Sturgeon Parasites: A Review of Their Diversity and Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sturgeons and Parasites
2.1. Protozoa, Monogenea and Crustaceans
2.2. Cestode, Trematode and Nematode
2.3. Copepods
2.4. Hirudinea and Polypodiozoa
2.5. Hyperoartia
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gardiner, B.G. Sturgeons as Living Fossils. In Living Fossils; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemis, W.E.; Kynard, B. Sturgeon rivers: An introduction to acipenseriform biogeography and life history. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1997, 48, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, S.; Moog, O. Dams: Ecological impacts and management. In Riverine Ecosystem Management: Science for Governing towards a Sustainable Future; University of Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 111–127. [Google Scholar]
- Birstein, V.J.; Bemis, W.E. How many species are there within the genus Acipenser? Environ. Biol. Fishes 1997, 48, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raischi, M.; Deák, H.G.; Oprea, L.; Raischi, N.; Dănălache, T.; Matei, S. The impact of anthropogenic pressures on sturgeon migration in the Lower Danube. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 012030. [Google Scholar]
- Raischi, M.C.; Deak, G.; Oprea, L. Research on the Monitoring of Sturgeon Populations by Telemetry Techniques in the Lower Danube Sector of Braila-Călărasi. Ph.D Thesis, Dunarea de Jos University of Galati, Galați, Romania, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Williot, P. Reproduction de L’esturgeon Sibérien (Acipenser baeri Brandt) en Élevage: Gestion des Génitrices, Compétence à la Maturation In Vitro de Follicules Ovariens et Caractéristiques Plasmatiques Durant L’induction de la Ponte; Université Bordeaux I: Bordeaux, Franch, 1997; pp. 1–227. [Google Scholar]
- Birstein, V.J.; Bemis, W.E.; Waldman, J.R. The threatened status of acipenseriform species: A summary. Sturgeon Biodivers. Conserv. 1997, 48, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KayiŞ, Ş.; SoykÖSe, G.; İPek, Z.Z.; Er, A. Türkiye’nin Doğu Karadeniz Bölgesinde Bulunan Bazı Alabalık Çiftliklerinin Kuluçkahanelerinde Bakteri Kontaminasyonu ve Bakterilerin Antibiyotik Direncinin Belirlenmesi. J. Limnol. Freshw. Fish. Res. 2021, 7, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljević, V.; Milićević, V.; Maksimović-Zorić, J.; Veljović, L.; Nešić, K.; Pavlović, M.; Ljubojević Pelić, D.; Marković, Z. Sturgeon diseases in aquaculture. Arch. Vet. Med. 2019, 12, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakić, P.; Đikanović, V.; Kulišić, Z.; Paunović, M.; Jakovčev-Todorović, D.; Milošević, S. The fauna of endoparasites in Acipenser ruthenus Linnaeus, 1758 from the Serbian part of the Danube River. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2008, 60, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazari Moghaddam, S.; Mokhayer, B.; Masoumian, M.; Shenavar Masouleh, A.; Jalilpour, J.; Masoumzadeh, M.; Alizadeh, M. Parasitic infection among larvae and fingerlings of the Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus) in Vniro tanks and earthen ponds. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2010, 9, 342–351. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulhusein, G.; Ramteke, P. Investigations on parasitic diseases in fish of river Yamuna during the summer season. European Academic Research 2014, 2, 10057–10097. [Google Scholar]
- Rogin, R.E. Conservation and sustainable use of wild sturgeon populations of the NW Black Sea and Lower Danube River in Romania. Master’s Thesis, Institutt for Biologi, Trondheim, Norway, 2011; pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Savickiy, J.; Alishova, Z. Infectious and parasitic diseases of sturgeon fish. In Proceedings of the Теoрия и практика сoвременнoй аграрнoй науки, Novosibirsk, Russia, 28 February 2022; pp. 1264–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Kuperman, B. Fish parasites as bioindicators of the pollution of bodies of water. Parazitologiia 1992, 26, 479–482. [Google Scholar]
- Palm, H.W.; Kleinertz, S.; Rueckert, S. Parasite diversity as an indicator of environmental change? An example from tropical grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus) mariculture in Indonesia. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barber, I. Parasites, behaviour and welfare in fish. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 104, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebanov, M.S.; Galich, E.V. Sturgeon hatchery manual. FAO Fish. Aquac. Tech. Pap. 2011, 558, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Vasile, D. Evidence of ichthyophthiriasis in cultured Acipenser stellatus (Pallas 1771). Acad. Rom. Sci. Ann.-Ser. Biol. Sci. 2019, 8, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Popielarczyk, R.; Kolman, R. Preliminary analysis of ectoparasites of the sturgeon Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus (Mitchill, 1815) originating from different water habitats. Ann. Parasitol. 2013, 59, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pazooki, J.; Masoumian, M. Cryptobia acipenseris and Haemogregarina acipenseris infections in Acipenser guldenstadti and A. persicus in the Southern part of the Caspian Sea. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 6, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Mohler, J.W.; King, M.K.; Farrell, P.R. Growth and survival of first-feeding and fingerling Atlantic sturgeon under culture conditions. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2000, 62, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayiş, Ş.; Er, A.; Kangel, P.; Kurtoğlu, İ. Bacterial pathogens and health problems of Acipenser gueldenstaedtii and Acipenser baerii sturgeons reared in the eastern Black Sea region of Turkey. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adel, M.; Safari, R.; Yaghoubzadeh, Z.; Fazli, H.; Khalili, E. Parasitic infection in various stages life of cultured Acipenser persicus. In Veterinary Research Forum; Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Urmia University: Urmia, Iran, 2016; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam, S.B. Study on internal helminthes parasites in Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus) spawners in southwest coasts of the Caspian Sea (2009–2011). Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Matsche, M.A.; Flowers, J.R.; Markin, E.L.; Stence, C.P. Observations and Treatment of Nitzschia sturionis on Atlantic Sturgeon from Chesapeake Bay. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2010, 22, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baska, F. The pathology of parasitic infections in mature sterlets (Acipenser ruthenus) and their importance in propagation. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 1999, 15, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, M.; Raissy, M.; Shamsi, S. Protozoan Parasites of Iranian Freshwater Fishes: Review, Composition, Classification, and Modeling Distribution. Pathogens 2023, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, E.; Voropaeva, E. The parasitofauna of the Siberian sterlet Acipenser ruthenus marsiglii of the Lower Irtysh. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2018, 9, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A. A New Deropristiid Species (Trematoda: Deropristiidae) from the Lake Sturgeon Acipenser fulvescens in Wisconsin, and Its Biogeographical Implications. J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.B.; Roberts, J.R.; Arias, C.R.; Koenigs, R.P.; Bullard, S.A. Acipensericola glacialis n. sp.(Digenea: Aporocotylidae) from heart of lake sturgeon Acipenser fulvescens Rafinesque (Acipenseriformes: Acipenseridae) in the Great Lakes basin, Lake Winnebago system, USA. Syst. Parasitol. 2017, 94, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, M.; Mokhayer, B.; Shafii, S. Parasitic worms of Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus Borodin, 1897) from the southwest of the Caspian Sea. Bull.-Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2006, 26, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhardt, M.; Jaric, I.; Cakic, P.; Cvijanovic, G.; Gacic, Z.; Kolarevic, J. Seasonal changes in condition, hepatosomatic index and parasitism in sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus L.). Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2009, 33, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atopkin, D.M.; Shedko, M.B. Genetic characterization of far eastern species of the genus Crepidostomum (Trematoda: Allocreadiidae) by means of 28S ribosomal DNA sequences. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2014, 5, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Choudhury, A. Systematics of the Deropristiidae Cable & Hunninen, 1942 (Trematoda) and biogeographical associations with sturgeons (Osteichthyes: Acipenseridae). Syst. Parasitol. 1998, 41, 21–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolov, S.; Voropaeva, E.; Atopkin, D. A new species of deropristid trematode from the sterlet Acipenser ruthenus (Actinopterygii: Acipenseridae) and revision of superfamily affiliation of the family Deropristidae. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 190, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noei, M. Parasitic worms of Acipenser stellatus, A. gueldenstaedtii, A. nudiventris and Huso huso (Chondrostei: Acipenseridae) from the southwest shores of the Caspian Sea. Casp. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 9, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Noei, M.R.; Ibrahimov, S.; Sattari, M. Parasitic worms of the Persian sturgeon, Acipenser persicus Borodin, 1897 from the southwestern shores of the Caspian Sea. Iran. J. Ichthyol. 2015, 2, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Fast, M.D.; Sokolowski, M.S.; Dunton, K.J.; Bowser, P.R. Dichelesthium oblongum (Copepoda: Dichelesthiidae) infestation in wild-caught Atlantic sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradil, A.M.; Wright, G.M.; Speare, D.J.; Wadowska, D.W.; Purcell, S.; Fast, M.D. The effects of temperature and body size on immunological development and responsiveness in juvenile shortnose sturgeon (Acipenser brevirostrum). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 40, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilean, I.; Cristea, V.; Dediu, L. Researches regarding the argulosis treatment to Huso huso juveniles with NaCl. Lucr. Științifice-Univ. De Științe Agric. Și Med. Vet. Ser. Zooteh. 2012, 58, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Andres, M.J.; Higgs, J.M.; Grammer, P.O.; Peterson, M.S. Argulus from the Pascagoula River, MS, USA, with an emphasis on those of the threatened Gulf Sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi. Diversity 2019, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, M.; Allam, B.; Dunton, K.; Clark, M.; Kurtz, E.; Fast, M. Immunophysiology of Atlantic sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus (Mitchill), and the relationship to parasitic copepod, Dichelesthium oblongum (Abilgaard) infection. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matvienko, N.; Levchenko, A.; Danchuk, O.; Kvach, Y. Assessment of the occurrence of microorganisms and other fish parasites in the freshwater aquaculture of Ukraine in relation to the ambient temperature. Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2020, 50, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, W. Redescription of Tracheliastes gigas Richiardi, 1881 from the type-specimens, and its relegation to synonymy with Pseudotracheliastes stellatus (Mayor, 1824) (Copepoda: Siphonostomatoida: Lernaeopodidae). Syst. Parasitol. 1993, 25, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, J.M.; Moerke, A.; Greil, R.; Gerig, B.; Baker, E.; Chiotti, J. Population status and demographics of lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens) in the St. Marys River, from 2000 to 2007. J. Great Lakes Res. 2011, 37, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A. Life Cycle and Population Dynamics of the marine ectoparasite Dichelesthium oblongum (Copepoda: Dichelesthiidae) on Atlantic sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus). Ph.D. Thesis, State University of New York at Stony Brook, New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Munroe, S.E.M.; Avery, T.S.; Shutler, D.; Dadswell, M.J. Spatial Attachment-Site Preferences of Macroectoparasites on Atlantic Sturgeons Acipenser oxyrinchus in Minas Basin, Bay of Fundy, Canada. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikova, E.V. Polypodium hydriforme infection in the eggs of acipenseriform fishes. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikova, E.V.; Suppes, V.C.; Hoffman, G.L. The Parasitic Coelenterate, Polypodium hydriforme Ussov, from the Eggs of the American Acipenseriform Polyodon spathula. J. Parasitol. 1979, 65, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matishov, G.; Kazarnikova, A. Analysis of the possible influence of fish parasites from the Tumnin River on fry of the Sakhalin sturgeon (Acipenser mikadoi, Hildendorf, 1892). In Doklady Biological Sciences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 290. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, G.L.; Raikova, E.; Yoder, W. Polypodium sp. (Coelenterata) found in North American sturgeon. J. Parasitol. 1974, 60, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, B.; Hartigan, A.; Long, P.F.; Ruggeri, P.; Smith-Easter, K.; Schooley, J.D. Epidemiology of Polypodium hydriforme in American Paddlefish. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, T.A.; Holloway, H.L.; Choudhury, A. Polypodium sp. (Coelenterata) from Lake Sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens Rafinesque) in the Prairie Region of Canada. J. Parasitol. 1991, 77, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, T.M.; Tripp, S.J.; Herzog, D.P. Cause of increased size of acipenseriform eggs infected with Polypodium hydriforme. J. Fish Biol. 2022, 100, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshelev, V.N.; Ruban, G.; Shmigirilov, A. Spawning migrations and reproductive parameters of the kaluga sturgeon, H uso dauricus (Georgi, 1775), and A mur sturgeon, A cipenser schrenckii (B randt, 1869). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikodina, E.V.; Ruban, G.I. Current Data on Sakhalin Sturgeon Acipenser mikadoi (Acipenseridae, Acipenseriformes) Biology (Review). Inland Water Biol. 2021, 14, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, M.S.; Stefanavage, T.; Goforth, R. First Record of a Polypodium sp. Parasitizing Eggs of Shovelnose Sturgeon from the Wabash River, Indiana. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2010, 22, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotov, I.N.; Maryinsky, V.V.; Palatov, D.M.; Kondakov, A.V.; Eliseeva, T.A.; Konopleva, E.S.; Gofarov, M.Y.; Vikhrev, I.V.; Bespalaya, Y.V. Host Range and Phylogenetic Position of Acipenserobdella volgensis (Zykoff, 1904) (Hirudinea: Piscicolidae) with a Global Checklist of Bivalve-Associated Fish Leeches. Water 2022, 14, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecki, A.; Kapusta, A.; Cichocka, J. Atlantic sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus Mitchill, infected by the parasitic leech, Caspiobdella fadejewi (Epshtein) (Hirudinea; Piscicolidae), in the Drwęca River. Arch. Pol. Fish. 2011, 19, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Taubert, B. New records of leeches (Annelida: Hirudinea) from the shortnose sturgeon (Acipenser brevirostrum) in the Connecticut River. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1980, 47, 147–148. [Google Scholar]
- Appy, R.G.; Dadswell, M.J. Marine and estuarine piscicolid leeches (Hirudinea) of the Bay of Fundy and adjacent waters with a key to species. Can. J. Zool. 1981, 59, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skóra, M.E.; Bogacka-Kapusta, E.; Morzuch, J.; Kulikowski, M.; Rolbiecki, L.; Kozłowski, K.; Kapusta, A. Exotic sturgeons in the Vistula Lagoon in 2011, their occurrence, diet and parasites, with notes on the fishery background. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2018, 34, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirov, A.; Bunyatova, K. Some peculiarities of the relationships between sturgeon of the Caspian Sea and their parasites. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 395–399. [Google Scholar]
- Skrjabina, E. Helminths of Sturgeons; Publishing house ‘Nauka’ M: Moscow, Russia, 1974; pp. 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Mikailov, T.; Buniatova, K.; Nasirov, A. The finding of the eggs of the nematode Eustrongylides excisus in true sturgeons of the Caspian Sea. Parazitologiia 1992, 26, 440–442. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, A.; Nadler, S.A. Phylogenetic relationships of spiruromorph nematodes (Spirurina: Spiruromorpha) in North American freshwater fishes. J. Parasitol. 2018, 104, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabpour, M.; Malek, M.; MacKenzie, K.; Aghlmandi, F. Helminth parasites of stellate sturgeon Acipenser stellatus Pallas, 1771 and Persian sturgeon Acipenser persicus Borodin, 1897 (Pisces: Acipenseridae) from the South–East Caspian Sea. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 102, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, G.T., Jr. Communications: Prevalence of the Parasite Cystoopsis acipenseri Nematoda) in Juvenile White Sturgeons in the Lower Columbia River. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1993, 5, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A. Parasites of the Lake Sturgeon, Acipenser fulvescens: Systematics and Biogeography. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Khajepour, F.; Paighambari, S.Y. Investigation of infected gill to Monogenea in Sturgeon at the Southern Part of the Caspian Sea. Global Vet 2013, 10, 285–287. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmati Holasoo, H.; Marandi, A.; Ebrahimzadeh Mousavi, H.; Azizi, A. Study of the losses of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) due to gill infection with Diclybothrium armatum in sturgeon farms of Qom and Mazandaran provinces. J. Anim. Environ. 2021, 13, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Dobson, A.P.; May, R.M. The effects of parasites on fish populations—Theoretical aspects. Int. J. Parasitol. 1987, 17, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, O.M.; Heckmann, R.A.; Halajian, A.; El-Naggar, A.M.; Tavakol, S. The description and histopathology of Leptorhynchoides polycristatus n. sp.(Acanthocephala: Rhadinorhynchidae) from sturgeons, Acipenser spp.(Actinopterygii: Acipenseridae) in the Caspian Sea, Iran, with emendation of the generic diagnosis. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3873–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foata, J.P.; Dezfuli, B.S.; Pinelli, B.; Marchand, B. Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis and spermatozoon of Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus (Acanthocephala, Palaeacanthocephala), a parasite of the sturgeon Acipenser naccarii (Osteichthyes, Acipenseriformes). Parasitol. Res. 2004, 93, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchta, R.; Pearson, R.; Scholz, T.; Ditrich, O.; Olson, P.D. Spathebothriidea: Survey of species, scolex and egg morphology, and interrelationships of a non-segmented, relictual tapeworm group (Platyhelminthes: Cestoda). Folia Parasitol. 2014, 61, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunanská, M.; Poddubnaya, L.G.; Xylander, W.E. A reinvestigation of spermiogenesis in Amphilina foliacea (Platyhelminthes: Amphilinidea). Folia Parasitol. 2013, 60, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biserova, N.; Dudicheva, V.; Terenina, N.; Reuter, M.; Halton, D.; Maule, A.; Gustafsson, M. The nervous system of Amphilina foliacea (Platyhelminthes, Amphilinidea). An immunocytochemical, ultrastructural and spectrofluorometrical study. Parasitology 2000, 121, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimov, S.; Mamedova, S. Ecological analysis of the fish cestode fauna of the mouth of Kura River. J. V.N.Karazin Kharkiv Natl. Univ. Ser. Biol. 2021, 36, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, A.S.; Chiotti, J.A.; Boase, J.C.; Hessenauer, J.M.; Wills, T.C. Incidence of lamprey marks on Lake Sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens Rafinesque, 1817) in the St. Clair–Detroit River System: Implications for Sea Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus Linnaeus, 1758) effects. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2021, 37, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, H.K.; Sutton, T.M.; Swink, W.D. Lethality of sea lamprey parasitism on lake sturgeon. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2009, 138, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, M.S.; Patrick, H.K.; Sutton, T.M. A single sea lamprey attack causes acute anemia and mortality in lake sturgeon. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2012, 24, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobiesz, N.E.; Bence, J.R.; Sutton, T.; Ebener, M.; Pratt, T.C.; O’Connor, L.M.; Steeves, T.B. Evaluation of sea lamprey-associated mortality sources on a generalized lake sturgeon population in the Great Lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, G.T., Jr. Frequency of Occurence of the Parasite Cystoopsis acipenseri in Juvenile White Sturgeon Acipenser transmontanus in the Lower Co1 mbia River. In Status and Habitat Requirements of the White Sturgeon Populations in the Columbia River Downstream from Mcnary Dam; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 1992; p. 365. [Google Scholar]
- Margolis, L.; McDonald, T. Parasites of white sturgeon, Acipenser transmontanus, from the Fraser River, British Columbia. J. Parasitol. 1986, 72, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Dick, T.A. Sturgeons (Chondrostei: Acipenseridae) and their metazoan parasites: Patterns and processes in historical biogeography. J. Biogeogr. 2001, 28, 1411–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, J.R. Biological factors impinging upon control of external protozoan fish parasites. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1991, 1, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, E.J. Skin ulcers in fish: Pfiesteria and other etiologies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, K. Impact and control of protozoan parasites in maricultured fishes. Parasitology 2015, 142, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David Sibley, L. Invasion and intracellular survival by protozoan parasites. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 240, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, A.; Rahimi Afzal, Z.; Taheri Mirghaed, A.; Soltani, M.; Ebrahimzadeh Mousavi, H.A.; Mollaeian, H. Study of ectoparasite contamination of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792) in Aquatic Animal Health Research Center’s farm, Faculty of Veterinary, University of Tehran. J. Appl. Ichthyol. Res. 2017, 5, 153–166. [Google Scholar]
- Zilberg, D. Amoebic gill disease of marine fish caused by Neoparamoeba pemaquidensis. Acta Zool. Sin. 2005, 51, 554–556. [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson, H.W. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis and Cryptocaryon irritans (phylum Ciliophora). Fish Dis. Disorders. Vol. 1 Protozoan Metazoan Infect. 2006, 1, 116–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, D.-H.; Klesius, P.H. Evaluation of an antiparasitic compound extracted from Galla chinensis against fish parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, R. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Fouquet and ichthyophthiriosis in freshwater teleosts. Adv. Parasitol. 2005, 59, 159–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, G.L. Parasites of North American Freshwater Fishes; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár, K.; Székely, C.; Láng, M. Field Guide to Warmwater Fish Diseases in Central and Eastern Europe, the Caucasus and Central Asia; Food & Agriculture Org: Quebec, QC, Canada, 2019; pp. 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- Modak, B.K.; Banerjee, P.; Basu, S. Studies on Identification, Prevalence and Intensity of Infestation of Trichodinid Ciliophorans (Protozoa: Ciliophora) in the Freshwater Edible Fishes of Purulia District, West Bengal. Environ. Ecol. 2021, 39, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, D.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Gong, X. Study of Apiosoma piscicola (Blanchard 1885) occurring on fry of freshwater fishes in Hongze, China with consideration of the genus Apiosoma. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 102, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.; Cojocaru, C.-D.; Mo, T.A. Infections with Gyrodactylus spp. (Monogenea) in Romanian fish farms: Gyrodactylus salaris Malmberg, 1957 extends its range. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejusová, I.; Gelnar, M.; Verneau, O.; Cunningham, C.O.; Littlewood, D. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the genus Gyrodactylus (Platyhelminthes: Monogenea) inferred from rDNA ITS region: Subgenera versus species groups. Parasitology 2003, 127, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, T.A.; Harris, P.D.; Cable, J. Host specificity dynamics: Observations on gyrodactylid monogeneans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogans, W.E. Northern range extension record for Ergasilus labracis (Copepoda, Ergasilidae) parasitic on the striped bass (Morone saxatilis). Crustaceana 1985, 49, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, I.P.M.; Gaikwad, J. Pathogenic cryptobia cataractae (redescribed) of fresh water fishes from masooli reser-voir, parbhani (M.S.). Rev. Res. 2019, 1, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, C. Haematozoa of fishes, with emphasis on north american. In A Symposium on Diseases of Fishes and Shellfishes; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MA, USA, 1970; p. 82. [Google Scholar]
- Athanassopoulou, F.; Billinis, C.; Prapas, T. Important disease conditions of newly cultured species in intensive freshwater farms in Greece: First incidence of nodavirus infection in Acipenser sp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2004, 60, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, R. Eye fluke (Diplostomum spathaceum) of fishes from the upper Salmon River near Obsidian, Idaho. Great Basin Nat. 1983, 43, 675–683. [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri, J.R.; Heckmann, R.A.; Evans, R.S. Life cycle and incidence of Diplostomum spathaceum Rudolphi (1819) (Trematoda: Diplostomatidae) in Utah. Great Basin Nat. 1976, 36, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Pylkkö, P.; Suomalainen, L.R.; Tiirola, M.; Valtonen, E.T. Evidence of enhanced bacterial invasion during Diplostomum spathaceum infection in European grayling, Thymallus thymallus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, R. On the systematic position of the genus Deropristis, of Dihemistephanus sturionis Little, 1930, and of a new digenetic trematode from a sturgeon. Parasitology 1952, 42, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibinu, I.E.; Smooker, P.M.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis nematodes in fish and shellfish-from infection to allergies. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahanandeh, M.; Rahanandeh, M.; Hallajian, A.; Avakh Keysami, M. Study of pathology of Diclobothrium armatum parasite in the gills of farmed Huso huso in Guilan. J. Anim. Environ. 2019, 11, 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Aghaee Moghadam, A.; Haghparast, S.; Pazooki, J.; Pouramini, M.; Darvish Bastami, K. Prevalence of helminth and nematode parasites in digestive tract, skin surface and blood of Sturgeon broodstocks from southeast of the Caspian Sea. J. Anim. Res. Iran. J. Biol. 2014, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sattari, M. Parasites of stellate sturgeon (Acipenser stellatus) from south-west of Caspian Sea. Casp. J. Environ. Sci. 2003, 1, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Morales, E.; Kim, I.-H.; Castellanos, I. A new geographic and host record for Argulus flavescens Wilson, 1916 (Crustacea, Arguloida), from southeastern Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1998, 62, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, O.; Pugachev, O.; Voronin, V. Study of parasites and diseases of sturgeons in Russia: A review. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorgnia, A.; Sharifi, N.; Youssefi, M. Acipenser stellatus as a new host record for Lernaea cyprinacea linnaeus, 1758 (crustacea; copepoda), a parasites of freshwater fishes in Iran. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2018, 7, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bielecki, A. Fish leeches of Poland in relation to the Palaearctic piscicolines [Hirudinea: Piscicolidae: Piscicolinae]. Genus. Int. J. Invertebr. Taxon. 1997, 8, 223–375. [Google Scholar]
- Nesemann, H.; Neubert, E. 6/2: Annelida, Clitellata: Branchiobdellida, Acanthobdellea, Hirudinea; Spektrum: Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; p. 187. [Google Scholar]
- Raikova, E. The nervous system of parasitic cnidarian Polypodium hydriforme. Cell Tissue Biol. 2013, 7, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.S. Transcriptomic Evidence That Enigmatic Parasites Polypodium Hydriforme and Myxozoa are Cnidarians. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Habil, G.D.; Holban, E.; Jawdhari, A.; Sadîca, I. Review on Polypodium Hydriforme Infestation of Sturgeon Eggs and Its Implications in Species Conservation. In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2023; p. 02007. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, P.R.; Mateus, C.S.; Alexandre, C.M.; Pedro, S.; Boavida-Portugal, J.; Belo, A.F.; Pereira, E.; Silva, S.; Oliveira, I.; Quintella, B.R. The decline of the ecosystem services generated by anadromous fish in the Iberian Peninsula. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 2927–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, R.A.; Mitrovic, D.; Wilkie, M.P. Disturbances to energy metabolism in juvenile lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens) following exposure to niclosamide. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 229, 112969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
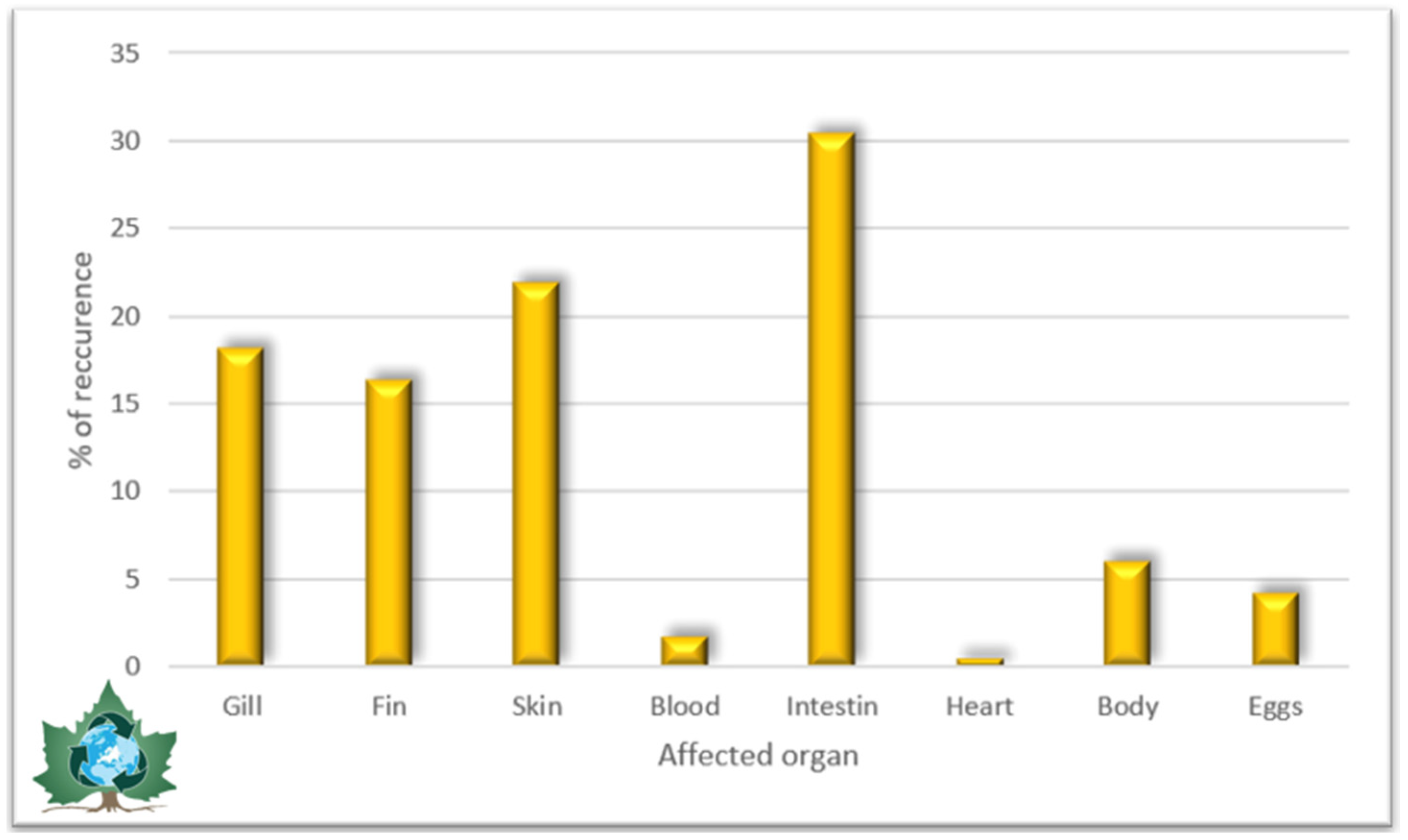
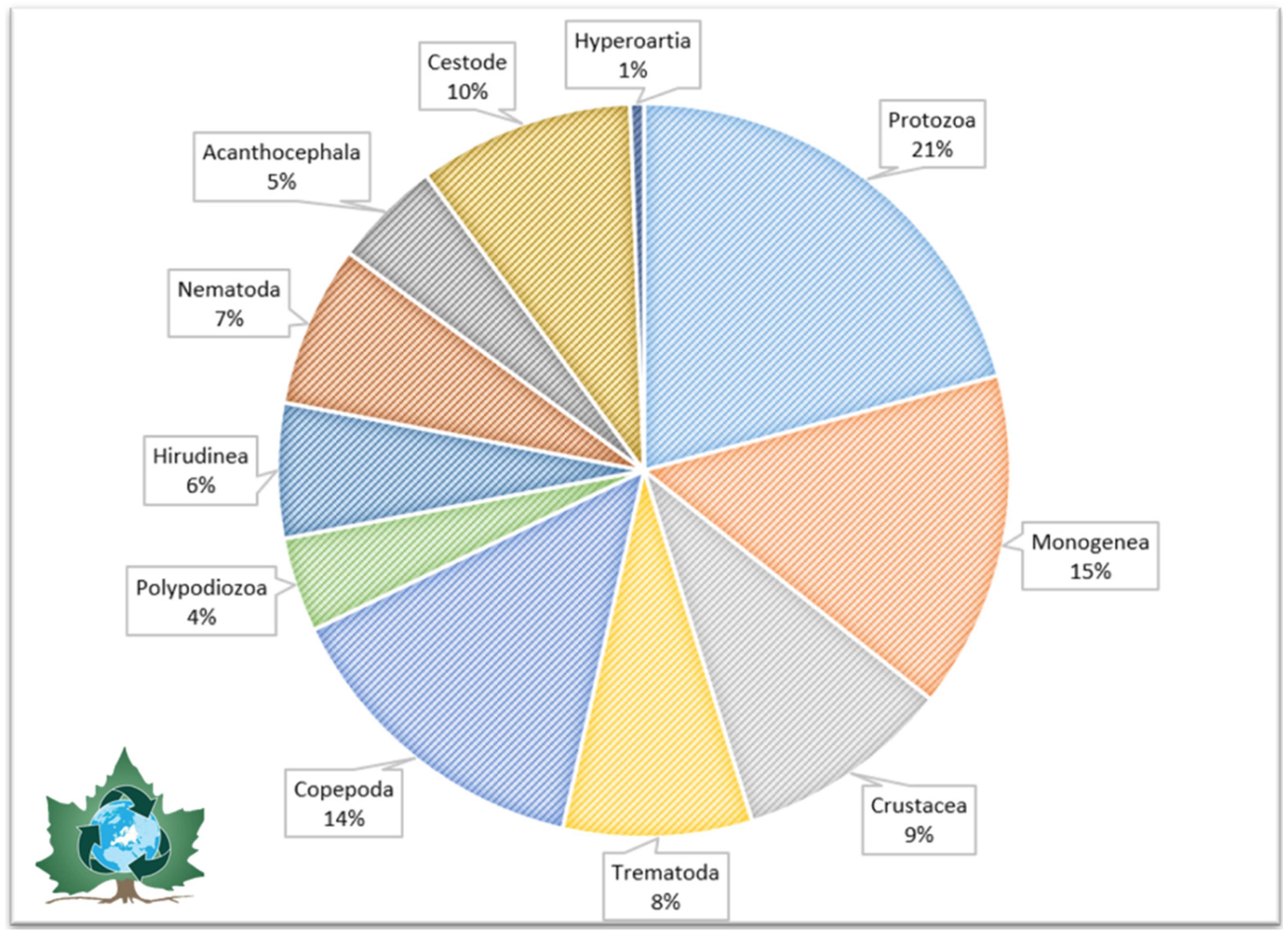
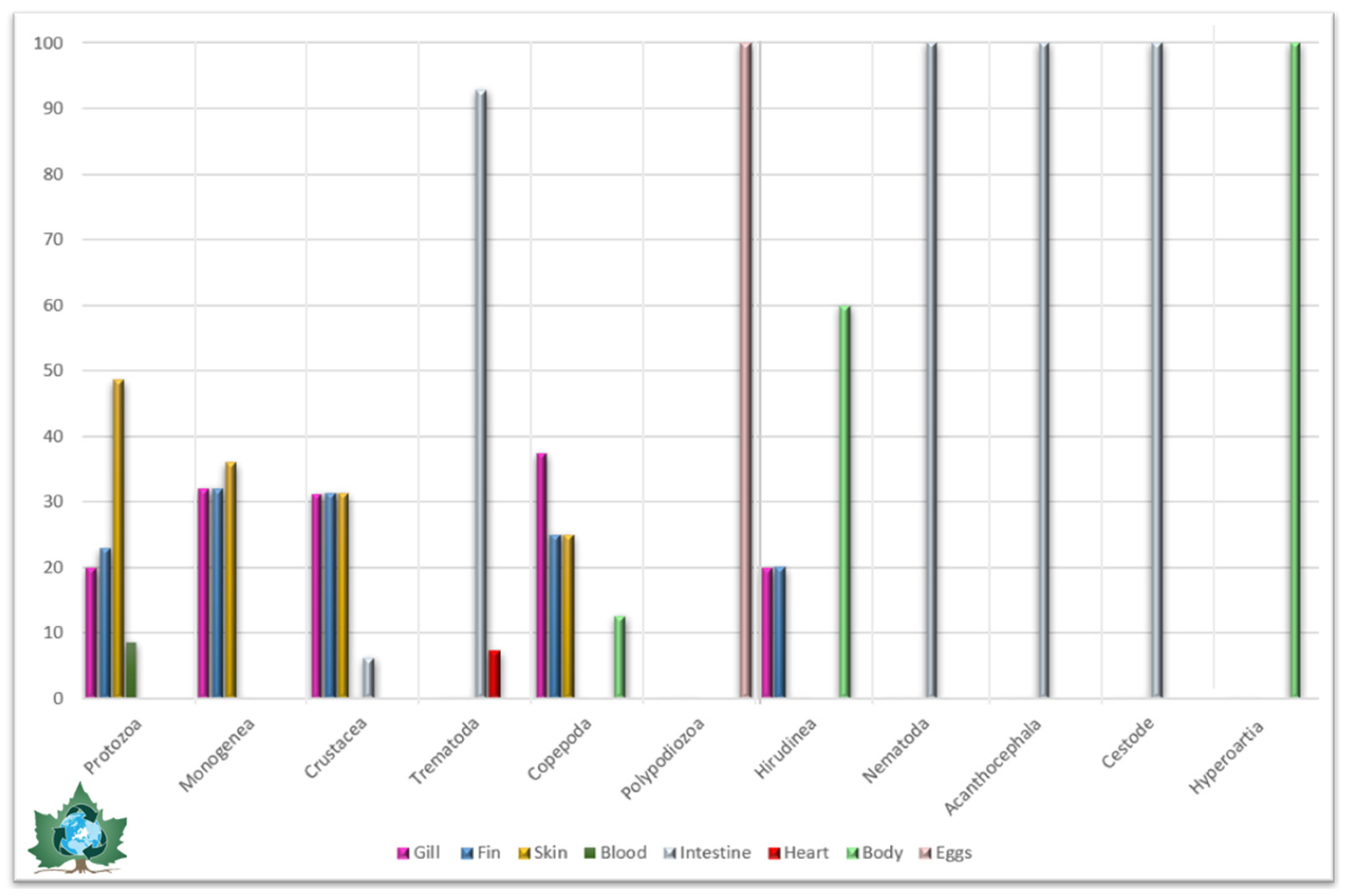
| Sturgeon Species | Parasitic Species | Infected Organs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acipenser stellatus (Pallas, 1771) | Protozoa Ichthyophthirius multifiliis | G. S. F | [20] |
| Acipenser oxyrhynchus (Mitchill, 1815) | Protozoa Trichodina sp., Apiosoma sp., Monogenea Gyrodactylus sp. Crustacea Ergasilus siebold, Argulus coregoni | G. S. F | [21] |
| Acipenser persicus (Borodin, 1897) Acipenser guldenstadti (Brandt & Ratzeburg, 1833) Acipenser stellatus | Protozoa Cryptobia acipenseris, Haemogregarina acipenseris | BL | [22] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Protozoa Chilodonella sp. | S. D | [23] |
| Acipenser gueldenstaedti and Acipenser baerii (Brandt, 1869) | Protozoa Trichodina reticulate, Trematoda Diplostomum spathaceum | G. S. N | [24] |
| Acipenser persicus (Borodin, 1897) | Protozoa Trichodina sp., Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Trematoda Diplostomum spathaceum Nematoda Cucullanus sphaerocephlaus, Anisakis sp., Skyrjabinopsilus semiarmatus and Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus | S. F. G. I | [25] |
| Acipenser persicus | Protozoa Trichodina reticulate Trematoda Diplostomum spathaceum | S. F. G. E | [26] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Monogenea Nitzschia sturionis | S. G | [27] |
| Acipenser gueldenstaedtii Acipenser persicus Acipenser stellatus, Acipenser sturio (Linnaeus, 1758) | Protozoa Ichthyobodo necatrix, Trichodinidae, Apiosoma, Epistylis Monogeneans Diclybothrium, Dactylogyrus and Crustaceans Agulus foliaceus | G. S. F | [19] |
| Acipenser ruthenus (Linnaeus, 1758) | Protozoa Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Trematoda Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus, Acrolichanus auriculatus | S. GU | [28] |
| Acipenser persicus | Protozoan Ichthyophthirius multifiliis | G | [29] |
| Acipenser ruthenus | Protozoa Cryptobia acipenseris, Haemogregarina acipenseris, Trichodina sp. Cestoda Proteocephalus sp. Trematoda Crepidostomum auriculatum, Diplostomum chromatophorum, Nematoda Capillospirura ovotrichuria, Acanthocephala Echinorhynchus cinctulus, Hirudinea Piscicola geometra, Copepoda Ergasilus sieboldi | BL. F. I. | [30] |
| Acipenseridae | Trematoda Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus, Sanguinicola Posthodiplostomum, Cestoda Amphilina foliacea Nematoda Contracaecum sp., Acanthocephala, Pomphorhynchus bosniacus. | I | [11] |
| Acipenser fulvescens (Rafinesque, 1817) | Trematoda Pristicola bruchi | I | [31] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Trematoda Acipensericola glacialis | H | [32] |
| Acipenser persicus | Trematode Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus Nematodes Cucullanus sphaerocephalus, Eustrongylides, Anisakis sp. cestode Amphilina foliacea Monogenea Diclybothrium armatum, Nitzschia storionis Acanthocephalan Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus Crustacea Pseudotracheliastes stellatus | G. S. F. I | [33] |
| Acipenser ruthenus | Trematoda Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus | Ds | [34] |
| Acipenser schrenkii (Brandt, 1869) | Trematoda Crepidostomum oschmarini | I | [35] |
| Acipenser sturio, Acipenser ruthenus, Acipenser fulvescens | Trematoda Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus, Distomum hispidum, Deropristis hispida, Cestrahelmins rivularis, Homalometron armatum. | I | [36] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Trematoda Skrjabinopsolus nudidorsalis sp. | I | [37] |
| Acipenser stellatus Acipenser gueldenstaedtii Acipenser nudiventris (Lovetsky, 1828) Acipenser Huso huso dauricus (Georgi, 1775) | Trematode Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus Nematode Cucullanus sphaerocephalus, Eustrongylides excisus Cestodes Amphilina foliacea, Bothrimonus fallax Acanthocephalan Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus | I | [38] |
| Acipenser persicus | Trematoda Skrjabinopsolus. Nematode Cucullanus sphaerocephalus, Eustrongylides excisus Cestodes Amphilina foliacea, Bothrimonus fallax Acanthocephalan Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus | I | [39] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Copepoda Dichelesthium oblongum Monogenea Nitzschia sp. | G. F. | [40] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Copepoda Dichelesthium oblongum | S | [41] |
| Husu huso | Copepoda Argulus | G. S. F | [42] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Copepoda Argulus flavescens | G | [43] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Copepoda Dichelesthium oblongum | G | [44] |
| Huso huso, Acipenser ruthenus, Acipenser gueldenstaedtii | Copepoda Lernaea cyprinacea, Argulus sp., Ergasilus sp. | G. S. F | [45] |
| Acipenseriformes | Copepoda Tracheliastes gigas | B | [46] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Copepoda Argulus sp. | G. S | [47] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Copepoda Dichelesthiidae oblongum | G | [48] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Copepoda Caligus elongatus, Dichelesthium Oblongum Hirudinea Calliobdella vivida Crustacea Argulus stizostethii and Monogenea Nitzschia sturionis | F. S. B | [49] |
| Acipenser ruthenus | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme | Eg | [50] |
| Acipenser ruthenus | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme | Eg | [51] |
| Acipenser mikadoi (Hilgendorf, 1892) | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme Cestoda Amphilina japonica Hirudinea Limnotrachelobdella sp. | Eg. B. I | [52] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme | Eg | [51] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme | Eg | [53] |
| Acipenseriform | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme | Eg | [54] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme | Eg | [55] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme | Eg | [56] |
| Acipenser, Huso dauricus, Acipenser schrenckii (Brandt, 1869) | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme | Eg | [57] |
| Acipenser mikadoi | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme Hirudinea Limnotrachelobdella | Eg. B | [58] |
| Acipenseriformes | Polypodiozoa Polypodium hydriforme | Eg | [59] |
| Acipenser gueldenstaedtii | Hirudinea Acipenserobdella volgensis | F | [60] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Hirudinea Caspiobdella fadejewi | B | [61] |
| Acipenser brevirostruin (Lesueur, 1818) | Hirudinea Placobdella montifera, Piscicola geometra | B | [62] |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | Hirudinea Calliobdella vivida | G | [63] |
| Acipenser baerii, Acipenser ruthenus | Nematoda Raphidascaris acus | I | [64] |
| Cestodes Amphilina foliacea, Bothrimonus fallax, Nematoda Cucullanus sphaerocephalus, Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus and Acanthocephalan Eustrongylides excisus | I | [65] | |
| Acipenser ruthenus | Nematoda Cystidicoloides ephemeridarum | I | [66] |
| Acipenser stellatus | Nematoda Eustrongylides excisus | Gu | [67] |
| Acipenser persicus | Nematoda Cucullanus sphaerocephalus, Trematode Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus, Cestoda Eubothrium acipenserinum. Acanthocephala Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus | I | [26] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Nematoda Capillospirura sp. | I | [68] |
| Acipenser filvescens | Nematoda Cucullanus sphaerocephala Trematoda Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus Acanthocephala Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus Cestoda Amphilina foliacea | I | [69] |
| Acipenser transmontanus (Richardson, 1836) | Nematoda Cystoopsis acipenseri | I | [70] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Monogenea Diclybothrium atriatum Trematoda Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus | G. S. I | [71] |
| Acipenser persicus Acipenser stellatus Acipenser gueldenstaedti Acipenser nudiventris | Monogenea Nitzschia sturionis, Diclybothrium | G. I | [72] |
| Acipenser baerii | Monogenea Diclybothrium armatum | G | [73] |
| Acipenser stellatus | Monogenea Nitzschia sturionis | G | [74] |
| Acipenser nudiventris | Acanthocephala Leptorhynchoides polycristatus | I | [75] |
| Acipenser naccarii (Bonaparte, 1836) | Acanthocephala Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus | T | [76] |
| Acipenser nudiventris | Cestoda Bothrimonus fallax | I | [77] |
| Acipenser stellatus | Cestoda Amphilina foliacea | I | [78] |
| Acipenser ruthenus | Cestoda Amphilina foliacea | I | [79] |
| Acipenser gueldenstadti | Cestoda Bothrimonus fallax, Eubothrium acipenserinum | I | [80] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Hyperoartia (Lamprey) Petromyzon marinus | B | [81] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Hyperoartia (Lamprey) Petromyzon marinus | B | [82] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Hyperoartia (Lamprey) Petromyzon marinus | B | [83] |
| Acipenser fulvescens | Hyperoartia (Lamprey) Petromyzon marinus | B | [84] |
| Acipenser transmontanus (Richardson, 1836) | Nematoda Cystoopsis acipenseri | I | [85] |
| Acipenser transmontanus | Trematoda Crepidostomum auriculatum Cestoda Diphyllobothrium sp, Amphilina bipunctata. Nematoda Anisakis simplex. Acanthocephala Corynosoma strumosum | I | [86] |
| Acipenser transmontanus | Allocreadiidae Crepidostomum auriculatum Monogenea Nitzschia quadritestes sp. Cestoda Amphilina foliacea | I | [87] |
| Parasites | Infected Organs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | F | S | I | Eg | B | BL | E | GU | Ds | N | SP | H | T | Ca | |
| Protozoa | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Monogenea | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Acanthocephala | X | X | |||||||||||||
| Trematoda | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Nematodes | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||
| Copepoda | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Cestoda | X | X | |||||||||||||
| Polypodiozoa | X | ||||||||||||||
| Hirudinea | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Hyperoartia (Lamprey) | X | ||||||||||||||
| Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ciliophora | Oligohymenophorea | Hymenostomatida | Ichthyophthiriidae | Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Fouquet 1876) |
| Ciliophora | Oligohymenophorea | Mobilida | Triochodinidae | Trichodina sp. Trichodina Ehrenberg, 1830 and Trichodina (reticulata Hirschmann & Partsch, 1955) |
| Ciliophora | Oligohymenophorea | Peritrichida | Epistylididae | Apiosoma sp. (Blanchard, 1885) |
| Ciliophora | Oligohymenophorea | Sessilida | Epistylididae | Epistylis sp. (Ehrenberg, 1830) |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Diplostomida | Diplostomidae | Diplostomum spathaceum (Rudolphi, 1819), Olsson, 1876) |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Diplostomida | Schistosomatidae | Schistosoma japonicum (Katsurada, 1904) |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Plagiorchiida | Allocreadiidae | Crepidostomum auriculatum (Wedl, 1858) Lühe, 1909 |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Plagiorchiida | Deropristidae | Pristicola bruchi (Choudhury, 2009) |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Diplostomida | Aporocotylidae | Acipensericola glacialis (Warren & Bullard, 2017) |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Plagiorchiida | Deropristidae | Skrjabinopsolus semiarmatus (Molin, 1858) Ivanov, 1937 |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Diplostomata | Aporocotylidae | Sanguinicola sp. (Plehn, 1905) |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Diplostomida | Diplostomidae | Posthodiplostomum sp. (Dubois, 1936) |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Plagiorchiida | Allocreadiidae | Crepidostomum auritum (MacCallum, 1919) |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Plagiorchiida | Allocreadiidae | Crepidostomum oschmarini (Zhokhov & Pugacheva, 1998) |
| Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Plagiorchiida | Deropristidae | Skrjabinopsolus nudidorsalis (Ivanov, 1937) |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea (Monogenoidea) | Capsalidea | Capsalidae | Nitzschia sturionis (Abildgaard, 1794) Krøyer, 1852 |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea (Monogenoidea) | Diclybothriidea | Diclybothriidae | Diclybothriidae gen. sp. (Bykhovskii and Gusev. 1950) |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea (Monogenoidea) | Diclybothriidea | Diclybothriidae | Diclybothrium sp. (Leuckart, 1835) |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea (Monogenoidea) | Dactylogyridea | Dactylogyridae | Dactylogyrus sp. (Diesing, 1850) |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea (Monogenoidea) | Diclybothriidea | Diclybothriidae | Diclybothrium sp. (Leuckart, 1835) |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea (Monogenoidea) | Dactylogyridea | Dactylogyridae | Dactylogyrus sp. (Diesing, 1850) |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea (Monogenoidea) | Diclybothriidea | Diclybothriidae | Diclybothrium armatum (Leuckart, 1835) |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea (Monogenoidea) | Diclybothriidea | Diclybothriidae | Diclybothrium hatum (Leuckart, 1835) |
| Platyhel mintes | Monogenea | Gyrodactylidea | Gyrodactylidae | Gyrodactylus sp. von Nordmann, 1832 |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea | Diclybothriidea | Diclybothriidae | Paradiclybothrium pacificum (Bychowsky & Gusev, 1950) |
| Platyhelminthes | Monogenea | Capsalidea | Capsalidae | Nitzchia Gervais, 1846 |
| Nematoda | Chromadorea | Rhabiditida | Cystidicolidae | Capillospirura sp. (Skrjabin, 1924) |
| Nematoda | Chromadorea | Rhabiditida | Cucullanidae | Truttaedacnitis (Cucullanus) (Müller, 1777) |
| Nematoda | Chromadorea | Rhabiditida | Cucullanidae | Cucullanus sphaerocephlaus (Rudolphi, 1809) Baylis, 1939 |
| Nematoda | Chromadorea | Rhabiditida | Anisakidae | Anisakis sp. (Dujardin, 1845) |
| Nematoda | Enoplea | Dioctophymatida | Dioctophymatidae | Eustrongylides excisus (Jägerskiöld, 1909) |
| Nematoda | Chromadorea | Rhabiditida | Raphidascarididae | Raphidascaris acus (Bloch, 1779) Railliet & Henry, 1915 |
| Nematoda | Enoplea | Trichinellida | Cystoopsidae | Cystoopsis acipenseri (Wagner, 1867) |
| Nematoda | Chromadorea | Rhabiditida | Anisakidae | Contracaecum bidentatum (Ward & Magath, 1917) |
| Nematoda | Chromadorea | Rhabiditida | Anisakidae | Contracaecum sinipercae (Dogiel & Achmerov, 1946) |
| Nematoda | Chromadorea | Rhabiditida | Cystidicolidae | Spinitectus gracilis Fourment, 1883 |
| Myzozoa | Conoidasida | Eucoccidiorida | Eimeriidae | Goussia vargai Cynthia R., Blazer, Vicki S. (2019) |
| Myzozoa | Conoidasida | Eucoccidiorida | Eimeriidae | Goussia acipensris (labbe 1896) |
| Myzozoa | Conoidasida | Eucoccidiorida | Haemogregarinidae | Haemogregarina acipenseris (Danilewsky, 1885) |
| Euglenozoa | Kinetoplastea | Eubodonida | Cryptobiaceae | Cryptobia acipenseris (Joff, Lewashow, Boschenko, 1926) |
| Euglenozoa | Kinetoplastea | Prokinetoplastida | Bodonidae | Ichthyobodo necatrix (Henneguy, 1883) |
| Annelida | Clitellata | Rhynchobdellida | Piscicolidae | Limnotrachelobdella sp. (Epshtein, 1968) |
| Annelida | Clitellata | Rhynchobdellida | Glossiphoniidae | Placobdella montifera (Moore, 1906) |
| Annelida | Clitellata | Rhynchobdellida | Piscicolidae | Acipenserobdella volgensis (Epstein, 1969) |
| Annelida | Clitellata | Rhynchobdellida | Piscicolidae | Piscicola geometra (Linnaeus, 1761) |
| Arthropoda | Copepoda | Cyclopoida | Ergasilidae | Ergasilus sp. (Nordmann, 1832) |
| Arthropoda | Copepoda | Cyclopoida | Lernaeidae | Lernaea cyprinacea (Linnaeus, 1758) |
| Arthropoda | Copepoda | Siphonostomatoida | Lernaeopodidae | Pseudotracheliastes stellatus (Mayor, 1824) |
| Arthropoda | Ichthyostraca | Arguloida | Argulidae | Argulus foliaceus (Linnaeus, 1758) |
| Arthropoda | Ichthyostraca | Arguloida | Argulidae | Argulus sp. (Müller O.F., 1785) |
| Arthropoda | Ichthyostraca | Arguloida | Argulidae | Argulus flavescens (Wilson C.B., 1916) |
| Arthropoda | Ichthyostraca | Arguloida | Argulidae | Argulus stizostethii (Kellicott, 1880) |
| Arthropoda | Copepoda | Siphonostomatoida | Caligidae | Caligus elongatus (von Nordmann, 1832) |
| Arthropoda | Copepoda | Siphonostomatoida | Dichelesthiidae | Dichelesthium oblongum (Abildgaard, 1794) |
| Arthropoda | Copepoda | Siphonostomatoida | Lernaeopodidae | Tracheliastes gigas Richiardi, 1881, Pseudotracheliastes stellatus (Mayor, 1824) |
| Platyhelminthes | Cestoda | Amphilinidea | Amphilinidae | Amphilina sp. (Wagener, 1858) |
| Platyhelminthes | Cestoda | Amphilinidea | Amphilinidae | Amphilina foliacea (Rudolphi, 1819) Wagener, 1858 |
| Platyhelminthes | Cestoda | Spathebothriidea | Acrobothriidae | Bothrimonus fallax (Lühe, 1900) |
| Platyhelminthes | Cestoda | Amphilinidea | Amphilinidae | Amphilina japonica (Goto & Ishii, 1936) |
| Platyhelminthes | Cestoda | Bothriocephalidea | Triaenophoridae | Eubothrium acipenserinum (Cholodkovsky, 1918) Dogiel & Bychowsky, 1939 |
| Annelida | Clitellata | Rhynchobdellida | Piscicolidae | Caspiobdella fadejewi (Epshtein, 1961) |
| Annelida | Clitellata | Rhynchobdellida | Piscicolidae | Calliobdella vivida (=Cystobranchus vividus) (Verrill, 1872) |
| Acanthocephala | Palaeacanthocephala | Echinorhynchida | Leptorhynchoididae | Leptorhynchoides polycristatus (Amin, Heckmann, Halajian, El-Naggar & Tavakol, 2013) |
| Acanthocephala | Palaeacanthocephala | Echinorhynchida | Paracanthocephalidae | Acanthocephalus anguillae (Müller, 1780) |
| Acanthocephala | Palaeacanthocephala | Echinorhynchida | Pomphorhynchidae | Pomphorhynchus bosniacus (Kistaroly & Cankovic, 1969) |
| Acanthocephala | Palaeacanthocephala | Echinorhynchida | Leptorhynchoididae | Leptorhynchoides plagicephalus (Westrumb, 1821) |
| Chordata | Petromyzonti | Petromyzontiformes | Petromyzontidae | Petromyzon marinus (Linnaeus, 1758) |
| Ciliophora | Phyllopharyngea | Chlamydodontida | Chilodonellidae | Chilodonella sp. (Strand, 1928) |
| Cnidaria | Polypodiozoa | Polypodiidea | Polypodiidae | Polypodium hydriforme (Ussow, 1887) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deák, G.; Holban, E.; Sadîca, I.; Jawdhari, A. Sturgeon Parasites: A Review of Their Diversity and Distribution. Diversity 2024, 16, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16030163
Deák G, Holban E, Sadîca I, Jawdhari A. Sturgeon Parasites: A Review of Their Diversity and Distribution. Diversity. 2024; 16(3):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16030163
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeák, György, Elena Holban, Isabela Sadîca, and Abdulhusein Jawdhari. 2024. "Sturgeon Parasites: A Review of Their Diversity and Distribution" Diversity 16, no. 3: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16030163
APA StyleDeák, G., Holban, E., Sadîca, I., & Jawdhari, A. (2024). Sturgeon Parasites: A Review of Their Diversity and Distribution. Diversity, 16(3), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16030163






