Relationships between Fish Community Structure and Environmental Factors in the Nearshore Waters of Hainan Island, South China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
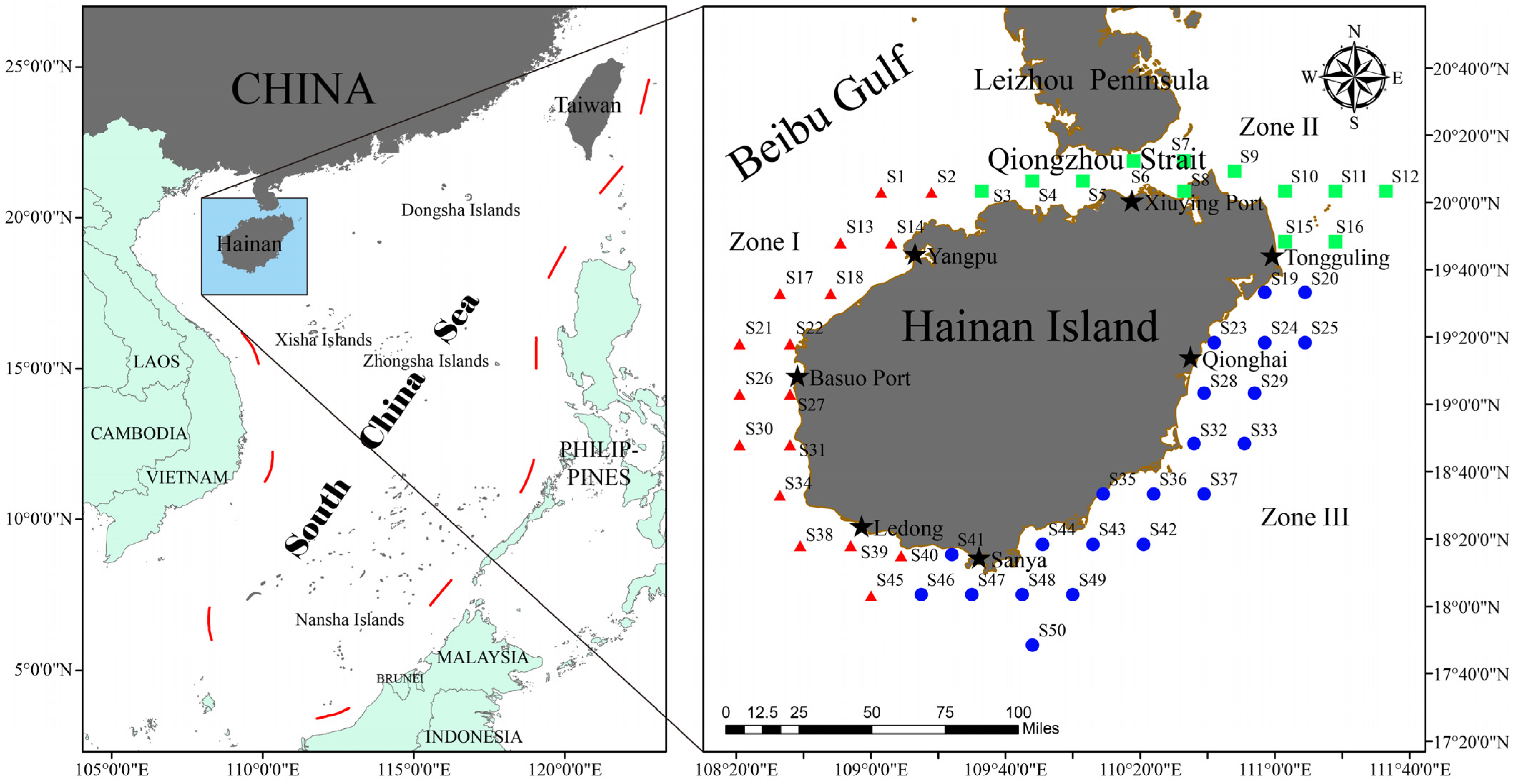
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Material Sources
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. The Index of Relative Importance (IRI)
2.3.2. Estimates of Fish Resource Density
2.3.3. Diversity Index Calculation
2.3.4. ANOSIM and SIMPER Analysis
2.3.5. Abundance Biomass Curve Analysis
2.3.6. Canonical Correspondence Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Species Composition and Dominant Species
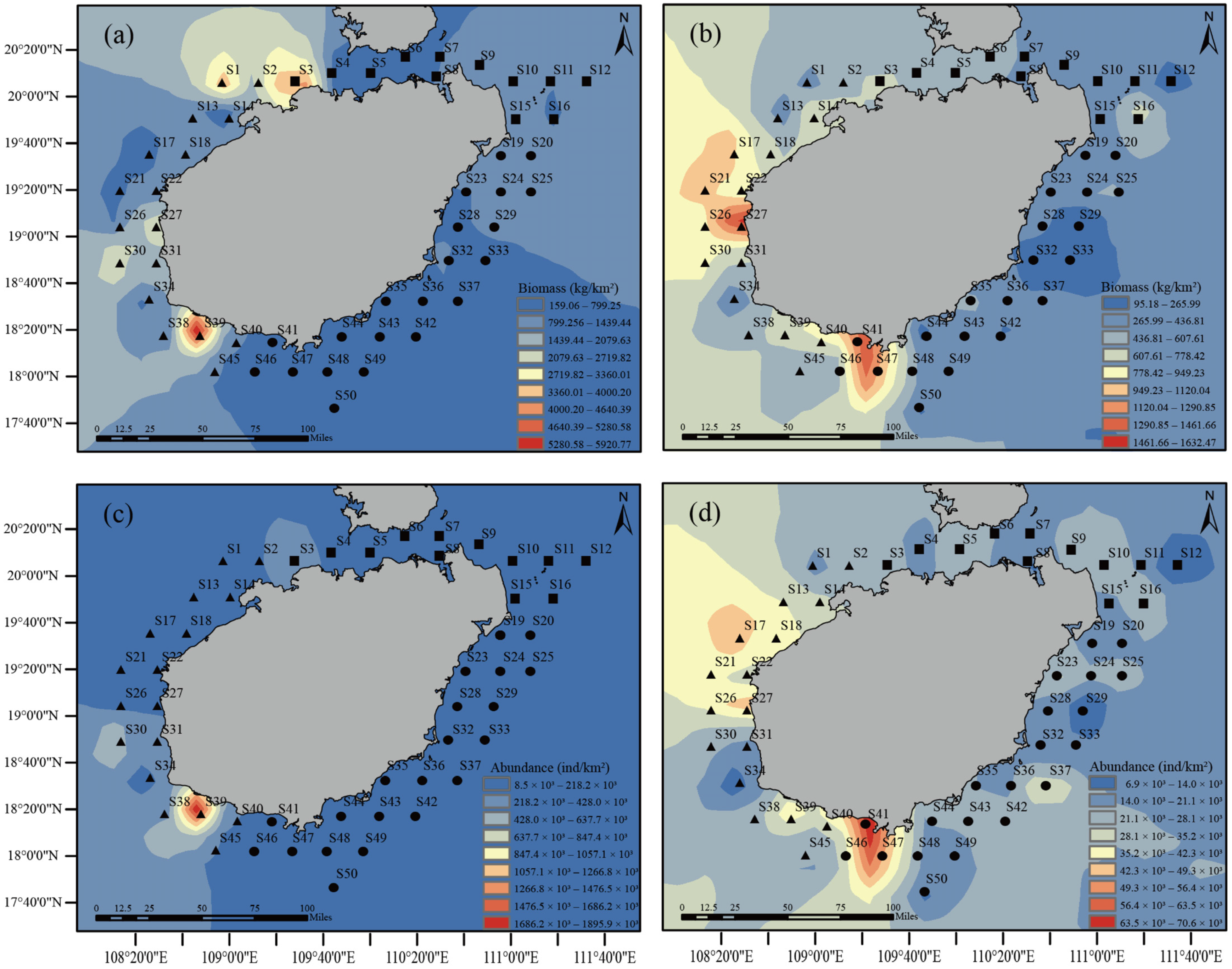
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Fish Stocks
3.3. Diversity Index
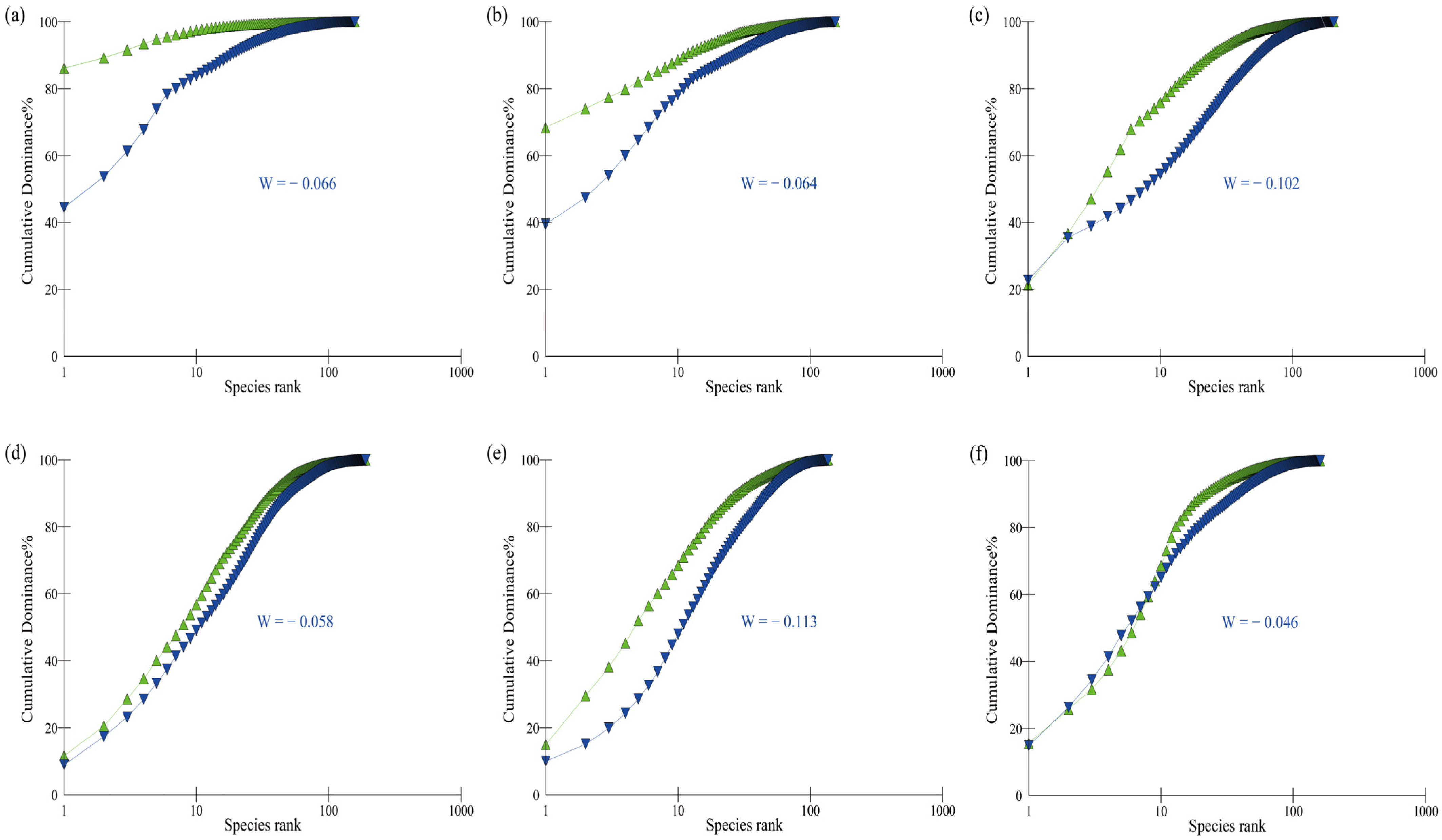
3.4. Community Stability
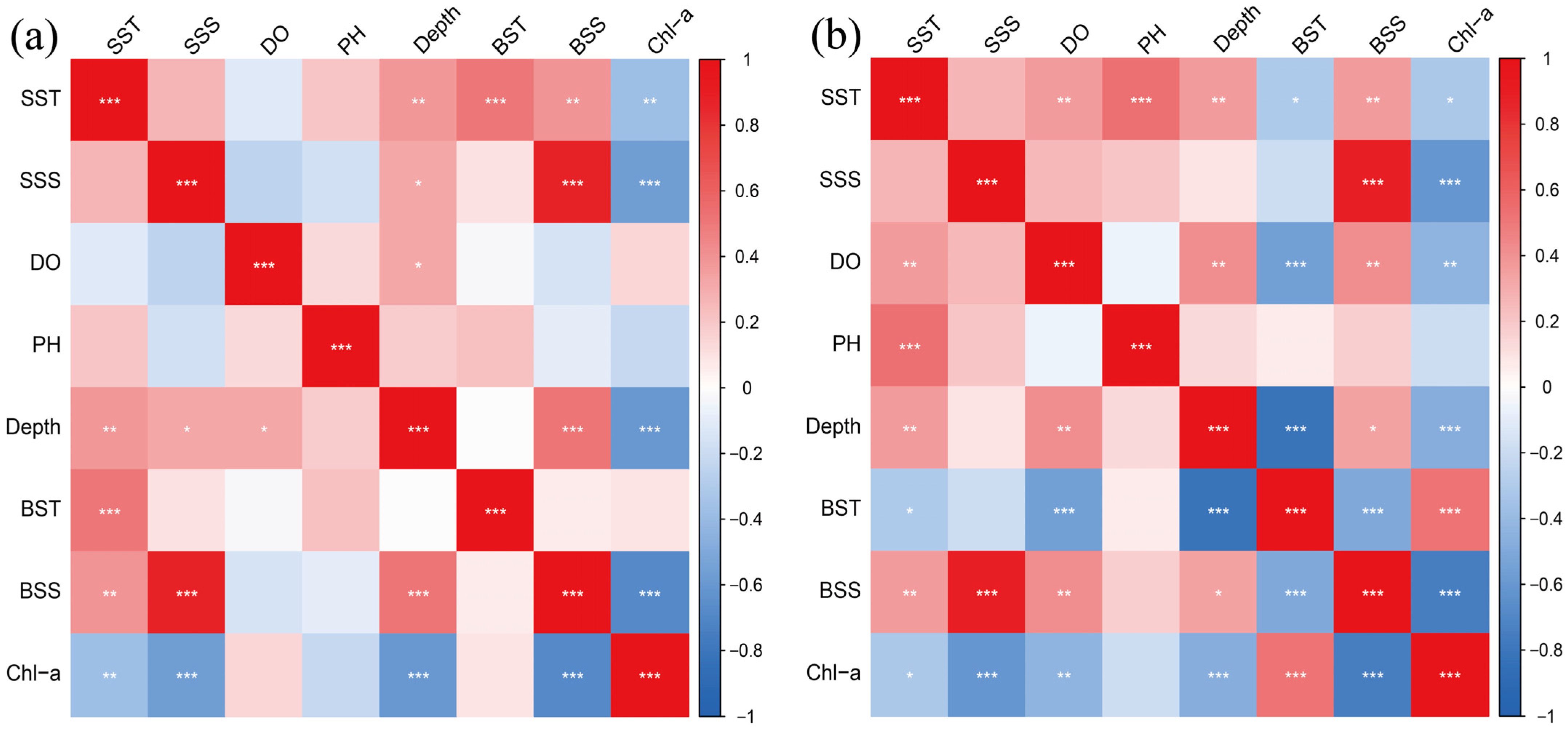
3.5. Correlation of Communities with Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Inshore Fish Stocks on Hainan Island
4.2. Fish Community Structure Characteristics
4.3. Relationships between Inshore Fish Communities and Environmental Factors on Hainan Island
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frank, K.T.; Petrie, B.; Choi, J.S.; Leggett, W.C. Trophic cascades in a formerly cod-dominated ecosystem. Science 2005, 308, 1621–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungblut, S.; Liebich, V.; Bode, M. YOUMARES 8–Oceans Across Boundaries: Learning from Each Other: Proceedings of the 2017 Conference for YOUng MARine RESearchers in Kiel, Germany; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 109–124. ISBN 978-3-319-93283-5. [Google Scholar]
- Poulard, J.C.; Blanchard, F. The impact of climate change on the fish community structure of the eastern continental shelf of the Bay of Biscay. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, L.M.; Oliphant, S.; Iverson, L.K. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and bonito in Californian waters. Fish. Bull. 1971, 152, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kamrani, E.; Sharifinia, M.; Hashemi, S.H. Analyses of fish community structure changes in three subtropical estuaries from the Iranian coastal waters. Mar. Biol. 2016, 46, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.J.; Klimley, A.P.; Muhlia-Melo, A.; Morgan, S.G. Seasonal changes in fish assemblage structure at a shallow seamount in the Gulf of California. PEERJ 2016, 4, e2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouillot, D.; Albouy, C.; Guilhaumon, F.; Lasram, F.B.R.; Coll, M.; Devictor, V.; Meynard, C.N.; Pauly, D.; Tomasini, J.A.; Troussellier, M.; et al. Protected and threatened components of fish biodiversity in the Mediterranean Sea. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Fan, J.T.; Yu, W.M.; Chen, Z.Z. Diversity and structure of demersal fish community over the northern slope in the South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkowski, D.J.; Ferguson, S.; Choy, E.S.; Loseto, L.L.; Brown, T.M.; Muir, D.C.G.; Semeniuk, C.A.D.; Fisk, A.T. Latitudinal variation in ecological opportunity and intraspecific competition indicates differences in niche variability and diet specialization of Arctic marine predators. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 1666–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Xie, J.; Lin, Y.B.; Chen, Y.M.; Mao, K.L.; Qin, Y.Q.; Diao, X. Microplastics in biota and surface seawater from tropical aquaculture area in Hainan, China. Gondwana Res. 2022, 108, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Liu, Y.S. Tourism-led land-use changes and their environmental effects in the southern coastal region of Hainan Island, China. J. Coast Res. 2013, 29, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos-Martínez, E.; Arizpe Covarrubias, O.A.; Maldonado-Alcudia, C.M.; Roldán-Clarà, B. Conservation of Biodiversity vs Tourism and Fishing at the Archipelago Espiritu Santo in the Gulf of California. In Mexican Natural Resources Management and Biodiversity Conservation: Recent Case Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 501–517. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, D.; Long, W.; Luo, W. Factors affecting the distribution pattern of wild plants with extremely small populations in Hainan Island, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, S.; He, J.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y. Tropical birds are declining in the Hainan Island of China. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 210, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, D.; Shen, X.; Li, S. Using an integrative mapping approach to identify the distribution range and conservation needs of a large threatened mammal, the Asiatic black bear, in China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 31, e01831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Wang, Q.; Xie, D.; Fletcher, D.H.; He, D. Factors influencing tropical Island freshwater fishes: Species, status, threats and conservation in Hainan Island. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2018, 419, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.Z.; Yin, J.Q.; Huang, L.M.; Lian, S.M.; Zhang, J.L.; Liu, C.G. Monsoon-forced distribution and assemblages of appendicularians in the northwestern coastal waters of South China Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 89, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.R.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z.J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.H. Community structure of fish in the coastal waters of Hainan Island. J. Ocean Univ. China 2011, 41, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.B. Hydrological characteristics of Hainan Island. J. China Hydrol. 1992, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Fang, N.Q.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Y.L.; Wang, X.M.; Yuan, X.B. Characteristics of the observed tide and tidal current at the southwest of Hainan Island. Mar. Forecasts 2016, 33, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.A.; Xing, C.Y.; Zhu, J.J. Analysis of climate characteristics in Hainan Island. J. Trop. Biol. 2022, 13, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J. Relationship between sea surface salinity and ocean circulation and climate change. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Curchitser, E.N.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.Q. Tidal effects on the surface water cooling northeast of Hainan Island, South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2019JC016016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.L.; Zhong, J.S. Key to Marine and Estuarial Fishes of China; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 1–1437. ISBN 9787109279995. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.G.; Zhang, M.Z. Marine Fishes of China; China Ocean University Press: Qingdao, China, 2015; pp. 1–2196. ISBN 9787567010659. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.J.; Wu, G.Y. Fishes of Taiwan; National Museum of Marine Biology & Aquarium Press: Pingdong, China, 2011; pp. 1–896. ISBN 9789860298994. [Google Scholar]
- Search Fish Base. Available online: https://fishbase.mnhn.fr/search.php (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Martin, G.R.; Twigg, L.E.; Robinson, D.J. Comparison of the diet of feral cats from rural and pastoral Western Australia. Wildl. Res. 1996, 23, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Technical Regulations for the Evaluation of the Impact of Construction Projects on Marine Living Resources (SC/T9110—2007); China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Q.; Chen, G.B. Research status of marine fish communities in Chinese sea area. Fish. Inf. 2008, 23, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhm, J.L. Range of diversity index in benthic macroinvertebrate populations. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1970, 42, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R. Nonparametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.Y.; Huang, B. K-dominance curve: A convenient and useful marine organic pollution monitoring tool. Mar. Sci. 1996, 1, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd ed.; Plymouth Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Devon, UK, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 121–134. ISBN 1855311402-9781855311404. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R. Comparisons of dominance curves. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1990, 138, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepš, J.; Šmilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cabridge, UK, 2003; pp. 1–253. ISBN 0-521-81409-X. [Google Scholar]
- NASA Ocean Color. Available online: https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/about/ (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Chevillot, X.; Pierre, M.; Rigaud, A.; Drouineau, H.; Chaalali, A.; Sautour, B.; Lobry, J. Abrupt shifts in the Gironde fish community: An indicator of ecological changes in an estuarine ecosystem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 549, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Du, J.; Su, S.; Tan, H.; Yang, W.; Ding, L.; Dong, P.; Yu, W.W.; Zheng, X.Q.; Chen, B. Effects of climate change in the seas of China: Predicted changes in the distribution of fish species and diversity. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Libralato, S.; Tudela, S.; Palomera, I.; Pranovi, F. Ecosystem overfishing in the ocean. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, T.P.; Neves, L.M.; Araújo, F.G. Effects of a nuclear power plant thermal discharge on habitat complexity and fish community structure in Ilha Grande Bay, Brazil. Mar. Environ. Res. 2009, 68, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.R.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.H. Seasonal Changes of species composition and diversity of fishes in coastal waters of Hainan Island, China. South China Fish. Sci. 2012, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H.L.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, M. Diversity analysis of nekton in the offshore waters of Hainan Island in spring and autumn. J. Fish. Res. 2021, 43, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Amara, R.; Paul, C. Seasonal patterns in the fish and epibenthic crustaceans community of an intertidal zone with particular reference to the population dynamics of plaice and brown shrimp. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbeck, L.S.; Unger, D.; Krumme, U.; Liu, S.M.; Jennerjahn, T.C. Typhoon-induced precipitation impact on nutrient and suspended matter dynamics of a tropical estuary affected by human activities in Hainan, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.Z.; Wu, X.J.; Tan, Y.H.; Huang, H.; Dong, J.D.; Huang, L.M. Spatial and temporal variability of copepod assemblages in Sanya Bay, northern South China Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 7, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.X.; Wang, Y.G.; Lian, G.S.; Lin, M. Distribution and community characteristics of planktonic copepods in the northwest coastal waters off Hainan Island. Chin. Biodivers. 2014, 22, 320–328. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.J.; Hu, Y.Q.; Huang, B.; Yang, X.Q.; Liu, F.X.; Ma, K. Characteristics of spring and autumn zooplankton community in Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan. Nat. Sci. J. Hainan Univ. 2016, 34, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, J.Y.; Ou, L.J.; Lu, S.G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.; Lu, S.H. Studies on ecological characteristics of plankton during jellyfish bloom in Qinglan Port. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2012, 43, 595–601. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.W.; Liang, J.L.; Xing, K.M. Distribution characteristics of zooplankton in summer and autumn in the coastal waters of Hainan Island. Coast. Eng. J. 2019, 38, 280–293. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; He, Y. Management of China’s capture fisheries: Review and prospect. Aquac. Fish. 2019, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V.; Dalsgaard, J.; Froese, R.; Torres, F. Fishing down marine food webs. Science 1998, 279, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queirós, A.M.; Fernandes, J.; Genevier, L.; Lynam, C.P. Climate change alters fish community size-structure, requiring adaptive policy targets. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoît, H.P.; Swain, D.P. Impacts of environmental change and direct and indirect harvesting effects on the dynamics of a marine fish community. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 2088–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, G.; Gislason, H.; Graham, K.; Hill, L.; Jin, X.; Koranteng, K.; Manickchand-Heileman, S.; Payá, I.; Sainsbury, K.; Sanchez, F.; et al. Impact of fishing on size composition and diversity of demersal fish communities. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerfield, P.J.; Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. A generalised analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) statistic for designs with ordered factors. Austral. Ecol. 2021, 46, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.Q.; Zhang, J.; Lin, L.S.; Xu, Z.C.; Zhu, X.M. Nekton species composition and biodiversity in Taiwan Strait. Chin. Biodivers. 2012, 20, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.P.; Xu, B.D.; Ye, Z.J.; Liu, Y.G. Preliminary study on community structure of Fishery resources during spring and autumn in the coastal waters of Qingdao. J. Ocean Univ. China 2005, 35, 792–798. [Google Scholar]
- Beukhof, E.; Dencker, T.S.; Pecuchet, L.; Lindegren, M. Spatio-temporal variation in marine fish traits reveals community-wide responses to environmental change. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 610, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, R.; Sepulveda, A.; Kafemann, R.; Nellen, W. Environmental factors as forces structuring the fish community of the Elbe Estuary. J. Fish. Biol. 1995, 46, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaureguizar, A.J.; Menni, R.; Guerrero, R.; Lasta, C. Environmental factors structuring fish communities of the Río de la Plata estuary. Fish. Res. 2004, 66, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snigirov, S.; Goncharov, O.; Sylantyev, S. The fish community in Zmiinyi Island waters: Structure and determinants. Mar. Biodivers. 2012, 42, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, M.J.; Potter, I.C.; Clarke, K.R.; Newman, S.J. Relationships between latitude and environmental conditions and the species richness, abundance and composition of tropical fish assemblages over soft substrata. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, J.; Martinho, F.; Martins, R.; Carneiro, M.; Azevedo, M.; Vieira, A.R.; Gomes, P.; Pardal, M.A. Water temperature gradient shapes the structure and composition of nearshore marine fish communities in southern Europe. J. Sea Res. 2019, 154, 101807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Konar, B.H.; Gorman, K.B.; Walker, C.M. Environmental factors important to high-latitude nearshore estuarine fish community structure. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2022, 201, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, W.H., Jr. Some relations of land drainage, nutrients, particulate material, and fish catch in two eastern Canadian bays. J. Fish. Board. Can. 1972, 29, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, W.H., Jr.; Drinkwater, K.; Muir, B.S. Correlations of fish catch and environmental factors in the Gulf of Maine. J. Fish. Board. Can. 1977, 34, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Fang, X.J.; Gong, Y.H.; Yu, H.L. Study on spatial and temporal characteristics of the SCS western boundary current. Tran. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 24, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, T.T. Analysis of the Current and Its Mechanism in the Gulf of Beibu; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Shi, M.C. Advances in study of Beibu Gulf circulation. Guangxi Sci. 2019, 26, 595–603. [Google Scholar]


| Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chondrichthyes | Carcharhiniformes | 3 (2.63%) | 3 (1.33%) | 3 (0.83%) |
| Orectolobiformes | 1 (0.88%) | 1 (0.44%) | 1 (0.28%) | |
| Myliobatiformes | 1 (0.88%) | 1 (0.44%) | 4 (1.10%) | |
| Rajiformes | 2 (1.75%) | 2 (0.88%) | 5 (1.38%) | |
| Torpediniformes | 1 (0.88%) | 1 (0.44%) | 2 (0.55%) | |
| Cyclostomata | Myxiniformes | 1 (0.88%) | 1 (0.44%) | 1 (0.28%) |
| Osteichthyes | Clupeiformes | 3 (2.63%) | 9 (3.98%) | 15 (4.13%) |
| Myctophiformes | 1 (0.88%) | 3 (1.33%) | 8 (2.20%) | |
| Siluriformes | 2 (1.75%) | 3 (1.33%) | 3 (0.83%) | |
| Anguilliformes | 8 (7.02%) | 13 (5.75%) | 22 (6.06%) | |
| Mugiliformes | 2 (1.75%) | 2 (0.88%) | 5 (1.38%) | |
| Beryciformes | 1 (0.88%) | 1 (0.44%) | 1 (0.28%) | |
| Scorpaeniformes | 8 (7.02%) | 31 (13.72%) | 39 (10.74%) | |
| Perciformes | 56 (49.12%) | 107 (47.35%) | 181 (49.86%) | |
| Tetraodontiformes | 2 (1.75%) | 11 (4.87%) | 15 (4.13%) | |
| Gasterosteiformes | 3 (2.63%) | 3 (1.33%) | 4 (1.10%) | |
| Gadiformes | 3 (2.63%) | 3 (1.33%) | 4 (1.10%) | |
| Pleuronectiformes | 7 (6.14%) | 19 (8.41%) | 34 (9.37%) | |
| Lophiiforme | 4 (3.51%) | 5 (2.21%) | 9 (2.48%) | |
| Ophidiiformes | 1 (0.88%) | 3 (1.33%) | 3 (0.83%) | |
| Zeiformes | 1 (0.88%) | 1 (0.44%) | 1 (0.28%) | |
| Salmoniformes | 1 (0.88%) | 1 (0.44%) | 1 (0.28%) | |
| Gonorhynchiformes | 1 (0.88%) | 1 (0.44%) | 1 (0.28%) | |
| Aulopiformes | 1 (0.88%) | 1 (0.44%) | 1 (0.28%) |
| Number | Spring | Autumn | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | |
| Eigenvalues | 0.9496 | 0.7931 | 0.6362 | 0.2663 | 0.8056 | 0.6219 | 0.4001 | 0.2344 |
| Cumulative percentage explained variation (%) | 9.44 | 17.33 | 23.65 | 26.30 | 9.05 | 16.04 | 20.53 | 23.17 |
| Gradient length | 4.51 | 6.35 | 3.89 | 3.37 | 7.06 | 4.34 | 3.84 | 2.74 |
| Number | Spring | Autumn | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | |
| Eigenvalues | 0.7768 | 0.5530 | 0.3346 | 0.2486 | 0.5827 | 0.3348 | 0.2923 | 0.2543 |
| Cumulative percentage explained variation (%) | 7.72 | 13.22 | 16.55 | 19.02 | 6.55 | 10.31 | 13.59 | 16.45 |
| Species–environ | 0.9238 | 0.8402 | 0.7273 | 0.6052 | 0.8913 | 0.8829 | 0.7927 | 0.7800 |
| Explained fitted variation (cumulative) | 34.81 | 59.59 | 74.58 | 85.72 | 27.61 | 43.47 | 57.32 | 69.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Shan, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Guo, T.; Sun, D. Relationships between Fish Community Structure and Environmental Factors in the Nearshore Waters of Hainan Island, South China. Diversity 2023, 15, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15080901
Luo Z, Yang C, Wang L, Liu Y, Shan B, Liu M, Chen C, Guo T, Sun D. Relationships between Fish Community Structure and Environmental Factors in the Nearshore Waters of Hainan Island, South China. Diversity. 2023; 15(8):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15080901
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Zhengli, Changping Yang, Liangming Wang, Yan Liu, Binbin Shan, Manting Liu, Cheng Chen, Tao Guo, and Dianrong Sun. 2023. "Relationships between Fish Community Structure and Environmental Factors in the Nearshore Waters of Hainan Island, South China" Diversity 15, no. 8: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15080901
APA StyleLuo, Z., Yang, C., Wang, L., Liu, Y., Shan, B., Liu, M., Chen, C., Guo, T., & Sun, D. (2023). Relationships between Fish Community Structure and Environmental Factors in the Nearshore Waters of Hainan Island, South China. Diversity, 15(8), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15080901






