The Recent Environmental History, Attempted Restoration and Future Prospects of a Challenged Lobelia Pond in Northeastern Belgium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
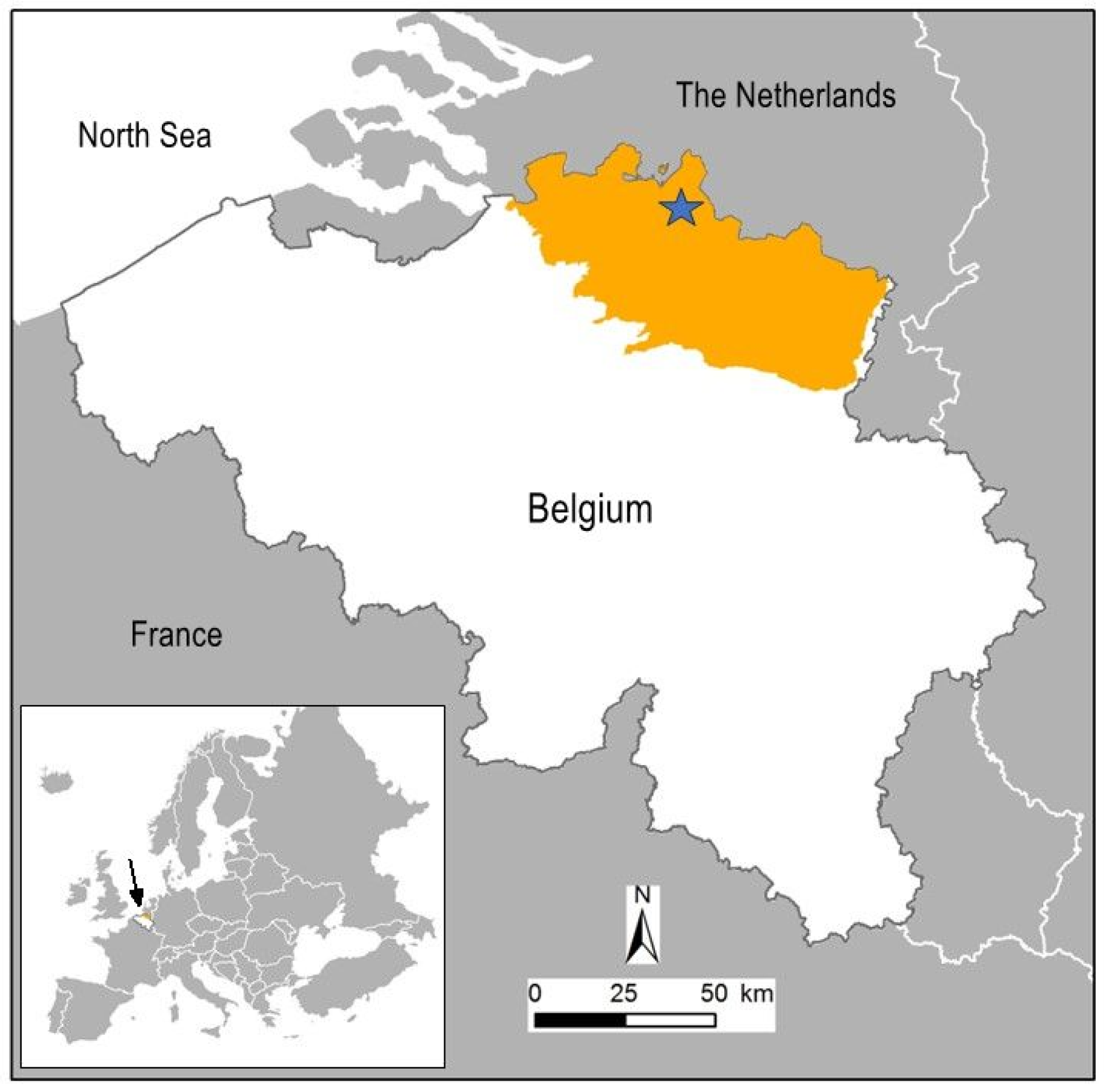
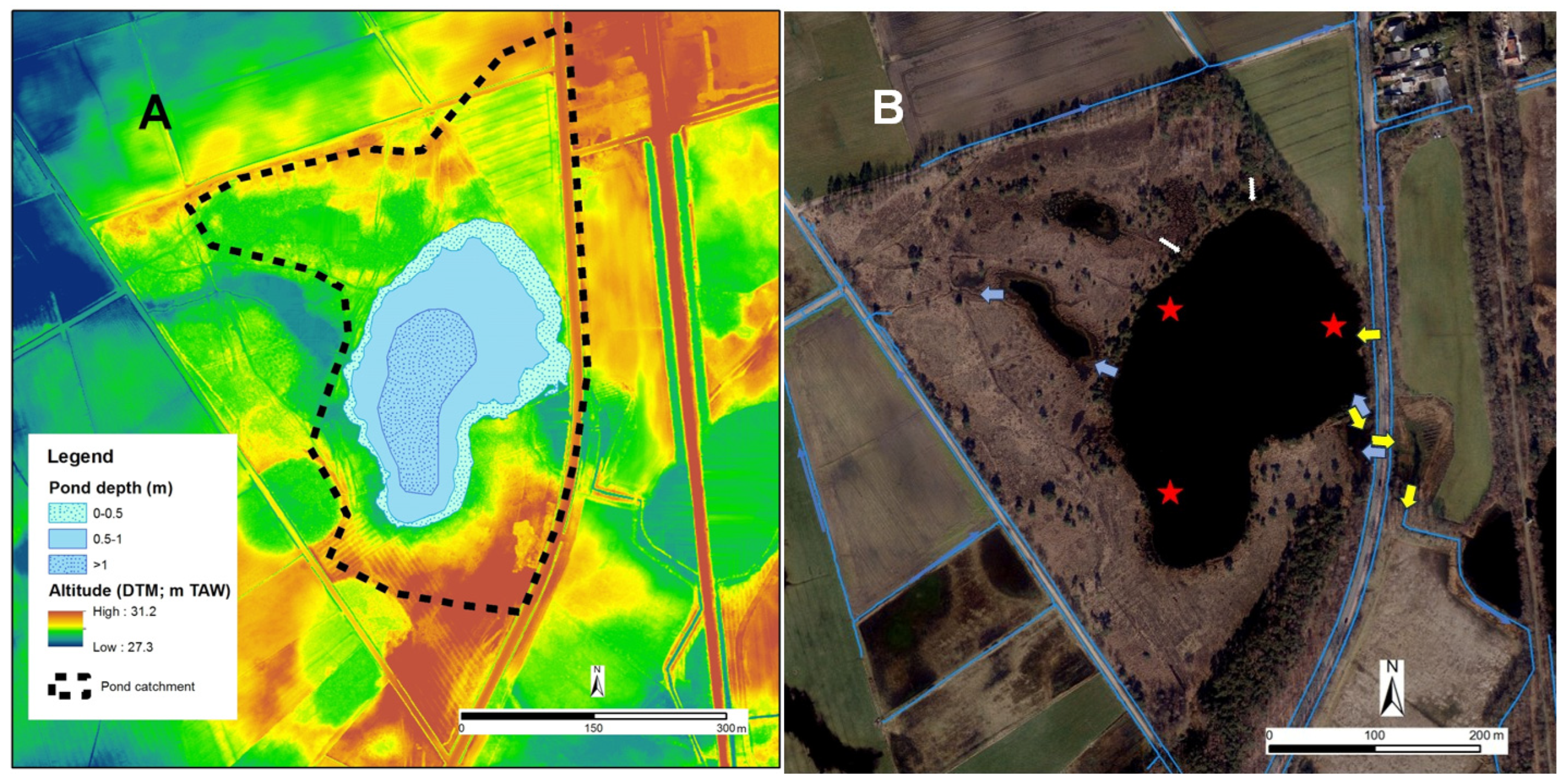
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Water Chemistry
2.3. Diatoms
2.4. Macrophytes
3. Results
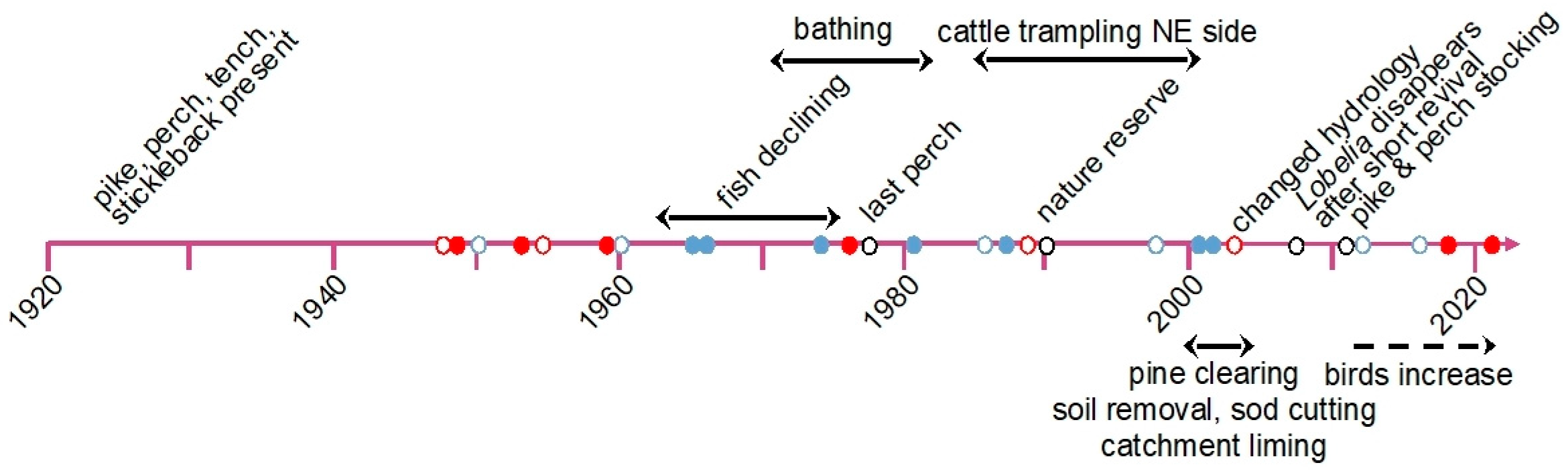
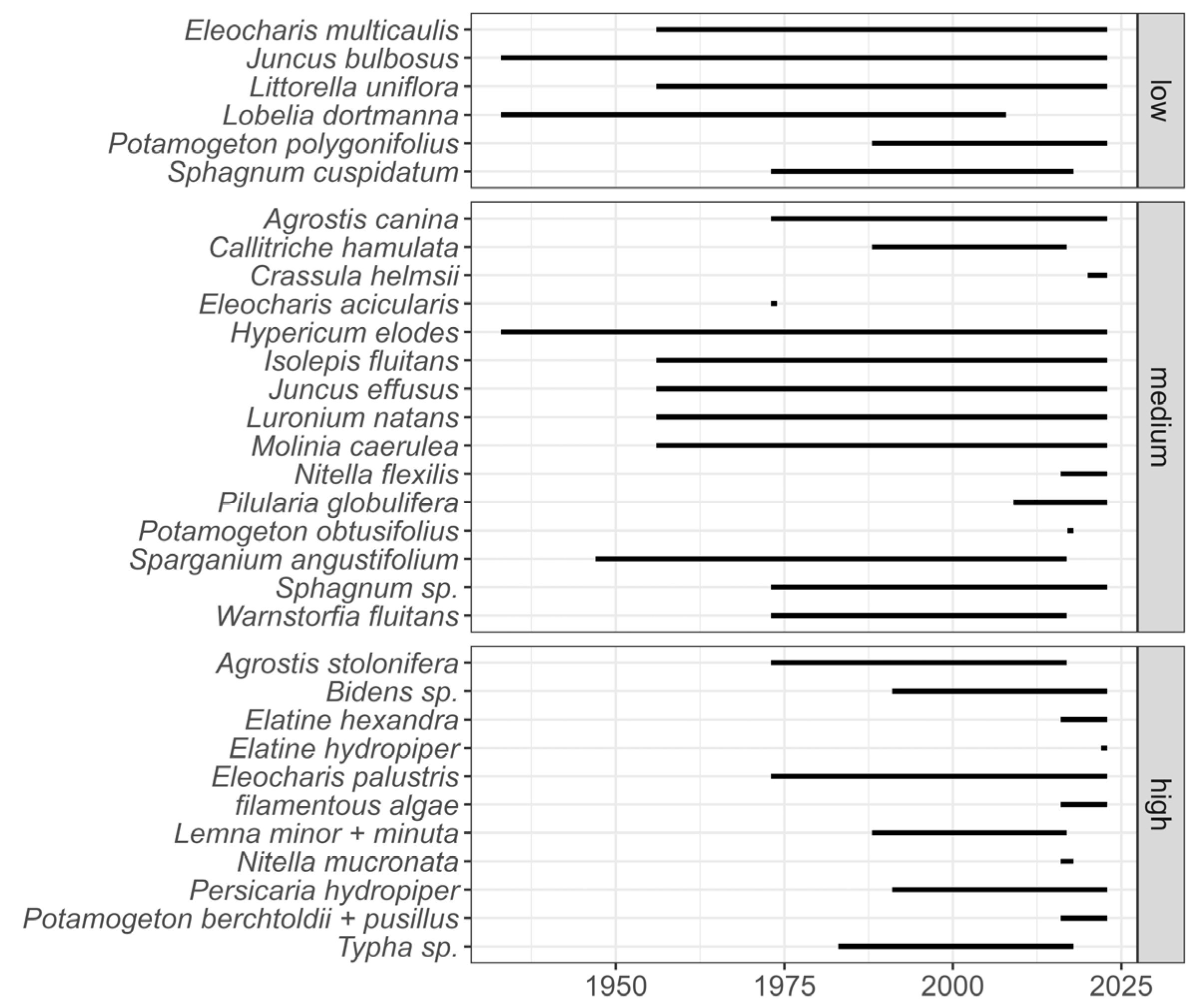
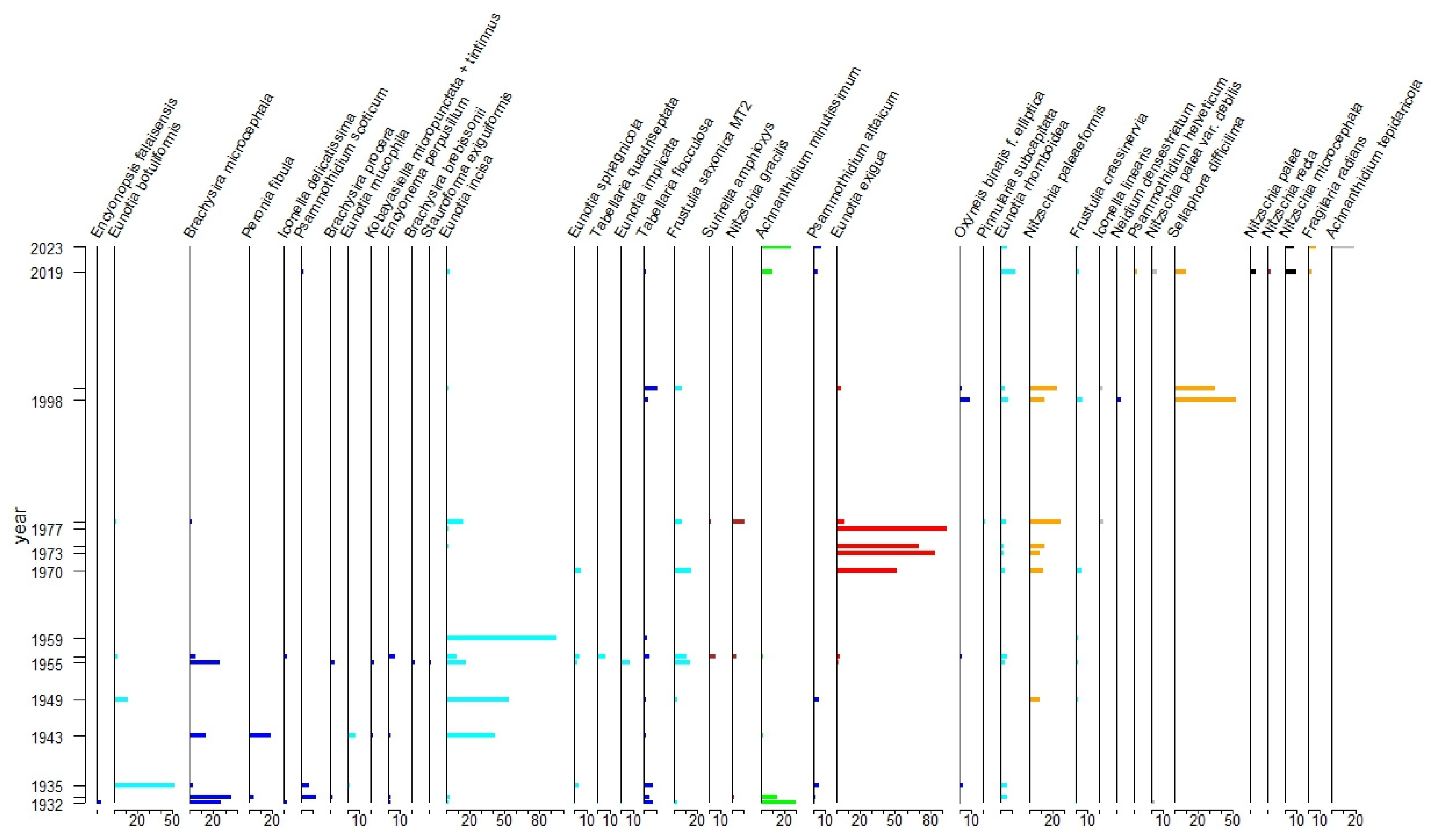
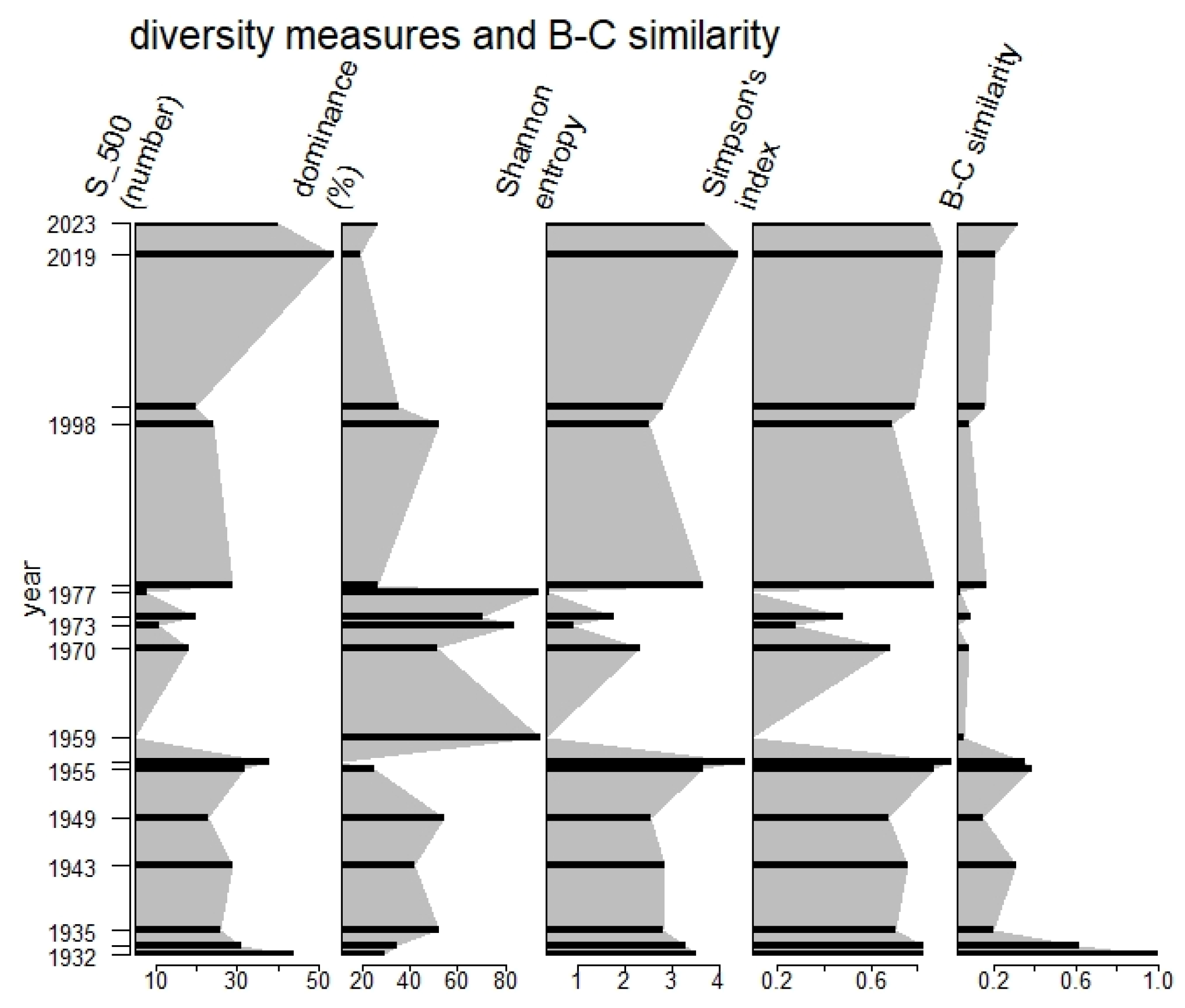
3.1. Up to the 1930s: The Baseline?
3.2. From the 1940s to the 1950s: Mild Acidification
3.3. The 1960s and 1970s: Mineral Acidity
3.4. Towards the 1980s: Mild Eutrophication
3.5. The Last Twenty Years: Alkalinisation and Further Nutrient Enrichment
3.6. Taxonomic Note
- Iconella densestriata (Hust.) L.Denys, comb. nov.;
- Registration: http://phycobank.org/104829 (accessed on 14 June 2024).
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Change and Biodiversity
4.2. Lobelia Decline
4.3. Restoration Goals, Management Measures and Obstacles
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Dam, H.; Beltman, B. Effects of climatic change on chemistry and vegetation of peatlands, with special reference to interaction with atmospheric deposition. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 1992, 2, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybowski, M. The principal threats to the standing water habitats in the continental biogeographical region of central Europe. J. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 12, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L.; Eckstein, R.L.; Relyea, R.A. Direct and indirect effects of climate change on distribution and community composition of macrophytes in lentic systems. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 1677–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eionet Portal. Article 17 Web Tool. Available online: https://nature-art17.eionet.europa.eu/article17/ (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Kirschke, S.; Häger, A.; Kirschke, D.; Völker, J. Agricultural nitrogen pollution of freshwater in Germany. The governance of sustaining a complex problem. Water 2019, 11, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, W.; Schulte-Uebbing, L.; Kros, H.; Voogd, J.C.; Louwagie, G. Spatially explicit boundaries for agricultural nitrogen inputs in the European Union to meet air and water quality targets. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.W. Setting ambitious goals for agriculture to meet environmental targets. One Earth 2021, 4, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoukens, H. (Ed.) De Stikstofcrisis in de Lage Landen Nader Ontleed: Richtlijnen voor een Duurzame Transitie; Die Keure: Brugge, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vlaamse Milieumaatschappij. Verzurende Depositie. Available online: https://www.vmm.be/lucht/stikstof/verzurende-depositie (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- De Schrijver, A.; Mertens, J.; Geudens, G.; Staelens, J.; Campforts, E.; Luyssaert, S.; De Temmerman, L.; De Keersmaeker, L.; De Neve, S.; Verheyen, K. Acidification of forested podzols in North Belgium during the period 1950–2000. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 361, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaamse Milieumaatschappij. Stikstofdepositie. Available online: https://www.vmm.be/lucht/stikstof/stikstofdepositie (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- van Dam, H.; Buskens, R.F.M. Ecology and management of moorland pools: Balancing acidification and eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 1993, 265, 225–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, E.; Bobbink, R.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Restoration of aquatic macrophyte vegetation in acidified and eutrophied softwater lakes: An overview. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 73, 405–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, J.; Brouwer, E.; Bobbink, R. Restoration of aquatic macrophyte vegetation in acidified and eutrophicated shallow soft water wetlands in the Netherlands. Hydrobiologia 2002, 478, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Uytvanck, J.; De Blust, G. (Eds.) Handboek voor Beheerders. Europese Natuurdoelstellingen op het Terrein. Deel 1. Habitats; Uitgeverij LannooCampus: Leuven, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Interpretation Manual of European Union Habitats—EUR28; European Commission DG Environment: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Scheers, K.; Packet, J.; Denys, L.; Smeekens, V.; De Saeger, S. BWK en Habitatkartering, een Praktische Handleiding. Deel 3: Veldsleutel voor het Typeren van Stilstaande Wateren in Vlaanderen. Rapporten van het Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek INBO.R.2016.11613720; Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Van Landuyt, W.; Hoste, I.; Vanhecke, L.; Van den Brempt, P.; Vercruysse, W.; De Beer, D. Atlas van de Flora van Vlaanderen en het Brussels Gewest; Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium; Nationale Plantentuin en Flo.Wer: Meise, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Delvosalle, L.; Demaret, F.; Lambinon, J. Plantes rares, disparues ou menacées de disparition en Belgique: L’appauvrissement de la flore indigène. Trav. Serv. Reserves Nat. Domaniales Conserv. Nat. 1969, 4, 1–129. [Google Scholar]
- Packet, J.; Louette, G.; De Becker, P.; Hendrick, L.; Gora, L.; Jacobs, L.; Leyssen, A.; Denys, L. Eerste natuurprojectovereenkomst in Vlaanderen: Ecologisch herstel van het Heuvelsven (Dilsen-Stokkem). Likona-Jaarboek 2014, 2013, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Paelinckx, D.; De Saeger, S.; Oosterlynck, P.; Vanden Borre, J.; Westra, T.; Denys, L.; Leyssen, A.; Provoost, S.; Thomaes, A.; Vandevoorde, B.; et al. Regionale Staat van Instandhouding voor de Habitattypen van de Habitatrichtlijn. Rapportageperiode 2013–2018; Rapporten van het Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek 2019.13; Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Saeger, S.; Dhaluin, P.; Erens, R.; Guelinckx, R.; Hennebel, D.; Jacobs, I.; Kumpen, M.; Van Oost, F.; Spanhove, T.; Leyssen, A.; et al. Biologische Waarderingskaart en Natura 2000 Habitatkaart, Uitgave 2023; Rapporten van het Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek INBO.R.2023.31; Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvreur, M.; Menschaert, J.; Sevenant, M.; Ronse, A.; Van Landuyt, W.; De Blust, G.; Antrop, M.; Hermy, M. Ecodistricten en ecoregio’s als instrument voor natuurstudie en milieubeleid. Natuur. Focus 2004, 3, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Penning, W.E.; Mjelde, M.; Dudley, B.; Hellsten, S.; Hanganu, J.; Kolada, A.; van den Berg, M.; Poikane, S.; Phillips, G.; Willby, N.; et al. Classifying aquatic macrophytes as indicators of eutrophication in European lakes. Aquat. Ecol. 2008, 42, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeye, D.; de Louw, P.; Stuurman, R. Ecohydrologische Systeemanalyse van het Turnhouts Vennengebied—Deel 1: Natuurlijke (Historische) Grondwatersituatie en Hydrogeologische Opbouw; Nederlands Instituut voor Toegepaste Wetenschappen TNO: Delft, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- de Louw, P.; Boeye, D.; Van der Aa, M.; Vanderhaeghe, F.; Stuurman, R. Ecohydrologische Systeemanalyse van het Turnhouts Vennengebied—Deel 2: Actuele en Gewenste Grond- en Oppervlaktewatersituatie; Report NITG 01-069-B; Nederlands Instituut voor Toegepaste Wetenschappen TNO: Delft, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickx, A.; Denys, L. Eindrapport Onderzoeksopdracht ‘Diatomeeënanalyse Turnhouts Vennengebied’; Universitair Centrum Antwerpen: Antwerpen, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhaeghe, F.; Brouwer, E.; van Kleef, H.; Van Den Broeck, S.; Vercoutere, B. Expertenadvies Prioritair Venherstel Turnhouts Vennengebied-West; Haskoning Belgium bvba: Mechelen, Belgium, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Large-Scale Habitat Restoration in “Turnhouts Vennengebied”. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/life/publicWebsite/project/LIFE06-NAT-B-000084/large-scale-habitat-restoration-in-turnhouts-vennengebied (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Biodiversity Information System for Europe. Vennen, Heiden en Moerassen Rond Turnhout. Available online: https://biodiversity.europa.eu/sites/natura2000/BE2100024 (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Vlaamse Regering. Besluit van de Vlaamse Regering tot Aanwijzing met Toepassing van de Habitatrichtlijn van de Speciale Beschermingszone BE2100024 ‘Vennen, Heiden en Moerassen Rond Turnhout’ en tot Definitieve Vaststelling voor die Zone en voor de met Toepassing van de Vogelrichtlijn Aangewezen Speciale Beschermingszone BE2101538 ‘Arendonk, Merksplas, Oud-Turnhout, Ravels en Turnhout’ van de Bijhorende Instandhoudingsdoelstellingen en Prioriteiten van 23/04/2014. Available online: https://natura2000.vlaanderen.be/sites/default/files/33_turnhouts_vennengebied_s-ihd-besluit_vr.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Agentschap voor Natuur en Bos Voortgangsdocumenten Turnhouts Vennengebied. Available online: https://voortgangsdocumenten.natuurenbos.be/turnhouts-vennengebied (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Birks, H.J.B. Contributions of Quaternary palaeoecology to nature conservation. J. Veg. Sci. 1996, 7, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.; Bunting, J. Applications of palaeoecology in conservation. Open Ecol. J. 2010, 3, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, R.K.; Finlayson, C.M.; Humphries, P.; Sims, N.C.; Hladyz, S. Anthropocene baselines: Assessing change and managing biodiversity in human-dominated aquatic ecosystems. BioScience 2015, 65, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, C.M.; Clarke, S.J.; Davidson, N.C.; Gell, P. Role of palaeoecology in describing the ecological character of wetlands. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 67, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, T.; Oosterlynck, P.; Van Calster, H.; Paelinckx, D.; Denys, L.; Leyssen, A.; Packet, J.; Onkelinx, T.; Louette, G.; Waterinckx, M.; et al. Monitoring Natura 2000—Habitats. Meetnet Habitatkwaliteit; Rapporten van het Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoeknstituut INBO.R.2014.1414229; Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Westra, T.; Oosterlynck, P.; Govaere, L.; Leyssen, A.; Denys, L.; Packet, J.; Scheers, K.; Vanderhaeghe, F.; Vanden Borre, J. Monitoring Scheme for Biotic Habitat Quality of Natura 2000 Habitat Types in Flanders, Belgium: Revision of the Monitoring Design; Rapporten van het Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek 2022(25); Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickman, M.D.; van Dam, H.; van Geel, B.; Klink, A.G.; van der Wijk, A. Acidification of a Dutch moorland pool—A palaeolimnological study. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1987, 109, 377–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, H.; van Geel, B.; van der Wijk, A.; Geelen, J.F.M.; van der Heijden, R.; Dickman, M.D. Palaeolimnological and documented evidence for alkalization and acidification of two moorland pools (The Netherlands). Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 1988, 55, 273–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, H.; Kooyman-van Blokland, H. Man-made changes in some Dutch moorland pools, as reflected by historical and recent data about diatoms and macrophytes. Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. 1978, 63, 587–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, L. Historical distribution of ‘Red List diatoms’ (Bacillariophyceae) in Flanders (Belgium). Syst. Geogr. Plants 2000, 70, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, L. Palaeolimnology without a core: 153 years of diatoms and cultural environmental change in a shallow lowland lake (Belgium). Fottea 2009, 9, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, H.; Mertens, A. A century of diatom monitoring in acidified and warmed Dutch moorland pools. Limnologica 2023, 99, 126059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koninlijk Meteorologisch Instituut. Klimaatstatistieken van de Belgische Gemeenten. Turnhout (nis 13040). Available online: https://www.meteo.be/nl/klimaat/klimaat-van-belgie/klimaat-in-uw-gemeente (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Craenen, H.; Van Ranst, E.; Tack, F.M.G.; Verloo, M.G. Calculation and mapping of critical loads of sulphur and nitrogen in Flanders, Belgium. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 254, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, W.; Hooybergs, H.; Deutsch, F. Emissie en Depositie van Stikstof in Vlaanderen Tijdens de Periode 2015–2021. Een Ruimtelijk-temporele Analyse. Vlaams Instituut voor Technologisch Onderzoek 2023/RMA/R/2843; Vlaams Instituut voor Technologisch Onderzoek: Mol, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sterckx, G.; Paelinckx, D.; Decleer, K.; De Saeger, S.; Provoost, S.; Denys, L.; Packet, J.; Wouters, J.; Demolder, H.; Thomaes, A.; et al. Habitattypen Bijlage 1 Habitatrichtlijn. In Europees Beschermde Natuur in Vlaanderen en het Belgisch deel van de Noordzee. Habitattypen, dier- en Plantensoorten; Mededelingen van het Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek INBO.M.2007.01; Decleer, K., Ed.; Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium, 2007; pp. 59–359. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1992, L206, 7–50.
- KBR. Ferraris Kaart—Kabinetskaart der Oostenrijkse Nederlanden en het Prinsbisdom Luik, 1771–1778. Available online: https://www.kbr.be/nl/projecten/kaart-van-ferraris/ (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Nationaal Geografisch Instituut. Carte du Dépôt de la Guerre 1872. Available online: http://www.cartesius.be/CartesiusPortal/ (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Nationaal Geografisch Instituut. Top25Map. Available online: https://topomapviewer.ngi.be/?l=nl&baselayer (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Mercator.net. Landgebruik—Vlaanderen—Toestand 2022. Available online: https://www.vlaanderen.be/datavindplaats/catalogus/landgebruik-vlaanderen-toestand-2022 (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Dorland, E.; Van Den Berg, L.J.L.; Brouwer, E.; Roelofs, J.G.M.; Bobbink, R. Catchment liming to restore degraded, acidified heathlands and moorland pools. Restor. Ecol. 2005, 13, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koninlijk Meteorologisch Instituut. Klimaattrends in Ukkel. Available online: https://www.meteo.be/nl/klimaat/klimaatverandering-in-belgie/klimaattrends-in-ukkel/neerslag/jaarlijks-totaal (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Van Oye, P.; Cornil, G. 1940 Desmidiées de la Campine Belge. Bull. Soc. R. Bot. Belg. 1940, 73, 7–90. [Google Scholar]
- Vangenechten, J.H.D. Fysiko-Chemisch Onderzoek van de Verzuring in Kempische Oppervlaktewaters en Invloed van de Zuurtegraad op de Ionenregeling van Waterwantsen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universiteit Antwerpen, Antwerpen, Belgium, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- De Blust, G. Venvegetaties in het Turnhoutse (Antw.). Master’s Thesis, Universiteit Gent, Gent, Belgium, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Caljon, A. Algologisch onderzoek van de vennen van Turnhout (Antw.). Biol. Jb. Dodonaea 1975, 43, 90–115. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhaeghe, F. Historisch-Ecologische Studie van de Vegetatie van Turnhoutse Vennen; Universiteit Gent: Gent, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pals, A. Ecology of Desmids in Flemish Softwater Lakes. Ph.D. Thesis, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Denys, L.; Moons, V.; Veraart, B. (Eds.) Ecologische Typologie en Onderzoek naar een Geïntegreerde Evaluatiemethode voor Stilstaande Wateren op Regionale Schaal: Hoekstenen voor Ontwikkeling, Herstel en Opvolging van Natuurwaarden. Eindverslag VLINA 97/02; Universiteit Antwerpen: Antwerpen, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Energie- en Milieu-Informatiesysteem voor Het Vlaamse Gewest. Compendium voor de Monsterneming, Meting en Analyse van Water (WAC). Available online: https://emis.vito.be/nl/erkende-laboratoria/water-gop/compendium-wac (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Reuss, J.O.; Johnson, D.W. The aquatic interface. In Acid Deposition and the Acidification of Soils and Waters; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pedersen, T.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D.; van den Brand, T. ggplot2: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics, R Package Version 3.5.1. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/tidyverse/ggplot2 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Denys, L. Calibration of littoral diatoms to water-chemistry variables in standing freshwaters of lower Belgium (Flanders): Inference models for sediment assemblages from historical samples. J. Paleolimnol. 2006, 35, 763–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Soecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.6-2-4. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- van Dam, H.; Mertens, A.; Sinkeldam, J. A coded checklist and ecological indicator values of freshwater diatoms from the Netherlands. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 1994, 28, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, H.; Mertens, A. Partial recovery of shallow acid-sensitive lakes from acidification. Environ. Sci. 2013, 22, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- van Dam, H.; Mertens, A. Monitoring Herstel Verzuring en Klimaatverandering Vennen 1978–2018: Temperatuur, Hydrologie, Chemie, Kiezelwieren. Rapport AWN 1702; Herman van Dam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Juggins, S. Rioja Package. Analysis of Quaternary Science Data. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/nsj3/rioja (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco for Windows 4.56; Plant Research International: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- De Blust, G. Littorelletea-vegetaties in de Antwerpse Noorderkempen. Biol. Jb. Dodonaea 1977, 45, 62–83. [Google Scholar]
- Aerts, J.; Vermeyen, A. Drijvende egelskop, Sparganium angustifolium Michaux, in het Zwart Water te Turnhout. Wielewaal 1982, 48, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- De Block, M.; Vermeulen, T.; Andries, T. Fen restoration in the northern part of Turnhout. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Ecological Restoration, Ghent, Belgium, 8–12 September 2008; Society for Ecological Restoration: Ghent, Belgium, 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Londo, G. Excursierapport. Zwarte Water of Boschven; Rijksinstituut voor Natuurbeheer: Driebergen, The Netherlands, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Flora Databank; Flo.Wer vzw, Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium; Plantentuin: Meise, Belgium; Available online: https://flora.inbo.be/Pages/Common/Default.aspx (accessed on 31 May 2024).
- van Duuren, L.; Rider, C.; Dijkstra, R.; Meijer, R. Biobase, Register Biodiversiteit; Centraal Bureau voor de Statistiek: Voorburg/Heerlen, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tichý, L.; Axmanová, I.; Dengler, J.; Guarino, R.; Jansen, F.; Midolo, G.; Nobis, M.P.; Van Meerbeek, K.; Aćić, S.; Attorre, F.; et al. Ellenberg-type indicator values for European vascular plant species. J. Veg. Sci. 2024, 34, e13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, M. Bijdrage tot de geschiedenis der blekerijen te Turnhout (1). Taxandria 1951, 15, 3–41. [Google Scholar]
- Caron, P. Vennen en tijkindustrie. In Water voor Groen. Vierde Vlaams Wetenschappelijk Congres over Groenvoorziening; Vereniging voor Groenvoorziening vzw: Brussel, Belgium, 1984; p. 465. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Vijver, B.; Schuster, T.M.; Kusber, W.-H.; Hamilton, P.B.; Wetzel, C.E.; Ector, L. Revision of European Brachysira species (Brachysiraceae, Bacillariophyta): I. The Brachysira microcephala—B. neoexilis enigma. Bot. Lett. 2021, 168, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, L.; van Straaten, D. A survey of the acid water diatom assemblages of two heathland relics in the Belgian northern Campine (Groot- and Klein Schietveld, Brassschaat) with an assessment of their conservational value. Diatom Res. 1992, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeder, U.; Busse, L.B. Composition and development of epipsammic diatoms in an oligotrophic lake (Lake Lustsee, Germany) under natural conditions and under artificial phosphate supply using enclosure experiments. In Lange-Bertalot Festschrift. Studies on Diatoms; Jahn, R., Kociolek, J.P., Witkowski, A., Compère, P., Eds.; A.R.G. Gantner Verlag, K.G.: Ruggell, Switzerland, 2001; pp. 383–400. [Google Scholar]
- Lebkuecher, J.G.; Atma, J.L.; Conn, H.; Redwine, D.J. Composition of epilithic diatom and soft-algal assemblages in infralittoral zones of Tennessee reservoirs and correlations of composition to trophic state. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2023, 38, 2182836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bont, W.; De Bont, A. Evolutie van de visfauna in de vennen. In Water voor Groen. Vierde Vlaams Wetenschappelijk Congres over Groenvoorziening; Vereniging voor Groenvoorziening vzw: Brussel, Belgium, 1984; pp. 467–468. [Google Scholar]
- Rask, M. 1984 The effect of low pH on perch, Perca fluviatilis L. III. The perch population in a small, acidic, extremely humic forest lake. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1984, 21, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Spierenburg, P.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Lotter, A.F.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Could rising aquatic carbon dioxide concentrations favour the invasion of elodeids in isoetid-dominated softwater lakes? Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, E.J. On the reproduction and biology of Elatine hexandra (Lapierre) DC. (Elatinaceae); a typical species of exposed mud. Kew Bull. 1967, 21, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeda, E.J.; Westra, R.; Westra, C.; Westra, T. Nederlandse Oecologische Flora. Wilde Planten en hun Relaties 2; IVN: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendaal, F.H.J.L.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Waterplanten en Waterkwaliteit; Koninklijke Nederlandse Natuurhistorische Vereniging: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Vijver, B.; Jarlman, A.; Lange-Bertalot, H.; Mertens, A.; de Haan, M.; Ector, L. Four new European Achnanthidium species (Bacillariophyceae). Algol. Stud. 2011, 136/137, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemer, S.C.; Hoagland, K.D.; Rosowski, J.R. Development of a freshwater periphyton community as influenced by diatom mucilages. Can. J. Bot. 1984, 62, 1799–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruck, E.C.; Nakov, T.; Alverson, A.J.; Theriot, E.C. Phylogeny, ecology, morphological evolution, and reclassification of the diatom orders Surirellales and Rhopalodiales. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 103, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A. Atlas der Diatomaceen-Kunde. Serie VI. Tafel 214-288; O.R. Reisland: Leipzig, Germany, 1912. [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Bertalot, H.; Krammer, K. Bacillariaceae, Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae. Neue und wenig bekannte Taxa, neue Kombinationen und Synonyme sowie Bemerkungen und Ergänzungen zu den Naviculaceae. Bibl. Diatomol. 1987, 15, 1–289. [Google Scholar]
- Alles, E.; Nörpel-Schempp, M.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Zur Systematik und Ökologie charakteristischer Eunotia-Arten (Bacillariophyceae) in elektrolytarmen Bachoberläufen. Nova Hedwig. 1991, 53, 171–213. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, B.; Buckley, Y.M. Use of seasonal epilithic diatom assemblages to evaluate ecological status in Irish lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, D.F.; Battarbee, R.W.; Renberg, I.; van Dam, H.; Smol, J.P. Palaeoecological analysis of lake acidification trends in North America and Europe using diatoms and chrysophytes. In Acid Precipitation. Vol. 4. Soils, Aquatic Processes, and Lake Acidification; Norton, S.A., Lindberg, S.E., Page, A.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 207–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siver, P.A.; Hamilton, P.B. Diatoms of North America: The freshwater flora of waterbodies on the Atlantic Coastal Plain. Iconogr. Diatomol. 2011, 22, 1–916. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, B.; Allott, T. A review of the genus Brachysira in Ireland with the description of Brachysira praegeri and Brachysira conamarae, new raphid diatoms (Bacillariophyceae) from high status waterbodies. Phytotaxa 2017, 326, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttner, I.; Hamilton, P.B.; Wetzel, C.E.; Van de Vijver, B.; King, L.; Kelly, M.G.; Williams, D.M.; Ector, L. A study of the morphology and distribution of four Achnanthidium Kütz. species (Bacillariophyta), implications for ecological status assessment, and description of two new European species. Cryptogam. Algol. 2022, 43, 147–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, L.; Wartel, S.; De Blust, G. Eutrophication and acidification history of a moorland pool in northern Belgium. Würzburger Geogr. Manuskr. 1997, 41, 57–58. [Google Scholar]
- De Bont, A.F. Changements de la faune ornithologique de la Campine Turnhoutoise. Le Gerfaut 1947, 37, 172–187. [Google Scholar]
- De Bont, A. Recente evolutie van het vennencomplex. In Water voor Groen. Vierde Vlaams Wetenschappelijk Congres over Groenvoorziening; Vereniging voor Groenvoorziening vzw: Brussel, Belgium, 1984; pp. 466–467. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerie van Landbouw. Atlas van de Algemeene Landbouwtelling van 31 December 1929; Laner: Brussel, Belgium, 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Denys, L. Diatomeeën in Turnhoutse vennen. Heden getoetst aan het verleden. Natuur. Focus 2020, 19, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Eerens, H.C.; van Dam, J.D. (Eds.) Grootschalige Luchtverontreiniging en Depositie in de Nationale Milieuverkenning, 5. Rapport 408129016; Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- van Dam, H.; Suurmond, G.; ter Braak, C.J.F. Impact of acidification on diatoms and chemistry of Dutch moorland pools. Hydrobiologia 1981, 83, 425–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, A.T.; Córdoba, F.; Antunes, C.; Loayza-Muro, R.; Grande, J.A.; Silva, B.; Diaz-Curiel, J.; Ferreira da Silva, E. Extremely acidic eukaryotic (micro) organisms: Life in acid mine drainage polluted environments-mini-review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuurkes, J.A.A.R.; Kok, C.J.; den Hartog, C. Ammonium and nitrate uptake by aquatic plants from poorly buffered and acidified waters. Aquat. Bot. 1986, 24, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Bobbink, R.; Oonk, M.M.A.; Brandrud, T.E.; Roelofs, J.G.M. The effects of liming and reacidification on the growth of Juncus bulbosus: A mesocosm experiment. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 64, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Roelofs, J.G.M.; Schneider, S.C.; Smolders, A.J.P. Long-term effects of liming in Norwegian softwater lakes: The rise and fall of bulbous rush (Juncus bulbosus) and decline of isoetid vegetation. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, G.H.P.; Leuven, R.S.E.W. Floristic changes in shallow soft waters in relation to underlying environmental factors. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 20, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangenechten, J.H.D.; Van Puyembroeck, S.; Vanderborght, O.L.J.; Bosmans, F.; Deckers, H. Physico-chemistry of surface waters in the Campine region of Belgium, with special reference to acid moorland pools. Hydrobiologia 1981, 90, 369–396. [Google Scholar]
- Dumortier, M.; De Schrijver, A.; Denys, L.; Vanreusel, W. Verzuring. In Natuurrapport. Toestand van de Natuur in Vlaanderen: Cijfers voor het Beleid; Dumortier, M., De Bruyn, L., Peymen, J., Schneiders, A., Van Daele, T., Weyembergh, G., Van Straaten, D., Kuijken, E., Eds.; Instituut voor Natuurbehoud: Brussel, Belgium, 2003; pp. 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Smolders, A.J.P.; Lamers, L.P.M.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Van der Velde, G.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Internal eutrophication: How it works and what to do about it—A review. Chem. Ecol. 2006, 22, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, A.J.P.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Bobbink, R.; Roelofs, J.G.M.; Lamers, L.P.M. How nitrate leaching from agricultural lands provokes phosphate eutrophication in groundwater fed wetlands: The sulphur bridge. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, A.J.P.; Moonen, M.; Zwaga, K.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Lamers, L.P.M.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Changes in pore water chemistry of desiccating freshwater sediments with different sulphur contents. Geoderma 2006, 132, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, H. Partial recovery of moorland pools from acidification: Indications by chemistry and diatoms. Aquat. Ecol. 1996, 30, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarek, S. Responses of the Lobelia-epiphyte complex to liming of an acidified lake. Aquat. Bot. 1986, 25, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Spierenburg, P.; Fraaije, R.; Smolders, A.J.P.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Alkalinity generation and sediment CO2 uptake influence establishment of Sparganium angustifolium in softwater lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 2300–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wichelen, J.; Declerck, S.; Muylaert, K.; Hoste, I.; Geenens, V.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Michels, E.; De Pauw, N.; Hoffmann, M.; De Meester, L.; et al. The importance of drawdown and sediment removal for the restoration of the eutrophied shallow Lake Kraenepoel (Belgium). Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemakers, M.J.S.; Maessen, M.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Effects of liming on water chemistry in shallow acidified pools in the Netherlands: Enclosure experiments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1994, 73, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clymo, R.S. Ion exchange in Sphagnum and its relation to bog ecology. Ann. Bot. N. S. 1963, 27, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clymo, R.S. Interactions of Sphagnum with water and air. In Effects of Atmospheric Pollutants on Forests, Wetlands and Agricultural Ecosystems; Hutchinson, T.C., Meema, K.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; pp. 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, H. The role of hydromorphology in the partial recovery of chemistry in acidified and warmed Dutch moorland pools. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kopáček, J.; Ulrich, K.-U.; Hejzlar, J.; Borovec, J.; Stuchlík, E. Natural inactivation of phosphorus by aluminum in atmospherically acidified water bodies. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3783–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorland, E.; Bobbink, R.; Messelink, J.H.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. Soil ammonium accumulation after sod cutting hampers the restoration of degraded wet heathlands. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorland, E.; van den Berg, L.J.L.; van de Berg, A.J.; Vermeer, M.L.; Roelofs, J.G.M.; Bobbink, R. The effects of sod cutting and additional liming on potential net nitrification in heathland soils. Plant Soil 2004, 265, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härdtle, W.; von Oheim, G.; Niemeyer, M.; Niemeyer, T.; Assmann, T.; Meyer, H. Nutrient leaching in dry heathland ecosystems: Effects of atmospheric deposition and management. Biogeochemistry 2007, 86, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, F.E. The effect of liming on the benthic diatom populations in three upland Welsh lakes. Diatom Res. 1990, 5, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemakers, M.J.S.; van Dam, H. Improvement of breeding success of the moor frog (Rana arvalis) by liming of acid moorland pools and the consequences of liming for water chemistry and diatoms. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 78, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, N.G. The representation of diatom communities by fossil assemblages in a small acid lake. J. Paleolimnol. 1995, 14, 185–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebee, T.J.C. Eutrophication of heathland ponds at a site in southern England: Causes and effects, with particular reference to the amphibia. Biol. Conserv. 1987, 42, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, O.; Sand-Jensen, K. Alkalinity and trophic state regulate aquatic plant distribution in Danish lakes. Aquat. Bot. 2000, 67, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, G.H.P.; van Beers, P.W.M.; Belgers, J.D.M.; Wortelboer, F.G. Gedifferentieerde Normstelling voor Nutriënten in Vennen: Onderbouwing en Toetsing van Kritische Depositieniveau’s en Effecten van Herstelmaatregelen op het Voorkomen van Isoëtiden. Alterra-Rapport 262; Alterra: Wageningen, The Netherlands; Rijksinsituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, O.; Andersen, T.; Ikejima, K.; Hossain, M.Z.; Andersen, F.Ø. A multidisciplinary approach to understanding the recent and historical occurrence of the freshwater plant, Littorella uniflora. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, G.; Bowman, J.; McGarrigle, M.; Caroni, R.; Donnelly, K.; Tierney, D.; Trodd, W.; Little, R. The identification, characterization and conservation value of isoetid lakes in Ireland. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2009, 19, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Calster, H.; Cools, N.; De Keersmaeker, L.; Denys, L.; Herr, C.; Leyssen, A.; Provoost, S.; Vanderhaeghe, F.; Vandevoorde, B.; Wouters, J.; et al. Gunstige Abiotische Bereiken voor Vegetatietypes in Vlaanderen. Rapporten van het Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek 2020 (44); Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, G.; Gray, E.; Gammell, M.; Roden, C.; Lally, H. Physico-chemical characterisation of protected lake habitats: A matter of dystrophy. Limnologica 2023, 103, 126123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek. Overwinterende Watervogels in Vlaanderen. Available online: https://watervogels.inbo.be/info (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Waarnemingen.be. Stichting Observation International en Lokale Partners. INBODATAVR-334. Available online: https://waarnemingen.be (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- Hahn, S.; Bauer, S.; Klaassen, M. Estimating the contribution of carnivorous waterbirds to nutrient loading in freshwater habitats. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 2421–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.; Bauer, S.; Klaassen, M. Quantification of allochthonous nutrient input into freshwater bodies by herbivorous waterbirds. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthaud, F.; Toury, J.; Romestaing, C.; Bornette, G. Photosynthetic and morphological traits control aquatic plant distribution according to light stress. Evol. Ecol. 2021, 35, 739–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.; Andersen, F.Ø. 2006 Effects of CO2 concentration on growth of filamentous algae and Littorella uniflora in a Danish softwater lake. Aquat. Bot. 2006, 84, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Moore, M.V.; Stewart, S.D.; Chandra, S.; Atkins, K.S.; Baron, J.S.; Bouma-Gregson, K.; Brothers, S.; Francoeur, S.N.; Genzoli, L.; et al. Blue waters, green bottoms: Benthic filamentous algal blooms are an emerging threat to clear lakes worldwide. BioScience 2021, 71, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierenburg, P.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Lotter, A.F.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Competition between isoetids and invading elodeids at different concentrations of aquatic carbon dioxide. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 1274–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koninlijk Meteorologisch Instituut. Klimaattrends in België. Available online: https://www.meteo.be/nl/klimaat/klimaatverandering-in-belgie/klimaattrends-in-belgie (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Arts, G.H.P.; de Haan, A.J.; Sieburn, M.B.; Verheggen, G.M. Extent and historical development of the decline of Dutch soft waters. Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. Ser. C. 1989, 92, 281–295. [Google Scholar]
- Roelofs, J.G.M. Impact of acidification and eutrophication on macrophyte communities in soft waters in The Netherlands I. Field observations. Aquat. Bot. 1983, 17, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, A.M. The effects of lake acidification on aquatic macrophytes—A review. Environ. Pollut. 1990, 65, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.R.; Martinsen, K.T.; Pedersen, O.; Baastrup-Spohr, L. Reasons for the dramatic loss of Lobelia dortmanna, a keystone plant species of softwater lakes in the Northern Hemisphere. Freshw. Biol. 2023, 68, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzewski, N.; Mueller, P.; Meier, R.J.; Liebsch, G.; Jensen, K.; Koop-Jakobsen, K. Dynamics of oxygen and carbon dioxide in rhizospheres of Lobelia dortmanna—A planar optode study of belowground gas exchange between plants and sediment. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, K.K.; Sand-Jensen, K. Precipitated iron and manganese plaques restrict root uptake of phosphorus in Lobelia dortmanna. Can. J. Bot. 1998, 76, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, C.L.; Sand-Jensen, K. High sensitivity of Lobelia dortmanna to sediment oxygen depletion following organic enrichment. New Phytol. 2011, 190, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido, C.; Keijsers, D.J.H.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Pedersen, O.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Elevated alkalinity and sulfate adversely affect the aquatic macrophyte Lobelia dortmanna. Aquat. Ecol. 2012, 46, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sand-Jensen, K.; Borum, J.; Binzer, T. Oxygen stress and reduced growth of Lobelia dortmanna in sandy lake sediments subject to organic enrichment. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, A.J.P.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Roelofs, J.G.M. The isoetid environment: Biogeochemistry and threats. Aquat. Biol. 2002, 73, 325–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierenburg, P.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Pulido, C.; Smolders, A.J.P.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Massive uprooting of Littorella uniflora (L.) Asch. during a storm event and its relation to sediment and plant characteristics. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makavičiūtė, J.; Sinkevičienė, Z. Unusual vegetative propagation of water lobelia (Lobelia dortmanna) in Lake Salinis (Lithuania). Bot. Lith. 2011, 17, 185–187. [Google Scholar]
- Irfanullah, H.M.; Moss, B. Factors influencing the return of submerged plants to a clear-water, shallow temperate lake. Aquat. Bot. 2004, 80, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, G.H.P. Deterioration of Atlantic soft water macrophyte communities by acidification, eutrophication and alkalinisation. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 73, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droppo, I.G. Biofilm and bed stability of five contrasting freshwater sediments. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Shang, Q.; Chen, M.; He, G. Changes in the critical erosion velocity for sediment colonized by biofilm. Sedimentology 2014, 61, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, J.A.; Paterson, D.M.; Thrush, S.F. The role of microphytobenthos in soft-sediment ecological networks and their contribution to the delivery of multiple ecosystem services. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, X.; Fujibayashi, M.; Niu, Q.; Tanaka, N.; Nishimura, O. Response of microalgae to elevated CO2 and temperature: Impact of climate change on freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 19847–19860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raun, A.L.; Borum, J.; Sand-Jensen, K. Influence of sediment organic enrichment and water alkalinity on growth of aquatic isoetid and elodeid plants. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand-Jensen, K.; Borum, J. Epiphyte shading and its effect on photosynthesis and diel metabolism of Lobelia dortmanna L. during the spring bloom in a Danish Lake. Aquat. Bot. 1984, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterlynck, P.; De Saeger, S.; Leyssen, A.; Provoost, S.; Thomaes, A.; Vandevoorde, B.; Wouters, J.; Paelinckx, D. Criteria voor de Beoordeling van de Lokale Staat van Instandhouding van de Natura2000 Habitattypen in Vlaanderen. Versie 3.0. Rapporten van het Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek 27; Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbink, R.; Loran, C.; Tomassen, H. Review and Revision of Empirical Critical Loads of Nitrogen for EUROPE. TEXTE 110/2022, CCE; Umweltbundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Borman, S.C.; Galatowitsch, S.M.; Newman, R.M. The effects of species immigrations and changing conditions on isoetid communities. Aquat. Bot. 2009, 91, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, E.; Denys, L.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; Buiks, M.; Onkelinx, T. Competitive strength of Australian swamp stonecrop (Crassula helmsii) invading moorland pools. Aquat. Invasions 2017, 12, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Loop, J.M.M.; Tjampens, J.; Vogels, J.J.; van Kleef, H.H.; Lamers, L.P.M.; Leuven, R.S.E.W. Reducing nutrient availability and enhancing biotic resistance limits settlement and growth of the invasive Australian swamp stonecrop (Crassula helmsii). Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kleef, H.H.; van der Loop, J.M.M.; van Veenhuisen, L.S. Low resource competition, availability of nutrients and water level fluctuations facilitate invasions of Australian swamp stonecrop (Crassula helmsii). Diversity 2024, 1631, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, J.; Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T.; van Roosmalen, M.I.J.T.; Smolders, A.J.P. Carbon limitation and aluminium toxicity prevents dominance of Crassula helmsii on weakly buffered soils. Aquat. Bot. 2024, 191, 103737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieker, V.C.; Martin, M.D. Implications and future prospects for evolutionary analyses of DNA in historical herbarium collections. Bot. Lett. 2018, 165, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daru, B.H.; Park, D.S.; Primack, R.B.; Willis, C.G.; Barrington, D.S.; Whitfeld, T.J.S.; Seidler, T.G.; Sweeney, P.W.; Foster, D.R.; Ellison, A.M.; et al. Widespread sampling biases in herbaria revealed from large-scale digitization. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 939–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

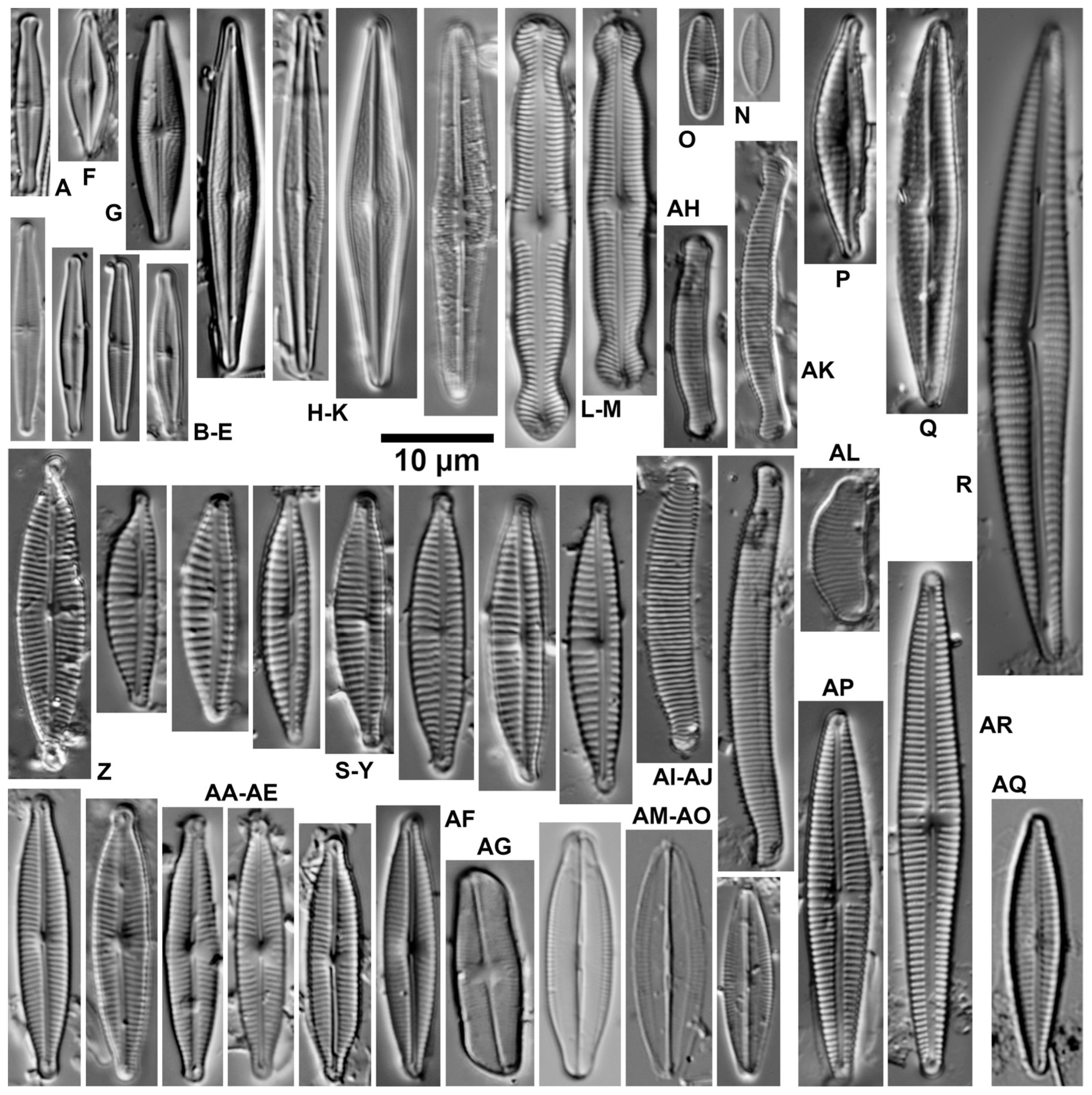
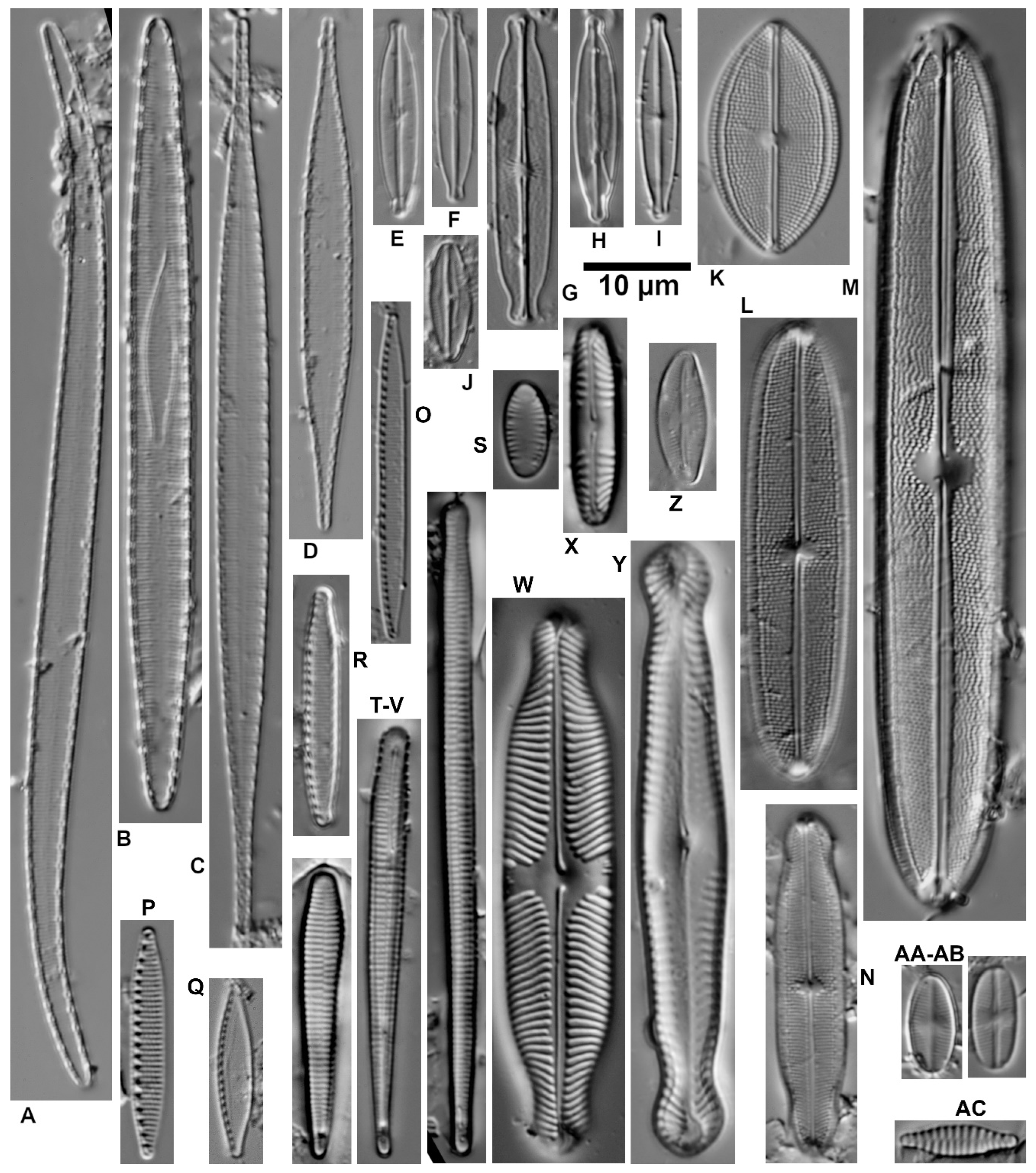
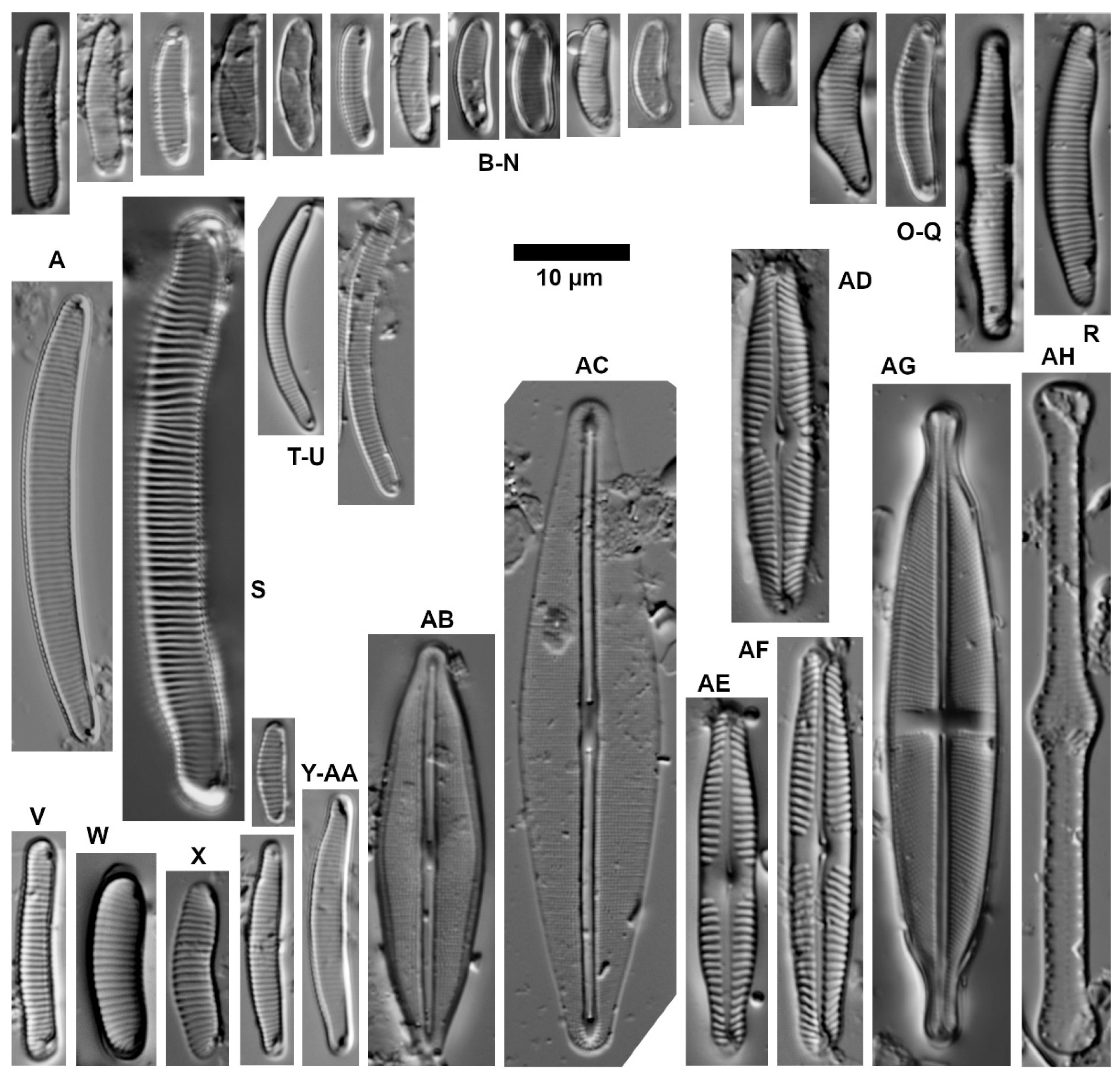

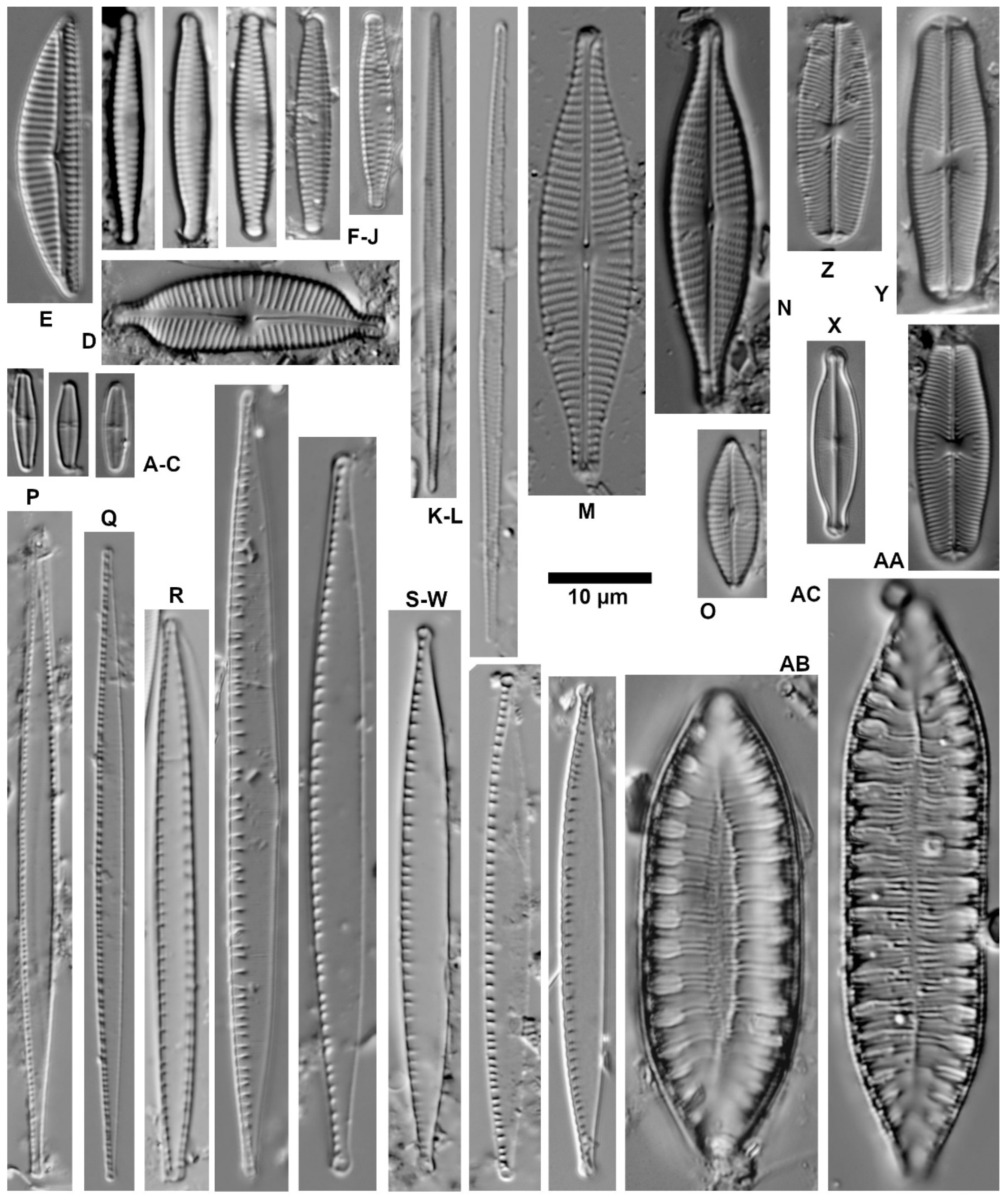
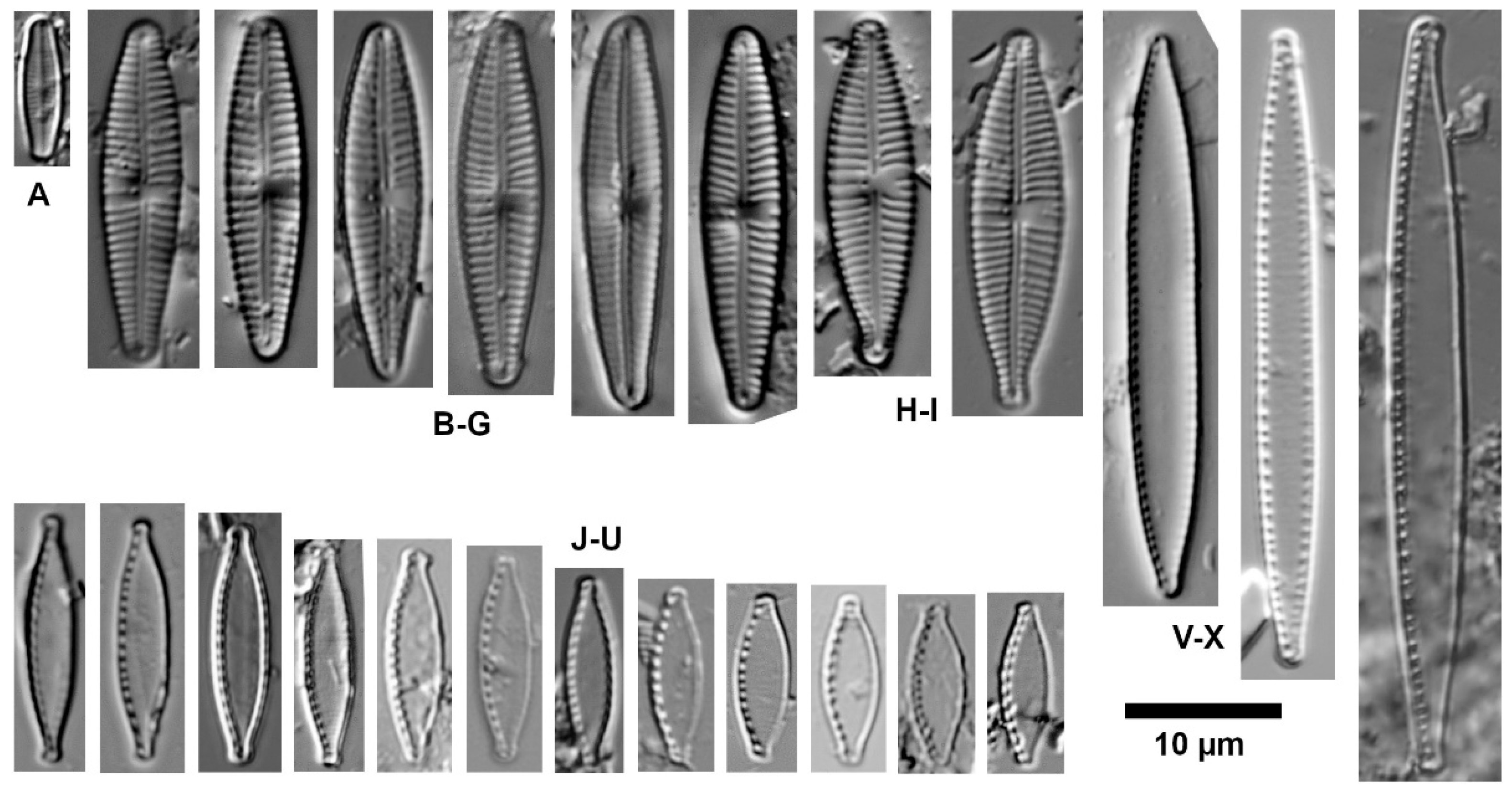
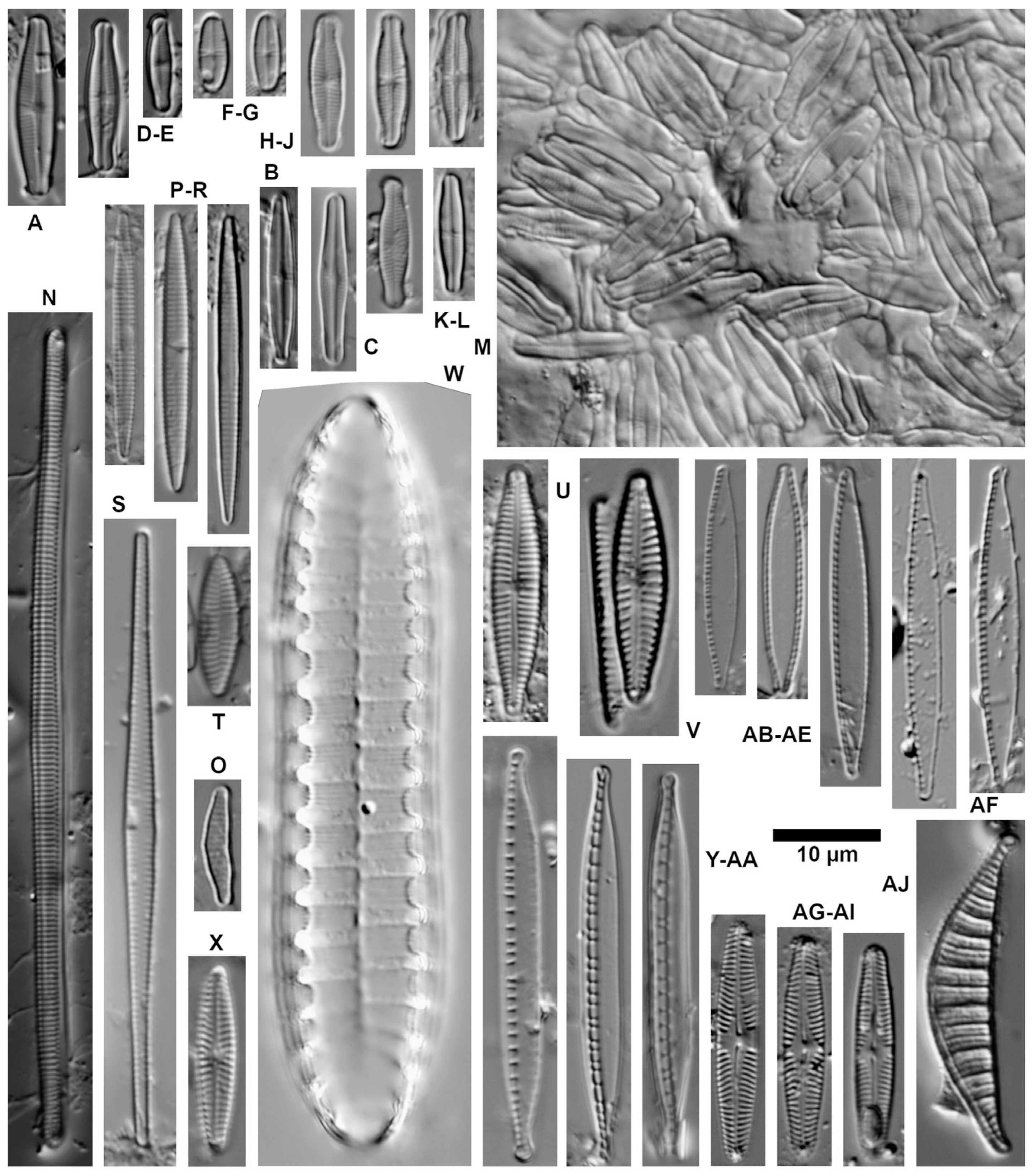
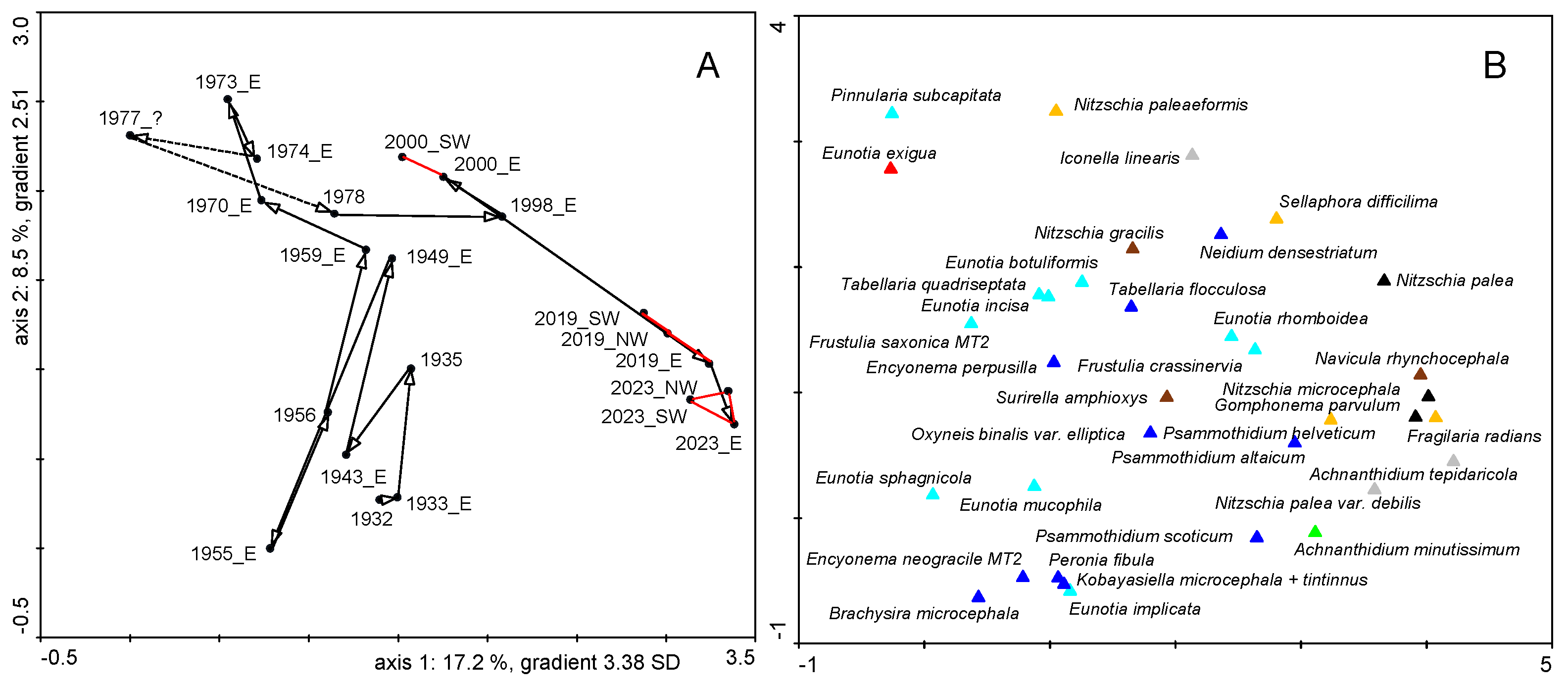
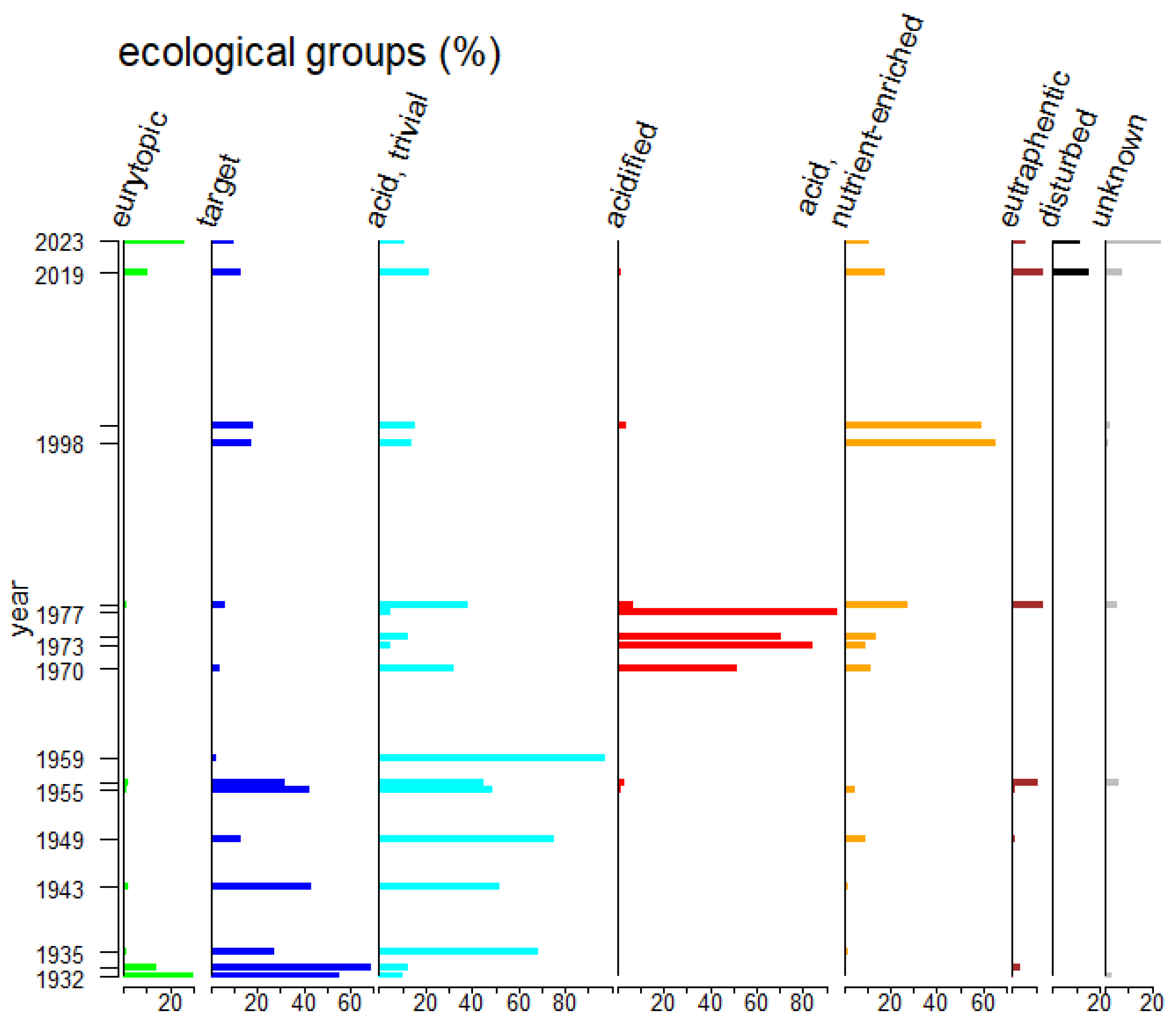
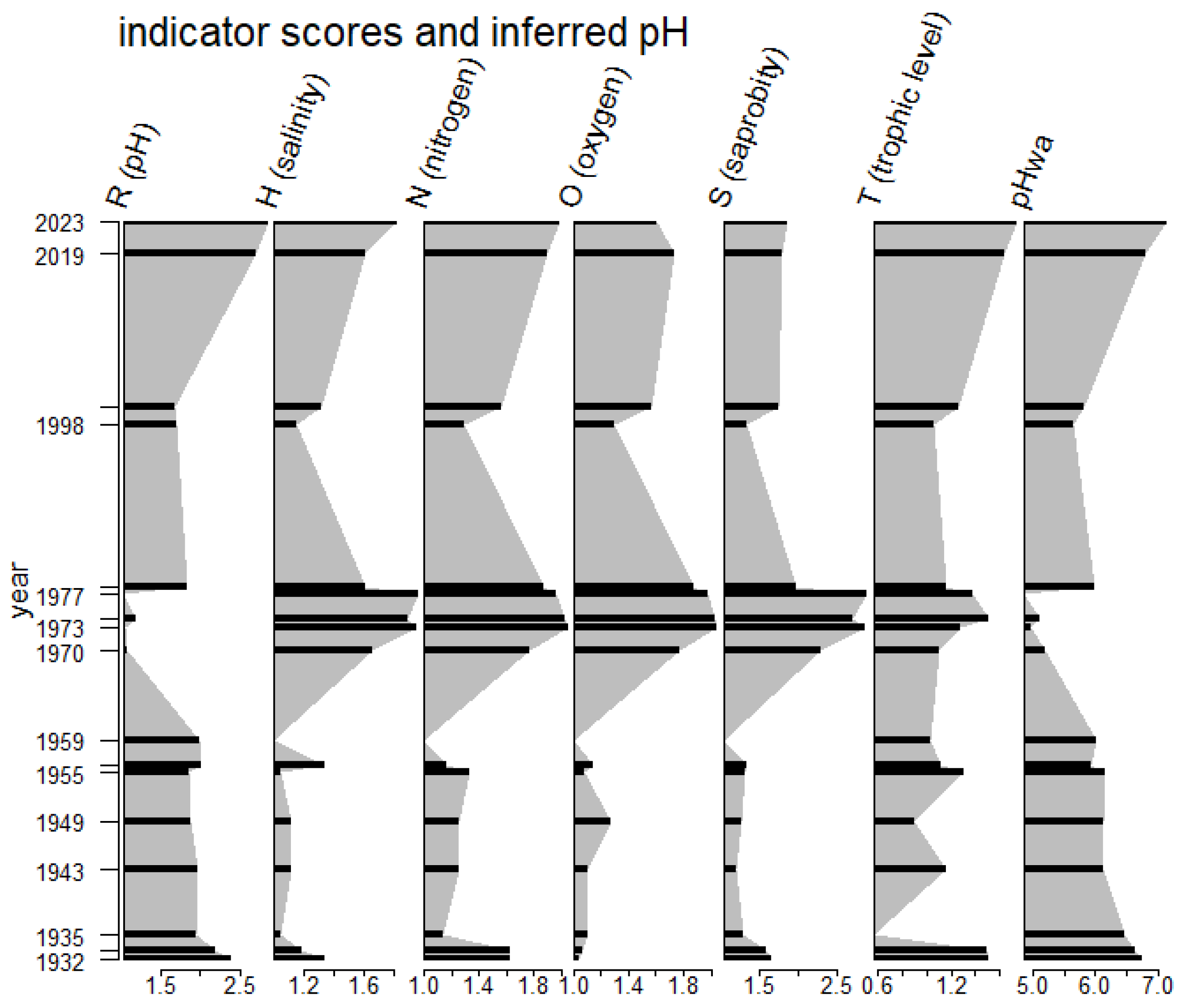
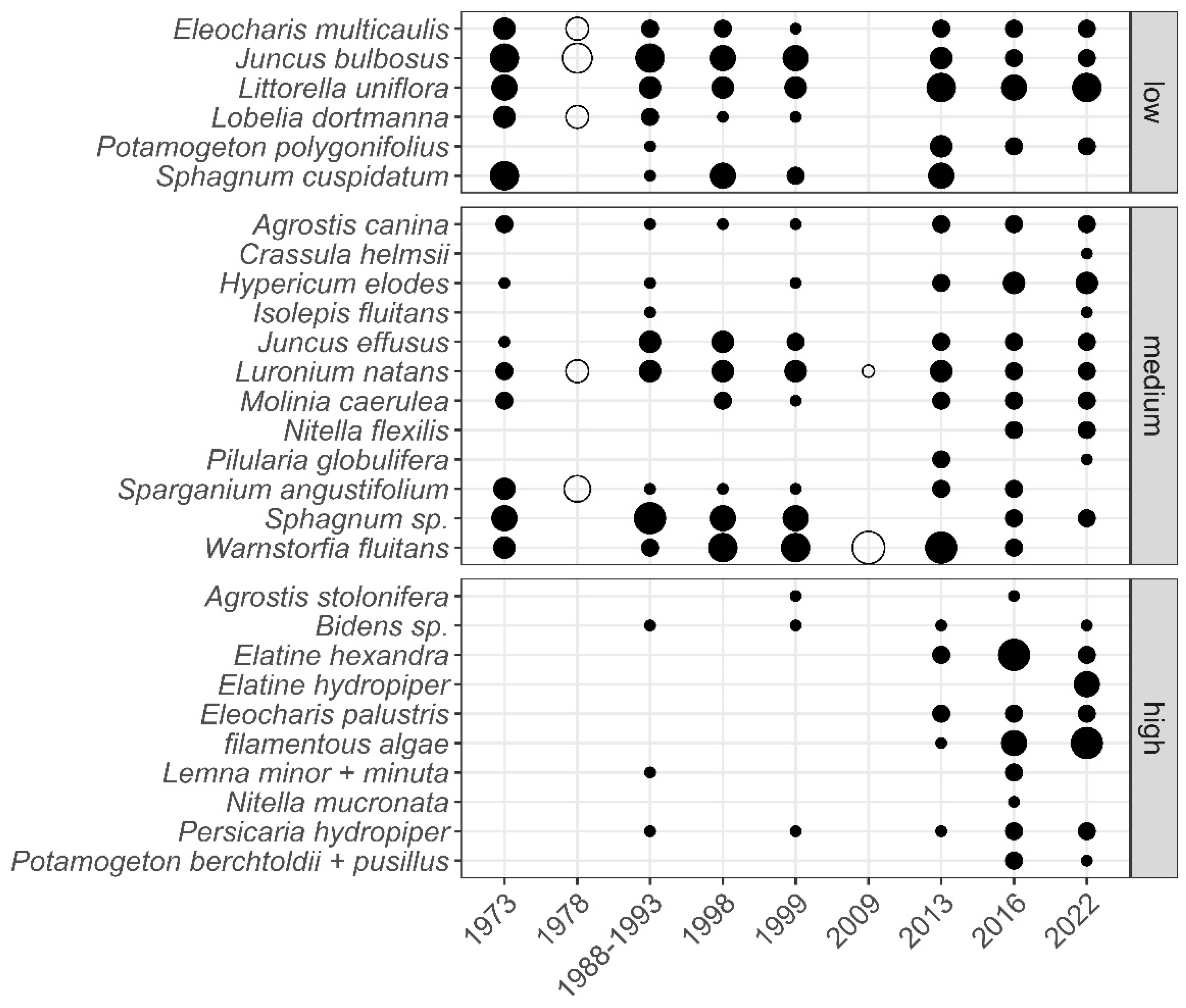

| Ecological Group | Environmental Indication |
|---|---|
| target species | optimally occurring in nutrient-poor and unpolluted, slightly buffered water (e.g., Figure 5 and Figure 6) |
| trivial taxa from acidic water | widely distributed in moderately acidic or dystrophic conditions (e.g., Figure 7) |
| acidification indicators | indicators of mineral-acidic conditions (extremely low pH, high sulphate concentrations, and metal tolerant, e.g., Eunotia exigua; Figure 8) |
| taxa from acidic nutrient-enriched water | occurring in acid(-ified) eutrophicated water (Figure 8) |
| eurytopic taxa | extremely widespread in nonacidic but not strongly polluted or hypertrophic conditions (Achnanthidium minutissimum *; Figure 9) |
| eutraphentic taxa from nonacidic water | common in ± neutral to alkaline, nutrient-rich conditions (e.g., Figure 9) |
| disturbance indicators | optimally occurring in organically polluted or high-conductivity (±brackish) water (e.g., Figure 10) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Denys, L.; Packet, J.; Leyssen, A.; Vanderhaeghe, F. The Recent Environmental History, Attempted Restoration and Future Prospects of a Challenged Lobelia Pond in Northeastern Belgium. Diversity 2024, 16, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080487
Denys L, Packet J, Leyssen A, Vanderhaeghe F. The Recent Environmental History, Attempted Restoration and Future Prospects of a Challenged Lobelia Pond in Northeastern Belgium. Diversity. 2024; 16(8):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080487
Chicago/Turabian StyleDenys, Luc, Jo Packet, An Leyssen, and Floris Vanderhaeghe. 2024. "The Recent Environmental History, Attempted Restoration and Future Prospects of a Challenged Lobelia Pond in Northeastern Belgium" Diversity 16, no. 8: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080487
APA StyleDenys, L., Packet, J., Leyssen, A., & Vanderhaeghe, F. (2024). The Recent Environmental History, Attempted Restoration and Future Prospects of a Challenged Lobelia Pond in Northeastern Belgium. Diversity, 16(8), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080487







