How Do Zooplankton Communities Respond to Environmental Factors across the Subsidence Wetlands Created by Underground Coal Mining in the North China Plain?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
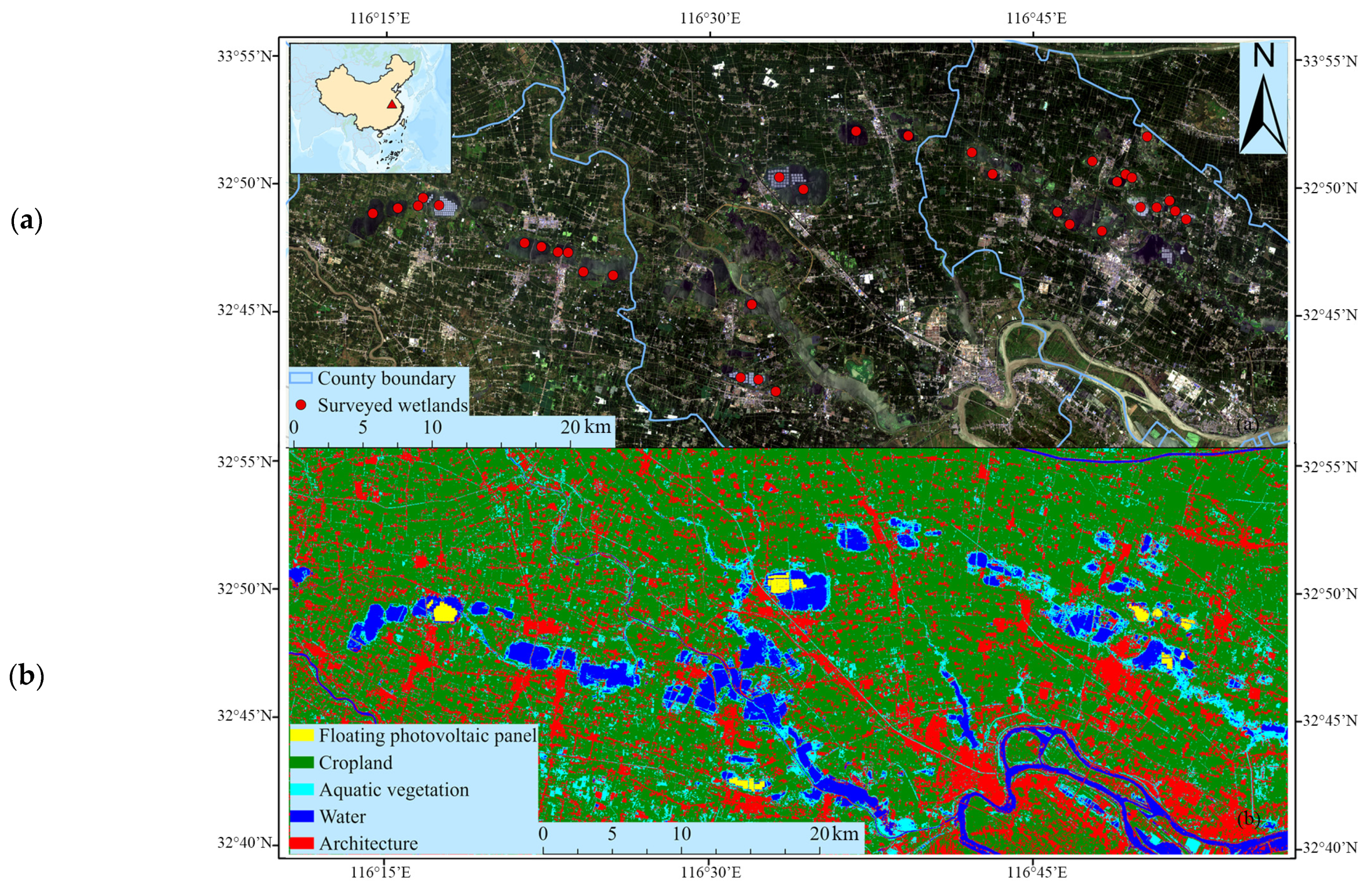
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Zooplankton Sampling
2.3. Habitat Variable
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Habitat Variables
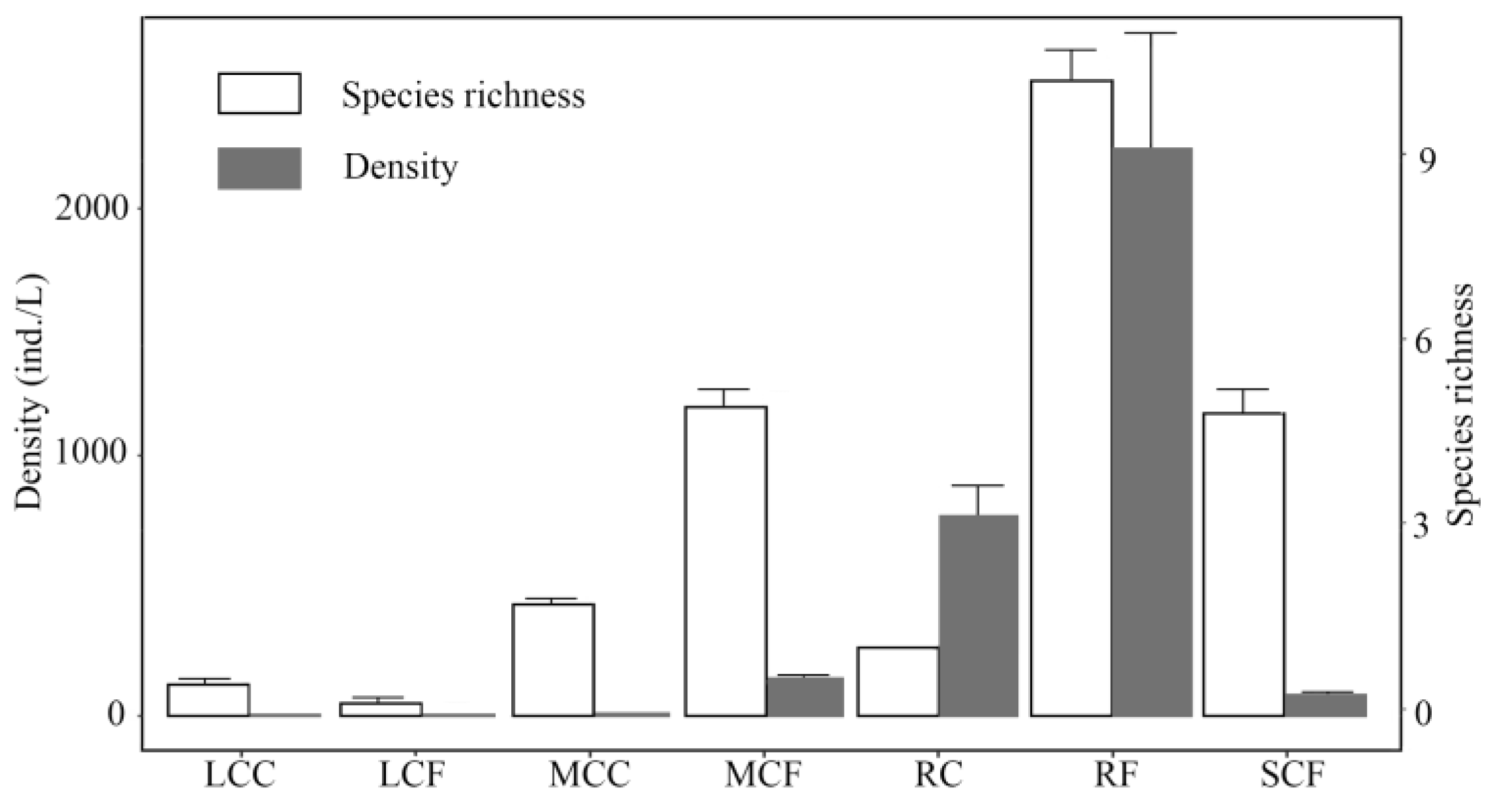
3.2. Composition of Zooplankton Community
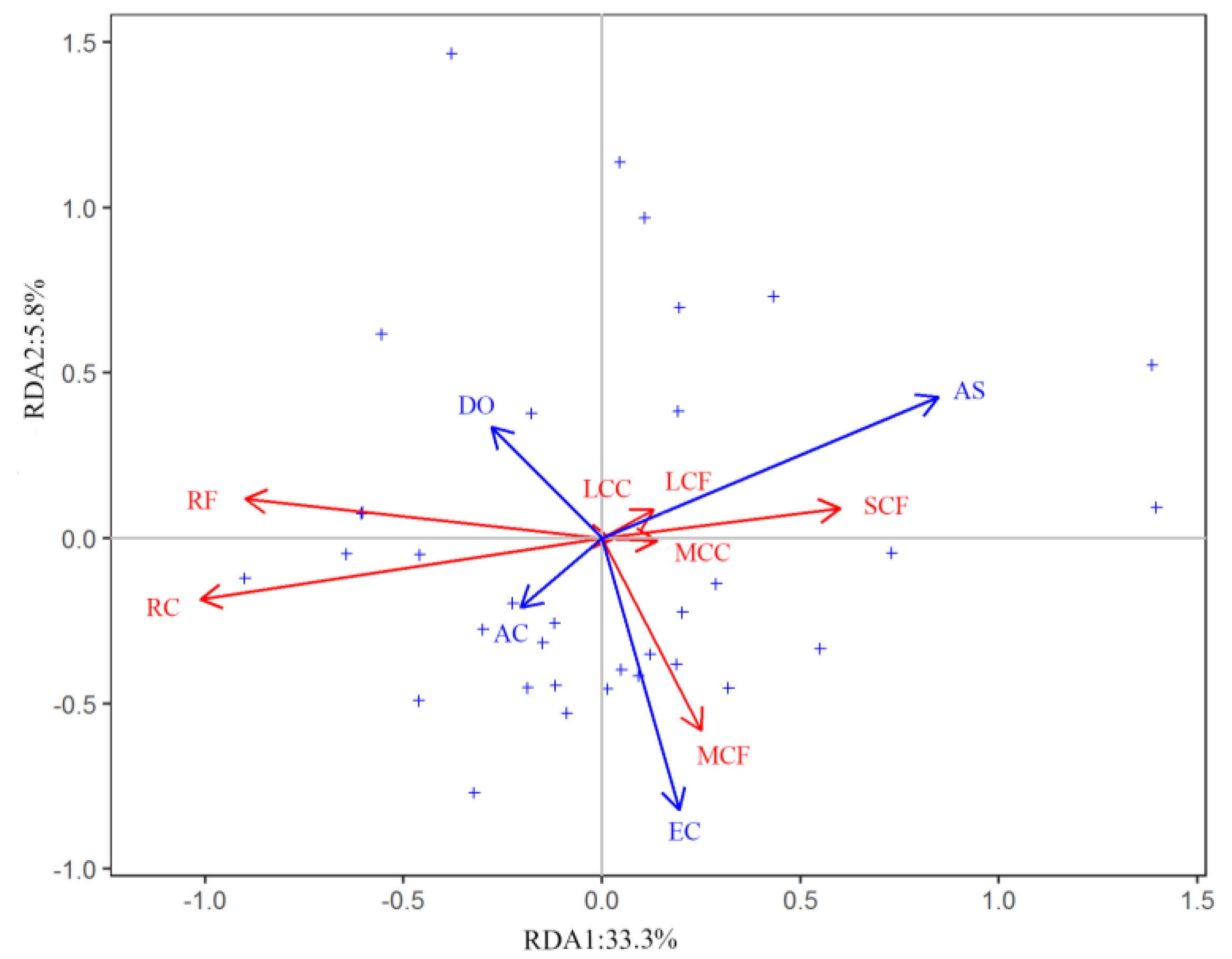
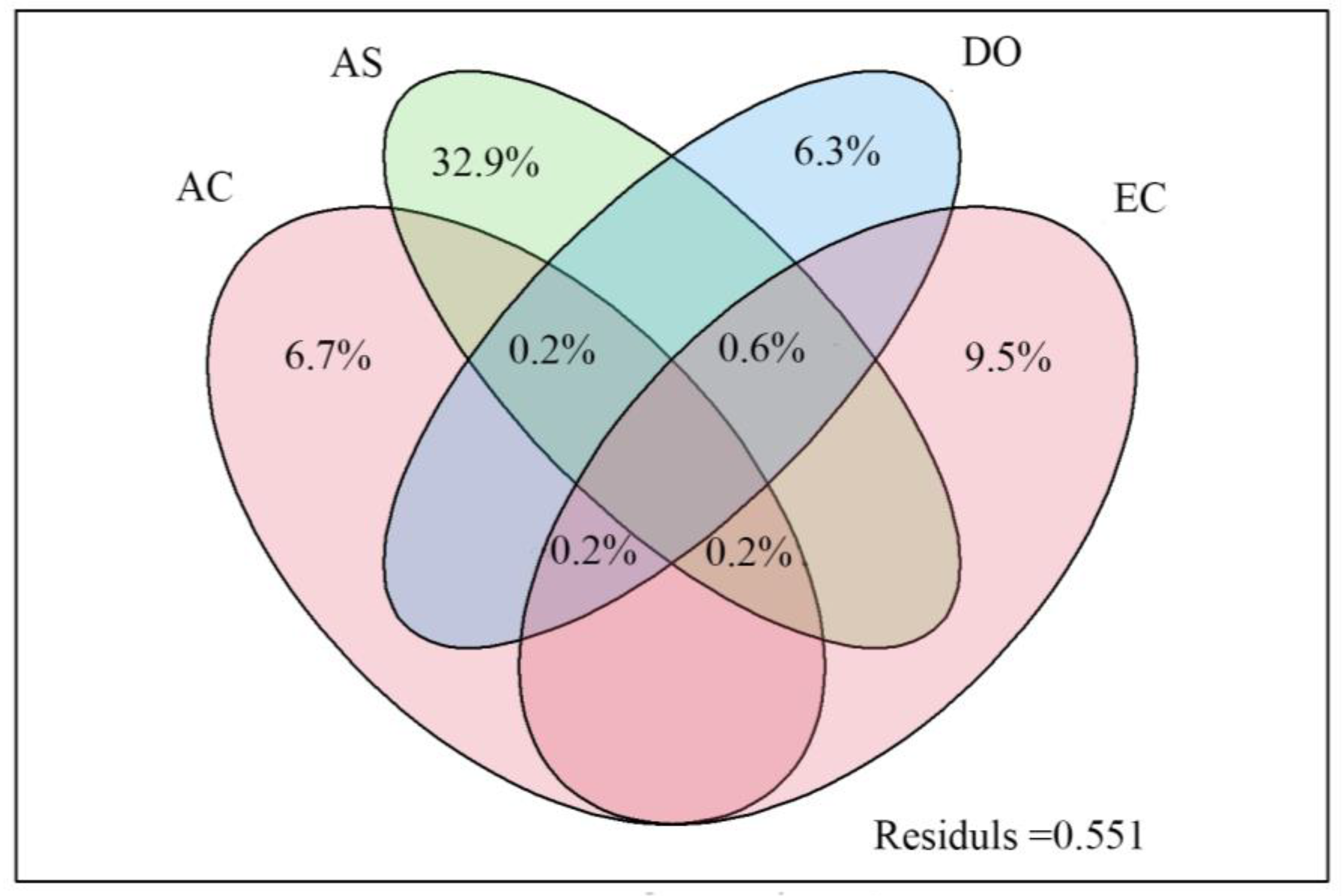
3.3. Effects of Environmental Variables on Zooplankton Community Diversity
3.4. Correlation between Functional Groups of Zooplankton and Habitat Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kingsford, R.T.; Basset, A.; Jackson, L. Wetlands: Conservation’s poor cousins. Aquat. Conserv. 2016, 26, 892–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, S.; Zha, D.; Zhang, Y.; de Boer, W.F. Waterbird Communities in Subsidence Wetlands Created by Underground Coal Mining in China: Effects of Multi-Scale Environmental and Anthropogenic Variables. Environ. Conserv. 2018, 46, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liang, Y.; Li, C.; Svenning, J.C. How do rotifer communities respond to floating photovoltaic systems in the subsidence wetlands created by underground coal mining in China? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Niu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, H. Global wetlands: Potential distribution, wetland loss, and status. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zedler, J.B.; Kercher, S. Wetland resources: Status, trends, ecosystem services, and restorability. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2005, 30, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegleb, G.; Dahms, H.U.; Byeon, W.; Choi, G. To what extent can constructed wetlands enhance biodiversity. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2017, 8, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Inyang, H.I.; Daniels, J.L.; Otto, F.; Struthers, S. Environmental issues from coal mining and their solutions. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Dai, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, L. Characteristics of zooplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in the South Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Jiang, F.; Chen, H.; Dibar, D.T.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Z. Temporal and spatial variations in zooplankton communities in relation to environmental factors in four floodplain lakes located in the middle reach of the Yangtze River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ji, L.; Chen, X.; Ni, J.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, M. Distribution of Zooplankton Functional Groups in the Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Water 2022, 14, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrehiwot, M. The overriding role of hydrological factors on zooplankton community: Evidence from a shallow tropical reservoir (Koka, Ethiopia). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29009–29018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, G.; Sun, J.; Xu, W. Effects of terrestrial inputs on mesozooplankton community structure in bohai bay, China. Diversity 2022, 14, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, R.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Lv, C.; Xu, J. Response of planktonic diversity and stability to environmental drivers in a shallow eutrophic lake. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilaka, M.L.; Bao, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y. Antibiotic pollution of planktonic ecosystems: A review focused on community analysis and the causal chain linking individual-and community-level responses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 1199–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, F. Are zooplankton useful indicators of water quality in subtropical lakes with high human impacts? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.J.; Han, S.R.; Choi, I.C.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Cheon, S.U.; Cho, K. Evaluation of physico-chemical parameters regulating zooplankton community structure in the Geum River, Korea. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2020, 19, 352–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, J.; Filker, S.; Stoeck, T.; Bi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Song, W. Spatio-temporal patterns of zooplankton in a main-stem dam affected tributary: A case study in the Xiangxi River of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, C.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Beisner, B.E. Environmental drivers of taxonomic and functional variation in zooplankton diversity and composition in freshwater lakes across Canadian continental watersheds. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2022, 67, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amritha, P.; Varunprasath, K. Anthropogenic factors change the ecological condition of wetlands in the Southern Kerala Districts in India. India II: Climate Change Impacts, Mitigation and Adaptation in Developing Countries. In India II: Climate Change Impacts, Mitigation and Adaptation in Developing Countries; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; He, H.S.; Liu, K.; Du, H.; Krohn, J. Impact of historical pattern of human activities and natural environment on wetland in Heilongjiang River Basin. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.W.; Chang, P.H.; Huang, Y.S.; Lin, T.S.; Yang, S.D.; Ye, X.L.; Tong, Z.H.; Guo, S.R.; Ni, H.S.; Cheng, Z.C. Effects of floating photovoltaic systems on water quality of aquaculture ponds. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, E.; Zhang, L.; Wei, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Long-term succession characteristics and driving factors of zooplankton communities in a typical subtropical shallow lake, central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 49435–49449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, C. Spatial Differences in Zooplankton Community Structure between Two Fluvial Lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River: Effects of Land Use Patterns and Physicochemical Factors. Diversity 2022, 14, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, G.; Xiao, W.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y. Farmland damage and its impact on the overlapped areas of cropland and coal resources in the eastern plains of China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 86, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ning, Z.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, P.; Sun, R.; Yang, X.; Liu, H. A novel calculation method of subsidence waterlogging spatial information based on remote sensing techniques and surface subsidence prediction. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 335, 130336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hu, B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Jia, X.; Li, J. Research on the Settlement Regulation and Stability of Large Building Foundation over Gobs: A Case Study in the Xiangcheng Coal Mine, China. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, X.; Xiao, W.; Tang, Y. A quantitative assessment of vulnerability using social-economic-natural compound ecosystem framework in coal mining cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hu, Z.; Li, P.; Yuan, D.; Wang, W.; Yang, K. The optimal framework and model to balance underground coal mining and cropland protection in Jining, eastern China. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Su, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Sun, A. A boundary model of terrain reconstruction in a coal-mining subsidence waterlogged area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zha, D.; Yang, S.; Huang, Z.Y.X.; de Boer, W.F. Assembly processes of waterbird communities across subsidence wetlands in China: A functional and phylogenetic approach. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chang, J.; Luo, P.; Kang, Y.; Li, S. Landscape dynamics and human disturbance processes in wetlands in a mining city: A case study in Huaibei, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pociecha, A.; Wojtal, A.Z.; Szarek-Gwiazda, E.; Cieplok, A.; Ciszewski, D.; Kownacki, A. Response of Cladocera fauna to heavy metal pollution, based on sediments from subsidence ponds downstream of a mine discharge (S. Poland). Water 2019, 11, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pęczuła, W.; Szczurowska, A.; Poniewozik, M. Phytoplankton Community in Early Stages of Reservoir Development—A Case Study from the Newly Formed, Colored, and Episodic Lake of Mining-Subsidence Genesis. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wan, L.; Zhou, Z. Effects of Stream Connectivity on Phytoplankton Diversity and Community Structure in Sunken Lakes: A Case Study from an August Survey. Diversity 2023, 15, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, F.T.T.; De, M.L.; Vanhamel, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Gianuca, A.T.; Verbeek, L. Bacterioplankton Assembly Along a Eutrophication Gradient Is Mainly Structured by Environmental Filtering, Including Indirect Effects of Phytoplankton Composition. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 85, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fintelman-Oliveira, E.; Kruk, C.; Lacerot, G.; Klippel, G.; Branco, C.W.C. Zooplankton functional groups in tropical reservoirs: Discriminating traits and environmental drivers. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazonato, A.J.; Silva, L.C.; Saggio, A.A.; Rocha, O. Zooplankton communities as eutrophication bioindicators in tropical reservoirs. Biota Neotrop. 2014, 14, e20140018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y. Overview of solid backfilling technology based on coal-waste underground separation in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Huang, X.F. A Manual for Freshwater Plankton Research; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991; pp. 1–427. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J. Fauna Sinica: Freshwater Rotifera; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, S.C.; Du, N.S. Fauna Sinica: Crustacean Freshwater Cladocera; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979; pp. 1–273. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of Zoology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Fauna Sinica: Crustacean; FreshwaterCopepoda; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979; pp. 1–417. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti, F.; Vogt, M.; Righetti, D.; Guilhaumon, F.; Ayata, S.D. Do functional groups of planktonic copepods differ in their ecological niches? J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwagona, P.C.; Ma, C.X.; Yu, H.X. Seasonal dynamics of Zooplankton functional groups in relation to environmental variables in Xiquanyan Reservoir, Northeast China. Ann. Limnol.-Int. J. Limnol. 2018, 54, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Environmental Protection Bureau (Sepb), 2002, Methods of Monitoring and Analysis for Water and Wastewate, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- Chi, S.; Li, M.; Zheng, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, M. Macroinvertebrate communities in the Big East Lake water network in relation to environmental factors. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.; Hu, J.; Li, M.; Wang, C. What Are the Relationships between Plankton and Macroinvertebrates in Reservoir Systems? Water 2023, 15, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Amzil, H.; Fang, W.; Xu, L.; Lu, A.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Pan, J.; Wei, X. Phytoplankton-Zooplankton Community Structure in Coal Mining Subsidence Lake. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Qu, X.; Xie, K. Eutrophication and nutrient limitation in the aquatic zones around Huainan coal mine subsidence areas, Anhui, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Noges, P.; Davidson, T.A.; Haberman, J.; Nõges, T.; Blank, K.; Torben, L.; Søndergaard, M.E.; Sayer, C.; Laugaste, R.; et al. Zooplankton as indicators in lakes: A scientific-based plea for including zooplankton in the ecological quality assessment of lakes according to the European Water Framework Directive (WFD). Hydrobiologia 2011, 676, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, L.; Chen, X.; Pang, Z.; Ge, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, M.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, X. Spectral characteristic changes of dissolved organic matter in aquatic systems under the influences of agriculture and coal mining. J. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 2549–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Chen, G. Characteristics of Water Pollution and Evaluation of Water Quality in Subsidence Water Bodies in Huainan Coal Mining Areas, China. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 2857700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lai, Z.; Liu, E.; Yang, W.; Liu, Q. Spatiotemporal Variation of Planktonic Rotifers in Surface Water of a Eutrophic Reservoir in the Southern Subtropical Region of China (2011–2020). Inland. Water Biol. 2023, 16, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharip, Z. Spatio-temporal variation of zooplankton community structure in tropical urban waterbodies along trophic and urban gradients. Ecol. Process. 2019, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Jiang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Feng, J. Effects of Environmental Concentrations of Total Phosphorus on the Plankton Community Structure and Function in a Microcosm Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.J.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, P.Z.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.J.; et al. Interactive effects of nutrients and salinity on zooplankton in subtropical plateau lakes with contrasting water depth. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Joniak, T. Zooplankton diversity and macrophyte biometry in shallow water bodies of various trophic state. Hydrobiologia 2016, 774, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzanelli, M.; Warming, T.P.; Christoffersen, K.S. Emergent and floating-leaved macrophytes as refuge for zooplankton in a eutrophic temperate lake without submerged vegetation. Hydrobiologia 2008, 605, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, M.; Fakour, H.; Lo, S.L.; Yuan, M.H.; Chen, C.K.; Mobasser, S.; Muangthai, I. Aquavoltaics Feasibility Assessment: Synergies of Solar PV Power Generation and Aquaculture Production. Water 2023, 15, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della, B.V.; Mancini, L. Freshwater diatom and macroinvertebrate diversity of coastal permanent ponds along a gradient of human impact in a Mediterranean eco-region. Hydrobiologia 2009, 634, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.D.; Dodson, S.I. Land Use, Primary Productivity, and Lake Area as Descriptors of Zooplankton Diversity. Ecology 2005, 86, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiyar, Y.; Arafat, M.Y.; Andrabi, S.; Tak, H.I. Zooplankton: The significant ecosystem service provider in aquatic environment. In Bioremediation and Biotechnology, Vol 3: Persistent and Recalcitrant Toxic Substances; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.J. Suppression of rotifer populations by Daphnia: A review of the evidence, the mechanisms, and the effects on zooplankton community structure1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 1286–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, R.; Yang, C.; Huang, K.; Han, G.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Letcher, R.J.; Liu, C. Application of agricultural pesticides in a peak period induces an abundance decline of metazoan zooplankton in a lake ecosystem. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneberg, P.; Celewicz-Gołdyn, S.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N. Ecological value of macrophyte cover in creating habitat for microalgae (diatoms) and zooplankton (rotifers and crustaceans) in small field and forest water bodies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castano-Sanchez, A.; Hose, G.C.; Reboleira, A. Salinity and temperature increase impact groundwater crustaceans. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Geng, M.; Yu, J.; Du, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Su, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, F. Eutrophication decrease compositional dissimilarity in freshwater plankton communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, Y.X.; Sun, X.; Jiang, M.; Yu, H.X.; Chai, F.Y. Seasonal dynamics of zooplankton functional groups in relation to environmental factors in Genheyuan wetland of Northeast China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2023, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scientific Name | Description | Functional Group | Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotaria tardigrada | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Colurella obtusa | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Lepadella quinquecostata | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Brachionus angularis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Brachionus calycifiorus | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Brachionus forficula | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Brachionus budapestiensis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Brachionus capsuliflorus | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Brachionus urceus | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Brachionus falcatus | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Brachionus caudatus | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Brachionus diversicornis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Platyias quadricornis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Platyias militaris | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Anuraeopsis fissa | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Keratella cochlearis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Keratella valga | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Keratella qudrata | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Notholca labis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Lecane luna | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Lecane ungulata | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Lecane pioenensis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Lecane eutarsa | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Lecane closterocerca | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Lecane ludwigii | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Lecane curvicornis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Monostyla stenroosi | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Monostyla hamata | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Monostyla closterocerca | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Monostyla crenata | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Monostyla bulla | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Monostyla elachis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Asplanchna priodonta | Rotifer carnivores | RCs | |
| Ascomorpha ecaudis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Diurella rousseoeti | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Diurella stylata | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Diurella dixon-nuttalli | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Diurella collaris | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Trichocerca cylindrica | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Trichocerca capucina | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Trichocerca pusilla | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Trichocerca lophoessa | Rotifer carnivores | RCs | |
| Trichocerca elongata | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Synchaeta pectinata | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Polyarthra euryptera | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Polyarthra trigla | Rotifer carnivores | RCs | |
| Polyarthra vulgaris | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Mytilina ventralis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Pompholyx complanata | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Pedalia mira | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Filinia minuta | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Filinia terminalis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| Filinia opoliensis | Rotifer filter feeders | RFs | |
| nauplius | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Sinocalanus Burckhardt | Large crustacean filter feeders | LCFs | >1.50 |
| Schmackeria inopinus | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Schmackeria forbesi | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Heliodiaptomus serratus | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Sinodiaptomus sarsi | Large crustacean filter feeders | LCFs | >1.50 |
| Neodiaptomus schmackeri | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Eodiaptomus sinensis | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.7–1.5 |
| Onychocamptus mohammed | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Limnoithona sinensis | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Macrocyclops albidus | Medium crustacean carnivores | MCCs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Macrocyclops distinctus | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Eucylops serrulatus | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Microcyclops varicans | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Mesocyclops leuckarti | Medium crustacean carnivores | MCCs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Thermocyclops hyalinus | Medium crustacean carnivores | MCCs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Cyclops strenuus | Large crustacean carnivores | LCCs | >1.50 |
| Leptodora kindti | Large crustacean carnivores | LCCs | >1.50 |
| Diaphanosoma leuchtenbergianum | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Diaphanosoma brachyurum | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Diaphanosoma sarsi | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Diaphanosoma excisum | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Daphnia pulex | Large crustacean filter feeders | LCFs | >1.50 |
| Daphnia hyalina | Large crustacean filter feeders | LCFs | >1.50 |
| Daphnia cucullata | Large crustacean filter feeders | LCFs | >1.50 |
| Ceriodaphnia pulchella | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Ceriodaphnia cornuta | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Ceriodaphnia quadrangula | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Scapholeberis mucronata | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Moina micrura | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Moina rectirostris | Medium crustacean feeders | MCFs | 0.70–1.50 |
| Bosmina longirostris | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Bosmina fatalis | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Bosmina coregoni | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Bosminopsis Richard | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Alona guttata | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Chydorus sphaericus | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Pleuroxus hamulatus | Small crustacean filter feeders | SCFs | <0.70 |
| Habitat Variables | Description | Range | Mean | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | pH | 7.15–9.00 | 7.98 | 0.08 |
| WD (m) | Water depth | 2.10–15.10 | 6.50 | 0.50 |
| DO (mg/L) | Dissolved oxygen | 4.00–13.85 | 7.26 | 0.38 |
| EC (us/cm) | Electric conductivity | 449.37–1788.63 | 764.80 | 44.14 |
| SD (m) | Transparency | 0.23–14.8 | 6.10 | 0.48 |
| TP (mg/L) | Total phosphorus concentration | 0.06–1.22 | 0.34 | 0.04 |
| TN (mg/L) | Total nitrogen concentration | 0.26–2.2 | 1.12 | 0.34 |
| Chl-a (μg/L) | Chlorophyll-a concentration | 730.24–813.85 | 281.54 | 32.61 |
| AW (km2) | Area of each wetland | 0.04–3.91 | 1.09 | 0.17 |
| AA (km2) | Area of aquatic vegetation in each wetland | 0.01–0.30 | 0.09 | 0.01 |
| AS (km2) | Area of floating photovoltaic panel in each wetland | 0.16–1.73 | 0.64 | 0.21 |
| AC (km2) | Area of cropland in each wetland within a 2 km buffer zone | 6.70–17.22 | 10.33 | 0.43 |
| AD (km2) | Area of architecture in each wetland within a 2 km buffer zone | 2.24–7.53 | 4.41 | 0.25 |
| Scientific Name | Relative Abundance (%) | McNaughton Dominance Index (Y) |
|---|---|---|
| Polyarthra trigla | 24.53 | 0.25 |
| Trichocerca pusilla | 15.28 | 0.23 |
| Anuraeopsis fissa and | 12.18 | 0.12 |
| nauplius | 10.73 | 0.02 |
| Diversity Index | Environment Variable | Coefficient | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Species richness | pH | −0.14 | 0.01 |
| Conductivity | −0.0002 | <0.05 | |
| Total phosphorus concentration | −0.30 | <0.05 | |
| Chlorophyll-a concentration | −0.04 | <0.05 | |
| Pielou evenness index | Transparency | 0.001 | <0.05 |
| Area of floating photovoltaic panel in each wetland | −0.10 | 0.02 | |
| Shannon–Weiner diversity index | Transparency | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Total phosphorus concentration | −1.45 | 0.04 | |
| Area of floating photovoltaic panel in each wetland | −1.34 | 0.03 |
| Information | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| Axis length | 0.79 |
| Significant variables in RDA model | AS (p < 0.05) |
| EC (p < 0.05) | |
| AC (p < 0.05) | |
| DO (p < 0.05) | |
| Proportion of total variance explained | 44.95% |
| Constrained eigenvalue of RDA 1 | 0.41 |
| Constrained eigenvalue of RDA 2 | 0.07 |
| Proportion of constrained variance explained by RDA 1 | 74.05% |
| Proportion of constrained variance explained by RDA 2 | 13.01% |
| Cumulative constrained variance explained | 87.06% |
| Model significance by Monte Carlo test | F = 7.74, p < 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Huo, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, C. How Do Zooplankton Communities Respond to Environmental Factors across the Subsidence Wetlands Created by Underground Coal Mining in the North China Plain? Diversity 2024, 16, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050304
Liang Y, Huo J, Li W, Wang Y, Wang G, Li C. How Do Zooplankton Communities Respond to Environmental Factors across the Subsidence Wetlands Created by Underground Coal Mining in the North China Plain? Diversity. 2024; 16(5):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050304
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yue, Jianjun Huo, Weiqiang Li, Yutao Wang, Guangyao Wang, and Chunlin Li. 2024. "How Do Zooplankton Communities Respond to Environmental Factors across the Subsidence Wetlands Created by Underground Coal Mining in the North China Plain?" Diversity 16, no. 5: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050304
APA StyleLiang, Y., Huo, J., Li, W., Wang, Y., Wang, G., & Li, C. (2024). How Do Zooplankton Communities Respond to Environmental Factors across the Subsidence Wetlands Created by Underground Coal Mining in the North China Plain? Diversity, 16(5), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050304





