Hemolymph Parameters Are a Useful Tool for Assessing Bivalve Health and Water Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Collection Areas
2.3. Hemolymph Sampling
2.4. Determination of Hemolytic Activity
2.5. Hemagglutination Reaction
2.6. Protein Concentration Assay
2.7. Haemocyte Oxygen-Dependent Systems Estimation
2.8. Phagocytosis Assay
2.9. Hemocyte Count and Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
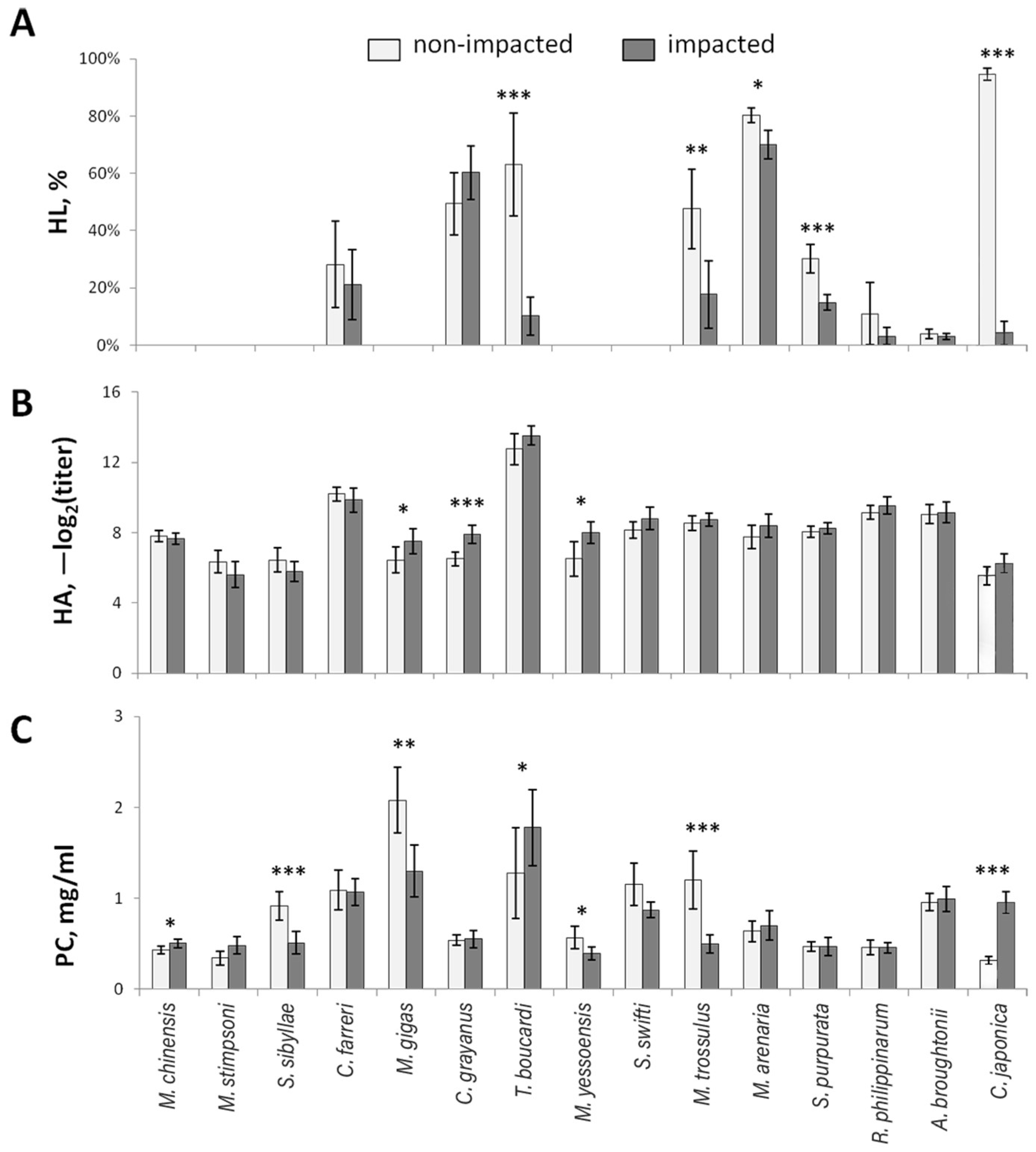
3.1. Hemolytic Activity
3.2. Hemagglutination
3.3. Protein Concentration
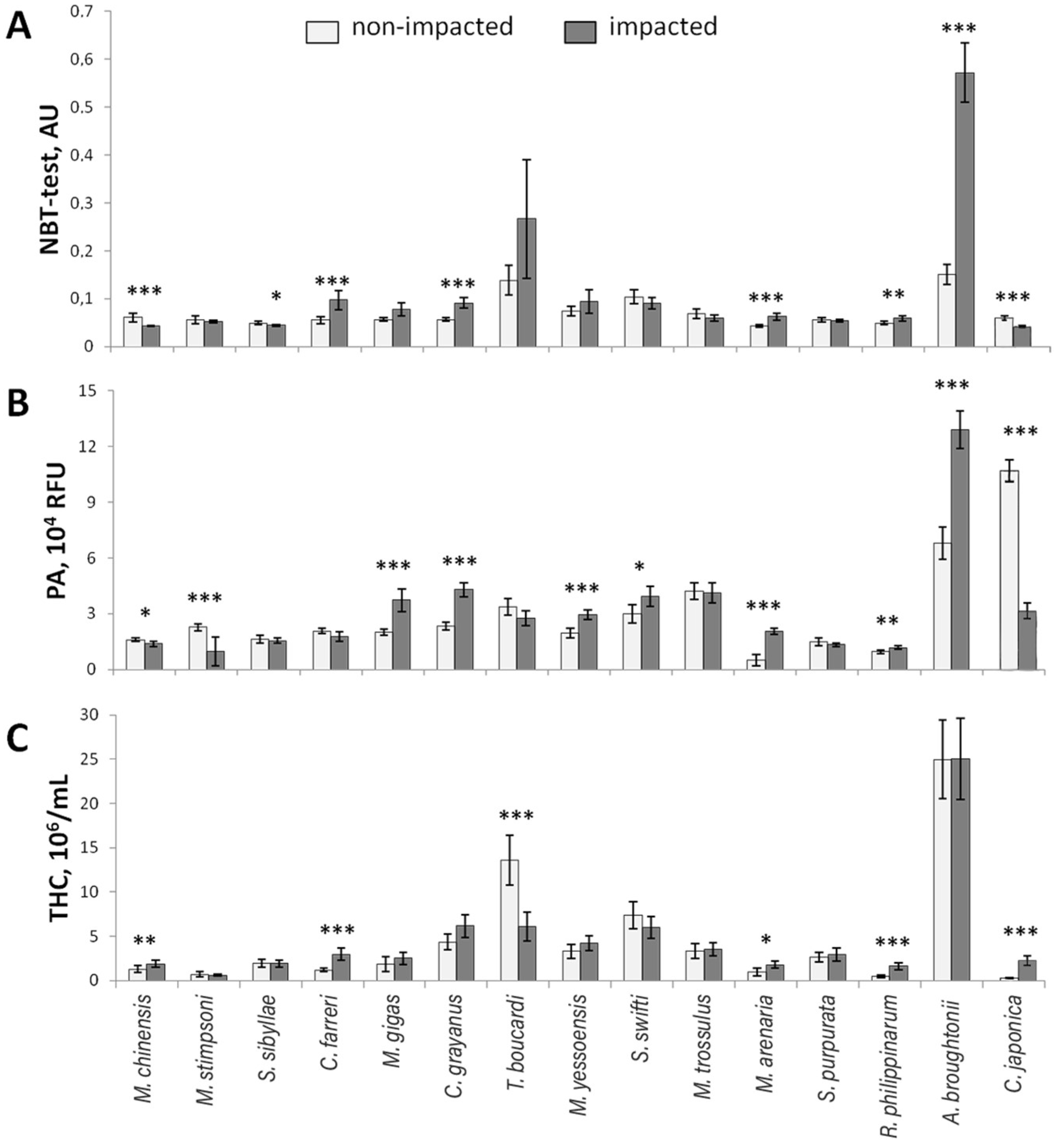
3.4. Nitroblue Tetrazolium Reduction Test
3.5. Phagocytic Activity
3.6. Total Hemocyte Count
3.7. Hemocyte Populations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Witeska, M.; Kondera, E.; Lugowska, K.; Bojarski, B. Hematological Methods in Fish—Not Only for Beginners. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanc, A.; Haskovic, E.; Jeremic, S.; Dekic, R. Hematological Evaluation of Welfare and Health of Fish. Prax. Vet. 2005, 53, 191–202. [Google Scholar]
- Clauss, T.M.; Dove, A.D.M.; Arnold, J.E. Hematologic Disorders of Fish. Vet. Clin. N. Am.—Exot. Anim. Pract. 2008, 11, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, K.R. Fish Hematology and Associated Disorders. Vet. Clin. N. Am.—Exot. Anim. Pract. 2015, 18, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docan, A.; Grecu, I.; Dediu, L. Use of Hematological Parameters as Assessment Tools in Fish Health Status. J. Agroaliment. Process. Technol. 2018, 24, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, F. Fish Hematology Analysis as an Important Tool of Aquaculture: A Review. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, L.M.; Fisher, W.S. Appraisal of Prospective Bivalve Immunomarkers. Biomarkers 1999, 4, 510–530. [Google Scholar]
- Donaghy, L.; Lambert, C.; Choi, K.S.; Soudant, P. Hemocytes of the Carpet Shell Clam (Ruditapes decussatus) and the Manila Clam (Ruditapes philippinarum): Current Knowledge and Future Prospects. Aquaculture 2009, 297, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestal, C.; Roch, P.; Renault, T.; Pallavicini, A.; Paillard, C.; Novoa, B.; Oubella, R.; Venier, P.; Figueras, A. Study of Diseases and the Immune System of Bivalves Using Molecular Biology and Genomics. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2008, 16, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, T. Immunotoxicological Effects of Environmental Contaminants on Marine Bivalves. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolnikova, Y.; Trubetskaya, E.; Beleneva, I.A.; Grinchenko, A.V.; Kumeiko, V.V. Fluorescent in Vitro Phagocytosis Assay Differentiates Hemocyte Activity of the Bivalve Molluscs Modiolus kurilensis (Bernard, 1983) Inhabiting Impacted and Non-Impacted Water Areas. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2015, 41, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumeiko, V.V.; Sokolnikova, Y.N.; Grinchenko, A.V.; Mokrina, M.S.; Kniazkina, M.I. Immune State Correlates with Histopathological Level and Reveals Molluscan Health in Populations of Modiolus kurilensis by Integral Health Index (IHI). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 154, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdol, M.; Gomez-Chiarri, M.; Castillo, M.G.; Figueras, A.; Fiorito, G.; Moreira, R.; Novoa, B.; Pallavicini, A.; Ponte, G.; Roumbedakis, K.; et al. Immunity in Molluscs: Recognition and Effector Mechanisms, with a Focus on Bivalvia. In Advances in Comparative Immunology; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 225–341. ISBN 9783319767680. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Immunological Assays of Hemocytes in Molluscan Bivalves as Biomarkers to Evaluate Stresses for Aquaculture. Bull. Jpn. Fish. Res. Educ. Agency 2021, 50, 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- de la Ballina, N.R.; Maresca, F.; Cao, A.; Villalba, A. Bivalve Haemocyte Subpopulations: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 826255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balbi, T.; Auguste, M.; Ciacci, C.; Canesi, L. Immunological Responses of Marine Bivalves to Contaminant Exposure: Contribution of the -Omics Approach. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 618726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girón-Pérez, M.I. Relationships between Innate Immunity in Bivalve Molluscs and Environmental Pollution. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2010, 7, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Leljuhin, S.; Shirjakov, D.; Razumova, J. The Structure and Raw Materials Base of Fisheries Industry in the Far East. Reg. Econ. Manag. Electron. Sci. J. 2018, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Saltykov, M.; Komogortseva, Z.; Kalyagin, M. International Trade of Aquatic Biological Resources with the Countries of Northeast Asia as a Factor of the Economic Growth of the Far Eastern Federal District Territories. Tomsk. State Univ. J. Econ. 2024, 65, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhudarova, S.M.; Gusakova, A.P.; Saltykov, M.A. Analysis of Development of the Fish Market of the Primorsk Territory and Vladivostok. Bull. Sci. Educ. 2018, 1, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lukyanova, O.; Cherkashin, S.; Simokon, M. Overview of the Current Ecological State of the Peter the Great Bay (2000–2010). Vestn. Far East. Branch Russ. Acad. Sci. 2012, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhenkova, S.; Chernova, E. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution of the Peter the Great Bay (North-West Pacific Region) Using Brown Algae. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2020, 8, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostov, I.D.; Rudykh, N.I.; Rostov, V.I.; Vorontsov, A.A. Tendencies of Climatic and anthropogenic Changes of the Marine Environments in the Coastal Areas of Russia in the Japan for the Last Decades. Izv. TINRO 2016, 186, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galysheva, Y.A. Biological Consequences of Organic Pollution for Marine Coastal in the Russian Part of the Japan Sea. Izv. TINRO 2009, 158, 209–227. [Google Scholar]
- Kiku, D.P.; Kovekovdova, L.T. Trace Elements in the Oyster Crassostrea gigas from Peter the Great Bay (Japan Sea). Izv. TINRO 2007, 150, 400–407. [Google Scholar]
- Moshchenko, A.V.; Belan, T.A.; Borisov, B.M.; Lishavskaya, T.S.; Sevastianov, A.V. Modern Contamination of Bottom Sediments and Ecological State of Macrozoobenthos in the Coastal Zone at Vladivostok (Peter the Great Bay, Japan Sea). Izv. TINRO 2019, 196, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravel, E.V.; Podgurskaya, O.V. Early Development of Sand Dollar Scaphechinus Mirabilis in the Water from Different Areas of Peter the Great Bay (Japan Sea). Izv. TINRO 2014, 178, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaschenko, M.A.; Almyashova, T.N.; Zhadan, P.M. Long-Term and Seasonal Dynamics of the Gonad State in the Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius under Anthropogenic Pollution (Amursky Bay, Sea of Japan). Vestn. Far East. Branch Russ. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yurchenko, O.V.; Vaschenko, M.A. Morphology of Spermatogenic and Accessory Cells in the Mussel Modiolus kurilensis under Environmental Pollution. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 70, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syasina, I.G.; Shcheblykina, A.V. Morphofunctional Characterization of the Reproductive System of the Gastropods Littorina brevicula, L. Mandshurica, and Nucella heyseana from Uncontaminated and Contaminated Areas of Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2007, 33, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khristoforova, N.K.; Naumov, Y.A.; Arzamastsev, I.S. Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of Vostok Bay (Japan Sea). Izv. TINRO 2004, 136, 278–289. [Google Scholar]
- Khristoforova, N.K.; Lazaryuk, A.Y.; Zhuravel, E.V.; Boychenko, T.V.; Emelyanov, A.A. Vostok Bay: Interseasonal Changes in Hydrological, Hydrochemical and Microbiological Properties. Izv. TINRO 2023, 203, 906–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barysheva, V.S.; Chernova, E.N.; Patrusheva, O.V. Pollution of the Marine Environment of the Vostok Bay (Japan Sea) by Organic Matter in 2016–2018. Vestn. Far East. Branch Russ. Acad. Sci. 2019, 2, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, V.G.; Kasyanov, V.L.; Adrianov, A.V.; Chernyshev, A.V.; Shulkin, V.M.; Semykina, G.I. The Ecological State and Bottom Communities in the Patrokl Bight and Sobol Bight (Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan): The Past and the Present. Vestn. Far East. Branch Russ. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Khristoforova, N.K.; Boychenko, T.V.; Kobzar, A.D. Hydrochemical and Microbiological Assessment of the Current State of the Vostok Bay. Vestn. Far East. Branch Russ. Acad. Sci. 2020, 210, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzoleva, L.S.; Bogatyrenko, E.A.; Golozubova, Y.S.; Kim, A.V. The Influence of Anthropogenous Pollution on Quality of Coastal Waters of Recreational Zones of Primorsky Kray. Fundam. Res. 2014, 11, 2423–2425. [Google Scholar]
- Galysheva, Y.A.; Khristoforova, N.K. Environments and Macrobenthos in the Vostok Bay (Japan Sea) in Conditions of Anthropogenic Impact. Izv. TINRO 2007, 149, 270–309. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoryeva, N.I. Environmental Conditions in Coastal Biotopes of Vostok Bay (Sea of Japan) as Habitats for Gastropods and Bivalves. Bull. Russ. Far East. Malacol. Soc. 2022, 26, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashchenko, M.A.; Zhadan, P.M.; Almyashova, T.N.; Kovalyova, A.L.; Slinko, E.N. Assessment of the Contamination Level of Bottom Sediments of Amursky Bay (Sea of Japan) and Their Potential Toxicity. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2010, 36, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigmatulina, L.V. Assessment of Anthropogenic Load of Coastal Sources on the Amursky Bay (Sea of Japan). Vestn. Far East. Branch Russ. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Chernyaev, A.P.; Nigmatulina, L.V. Quality Monitoring of Coastal Waters in Peter the Great Bay (Japan Sea). Izv. TINRO 2013, 173, 230–238. [Google Scholar]
- Tevs, K.O.; Shevchenko, O.G. Dynamics of Phytoplankton in the Coastal Waters at Vladivostok in 2019–2021. Izv. TINRO 2022, 202, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaschenko, M.A.; Zhadan, P.M. Developmental Disturbances in the Progeny of Sea Urchins as an Index of Environmental Pollution. Russ. J. Ecol. 2003, 34, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syasina, I.G.; Vaschenko, M.A.; Zhadan, P.M. Morphological Alterations in the Digestive Diverticula of Mizuhopecten Yessoensis (Bivalvia: Pectinidae) from Polluted Areas of Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan. Mar. Environ. Res. 1997, 44, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markina, Z.V.; Aizdaicher, N.A. Biotesting of Water from Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan, Using the Microalga Dunaliella Salina. Russ. J. Ecol. 2008, 39, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boychenko, T.V.; Khristohorova, N.K.; Buzoleva, L.S. Microbial indication of Coastal Waters in the Northern Amur Bay. Izv. TINRO 2009, 158, 324–332. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrieva, G.Y.; Bezverbnay, I.P.; Semikina, G.I. Microbiological Monitoring of Heavy Metal Pollution in Coastal Waters of the Peter the Great Bay. Izv. TINRO 2000, 127, 657–676. [Google Scholar]
- Grinchenko, A.; Sokolnikova, Y.; Korneiko, D.; Kumeiko, V. Dynamics of the Immune Response of the Horse Mussel Modiolus kurilensis (Bernard, 1983) Following Challenge with Heat-Inactivated Bacteria. J. Shellfish Res. 2015, 34, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Liñán, L.; Bellas, J. Practical Procedures for Selected Biomarkers in Mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis—Implications for Marine Pollution Monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschino, V.; Del Negro, P.; De Vittor, C.; Da Ros, L. Biomonitoring of a Polluted Coastal Area (Bay of Muggia, Northern Adriatic Sea): A Five-Year Study Using Transplanted Mussels. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, J.; Green, N.W.; Brooks, S.; Allan, I.J.; Ruus, A.; Gomes, T.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Schøyen, M. Blue Mussels (Mytilus edulis Spp.) as Sentinel Organisms in Coastal Pollution Monitoring: A Review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 338–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggio, C.; Tsarpali, V.; Dailianis, S. Mussel Digestive Gland as a Model Tissue for Assessing Xenobiotics: An Overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melwani, A.R.; Gregorio, D.; Jin, Y.; Stephenson, M.; Ichikawa, G.; Siegel, E.; Crane, D.; Lauenstein, G.; Davis, J.A. Mussel Watch Update: Long-Term Trends in Selected Contaminants from Coastal California, 1977–2010. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrington, J.W.; Tripp, B.W.; Tanabe, S.; Subramanian, A.; Sericano, J.L.; Wade, T.L.; Knap, A.H.; Edward, D. Goldberg’s Proposal of “the Mussel Watch”: Reflections after 40 Years. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, T.; Gregory Cope, W. Biomarker Responses of Unionid Mussels to Environmental Contaminants. In Freshwater Bivalve Ecotoxicology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 257–284. [Google Scholar]
- van der Oost, R.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P.E. Fish Bioaccumulation and Biomarkers in Environmental Risk Assessment: A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 57–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matozzo, L.B.D.M.P.V. Effects of Copper and Cadmium Exposure on Functional Responses of Hemocytes in the Clam, Tapes Philippinarum. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnaire, B.; Soletchnik, P.; Faury, N.; Kerdudou, N.; Le Moine, O.; Renault, T. Analysis of Hemocyte Parameters in Pacific Oysters, Crassostrea gigas, Reared in the Field—Comparison of Hatchery Diploids and Diploids from Natural Beds. Aquaculture 2007, 264, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouin, H.; Pellerin, J.; Fournier, M.; Pelletier, E.; Richard, P.; Pichaud, N.; Rouleau, C.; Garnerot, F. Physiological Effects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons on Soft-Shell Clam Mya Arenaria. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 82, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.C.; Sullivan, J.T. Effects of Heavy Metals on Phagocytosis by Molluscan Hemocytes. Mar. Environ. Res. 1984, 14, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipe, R.K.; Coles, J.A. Environmental Contaminants Influencing Immunefunction in Marine Bivalve Molluscs. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1995, 5, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, J.; Farley, S.; Pipe, R. Alteration of the Immune Response of the Common Marine Mussel Mytilus edulis Resulting from Exposure to Cadmium. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1995, 22, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipe, R.K.; Coles, J.A.; Carissan, F.M.M.; Ramanathan, K. Copper Induced Immunomodulation in the Marine Mussel, Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 1999, 46, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrynda, E.A.; Pipe, R.K.; Burt, G.R.; Ratcliffe, N.A. Modulations in the Immune Defences of Mussels (Mytilus edulis) from Contaminated Sites in the UK. Aquat. Toxicol. 1998, 42, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrynda, E.; Law, R.; Dyrynda, P.; Kelly, C.; Pipe, R.; Ratcliffe, N. Changes in Immune Parameters of Natural Mussel Mytilus edulis Populations Following a Major Oil Spill (“Sea Empress”, Wales, UK). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 206, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffret, M.; Duchemin, M.; Rousseau, S.; Boutet, I.; Tanguy, A.; Moraga, D.; Marhic, A. Monitoring of Immunotoxic Responses in Oysters Reared in Areas Contaminated by the “Erika” Oil Spill. Aquat. Living Resour. EDP Sci. 2004, 17, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, W.S. Relationship of Amebocytes and Terrestrial Elements to Adult Shell Deposition in Eastern Oysters. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 353–367. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, W.S. Antimicrobial Activity of Copper and Zinc Accumulated in Eastern Oyster Amebocytes. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 321–351. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, F.-L.E.; La Peyre, J.F. Effect of Environmental Factors and Parasitism on Hemolymph Lysozyme and Protein of American Oysters (Crassostrea virginica). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1989, 54, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, B.; Paillard, C.; Auffret, M. Alterations in Hemolymph and Extrapallial Fluid Parameters in the Manila Clam, Ruditapes philippinarum, Challenged with the Pathogen Vibrio Tapetis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2000, 76, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, B.; Gagné, F.; Fortier, M.; Fournier, M. An In-Situ Study of the Impacts of Urban Wastewater on the Immune and Reproductive Systems of the Freshwater Mussel Elliptio Complanata. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 150, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.A.; Roesijadi, G. Metallothionein (MT) Gene Expression and Cadmium-Induced Immunotoxicity in Hemocytes of the Eastern Oyster Crassostrea virginica. Mar. Environ. Res. 2000, 50, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouilly, K.; Gagnaire, B.; Thomas-Guyon, H.; Bonnard, M.; Renault, T.; Miramand, P.; Lapègue, S. Effects of Cadmium on Aneuploidy and Hemocyte Parameters in the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gómez-Mendikute, A.; Cajaraville, M.P. Comparative Effects of Cadmium, Copper, Paraquat and Benzo[a]Pyrene on the Actin Cytoskeleton and Production of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Mussel Haemocytes. Toxicol. Vitr. 2003, 17, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, M.; Pellerin, J.; Clermont, Y.; Morin, Y.; Brousseau, P. Effects of in Vivo Exposure of Mya Arenaria to Organic and Inorganic Mercury on Phagocytic Activity of Hemocytes. Toxicology 2001, 161, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, H.E.; Pipe, R.K. Interactive Effects of Temperature and Copper on Immunocompetence and Disease Susceptibility in Mussels (Mytilus edulis). Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 69, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T. In Vivo Effects of Heavy Metals on Cellular Defense Mechanisms of Crassostrea virginica: Total and Differential Cell Counts. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1988, 51, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T. In Vivo Effects of Heavy Metals on Cellular Defense Mechanisms of Crassostrea virginica: Phagocytic and Endocytotic Indices. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1988, 51, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaghy, L.; Hong, H.-K.; Lee, H.-J.; Jun, J.-C.; Park, Y.-J.; Choi, K.-S. Hemocyte Parameters of the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas a Year after the Hebei Spirit Oil Spill off the West Coast of Korea. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2010, 64, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.-K.; Donaghy, L.; Kang, C.-K.; Kang, H.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, H.-S.; Choi, K.-S. Substantial Changes in Hemocyte Parameters of Manila Clam Ruditapes philippinarum Two Years after the Hebei Spirit Oil Spill off the West Coast of Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 108, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandurvelan, R.; Marsden, I.D.; Gaw, S.; Glover, C.N. Waterborne Cadmium Impacts Immunocytotoxic and Cytogenotoxic Endpoints in Green-Lipped Mussel, Perna Canaliculus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142–143, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, A.; Benedetti, M.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Interactive Immunomodulation in the Mediterranean Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis under Thermal Stress and Cadmium Exposure. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 751983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandurvelan, R.; Marsden, I.D.; Glover, C.N.; Gaw, S. Assessment of a Mussel as a Metal Bioindicator of Coastal Contamination: Relationships between Metal Bioaccumulation and Multiple Biomarker Responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladhar-Chaabouni, R.; Ayadi, W.; Sahli, E.; Mokdad-Gargouri, R. Establishment of Primary Cell Culture of Ruditapes decussatus Haemocytes for Metal Toxicity Assessment. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2021, 57, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evariste, L.; Rioult, D.; Brousseau, P.; Geffard, A.; David, E.; Auffret, M.; Fournier, M.; Betoulle, S. Differential Sensitivity to Cadmium of Immunomarkers Measured in Hemocyte Subpopulations of Zebra Mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evariste, L.; Auffret, M.; Audonnet, S.; Geffard, A.; David, E.; Brousseau, P.; Fournier, M.; Betoulle, S. Functional Features of Hemocyte Subpopulations of the Invasive Mollusk Species Dreissena polymorpha. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, W.-X. Immune Responses of Oyster Hemocyte Subpopulations to In Vitro and In Vivo Zinc Exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 242, 106022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. Morphological and Functional Characterization of Clam Ruditapes philippinarum Haemocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Giuliani, M.E.; d’Errico, G.; Keiter, S.H.; Cormier, B.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Microplastics as Vehicles of Environmental PAHs to Marine Organisms: Combined Chemical and Physical Hazards to the Mediterranean Mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Milan, M.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; d’Errico, G.; Pauletto, M.; Bargelloni, L.; Regoli, F. Pollutants Bioavailability and Toxicological Risk from Microplastics to Marine Mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 198, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, X.; Sun, T.; Wang, Y. BDE-47 Exposure Changed the Immune Function of Haemocytes in Mytilus edulis: An Explanation Based on ROS-Mediated Pathway. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 182, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bado-Nilles, A.; Gagnaire, B.; Thomas-Guyon, H.; Le Floch, S.; Renault, T. Effects of 16 Pure Hydrocarbons and Two Oils on Haemocyte and Haemolymphatic Parameters in the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg). Toxicol. Vitr. 2008, 22, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannam, M.L.; Bamber, S.D.; Galloway, T.S.; John Moody, A.; Jones, M.B. Effects of the Model PAH Phenanthrene on Immune Function and Oxidative Stress in the Haemolymph of the Temperate Scallop Pecten Maximus. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renwrantz, L. Internal Defence System of Mytilus edulis. In Neurobiology of Mytilus edulis; Stefano, G.B., Ed.; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 1990; pp. 256–275. [Google Scholar]
- Fries, C.R.; Tripp, M.R. Depression of Phagocytosis in Mercenaria Following Chemical Stress. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1980, 4, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matozzo, V. Aspects of Eco-Immunology in Molluscs. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2016, 13, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Nusetti, O.A.; Marcano, L.; Zapata, E.; Nusetti, S.; Esclapes, M.; Lodeiros, C. Immunological and Antioxidant Enzyme Responses in the Pearl Oyster Pinctada Imbricata (Mollusca: Pteridae) Exposed to Sublethal Levels of Fuel Oil No 6. Interciencia 2004, 29, 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Andreyeva, A.Y.; Efremova, E.S.; Kukhareva, T.A. Morphological and Functional Characterization of Hemocytes in Cultivated Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and Effect of Hypoxia on Hemocyte Parameters. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Chiarri, M.; Warren, W.C.; Guo, X.; Proestou, D. Developing Tools for the Study of Molluscan Immunity: The Sequencing of the Genome of the Eastern Oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, D.L.; Cope, W.G. The Status of Mussel Health Assessment and a Path Forward. Freshw. Mollusk Biol. Conserv. 2019, 22, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, R.D. Future Directions in Breeding for Disease Resistance in Aquaculture Species. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2017, 46, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
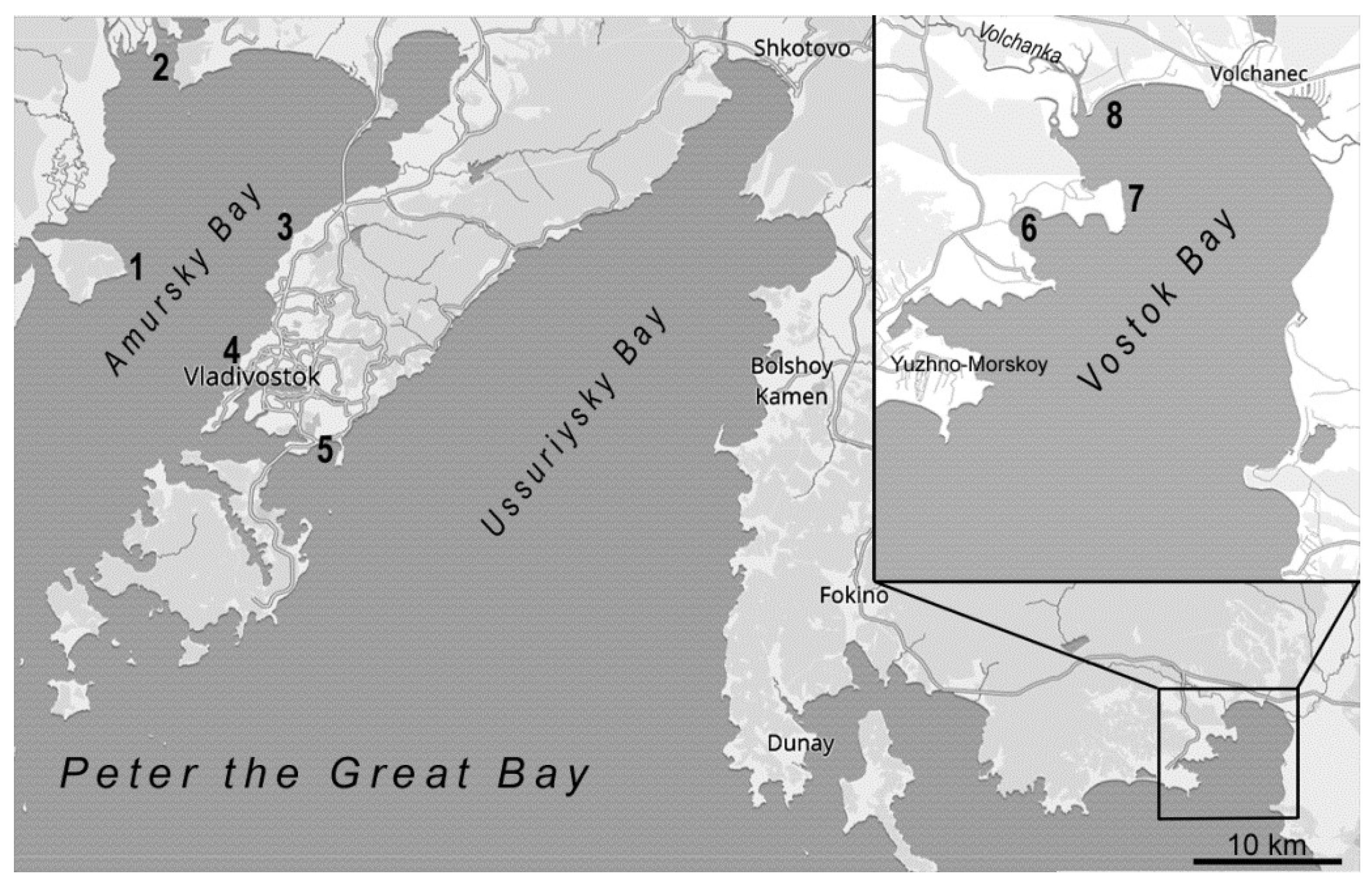

| Species | Age, Years (Shell Length, mm) | Stations | Degree of Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Impacted | Impacted | |||
| C. farreri | 4–5 (75–90) | Vostok Bay | Patrokl Bay | extremely |
| M. arenaria | 6–7 (40–50) | Vostok Bay | Patrokl Bay | |
| S. sibyllae | 5–6 (95–100) | Vostok Bay | Vostok Cove | |
| M. chinensis | 5–6 (60–70) | Vostok Bay | Vostok Cove | |
| M. stimpsoni | 6–7 (50–55) | Vostok Bay | Vostok Cove | |
| C. japonica | 4–7 (20–30) | Tavrichansky Estuary | Vostok Cove (Volchanka Estuary) | |
| S. swifti | 4–6 (80–115) | Vostok Bay | Sredneya Bay | strongly |
| T. boucardi | 4–5 (35–40) | Cape Peschany | Sportivnaya Gavan Bay | |
| M. yessoensis | 5–7 (110–130) | Vostok Bay | Sportivnaya Gavan Bay | |
| M. gigas | 6–7 (100–115) | Vostok Bay | Cape Krasny | moderate |
| C. grayanus | 6–7 (50–80) | Vostok Bay | Cape Krasny | |
| M. trossulus | 4–5 (50–60) | Vostok Bay | Cape Krasny | |
| S. purpurata | 5–7 (50–55) | Vostok Bay | Cape Krasny | |
| R. philippinarum | 4–5 (35–40) | Vostok Bay | Cape Krasny | |
| A. broughtonii | 5–6 (80–90) | Cape Peschany | Cape Krasny | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grinchenko, A.; Sokolnikova, Y.; Tumas, A.; Mokrina, M.; Tsoy, E.; Buriak, I.; Kumeiko, V.; Onishchenko, M. Hemolymph Parameters Are a Useful Tool for Assessing Bivalve Health and Water Quality. Diversity 2024, 16, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16070404
Grinchenko A, Sokolnikova Y, Tumas A, Mokrina M, Tsoy E, Buriak I, Kumeiko V, Onishchenko M. Hemolymph Parameters Are a Useful Tool for Assessing Bivalve Health and Water Quality. Diversity. 2024; 16(7):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16070404
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrinchenko, Andrei, Yulia Sokolnikova, Ayna Tumas, Mariia Mokrina, Elizaveta Tsoy, Ivan Buriak, Vadim Kumeiko, and Mariia Onishchenko. 2024. "Hemolymph Parameters Are a Useful Tool for Assessing Bivalve Health and Water Quality" Diversity 16, no. 7: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16070404
APA StyleGrinchenko, A., Sokolnikova, Y., Tumas, A., Mokrina, M., Tsoy, E., Buriak, I., Kumeiko, V., & Onishchenko, M. (2024). Hemolymph Parameters Are a Useful Tool for Assessing Bivalve Health and Water Quality. Diversity, 16(7), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16070404






