Polychaete Diversity and Functional Trait Composition in Subtropical Mangrove Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
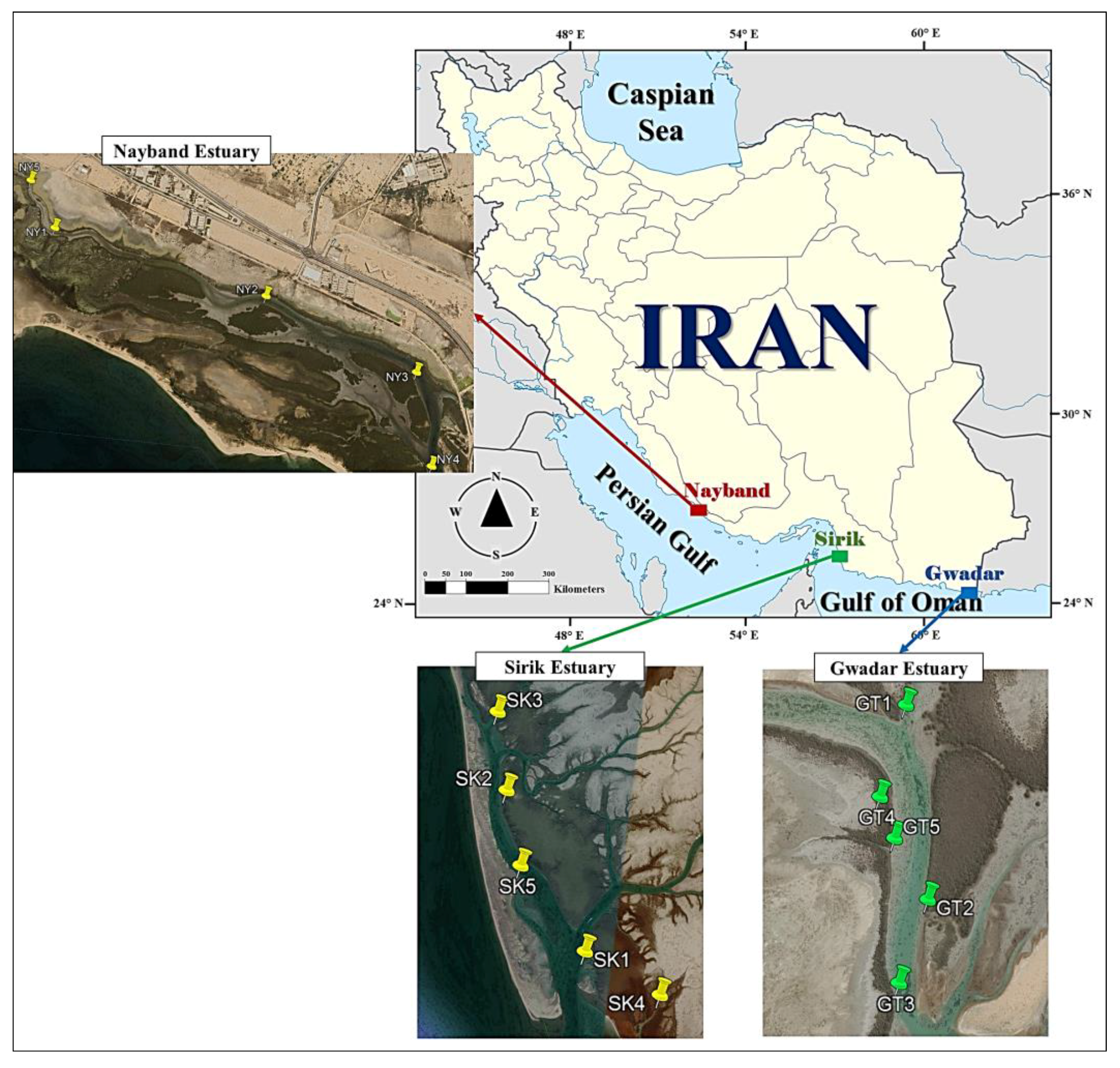
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling of Polychaetes
2.3. Environmental Data
2.4. Trait Data
2.5. Data Analysis
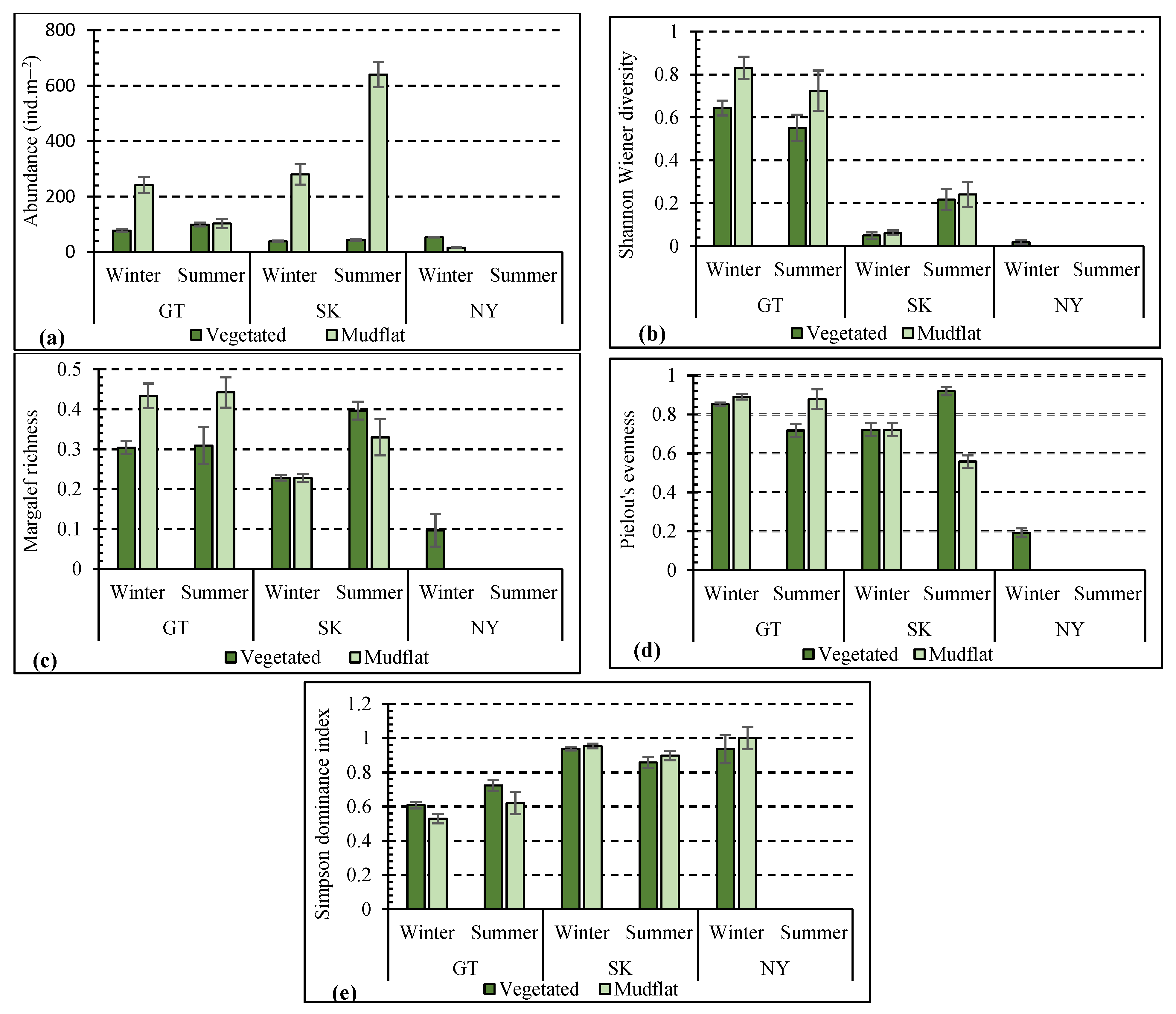
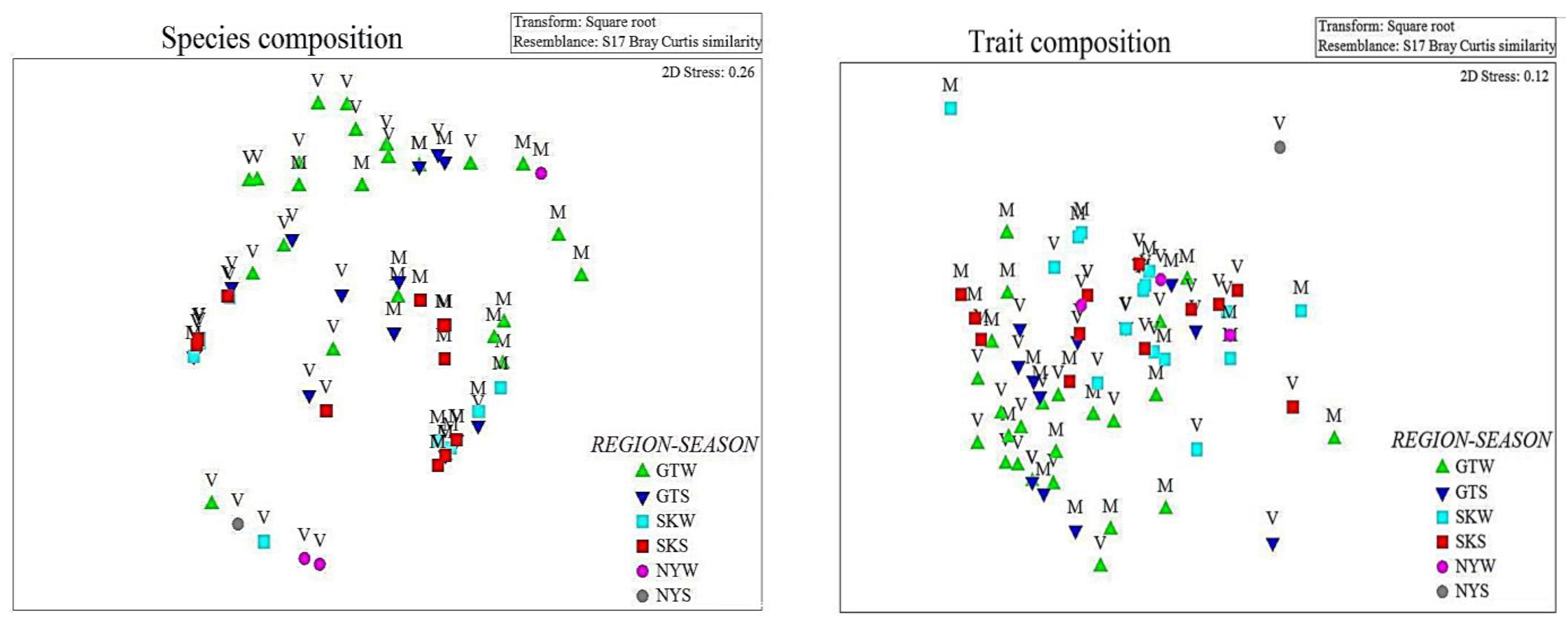
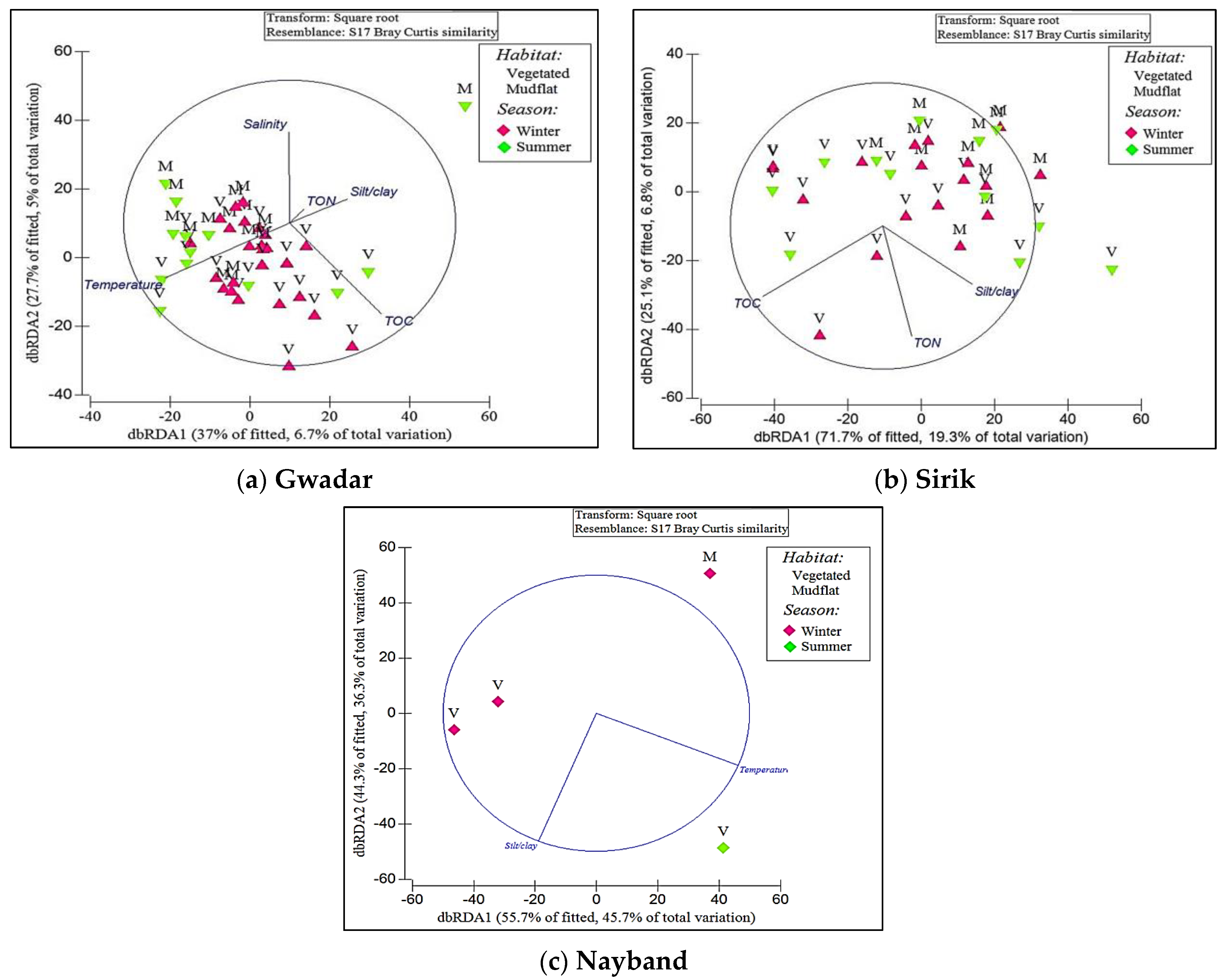
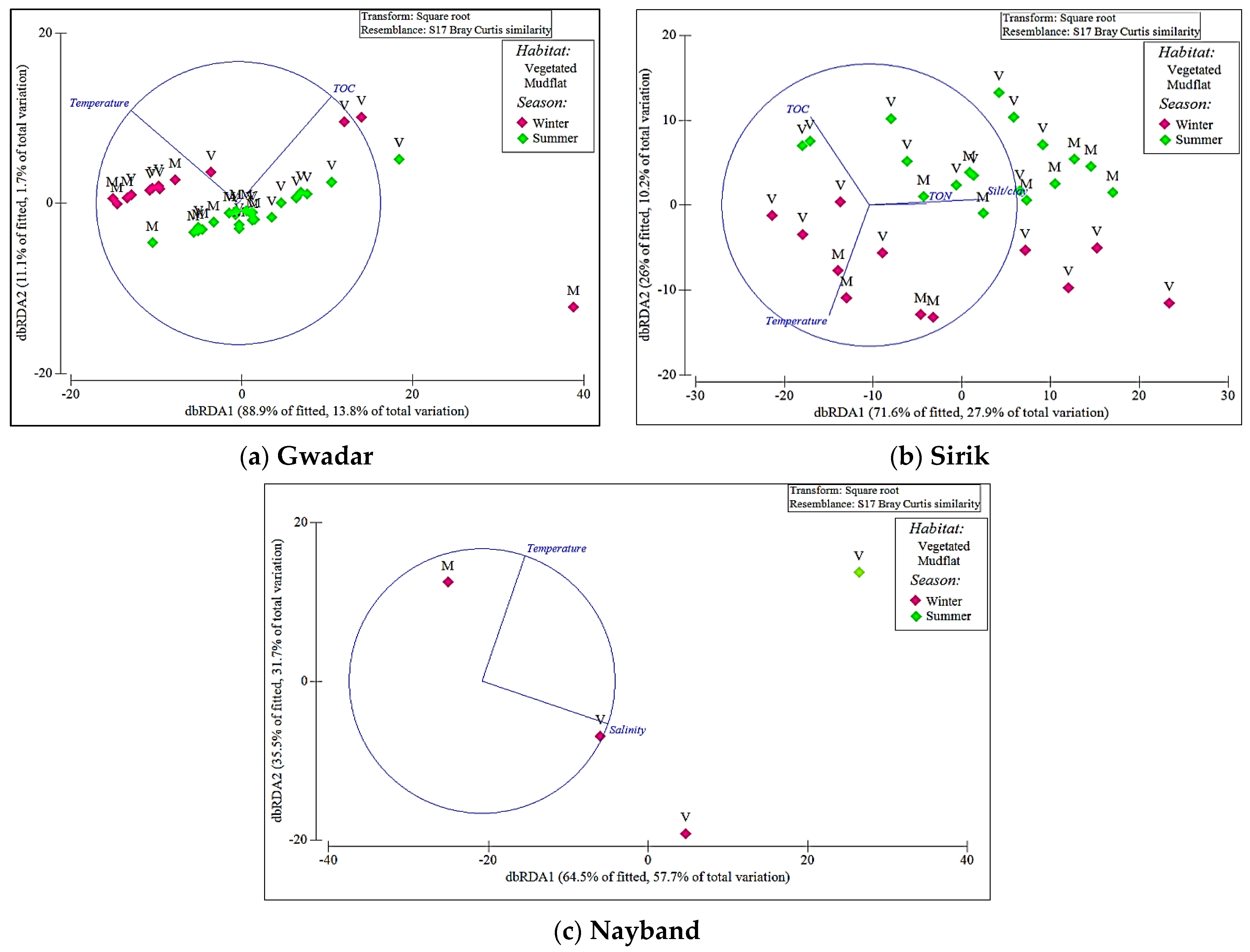
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, R.S. A review of biodiversity studies of soil dwelling organisms in indian mangroves. Zoos Print J. 2000, 7, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.R. Monitoring of Pollution Using Density, Biomass and Diversity Indices of Macrobenthos from Mangrove Ecosystem of Uran, Navi Mumbai, West Coast of India. J. Bioremediation Biodegrad. 2015, 6, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame, M.F.; Reef, R.; Santini, N.S.; Najera, E.; Turschwell, M.P.; Hayes, M.A.; Masque, P.; Lovelock, C.E. Mangroves in arid regions: Ecology, threats, and opportunities. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 248, 106796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, N.C.; Finlayson, C.M.; Davidson, N.C.; Finlayson, C.M. Updating global coastal wetland areas presented in Davidson and Finlayson (2018). Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-H.; Ho, C.-W.; Lin, C.-W.; Huang, S.-C.; Lin, H.-J. Differential Response of Macrobenthic Abundance and Community Composition to Mangrove Vegetation. Forests 2021, 12, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coblentz, K.E.; Henkel, J.R.; Sigel, B.J.; Taylor, C.M. Technical Note: The Use of Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyzers for Inference on Infauna-Sediment Relationships. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchald, K.; Jumars, P.A. The diet of worms: A study of polychaete feeding guilds. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1979, 17, 193–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cutrim, A.; Sousa, L.; Ribeiro, R.; Oliveira, V.; Almeida, Z. Structure of a polychaete community in a mangrove in the northern coast of Brazil. Acta Biol. Colomb. 2018, 23, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, P.; Borja, A.; Rodríquez, J.G.; Muxika, I.; Galparsoro, I.; Patrício, J.; Veríssimo, H.; Marques, J.C. Spatial and temporal response of multiple trait-based indices to natural- and anthropogenic seafloor disturbance (effluents). Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, J.M.; Gusmao, J.B.; Mattos, G.; Lana, P. Polychaete functional diversity in shallow habitats: Shelter from the storm. J. Sea Res. 2018, 135, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doney, S.C.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Duffy, J.E.; Barry, J.P.; Chan, F.; English, C.A.; Galindo, H.M.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Hollowed, A.B.; Knowlton, N.; et al. Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasi, F.; Nordström, M.C.; Bonsdorff, E.; Auriemma, R.; Cibic, T.; Del Negro, P. Functional biodiversity of marine soft-sediment polychaetes from two Mediterranean coastal areas in relation to environmental stress. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 137, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureto, L.M.O.; Cianciaruso, M.V.; Samia, D.S.M. Functional diversity: An overview of its history and applicability. Nat. Conserv. 2015, 13, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.; Rogers, S.; Frid, C. Assessing functional diversity in marine benthic ecosystems: A comparison of approaches. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 254, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culhane, F.E.; Briers, R.A.; Tett, P.; Fernandes, T.F. Structural and functional indices show similar performance in marine ecosystem quality assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, R.; Aune, M.; Bluhm, B.A.; Cassidy, C.; Kędra, M.; Kraan, C.; Vandepitte, L.; Włodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; Zhulay, I.; Albano, P.G.; et al. Trait-based approaches in rapidly changing ecosystems: A roadmap to the future polar oceans. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winemiller, K.O.; Fitzgerald, D.B.; Bower, L.M.; Pianka, E.R. Functional traits, convergent evolution, and periodic tables of niches. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolédec, S.; Chessel, D.; ter Braak, C.J.F.; Champely, S. Matching species traits to environmental variables: A new three-table ordination method. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 1996, 3, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usseglio-Polatera, P.; Bournaud, M.; Richoux, P.; Tachet, H. Biological and ecological traits of benthic freshwater macroinvertebrates: Relationships and definition of groups with similar traits. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 43, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darr, A.; Gogina, M.; Zettler, M.L. Functional changes in benthic communities along a salinity gradient—A western Baltic case study. J. Sea Res. 2014, 85, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogina, M.; Darr, A.; Zettler, M.L. Approach to assess consequences of hypoxia disturbance events for benthic ecosystem functioning. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 129, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajializadeh, P.; Safaie, M.; Naderloo, R.; Shojaei, M.G.; Gammal, J.; Villnäs, A.; Norkko, A. Species Composition and Functional Traits of Macrofauna in Different Mangrove Habitats in the Persian Gulf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 575480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfan, N.; Shojaei, M.G.; Naderloo, R. Patterns of structural and functional diversity of macrofaunal communities in a subtropical mangrove ecosystem. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 252, 107288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozarpour, R.; Shojaei, M.G.; Naderloo, R.; Nasi, F. Crustaceans functional diversity in mangroves and adjacent mudflats of the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 186, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, C.R.; Paiva, F.F.; Ligeiro, R.; Molozzi, J.; Melo, A.S. Saline gradient drives functional nestedness of polychaete communities in tropical estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 251, 107185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari Noghabi, N.; Shojaei, M.G.; Farahani, M.M.; Weigt, M. Stable Isotopes Reveal the Food Sources of Benthic Macroinvertebrates in the Arid Mangrove Ecosystem of the Persian Gulf. Estuaries Coasts 2022, 45, 2241–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorsatz, L.D.; Pattrick, P.; Porri, F. Quantifying the in situ 3-dimensional structural complexity of mangrove tree root systems: Biotic and abiotic implications at the microhabitat scale. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardino, A.F.; Gomes, L.E.d.O.; Hadlich, H.L.; Andrades, R.; Correa, L.B. Mangrove clearing impacts on macrofaunal assemblages and benthic food webs in a tropical estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checon, H.H.; Corte, G.N.; Silva, C.F.; Schaeffer-Novelli, Y.; Amaral, A.C.Z. Mangrove vegetation decreases density but does not affect species richness and trophic structure of intertidal polychaete assemblages. Hydrobiologia 2017, 795, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte, G.; Checon, H.; Shah Esmaeili, Y.; Lefcheck, J.; Amaral, A. Mangrove fragments as key coastal reservoirs of taxonomic and functional biodiversity. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 1573–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.Y.S. Habitat Heterogeneity Determining the Macrobenthic Infaunal Community in a Mangrove Swamp in South China: Implication for Plantation and Plant Invasion. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 313, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.Y.S.; Tam, N.F.Y. Influence of plantation of an exotic mangrove species, Sonneratia caseolaris (L.) Engl., on macrobenthic infaunal community in Futian Mangrove National Nature Reserve, China. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 448, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.S. Mangrove Forests of the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. In Threats to Mangrove Forests: Hazards, Vulnerability, and Management; Makowski, C., Finkl, C.W., Eds.; Coastal Research Library; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 53–75. ISBN 978-3-319-73016-5. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, S.N.; Sajadi, J.; Sadough Vanini, S.H. Application of Vegetation Indices Derived from IRS Data for Detecting the Avicennia Forest Area Near the South Pars Oil Apparatus. Environ. Sci. 2010, 8, 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Taherizadeh, M.; Sharifinia, M. Applicability of ecological benthic health evaluation tools to three subtropical estuaries (Azini, Jask and Khalasi) from the Iranian coastal waters. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3485–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, M.; Nouri, G.; Danekar, A.; Marvi Mohajer, M.R.; Mahmoudi, B. Vegetative parameters of Mangrove forest on the Govater bay in southeast of Iran. Taxon. Biosyst. 2009, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bonyadi Naeini, A.; Rastegar-Pouyani, N.; Rastegar Pouyani, E.; Glasby, C.; Rahimian, H. Nereididae (Annelida: Phyllodocida) of the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman, including description of two new species and 11 new records. Zootaxa 2017, 4244, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonyadi Naeini, A.; Rahimian, H. Intertidal scale worms (Polychaeta, Polynoidae and Sigalionidae) from the northern coasts of the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman. ZooKeys 2009, 31, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jones, D.A. A Field Guide to the Sea Shores of Kuwait and the Arabian Gulf; University of Kuwait: Kuwait City, Kuwait, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimian, H.; Yousefi, S.; Nabavi, S.; Glasby, C. Nereididae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from intertidal habitats in the Gulf of Oman, Iran. Zootaxa 2011, 3013, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, M.; Ghoshal, P.; Salazar-Vallejo, S.; Mandal, S. Sigambra sundarbanensis sp. nov. (Annelida, Pilargidae) from the Indian sector of Sundarbans Estuarine System, with remarks on parapodial glands. Eur. J. Taxon. 2021, 744, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M.; Mulvaney, C.S. Nitrogen—Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983; pp. 595–624. ISBN 978-0-89118-977-0. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer Method Improved for Making Particle Size Analyses of Soils. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevene, F.; Doléadec, S.; Chessel, D. A fuzzy coding approach for the analysis of long-term ecological data. Freshw. Biol. 1994, 31, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumars, P.A.; Dorgan, K.M.; Lindsay, S.M. Diet of worms emended: An update of polychaete feeding guilds. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscarella, R.; Uriarte, M. Do community-weighted mean functional traits reflect optimal strategies? Proc. Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20152434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.; Gorley, R.N. Primer v6: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006; pp. 52–182. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Multimodel Inference: Understanding AIC and BIC in Model Selection. Sociol. Methods Res. 2004, 33, 261–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götzenberger, L.; de Bello, F.; Dias, A.T.C.; Moretti, M.; Berg, M.P.; Carmona, C.P. Trait-Based Ecology Tools in R 2020; CSIC-GV-UV-Centro de Investigaciones sobre Desertificación (CIDE): Moncada, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmia, B.; Bartoli, M.; Laini, A.; Bolpagni, R.; Ferrari, C.; Viaroli, P. Effects of Drying and Re-Wetting on Litter Decomposition and Nutrient Recycling: A Manipulative Experiment. Water 2019, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.D.; Barros, F. Ecological Functions of Polychaetes Along Estuarine Gradients. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 780318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooraki, N.; Moghadasi, B.; Manoochehri, H.; Changizi, R. Determining the concentration of Heavy metals and evaluating the contamination degree of Haleh Estuary and Nayband Gulf sediment’s and their effects on foraminifera assemblages. J. Wetl. Ecobiol. 2016, 8, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Evin, L.; Talley, T. Influences of Vegetation and Abiotic Environmental Factors on Salt Marsh Invertebrates. In Concepts and Controversies in Tidal Marsh Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 661–707. ISBN 978-0-7923-6019-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ringold, P. Burrowing, root mat density, and the distribution of fiddler crabs in the eastern United States. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1979, 36, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaida, S.; Nanjo, K.; Ohtsuchi, N.; Kohno, H.; Sano, M. Cellulose digestion abilities determine the food utilization of mangrove estuarine crabs. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 222, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-C.; Ye, Y.; Lu, C.-Y. Changes of macro-benthic faunal community with stand age of rehabilitated Kandelia candel mangrove in Jiulongjiang Estuary, China. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 31, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capehart, A.A.; Hackney, C.T. The potential role of roots and rhizomes in structuring salt-marsh benthic communities. Estuaries 1989, 12, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto, S.A.; Lana, P.C. The role of above- and below-ground components of Spartina alterniflora (Loisel) and detritus biomass in structuring macrobenthic associations of Paranaguá Bay (SE, Brazil). Hydrobiologia 1999, 400, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, B.C.G.; Lana, P. Functional redundancy in polychaete assemblages from a tropical Large Marine Ecosystem (LME). Zoosymposia 2020, 19, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, S.A.; Hahn, A.E.; Schrage, M. Size spectra of benthic biomass and metabolism. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1985, 26, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norkko, A.; Villnäs, A.; Norkko, J.; Valanko, S.; Pilditch, C. Size matters: Implications of the loss of large individuals for ecosystem function. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posey, M.H. Influence of relative mobilities on the composition of benthic communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Oldendorf 1987, 39, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lin, H.; He, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Mou, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Functional trait composition and diversity patterns of marine macrobenthos across the Arctic Bering Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluhm, B.A.; Gradinger, R.; Hopcroft, R.R. Editorial—Arctic Ocean Diversity: Synthesis. Mar. Biodivers. 2011, 41, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iken, K.; Bluhm, B.; Dunton, K. Benthic food-web structure under differing water mass properties in the southern Chukchi Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro-Torres, V.M.; Amezcua, F.; Soto-Jiménez, M.; Balart, E.F.; Serviere-Zaragoza, E.; Green, L.; Rajnohova, J. Primary Sources and Food Web Structure of a Tropical Wetland with High Density of Mangrove Forest. Water 2020, 12, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, V.J.; McQuaid, K.A.; McQuaid, C.D. Examination of small- and large-scale influences on the diet of an omnivorous polychaete indicates weak effects of upwelling. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 436–437, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, D.; Keck, R.T.; Tinsman, J.C.; Leathem, W.A. Vertical migration and mortality of benthos in dredged material—Part I: Mollusca. Mar. Environ. Res. 1981, 4, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, P.; Sarathy, P.P.; Muthuvelu, S.; Mahadevan, G. Diversity and Distribution of Polychaetes in Mangroves of East Coast of India. In Mangrove Ecosystem Ecology and Function; Sharma, S., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78984-277-7. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, R.; Wei, C.-L.; Rowe, G.; Schulze, A. Complex depth-related patterns in taxonomic and functional diversity of polychaetes in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep Sea Res. Part Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2013, 80, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shillabeer, N.; Tapp, J.F. Improvements in the benthic fauna of the Tees estuary after a period of reduced pollution loadings. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1989, 20, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudlou, A.; Momtazi, F.; Hashtroudi, M.S. Ecological Quality Status (EcoQs) of Chabahar sub-tropical bay based on multimetric macrobenthos-indexes approach: Response of bio-indexes to sediment structural/pollutant variables. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 40, 101524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczyk, R.; Czortek, P.; Serigstad, B.; Pabis, K. Modelling of polychaete functional diversity: Large marine ecosystem response to multiple natural factors and human impacts on the West African continental margin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.-W.; Qian, P.-Y. Combined effects of salinity, temperature and food on early development of the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. MEPS 1997, 152, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.; Pires, A.; Velez, C.; Almeida, Â.; Wrona, F.J.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Figueira, E. The effects of salinity changes on the Polychaete Diopatra neapolitana: Impacts on regenerative capacity and biochemical markers. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 163, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Thu, E.V.; Rahman, M.; Phoo, W.W.; Kim, C. Salinity Effects on Growth and Survival of the Polychaete Rockworm Marphysa sanguinea (Montagu, 1813) Juveniles and Adults. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Arrighetti, F.; Penchaszadeh, P. Macrobenthos–sediment relationships in a sandy bottom community off Mar del Plata, Argentina. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2010, 90, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.L.; Lee, H.G.; Yu, O.H. Correlation between rocky reefs and surrounding benthic habitats: Distribution and diversity patterns of polychaetes in the macrobenthic community in the East Sea of South Korea. J. Sea Res. 2021, 174, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, E.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Aguado-Giménez, F.; Ávila, P.; Guerrero, A.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, V.; González, N.; Gairin, J.I.; Carballeira, C.; et al. A meta-analysis approach to the effects of fish farming on soft bottom polychaeta assemblages in temperate regions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 69, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
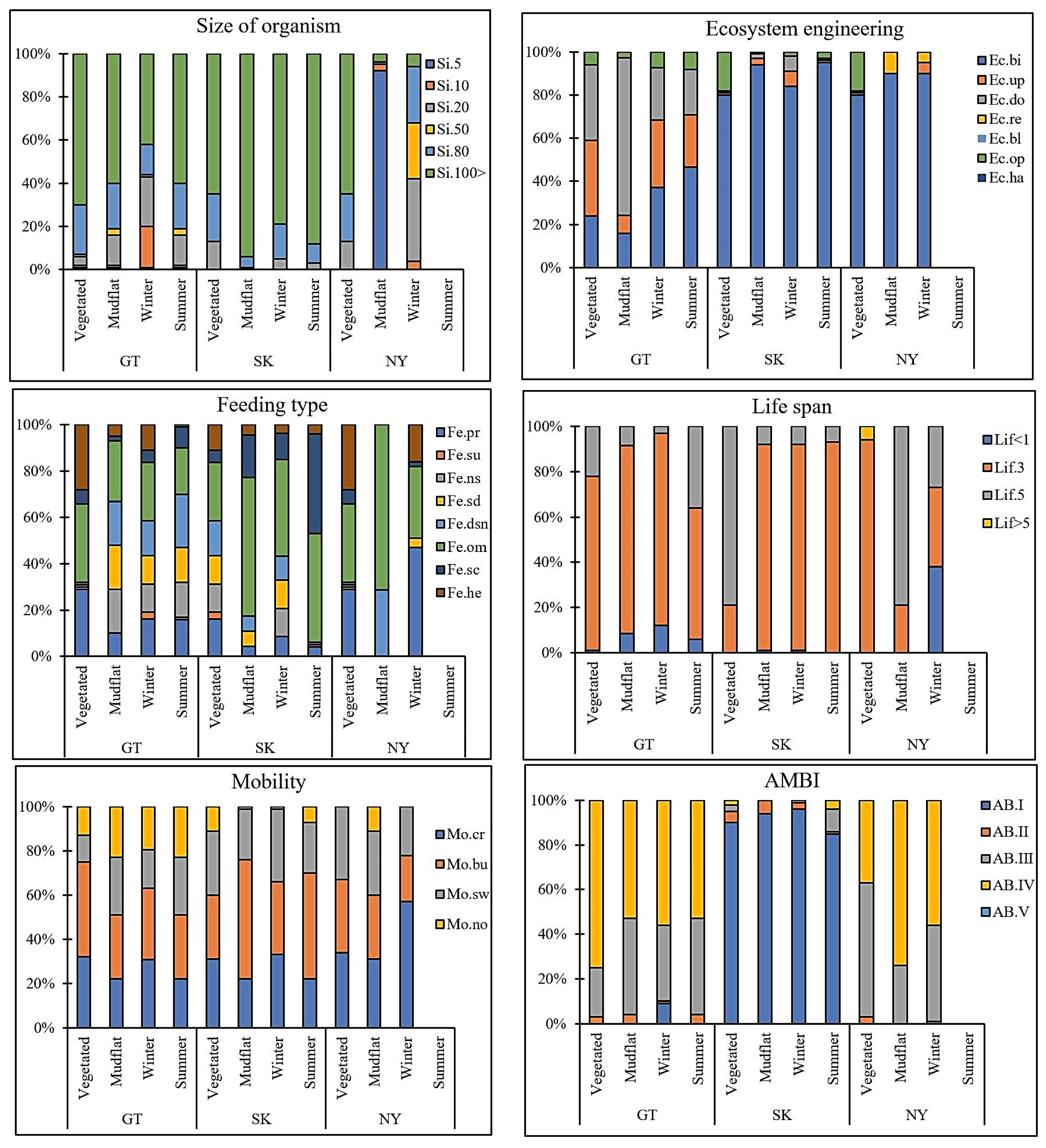
| Trait | Modalities | Label | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size of organism (mm) | 5–10 mm | Si.5 | The largest reported size for the species during adult stage. |
| 10–20 mm | Si.10 | ||
| 20–50 mm | Si.20 | ||
| 50–80 mm | Si.50 | ||
| 80–100 mm | Si.80 | ||
| >100 mm | Si > 100 | ||
| Ecosystem engineering | Biodiffuser | Ec.bi | The biodiffusers provide constant and random biomixing of sediment over short distances through their activities. |
| Upward conveyor | Ec.up | Vertically oriented species that typically feed head-down at depth in the sediment. Vertically oriented head-down feeders actively select and ingest particles at the deeper sediments and egest these non-locally as feces in the sediment surface. | |
| Downward conveyor | Ec.do | Downward conveyors exhibit a feeding strategy opposite to that of upward conveyors. | |
| Regenerator | Ec.re | They mechanically transfer sediment from depth to surface by digging and maintaining burrows in the sediment. | |
| Blind-ended ventilation | Ec.bl | For breathing and feeding, animals flush their burrows with overlying water. | |
| Open-ended ventilation | Ec.op | Open-ended ventilation consists of U-shaped burrows that can be flushed easily one after another. | |
| Habitat building | Ec.ha | Species that create habitats for other species by building structures. | |
| Feeding type | Predator | Fe.pr | A predatory organism that feeds by killing other organisms. |
| Suspension feeder | Fe.su | Organisms that consume particulate organic matter in the water column, including plankton. | |
| Non-selective deposit feeder | Fe.ns | An organism that feeds on mud or sand and may show some discrimination in particle size or type. | |
| Selective deposit feeder | Fe.sd | Deposit feeders do not ingest sediment haphazardly, but sort organic material from sediment using their palps or buccal organs. | |
| Deposit feeder (selective or non-selective) | Fe.dsn | An organism that feeds on fragmented particulate organic matter. | |
| Omnivore | Fe.om | Mixed-diet organisms that consume plant and animal material. | |
| Scavenger | Fe.sc | An organism that consumes dead animals actively. | |
| Herbivore | Fe.he | An organism that feeds on plants or algae, or parts of them. | |
| Mobility of adult | Crawler | Mo.cr | Moving along the substratum by using its legs and appendages (e.g., parapodia and chaetae or muscles). |
| Burrower | Mo.bu | Burrowing organisms that live and move in soft sediments. | |
| Swimmer | Mo.sw | An organism that moves through the water column using its fins, legs, or appendages. | |
| Non-motile/Semi-motile | Mo.no | ||
| Life span (years) | ≤1 year | Lif < 1 | Maximum length of time that any particular organism can be expected to live. |
| 1–3 years | Lif.3 | ||
| 3–5 years | Lif.5 | ||
| ≥5 years | Lif > 5 | ||
| Tolerance (AMBI index) | Group I | AB.I | Based on the AMBI index, the sensitivity of an organism to organic enrichment. |
| Group II | AB.II | ||
| Group III | AB.III | ||
| Group IV | AB.IV | ||
| Group V | AB.V |
| Factor | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abundance (ind.m−2) | Region | 2.28 | 0.002 |
| Habitat (Region) | 6.33 | 0.000 | |
| Season | 1.9 | 0.024 | |
| Shannon–Wiener diversity | Region | 10.53 | 0.000 |
| Habitat (Region) | 3.36 | 0.048 | |
| Season | 6.01 | 0.026 | |
| Margalef richness | Region | 2.17 | 0.017 |
| Habitat (Region) | 1.98 | 0.03 | |
| Season | 1.39 | 0.05 | |
| Pielou’s evenness | Region | 5.97 | 0.01 |
| Habitat (Region) | 1.3 | 0.085 | |
| Season | 2.42 | 0.068 | |
| Simpson dominance | Region | 13.59 | 0.000 |
| Habitat (Region) | 2.23 | 0.12 | |
| Season | 2.65 | 0.09 | |
| CWM index | Region | 2.22 | 0.000 |
| Habitat (Region) | 2.93 | 0.002 | |
| Season | 1.71 | 0.28 |
| Region | Winter | Summer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gwadar | Vegetated | Mudflat | Vegetated | Mudflat |
| TON (mg/g) | 0.14 ± 0.09 | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.06 | 0.09 ± 0.008 |
| TOC (mg/g) | 0.68 ± 0.3 | 0.35 ± 0.15 | 0.85 ± 0.4 | 0.58 ± 0.26 |
| Silt/Clay (%) | 1.34 ± 0.54 | 0.93 ± 0.34 | 2.2 ± 1.5 | 1.67 ± 0.6 |
| Temperature (°C) | 22.5 ± 0.75 | 22.53 ± 0.71 | 30.82 ± 0.32 | 30.56 ± 1.85 |
| Salinity (PPT) | 30.54 ± 0.37 | 30.6 ± 0.34 | 31 ± 0.46 | 31.33 ± 0.49 |
| Sirik | Vegetated | Mudflat | Vegetated | Mudflat |
| TON (mg/g) | 0.025 ± 0.001 | 0.019 ± 0.009 | 0.03 ± 0.008 | 0.01 ± 0.007 |
| TOC (mg/g) | 0.78 ± 0.2 | 0.36 ± 0.15 | 0.75 ± 0.3 | 0.22 ± 0.1 |
| Silt/Clay (%) | 2.12 ± 0.91 | 1.8 ± 1 | 2.13 ± 0.88 | 1.11 ± 0.61 |
| Temperature (°C) | 23.8 ± 0.54 | 23.45 ± 0.44 | 30.8 ± 0.51 | 31.48 ± 0.37 |
| Salinity (PPT) | 30.68 ± 0.52 | 30.86 ± 0.45 | 32.3 ± 0.74 | 31.87 ± 1 |
| Nayband | Vegetated | Mudflat | Vegetated | Mudflat |
| TON (mg/g) | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.002 | 0.06 ± 0.006 | 0.04 ± 0.003 |
| TOC (mg/g) | 2.34 ± 0.18 | 1.76 ± 0.66 | 2.23 ± 0.2 | 1.49 ± 0.89 |
| Silt/Clay (%) | 1.37 ± 0.58 | 0.88 ± 0.35 | 2.93 ± 1.48 | 1.05 ± 0.63 |
| Temperature (°C) | 24.7 ± 0.51 | 25.23 ± 0.2 | 32.74 ± 2.74 | 33 ± 1.07 |
| Salinity (PPT) | 28.72 ± 0.52 | 29.1 ± 0.14 | 30.57 ± 0.85 | 30.04 ± 1.23 |
| Variables | GT | SK | NY | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS (Trace) | Pseudo-F | p | SS (Trace) | Pseudo-F | p | SS (Trace) | Pseudo-F | p | |
| TON | 4338.1 | 1.1593 | 0.3 | 4788.1 | 1.5751 | 0.191 | 2932.7 | 0.54555 | 1 |
| TOC | 6052.9 | 1.6384 | 0.05 | 10,637 | 3.7575 | 0.019 | 3396.1 | 0.66021 | 1 |
| Silt/Clay | 3491.9 | 0.92736 | 0.5 | 6416.5 | 2.152 | 0.125 | 5010.7 | 1.1554 | 0.48 |
| Temperature (°C) | 5742.4 | 1.5508 | 0.12 | 2539.9 | 0.81402 | 0.471 | 5412 | 1.3085 | 0.49 |
| Salinity (PPT) | 4504.8 | 1.2053 | 0.29 | 1202.3 | 0.37954 | 0.761 | 5121.7 | 1.1964 | 0.5 |
| GT | SK | NY | |||||||
| Overall best solution | AIC | R2 | Variables | AIC | R2 | Variables | AIC | R2 | Variables |
| 314.1 | 4.3531 | TOC | 238.73 | 0.26977 | TON, TOC, silt/clay | 31.688 | 0.820 | Temperature, silt/clay | |
| 314.12 | 9.2068 | TOC, temperature | 238.85 | 0.21625 | TOC, silt/clay | 32.299 | 0.790 | Temperature, salinity | |
| 314.19 | 4.1298 | Temperature | 239.91 | 0.28942 | TON, TOC, silt/clay, salinity | 33.7 | 0.702 | Salinity, silt/clay | |
| Variables | GT | SK | NY | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS (Trace) | Pseudo-F | p | SS (Trace) | Pseudo-F | p | SS (Trace) | Pseudo-F | p | |
| TON | 229.9 | 0.26594 | 0.764 | 578.22 | 1.1284 | 0.332 | 235.56 | 0.217 | 1 |
| TOC | 1838.7 | 2.2429 | 0.109 | 924.14 | 1.848 | 0.151 | 336.83 | 0.326 | 1 |
| Silt/Clay | 361.36 | 0.41979 | 0.605 | 2485 | 5.5926 | 0.005 | 1208.8 | 2.033 | 0.129 |
| Temperature (°C) | 2635 | 3.3034 | 0.065 | 1346.1 | 2.7754 | 0.072 | 1188.7 | 1.966 | 0.151 |
| Salinity (PPT) | 617.63 | 0.72347 | 0.497 | 852 | 1.695 | 0.184 | 1321.5 | 2.455 | 0.044 |
| GT | SK | NY | |||||||
| Overall best solution | AIC | R2 | Variables | AIC | R2 | Variables | AIC | R2 | Variables |
| 254.77 | 0.15525 | TOC, Temperature | 181.46 | 0.39001 | TON, TOC, Silt/Clay, Salinity | 22.609 | 0.893 | Temperature, Salinity | |
| 255.21 | 7.5335 | Temperature | 182.41 | 0.32704 | TO, Silt/Clay, Salinity | 25.793 | 0.764 | Temperature, Silt/Clay | |
| 255.4 | 0.16345 | TON, TOC, Temperature, Salinity | 182.9 | 0.36004 | TON, Temperature, Silt/Clay, Salinity | 26.38 | 0.551 | Salinity | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miri, M.; Seyfabadi, J.; Ghodrati Shojaei, M.; Rahimian, H.; Valipour, M. Polychaete Diversity and Functional Trait Composition in Subtropical Mangrove Ecosystems. Diversity 2023, 15, 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15090998
Miri M, Seyfabadi J, Ghodrati Shojaei M, Rahimian H, Valipour M. Polychaete Diversity and Functional Trait Composition in Subtropical Mangrove Ecosystems. Diversity. 2023; 15(9):998. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15090998
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiri, Mohadeseh, Jafar Seyfabadi, Mehdi Ghodrati Shojaei, Hassan Rahimian, and Mohammad Valipour. 2023. "Polychaete Diversity and Functional Trait Composition in Subtropical Mangrove Ecosystems" Diversity 15, no. 9: 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15090998
APA StyleMiri, M., Seyfabadi, J., Ghodrati Shojaei, M., Rahimian, H., & Valipour, M. (2023). Polychaete Diversity and Functional Trait Composition in Subtropical Mangrove Ecosystems. Diversity, 15(9), 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15090998









