Distribution of Alien and Translocated Freshwater Fish Species in Bulgarian Lotic Ecosystems, according to the WFD Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manchester, S.; Bullock, J.M. The impacts of non-native species on UK biodiversity and the effectiveness of control. J. Appl. Ecol. 2000, 37, 845–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, K.E.; Scalera, R.; Nunes, A.L.; Smith, K. An introduction to EU Regulation on Invasive Alien Species; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022; Volume 41, p. 187. [Google Scholar]
- Havel, J.E.; Kovalenko, K.E.; Thomaz, S.M.; Amalfitano, S.; Kats, L.B. Aquatic invasive species: Challenges for the future. Hydrobiologia 2015, 740, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yankova, M. Alien invasive fish species in Bulgarian waters: An overview. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2016, 4, 282–290. [Google Scholar]
- EU Regulation (EU). No 1143/2014 of the European parliament and of the council of 22 October 2014 on the prevention and management of the introduction and spread of invasive alien species. OJL 2014, 317, 35–55. [Google Scholar]
- Simonović, P.; Tošić, A.; Vassilev, M.; Apostolou, A.; Mrdak, D.; Ristovska, M.; Kostov, V.; Nikolić, V.; Škraba, D.; Vilizzi, L.; et al. Risk assessment of non-native fishes in the Balkans Region using FISK, the invasiveness screening tool for non-native freshwater fishes. Meditteranean Mar. Sci. 2013, 14, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- East and South European Network for Invasive Alien Species–A Tool to Support the Management of Alien Species in Bulgaria (ESENIAS-TOOLS) (2015–2017), Contract No. D-33-51/30.06.2015, Financial Mechanism of European Economic Area 2009–2014, Programme BG03 ‘Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services’. Available online: http://esenias.org/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=367:esenias-tools-news-1&catid=88:esenias-tools-project-category&Itemid=127 (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Paunović, M.; Csányi, B.; Simonović, P.; Zorić, K. Invasive Alien Species in the Danube. In The Danube River Basin; Liska, I., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 384–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piria, M.; Simonović, P.; Kalogianni, E.; Vardakas, L.; Koutsikos, N.; Zanella, D.; Ristovska, M.; Apostolou, A.; Adrović, A.; Mrdak, D.; et al. Alien freshwater fish species in the Balkans—Vectors and pathways of introduction. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 138–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichkova, T.; Todorov, M.; Kenderov, M.; Hubenov, Z.; Botev, I.; Stefanov, T.; Georgiev, D.; Jurajda, P. Invasive Alien Species of Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish in the Bulgarian Sector of the Danube River—Results of the Joint Danube Survey 4 (JDS4). Water 2022, 14, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, T. Ichthyofauna of the Bulgarian stretch of the Danube River and lower courses of its tributaries. In Biodiversity of the Bulgarian-Romanian Section of the Lower Danube; Shurulinkov, P., Hubenov, Z., Beshkov, S., Popgeorgiev, G., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 241–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunova, E.; Velkov, B.; Studenkov, S.; Georgieva, M.; Pavlova, M.; Pehlivanov, L.; Parvanov, D. Growth, age and size structure of the introduced pumpkinseed (Lepomis gibbosus L.) population from small ponds along the Vit River (Bulgaria). Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 14, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Uzunova, E.; Georgieva, M.; Studenkov, S.; Nikolova, M.; Traikov, I. Pumpkinseed (Lepomis gibbosus) distribution and abundance in littoral zones of sand—Pit lakes. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 16, 275–283. [Google Scholar]
- Pehlivanov, L.; Stefanov, T.; Todorov, M.; Kutsarov, Y.; Trichkova, T. First records of the black bullhead Ameiurus melas (Rafinesque, 1820) along the Bulgarian section of the Danube River. In Proceedings of the 41st International Association for Danube Research (IAD) Conference–60 Years of IAD existence “Tributaries as Key Elements in Sustainable Management of the Danube River Basin”, Sibiu, Romania, 13–16 September 2016; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Jurajda, P.; Vassilev, M.; Polacik, M.; Trichkova, T. First record of Perccottus glenii (Perciformes: Odontobutidae) in the Danube River in Bulgaria. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2006, 58, 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- NOBANIS. European Network on Alien Species. Available online: https://www.nobanis.org/ (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Todo, K.; Sato, K. European Parliament; Council of the European Union. In Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; EU Publications: Luxemburg, 2000; Volume 327, pp. 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- MOEW. Ordinance 37 from 10 November 2008 for the Use of Reservoirs-State Property, in Terms of Fisheries and the Rules for Commercial, Recreational Fishing, and Aquaculture in the Sites-State Property under Art. 3, Para. 1 of the Fisheries and Aquaculture Law. 2018; pp. 1–24. Available online: https://www.mzh.government.bg/media/filer_public/2020/12/22/naredba__37_ot_2008_g.pdf. (accessed on 17 August 2023). (In Bulgarian)
- EU Guidance document no. 4, 2003. In Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC): Identification and Designation of Heavily Modified and Artificial Water Bodies; EU Publications: Luxemburg, 2003; pp. 1–61.
- Johnson, P.T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Dam invaders: Impoundments facilitate biological invasions into freshwaters. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozon, J.; MacIsaac, H. Biological invasions: Are they dependent on disturbance? Environ. Rev. 1977, 5, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilby, R.; Battarbee, R.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A. A Review of the Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Surface Water Quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernan, M. Climate change and the impact of invasive species on aquatic ecosystems. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2015, 18, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solheim, A.; Globevnik, L.; Austnes, K.; Kristensen, P.; Moe, S.; Persson, J.; Phillips, G.; Poikane, S.; van de Bund, W.; Birk, S. A new broad typology for rivers and lakes in Europe: Development and application for large-scale environmental assessments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amen, M.; Azzurro, E. Integrating univariate niche dynamics in species distribution models: A step forward for marine research on biological invasions. J. Biogeogr. 2020, 47, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEN-EN 14011; Water Quality-Sampling of Fish with Electricity. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2003; pp. 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Apostolou, A.; Pehlivanov, L.; Schabuss, M.; Zornig, H.; Wolfram, G. Fish Biozonation in the Balkan Peninsula, Especially in Bulgaria: A Challenge. Fishes 2023, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshmedjiev, S.; Karagiozova, T.; Michailov, M.; Valev, V. Revision of River & Lake Typology in Bulgaria within Ecoregion 12 (Pontic Province) and Ecoregion 7 (Eastern Balkans) According to the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Balk 2010, 2, 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- MOEW. Ordinance H-4 from 14 September 2012 for Characterization of Surface Waters. Issued by the Minister of Environment and Water, Promulgated, SG, No. 22 of 5 March 2013, in Force from 5 March 2013, Amended and Add., no. 79 of 23 September 2014, in Force since 23 September 2014, Amended and Ext. DV. Issue 85 of 2 October 2020. Sofia, pp.1–119. Available online: https://www.moew.government.bg/static/media/ups/tiny/filebase/Water/Legislation/Naredbi/vodi/Naredba%20H-4.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2023). (In Bulgarian)
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis, Versus 4.11. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- QGIS.org, %Y. QGIS Geographic Information System. QGIS Association. Available online: http://www.qgis.org (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Belkinova, D.; Gecheva, G.; Cheshmedjiev, S.; Dimitrova-Dyulgerova, I.; Mladenov, R.; Marinov, M.; Teneva, I.; Stoyanov, P.; Mihov, S.; Pehlivanov, L.; et al. Biological Analysis and Ecological Status Assessment of Bulgarian Surface Water Ecosystems; University of Plovdiv, Publishing House: Plovdiv, Bulgaria, 2013; pp. 1–235. (In Bulgarian) [Google Scholar]
- Uzunova, E.; Studenkov, S.; Dashinov, D. First records of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides (Lacépède, 1802) from Bulgaria (Balkan Peninsula). BioInvasions Rec. 2019, 8, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunova, E.; Zlatanova, S. A review of the fish introductions in Bulgarian freshwaters. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2007, 37, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Walker, B.; Kinzig, A.; Langridge, L. Plant attribute diversity, resilience, and ecosystem function: The nature and significance of dominant and minor species. Ecosystems 1999, 2, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalóky, Z.; Bammer, V.; György, Á.I.; Pehlivanov, L.; Schabuss, M.; Zornig, H.; Weiperth, A.; Erős, T. Offshore distribution of invasive gobies (Pisces: Gobiidae) along the longitudinal profile of the Danube River. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. Arch. Für Hydrobiol. 2015, 18, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.; Mooney, H.; Castri, D.; Groves, F.; Kruger, F.; Williamson, M. Biological Invasions: A Global Perspective; Published for the Scientific Committee on Problems of the Environment, International Council of Scientific Unions; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 25, pp. 1–525. [Google Scholar]
- Stork, N.E. Re-assessing current extinction rates. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylková, K.; Kalous, L.; Bohlen, J.; Lamatsch, D.K.; Petrtýl, M. Phylogeny and biogeographic history of the cyprinid fish genus Carassius (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) with focus on natural and anthropogenic arrivals in Europe. Aquaculture 2013, 383, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOEW. River Basin Management Plans 2016–2021. Available online: https://www.moew.government.bg/bg/ (accessed on 18 August 2023). (In Bulgarian)
- MOEW. Information System on Protected Areas from the Ecological Network NATURA 2000. Available online: https://natura2000.egov.bg/EsriBg.Natura.Public.Web.App (accessed on 18 August 2023). (In Bulgarian).
- Almeida, D.; Stefanoudis, P.; Fletcher, D.; Rangel, C.; Silva, E. Population traits of invasive bleak Alburnus between different habitats in Iberian fresh waters. Limnol. Ecol. Manag. Inland Waters 2013, 46, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Soto, S.; Garofalo, G.; Maynou, F. Fistularia commersonii in the Mediterranean Sea: Invasion history and distribution modeling based on presence-only records. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.; Schwarzkopf, L.; Gordon, I.; Hirsch, B. Population growth lags in introduced species. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 4577–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catford, J.A.; Vesk, P.A.; Richarson, D.M.; Pysek, P. Quantifying levels of biological invasion: Towards the objective classification of invaded and invasible ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
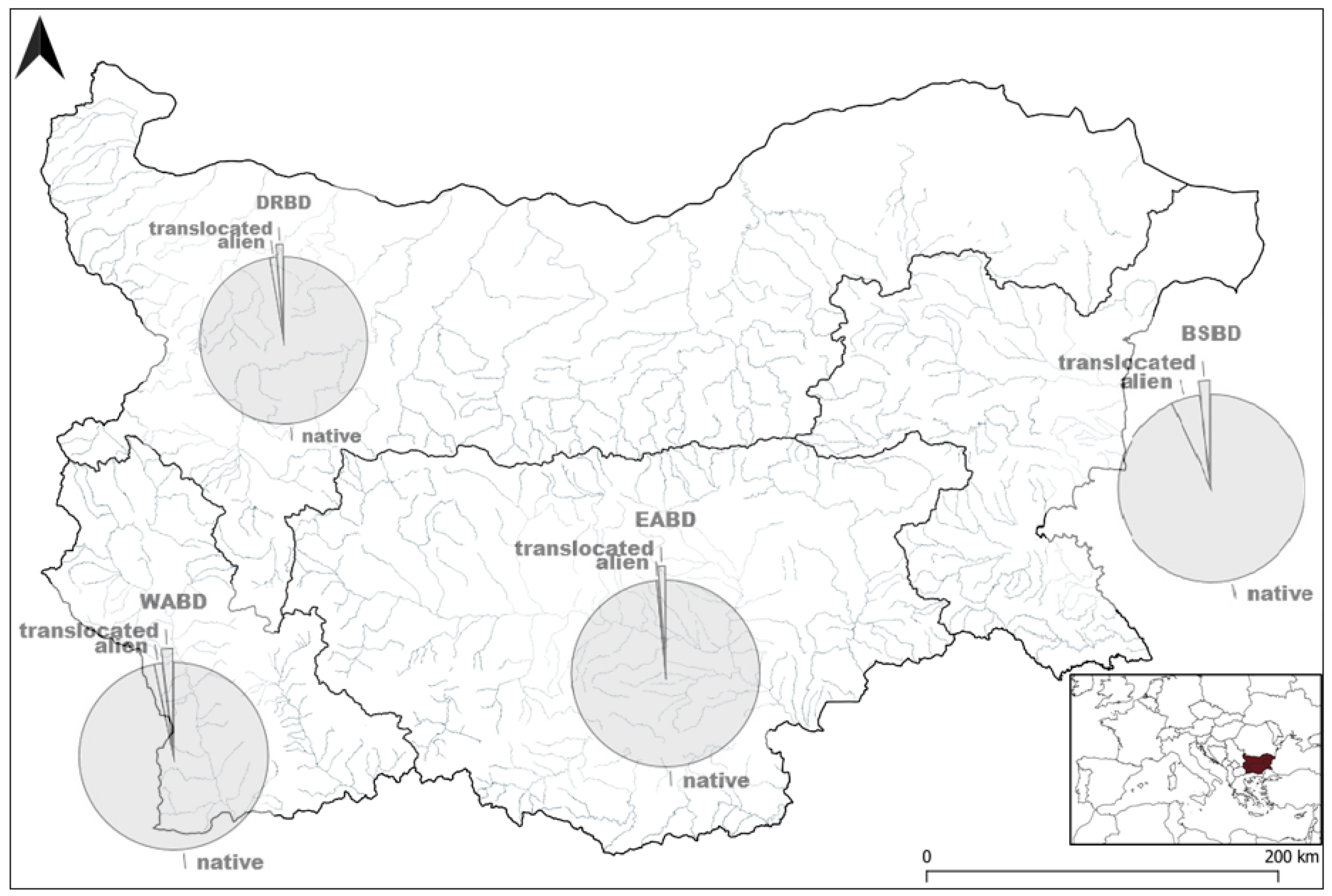
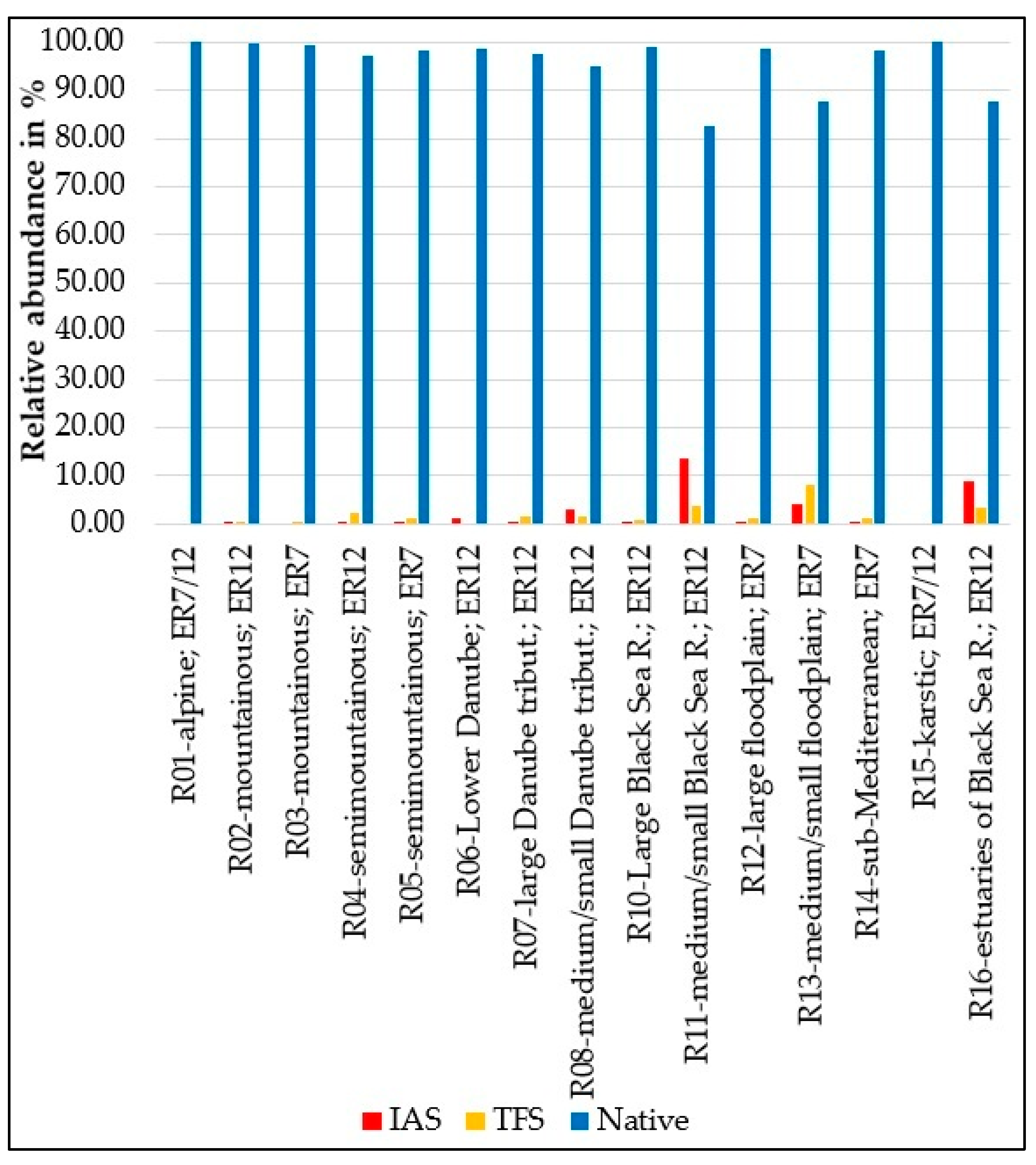
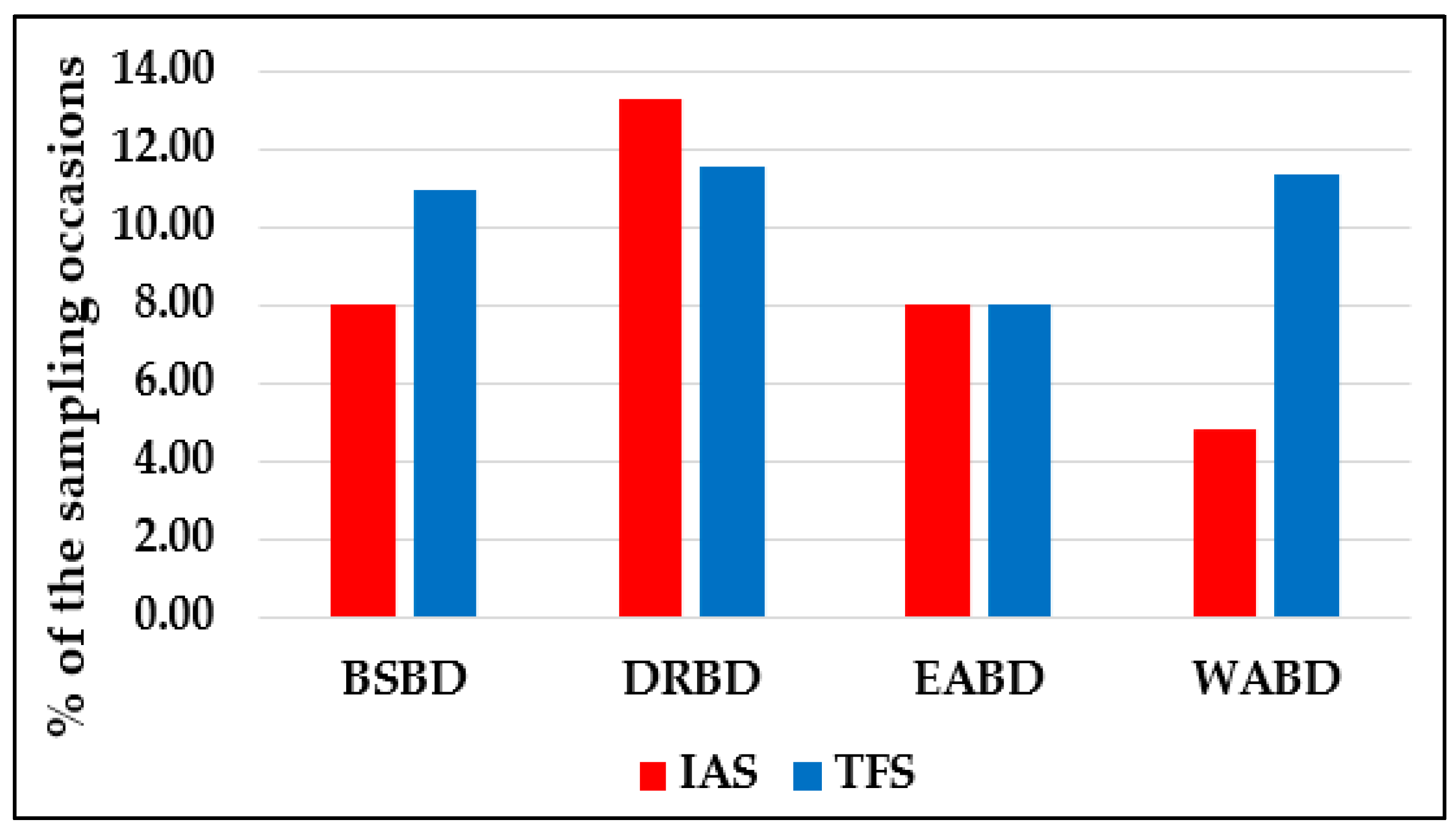
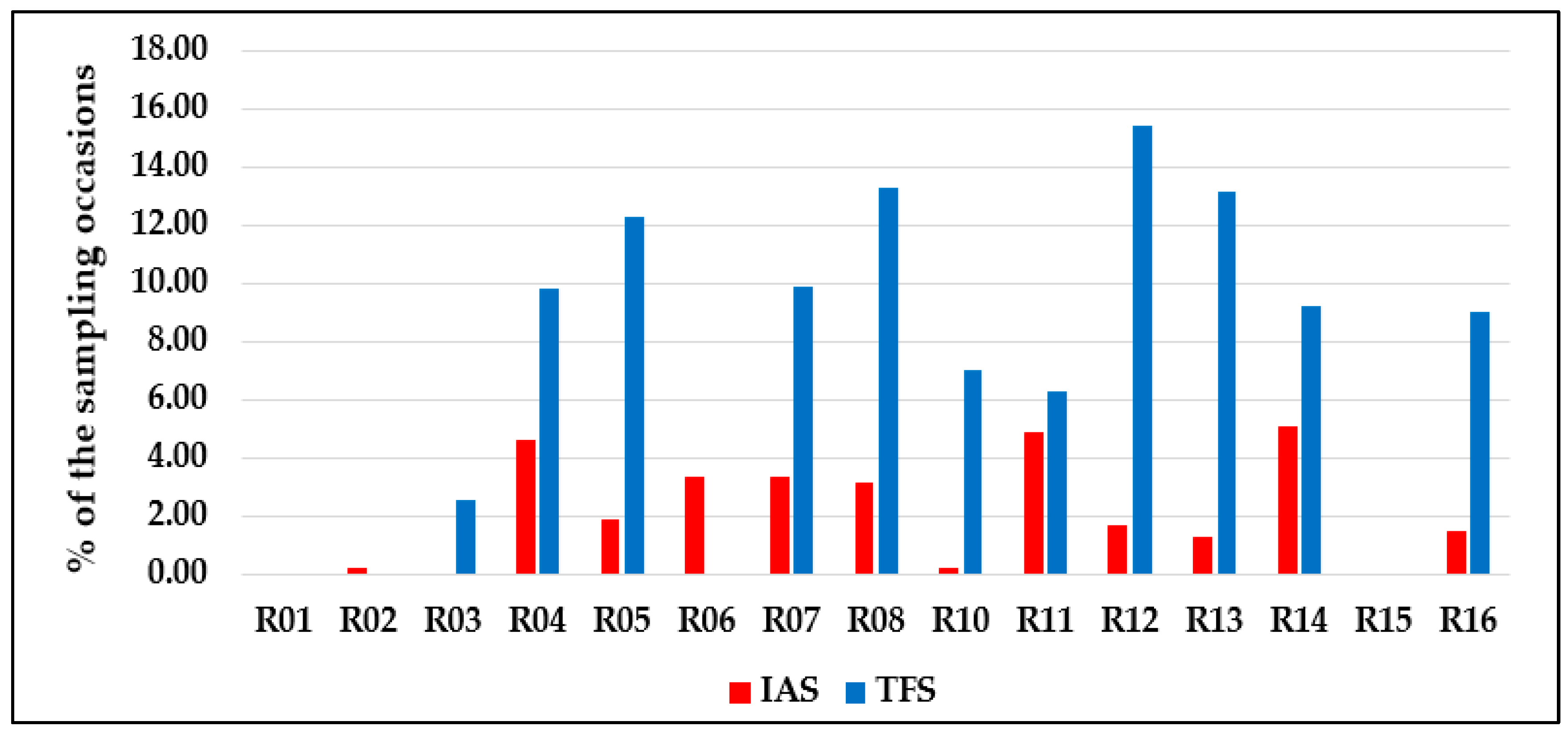
| Species | Sampling Occasions | Total Specimens | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native | 76 * | 5212 | 295,440 |
| Alien | 7 | 287 | 5059 |
| Translocated | 15 | 368 | 4783 |
| Species | Occurred on Fishing Occasions | Registered Specimens | Mean Specimens per Occurrence (Column 2/Column 1) | Specimens per Total of Sampled Sites | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alien | Ctenopharyngodon idella Valenciennes 1844 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.005 |
| Gambusia holbrooki Girard 1859 | 21 | 3295 | 157 | 7.645 | |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix Valenciennes 1844 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | |
| Lepomis gibbosus Linnaeus 1758 | 110 | 671 | 6 | 1.557 | |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum 1792 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 0.012 | |
| Perccottus glenii Dybowski 1877 | 2 | 22 | 11 | 0.051 | |
| Pseudorasbora parva Temminck & Schlegel1846 | 149 | 1063 | 7 | 2.466 | |
| Total 7 | 287 | 5059 | 18 | 11.738 | |
| Translocated | Abramis brama Linnaeus 1758 | 2 | 19 | 10 | 0.044 |
| Alburnus alburnus Linnaeus 1758 | 13 | 255 | 20 | 0.592 | |
| Barbatula barbatula Linnaeus 1758 | 6 | 59 | 10 | 0.137 | |
| Carassius gibelio Bloch 1782 | 184 | 2383 | 13 | 5.529 | |
| Esox lucius Linnaeus 1758 | 17 | 41 | 2 | 0.095 | |
| Neogobius fluviatilis Pallas 1814 | 6 | 245 | 41 | 0.568 | |
| Babka gymnotrachelus Kessler 1857 | 1 | 31 | 31 | 0.072 | |
| Oxynoemacheilus bureschi Drensky 1928 | 2 | 73 | 37 | 0.169 | |
| Perca fluviatilis Linnaeus 1758 | 56 | 853 | 15 | 1.979 | |
| Rutilus rutilus Linnaeus 1758 | 67 | 784 | 12 | 1.819 | |
| Salmo trutta Linnaeus 1758 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 0.012 | |
| Sander lucioperca Linnaeus 1758 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.005 | |
| Silurus glanis Linnaeus 1758 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 0.014 | |
| Squalius cephalus Linnaeus, 1758 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 0.023 | |
| Tinca tinca Linnaeus 1758 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | |
| Total 15 | 368 | 4783 | 13 | 11.097 |
| Species | Pathway in: | Species | Pathway in: |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abramis brama | Targeted introduction; atypical river type | Perca fluviatilis | Carp introduction, targeted introduction, dam escape, bait-fish; atypical river type |
| Alburnus alburnus | Carp introduction, dam escape; atypical river type, new biogeographic area | Rutilus rutilus | Carp introduction, targeted introduction, dam escape; atypical river type |
| Barbatula barbatula | Baitfish; new biogeographic area | Salmo trutta | Targeted introduction; atypical river type |
| Carassius gibelio | Carp introduction, targeted introduction, dam escape, baitfish; atypical river type, new biogeographic area | Sander lucioperca | Targeted introduction, dam escape; atypical river type |
| Esox lucius | Targeted introduction, dam escape; atypical river type | Silurus glanis | Targeted introduction, dam escape; atypical river type |
| Neogobius fluviatilis | Carp introduction, baitfish; new biogeographic area | Squalius cephalus | Carp introduction; new biogeographic area |
| Babka gymnotrachelus | Carp introduction, baitfish; atypical river type | Tinca tinca | Targeted introduction; atypical river type |
| Oxynoemacheilus bureschi | Baitfish; new biogeographical area |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apostolou, A. Distribution of Alien and Translocated Freshwater Fish Species in Bulgarian Lotic Ecosystems, according to the WFD Classification. Diversity 2023, 15, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15090954
Apostolou A. Distribution of Alien and Translocated Freshwater Fish Species in Bulgarian Lotic Ecosystems, according to the WFD Classification. Diversity. 2023; 15(9):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15090954
Chicago/Turabian StyleApostolou, Apostolos. 2023. "Distribution of Alien and Translocated Freshwater Fish Species in Bulgarian Lotic Ecosystems, according to the WFD Classification" Diversity 15, no. 9: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15090954
APA StyleApostolou, A. (2023). Distribution of Alien and Translocated Freshwater Fish Species in Bulgarian Lotic Ecosystems, according to the WFD Classification. Diversity, 15(9), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15090954






