators like Rhizobium, some are pathogenic like E. faecalis. The co-inhabitants of these consortia are some Protozoa and parasites that can be beneficial with regard to bioremediating heavy metals and hydrocarbons like Euglena sp., but some can also prey on beneficial bioremediating microorganisms like Paramedcium sp. Others can even be pathogenic like Entamoeba and Balantidium and cause diseases. We recommend the selection of the non-harmful bioremediating consortia, their in vitro proliferation under optimal conditions, and their use in bioremediation while eradicating the pathogenic flora and fauna. This wise strategy can lead to economic and sustainable restoration using an eco-friendly approach.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.E.S.; Methodology, M.F.A. and D.A.; Validation, F.A.T., N.E.S., and M.F.A.; Formal analysis, F.A.T. and G.A.; Investigation, F.A.T., M.F.A., N.E.S., D.A. and G.A.; Resources, N.E.S. and M.F.A.; Data curation, F.A.T., N.E.S., M.F.A., G.A. and D.A.; Writing—original draft, F.A.T., N.E.S., D.A. and G.A.; Rewriting and response to reviewers: N.E.S. Supervision, N.E.S. and M.F.A.; Funding acquisition, M.F.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to express their gratitude to The Deanship for Scientific Research, King Faisal University, for financial support and funding the research, grant number: KFU242199.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are reported in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to King Faisal University, Alhufuf, Al-Ahsa, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, post code: 31982, po box: 400 for both financial and moral support. The authors are thankful for Hany AlFarhan, College of Medicine, King Faisal University for conducting the investigation on the Vitek System.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sui, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ji, H. Remediation of Petroleum-Contaminated Soils with Microbial and Microbial Combined Methods: Advances, Mechanisms, and Challenges. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Bharadvaja, N. Microbial remediation of heavy metals. In Microbial Bioremediation & Biodegradation; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 49–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ojuederie, O.B.; Babalola, O.O. Microbial and plant-assisted bioremediation of heavy metal polluted environments: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1504. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/14/12/1504/pdf (accessed on 30 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Shaikh, S.; Jain, K.R.; Desai, C.; Madamwar, D. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Sources, toxicity, and remediation approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 562813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, B.; Ravishankar, G.A. Phytoremediation—A novel and promising approach for environmental clean-up. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2004, 24, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, S.; Poudel, D.K.; Marahatha, R.; Dawadi, S.; Khadayat, K.; Phuyal, S.; Shrestha, S.; Gaire, S.; Basnet, K.; Khadka, U.; et al. Microbial enzymes used in bioremediation. J. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, P.; Parthipan, P.; Huang, M.; Muthukumar, B.; Cheng, L.; Govarthanan, M.; Rajasekar, A. Enhanced biodegradation of hydrophobic organic pollutants by the bacterial consortium: Impact of enzymes and biosurfactants. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igiri, B.E.; Okoduwa, S.I.; Idoko, G.O.; Akabuogu, E.P.; Adeyi, A.O.; Ejiogu, I.K. Toxicity and bioremediation of heavy metals contaminated ecosystem from tannery wastewater: A review. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 2568038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekroun, K.B.; Sánchez, E.; Baghour, M. The role of algae in bioremediation of organic pollutants. Int. Res. J. Public Environ. Health 2014, 1, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Altammar, F.; El Semary, N.; Aldayel, M. The Use of Some Species of Bacteria and Algae in the Bioremediation of Pollution Caused by Hydrocarbons and Some Heavy Metals in Al Asfar Lake Water. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.H.; El Mahmoudi, A.S.; Al Naeem, A.A. Assessment of the Heavy Metals in Al Asfar Lake, Al-Hassa, Saudi Arabia. Water Environ. Res. 2016, 88, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, G.H.; Fathi, A.A. Limnological studies on the wetland Lake, Al-Asfar, with special references to heavy metal accumulation by fish. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 515. [Google Scholar]
- Kebede, A.; Abebe, B.; Zewdie, T. Study on Prevalence of Ectoparasites of Poultry in and Around Jimma Town. Eur. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Patz, J.A.; Graczyk, T.K.; Geller, N.; Vittor, A.Y. Effects of environmental change on emerging parasitic diseases. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1395–1405. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11113264/ (accessed on 30 December 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Semary, N.A. Anabaena and Associated Bacteria: Molecular Approaches to Studying Microbial Community Structure and Taxonomy. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, A.; Aldayel, M. Metabolic diversity of the diesel oil-degrading bacterium Achromobacter pulmonis HDK3 obtained from Eastern region of Saudi Arabia. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2018, 20, 778–785. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, N.S.; Bakir, E.M.; Mohamed, M.E.; El Semary, N.A. Cyanobacteria as nanogold factories II: Chemical reactivity and anti-myocardial infraction properties of customized gold nanoparticles biosynthesized by Cyanothece sp. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Chandran, P. Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contaminants: An Overview. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 941810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, S.J.; Lee, I.H. Extracellular Gelatinase of Enterococcus faecalis Destroys a Defense System in Insect Hemolymph and Human Serum. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Peng, F.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Song, H. Efficient removal of azo dyes by Enterococcus faecalis R1107 and its application in simulated textile effluent treatment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Luo, Y. Rhizobia and their bio-partners as novel drivers for functional remediation in contaminated soils. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Beaino, M.; Fares, J.; Malek, A.; Hachem, R. Sphingomonas paucimobilis-related bone and soft-tissue infections: A systematic review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 77, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Zhu, J.; Rensing, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.-R. Recent advances in exploring the heavy metal(loid) resistant microbiome. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 94–109. [Google Scholar]
- Al Mousa, A.; Aldayel, M.; Genena, M.M.; El-Moaty, Z.A.; Khalifa, A. Bacterial Diversity in Al-Asfar Lake, Al Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 18, 1358–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcogliese, D.J. Parasites of the superorganism: Are they indicators of ecosystem health? Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, O.M.S.; Abd El-Hady, N.A.A.; Nigm, A.M.H. Protozoa as Bioindicator for the Water Quality Assessment (Mini Review). Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2023, 27, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R.; Valtonen, E.T. The predictability of helminth community structure in space: A comparison of fish populations from adjacent lakes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luqman, M.; Awan, M.U.F.; Muhammad, S.; Daud, S.; Yousafzai, A.; Arooj, F. Microbial pollution in inland recreational freshwaters of Quetta, Pakistan: An initial report. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.-G.; Wu, S.-G.; Shen, Y.-F. Effects of seasonal succession and water pollution on the protozoan community structure in an eutrophic lake. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sures, B.; Siddall, R.; Taraschewski, H. Parasites as accumulation indicators of heavy metal pollution. Parasitol. Today 1999, 15, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Yen, T.T.; Rijsdijk, L.; Sures, B.; Jan, H.A. Accumulation of persistent organic pollutants in parasites. Chemosphere 2014, 108, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotez, P.J. Neglected Infections of Poverty in the United States of America. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ijaz, M.; Ayyub, R.M.; Ghaffar, A.; Ghauri, H.N.; Aziz, M.U.; Ali, S.; Altaf, M.; Awais, M.; Naveed, M.; et al. Balantidium coli in domestic animals: An emerging protozoan pathogen of zoonotic significance. Acta Trop. 2020, 203, 105298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzik, J.M. The Role of Environmental Factors in the Transmission of Soil-Transmitted Helminths. Parasitology 2010, 137, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Garnier, J.; Pacheco, F.; Oger, P. Role of protozoa in nutrient cycling in aquatic ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 2015, 745, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Foissner, W. Protozoa as bioindicators: A case study from a moderately polluted river. J. Appl. Protozool. 1999, 25, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.A. Euglena: A Unique Model Organism for Studies in Biology and Biotechnology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, F.; Pizarro, G. Heavy metal accumulation in aquatic protozoa: Environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar]
- El-Tohamy, W.S.; Taher, M.E.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Hopcroft, R.R. Protozoan communities serve as a strong indicator of water quality in the Nile River. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).