Factors Affecting Financial Losses Caused by Wild Boars in Ningxia, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
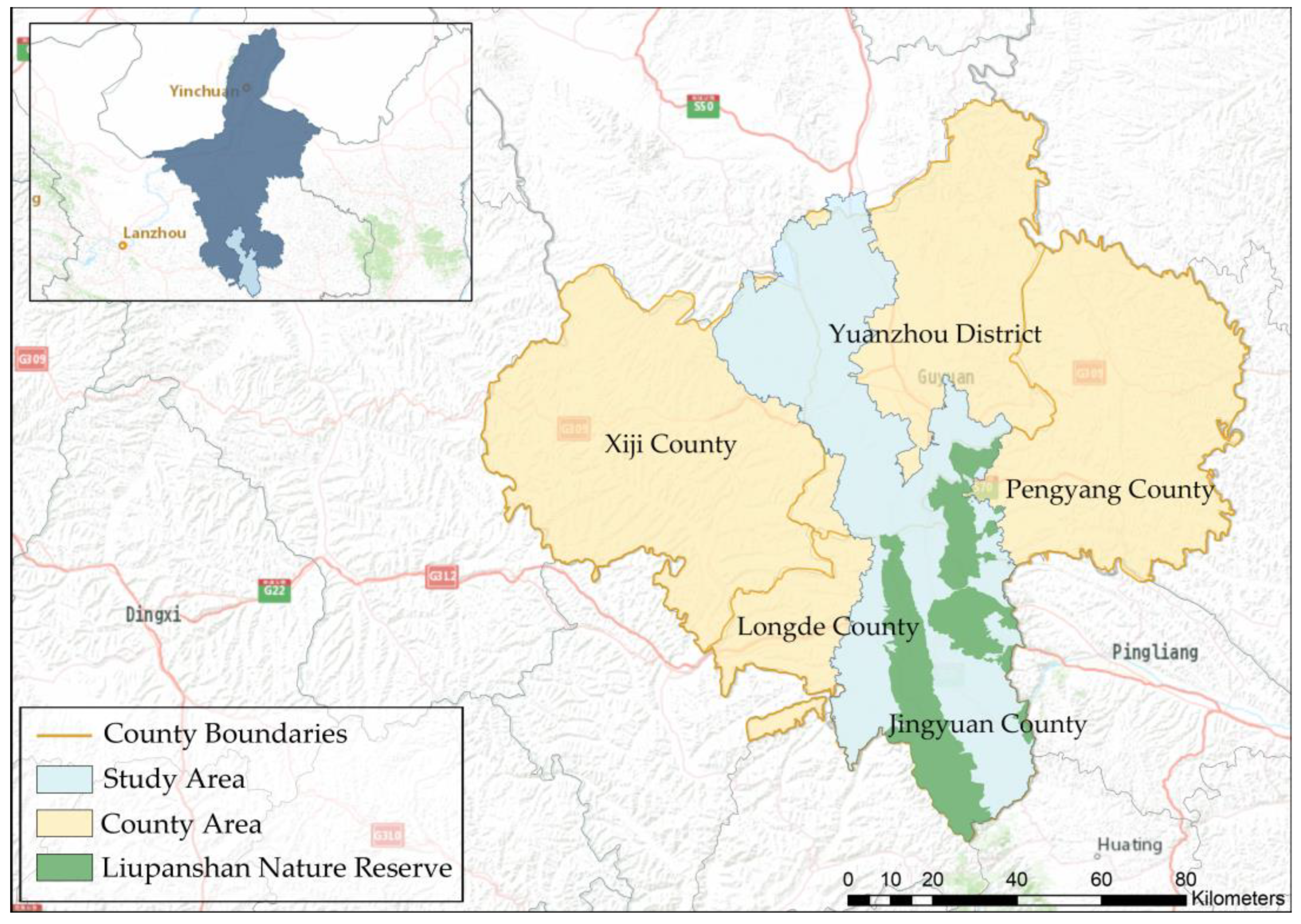
2.1. Study Area
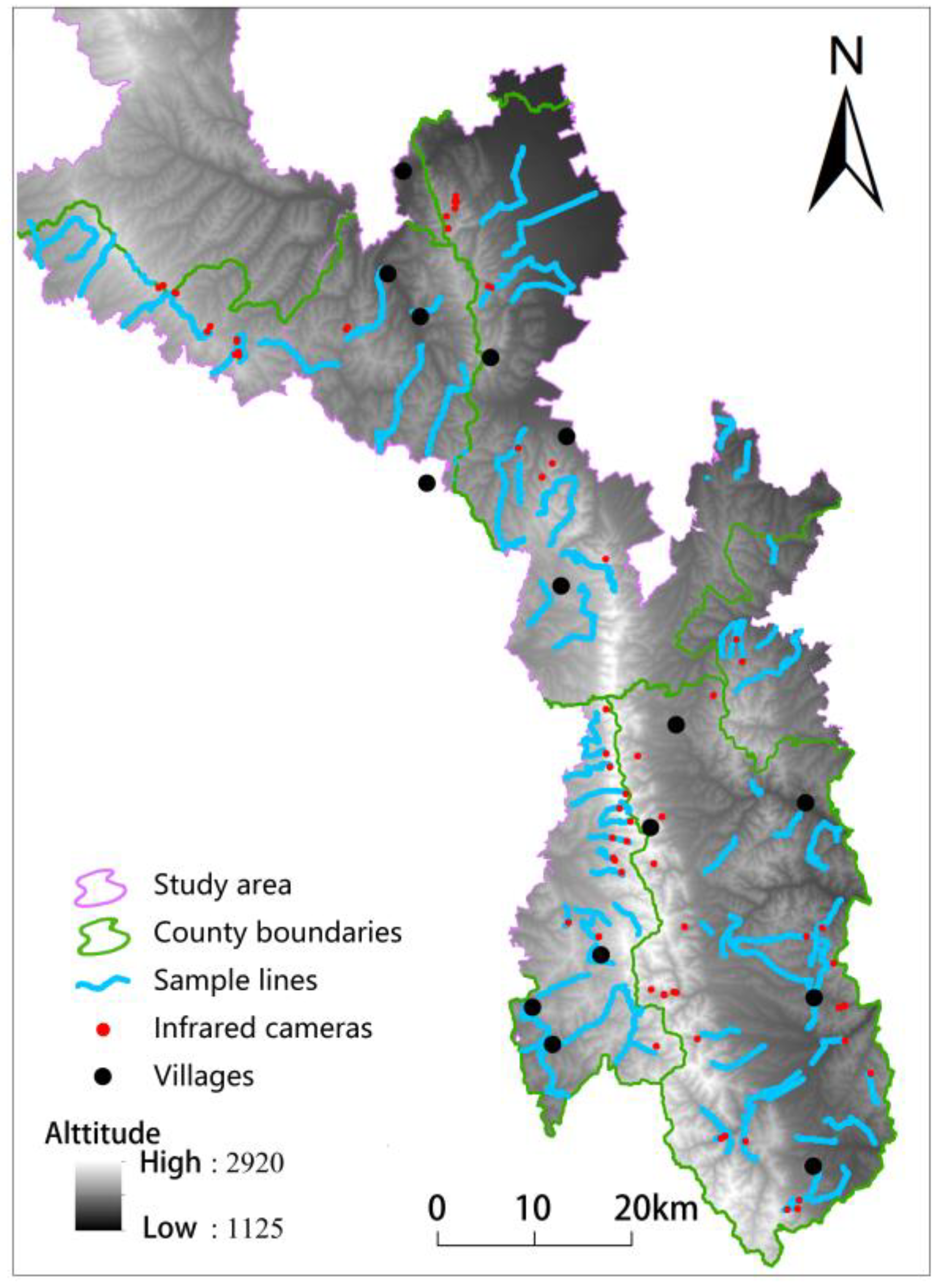
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
- The population density of the wild boars on each sample line was calculated using the following formula:where x is the total number of fresh footprint chains of the wild boars, s is the length of the total sample line, and l is the average daily active distance [26] (search for keywords such as “Wild boar” and “daily moving distance”, corresponding articles and data, and obtain the daily activity distance of wild boars in the corresponding area). The daily activity distance of the wild boars was determined using relevant articles and data.
- The formula for calculating the average density of the wild boars in the entire survey area was:where is the average density of the wild boars on all the survey lines, n is the number of sample lines, and Di is the distribution density of the wild boars on the ith sample line.
- The population of the wild boars in the survey area was calculated using the following formula:where N represents the population size of the wild boars, and A represents the total area of the survey area.
2.4. Model Selection
3. Results
3.1. Wild Boar Status
3.2. Livelihood System in the Study Area
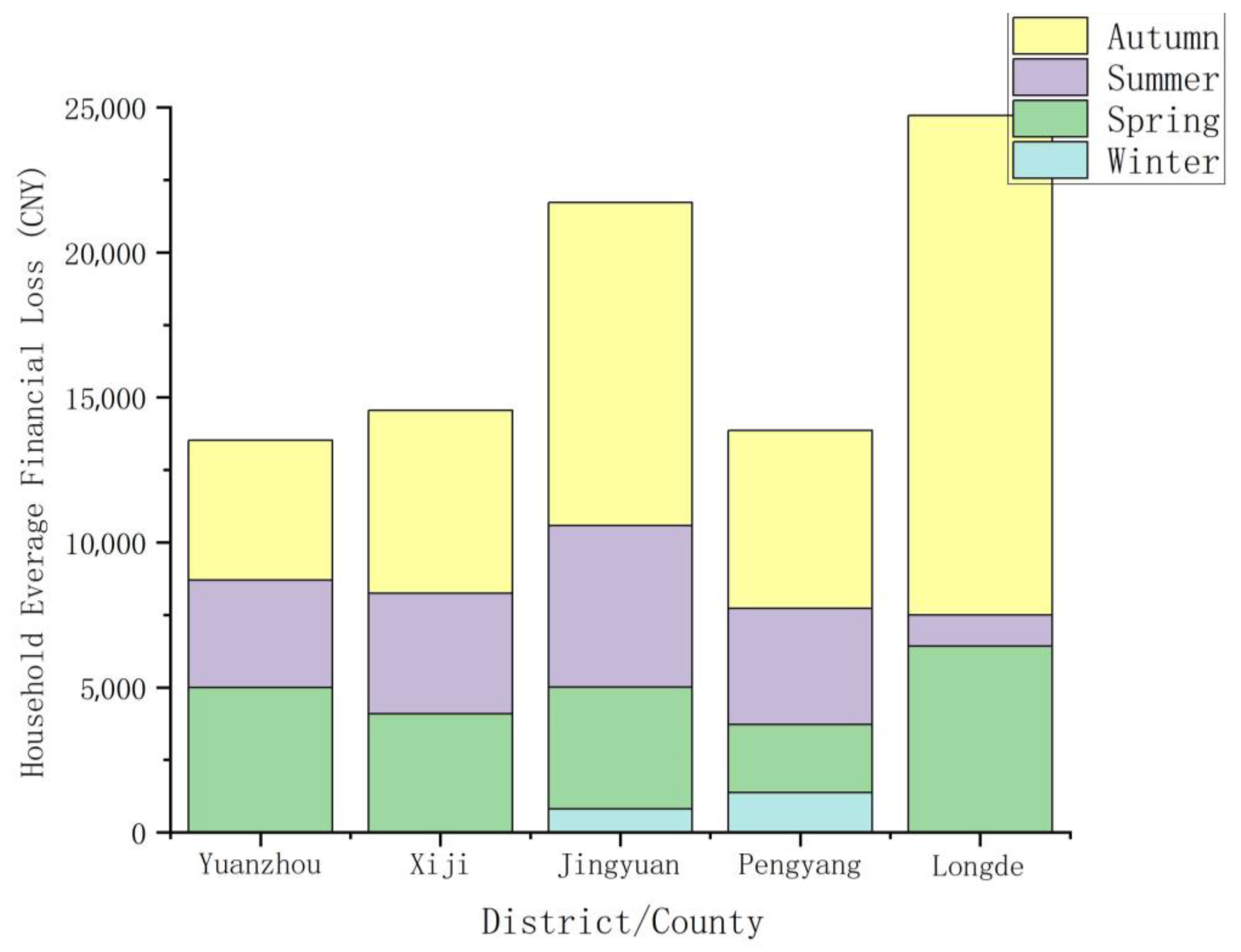
3.3. Crop Damage and Financial Losses
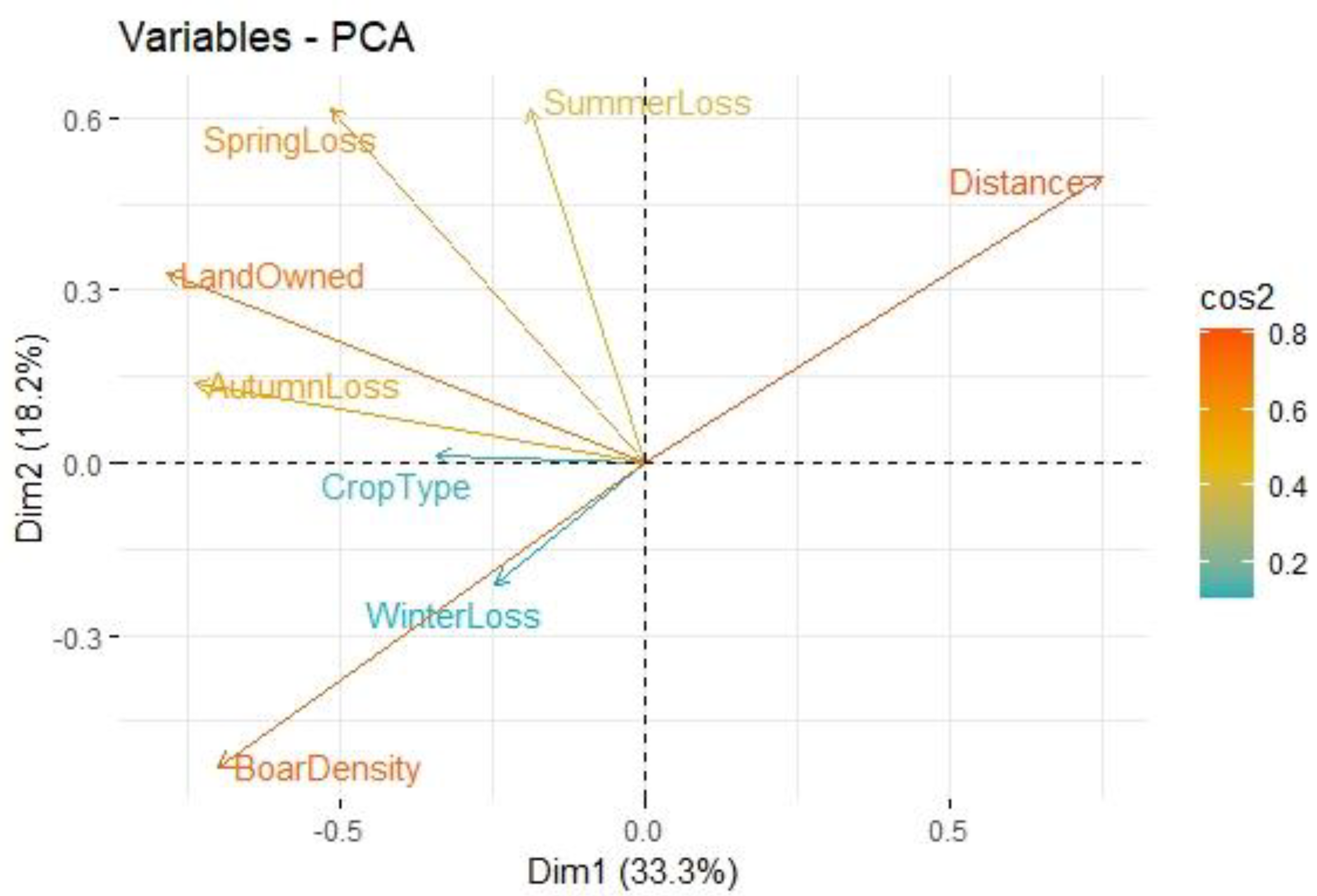
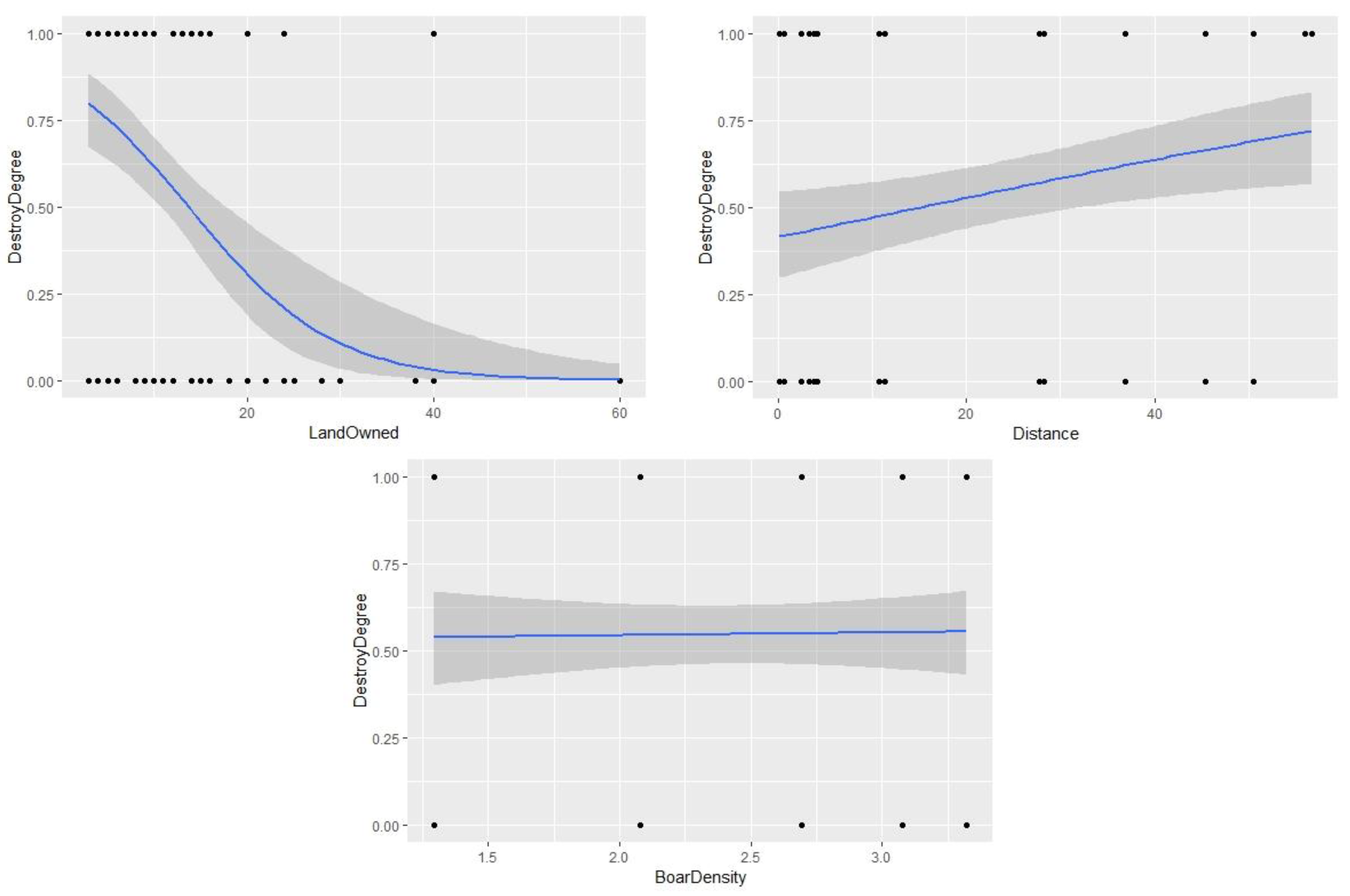
3.4. Damage Degree and Affecting Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fletcher, R.; Toncheva, S. The Political Economy of Human-Wildlife Conflict and Coexistence. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 260, 109216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, J.C. A Methodological Study on Negative Value Evaluation on Wildlife Resources. J. Northwest For. Coll. 2008, 23, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, Y.; Mago, Y.; Rawal, V. The Dynamics of the First Wave of COVID-19 on Environment and Wildlife—A Boon or a Bane? ECJ 2022, 23, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, A.M.; Hilbers, J.P.; Meijer, J.R.; Antao, L.H.; Benitez-Lopez, A.; de Jonge, M.M.J.; Leemans, L.H.; Scheper, E.; Alkemade, R.; Doelman, J.C.; et al. Projecting Terrestrial Biodiversity Intactness with GLOBIO 4. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.W.; Macdonald, D.W. Livestock Predation by Carnivores in Jigme Singye Wangchuck National Park, Bhutan. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 129, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S.; Fuller, R.A.; Brooks, T.M.; Watson, J.E.M. The Ravages of Guns, Nets and Bulldozers. Nature 2016, 536, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sütő, D.; Heltai, M.; Katona, K. Quality and Use of Habitat Patches by Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) along an Urban Gradient. Biol. Futur. 2020, 71, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, A.; Yang, Q.; Kong, X.; Fan, H. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Human and Wild Boar Conflicts in Rural China and Its Implications for Social-Ecological Systems Coevolution. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 1614–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustsson, E.; Kim, H.; Andren, H.; Graf, L.; Kjellander, P.; Widgren, S.; Mansson, J.; Malmsten, J.; Thurfjell, H. Density-Dependent Dinner: Wild Boar Overuse Agricultural Land at High Densities. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2024, 70, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.-Y.; Hu, J.; Song, J.-S.; Wan, Y.-Q.; Guo, Z.-H.; Song, S.; Li, J.-Q. A Survey of Mammal and Bird Diversity Using Camera-trapping in Liupanshan National Nature Reserve in Ningxia. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2022, 2, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, A.; Noelia, M. A Review of Wild Boar Sus scrofa Diet and Factors Affecting Food Selection in Native and Introduced Range. Mammal Rev. 2014, 44, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gren, I.M.; Andersson, H.; Mensah, J.; Pettersson, T. Cost of Wild Boar to Farmers in Sweden. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2020, 47, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baublys, V.; Tubelyte, V. Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) as Study Object; Vytautas Magnus University: Kaunas, Lithuania, 2009; Volume 3, pp. 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ravenelle, J.; Nyhus, P.J. Global Patterns and Trends in Human–Wildlife Conflict Compensation. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Z.; An, K.; Tan, Y.; Ji, W.; Su, J. Possibility of Wild Boar Harm Occurring in Five Provinces of Northwest China. Animals 2023, 13, 3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukeka, J.M.; Ogutu, J.O.; Kanga, E.; Roskaft, E. Human-Wildlife Conflicts and Their Correlates in Narok County, Kenya. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 18, e00620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, C.; Ruf, T. Population Dynamics in Wild Boar Sus scrofa: Ecology, Elasticity of Growth Rate and Implications for the Management of Pulsed Resource Consumers. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, E.P.; Burrow, J.F.; Dytham, C.; Aegerter, J.N. Modelling with Uncertainty: Introducing a Probabilistic Framework to Predict Animal Population Dynamics. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuling, O.; Baubet, E.; Duscher, A.; Ebert, C.; Fischer, C.; Monaco, A.; Podgorski, T.; Prevot, C.; Ronnenberg, K.; Sodeikat, G.; et al. Mortality Rates of Wild Boar Sus Scrofa L. in Central Europe. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2013, 59, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, R.H.; Teng, L.; Mehmood, T.; Ahmad, S.; Liu, Z. Impacts of the Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) on the Livelihood of Rural Communities in Pakistan and Understanding Public Attitudes towards Wild Boars. Animals 2022, 12, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, J.H.; Palka, D.; Buckland, S.T. Adaptive Line Transect Sampling. Biometrics 2002, 58, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.-Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Zhang, M.-H. Wintering Diet of Red and Roe Deer in Heilongjiang Muling Japnaese Yew National Reserve. J. North-East For. Univ. 2019, 47, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Minghao, G.; Jianjun, Z. Discussion on Wildlife Survey Methods in Desert Area: Introduction of a New Survey Method-All Databases. Sichuan J. Zool. 2010, 29, 320–324. [Google Scholar]
- Kathryn, A.; Paul, F.; Jacob, S.; John, P. Testing Infrared Camera Surveys and Distance Analyses to Estimate Feral Horse Abundance in a Known Population. J. Wildl. Manag. 2018, 42, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, R.H.; Teng, L.; Mehmood, T.; Ahmad, S.; Bari, F.; Rehman, E.U.; Liu, Z. Understanding the Dynamics of Human-Wildlife Conflicts in North-Western Pakistan: Implications for Sustainable Conservation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X. Study on Seasonal Home Range and Habitat Selection of Wild Boar in Southern Lesser Khingan Mountains Based on GPS Tracking Technology. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, X. Removing the ‘Three Haves’ and achieving better harmony with wild boars. Green. Life 2023, 8, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Joana, C.; Carme, R.; Jose, D.; Giovanna, M. “Reserve Effect”: An Opportunity to Mitigate Human-Wild Boar Conflicts. Natl. Livrary Med. 2021, 795, 148721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X. Investigation of Wildlife Resources such as Leopard in Liupanshan National Nature Reserve, Ningxia. Ningxia Liupanshan Natl. Nat. Reserve Manag. Bur. 2019, 11, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkinson, S.M.; Schmidt, M.; Ulloa, N. Comparison of the Digestible Energy Content of Maize, Oats and Alfalfa between the European Wild Boar (Sus scrofa L.) and Landrace x Large White Pig (Sus scrofa domesticus). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 144, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopij, G.; Panek, K. Effect of Winter Temperature and Maize Food Abundance on Long-Term Population Dynamics of the Wild Boar Sus scrofa. Pol. J. Ecol. 2016, 64, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Luan, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Richards, M.P. Preliminary Attempt to Distinguish the Domesticated Pigs from Wild Boars by the Methods of Carbon and Nitrogen Stable Isotope Analysis. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.M.; Lahkar, B.P.; Subedi, N.; Nyirenda, V.R.; Lichtenfeld, L.L.; Jakoby, O. Seasonality, Crop Type and Crop Phenology Influence Crop Damage by Wildlife Herbivores in Africa and Asia. Biodivers. Conserv. 2018, 27, 2029–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Li, C.; Bravery, B.D. Factors Affecting Crop Damage by Wild Boar and Methods of Mitigation in a Giant Panda Reserve. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2008, 54, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P. The Human Impact on Biological Diversity. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, E.; Pellikka, J.; Kunnasranta, M.; Huitu, O. Agricultural Damage Following the Recent Expansion of Wild Boar (Sus scrofa)—Farmer Perceptions and Preconditions. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.S.; Kwon, J.H.; Namgung, H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, E.-K.; Park, Y.-C. Long-Term Monitoring of the Barrier Effect of the Wild Boar Fence. J. For. Environ. Sci. 2022, 38, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mumby, H.S.; Plotnik, J.M. Taking the Elephants’ Perspective: Remembering Elephant Behavior, Cognition and Ecology in Human-Elephant Conflict Mitigation. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Yan, J.; Li, H.; He, W.; Li, X. Wildlife Damage and Cultivated Land Abandonment: Findings from the Mountainous Areas of Chongqing, China. Crop. Prot. 2016, 84, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshey; Ford, R.M.; Keenan, R.J.; Nitschke, C.R. Subsistence Farmers’ Understanding of the Effects of Indirect Impacts of Human Wildlife Conflict on Their Psychosocial Well-Being in Bhutan. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massei, G.; Kindberg, J.; Licoppe, A.; Gacic, D.; Sprem, N.; Kamler, J.; Baubet, E.; Hohmann, U.; Monaco, A.; Ozolins, J.; et al. Wild Boar Populations up, Numbers of Hunters down? A Review of Trends and Implications for Europe. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korohoda, W.; Wilk, A. Cell Electrophoresis—A Method for Cell Separation and Research into Cell Surface Properties. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2008, 13, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrzejewski, W.; Jedrzejewska, B.; Okarma, H.; Ruprecht, A.L. Wolf Predation and Snow Cover as Mortality Factors in the Ungulate Community of the Bialowieza National Park, Poland. Oecologia 1992, 90, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart-King, C.A.; Dembo, M.; Hammer, D.A. Cell-Cell Mechanical Communication through Compliant Substrates. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 6044–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miloš, J.; Michaela, H.; Tomáš, K.; Jaroslav, Č. Creeping into a Wild Boar Stomach to Find Traces of Supplementary Feeding. Wildl. Res. 2016, 43, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Location | Area | Urban Population | Rural Population | Average Temperature | Average Rainfall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yuanzhou District | 3501 km2 | 476.7k (58.21%) | 199.2k (41.79%) | 4–15 °C | 631.7 mm |
| Xiji County | 4000 km2 | 70.27k (14.82%) | 403.8k (85.18%) | 2–15 °C | 686.4 mm |
| Pengyang County | 3238 km2 | 66.10k (26.85%) | 180.1k (73.15%) | 3–17 °C | 463.5 mm |
| Longde County | 1268 km2 | 41.74k (38.14%) | 67.7k (61.86%) | 2–14 °C | 760.0 mm |
| Jingyuan County | 1443 km2 | 31.00k (36.05%) | 55.0k (63.95%) | 3–14 °C | 745.2 mm |
| Location | Number of Boars | Distribution Area (km2) | Inferred Population | Boar Density (n/km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yuanzhou District | 406 | 1667 | 4488 | 2.691 |
| Xiji County | 13 | 1988 | 2576 | 1.296 |
| Pengyang County | 43 | 1543 | 3205 | 2.077 |
| Longde County | 262 | 1004 | 3091 | 3.078 |
| Jingyuan County | 628 | 1111 | 3689 | 3.320 |
| Crop Type | Number of Farmers That Were Affected | % | Average Loss USD | Loss in CNY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maize | 115 | 85.2 | 2710 | 19,592 |
| Potato | 20 | 14.8 | 1414 | 10,227 |
| Mean | Median | SD | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter | 274 | 0 | 274 | 6410 |
| Spring | 4629 | 3205 | 4629 | 38,460 |
| Summer | 3822 | 3205 | 3288 | 16,025 |
| Autumn | 9479 | 6410 | 8505 | 48,075 |
| Odds Ratio | Estimate | Standard Error | z-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.91 | −2.39 | 1.63 | −1.46 | 0.14 |
| Boar Number | 1 | 0 | 0 | −1.83 | 0.07 |
| Boar Density | 9.27 | 2.23 | 0.68 | 3.28 | <0.01 |
| Distance | 1.08 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 3.14 | <0.01 |
| Land Owned | 0.90 | −0.10 | 0.03 | −3.10 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qing, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhan, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hu, T.; Liu, F.; et al. Factors Affecting Financial Losses Caused by Wild Boars in Ningxia, China. Diversity 2024, 16, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16100616
Qing Y, Dong Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Meng D, Zhan M, Li Z, Zhang X, Hu T, Liu F, et al. Factors Affecting Financial Losses Caused by Wild Boars in Ningxia, China. Diversity. 2024; 16(10):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16100616
Chicago/Turabian StyleQing, Yan, Yaxin Dong, Zhirong Zhang, Yi Zhang, Dehuai Meng, Meiling Zhan, Zongzhi Li, Xu Zhang, Tianhua Hu, Fubin Liu, and et al. 2024. "Factors Affecting Financial Losses Caused by Wild Boars in Ningxia, China" Diversity 16, no. 10: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16100616
APA StyleQing, Y., Dong, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y., Meng, D., Zhan, M., Li, Z., Zhang, X., Hu, T., Liu, F., Sun, K., Liu, Z., & Teng, L. (2024). Factors Affecting Financial Losses Caused by Wild Boars in Ningxia, China. Diversity, 16(10), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16100616






