Phylogenetic Trends in the Dissymmetrisation of Genitalia in Hadenini (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
- In the male copulatory organ, the endophallus/vesica (the term “vesica” is generally used in the Noctuidae taxonomy and morphology) is long and tubular, with a subbasal diverticulum armed by a single small, spine-like cornutus, and with a stripe of fasciculate cornuti distally; the ductus ejaculatorius is positioned terminally (Poliina, Mamestrina, Hadenina) as opposed to the short, globular endophallus, without fasciculate cornuti, elongated diverticulum armed with terminal cornutus, and basally positioned ductus ejaculatorius (Discestrina);
- In the female genitalia, the appendix bursae is well differentiated, elongated or laterally positioned, with ductus seminalis originating at the posterior end of the appendix bursae (Poliina, Mamestrina, Hadenina) versus the completely reduced appendix bursae and the ductus seminalis positioned near the end of the ductus bursae (Discestrina).
- The secondary dissymmetrisation of homologous structures is most often connected with functional changes in which the clasping and stimulating functions of saccular extensions are bilaterally differentiated.
- Dissymmetrisation should enhance species diversity. This will be demonstrated in the phylogenetic and biogeographical patterns in the genera of subtribes Poliina and Discestrina of the subfamily Hadeninae.
- Furthermore, we have to demonstrate that the characteristics of the genital capsule and the traits connected with sperm transfer and their changes appear highly correlated and co-evolved.
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
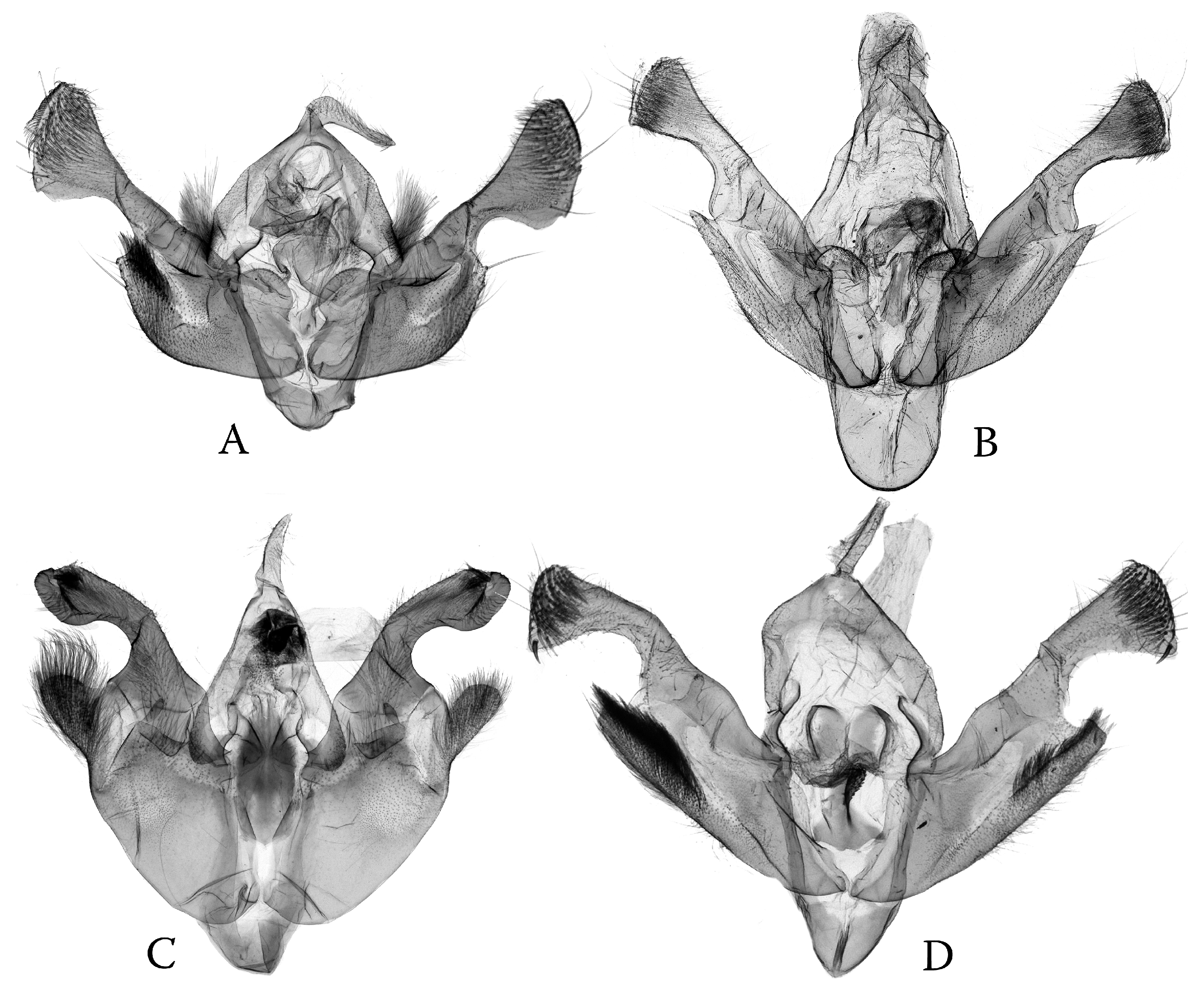
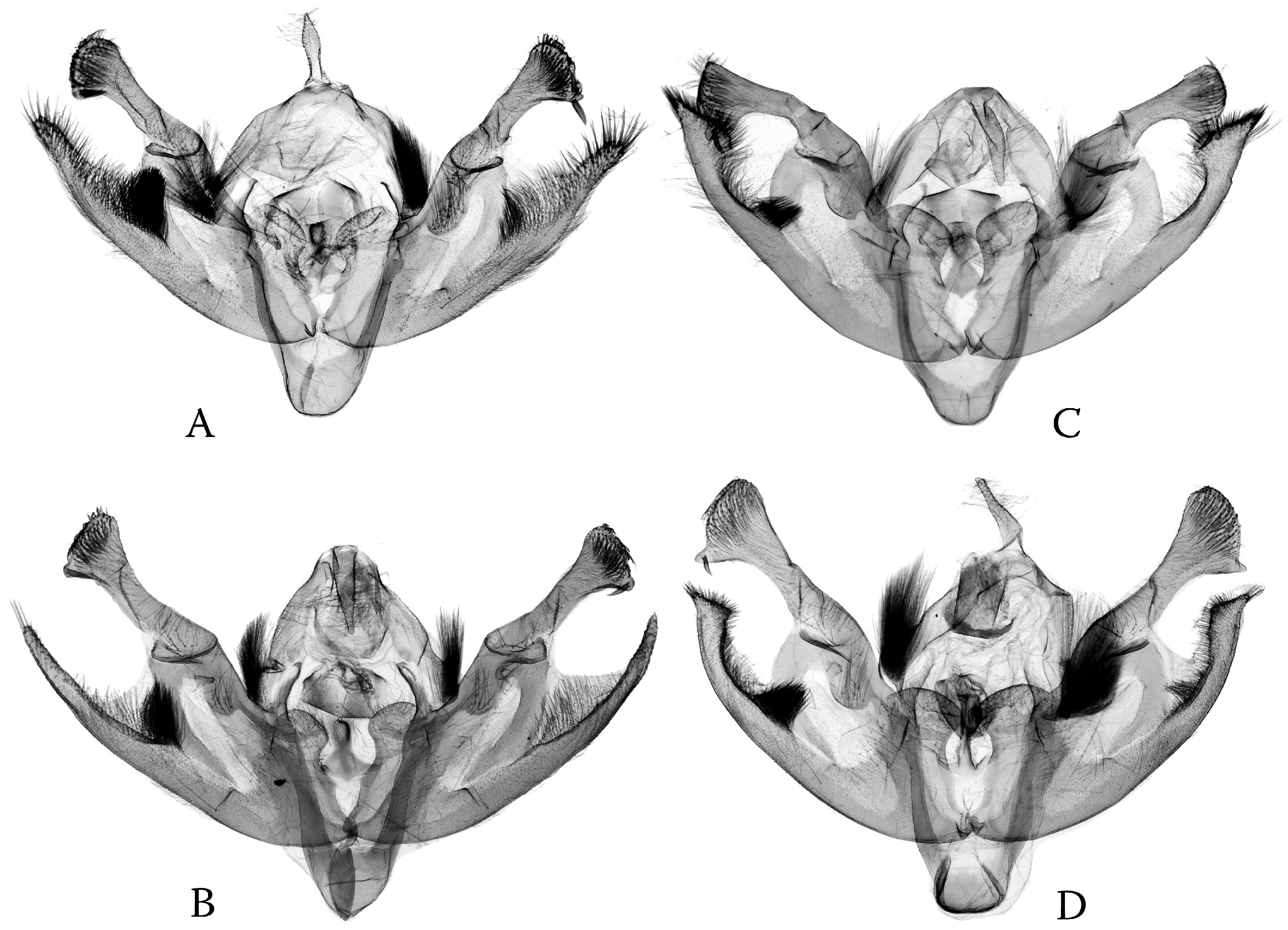
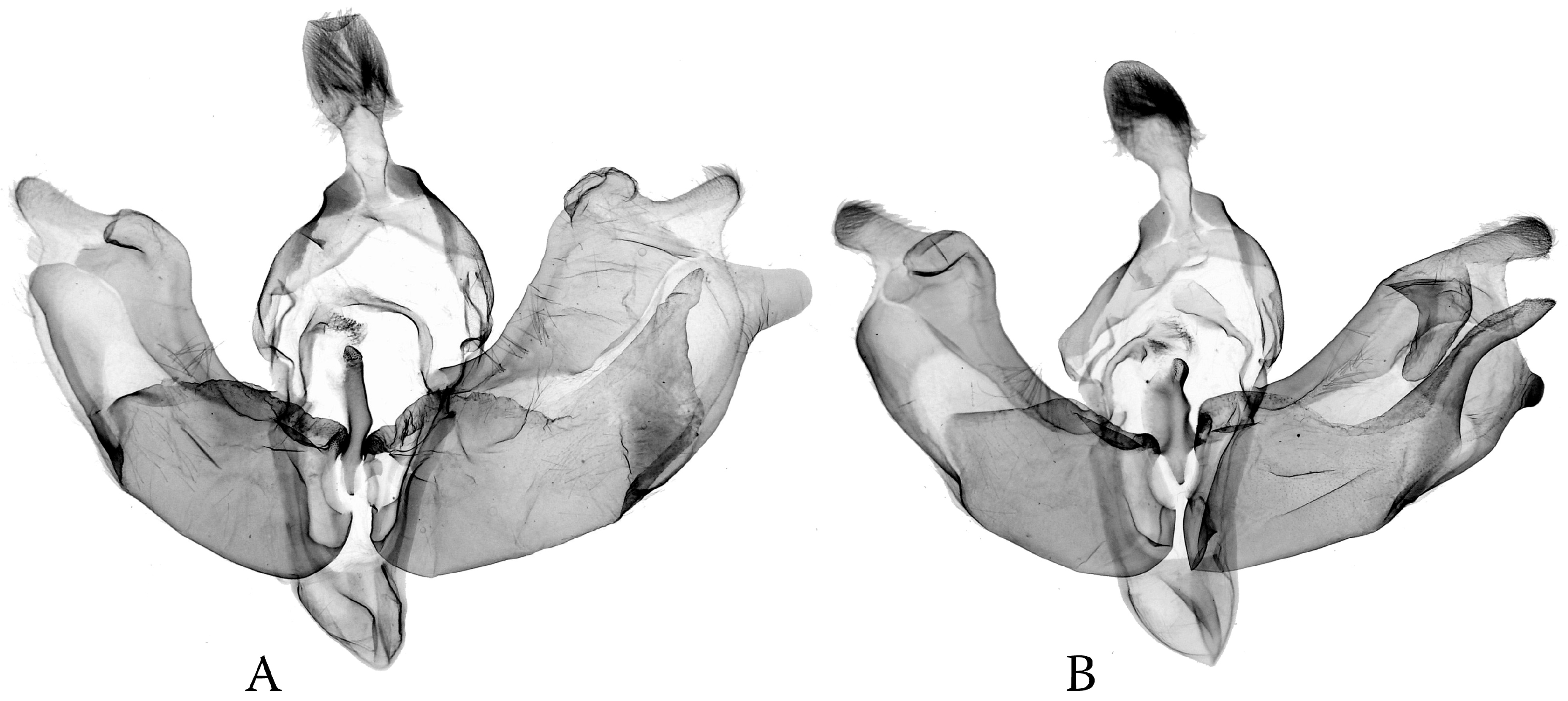
3.1. Morphological Trends in the Asymmetry of the Genital Capsule: Poliina
3.2. Morphological Trends in the Asymmetry of the Genital Capsule: Discestrina
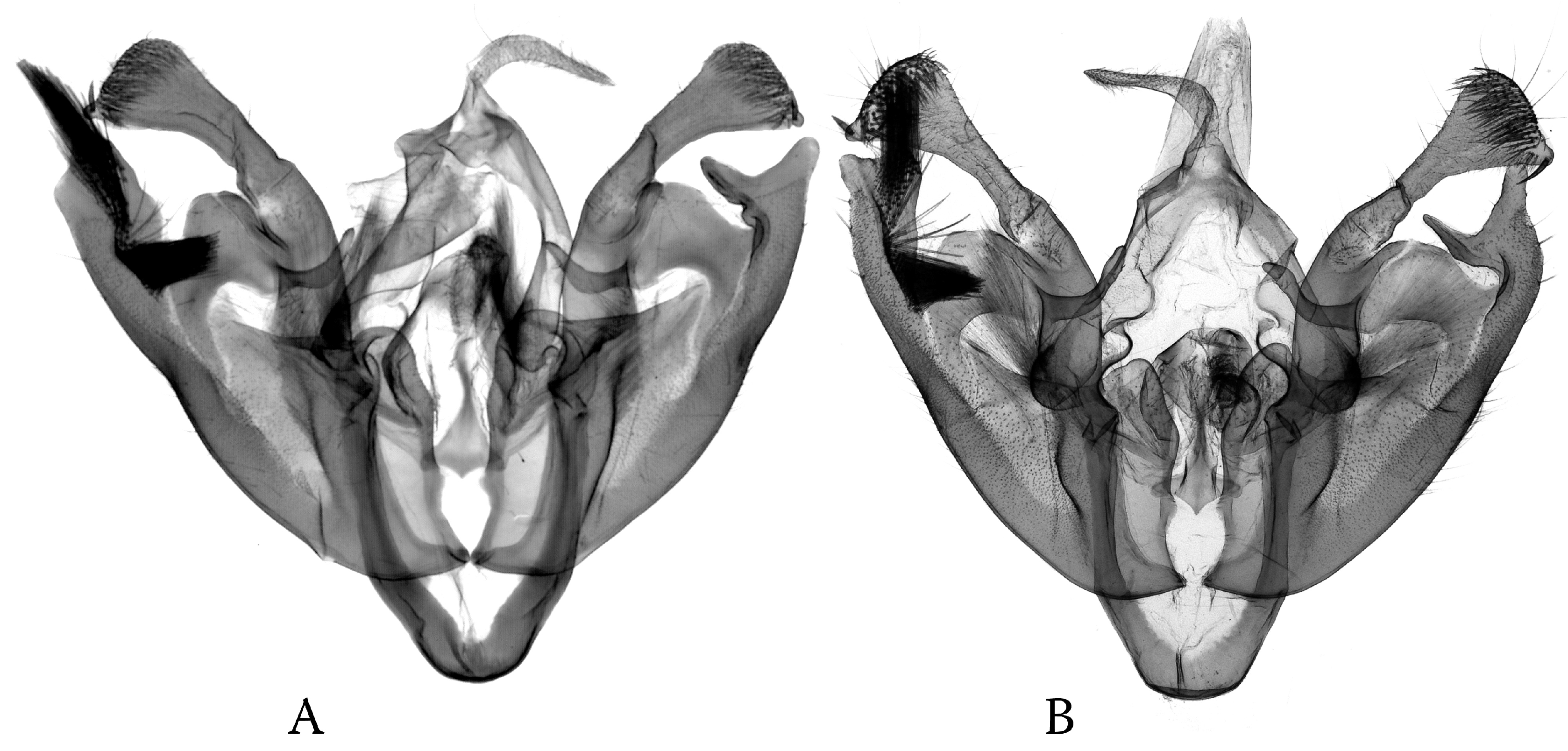
- Odontelia–Thargelia lineage: Only the right saccular process has become elongated, often digitiform; however, the whole capsule is changed to be distorted and asymmetrical in the Thargelia species (Figure 8). The taxa of the entire lineage are geographically restricted to the eremic belts of West and Central Asia.
- Anarta (s. l.) (including Hadula, Trichoclea, and Calocestra) lineage: The saccular processes have become asymmetrically elongated and differentiated on both sides; in Hadula, it is relatively simple on the left side, and in Trichoclea and Calocestra, there is a high diversity of variations on both sides (Figure 9). The species of these genera show a considerable ecological divergence from the eremic belts (Hadula, Trichoclea) to multizonal ranges (Calocestra).
3.3. Phylogenetic Diversification as Consequence of Dissymmetry: “Lock-and-Key” Structures in Poliina vs. Discestrina—Trends and Trade-Offs
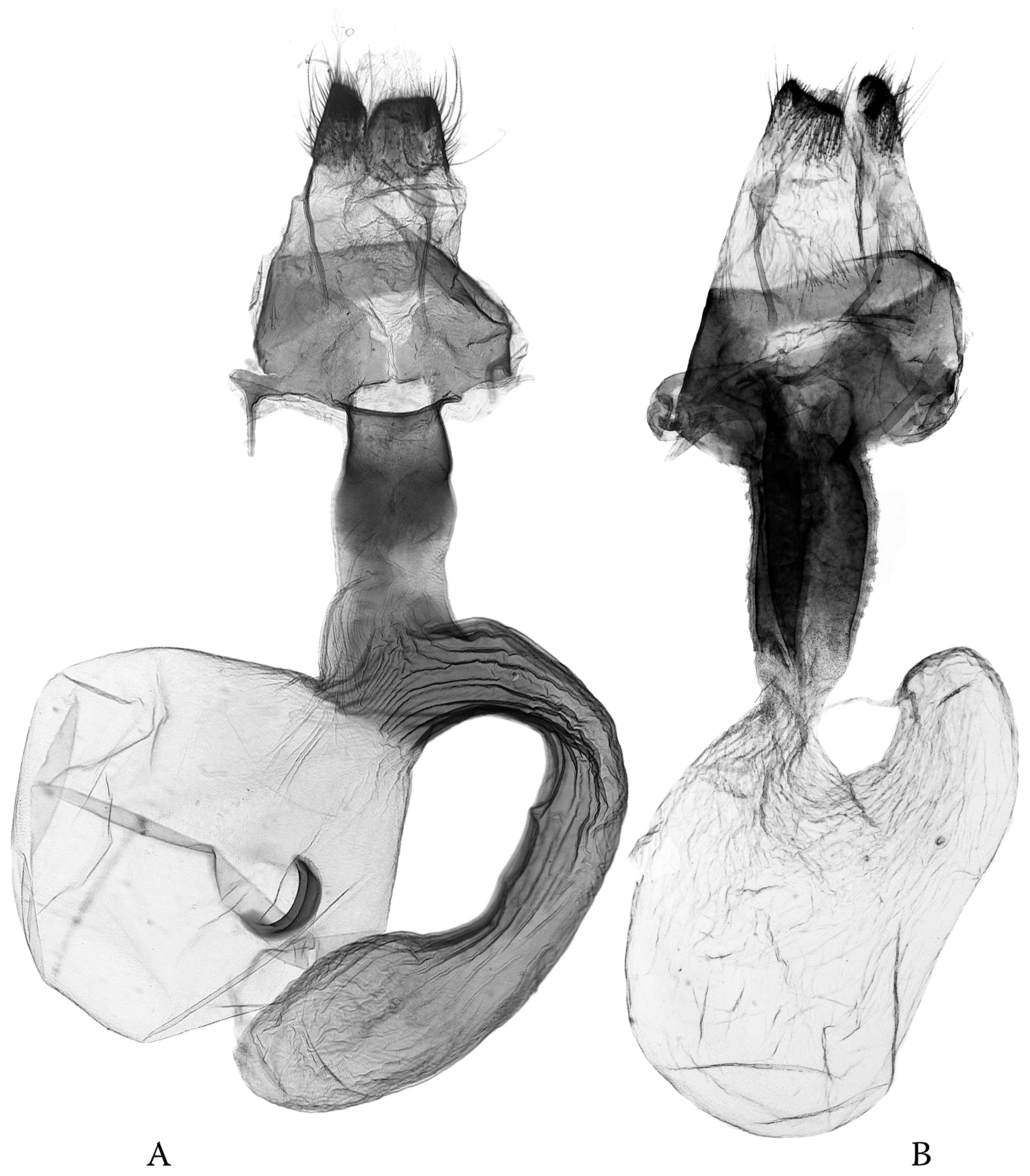
- The elongate tubular endophallus with a terminal ductus ejaculatorius is associated with a strongly differentiated appendix bursae in Poliina;
- The simplified endophallus with a basally located ductus ejaculatorius is associated with an extremely reduced appendix bursae in the Discestrina.
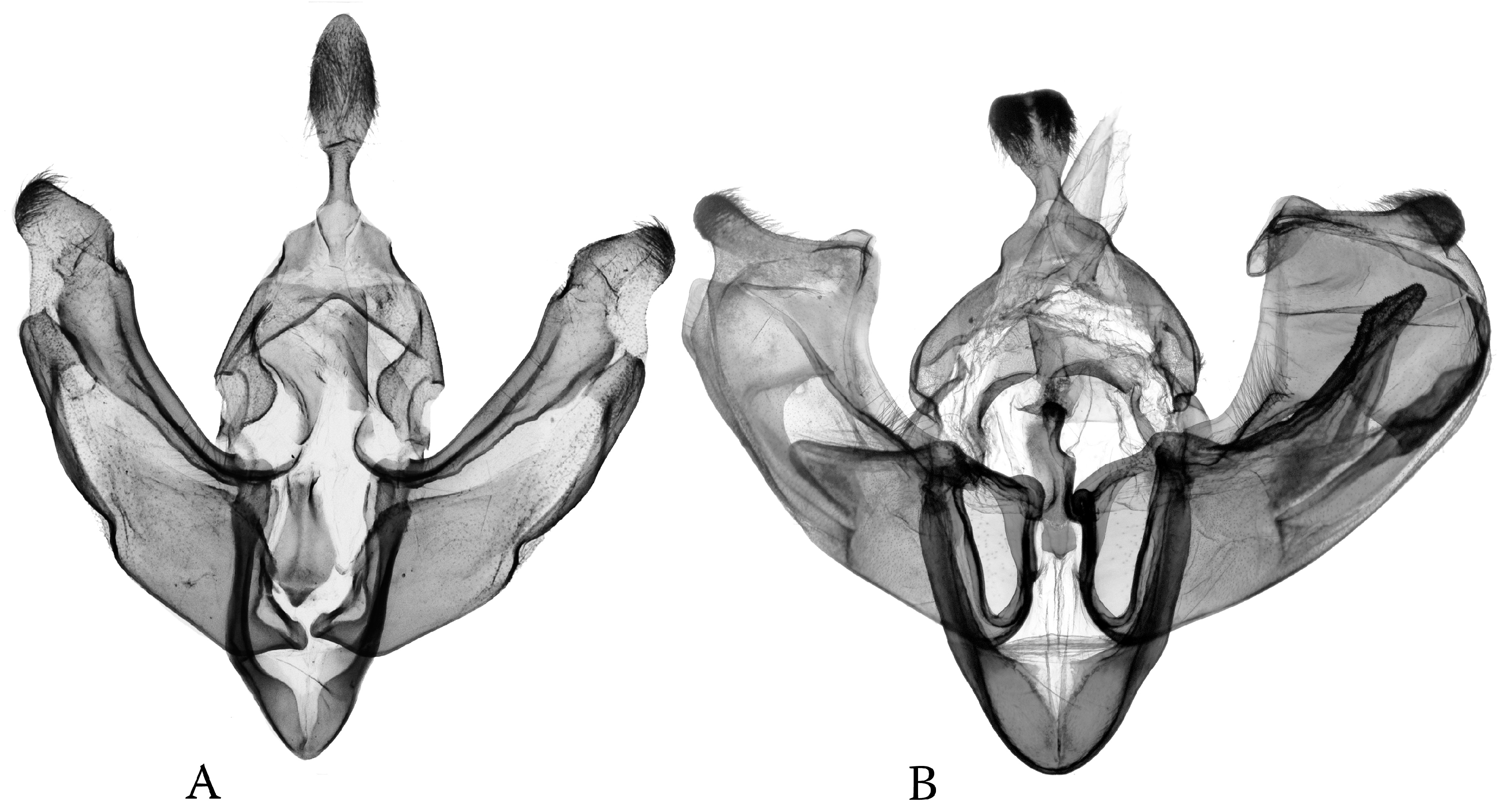
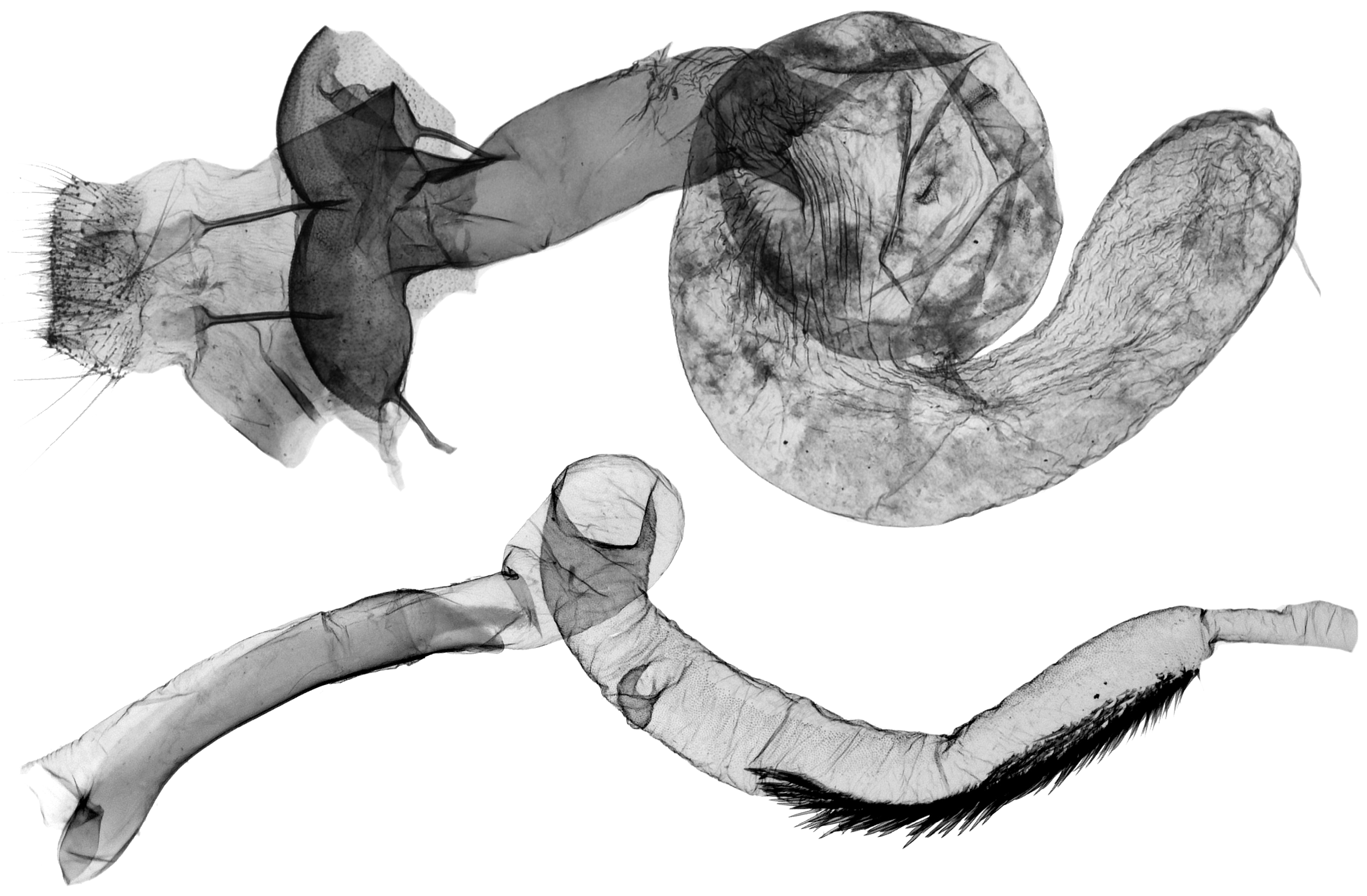
- The simplified genital capsule is associated with a sophisticated “lock-and-key” structure in the diverse genus Ctenoceratoda. The “loop” of the endophallus interlocks with the globular corpus bursae, and the long tubular section of the endophallus is armed by the fasciculate cornute, which fits to the elongated, tubular appendix bursae (Figure 15).
- The sophisticated genital capsule is associated with a somewhat simplified “lock-and-key”; in the multi-diverse Polia, even the fasciculate cornuti are sometimes reduced.
- Independently, a similar trend was found in both phyletic lines of the Discestrina clade as well, in Hadula, Trichoclea, and Calocestra.
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnqvist, G. Comparative evidence for the evolution of genitalia by sexual selection. Nature 1998, 393, 784–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnqvist, G. Antagonistic coevolution between the sexes in a group of insects. Nature 2002, 415, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnqvist, G.; Edvardsson, M.; Friberg, U.; Nilsson, T. Sexual conflict promotes speciation in insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10460–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, C.; Baixeras, J. Sexual Selection Within the Female Genitalia in Lepidoptera. In Cryptic Female Choice in Arthropods; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 325–350. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard, W.G. Sexual Selection and Animal Genitalia; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985; 244p. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard, W.G. Evaluating models of sexual selection: Genitalia as a test case. Am. Nat. 1993, 142, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, W.G.; Lehmann, G.U.C. Demonstrating sexual selection by cryptic female choice on male genitalia: What is enough? Evolution 2019, 73, 2415–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosken, D.J.; Stockley, P. Sexual selection and genital evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkola, K. The lock-and-key mechanisms of the internal genitalia of the Noctuidae (Lepidoptera): How are they selected for? Eur. J. Entomol. 2008, 105, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Ronkay, L. Structural constraints of secondary asymmetry in male external genitalia of Noctuidae. Insect Syst. Evol. 2013, 44, 349–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.J. The exaptive excellence of spandrels as a term and prototype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10750–10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, W.K. Habitus factors in the skeleton of fossil and recent mammals. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 1936, 76, 429–444. [Google Scholar]
- Hacker, H.; Ronkay, L.; Hreblay, M. Hadeninae I. Noctuidae Europaeae Volume 4; Entomological Press: Sorø, Denmark, 2002; 419p. [Google Scholar]
- Ronkay, L.; Varga, Z. On the taxonomy of the genera Odontelia Hampson, 1905, and Thargelia Püngeler, 1900 (Noctuidae, Hadeninae). Ann. Hist.-Nat. Musei Natl. Hung. 1998, 90, 175–193. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, Z.; Ronkay, L.; Ronkay, G. Metallopolia, a new subgenus of Polia, with the description of two new species and a new subspecies (Noctuidae, Noctuinae, Hadenini). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 21, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Ronkay, L.; Ronkay, G. Revised taxonomic check list of the Eurasiatic species of the subtribe Poliina (Noctuidae, Noctuinae, Hadenini). Dtsch. Entomol. Z. 2017, 64, 133–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Gyulai, P.; Ronkay, G.; Ronkay, L. Review of the species groups of the genus Ctenoceratoda Varga, 1992 with description of four new species and a new subspecies (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 2018, 64, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Ronkay, G.; Ronkay, L. Taxonomic survey of the Polia (Polia) nebulosa species complex (Noctuidae, Noctuinae, Hadenini) with the description of two new subspecies. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 2019, 65, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, R.W. Sphingoidea. In The Moths of America North of Mexico Volume 21; Wedge Entomological Research Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 1971; pp. 1–158, pl. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Heppner, J.B. Butterflies and Moths (Lepidoptera). In Encyclopedia of Entomology; Capinera, J.L., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 627–675. [Google Scholar]
- Lafontaine, J.D. Noctuoidea, Noctuidae (Part) Noctuinae (Part-Euxoa). In The Moths of America North of Mexico, Fascicle 27.2; Dominick, R.B., Ed.; Wedge Entomological Research Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 1987; 238p. [Google Scholar]
- Lafontaine, J.D. Noctuoidea, Noctuidae (part Noctuinae II). In The Moths of America North of Mexico, Fascicle 27.3; Dominick, R.B., Ed.; Wedge Entomological Research Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; 348p. [Google Scholar]
- Fibiger, M. Noctuidae Europaeae Volume 3. Noctuinae III; Entomological Press: Sorø, Denmark, 1997; 418p. [Google Scholar]
- Fibiger, M.; Lafontaine, J.D. A review of the higher classification of Noctuoidea (Lepidoptera) with special reference to the Holarctic fauna. Esperiana 2005, 11, 7–92. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkola, K.; Lafontaine, J.D.; Gill, J. Noctuoidea: Noctuidae (part): Xyleninae (part): Apameini (part-Apamea group of genera). In The Moths of America North of Mexico. Fascicle 26.9; Hodges, R.W., Ed.; The Wedge Entomological Research Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; 192p. [Google Scholar]
- Lafontaine, D.; Schmidt, B.C. Annotated check list of the Noctuoidea (Insecta, Lepidoptera) of North America North of Mexico. ZooKeys 2010, 40, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibiger, M.; Hacker, H.H. Systematic List of the Noctuoidea of Europe (Notodontidae, Nolidae, Arctiidae, Lymantriidae, Erebidae, Micronoctuidae, and Noctuidae). Esperiana 2005, 11, 93–182. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, T.M. A reclassification of the Polia complex for North America (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In New York State Museum, Bulletin; The University of the State of New York: Albany, NY, USA, 1980; 432, i–vi, pp. 1–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zahiri, R.; Lafontaine, J.D.; Schmidt, B.C.; deWaard, J.R.; Zakharov, E.V.; Hebert, P.D.N. A transcontinental challenge—A test of DNA barcode performance for 1,541 species of Canadian Noctuoidea (Lepidoptera). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, R.D.; Marshall, D.C.; Cooley, J.R. Evolutionary perspectives on insect mating. In The Evolution of Mating Systems in Insects and Arachnids; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, B.; Rice, W.R. Experimental removal of sexual selection reverses intersexual antagonistic coevolution and removes a reproductive load. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5083–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrilets, S.; Arnqvist, G.; Friberg, U. The evolution of female mate choice by sexual conflict. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 268, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, C.; Eberhard, W.G. Female choice of sexually antagonistic male adaptations: Critical review of some recent research. J. Evol. Biol. 2003, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, P.S.; Chapin, J.B. Morphology of the reproductive system and mating in two representative members of the family Noctuidae, Pseudaletia unipuncta and Peridroma margaritosa with comparison to Heliothis zea. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1960, 53, 763–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, B.A. Multiple mating and sperm competition in the Lepidoptera. In Sperm Competition and the Evolution of Animal Mating Systems; Smith, R.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1984; pp. 291–371. [Google Scholar]
- Birkhead, T.; Møller, A.P. (Eds.) Sperm Competition and Sexual Selection; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; 826p. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkola, K. Evidence for lock-and-key mechanisms in the internal genitalia of the Apamea moths (Lep.: Noctuidae). Syst. Entomol. 1992, 17, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekolnikov, A.A.; Kuznetzov, V.I. Functional morphology of the male genitalia and a new tribal division of the Ennominae (Lepidoptera, Geometridae). Entomol. Rev. 1982, 61, 92–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zilli, A.; Varga, Z.; Ronkay, G.; Ronkay, L. Apameini I. Taxonomic Atlas of the Eurasian and North African Noctuoidea, Heterocera Press: Budapest, Hungary, 2009; Volume 3, 393p.
- Varga, Z.; Ronkay, L. New and revised taxa of the genera Chersotis Boisduval, 1840 and Dichagyris Lederer, 1857 from Central Asia (Lep.: Noctuidae). Esperiana 1996, 5, 175–214. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, Z. Taxonomic notes on the Genus Haderonia Staudinger, 1896 with the description of a new Genus Ctenoceratoda and four new species (Lep.: Noctuidae). Acta Zool. Hung. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1992, 38, 95–112. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, Z.; Gyulai, P. Taxonomy of the genus Ctenoceratoda Varga, 1992 (Lep.: Noctuidae, Hadeninae) with the description of seven new species. Acta Zool. Hung. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1999, 45, 169–197. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, B.A.; Sinclair, B.I.; Schmitt, M. The evolution of asymmetric genitalia in spiders and insects. Biol. Rev. 2007, 82, 647–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.A. Mating of butterflies. J. Res. Lepid. 1973, 11, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husemann, M.; Schmitt, T.; Zachos, F.E.; Ulrich, W.; Habel, J.C. Palaearctic biogeography revisited: Evidence for the existence of a north African refugium for Western Palaearctic biota. J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podnar, M.; Grbac, I.; Tvrtkovic, N.; Hörweg, C.; Haring, E. Hidden diversity, ancient divergences, and tentative Pleistocene microrefugia of European scorpions (Euscorpiidae: Euscorpiinae) in the eastern Adriatic region. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2021, 59, 1824–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, D.; Pinho, C.; Mendes, J.; Harris, D.J. Fossil-calibrated time tree of Podarcis wall lizards provides limited support for biogeographic calibration models. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 161, 107169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajer, A.J.; Sebestyén, V.; Padisák, J. The impacts of the Messinian salinity crisis on the biogeography of three Mediterranean sandfly (Diptera: Psychodidae) species. Geobios 2021, 65, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.J.; Nunes, V.L.; Marabuto, E.; Mendes, R.; Silva, D.N.; Pons, P.; Bas, J.M.; Hertach, T.; Paulo, O.S.; Simões, P.C. The effect of the Messinian salinity crisis on the early diversification of the Tettigettalna cicadas. Zool. Scr. 2023, 52, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z. Biogeography and Evolution of the oreal Lepidoptera in the Palearctic. Acta Zool. Hung. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1997, 42, 289–330. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, Z. Centres of endemism of Noctuidae (Lepidoptera) in the Palaearctic arid mountains: Biogeographical and phylogenetic implications. Beiträge Entomol.–Contrib. Entomol. 2022, 72, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varga, Z.; Ronkay, G.; Ronkay, L. Phylogenetic Trends in the Dissymmetrisation of Genitalia in Hadenini (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Diversity 2024, 16, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16040248
Varga Z, Ronkay G, Ronkay L. Phylogenetic Trends in the Dissymmetrisation of Genitalia in Hadenini (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Diversity. 2024; 16(4):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16040248
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarga, Zoltán, Gábor Ronkay, and László Ronkay. 2024. "Phylogenetic Trends in the Dissymmetrisation of Genitalia in Hadenini (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae)" Diversity 16, no. 4: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16040248
APA StyleVarga, Z., Ronkay, G., & Ronkay, L. (2024). Phylogenetic Trends in the Dissymmetrisation of Genitalia in Hadenini (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Diversity, 16(4), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16040248





