Morphological and Molecular Identification of Porpita porpita (Hydrozoa: Porpitidae) Larval and Colonial Phases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
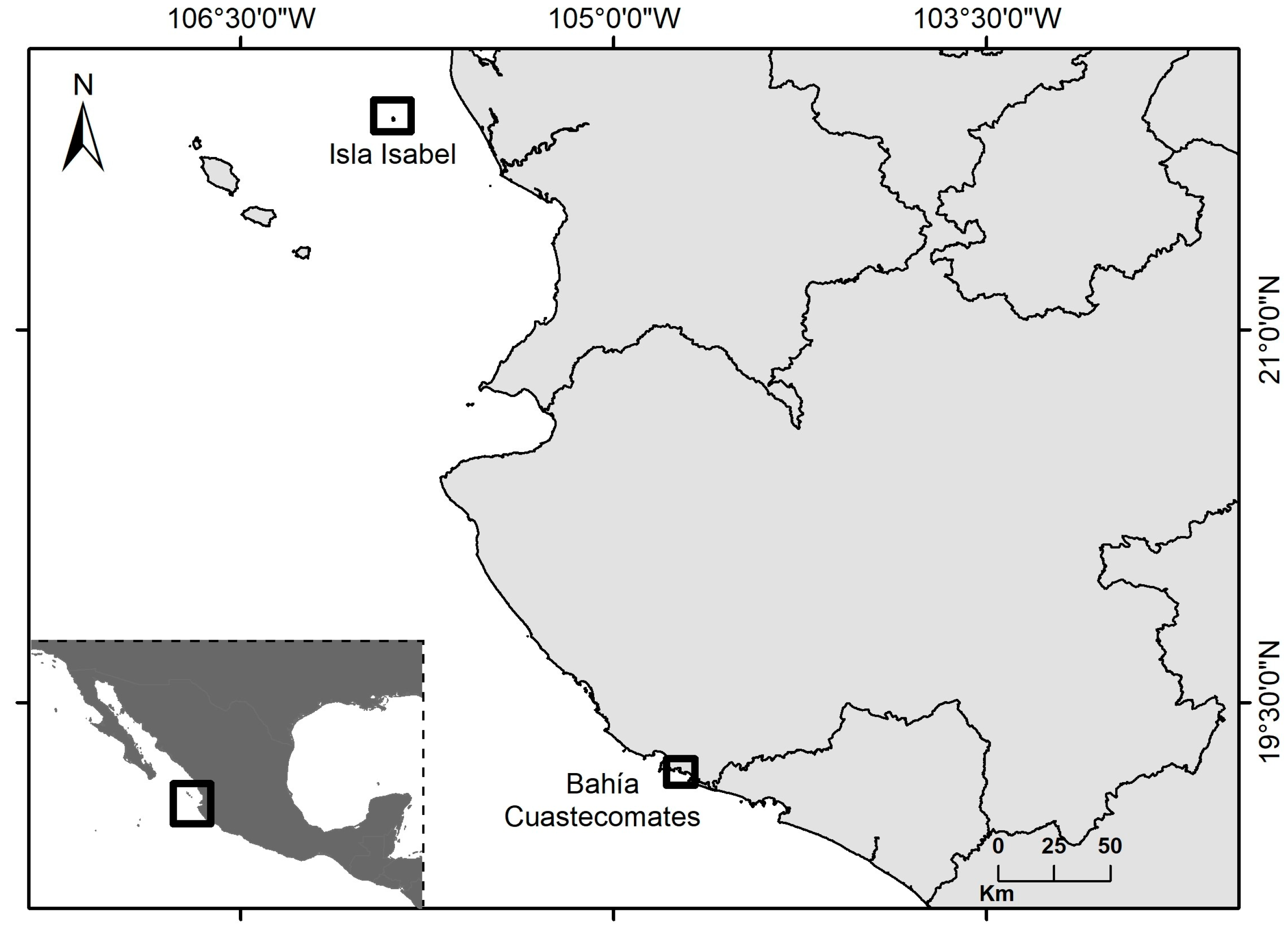
2.1. Study Area and Collected Samples
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Molecular Identification
3. Results
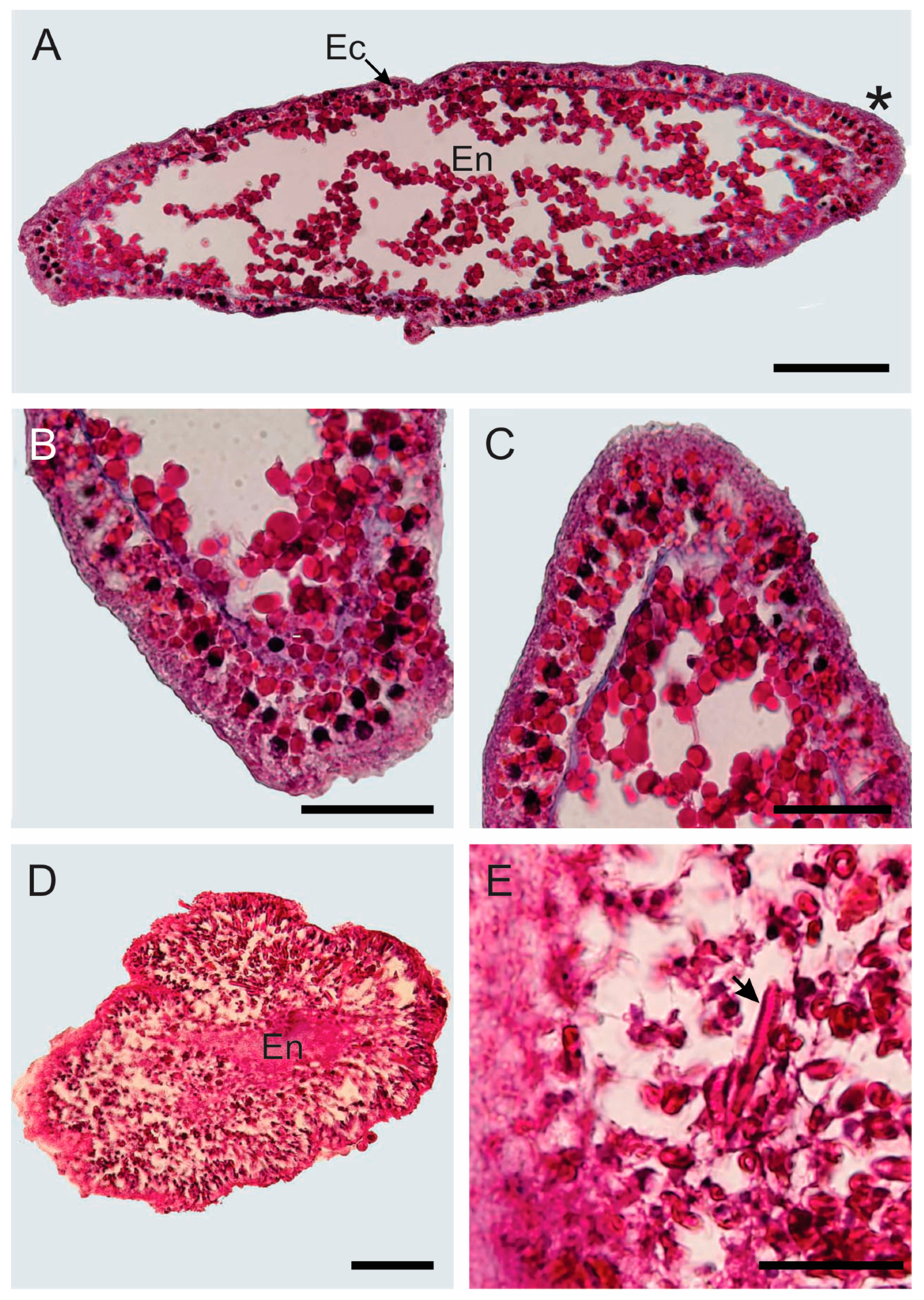
3.1. Morphological and Histological Description
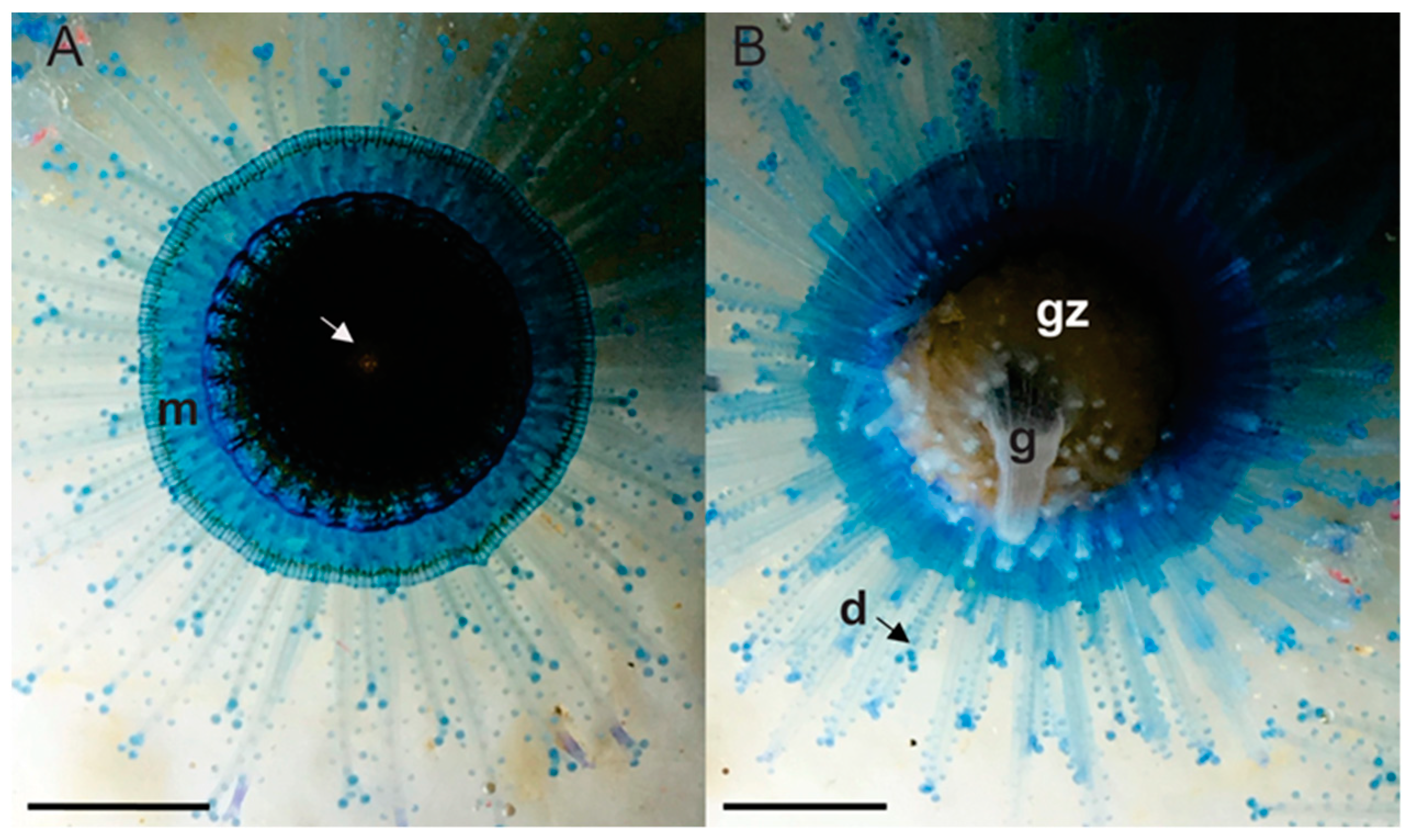
3.1.1. Hydroid Colony
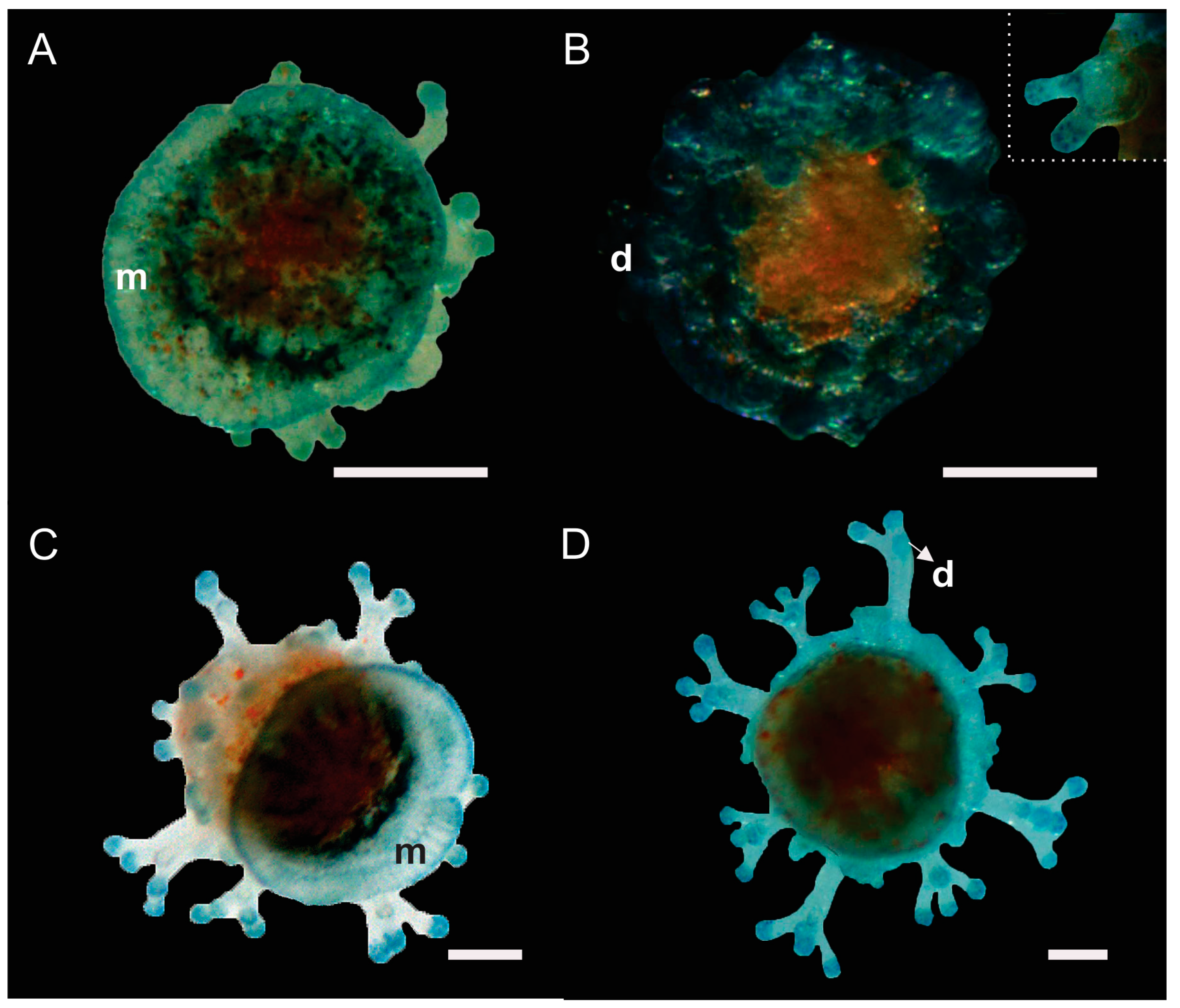
3.1.2. Young Hydroid Colony Stage
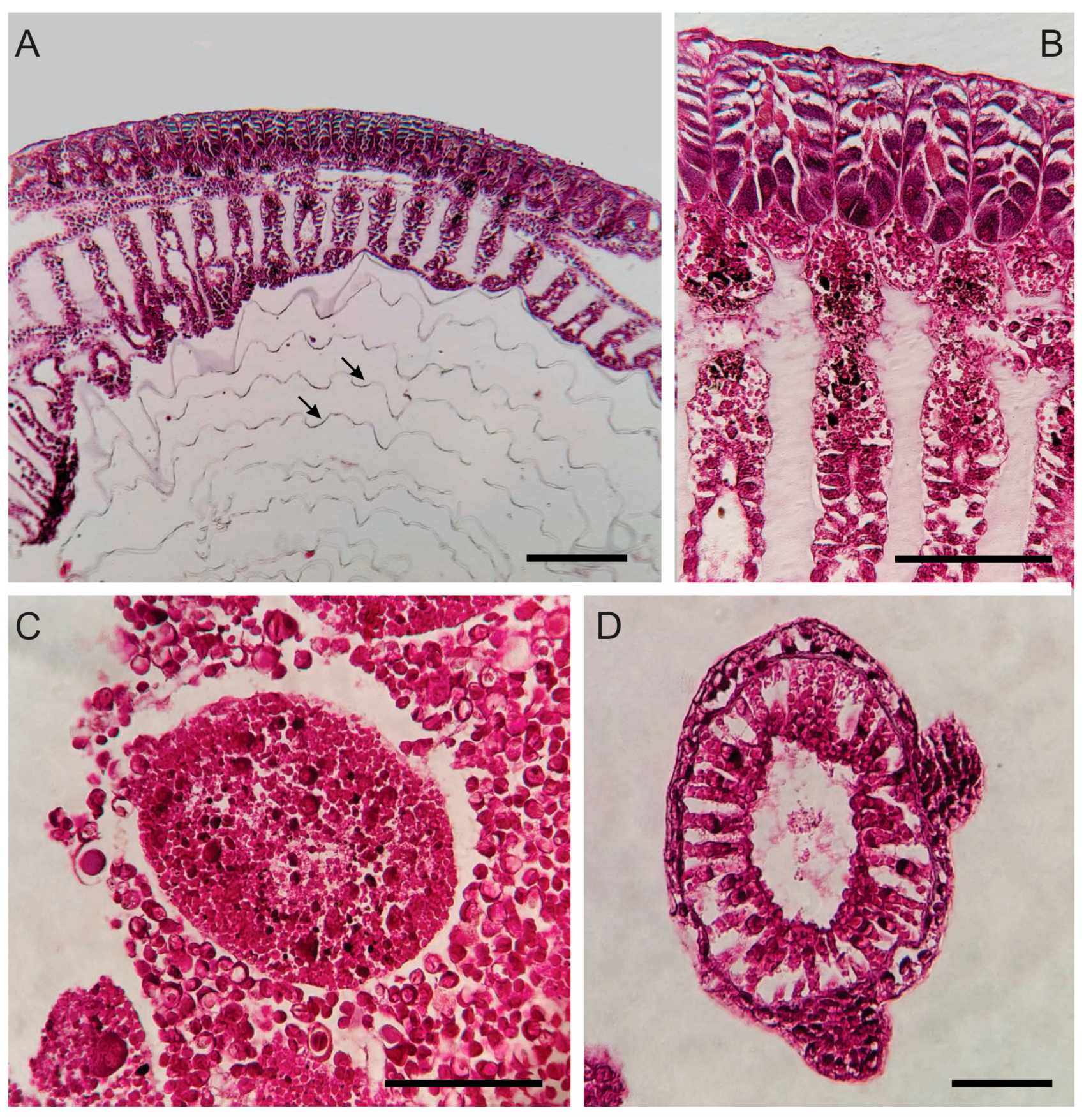
3.1.3. Planula Larva
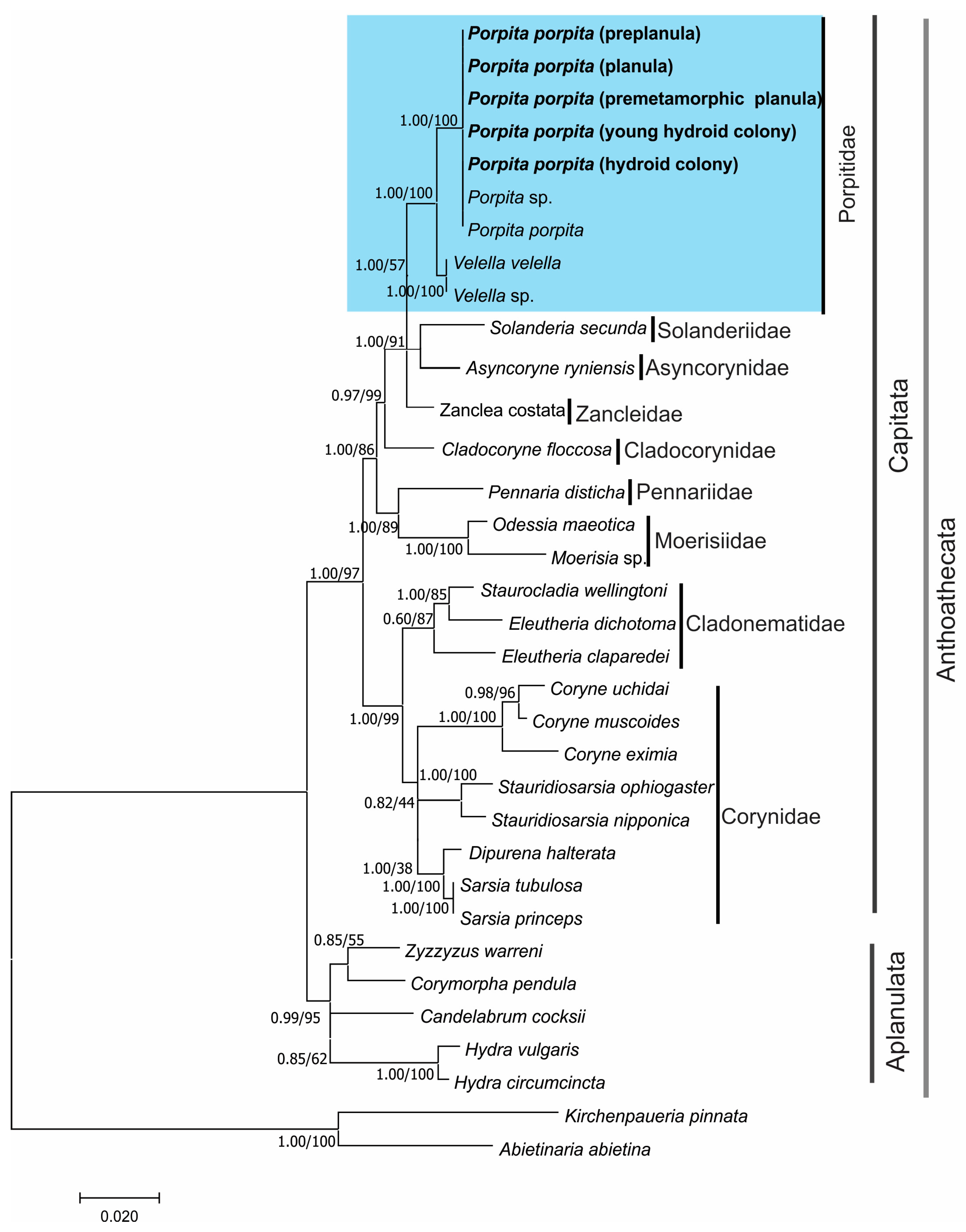
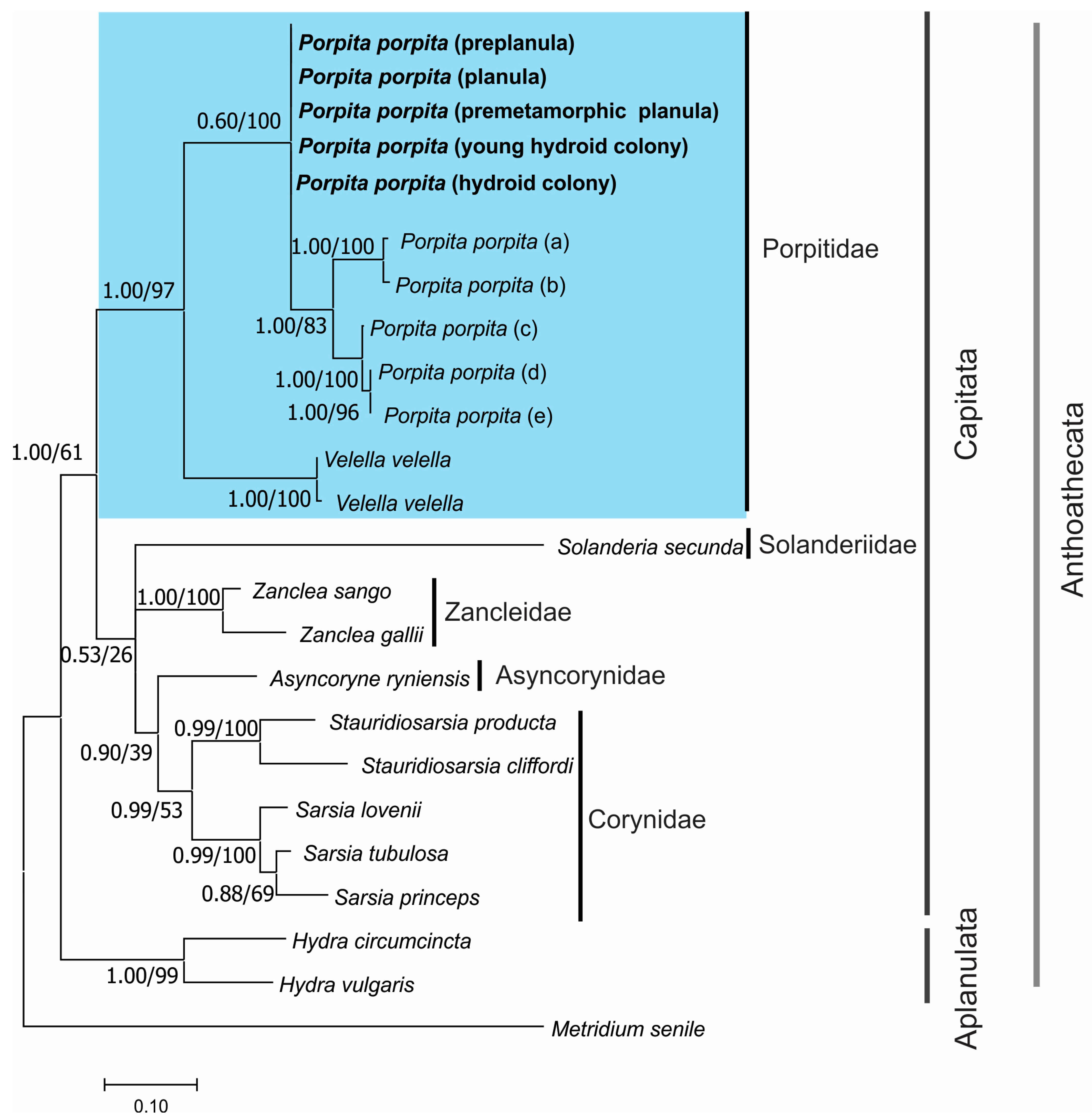
3.2. Molecular Identification
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouillon, G.C.; Gili, F.P.; Boero, J.M. An Introduction to Hydrozoa. In Mémoires du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle; Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle: Paris, France, 2006; Volume 194, pp. 1–591. ISBN 2-85653-580-1. [Google Scholar]
- Schuchert, P. The European anthecate hydroids and their medusa (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria): Capitata Part 2. Rev. Suisse Zool. 2010, 117, 337–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.W.; Wagner, G.P. The evolution of colony-level development in the Siphonophora (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). Dev. Genes Evol. 2006, 216, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürlek, M.; Uyan, A.; Doğdu, S.A.; Karan, S.; Gökçen, A.; Turan, C. Occurrence of the Blue Button Porpita porpita (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Iskenderun Bay, Northeastern Mediterranean Coast of Turkey. Acta Adriat. 2020, 61, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkendale, L.; Calder, D. Hydroids (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) from Guam and the Commonwealth of the Northern Marianas Islands (CNMI). Micronesica 2003, 3536, 159–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, S.; Gravili, C. On the occurrence of Porpita porpita (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) at Pakistan coast (North Arabian Sea). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2014, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msn, C.; Sharifuzzaman, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Nabi, M.; Hossain, M. First Record of Porpita porpita (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) from the coral reef ecosystem, Bangladesh. Ocean Sci. 2016, 51, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillo, A.; Tiralongo, O.; Tondo, E. New records of Porpita porpita (Linnaeus, 1758) (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) in the mediterranean sea. NESciences 2019, 4, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, F.; Zaghloul, W.; Mohammad, S. First record of Porpita porpita (Linnaeus, 1758) (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa, Porpitidae) from the Red Sea of Egypt. J. Aquat. Sci. Mar. Biol. 2019, 2, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, G. Notes on the occurrence of Porpita porpita (Blue button) from Pulicat Lagoon. J. Res. Biol. 2019, 4, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Bieri, R. Feeding preferences and rates of the snail, Ianthina prolongata, the barnacle, Lepas anserifera, the nudibranchs, Glaucus atlanticus and Fiona pinnata, and the food web in the marine neuston. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1996, 14, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.E.; Bennett, I. Observations on Australian Glaucidae (Mollusca: Opisthobranchia). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1970, 49, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.K.; Baliarsingh, S.K.; Samanta, A.; Srichandan, S.; Singh, S. Mass beach stranding of blue button jellies (Porpita porpita, Linnaeus, 1758) along Odisha coast during summer season. Indian. J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2020, 49, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Umamageswari, P.; Dineshkumar, R.; Jayasingam, P.; Sampathkumar, P. Antimicrobial activities of jellyfish, Porpita porpita from Southeast Coast of India. Pharm. Biotechnol. Microbiol. 2016, 2016, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, F. Die Siphonophoren der Deutschen Südpolar-Expedition, 1901–1903. In Deutsche Südpolar-Expedition 1901–1903; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1925; Volume 17, pp. 1–541. [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright, P.; Nawrocki, A. Character Evolution in Hydrozoa (phylum Cnidaria). Integr. Comp. Biol. 2010, 50, 456–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortman, B.D.; Bucklin, A.; Pages, F.; Youngbluth, M. DNA barcoding the Medusozoa using mtCOI. Deep-Sea Res. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalturin, K.; Shinzato, C.; Khalturina, M.; Hamada, M.; Fujie, M.; Koyanagi, R.; Kanda, M.; Goto, H.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Toyokawa, M.; et al. Medusozoan genomes inform the evolution of the jellyfish body plan. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinckmann, A. Observations on the biology and development of Staurocladia portmanni sp. n. (Anthomedusae, Eleutheridae). Can. J. Zool. 1964, 42, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, R.R. The mysterious ecosystem at the ocean’s surface. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyataeva, S.V.; Hopcroft, R.R.; Lindsay, D.J.; Collins, A.G. DNA barcodes unite two problematic taxa: The meiobenthic Boreohydra simplex is a life-cycle stage of Plotocnide borealis (Hydrozoa: Aplanulata). Zootaxa 2016, 4150, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.M.; Lindsay, D.J.; Collins, A.G. The end of an enigmatic taxon: Eudoxia macra is the eudoxid stage of Lensia cossack (Siphonophora, Cnidaria). Syst. Biodivers. 2013, 11, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.M.; Collins, A.G.; Lindsay, D.J. Description of the eudoxid stages of Lensia havock and Lensia leloupi (Cnidaria: Siphonophora: Calycophorae), with a review of all known Lensia eudoxid bracts. Syst. Biodivers. 2014, 12, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchert, P. The polyps of Oceania armata identified by DNA barcoding (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa). Zootaxa 2016, 4175, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, D.R. Some anthoathecate hydroids and limnopolyps (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa) from the Hawaiian archipelago. Zootaxa. 2010, 2590, 1–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Valentín, J.D.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P.; Bautista-Guerrero, E.; López-Pérez, A.; Cupul-Magaña, A.L. Successful sexual reproduction of the scleractinian coral Porites panamensis: Evidence of planktonic larvae and recruitment. Invertebr. Biol. 2019, 138, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.; Raphael, S.; Mellor, L.; Spare, P.; Inwood, M. Métodos de Laboratorio, 2nd ed.; Interamericana: Puebla, Mexico, 1972; 1522p. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Redmond, N.E.; Morrow, C.C.; Thacker, R.W.; Diaz, M.C.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Cárdenas, P.; Hajdu, E.; Lobo-Hajdu, G.; Picton, B.E.; Pomponi, S.A.; et al. Phylogeny and systematics of Demospongiae in light of new small-subunit ribosomal DNA (18S) sequences. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2013, 53, 388–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, M.; Collins, A.G.; Silberman, J.D.; Sogin, M.L. Evaluating hypotheses of basal animal phylogeny using complete sequences of large and small subunit rRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9707–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.W. Evolution and taxonomy in capitate hydroids and medusae (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1990, 100, 101–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, J. Essai de classification des Hydropolypes-Hydroméduses (Hydrozoa-Cnidaria). Indo-Malay. Zool. 1985, 1, 29–243. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, M.; Brugler, M.R.; Cartwright, P.; Collins, A.G.; Dawson, M.N.; Fautin, D.G.; France, S.C.; Mcfadden, C.S.; Opresko, D.M.; Rodríguez, E.; et al. The phylum Cnidaria: A review of phylogenetic patterns and diversity 300 years after Linnaeus. Zootaxa 2007, 1668, 127–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, A.S. Contribución al estudio faunístico de celenterados y ctenóforos del plancton estuarino del noroeste de México. An. Inst. Biol. Univ. Nac. Autón. Mex. Bot. 1991, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gamero-Mora, E.; Ceballos-Corona, G.; Gasca, R.; Morales-Blake, A. Análisis de la comunidad del zooplancton gelatinoso (Hydrozoa, Ctenophora, Thaliacea) en el Pacífico central mexicano, abril-mayo 2011. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2015, 50, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Morales, E.; Segura-Puertas, L.; Gasca, R. Medusan (Cnidaria) assemblages off the Caribbean coast of Mexico. J. Coast. Res. 1999, 15, 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A.; Färber-Lorda, J. Zooplankton and the Oceanography of the Eastern Tropical Pacific: A Review. Prog. Oceanogr. 2006, 61, 318–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONABIO, 2022. Biodiversidad Mexicana. Available online: https://www.biodiversidad.gob.mx/region/ecorregiones-marinas (accessed on 13 April 2024).
- Ambriz-Arreola, I.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, J.; del Carmen Franco-Gordo, M.; Lavaniegos, B.E.; Godínez-Domínguez, E. Influence of coastal upwelling downwelling variability on tropical euphausiid abundance and community structure in the inshore Mexican central Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 451, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.W.; Pugh, P.R.; Haddock, S.H. Molecular phylogenetics of the Siphonophora (Cnidaria), with implications for the evolution of functional specialization. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 916–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.G.; Schuchert, P.; Marques, A.C.; Jankowski, T.; Medina, M.; Schierwater, B. Medusozoan phylogeny and character evolution clarified by new large and small subunit rDNA data and an assessment of the utility of phylogenetic mixture models. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclère, L.; Schuchert, P.; Manuel, M. Phylogeny of the Plumularioidea (Hydrozoa, Leptothecata): Evolution of Colonial Organisation and Life Cycle. Zool. Scr. 2007, 36, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclère, L.; Copley, R.R.; Momose, T.; Houliston, E. Hydrozoan insights in animal development and evolution. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2016, 39, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeulen, J.H. Studies on reef corals. II. Fine structure of planktonic planula larva of Pocillopora damicornis, with emphasis on the aboral epidermis. Mar. Biol. 1974, 27, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, M.; Kinzie, R.A.; Hidaka, M. Early development of zooxanthella-containing eggs of the corals Pocillopora verrucosa and P. eydouxi with special reference to the distribution of zooxanthellae. Biol. Bull. 2000, 199, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, M.; Hidaka, M. Early development of zooxanthella-containing eggs of the corals Porites cylindrica and Montipora digitata: The endodermal localization of zooxanthellae. Zool. Sci. 2006, 23, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Valentín, J.D.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P.; Bautista-Guerrero, E.; López-Pérez, A.; Cupul-Magaña, A.L. Internal ultrastructure of the planktonic larva of the coral Porites panamensis (Anthozoa: Scleractinia). Rev. Biol. Trop. 2022, 70, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, G. The role of polarity in the development of the hydrozoan planula larva. Wilehm. Roux. Arch. Dev. Biol. 1981, 190, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piraino, S.; Zega, G.; Di Benedetto, C.; Leone, A.; Dell’Anna, A.; Pennati, R.; Carnevali, D.C.; Schmid, V.; Reichert, H. Complex neural architecture in the diploblastic larva of Clava multicornis (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 1931–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandermeulen, J.H. Studies on reef corals. III. Fine structural changes of calicoblast cells in Pocillopora damicornis during settling and calcification. Mar. Biol. 1975, 31, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.; Chia, F.S.; Koss, R. A fine structural study of metamorphosis of the hydrozoan Mitrocomella polydiademata. J. Morphol. 1983, 176, 261–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.J.; Archer, W.E. Stages of larval development and stem cell population changes during metamorphosis of a hydrozoan planula. Biol. Bull. 1997, 192, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strömberg, S.M.; Östman, C.; Larsson, A.I. The cnidome and ultrastructural morphology of late planulae in Lophelia pertusa (Linnaeus, 1758)—With implications for settling competency. Acta Zool. 2019, 100, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, R.E.; Robison, B.H. Effects of temperature on the development and survival of Nanomia bijuga (Hydrozoa, Siphonophora). Invertebr. Biol. 2000, 119, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickwell, G.V. Physiological Dynamics of Siphonophores from Deep Scattering Layers: Size of Gas-Filled Floats and Rate of Gas Production; Report 1369; Navy Electronics Laboratory (NEL): San Diego, CA, USA, 1966; 50p. [Google Scholar]
- Mackie, G.O.; Pugh, P.R.; Purcell, J.E. Siphonophore biology. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1987, 24, 97–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchert, P. DNA barcoding of some Pandeidae species (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa, Anthoathecata). Rev. Suisse Zool. 2020, 125, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, C.J.; Harris, D.J.; Cunha, M.R.; Rogers, A.D. DNA barcoding reveals cryptic diversity in marine hydroids (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa) from coastal and deep-sea environments. Zool. Scr. 2008, 37, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, P.; Evans, N.M.; Dunn, C.W.; Marques, A.C.; Miglietta, M.P.; Schuchert, P.; Collins, A.G. Phylogenetics of Hydroidolina (Hydrozoa: Cnidaria). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2008, 88, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellberg, M.E.; Burton, R.S.; Neigel, J.E.; Palumbi, S.R. Genetic assessment of connectivity among marine populations. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2002, 70, 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Schroth, W.; Jarms, G.; Streit, B.; Schierwater, B. Speciation and phylogeography in the cosmopolitan marine moon jelly, Aurelia sp. BMC Evol. Biol. 2002, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, D.H.; Abraham, A.; Cho, J.H. A hybrid genetic algorithm and bacterial foraging approach for global optimization. Inf. Sci. 2007, 177, 3918–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, B.; Bo, M.; Betti, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Abbiati, M.; Costantini, F. Spatial and temporal genetic structure of Velella velella (Hydrozoa, Porpitidae) and its predator Janthina pallida (Gastropoda, Epitoniidae). Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, D.R. Shallow-Water Hydroids of Bermuda: The Athecatae; Life sciences contributions; Royal Ontario Museum: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1988; Volume 148, pp. 1–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totton, A.K. Siphonophora of the Indian Ocean together with systematic and biological notes on related specimens from other oceans. Discov. Rep. 1954, 27, 1–162. [Google Scholar]
- Schuchert, P. Revision of the European athecate hydroids and their medusae (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria): Families of Oceanidae and Pachycordylidae. Rev. Suisse. Zool. 2004, 111, 315–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.S.; Collins, A.G.; Marques, A.C. Molecules clarify a Cnidarian life cycle: The “Hydrozoan” Microhydrula limopsicola is an early life stage of the Staurozoan Haliclystus antarcticus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandini, A.C.; Schiariti, A.; Stampar, S.N.; Maronna, M.M.; Straehler-Pohl, I.; Marques, A.C. Succession of generations is still the general paradigm for scyphozoan life cycles. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2016, 92, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 28s and 18s | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Porpita porpita (preplanula) | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 2 | Porpita porpita (planula) | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 3 | Porpita porpita (premetamorphic planula) | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 4 | Porpita porpita (young hydroid colony) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 5 | Porpita porpita (hydroid colony) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 6 | Porpita porpita | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 7 | Porpita sp. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 8 | Vellella velella | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | - | 0.000 |
| 9 | Velella sp. | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.000 | - |
| COI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Porpita porpita (preplanula) | - | 0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.021 |
| 2 | Porpita porpita (planula) | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.021 |
| 3 | Porpita porpita (premetamorphic planula) | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.021 |
| 4 | Porpita porpita (young hydroid colony) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.021 |
| 5 | Porpita porpita (hydroid colony) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.021 |
| 6 | Porpita porpita (a) Mediterranean Sea | 0.087 | 0.087 | 0.087 | 0.087 | 0.087 | - | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.023 | 0.022 | 0.024 |
| 7 | Porpita porpita (b) North Atlantic Ocean | 0.087 | 0.087 | 0.087 | 0.087 | 0.087 | 0.012 | - | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.023 | 0.022 | 0.025 |
| 8 | Porpita porpita (c) Indian Ocean | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.080 | 0.083 | - | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.025 |
| 9 | Porpita porpita (d) Indian Ocean | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.078 | 0.081 | 0.010 | - | 0.004 | 0.010 | 0.022 | 0.025 |
| 10 | Porpita porpita (e) Indian Ocean | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.080 | 0.083 | 0.000 | 0.010 | - | 0.023 | 0.025 | |
| 11 | Velella velella | 0.171 | 0.171 | 0.171 | 0.171 | 0.171 | 0.207 | 0.201 | 0.209 | 0.207 | 0.209 | - | 0.003 | 0.023 |
| 12 | Velella velella | 0.171 | 0.171 | 0.171 | 0.171 | 0.171 | 0.204 | 0.201 | 0.212 | 0.204 | 0.212 | 0.006 | 0.024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santiago-Valentín, J.D.; Bautista-Guerrero, E.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P.; Franco-Gordo, M.d.C.; Razo-López, M.A.; Godínez-Domínguez, E. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Porpita porpita (Hydrozoa: Porpitidae) Larval and Colonial Phases. Diversity 2024, 16, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16070425
Santiago-Valentín JD, Bautista-Guerrero E, Rodríguez-Troncoso AP, Franco-Gordo MdC, Razo-López MA, Godínez-Domínguez E. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Porpita porpita (Hydrozoa: Porpitidae) Larval and Colonial Phases. Diversity. 2024; 16(7):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16070425
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantiago-Valentín, Jeimy Denisse, Eric Bautista-Guerrero, Alma Paola Rodríguez-Troncoso, María del Carmen Franco-Gordo, Mauricio Alejandro Razo-López, and Enrique Godínez-Domínguez. 2024. "Morphological and Molecular Identification of Porpita porpita (Hydrozoa: Porpitidae) Larval and Colonial Phases" Diversity 16, no. 7: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16070425
APA StyleSantiago-Valentín, J. D., Bautista-Guerrero, E., Rodríguez-Troncoso, A. P., Franco-Gordo, M. d. C., Razo-López, M. A., & Godínez-Domínguez, E. (2024). Morphological and Molecular Identification of Porpita porpita (Hydrozoa: Porpitidae) Larval and Colonial Phases. Diversity, 16(7), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16070425







